Unraveling the Impact of Microplastic–Tetracycline Composite Pollution on the Moon Jellyfish Aurelia aurita: Insights from Its Microbiome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stock Culture of Polyps
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing and Analysis
2.4. Sequencing Library Construction
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
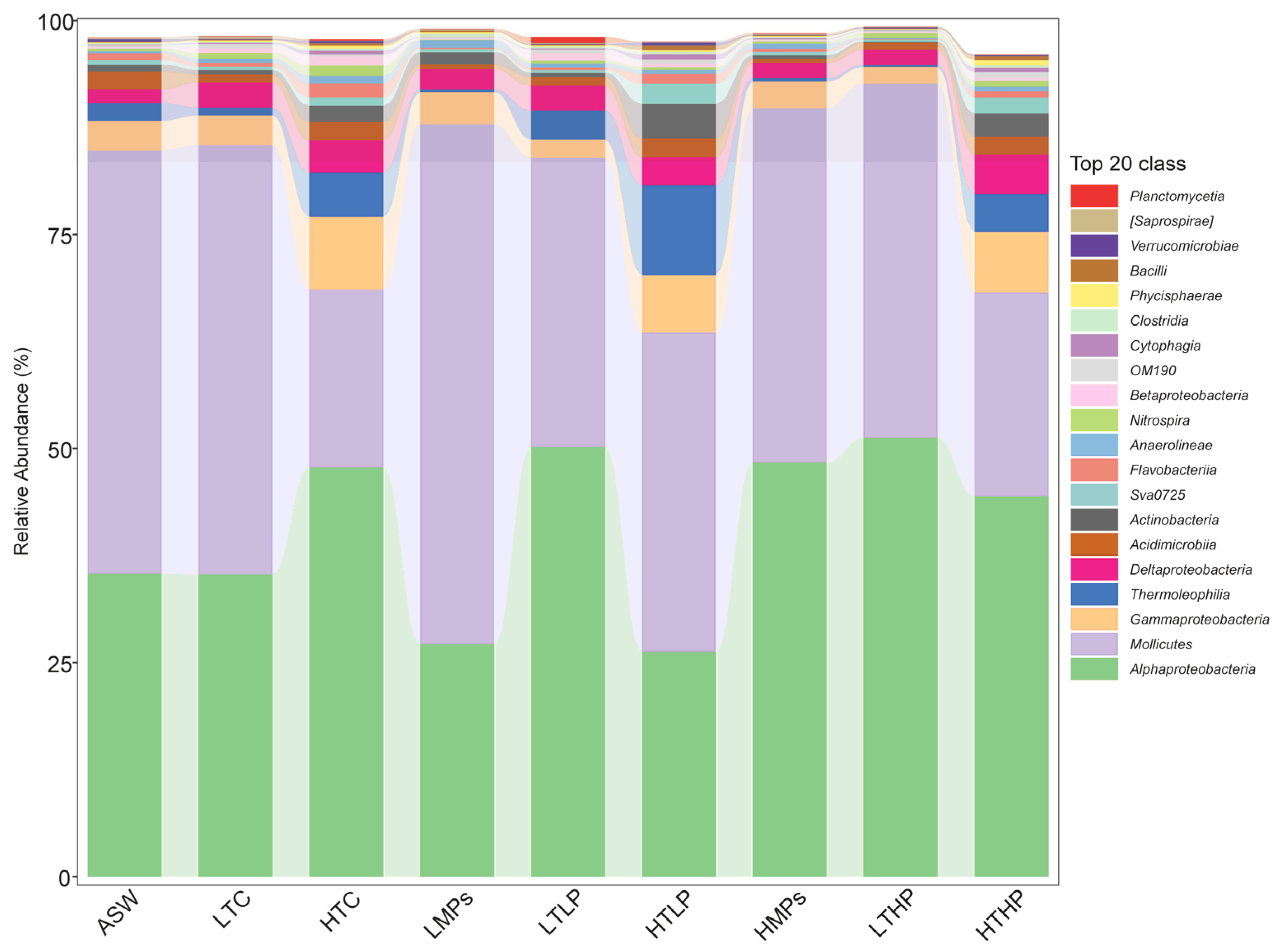
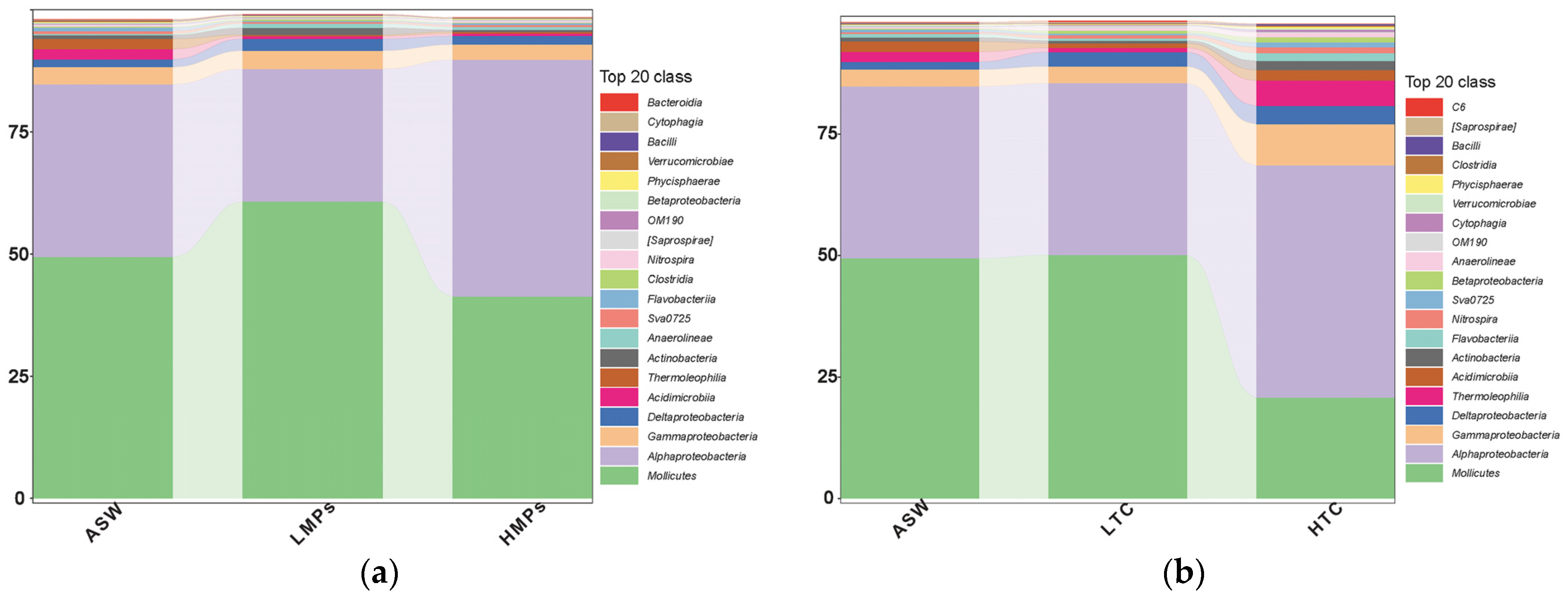
3.1. Microbiome Composition
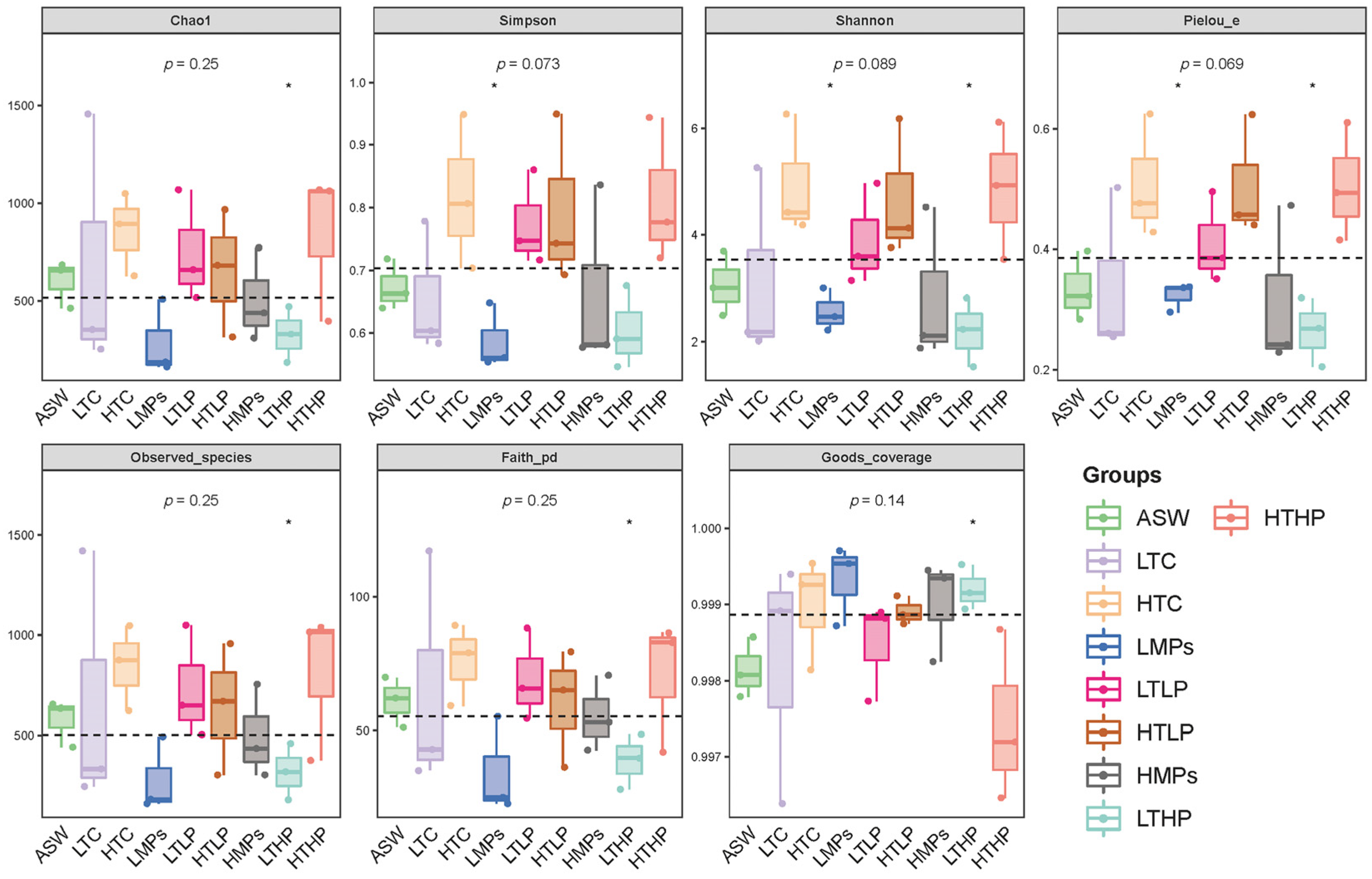
3.2. Alpha Diversity Analysis
3.3. Beta Diversity Analysis
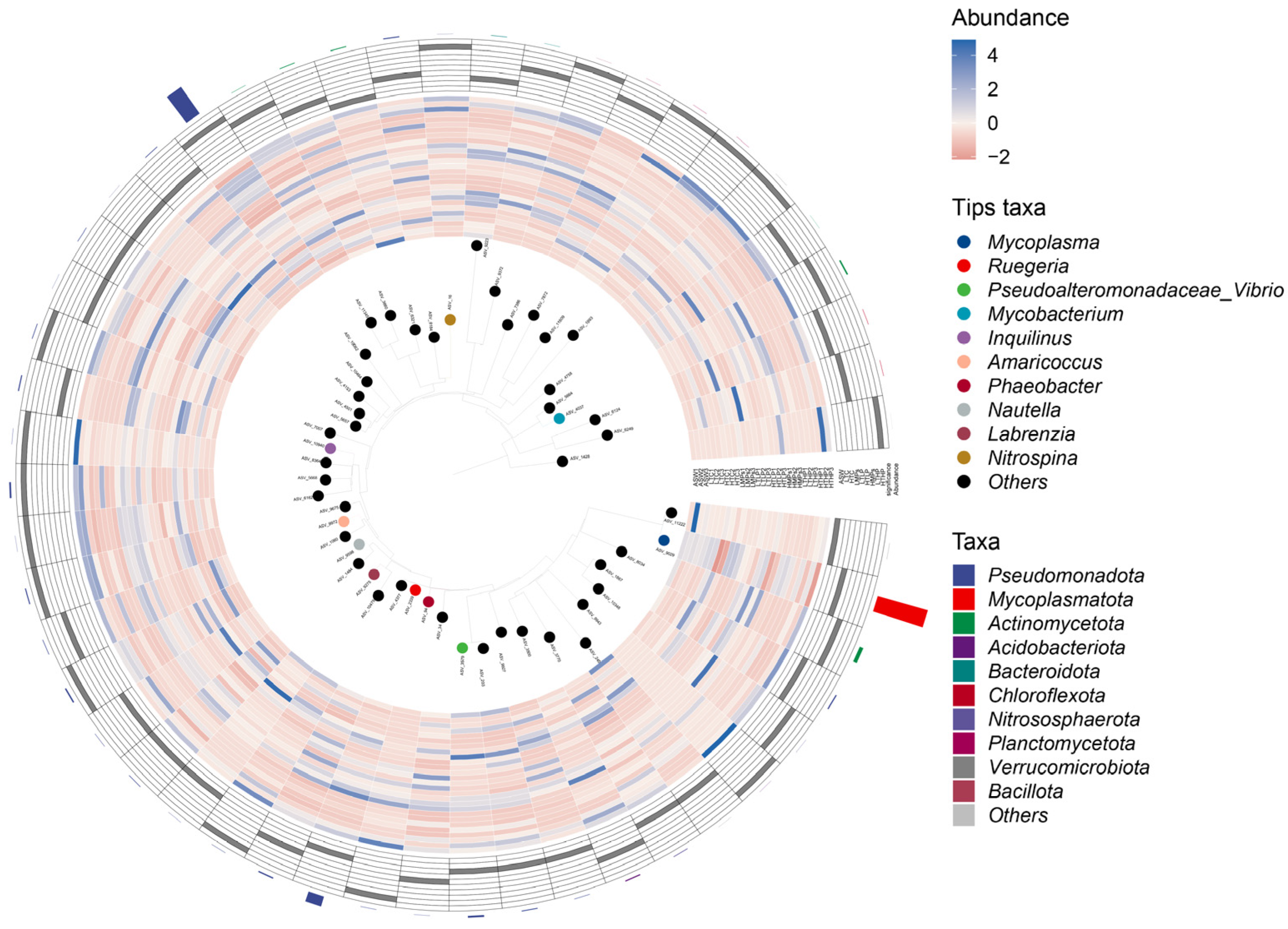
3.4. Species Difference Analysis and Landmark Species
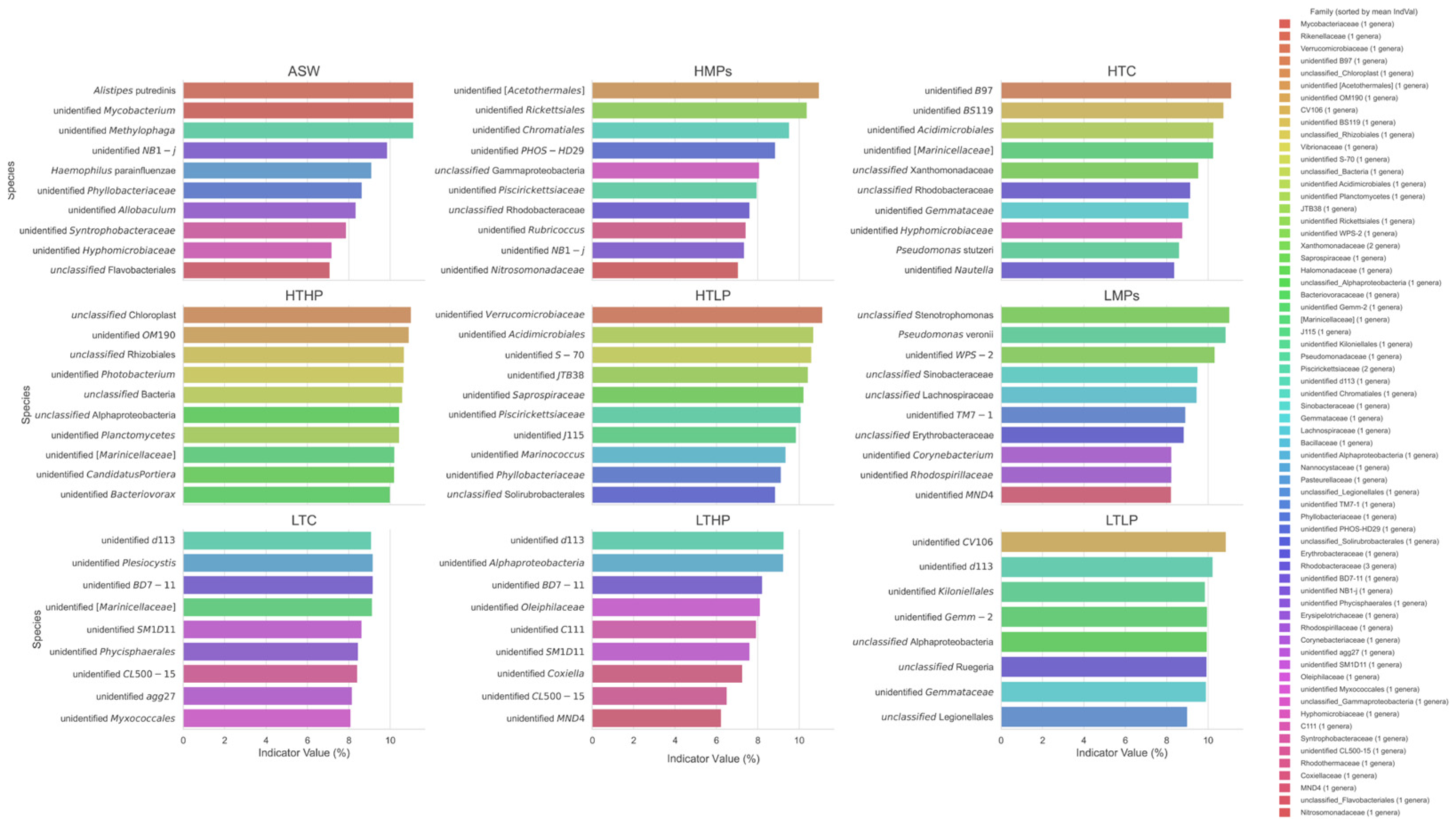
3.5. Species Indicator Analysis
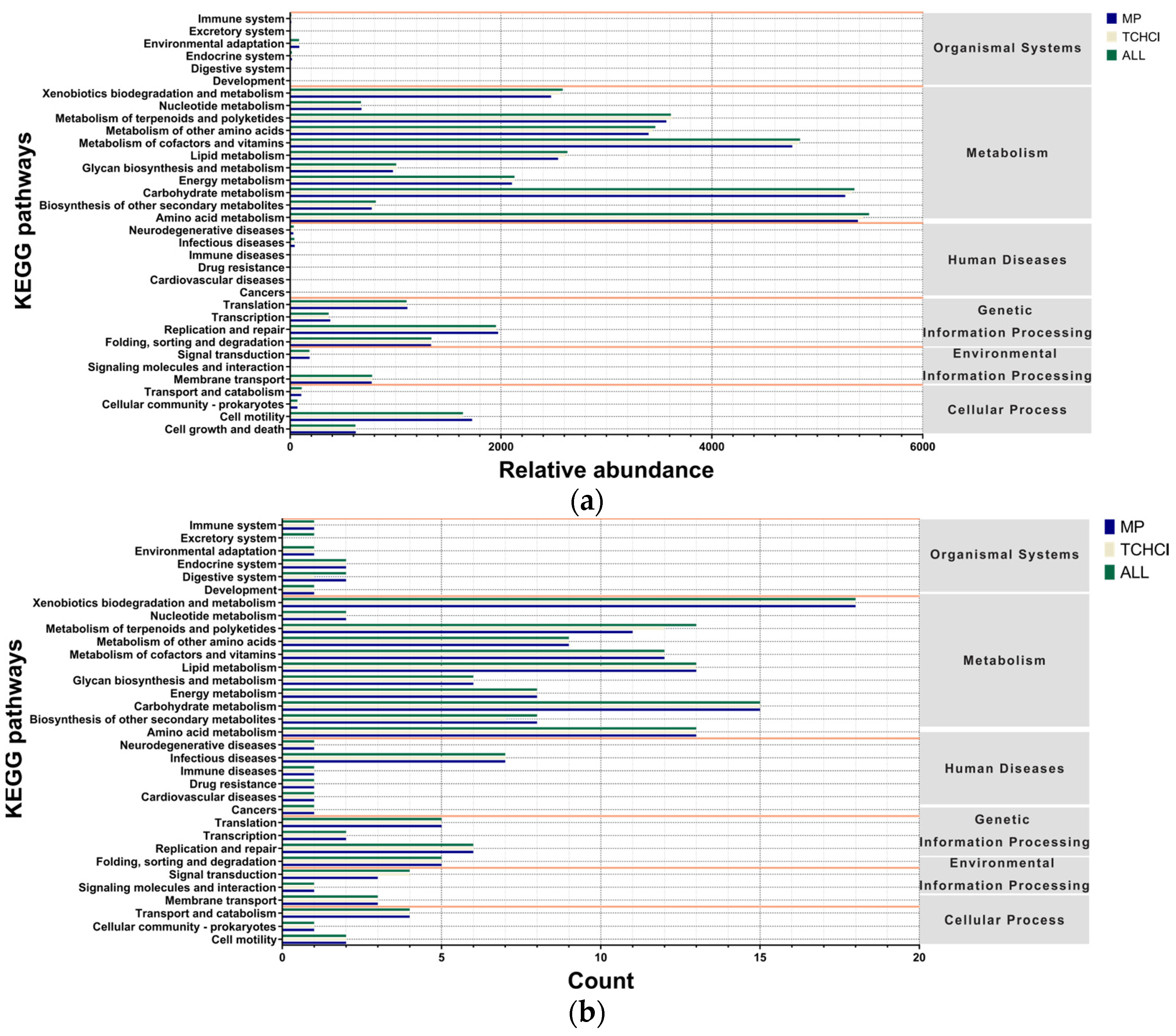
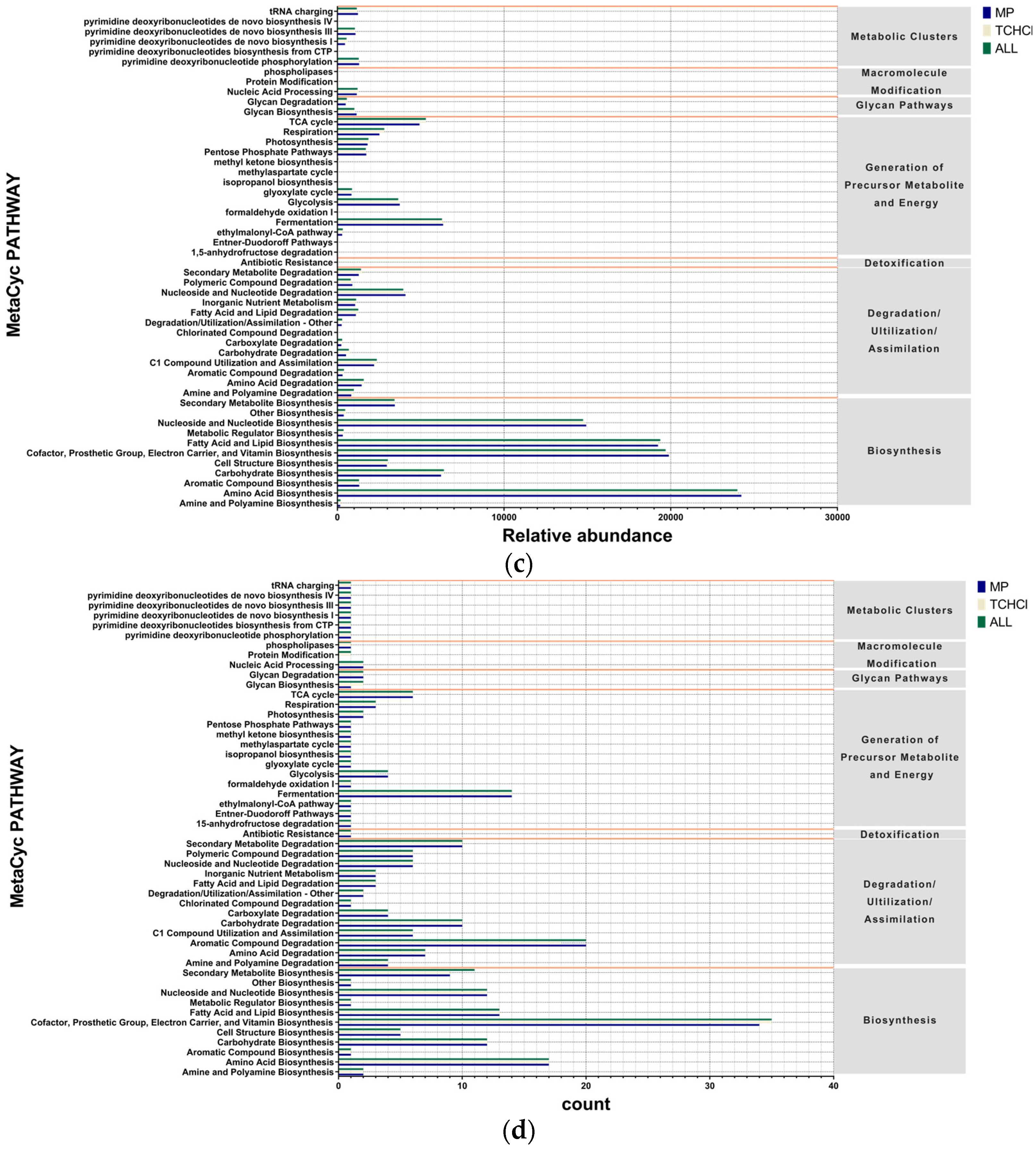
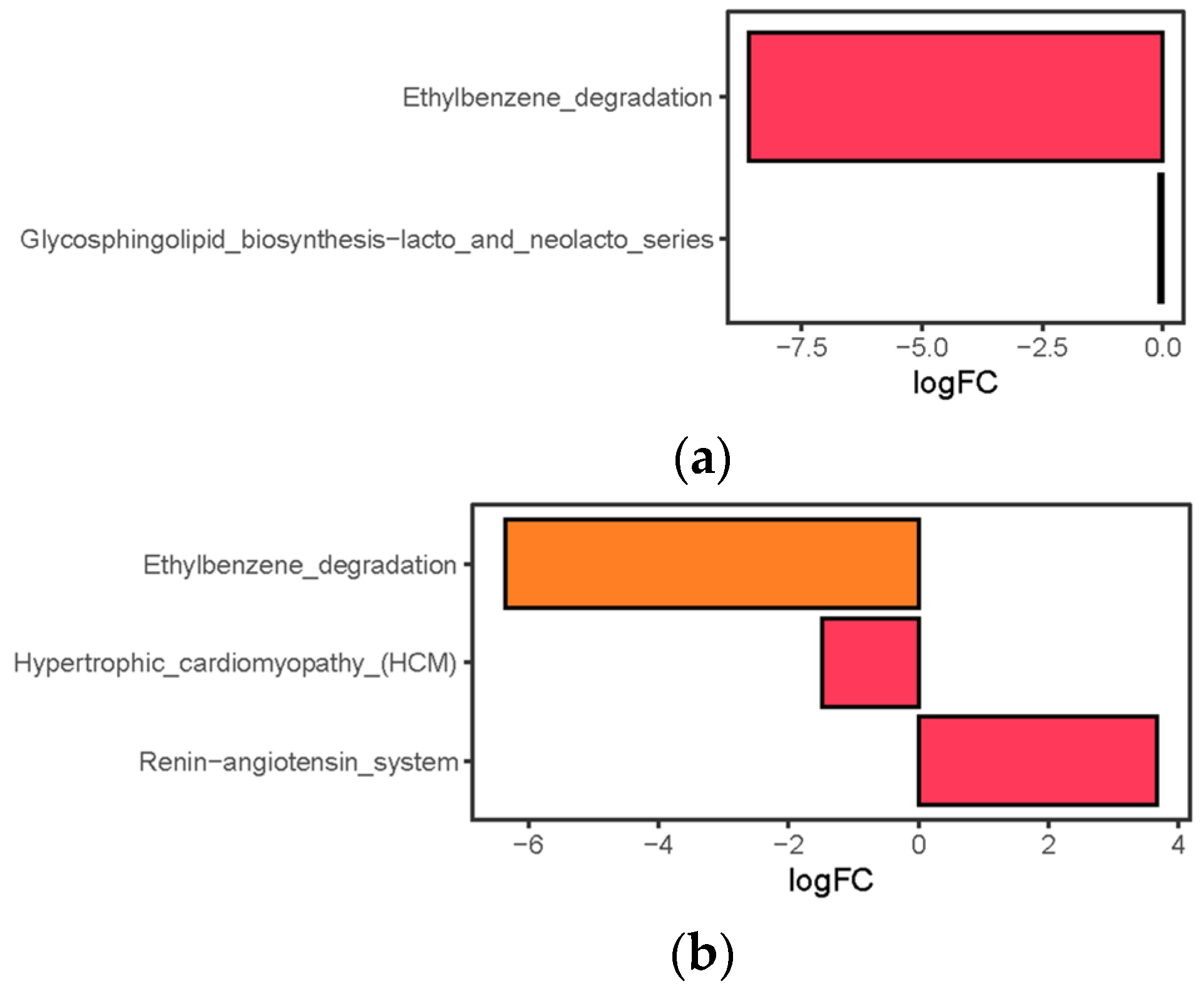
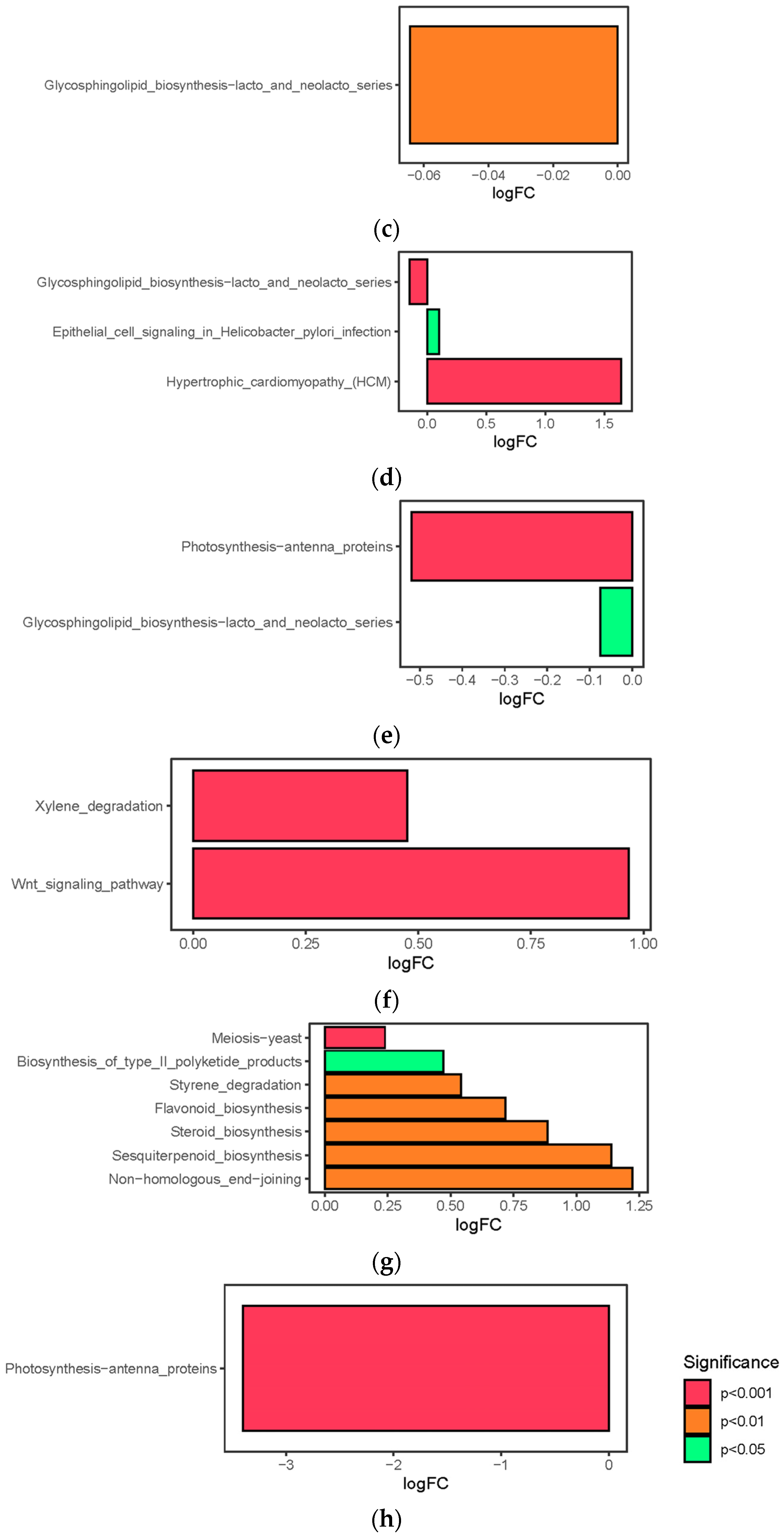
3.6. Pathway Differences
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Microbiome
4.2. Alterations in Metabolic Pathways
4.3. Potential Life Stage-Changing Factor
4.4. Ecological Impact
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MP | Microplastic |
| ARG | Antibiotic resistance gene |
| TC | Tetracycline |
| TCHCl | Tetracycline hydrochloride |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| ASW | Artificial seawater treatment control group |
| LTC | Low-concentration tetracycline treatment group |
| HTC | High-concentration tetracycline treatment group |
| LMPs | Low-concentration MP treatment group |
| LTLP | Low-concentration tetracycline combined with low-concentration MP treatment group |
| HTLP | High-concentration tetracycline combined with low-concentration MP treatment group |
| HMPs | High-concentration MP treatment group |
| LTHP | Low-concentration tetracycline combined with high-concentration MP treatment group |
| HTHP | Low-concentration tetracycline combined with high-concentration MP treatment group |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variant |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| PCB | Polychlorinated biphenyls |
