Abstract
COVID-19 presents a wide range of symptoms, including gastrointestinal manifestations such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. Lactobacillus acidophilus has been proposed as a potential adjunct therapy to alleviate these symptoms due to its probiotic properties, which help restore gut microbiota balance and modulate immune responses. This review systematically analyzed studies assessing the effects of L. acidophilus in COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. The literature search was conducted through PubMed and the WHO COVID-19 database using keywords such as “Lactobacillus acidophilus”, “COVID-19”, “gastrointestinal symptoms”, and “inflammation markers”. The search covered studies published until February 2025. Inclusion criteria: observational and clinical trials with L. acidophilus for symptom relief. Exclusion: animal studies and non-ethical approvals. The findings suggest that L. acidophilus supplementation may contribute to faster resolution of diarrhea, improved gut microbiota balance, and reduced inflammatory markers. However, some studies have found no significant impact on hospitalization rates or disease progression. The probiotic’s mechanisms of action appear to involve microbiota modulation, intestinal barrier reinforcement, and anti-inflammatory effects rather than direct viral inhibition in COVID-19 after progression. Some L. acidophilus strains show promise, and clinical validation should follow careful preclinical studies (in vitro, cell lines, and animal models), especially in vulnerable populations such as immunocompromised individuals. Understanding the gut–lung axis and its role in immune response regulation, together with the need for a thorough characterization of the specific strains, including biochemical, genomic, and functional properties, before testing in humans, may provide deeper insights into the therapeutic potential of probiotics in viral infections.
1. Introduction
In December 2019, a new disease caused by a coronavirus, later named COVID-19, was first identified in Wuhan, China [1]. This disease was linked to a β-coronavirus similar to the strains responsible for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV) [2] and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS-CoV) [3]. The virus was officially named SARS-CoV-2 [4]. On 11 March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared COVID-19 a global pandemic [5]. The clinical manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection vary widely, from asymptomatic to mild/moderate, severe, and critical forms, with corresponding mortality rates of 0%, 15%, and 50%, respectively. Mild cases typically include symptoms such as dry cough, sore throat, and fever, while more severe cases progress to pneumonia and difficulty breathing. In critical cases, respiratory failure, septic shock, and multiple organ dysfunction can occur [6,7,8]. Additionally, gastrointestinal issues, including vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, have been frequently observed [9,10], possibly linked to the involvement of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which serves as the receptor facilitating SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells [11]. ACE2 expression is notably high in various organs, including the gastrointestinal tract, lungs, heart, and kidneys [12]. Specifically, diarrhea has been observed both in the early stages of infection [13] and during ongoing infection [14], and may even persist even after recovery.
Probiotics have been proposed as a potential therapeutic approach for preventing antibiotic-associated diarrhea [15], primarily by enhancing immune responses, competing for essential nutrients, preventing pathogen adhesion to epithelial and mucosal surfaces, reducing epithelial invasion, and producing antimicrobial compounds [16,17]. The first global references discussing the use of probiotics in the context of COVID-19 were published in the British Medical Journal [18,19]. However, scientific evidence regarding the role of probiotics in COVID-19 remains fragmented across various publications, including those that clearly define specific probiotic types [20] and others that lack detailed information (grey literature) [21], as well as clinical practice guidelines [22]. In one reported case, Ji et al. [23] mentioned that “oral probiotics were given to a boy with COVID-19 symptoms, and his symptoms disappeared after two days of treatment”. Following an inquiry to the author by one of the authors of this manuscript (J.M. Soriano, personal communication, 7 April 2020), Ji clarified that the probiotic used was Lactobacillus acidophilus (Li-Na, personal communication, 8 April 2020).
In fact, the genus Lactobacillus represents a large and diverse group of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) [24], which are widely used in the food [25], pharmaceutical [26], and agricultural [27] industries due to their probiotic properties. L. acidophilus exhibits stronger acid tolerance, allowing it to survive harsh gastric conditions and reach the small intestine, where it contributes to microbiota balance, immune modulation, and pathogen inhibition [28]. Based on Ji’s personal communication and manuscript [23], we sought to investigate whether this microorganism could be used to address COVID-19-related gastrointestinal symptoms. To this end, a review was conducted to assess whether L. acidophilus could potentially serve as a therapeutic option to alleviate gastrointestinal symptoms in COVID-19 patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Focused Question
Can L. acidophilus contribute to the mitigation of gastrointestinal and systemic symptoms in COVID-19 patients?
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
First, we analyzed studies according to the following inclusion criteria:
Type of studies. Observational studies and clinical trials.
Type of participants. COVID-19 patients (reflecting information about age, sex, and other demographic factors) who received L. acidophilus as an intervention.
Type of interventions. Studies that evaluated the effects of L. acidophilus on COVID-19 patients.
