Piceatannol Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
2.2. Culture of Cells and Parasites
2.3. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.4. Detection of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (ΔΨm)
2.5. ATP Level Determination
2.6. ROS Assay
2.7. RNA Extraction and RNA-Seq
2.8. Bioinformatics
2.9. In Vivo Anti-Toxoplasma Efficacy Evaluation
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
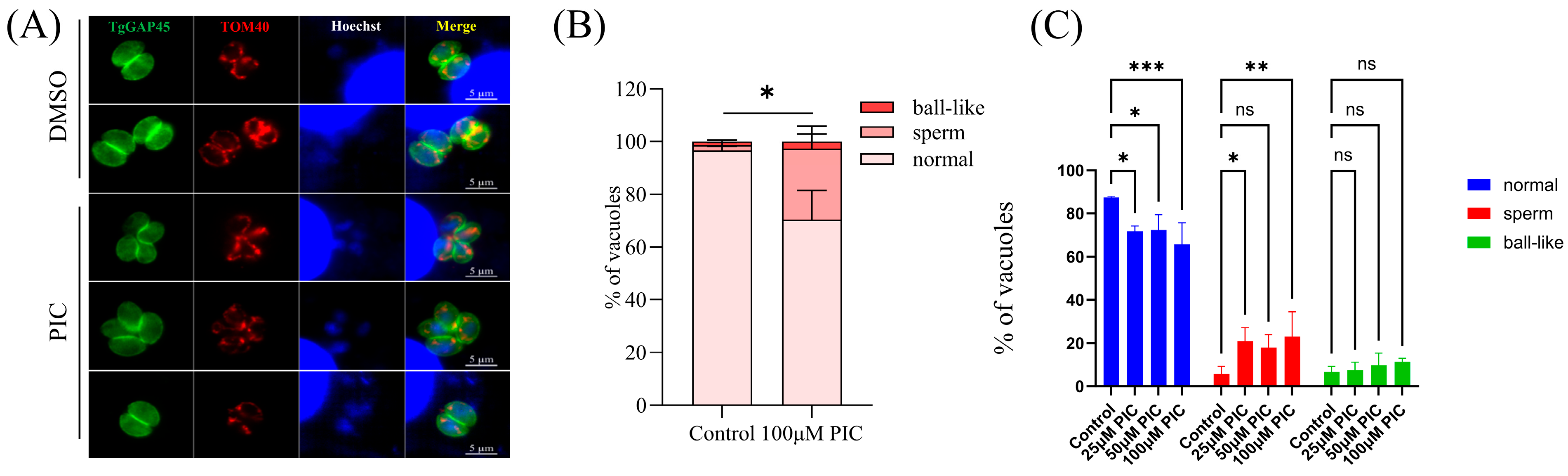
3.1. Influence of PIC on Mitochondrial Morphology in T. gondii Tachyzoites
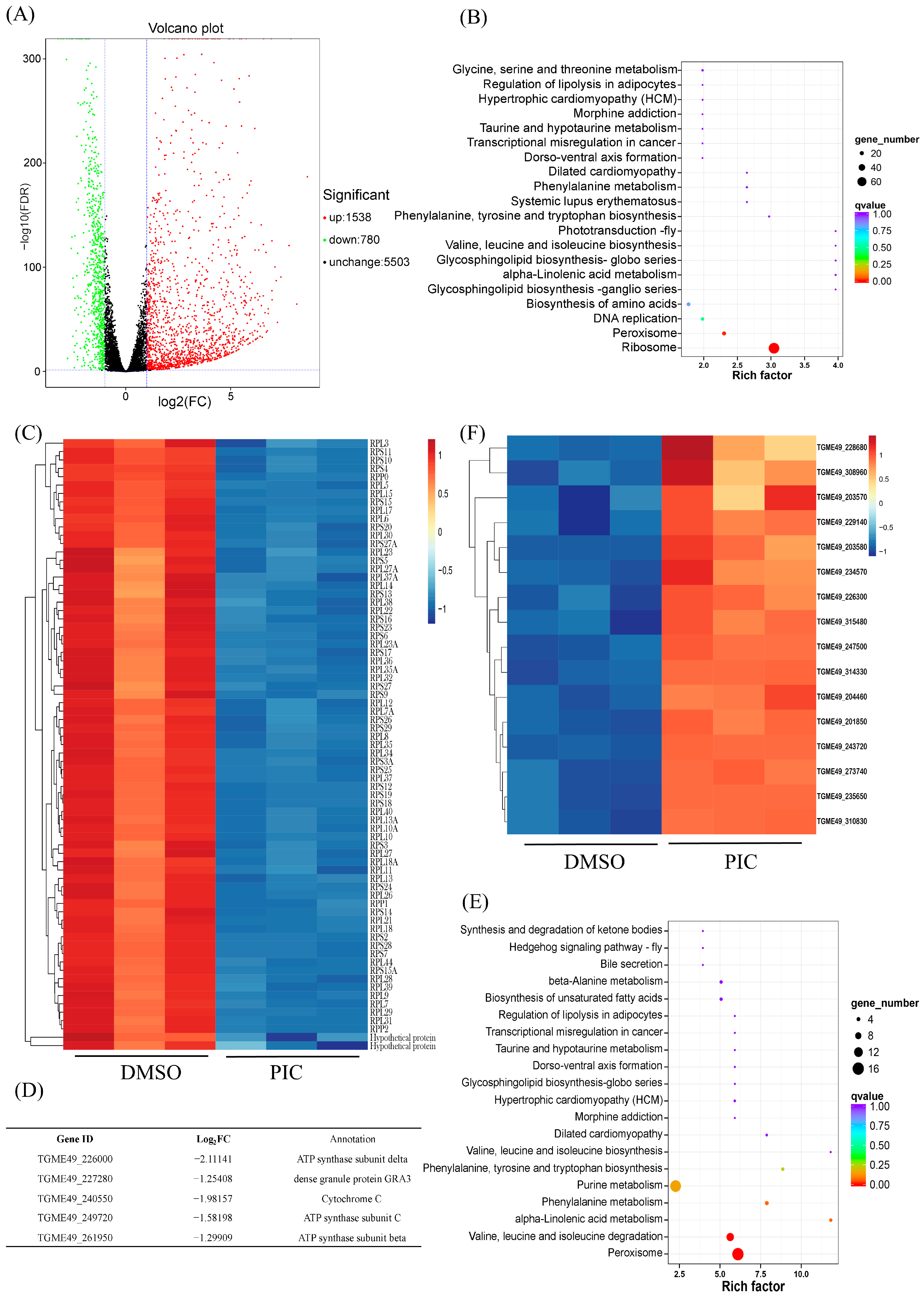
3.2. PIC Modulates Oxidative Phosphorylation Gene Transcription in T. gondii
3.3. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by PIC
3.4. Treatment with PIC Reduces Parasite Virulence in Mice
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuomo, G.; D’Abrosca, V.; Rizzo, V.; Nardiello, S.; La Montagna, G.; Gaeta, G.B.; Valentini, G. Severe polymyositis due to Toxoplasma gondii in an adult immunocompetent patient: A case report and review of the literature. Infection 2013, 41, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, S.K.; Rinkenberger, N.; Dunay, I.R.; Sibley, L.D. Toxoplasma gondii infection and its implications within the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fond, G.; Capdevielle, D.; Macgregor, A.; Attal, J.; Larue, A.; Brittner, M.; Ducasse, D.; Boulenger, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: A potential role in the genesis of psychiatric disorders. L’Encephale 2013, 39, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalın Sapmaz, Ş.; Şen, S.; Özkan, Y.; Kandemir, H. Relationship between Toxoplasma gondii seropositivity and depression in children and adolescents. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 278, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Driessen, L.H.; Verbraak, F.D.; Suttorp-Schulten, M.S.; van Ruyven, R.L.; Klok, A.M.; Hoyng, C.B.; Rothova, A. A prospective, randomized trial of pyrimethamine and azithromycin vs pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine for the treatment of ocular toxoplasmosis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, M.A.; Taheri, M.M.; Ahmadpour, E.; Montazeri, M.; Sarvi, S.; Akbari, M.; Daryani, A. Anti-Toxoplasma Effects of Methanol Extracts of Feijoa sellowiana, Quercus castaneifolia, and Allium paradoxum. J. Pharmacopunct. 2017, 20, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Cerebral Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huskinson-Mark, J.; Araujo, F.G.; Remington, J.S. Evaluation of the effect of drugs on the cyst form of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 164, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romand, S.; Pudney, M.; Derouin, F. In vitro and in vivo activities of the hydroxynaphthoquinone atovaquone alone or combined with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, clarithromycin, or minocycline against Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 2371–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Park, H.; Quan, H.; Jin, C. Antiparasitic effects of oxymatrine and matrine against Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 165, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghipour, K.; Masoori, L.; Ezzatpour, B.; Roozbehani, M.; Sheikhian, A.; Malekara, V.; Niazi, M.; Mardanshah, O.; Moradpour, K.; Mahmoudvand, H. The Experimental Role of Medicinal Plants in Treatment of Toxoplasma gondii Infection: A Systematic Review. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 303–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit-Vical, F.; Santillana-Hayat, M.; Kone-Bamba, D.; Mallie, M.; Derouin, F. Anti-Toxoplasma activity of vegetal extracts used in West African traditional medicine. Parasite 2000, 7, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.X.; Wu, L.; Jiang, X.G.; Feng, Y.Y.; Cao, J.P. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii activity of GAS in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitha, N.; Noordin, R.; Chan, K.L.; Sasidharan, S. In vitro anti-Toxoplasma gondii activity of root extract/fractions of Eurycoma longifolia Jack. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Yao, N.; He, J.K.; Pan, M.; Hou, Z.F.; Fan, Y.M.; Du, A.; Tao, J.P. In vitro Anti-parasitic Activity of Pelargonium X. asperum Essential Oil Against Toxoplasma gondii. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 616340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; He, J.K.; Pan, M.; Hou, Z.F.; Xu, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Tao, J.P.; Huang, S.Y. In Vitro Evaluation of Lavandula angustifolia Essential Oil on Anti-Toxoplasma Activity. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 755715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.M. Antimicrobial effect of resveratrol on dermatophytes and bacterial pathogens of the skin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, H.; Kucinska, M.; Murias, M. Biological activity of piceatannol: Leaving the shadow of resveratrol. Mutat. Res./Rev. Mutat. Res. 2012, 750, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais-Morales, J.; Betanzos, A.; García-Rivera, G.; Chávez-Munguía, B.; Shibayama, M.; Orozco, E. Resveratrol Induces Apoptosis-Like Death and Prevents In Vitro and In Vivo Virulence of Entamoeba histolytica. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hu, D.; Song, X. The anti-Toxoplasma activity of the plant natural phenolic compound piceatannol. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 972500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, M.; Nakamoto, R.K.; Nakanishi-Matsui, M.; Futai, M. Binding of phytopolyphenol piceatannol disrupts β/γ subunit interactions and rate-limiting step of steady-state rotational catalysis in Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 22771–22780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Hu, D.; Song, X. Mitochondrial dysfunction induced by bedaquiline as an anti-Toxoplasma alternative. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Si, H.; Lv, K.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, J.; Bai, Y.; Li, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J. Licarin-B Exhibits Activity Against the Toxoplasma gondii RH Strain by Damaging Mitochondria and Activating Autophagy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 684393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenführer, J.; Lengauer, T. Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K.; Charvat, R.; Arrizabalaga, G. Identification of Fis1 Interactors in Toxoplasma gondii Reveals a Novel Protein Required for Peripheral Distribution of the Mitochondrion. mBio 2020, 11, e02732-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salunke, R.; Mourier, T.; Banerjee, M.; Pain, A.; Shanmugam, D. Highly diverged novel subunit composition of apicomplexan F-type ATP synthase identified from Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovciarikova, J.; Lemgruber, L.; Stilger, K.L.; Sullivan, W.J.; Sheiner, L. Mitochondrial behaviour throughout the lytic cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Walton, J.L.; Roepe, P.D.; Sinai, A.P. Autophagy is a cell death mechanism in Toxoplasma gondii. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, J.G.; Bordón, C.; Posner, G.H.; Yolken, R.; Jones-Brando, L. Artemisinin derivatives inhibit Toxoplasma gondii in vitro at multiple steps in the lytic cycle. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talman, A.M.; Clain, J.; Duval, R.; Ménard, R.; Ariey, F. Artemisinin Bioactivity and Resistance in Malaria Parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.W.; Dong, K.; Qin, H.X.; Yang, Y.K.; He, J.L.; Li, J.; Zheng, Z.W.; Chen, D.L.; Chen, J.P. Direct and Indirect Inhibition Effects of Resveratrol against Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites In Vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01233-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, H.; Ito, R.; Setoguchi, Y.; Oritani, Y.; Ito, T. Administration of Piceatannol Complexed with α-Cyclodextrin Improves Its Absorption in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Cochemé, H.M. Redox metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling and function. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3691–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiriveedi, V.R.; Mattam, U.; Pattabhi, P.; Bisoyi, V.; Talari, N.K.; Krishnamoorthy, T.; Sepuri, N.B.V. Glutathionylated and Fe-S cluster containing hMIA40 (CHCHD4) regulates ROS and mitochondrial complex III and IV activities of the electron transport chain. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröse, S.; Brandt, U. The mechanism of mitochondrial superoxide production by the cytochrome bc1 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21649–21654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Vazquez, E.J.; Moghaddas, S.; Hoppel, C.L.; Lesnefsky, E.J. Production of reactive oxygen species by mitochondria: Central role of complex III. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36027–36031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoguchi, Y.; Oritani, Y.; Ito, R.; Inagaki, H.; Maruki-Uchida, H.; Ichiyanagi, T.; Ito, T. Absorption and metabolism of piceatannol in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Qiu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Mo, Y.; Lu, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, D.; Song, X. Piceatannol Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Toxoplasma gondii. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061203
Liu Z, Qiu H, Jiang Y, Mo Y, Lu L, Wang Y, Hu D, Song X. Piceatannol Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Toxoplasma gondii. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061203
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhenhe, Haolong Qiu, Yucong Jiang, Yuxi Mo, Linlin Lu, Yan Wang, Dandan Hu, and Xingju Song. 2025. "Piceatannol Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Toxoplasma gondii" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061203
APA StyleLiu, Z., Qiu, H., Jiang, Y., Mo, Y., Lu, L., Wang, Y., Hu, D., & Song, X. (2025). Piceatannol Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Toxoplasma gondii. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061203