Appendix A

References
- Albaseer, S.S.; Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Xu, X.; Abdulrahman, S.A.; Ezzati, P.; Habibzadeh, S.; Hollert, H.; Rabiee, N.; Lima, E.C. Microplastics in water resources: Global pollution circle, possible technological solutions, legislations, and future horizon. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 173963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, C.; Huang, C.; Luo, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, F.; Huang, X.; Sun, R. Ocean current modulation of the spatial distribution of microplastics in the surface sediments of the Beibu Gulf, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, I.A.; Clare, M.A.; Miramontes, E.; Wogelius, R.; Rothwell, J.J.; Garreau, P.; Pohl, F. Seafloor microplastic hotspots controlled by deep-sea circulation. Science 2020, 368, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Barnes, D.K. Microplastic pollution in a rapidly changing world: Implications for remote and vulnerable marine ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Sul, J.A.I.; Costa, M.F. The present and future of microplastic pollution in the marine environment. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, A.L.; Kawaguchi, S.; King, C.K.; Townsend, K.A.; King, R.; Huston, W.M.; Bengtson Nash, S.M. Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchi, S.; Bianchi, J.; Scalici, M.; Fabroni, F.; Tomassetti, P. Field evidence for microplastic interactions in marine benthic invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, H.; Raley-Susman, K.M.; He, D. Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafish Danio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, L.; Dierkes, G.; Ternes, T.A.; Völker, C.; Wagner, M. Benchmarking the in vitro toxicity and chemical composition of plastic consumer