Outcome type. Symptomatic relief, modulation of gut microbiota, reduction in inflammation markers, and overall patient recovery.
In the second phase, we included only studies that met all the inclusion criteria while applying the following exclusion criteria: (i) studies that did not report at least one of the selected outcome parameters, (ii) studies involving participants with severe underlying systemic diseases that could have influenced outcomes, (iii) in vitro or animal-based studies, and (iv) studies conducted without ethical approval.
2.3. Search Strategy
This systematic narrative review adheres to the guidelines set by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [29] and was conducted using the WHO COVID-19 publications database alongside PubMed. The search methodology was designed based on the Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome (PICO) framework [30]. We included studies published in English and other languages, which were translated using Google Translate (Google, Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA). For manuscripts written in Asian languages, assistance was provided by the Confucius Institute at the University of Valencia prior to reviewing the full texts. Two separate teams of reviewers, skilled in medical assessments and research methods, independently evaluated studies for eligibility, relevance, and data collection, following standardized institutional procedures.
2.4. Research
We carried out a literature search including three main searches based on coronavirus (as a causative agent or disease) and probiotics: “novel coronavirus” OR “2019 Novel Coronavirus” OR “2019-nCoV” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “COVID-19” OR “coronavirus disease 2019” AND “probiotics” OR “intestinal microecological modulator” (according to Wei et al. [21]) OR “probiotics” OR “Lactobacillus” OR using the new names for the probiotic species of Lactobacillus [28], such as “Lacticaseibacillus” AND “gastrointestinal symptoms” OR “diarrhea” OR “nausea” OR “vomiting” OR “abdominal pain” OR “gut inflammation” OR “gastrointestinal distress” OR “irritable bowel” OR “intestinal dysbiosis” OR “microbiota imbalance” OR “gut–lung axis” OR “COVID-19 gastrointestinal symptoms” OR “gastrointestinal COVID-19 complications”. The search date was until 2 February 2025. Based on information from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute [31], the validity of each included study was assessed using nine items, to which the answer was affirmative (+), negative (–), or other, including “cannot determine”, “not applicable”, and “not reported”, which were considered unclear (?) answers. We have classified the studies using a rating of good (7–9), fair (4–6), or poor (≤3) for each individual study.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Results
The PRISMA flow diagram for this narrative review is presented in Figure 1. From a total of 75,120 records identified through database searches, 5043 duplicate records were removed, leaving 70,077 for screening. After an initial assessment, 69,149 records were excluded because they involved animal studies or lacked full-text availability. This left 928 studies eligible for screening. Of these, 857 studies were excluded because they did not investigate L. acidophilus as a probiotic. The remaining 71 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. During this stage, 64 articles were further excluded because they did not focus on the treatment of gastrointestinal symptoms with L. acidophilus, together with articles excluded for being bibliographic reviews. After applying the eligibility criteria, a total of seven observational studies were included in the qualitative synthesis, but several completed trials, including NCT05474144 [32] and NCT04420676 [33], were not included because the results were not publicly available, limiting quantitative analysis. These studies were analyzed to determine the effects of L. acidophilus on COVID-19 symptoms, focusing on gastrointestinal outcomes.
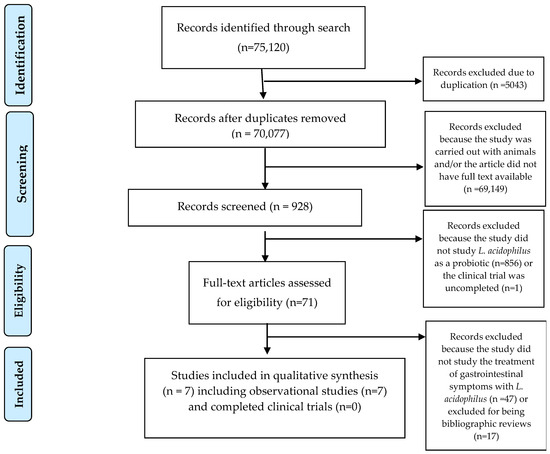
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram for studies retrieved through the searching and selection process.
The methodological quality of the selected studies was assessed using the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) criteria [29], as demonstrated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Methodological quality assessment of studies selected for this review, according to the criteria of the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute [31].
The quality rating is presented in Table 1. Among the seven studies included in the qualitative synthesis, six studies were rated as good quality, and one study was considered fair quality. Most high-quality studies provided a clear research question, well-defined intervention protocols, and robust statistical analyses. Conversely, studies rated as fair had limitations, such as unclear descriptions of intervention methods, inconsistent reporting of outcomes, or inadequate statistical approaches.
