The Role of TLR4 in Lung Epithelial Cell Injury Caused by Influenza Virus Combined with Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Influenza A Virus
2.2. Bacterium Strain
2.3. Cell Strain
2.4. Detection of Influenza Virus Nucleoprotein mRNA Expression Levels and Post-IAV-Stimulated Lung Epithelial Cell Viability
2.5. Detection of Lung Epithelial Cell Viability and Levels of Cell-Free DNA and Citrullinated histone H3 After Co-Stimulation with IAV and SA
2.6. Detection of mRNA Expression Levels of TLR4, NF-κB, and Inflammatory Cytokines in Lung Epithelial Cells Following Co-Stimulation with Influenza Virus and SA
2.7. Detection of TLR4, NF-κB, and Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression Levels in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells Following TAK-242 Treatment
2.8. Detection of TLR4 (mRNA/Protein), NF-κB, and Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells Post-TLR4 Silencing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression Level of Influenza Virus NP mRNA and Viability Changes in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells After Influenza Virus Stimulation
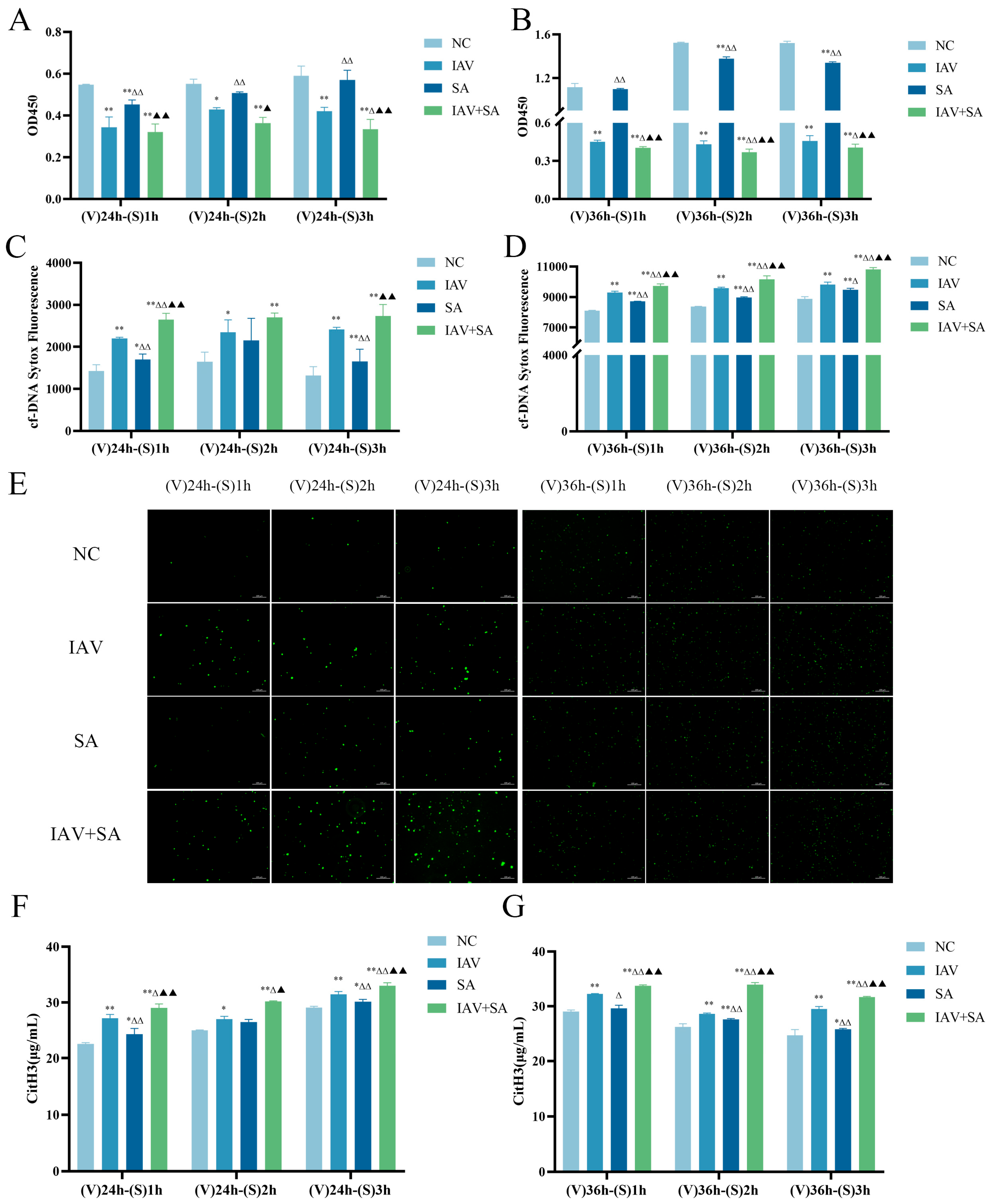
3.2. Effects of Influenza Virus and SA Co-Stimulation on Pulmonary Epithelial Cell Viability and Levels of Cell-Free DNA and Citrullinated histone H3
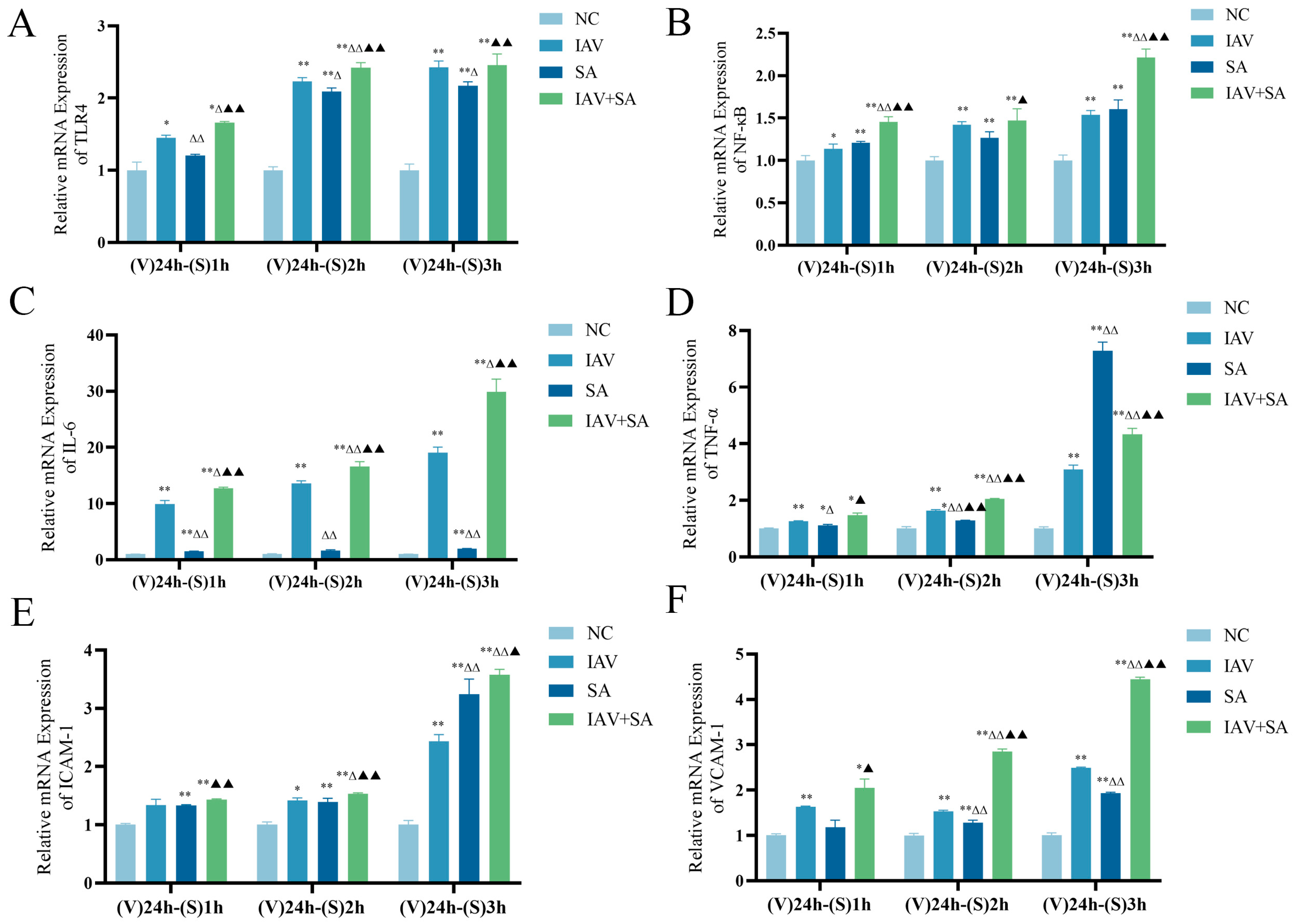
3.3. Effects of Influenza Virus Combined with SA Stimulation on TLR4 and Downstream Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression in Lung Epithelial Cells
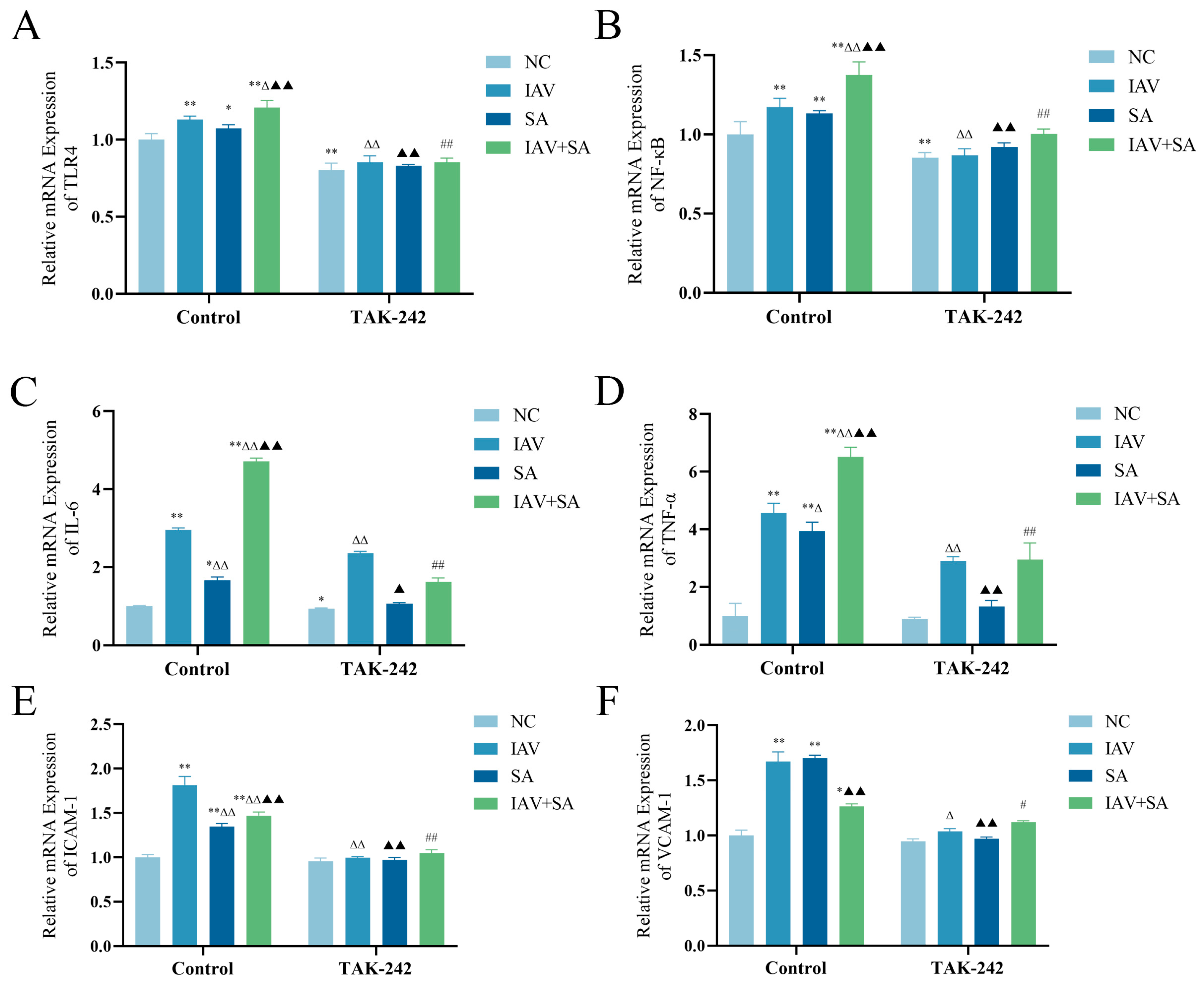
3.4. Changes in mRNA Expression Levels of TLR4, NF-κB, and Inflammatory Cytokines in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells Following TAK-242 Treatment
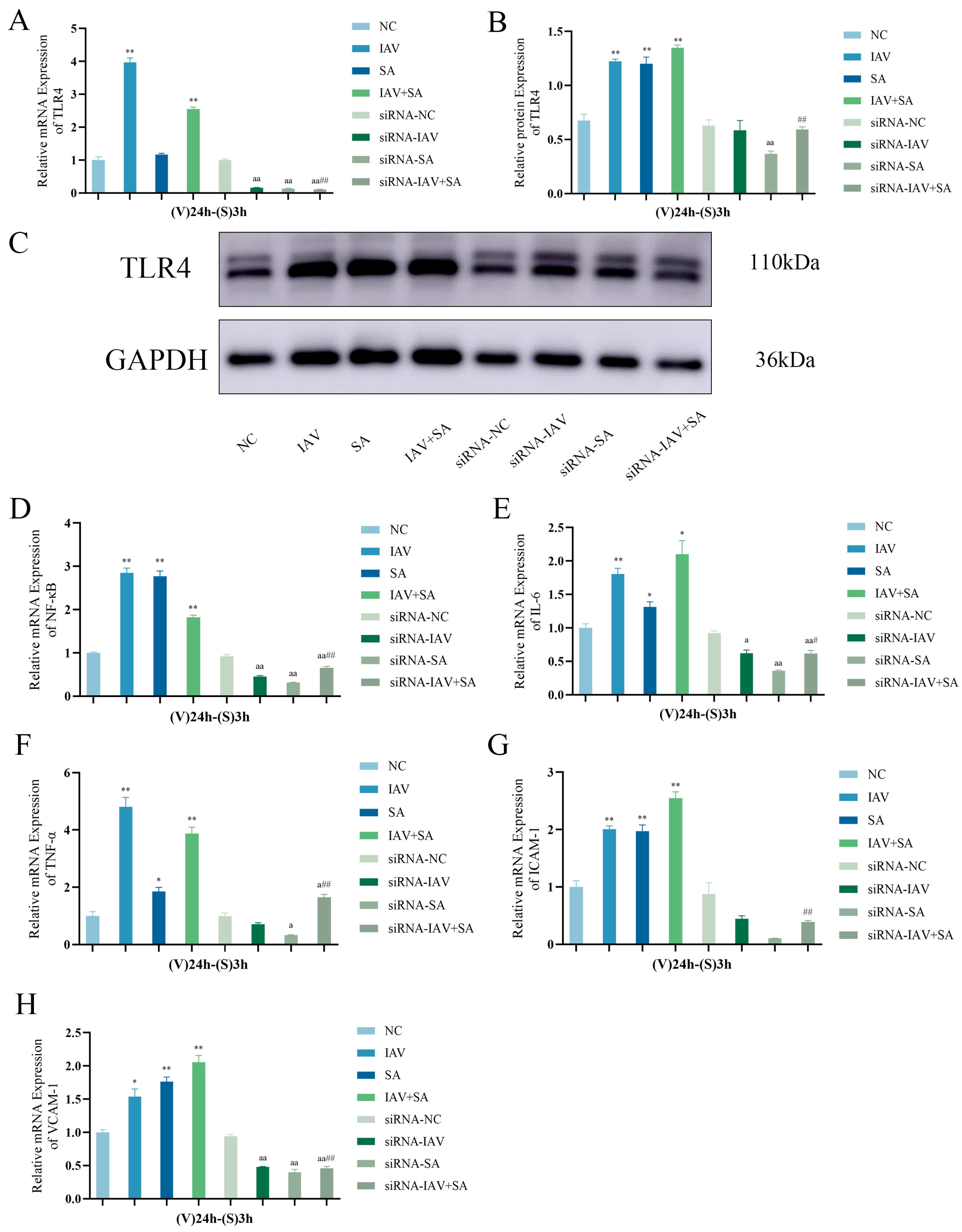
3.5. Changes in TLR4, NF-κB, and Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression Levels and TLR4 Protein Expression in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells Following TLR4 Gene Silencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALI | Acute lung injury |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| CitH3 | Citrullinated histone H3 |