products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11467–11477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Liu, W.; Ali, N.; Shi, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yin, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, M. Microplastic pollution in terrestrial ecosystems: Global implications and sustainable solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A.A.; Tomio, Y.; Rosso, B.; Gambaro, A.; Sfriso, A.; Corami, F.; Rastelli, E.; Corinaldesi, C.; Mistri, M.; Munari, C. Microplastic accumulation in benthic invertebrates in Terra Nova bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.L.; Lin, S.Y.; Dungan, A.M.; Colwell, J.M.; Ede, S.; Lwanga, E.H.; Meng, K.; Geissen, V.; Blackall, L.L.; Chen, D. Microplastic pollution alters forest soil microbiome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sababadichetty, L.; Miltgen, G.; Vincent, B.; Guilhaumon, F.; Lenoble, V.; Thibault, M.; Bureau, S.; Tortosa, P.; Bouvier, T.; Jourand, P. Microplastics in the insular marine environment of the Southwest Indian Ocean carry a microbiome including antimicrobial resistant (AMR) bacteria: A case study from Reunion Island. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 198, 115911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xia, S.; Zhao, J. Effects of coexistence of tetracycline, copper and microplastics on the fate of antibiotic resistance genes in manured soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ya, H.; Zhang, T.; Xing, Y.; Lv, M.; Wang, X.; Jiang, B. Co-existence of polyethylene microplastics and tetracycline on soil microbial community and ARGs. Chemosphere 2023, 335, 139082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Sheng, G.D.; O’Connor, P. Microplastics combined with tetracycline in soils facilitate the formation of antibiotic resistance in the Enchytraeus crypticus microbiome. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhao, P.; Hou, L.; Adyari, B.; Xu, E.G.; Huang, Q.; Hu, A. Network analysis reveals significant joint effects of microplastics and tetracycline on the gut than the gill microbiome of marine medaka. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 129996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S. A Study on the Toxicity Effect of Microplastics/Tetracycline Complex on Button Polyps. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Y. Life cycle reversal in Aurelia sp. 1 (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Kutzner, V.; Tarí, J.; Herrera, A.; Martínez, I.; Bondyale-Juez, D.; Gómez, M. Ingestion of polyethylene microspheres occur only in presence of prey in the jellyfish Aurelia aurita. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Pinnow, N.; Langfeldt, D.; Roik, A.; Güllert, S.; Chibani, C.M.; Reusch, T.B.; Schmitz, R.A. The native microbiome is crucial for offspring generation and fitness of Aurelia aurita. mBio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.; Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Joel, S.; Chibani, C.M.; Schmitz, R.A. The life cycle of Aurelia aurita depends on the presence of a microbiome in polyps prior to onset of strobilation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00262-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohdera, A.H.; Mansbridge, M.; Wang, M.; Naydenkov, P.; Kamel, B.; Goentoro, L. The microbiome of a Pacific moon jellyfish Aurelia coerulea. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Koutsouveli, V.; Langfeldt, D.; Schmitz, R.A. First insights into the Aurelia aurita transcriptome response upon manipulation of its microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1183627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland-Bräuer, N.; Neulinger, S.C.; Pinnow, N.; Künzel, S.; Baines, J.F.; Schmitz, R.A. Composition of bacterial communities associated with Aurelia aurita changes with compartment, life stage, and population. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6038–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, V.; Fortič, A.; Kos Kramar, M.; Žnidarič, M.T.; Štrus, J.; Kostanjšek, R.; Malej, A. Observations on the Surface Structure of Aurelia solida (Scyphozoa) Polyps and Medusae. Diversity 2021, 13, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnow, N.; Chibani, C.M.; Güllert, S.; Weiland-Bräuer, N. Microbial community changes correlate with impaired host fitness of Aurelia aurita after environmental challenge. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, J.; Lu, W.; Cui, J.; Xiao, L. The distinct microbial community in Aurelia coerulea polyps versus medusae and its dynamics after exposure to 60Co-γ radiation. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; He, M.; Xu, P.; Ye, L.; Dong, Z. Effects of seawater acidification on microorganisms associated with Aurelia coerulea polyps. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2023, 42, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza-Silva, T.G.; Oliveira, I.A.; da Silva, G.G.; Giusti, F.C.V.; Novaes, R.D.; de Almeida Paula, H.A. Impact of microplastics on the intestinal microbiota: A systematic review of preclinical evidence. Life Sci. 2022, 294, 120366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian-yan, W.; Yu, Z.; Guo-shan, W.; Tie-zhu, M.; Zhi-gang, Y. Molecular identification and detection of moon jellyfish (Aurelia sp.) based on partial sequencing of mitochondrial 16S rDNA and COI. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 24, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Li, M.; He, X.; Ji, N.; Qin, Y.; Dai, L.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation of encapsulated starch constructed via layer-by-layer coating of calcium alginate. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 148, 109441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z., Jr.; Hugenholtz, P.; Keller, K.; Brodie, E.L.; Larsen, N.; Piceno, Y.M.; Phan, R.; Andersen, G.L. NAST: A multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W394–W399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y. Multi-omics-based approach reveals the effects of microplastics on microbial abundance and function of sediments in Shenzhen coastal waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1189876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Östman, C. Abundance, feeding behaviour and nematocysts of scyphopolyps (Cnidaria) and nematocysts in their predator, the nudibranch Coryphella verrucosa (Mollusca). Dev. Hydrobiol. 