3.2. Selected Studies
The study by Ji et al. [23] demonstrated the use of L. acidophilus in managing gastrointestinal symptoms in COVID-19 patients (15- and 9-year-old boys). In one documented case, a boy presented mild diarrhea as the only symptom of COVID-19, without fever or respiratory distress. The child was administered an oral probiotic containing L. acidophilus and the diarrhea resolved completely within two days. This case highlights the potential benefit of probiotics in alleviating gastrointestinal manifestations of COVID-19, particularly the kind of symptoms that the patient showed. While the study does not provide extensive details on probiotic treatment protocols, the rapid symptom resolution following probiotic administration suggests a clinically relevant effect. Horowitz et al. [34] studied the use of probiotics, including L. acidophilus, in the treatment of symptoms such as diarrhea due to COVID-19. In a 53-year-old male patient, L. acidophilus was administered as part of an immune and nutritional support regimen, alongside Bifidobacterium and Saccharomyces boulardii, in combination with an antibiotic regimen. The study suggests that this probiotic mixture was associated with improved gut health and immune function, though it does not specify direct clinical outcomes related solely to L. acidophilus. The probiotic supplementation was used in conjunction with zinc (40 mg/day), Vitamin C (up to 2 g, three times daily), beta-glucan (1000 mg daily), curcumin (1 g twice daily), sulforaphane glucosinolates (100 mg twice daily), N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) (600 mg twice daily), alpha-lipoic acid (600 mg twice daily), and glutathione (500 mg capsules twice daily, increased up to 2 g pro re nata (PRN) for acute respiratory distress). These findings suggest that probiotics, including L. acidophilus, may contribute to gut microbiota modulation and systemic immune regulation, potentially aiding in managing COVID-19-associated gastrointestinal symptoms. The study by Feng et al. [35] highlights the gastrointestinal implications of SARS-CoV-2 infection, emphasizing that enterocytes serve as a viral reservoir due to the high expression of ACE2 receptors in the small intestine, which may contribute to COVID-19-associated diarrhea and prolonged viral shedding in feces. The study reports that probiotics, including L. acidophilus, were widely used in Wuhan for COVID-19 patients experiencing diarrhea, aiming to restore gut microbiota balance. However, the findings indicate that while L. acidophilus and Bacillus clausii contributed to microbial modulation, they did not significantly reduce ACE2 receptor expression in the gut, suggesting that probiotics may help alleviate inflammation and dysbiosis but may not directly block viral entry into intestinal cells.
On the other hand, Saviano et al. [36] investigated the impact of a probiotic mix, including L. acidophilus LA 201, Bifidobacterium lactis LA 304, and Lactobacillus salivarius LA 302, on gastrointestinal inflammation in COVID-19 patients. The results showed that probiotic supplementation led to a significant reduction in fecal calprotectin levels, a key marker of gut inflammation, with a 35% decrease in the probiotic group compared to only 16% in the control group. Additionally, C-reactive protein (CRP), a systemic inflammatory marker, decreased by 72.7% in the probiotic-treated patients, whereas the control group exhibited a reduction of 62%. The study also observed a trend toward a lower need for oxygen support in the probiotic group, although this result was not statistically significant. These findings suggest that L. acidophilus, in combination with other probiotics, may help reduce gut and systemic inflammation in COVID-19 patients, highlighting its potential role as an adjunct therapy in managing gastrointestinal symptoms associated with the disease. Gutiérrez-Castrellón et al. [37] evaluated the effects of a daily oral capsule containing 2 × 109 CFU of a probiotic formula, which contained Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains KABP022, KABP023, KABP033 (which are part of the Lactobacillaceae family), and Pediococcus acidilactici strain KABP021. Furthermore, they were instructed to use it for 30 days, before breakfast, instead of from day 1 to day 30. The probiotic product was stored at room temperature and monitored for its microbial quality throughout the study. During these visits, various assessments were made, including the severity of COVID-19 symptoms, chest X-rays, and blood and fecal sample collections. The participants were also contacted by phone on several days for outpatient follow-up. The study design adhered to ethical protocols, and the product was placebo-controlled. It was blinded, randomized, and followed CONSORT guidelines. Only acetaminophen was permitted as co-medication. Patients receiving supplementation experienced a significant reduction in diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, and loose stools compared to those in the placebo group. The study also noted that probiotic-treated individuals had faster overall symptom resolution, suggesting that those probiotics contributed to restoring gut homeostasis and alleviating inflammation. Furthermore, the probiotic group showed improved gut microbiota composition, with increased levels of beneficial bacteria and a decrease in pathogenic microbial species commonly associated with dysbiosis in COVID-19 patients. These findings indicate that the dose may serve as an adjunctive therapy to counteract gastrointestinal disturbances in COVID-19, helping to regulate microbial balance and reduce gut inflammation. Horvath et al. [38] analyzed the use of probiotics for gastrointestinal symptoms during COVID-19. It reports on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study where patients with mild COVID-19 in home quarantine were given a multispecies probiotic, including L. acidophilus W37 and W55, among