| cfDNA | Cell-free DNA |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| IAV | Influenza A virus |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LSD | Least significant difference |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| NC | Negative control |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SA | Staphylococcus aureus |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| TAK-242 | Resatorvid |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
References
- Goraya, M.U.; Zaighum, F.; Sajjad, N.; Anjum, F.R.; Sakhawat, I.; Rahman, S.U. Web of interferon stimulated antiviral factors to control the influenza A viruses replication. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demuth, L.; Ohm, M.; Michaelsen-Preusse, K.; Schulze, K.; Riese, P.; Guzmán, C.A.; Korte, M.; Hosseini, S. Influenza vaccine is able to prevent neuroinflammation triggered by H7N7 IAV infection. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1142639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalil, A.C.; Thomas, P.G. Influenza virus-related critical illness: Pathophysiology and epidemiology. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmit, T.; Guo, K.; Tripathi, J.K.; Wang, Z.; McGregor, B.; Klomp, M.; Ambigapathy, G.; Mathur, R.; Hur, J.; Pichichero, M.; et al. Interferon-γ promotes monocyte-mediated lung injury during influenza infection. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussell, T.; Wissinger, E.; Goulding, J. Bacterial complications during pandemic influenza infection. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.E.; Cleary, D.W.; Clarke, S.C. Secondary Bacterial Infections Associated with Influenza Pandemics. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braverman, J.; Monk, I.R.; Ge, C.; Westall, G.P.; Stinear, T.P.; Wakim, L.M. Staphylococcus aureus specific lung resident memory CD4(+) Th1 cells attenuate the severity of influenza virus induced secondary bacterial pneumonia. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirigotaki, M.; Giormezis, N.; Maraki, S.; Spiliopoulou, I.; Galanakis, E. Predominance of community-associated, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus infections among hospitalized children and adolescents. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 71, 001511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Ouyang, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Cen, M.; Yang, L.; Han, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, F. IFP35 aggravates Staphylococcus aureus infection by promoting Nrf2-regulated ferroptosis. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 62, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Du, H.; Wan, H.; Yang, J.; Wan, H. Amygdalin prevents multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced lung epithelial cell injury by regulating inflammation and oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Shu, C. USP18 promotes innate immune responses and apoptosis in influenza A virus-infected A549 cells via cGAS-STING pathway. Virology 2023, 585, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.K.; Bansal, S.; Bauer, C.; Muralidharan, A.; Sun, K. Influenza Infection Induces Alveolar Macrophage Dysfunction and Thereby Enables Noninvasive Streptococcus pneumoniae to Cause Deadly Pneumonia. J. Immunol. 2020, 205, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitomo, T.; Nakata, M.; Nagase, S.; Takahara, Y.; Honda-Ogawa, M.; Mori, Y.; Akamatsu, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Okamoto, S.; Kawabata, S. GP96 Drives Exacerbation of Secondary Bacterial Pneumonia following Influenza A Virus Infection. mBio 2021, 12, e0326920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeMessurier, K.S.; Tiwary, M.; Morin, N.P.; Samarasinghe, A.E. Respiratory Barrier as a Safeguard and Regulator of Defense Against Influenza A Virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomp, M.; Ghosh, S.; Mohammed, S.; Khan, M.N. From virus to inflammation, how influenza promotes lung damage. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 110, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palani, S.; Uddin, M.B.; McKelvey, M.; Shao, S.; Sun, K. Immune predisposition drives susceptibility to pneumococcal pneumonia after mild influenza A virus infection in mice. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1272920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, S.; Falcao-Pires, I.; Balligand, J.L.; Bauersachs, J.; Brutsaert, D.; Ciccarelli, M.; Dawson, D.; de Windt, L.J.; Giacca, M.; Hamdani, N.; et al. The innate immune system in chronic cardiomyopathy: A European Society of Cardiology (ESC) scientific statement from the Working Group on Myocardial Function of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, N.; Fernández-Veledo, S.; Punzón, C.; Moreno, C.; Barrocal, B.; Sreeramkumar, V.; Desco, M.; Fresno, M. Opposing Actions of TLR2 and TLR4 in Adipocyte Differentiation and Mature-Onset Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, M.; Nakamura, N.; Saiki, T.; Miyabe, S.; Ito, M.; Sasajima, S.; Minato, T.; Matsubara, T.; Naruse, K. Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharides Promote Proliferation and Migration of Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells through the MAPK/TLR4 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Han, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Cai, B.; Wu, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, F.; Han, D.; et al. Jinhua Qinggan granules attenuates acute lung injury by promotion of neutrophil apoptosis and inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Ren, Z.; Goraya, M.U.; Lin, Y.; Ye, J.; Li, R.; Dai, J. Anti-influenza drug screening and inhibition of apigetrin on influenza A virus replication via TLR4 and autophagy pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T. Pharmacological Effects of Polyphenol