1997, 121, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-G.; Huang, B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, S.-X. Effect of dinoflagellates and diatoms on the feeding response and survival of Aurelia sp. polyps. Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T. Planktonic ciliates as a food source for the scyphozoan Aurelia aurita (sl): Feeding activity and assimilation of the polyp stage. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 407, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liao, H.; Guo, J.; Ma, Z.; Fu, Z. Microplastics and tetracycline affecting apoptosis, enzyme activities and metabolism processes in the Aurelia aurita polyps: Insights into combined pollutant effects. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1545131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Regulation of Metamorphosis and the Evolution of Life Cycles: Insights from the Common Moon Jelly Aurelia aurita. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitätsbibliothek Kiel, Kiel, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, B.; Wang, W.; Graspeuntner, S.; Li, Y.; Insua, S.; Herbst, E.-M.; Dirksen, P.; Böhm, A.-M.; Hemmrich, G.; Sommer, F. Regulation of polyp-to-jellyfish transition in Aurelia aurita. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, J.; Beníšek, M.; Hilscherová, K. Disruption of retinoid transport, metabolism and signaling by environmental pollutants. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 898–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, H.; Morita, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Imanishi, S.; Manabe, N. Effects of in utero exposure to bisphenol A on mRNA expression of arylhydrocarbon and retinoid receptors in murine embryos. J. Reprod. Dev. 2005, 51, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Torre, C.; Bergami, E.; Salvati, A.; Faleri, C.; Cirino, P.; Dawson, K.; Corsi, I. Accumulation and embryotoxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles at early stage of development of sea urchin embryos Paracentrotus lividus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12302–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antos, J.; Piosik, M.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D.; Zembrzuska, J.; Kruszelnicka, I. Tetracyclines contamination in European aquatic environments: A comprehensive review of occurrence, fate, and removal techniques. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Shim, W.J. Nanoplastics in the aquatic environment. Critical review. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besseling, E.; Wang, B.; Lurling, M.; Koelmans, A.A. Nanoplastic affects growth of S. obliquus and reproduction of D. magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12336–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, fate, and risk assessment of typical tetracycline antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-R.; Li, X.-Y. Sorption and desorption of antibiotic tetracycline on marine sediments. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elena, A.X.; Orel, N.; Fang, P.; Herndl, G.J.; Berendonk, T.U.; Tinta, T.; Klümper, U. Jellyfish blooms—An overlooked hotspot and potential vector for the transmission of antimicrobial resistance in marine environments. mSystems 2025, 10, e01012-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Austin, B. Significance of Vibrio species in the marine organic carbon cycle—A review. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triga, A.; Smyrli, M.; Katharios, P. Pathogenic and opportunistic Vibrio spp. associated with vibriosis incidences in the Greek aquaculture: The role of Vibrio harveyi as the principal cause of vibriosis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, F.H.; Visick, K.L. Vibrio biofilms: So much the same yet so different. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Orozco, L.; Acedo-Félix, E.; Higuera-Ciapara, I.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; Cano, R. Pathogenic and non pathogenic Vibrio species in aquaculture shrimp ponds. Rev. Latinoam. Microbiol. 2007, 49, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafi, N.F.; Lisa, N. The diversity of multi-drug resistance profiles in tetracycline-resistant Vibrio species isolated from coastal sediments and seawater. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 64–68. [Google Scholar]





| Groups | MP Concentration (mg/L) | TCHCl Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| ASW | 0 | 0 |
| LTC | 0 | 0.5 |
| HTC | 0 | 5 |
| LMPs | 0.1 | 0 |
| LTLP | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| HTLP | 0.1 | 5 |
| HMPs | 1 | 0 |
| LTHP | 1 | 0.5 |
| HTHP | 1 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Liao, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Fu, Z. Unraveling the Impact of Microplastic–Tetracycline Composite Pollution on the Moon Jellyfish Aurelia aurita: Insights from Its Microbiome. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040882
Wu X, Liao H, Zhang X, Ma Z, Fu Z. Unraveling the Impact of Microplastic–Tetracycline Composite Pollution on the Moon Jellyfish Aurelia aurita: Insights from Its Microbiome. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040882
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuandong, Hongze Liao, Xiaoyong Zhang, Zhenhua Ma, and Zhilu Fu. 2025. "Unraveling the Impact of Microplastic–Tetracycline Composite Pollution on the Moon Jellyfish Aurelia aurita: Insights from Its Microbiome" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040882
APA StyleWu, X., Liao, H., Zhang, X., Ma, Z., & Fu, Z. (2025). Unraveling the Impact of Microplastic–Tetracycline Composite Pollution on the Moon Jellyfish Aurelia aurita: Insights from Its Microbiome. Microorganisms, 13(4), 882. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040882