other strains (Bifidobacterium bifidum W23, Bifidobacterium lactis W51, Enterococcus faecium W54, Lactocaseibacillus paracasei W20, Lactoplantibacillus plantarum W1/W62, and Lactocaseibacillus rhamnosus W71). The study aimed to assess changes in the microbiome and gastrointestinal symptoms. The findings indicated that COVID-19 patients experienced significant alterations in their gut microbiome, including a reduction in beneficial bacteria such as Christensenellaceae and Ruminococcaceae and an increase in Bacteroidetes. Although probiotic treatment modulated microbiome diversity and introduced Enterococcus faecium W54, no significant effect was observed on COVID-19-related symptoms, including diarrhea or stool consistency. While probiotics did not lead to a measurable improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms during the study period, the microbiome modulation observed suggests a potential long-term benefit. However, L. acidophilus was only detected in a small number of samples, indicating that its colonization may be inconsistent or require longer administration periods for a measurable effect. These authors emphasized that the beneficial effects were more associated with inflammation modulation rather than a direct impact on ACE2 receptor expression. Finally, Hassan et al. [39] reflected the effects of L. acidophilus and colchicine on the symptoms, duration, and disease progression of mild and moderate COVID-19 cases in a randomized controlled trial. The study included 150 patients, divided into three groups: one receiving colchicine, one receiving L. acidophilus, and one as a control group. The findings revealed that gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, were commonly reported among COVID-19 patients, and gut microbiota alterations persisted even after viral clearance. While probiotics, including L. acidophilus, were administered to improve gut health and modulate the immune response, the study found no statistically significant difference in symptom improvement, disease duration, or hospitalization rates between the probiotic group and the control group. These results suggest that while L. acidophilus may support gut microbiota balance, it did not significantly alter clinical outcomes in mild and moderate COVID-19 patients in this particular study.
3.3. Mechanism of Action of L. acidophilus in Counteracting Gastrointestinal Effects
L. acidophilus exerts its beneficial effects on gastrointestinal health through multiple mechanisms, including modulation of gut microbiota, reinforcement of the intestinal barrier, immunomodulation, interaction with the gut–brain axis, antiviral properties, and regulation of ACE2 expression. These mechanisms contribute to its ability to counteract gastrointestinal disturbances, including those associated with infections, inflammatory diseases, and functional disorders. The first mechanism through which L. acidophilus provides gastrointestinal benefits is by modulating gut microbiota and competing with pathogenic bacteria. This probiotic has the ability to colonize the intestinal mucosa and form a protective biofilm, which prevents the adhesion and overgrowth of harmful bacteria such as Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli, and Clostridium difficile [40,41]. It produces bacteriocins, antimicrobial peptides that inhibit the growth of pathogens, and organic acids such as lactic acid and acetic acid, which lower the gut pH and create an inhospitable environment for many harmful microorganisms [42]. By maintaining a balanced microbiota composition, L. acidophilus helps prevent dysbiosis, a condition associated with several gastrointestinal disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [43]. Studies have shown that supplementation with L. acidophilus can lead to an increase in beneficial bacteria such as Bifidobacterium and a decrease in opportunistic pathogens, thereby improving gut health and reducing symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, and constipation [44].
Another crucial function of L. acidophilus is its role in strengthening the intestinal barrier. The intestinal epithelium serves as the first line of defense against pathogens and toxins, and its integrity is essential for maintaining gut health [45]. L. acidophilus enhances the production of tight junction proteins, including occludin, claudin-1, and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), which are responsible for sealing the spaces between epithelial cells and preventing the translocation of harmful bacteria and toxins into the bloodstream [46]. Additionally, this probiotic stimulates the secretion of mucins (MUC2, MUC3), which reinforce the mucus layer that lines the gut, acting as a physical barrier against microbial invasion [47]. Studies have demonstrated that L. acidophilus supplementation can restore intestinal barrier integrity in conditions such as leaky gut syndrome [48], Crohn’s disease [49], and ulcerative colitis [50], thereby reducing inflammation and improving overall gut function [51].
L. acidophilus also exerts significant anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, which play a crucial role in maintaining gastrointestinal homeostasis [52]. This probiotic modulates the immune system by promoting the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-10 (IL-10) [53] while reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-8 (IL-8) [54]. Additionally, L. acidophilus enhances the activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which help in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing excessive inflammatory responses [55]. This immunomodulatory effect is particularly beneficial in conditions such as IBD and IBS, where an overactive immune response contributes to chronic inflammation and tissue damage [56]. By modulating immune function, L. acidophilus not only helps in reducing gut inflammation but also supports systemic immune health [57].