Phytochemicals on the Intestinal Inflammation via Targeting TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Xin, Z.T.; Liang, Y.; Ly, H.; Liang, Y. NF-kappaB signaling differentially regulates influenza virus RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9880–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.; Hossain, M.F.; Neef, J.; Zwack, E.E.; Tsai, C.-M.; Raafat, D.; Fechtner, K.; Herzog, L.; Kohler, T.P.; Schlüter, R.; et al. TLR4 sensing of IsdB of Staphylococcus aureus induces a proinflammatory cytokine response via the NLRP3-caspase-1 inflammasome cascade. mBio 2024, 15, e0022523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhao, C.; Lu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; He, L.; Chen, B. Role of Nedd4L in Macrophage Pro-Inflammatory Polarization Induced by Influenza A Virus and Lipopolysaccharide Stimulation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artner, T.; Sharma, S.; Lang, I.M. Nucleic acid liquid biopsies in cardiovascular disease: Cell-free DNA liquid biopsies in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2024, 398, 118583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Q.; Pan, B.; Stringer, K.A.; Alam, H.B.; Standiford, T.J.; Li, Y. Citrullinated Histone H3 Mediates Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury Through Activating Caspase-1 Dependent Inflammasome Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 761345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, Y.; Maejima, Y.; Saito, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Horita, S.; Shimomura, K.; Inoue, S.; Kotani, J. TAK-242, a specific inhibitor of Toll-like receptor 4 signalling, prevents endotoxemia-induced skeletal muscle wasting in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.-M.; Guan, Y.-Q.; Liang, J.-F.; Wu, W.