Bacillus multifaciens sp. nov., a Crucial and Highly-Active Flavor and Protease Producer Isolated from the qu-Starter of Chinese Wuliangye Baijiu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Culture Media
2.3. Isolation and Ecology
2.4. Physiology and Chemotaxonomy
2.5. Phylogenetic and Genomic Analyses
2.6. Protease Enzyme Production Analyses
2.6.1. Tyrosine Standard Curve
2.6.2. Protease Crude Enzyme Solution
2.6.3. Determination of Protease Activity
2.7. Flavor Compound Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
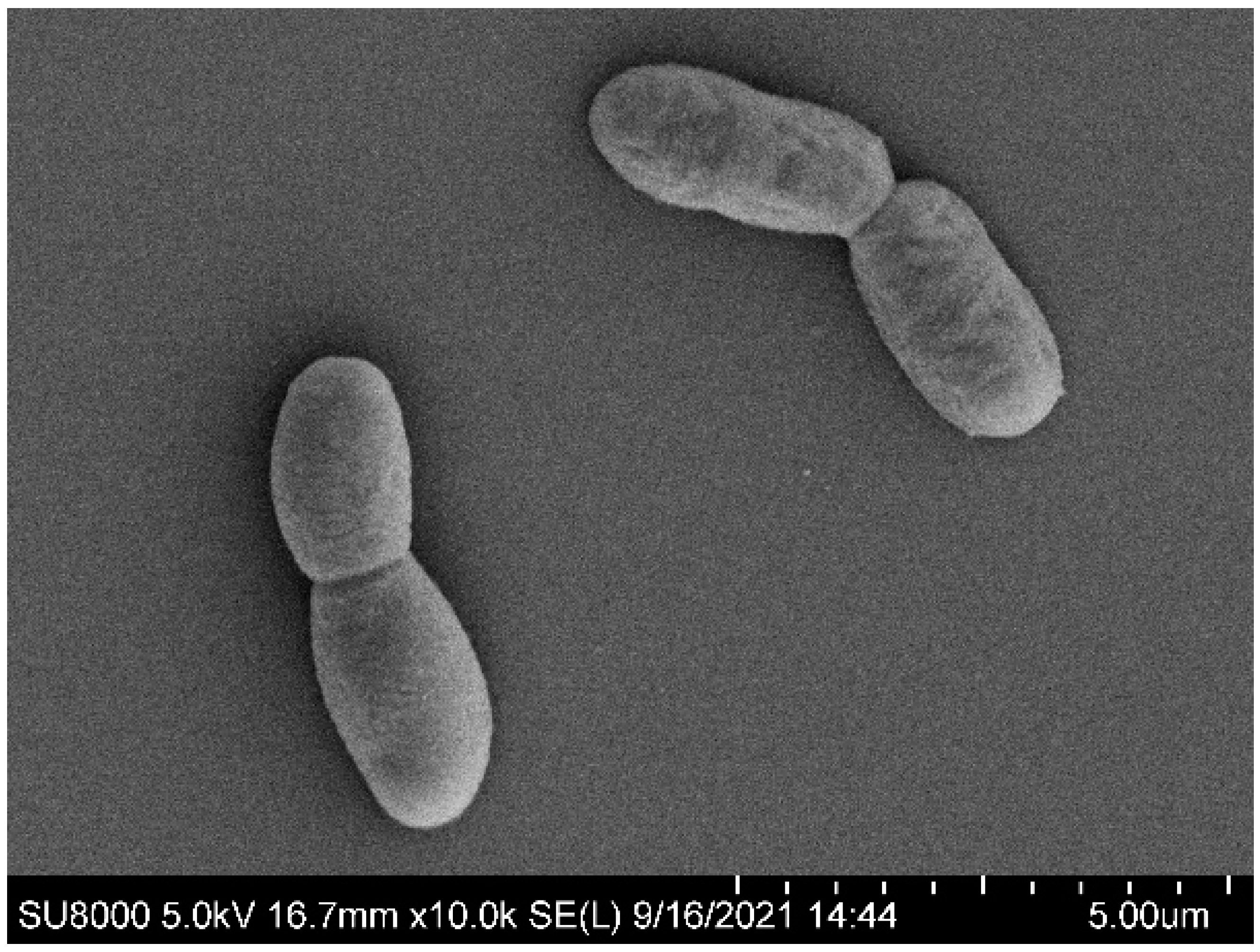
3.1. Isolation and Morphological Characterization
3.2. Phylogenic Analysis
3.3. Physiological and Chemotaxonomic Characteristics
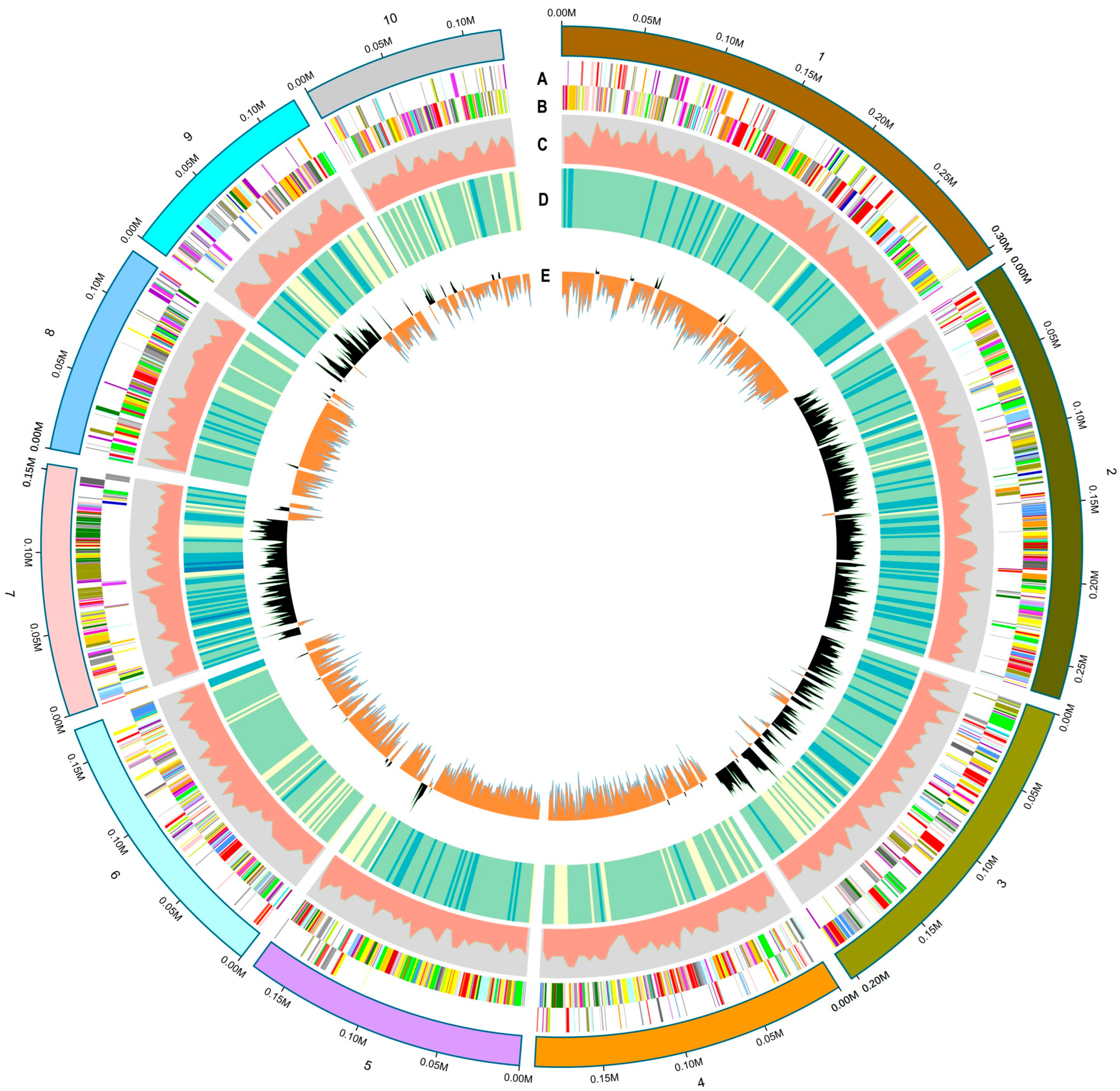
3.4. Genomic Features
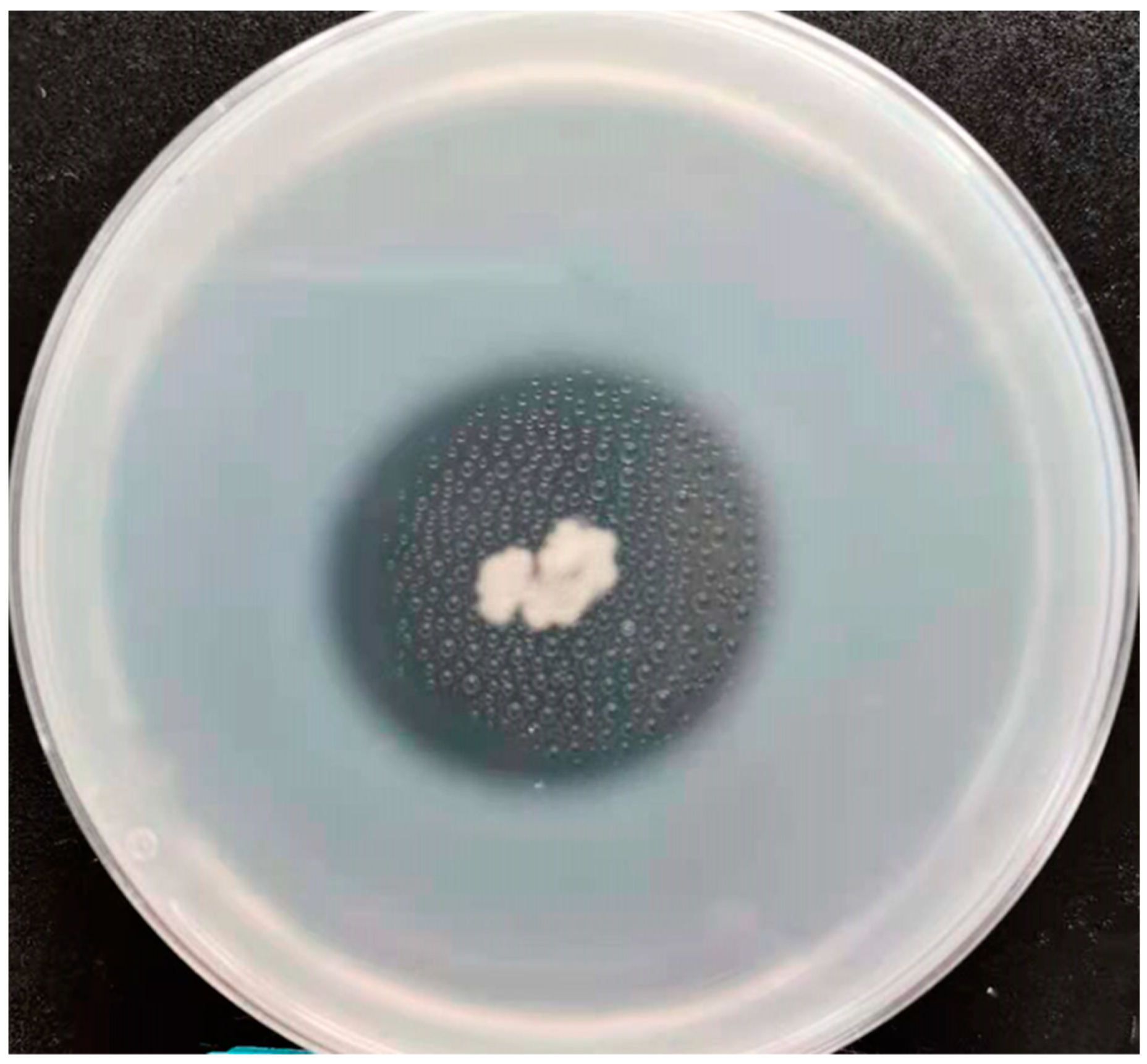
3.5. Protease Enzyme Production Analyses
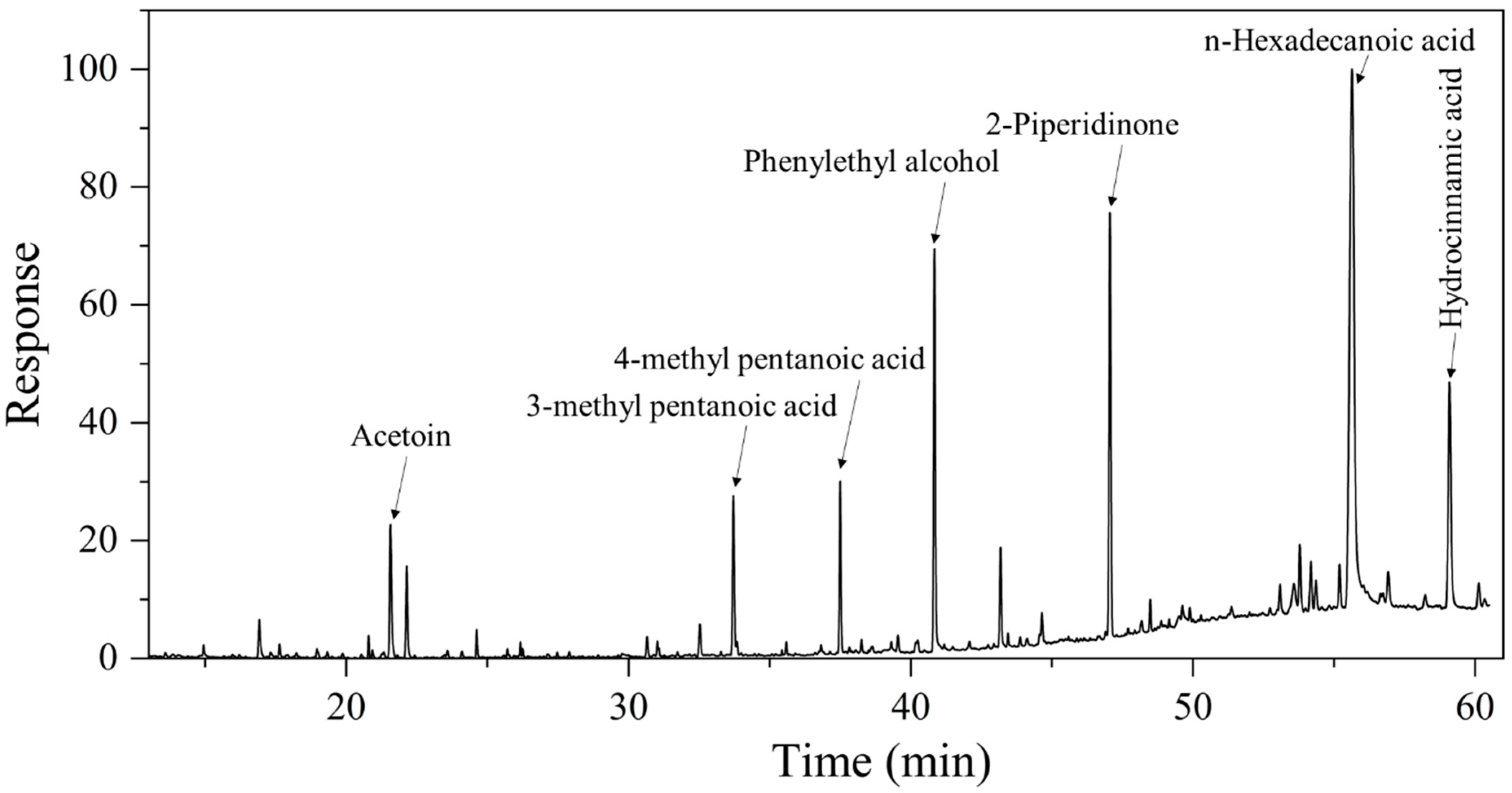
3.6. Flavor Compound Analyses
3.7. Description of Bacillus multifaciens sp. nov.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Logan, N.A.; De Vos, P. Genus Bacillus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; De Vos, P., Garrity, G.M., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.H., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Logan, N.A.; Halket, G. Endospore-Forming Soil Bacteria; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Cheng, K.; Zhao, D.; Yang, G.; Qiao, Z.; Qiu, S.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Feng, H.; et al. Bacillus aquiflavi sp. nov., isolated from yellow water of strongly flavored Chinese baijiu. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3406–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Ghosh, K.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Kumar, V.; Lymbery, A.J.; Roy, S.; Ringø, E. Genusbacillus, promising probiotics in aquaculture: Aquatic animal origin, bio-active components, bioremediation and efficacy in fish and shellfish. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2019, 27, 331–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Research trends in Jiang-flavor baijiu fermentation: From fermentation microecology to environmental ecology. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, D.; Peng, Z.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Variation of aroma profile in fermentation process of Wuliangye baobaoqu starter. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Qiao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, X. Systematic analysis of Baobaoqu fermentation starter for Wuliangye Baijiu by the combination of metagenomics and metabolomics. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1062547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Du, G. Genome sequencing and flavor compound biosynthesis pathway analyses of Bacillus licheniformis isolated from Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor-brewing microbiome. Food Biotech. 2020, 34, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Xu, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Qin, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, C.; He, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guan, T. Comprehensive analysis of spatial heterogeneity reveals the important role of the upper-layer fermented grains in the fermentation and flavor formation of Qingxiangxing baijiu. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Liang, X.; Fei, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liang, J.; Bai, W.; He, S. Effect of Mixed Strains on Microbial Community and Flavor Metabolites in Fermentation Process of Chi-Flavor Baijiu. Foods 2024, 13, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, Z.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Qian, M.C. Volatile analysis of Wuliangye Baijiu by LiChrolut EN SPE fractionation coupled with comprehensive GCxGC-TOFMS. Molecules 2022, 27, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.P.; Kiprianova, E.A.; Mikhailov, V.V.; Levanova, G.F.; Garagulya, A.D.