The interaction of L. acidophilus with the gut–brain axis represents another important mechanism by which it alleviates gastrointestinal symptoms [58]. The gut–brain axis is a bidirectional communication network between the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system, influenced by gut microbiota and microbial metabolites [59]. L. acidophilus has been shown to modulate the production of neurotransmitters such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and serotonin, which play essential roles in regulating gut motility, visceral sensitivity [60], and mood [61]. Research indicates that supplementation with L. acidophilus can help in reducing stress-induced gastrointestinal symptoms, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating, by modulating vagus nerve activity and reducing the perception of gut discomfort [13]. Additionally, clinical studies have demonstrated that probiotics, including L. acidophilus, may have potential therapeutic applications in conditions such as anxiety, depression, and functional gastrointestinal disorders, where gut–brain interactions are disrupted [62].
Another important mechanism through which L. acidophilus provides gastrointestinal benefits is its antiviral properties and protective effects against enteric infections [63]. This probiotic produces antimicrobial metabolites, including hydrogen peroxide [64], short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) [65], and bacteriocins [66], which exhibit antiviral activity against enteric viruses such as rotavirus [67] and norovirus [68]. Additionally, L. acidophilus enhances the secretion of mucins [69] and immunoglobulin A (IgA) [70], which contribute to the neutralization and clearance of viral pathogens from the gut. Studies have shown that L. acidophilus may reduce the severity and duration of viral gastroenteritis in some COVID-19 patients by improving immune response and gut barrier function [71,72].
On the other hand, SARS-CoV-2 has been suggested to exhibit bacteriophage-like behavior, interacting with the gut microbiota and possibly altering the microbial composition, leading to gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea and vomiting. This interaction is thought to occur through the virus’s use of the ACE2 receptor, which is highly expressed not only in the lungs but also in the gastrointestinal tract, making the gut a key site for viral entry. Studies indicate that the virus could influence gut microbiota by modifying bacterial populations, similar to the mechanisms of bacteriophages, which infect and alter bacterial behavior. This has important implications for understanding how the virus contributes to gut dysbiosis and inflammation and highlights the potential role of probiotics in modulating these effects, potentially reducing viral load and improving gastrointestinal health. A better understanding of these interactions can guide therapeutic strategies for managing COVID-19 symptoms related to the gastrointestinal system [73].
Finally, the regulation of ACE2 expression in the gut represents a novel area of research regarding the potential implications of L. acidophilus in COVID-19-associated gastrointestinal symptoms [74]. ACE2 is a key receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells and is highly expressed in enterocytes of the small intestine [75]. The challenge then is finding potential probiotic strains able to significantly reduce ACE2 receptor expression in a gut cell line. Some studies suggest that probiotics, including L. acidophilus, may influence ACE2 expression and modulate gut inflammation during viral infections [76,77,78].
4. Conclusions
This review highlights the potential of some L. acidophilus strains and their combinations with other bacteria in alleviating gastrointestinal symptoms in COVID-19 patients. Evidence suggests it may help modulate gut microbiota, regulate immune responses, reduce inflammation, and enhance the production of tight junction proteins, reinforcing the intestinal barrier. The primary mechanism appears to involve gut inflammation and dysbiosis modulation rather than direct viral inhibition. However, some probiotic strains, including L. acidophilus, have also been shown to influence the expression of ACE2 receptors. ACE2, which is the entry point for SARS-CoV-2 into host cells, is highly expressed in the intestinal epithelial cells. By modulating the expression of ACE2 receptors, L. acidophilus may indirectly affect the host’s susceptibility to the virus. This effect could help reduce viral entry and subsequent inflammation, further supporting its role in managing COVID-19-related gastrointestinal symptoms. Therefore, L. acidophilus may provide a dual benefit by enhancing the intestinal barrier through tight junction modulation and potentially influencing ACE2 expression, which could complement the immune response against viral infections. However, further rigorous investigation is required to establish optimal dosages, type of strain, treatment duration, and the specific patient populations that may derive the most benefit, in addition to elucidating the role of the gut–lung axis in immune response regulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, B.B., A.C.-C., N.S.O. and J.M.S.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B. and J.M.S.; writing—review and editing, A.C.-C. and N.S.O.; supervision, J.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy reason.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| IBS | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| MERS-CoV | Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| NAC | N-acetyl-cysteine |
| PICO | Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PRN | Pro re nata |
