Microbial Diversity, Co-Occurrence Patterns, and Functional Genes of Bacteria in Aged Coking Contaminated Soils by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Implications to Soil Health and Bioremediation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. PAH Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Metagenome Sequencing Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
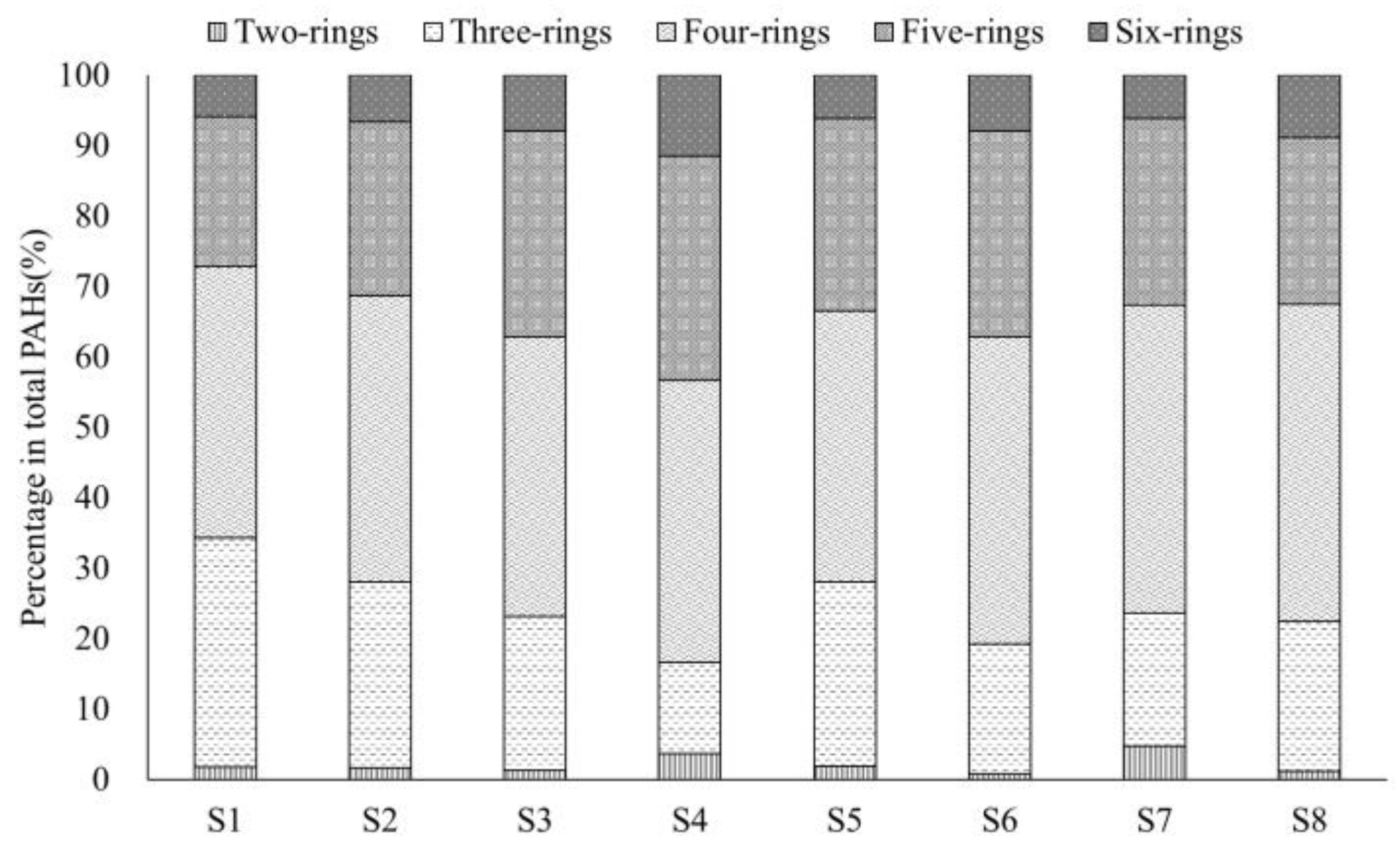
3.1. Concentration Distributions of PAHs
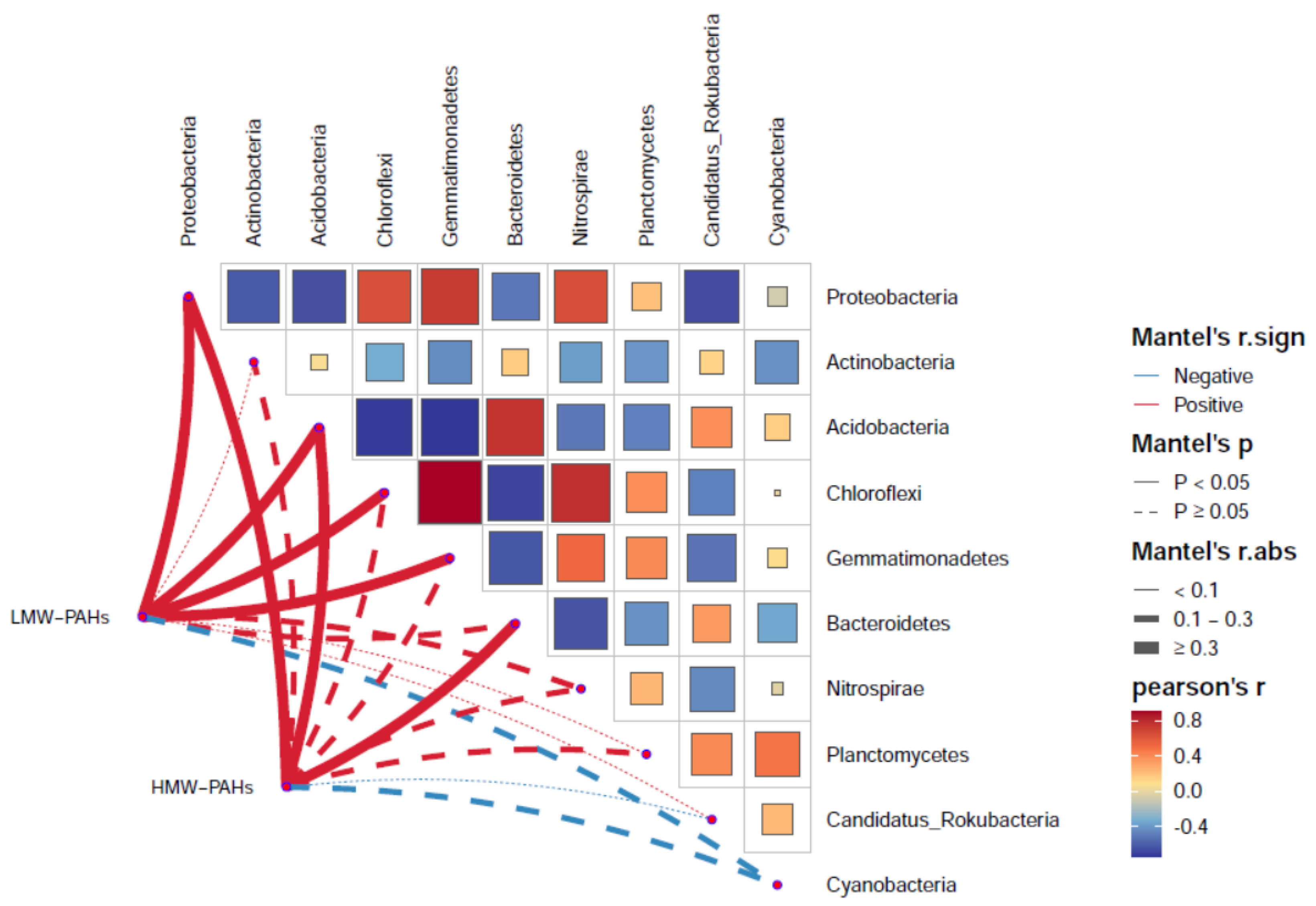