-D. TAK-242 improves sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in rats by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2313176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.L.; Potts, R.; Huber, V.C.; Chaussee, M.S. Influenza enhances host susceptibility to non-pulmonary invasive Streptococcus pyogenes infections. Virulence 2023, 14, 2265063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lv, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, L. Biomarkers of peripheral blood neutrophil extracellular traps in the diagnosis and progression of malignant tumors. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyishi, C.U.; Desanti, G.E.; Wilkinson, A.L.; Lara-Reyna, S.; Frickel, E.M.; Fejer, G.; Christophe, O.D.; Bryant, C.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gordon, S.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 and macrophage scavenger receptor 1 crosstalk regulates phagocytosis of a fungal pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, G.; Li, W. ACOD1 mediates Staphylococcus aureus-induced inflammatory response via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lani, R.; Thariq, I.M.; Suhaimi, N.S.; Hassandarvish, P.; Abu Bakar, S. From defense to offense: Modulating toll-like receptors to combat arbovirus infections. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2024, 20, 2306675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullers, J.A.; Rehg, J.E. Lethal synergism between influenza virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae: Characterization of a mouse model and the role of platelet-activating factor receptor. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Q.; Zheng, H.; Lv, J.; Fu, Z.; Mao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B. Mechanism of Zhenwu Decoction modulating TLR4/NF-κB/HIF-1α loop through miR-451 to delay renal fibrosis in type 2 CRS. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Sun, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, F.; Sun, H.; Zheng, H.; Dai, J. TAK-242 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Pharmazie 2016, 71, 583–587. [Google Scholar]