| SARS-CoV | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| TNF-α | Necrosis factor-alpha |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Raveendran, A.V.; Giordano, R.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Long COVID or Post-COVID-19 Condition: Past, present and future research directions. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayanand, P.; Wilkins, M.W. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): A review. Clin. Med. 2004, 4, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Kandeil, A.; Shehata, M.; El Shesheny, R.; Samy, A.M.; Kayali, G.; Ali, M.A. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV): State of the science. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classification of 2019-nCoV and designation SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19–11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Lauer, S.A.; Grantz, K.H.; Bi, Q.; Jones, F.K.; Zheng, Q.; Meredith, H.R.; Lessler, J. The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: Estimation and application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 172, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boselli, P.M.; Soriano, J.M. COVID-19 in Italy: Is the mortality analysis a way to estimate how the epidemic lasts? Biology 2023, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothan, H.A.; Byrareddy, S.N. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19). J. Autoimmun. 2020, 109, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabakova, Y.; Gerasoudis, S.; Miteva, D.; Peshevska-Sekulovska, M.; Batselova, H.; Snegarova, V.; Vasilev, G.V.; Vasilev, G.H.; Sekulovski, M.; Lazova, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variant-Specific Gastrointestinal Symptoms of COVID-19: 2023 Update. Gastroenterol. Insights 2023, 14, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernia, F.; Ashktorab, H.; Cesaro, N.; Monaco, S.; Faenza, S.; Sgamma, E.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. COVID-19 and Gastrointestinal Tract: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Manifestations. Medicina 2023, 59, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.; Costa de Oliveira, S. The Impact of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Expression Levels in Patients with Comorbidities on COVID-19 Severity: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.J.; Hiscox, J.A.; Hooper, N.M. ACE2: From vasopeptidase to SARS virus receptor. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gou, X.; Pu, K.; Chen, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, Y. Prevalence of comorbidities in Wuhan novel coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Ou, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Du, B. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infusino, F.; Marazzato, M.; Mancone, M.; Fedele, F.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Severino, P.; Ceccarelli, G.; Santinelli, L.; Cavarretta, E.; Marullo, A.G.M.; et al. Diet Supplementation, Probiotics, and Nutraceuticals in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serek, P.; Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M. The Effect of Bacterial Infections, Probiotics and Zonulin on Intestinal Barrier Integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabczyk, M.; Nowak, J.; Hudzik, B.; Zubelewicz-Szkodzińska, B. Diet, Probiotics and Their Impact on the Gut Microbiota during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Koh, G.C.H.; Car, J. COVID-19: A remote assessment in primary care. BMJ 2020, 368, m1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Wu, X.X.; Jiang, X.G.; Xu, K.J.; Ying, L.J.; Ma, C.L.; Sheng, J.F. Clinical findings in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 outside Wuhan, China: Retrospective case series. BMJ 2020, 368, m606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Cai, H.; Shen, Y.; Ni, Q.; Chen, Y.; Hu, S.; Qiu, Y. Managing Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): The Experience of Zhejiang. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2020, 49, 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.S.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y.R.; Ye, L.L.; Peng, W.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, X.R. Clinical Features of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Pneumonia with Diarrhea. SSRN 2020. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3546120 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Bhimraj, A.; Morgan, R.L.; Shumaker, A.H.; Lavergne, V.; Baden, L.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Shoham, S. Guidelines from the Infectious Diseases Society of America on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 78, e83–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.-N.; Chao, S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, X.-J.; Mu, X.-D.; Lin, M.-G.; Jiang, R.-M. Clinical Features of Pediatric Patients with COVID-19: A Report of Two Family Cluster Cases. World J. Pediatr. 2020, 16, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarocki, P.; Komoń-Janczara, E.; Glibowska, A.; Dworniczak, M.; Pytka, M.; Korzeniowska-Kowal, A.; Wzorek, A.; Kordowska-Wiater, M. Molecular Pathways for Specific Identification of the Lactobacillus Casei Group at the Species, Subspecies, and Strain Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, Ó.J.; Barragán, P.J.; Serna, L. Review of Lactobacillus in the Food Industry and Their Culture Media. Rev. Colomb. Biotecnol. 2019, 21, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorakkattu, P.; Khanashyam, A.C.; Shah, K.; Babu, K.S.; Mundanat, A.S.; Deliephan, A.; Deokar, G.S.; Santivarangkna, C.; Nirmal, N.P. Postbiotics: Current Trends in Food and Pharmaceutical Industry. Foods 2022, 11, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, J.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, K.R.; Eun, H.; Yang, D.; Ko, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-J. Application of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) in Sustainable Agriculture: Advantages and Limitations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Wu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, W.; Yue, J.; Xiao, B.; Luo, Z. Lactobacillus and Intestinal Diseases: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 260, 127019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Elements for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for the Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies Evaluating Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Quality Assessment Tool for Case Series Studies. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Monitoring the Efficacy of a Probiotic Dietary Supplement SmartProbio C in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Infection. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05474144 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Synbiotic Therapy of Gastrointestinal Symptoms During COVID-19 Infection. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04420676 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Horowitz, R.I.; Freeman, P.R.; Bruzzese, J. Efficacy of glutathione therapy in relieving dyspnea associated with COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 2 cases. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 30, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, W. The small intestine, an underestimated site of SARS-CoV-2 infection: From Red Queen effect to probiotics. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviano, A.; Potenza, A.; Siciliano, V.; Petruzziello, C.; Tarli, C.; Migneco, A.; Nasella, F.; Franceschi, F.; Ojetti, V. COVID-19 Pneumonia and Gut Inflammation: The Role of a Mix of Three Probiotic Strains in Reducing Inflammatory Markers and Need for Oxygen Support. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Castrellón, P.; Gandara-Martí, T.; Abreu, Y.; Abreu, A.T.; Nieto-Rufino, C.D.; López-Orduña, E.; Jiménez-Escobar, I.; Jiménez-Gutiérrez, C.; López-Velazquez, G.; Espadaler-Mazo, J. Probiotic improves symptomatic and viral clearance in COVID-19 outpatients: A randomized, quadruple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2018899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, A.; Haller, R.; Feldbacher, N.; Habisch, H.; Žukauskaitė, K.; Madl, T.; Stadlbauer, V. Probiotic Therapy of Gastrointestinal Symptoms During COVID-19 Infection: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Remote Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.O.A.; Hassan, A.N.E.-D.; Mohamed, M.S.; Al Ashram, M.N.B.; Nesim, M.M.; Allam, M.F. The effects of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus and colchicine on the control of symptoms, duration, and disease progression of mild and moderate cases of COVID-19: Randomized controlled clinical trial. Microbes Infect. Dis. 2024, 5, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero-Sariñena, S.; Barlow, J.; Costabile, A.; Gibson, G.R.; Rowland, I. Antipathogenic activity of probiotics against Salmonella Typhimurium and Clostridium difficile in anaerobic batch culture systems: Is it due to synergies in probiotic mixtures or the specificity of single strains? Anaerobe 2013, 24, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellin-Pena, M.J.; Griffiths, M.W. Effect of molecules secreted by Lactobacillus acidophilus strain La-5 on Escherichia coli O157: H7 colonization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, B.; Guha, D.; Naik, A.K.; Banerjee, A.; Tambat, S.; Chawla, S.; Aich, P. Probiotics Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bacillus clausii modulate gut microbiota in Th1- and Th2-biased mice to ameliorate Salmonella typhimurium-induced diarrhea. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Lara, M.J.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A. The role of probiotic lactic acid bacteria and Bifidobacteria in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and other related diseases: A systematic review of randomized human clinical trials. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 505878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maftei, N.-M.; Raileanu, C.R.; Balta, A.A.; Ambrose, L.; Boev, M.; Marin, D.B.; Lisa, E.L. The Potential Impact of Probiotics on Human Health: An Update on Their Health-Promoting Properties. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, R.; Hosseinzadeh, D. Probiotics and Gastro-Intestinal Disorders: Augmentation, Enhancement, and Strengthening of Epithelial Lining. In Probiotics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 188–215. [Google Scholar]
- di Vito, R.; Conte, C.; Traina, G. A multi-strain probiotic formulation improves intestinal barrier function by the modulation of tight and adherent junction proteins. Cells 2022, 11, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Tyagi, A.; Kumar, A.; Panwar, S.; Grover, S.; Saklani, A.C.; Batish, V.K. Adhesion of lactobacilli and their anti-infectivity potential. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2042–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleman, R.S.; Moncada, M.; Aryana, K.J. Leaky Gut and the Ingredients That Help Treat It: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ren, L.F.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, L. How do intestinal probiotics restore the intestinal barrier? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Pei, C.; Chen, Y.; Gong, J.; Liao, Q. Live Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates ulcerative colitis via the SCFAs/mitophagy/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2985–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Hai, D.; Wei, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. The functional roles of Lactobacillus acidophilus in different physiological and pathological processes. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: A door to the body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paturi, G.; Phillips, M.; Jones, M.; Kailasapathy, K. Immune enhancing effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus LAFTI L10 and Lactobacillus paracasei LAFTI L26 in mice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walana, W.; Ye, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Cheng, J.W.; Li, F. IL-8 antagonist, CXCL8 (3-72) K11R/G31P coupled with probiotic exhibit variably enhanced therapeutic potential in ameliorating ulcerative colitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, Y.; Choi, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Cho, M.L.; Kwok, S.K. Lactobacillus acidophilus supplementation exerts a synergistic effect on tacrolimus efficacy by modulating Th17/Treg balance in lupus-prone mice via the SIGNR3 pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayesiga, I.; Iqbal, S.; Kyejjusa, Y.; Okoboi, J.; Omara, T.; Adelina, T.; Kahwa, I. Key regulatory aspects of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in the management of metabolic disorders. In Synbiotics in Metabolic Disorders; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 214–244. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Kwok, L.Y.; Cai, T.; Zhang, W. The immune regulatory role of Lactobacillus acidophilus: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Marlicz, W.; Misera, A.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Łoniewski, I. Microbiome—The Missing Link in the Gut-Brain Axis: Focus on Its Role in Gastrointestinal and Mental Health. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnani, M.; Bottalico, L.; Potenza, M.A.; Charitos, I.A.; Topi, S.; Colella, M.; Santacroce, L. The Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Nervous System: A Bidirectional Interaction between Microorganisms and Metabolome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liwinski, T.; Lang, U.E.; Brühl, A.B.; Schneider, E. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid in Stress and Depressive Disorders through the Gut–Brain Axis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Maleki, V.; Behrooz, M.; Ranjbar, F.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M. Can psychobiotics “mood” ify gut? An updated systematic review of randomized controlled trials in healthy and clinical subjects, on anti-depressant effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1395–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, F.; Pourjafar, H.; Tabrizi, A.; Homayouni, A. The effects of probiotics and prebiotics on mental disorders: A review on depression, anxiety, Alzheimer, and autism spectrum disorders. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Santamarina, A.; Lamas, A.; del Carmen Mondragón, A.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Regal, P.; Rodriguez-Avila, J.A.; Miranda, J.M.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A. Probiotic Effects against Virus Infections: New Weapons for an Old War. Foods 2021, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarid, L.; Zanditenas, E.; Ye, J.; Trebicz-Geffen, M.; Ankri, S. Insights into the mechanisms of Lactobacillus acidophilus activity against Entamoeba histolytica by using thiol redox proteomics. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowiak-Kopeć, P.; Śliżewska, K. The effect of probiotics on the production of short-chain fatty acids by human intestinal microbiome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, A.J.; Patel, M.; Adnan, M.; Jahan, S.; Saxena, J.; Alshahrani, M.M.; Abdelgadir, A.; Bardakci, F.; Sachidanandan, M.; Badraoui, R.; et al. Bacteriocin-Nanoconjugates (Bac10307-AgNPs) Biosynthesized from Lactobacillus acidophilus-Derived Bacteriocins Exhibit Enhanced and Promising Biological Activities. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Song, L.Y.; Rao, R.; Yang, H.W.; Wen, Y.P.; Lv, L.; Wang, L. The impact of combined therapy with Lactobacillus acidophilus and montmorillonite powder on the inflammatory response in pediatric rotavirus enteritis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyer, A.; Mičetić-Turk, D.; Fijan, S. The Efficacy of Probiotics as Antiviral Agents for the Treatment of Rotavirus Gastrointestinal Infections in Children: An Updated Overview of Literature. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celebioglu, H.U.; Olesen, S.V.; Prehn, K.; Lahtinen, S.J.; Brix, S.; Abou Hachem, M.; Svensson, B. Mucin- and carbohydrate-stimulated adhesion and subproteome changes of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. J. Proteomics 2017, 163, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus fermentum Stimulates Intestinal Secretion of Immunoglobulin A in an Individual-Specific Manner. Foods 2022, 11, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săsăran, M.O.; Mărginean, C.O.; Adumitrăchioaiei, H.; Meliț, L.E. Pathogen-Specific Benefits of Probiotic and Synbiotic Use in Childhood Acute Gastroenteritis: An Updated Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2023, 15, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, A.; Liang, L.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S. Modulatory effects of probiotics during pathogenic infections with emphasis on immune regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.N.; Kumari, N.; Pathak, A.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Gupta, A.K.; Chaurasia, R.N. Possible Role for Bacteriophages in the Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8844963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odun-Ayo, F.; Reddy, L. Gastrointestinal Microbiota Dysbiosis Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Colorectal Cancer: The Implication of Probiotics. Gastroenterol. Insights 2022, 13, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, S.D.; Mirsaeidi, M. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry beyond the ACE2 receptor. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 10715–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, R.; Yasavoli-Sharahi, H.; Alsadi, N.; Ismail, N.; Matar, C. Probiotics in Treatment of Viral Respiratory Infections and Neuroinflammatory Disorders. Molecules 2020, 25, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasti, A.N.; Synodinou, K.D.; Pyrousis, I.A.; Nikolaki, M.D.; Triantafyllou, K.D. Probiotics Regulating Inflammation via NLRP3 Inflammasome Modulation: A Potential Therapeutic Approach for COVID-19. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synodinou, K.D.; Nikolaki, M.D.; Triantafyllou, K.; Kasti, A.N. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics on COVID-19 Infection by Targeting the Gut–Lung Axis Microbial Cross-Talk. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).