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Vysotskii, M.V.; Nicolau, D.V.; Yumoto, N.; Taguchi, T.; et al. Phenotypic diversity of Pseudoalteromonas citrea from different marine habitats and emendation of the description. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48 Pt 1, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, P.; Murray, R.; Wood, W.A.; Krieg, N.R. Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematic; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; John. Willey and Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, C.G.; Steffens, M.B.R.; Etto, R.M.; Galvão, C.W.; Martins, C.D.C.; Pedrosa, F.D.O.; Kolm, H.E. Ardra profiles of bacteria and archaea in mangrove sediments with different levels of contamination in the estuarine complex of Paranaguá, Brazil. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.S.; Cho, Y.J.; Lee, K.; Yoon, S.H.; Kim, M.; Na, H.; Park, S.C.; Jeon, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, H.; et al. Introducing EzTaxon-e: A prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62 Pt 3, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benndorf, R.; Guo, H.; Sommerwerk, E.; Weigel, C.; Garcia-Altares, M.; Martin, K.; Hu, H.; Kufner, M.; de Beer, Z.W.; Poulsen, M.; et al. Natural products from Actinobacteria associated with Fungus-Growing termites. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Goker, M. Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Ha, S.M.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.; Chun, J. A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Hao, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, X.; Huang, J.; Lai, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Shao, Z. Aquibium pacificus sp. nov., a novel mixotrophic bacterium from bathypelagic seawater in the western pacific ocean. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, J.; Han, B.-Z.; Chen, X. Wheat-origin Bacillus community drives the formation of characteristic metabolic profile in high-temperature Daqu. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 191, 115597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhao, X.; Du, G.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Zhao, D. Metaproteomic analysis of enzymatic composition in Baobaoqu fermentation starter for Wuliangye baijiu. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 4170–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; Freitas, J.; Nunes, F.M.; Camara, J.S. Chemical differentiation of sugarcane cultivars based on volatile profile and chemometric analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3548–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wenlai, F.; Qian, M.C. Characterization of aroma compounds in apple cider using solvent-assisted flavor evaporation and headspace solid-phase microextraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar]
- Kampfer, P.; Lipski, A.; McInroy, J.A.; Clermont, D.; Criscuolo, A.; Glaeser, S.P. Bacillus rhizoplanae sp. nov. from maize roots. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Chen, L.; Jin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, N.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, K.; He, K.; et al. Insight into broad substrate specificity and synergistic contribution of a fungal α-glucosidase in Chinese Nong-flavor daqu. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomandé, S.E.; Nguyen-The, C.; Guinebretière, M.H.; Broussolle, V.; Brillard, J. Role of fatty acids in Bacillus environmental adaptation. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, M.J.; Nam, Y.D.; Park, E.J.; Roh, S.W.; Bae, J.W. Brachybacterium squillarum sp. nov., isolated from salt-fermented seafood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61 Pt 5, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rossello-Mora, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contesini, F.J.; Melo, R.R.; Sato, H.H. An overview of Bacillus proteases: From production to application. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yuan, L.; Ma, D.; Liu, S.; Ji, Z.; Han, X.; Shen, C.; Mao, J. Relationship between microbial protein and amino acid metabolism in fermented grains of long fermentation period strong-flavor Baijiu. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanuf. 2025, 5, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, R.; Ahmed, M.; Siddique, A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Jamal, A. Catalytic role of thermostable metalloproteases from Bacillus subtilis KT004404 as dehairing and destaining agent. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Shang, M.; Yuan, F.; Guo, W.; Wang, C. EF24 exerts cytotoxicity against NSCLC via inducing ROS accumulation. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.-Y.; Jia, C.-C.; Han, P.-R.; Yang, J. 3,5-Bis(2-fluorobenzylidene)-4-piperidone induce reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis in A549 cells. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.G.; Neis, V.B.; Balen, G.O.; Colla, A.; Cunha, M.P.; Dalmarco, J.B.; Pizzolatti, M.G.; Prediger, R.D.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Antidepressant-like effect of ursolic acid isolated from Rosmarinus officinalis L. in mice: Evidence for the involvement of the dopaminergic system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 103, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruisinger, B.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in rape honey by means of the molecular sensory science concept. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4186–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell length (μm) | 1.6–3.4 | 3.0–4.0 | 3.0–5.0 | NR |
| Cell width (μm) | 0.7–1.3 | >1.0 | >1.0 | >1.0 |
| Oxidase/catalase | −/+ | +/+ | +/+ | +/+ |
| Rhizoid colony | − | − | − | − |
| Growth temperature range (°C) | 20–40 | 10–36 | 10–45 | 20–50 |
| Optimal growth temperature (°C) | 40 | 30 | 30(37) | 30–37 |
| Growth NaCl range (%) | 0–2 | 0–3 | 0–4 | NR |
| Optimal growth NaCl (%) | 1 | 1.0–2.0 | 0 | NR |