- Renatto, A.; Raúl, V.; Pedro, A.; Fabiola, G.; Claudio, E.; José Miguel, O.; Mauricio, R.; Samir, B.; Guillermo, D. Interferon-β decreases LPS-induced neutrophil recruitment to cardiac fibroblasts. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1122408. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Quercetin inhibits TNF-α induced HUVECs apoptosis and inflammation via downregulating NF-kB and AP-1 signaling pathway in vitro. Medicine 2020, 99, e22241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Vo, T.T.T.; Hong, Y.C.; Wang, C.S.; Vo, Q.C.; Chou, H.C.; Huang, T.W.; Lee, I.T. CORM-2 prevents human gingival fibroblasts from lipoteichoic acid-induced VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 expression by inhibiting TLR2/MyD88/TRAF6/PI3K/Akt/ROS/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 201, 115099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.N.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, X.C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Peng, Y.Y.; Ren, J.; Dong, M.L. Deletion of TLR4 attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Chen, C.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. The Role of TLR4 in Lung Epithelial Cell Injury Caused by Influenza Virus Combined with Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061201
Chen B, Chen C, Lu F, Wang X, Zhang X, Wang Z, Liu H. The Role of TLR4 in Lung Epithelial Cell Injury Caused by Influenza Virus Combined with Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061201
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Bei, Chunjing Chen, Fangguo Lu, Xiaoqi Wang, Xianggang Zhang, Zhibin Wang, and Huihui Liu. 2025. "The Role of TLR4 in Lung Epithelial Cell Injury Caused by Influenza Virus Combined with Staphylococcus aureus" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061201
APA StyleChen, B., Chen, C., Lu, F., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., & Liu, H. (2025). The Role of TLR4 in Lung Epithelial Cell Injury Caused by Influenza Virus Combined with Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061201