| Growth pH range | 5.0–10.0 | 5.5–10.5 | 5.0–9.5 | NR |
| Optimal growth pH | 8.0–9.0 | 7.0–8.0 | 6.0 | NR |
| Starch hydrolysis | + | − | + | − |
| API 20E results | ||||
| β-Galacosidase | − | − | − | − |
| Arginine dihydrolase | − | − | + | − |
| Citrate utilization | − | − | + | − |
| Urease | − | − | − | − |
| Acetoin production (Voges−Proskauer) | − | + | + | +w |
| Gelatinase | + | − | + | + |
| Fermentation/oxidation of glucose | − | − | − | − |
| API 50CH results | ||||
| D-Ribose | − | − | + | + |
| D-Xylose | − | − | − | − |
| D-Galactose | − | − | − | − |
| D-Glucose | + | + | + | + |
| D-Fructose | + | + | + | + |
| D-Mannose | − | − | − | + |
| D-maltose | + | + | + | + |
| N-Acetylglucosamine | + | + | + | + |
| Arbutin | − | − | + | + |
| Aesculin ferric citrate | − | − | + | + |
| Salicin | +w | − | + | + |
| Cellobiose | − | + | + | + |
| Sucrose | + | − | + | − |
| Trehalose | − | − | + | − |
| Starch | + | + | + | − |
| Glycogen | − | + | + | − |
| Potassium gluconate | − | − | − | − |
| DNA G+C content (mol%) | 35.97 | 36.39 | 35.37 | 35.87 |
| Fatty Acid | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12:0 | - | ND | 1.4 | ND |
| C14:0 | 1.1 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.2 |
| C16:0 | 3.9 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 5.6 |
| C15:1ω5c | 1.9 | ND | ND | ND |
| C16:1ω6c | - | 8.4 | 12.3 | ND |
| C16:0N alcohol | 1.2 | ND | ND | ND |
| C17:0 | 1.3 | ND | ND | ND |
| C18:0 | 1.7 | ND | TR | ND |
| C18:3ω6c | 4.3 | ND | ND | ND |
| iso-C12:0 | 4.8 | ND | 8.7 | ND |
| iso-C13:0 | 7.9 | 8.1 | 12.6 | 7.1 |
| iso-C14:0 | 1.3 | 2.9 | 5.5 | 2.3 |
| iso-C15:0 | 23.0 | 19.9 | 13.3 | 38.6 |
| iso-C16:0 | 3.5 | 6.9 | 8.3 | 5.1 |
| iso-C16:1cis10 | - | 2.9 | - | - |
| iso-C16:1ω5 | - | ND | 2.9 | ND |
| iso-C17:0 | 8.9 | 16.9 | 7.0 | 11.4 |
| iso-C17:1ω5c | 7.0 | ND | ND | ND |
| iso-C17:1ω6 | - | ND | 2.3 | ND |
| anteiso-C13:0 | 6.3 | 3.5 | 4.9 | ND |
| anteiso-C15:0 | 2.9 | 10.6 | 3.6 | 3.1 |
| anteiso-C17:0 | 1.4 | 3.3 | 1.6 | ND |
| anteiso-C17:1a | 2.1 | ND | ND | ND |
| anteiso-C17:1cis5 | - | 4.6 | - | - |
| anteiso-C17:1ω6 | - | ND | 1.1 | ND |
| Summed feature 2 | 2.6 | - | ND | 1.5 |
| Summed feature 3 | 6.7 | - | ND | 11.5 |
| Volatile Compounds | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| Acetoin | 7.58 ± 0.11 |
| 3-methyl pentanoic acid | 8.80 ± 0.24 |
| 4-methyl pentanoic acid | 7.42 ± 0.19 |
| Phenylethyl alcohol | 19.08 ± 0.82 |
| 2-Piperidinone | 21.95 ± 1.56 |
| n-Hexadecanoic acid | 78.25 ± 2.19 |
| Hydrocinnamic acid | 18.60 ± 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, P.; Lu, Y.; Liu, D.; Su, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, D.; et al. Bacillus multifaciens sp. nov., a Crucial and Highly-Active Flavor and Protease Producer Isolated from the qu-Starter of Chinese Wuliangye Baijiu. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050993
Luo Q, Zhao X, Li X, Li Y, Zhao P, Lu Y, Liu D, Su J, Chen J, Zhao D, et al. Bacillus multifaciens sp. nov., a Crucial and Highly-Active Flavor and Protease Producer Isolated from the qu-Starter of Chinese Wuliangye Baijiu. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):993. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050993
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Qingchun, Xinrui Zhao, Xi Li, Yuzhu Li, Pengju Zhao, Yanping Lu, Duotao Liu, Jian Su, Jian Chen, Dong Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Bacillus multifaciens sp. nov., a Crucial and Highly-Active Flavor and Protease Producer Isolated from the qu-Starter of Chinese Wuliangye Baijiu" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050993
APA StyleLuo, Q., Zhao, X., Li, X., Li, Y., Zhao, P., Lu, Y., Liu, D., Su, J., Chen, J., Zhao, D., Li, J., & Zheng, J. (2025). Bacillus multifaciens sp. nov., a Crucial and Highly-Active Flavor and Protease Producer Isolated from the qu-Starter of Chinese Wuliangye Baijiu. Microorganisms, 13(5), 993. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13050993