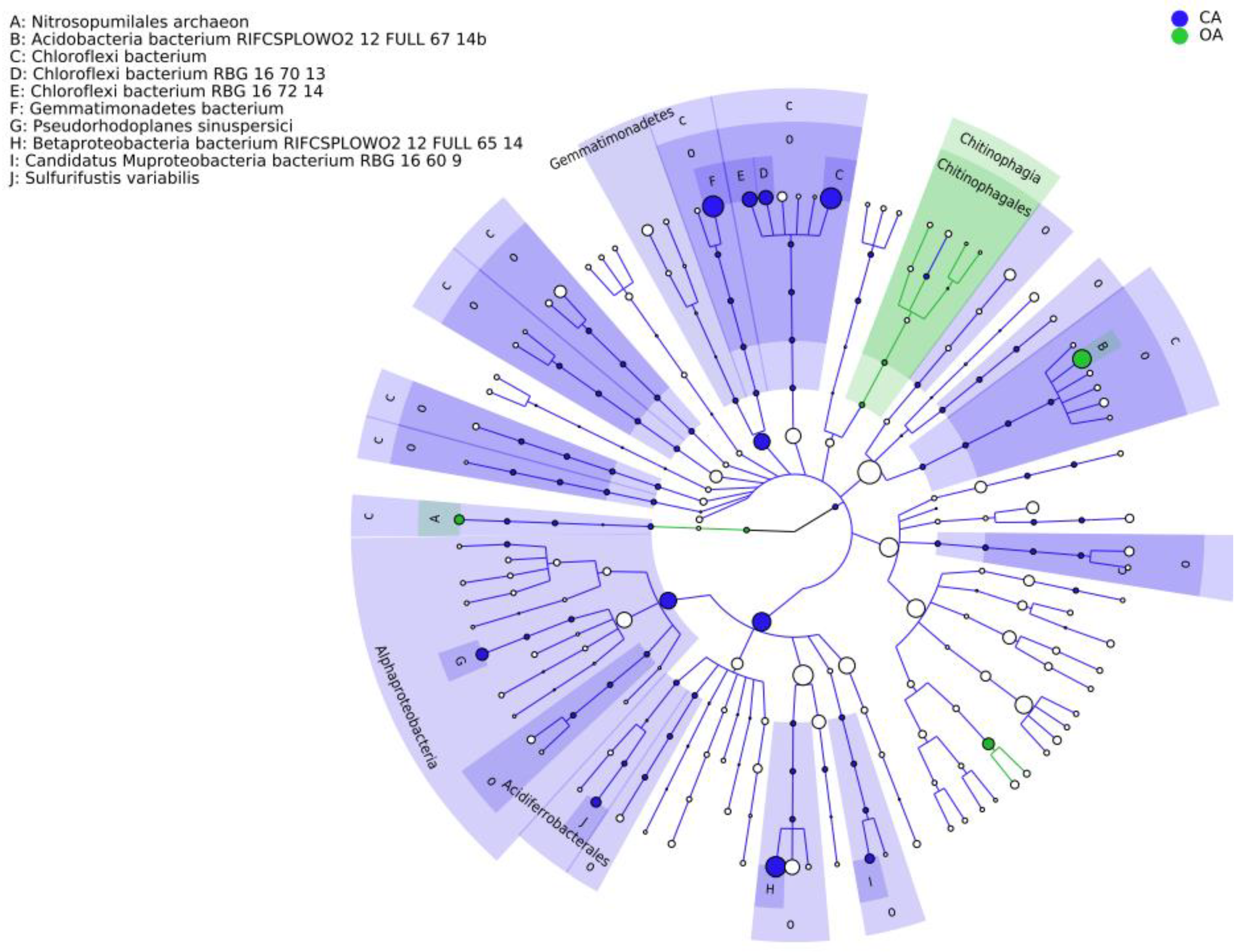
3.2. Relationship Between Bacterial Communities and PAHs
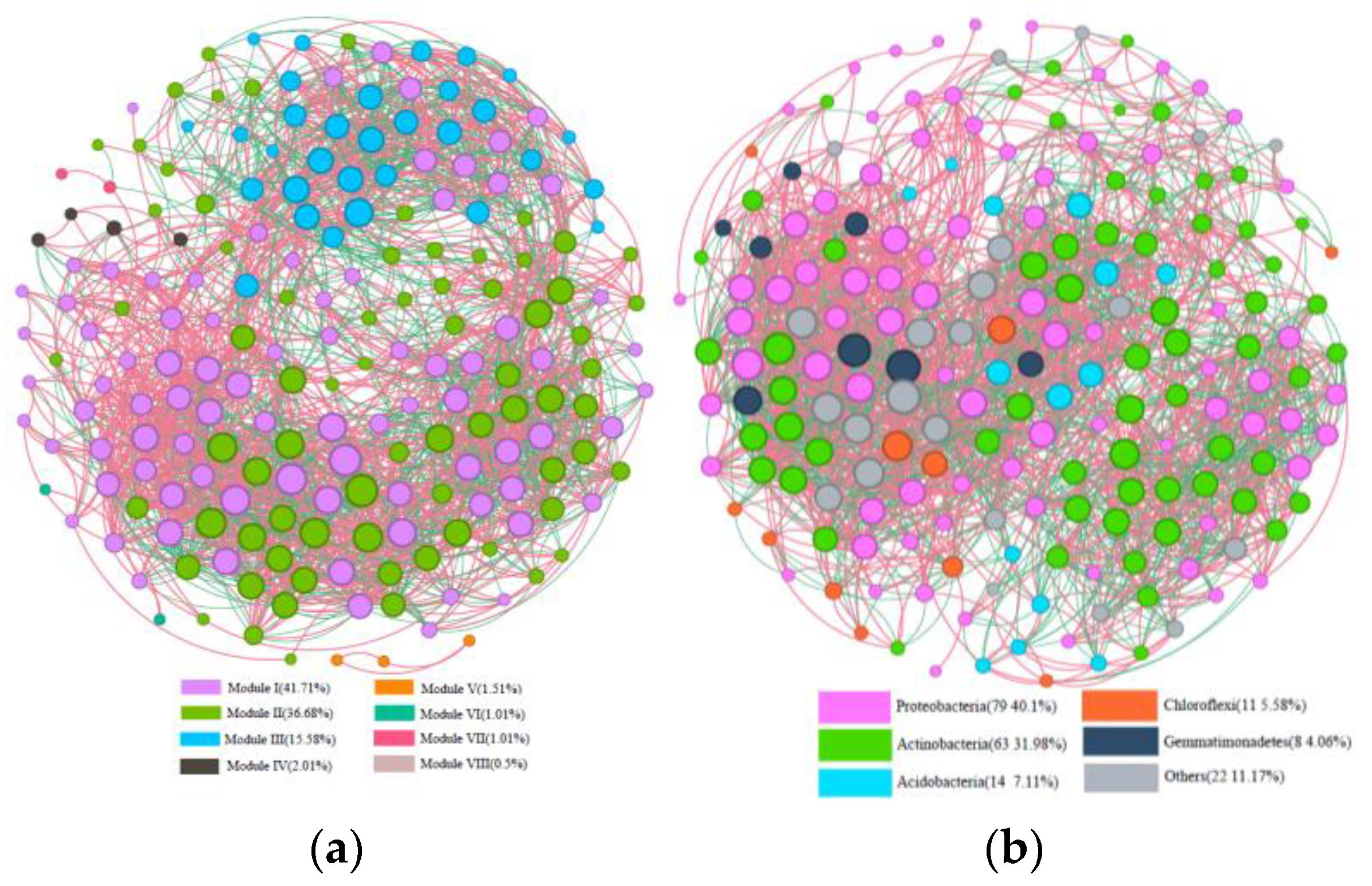
3.3. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
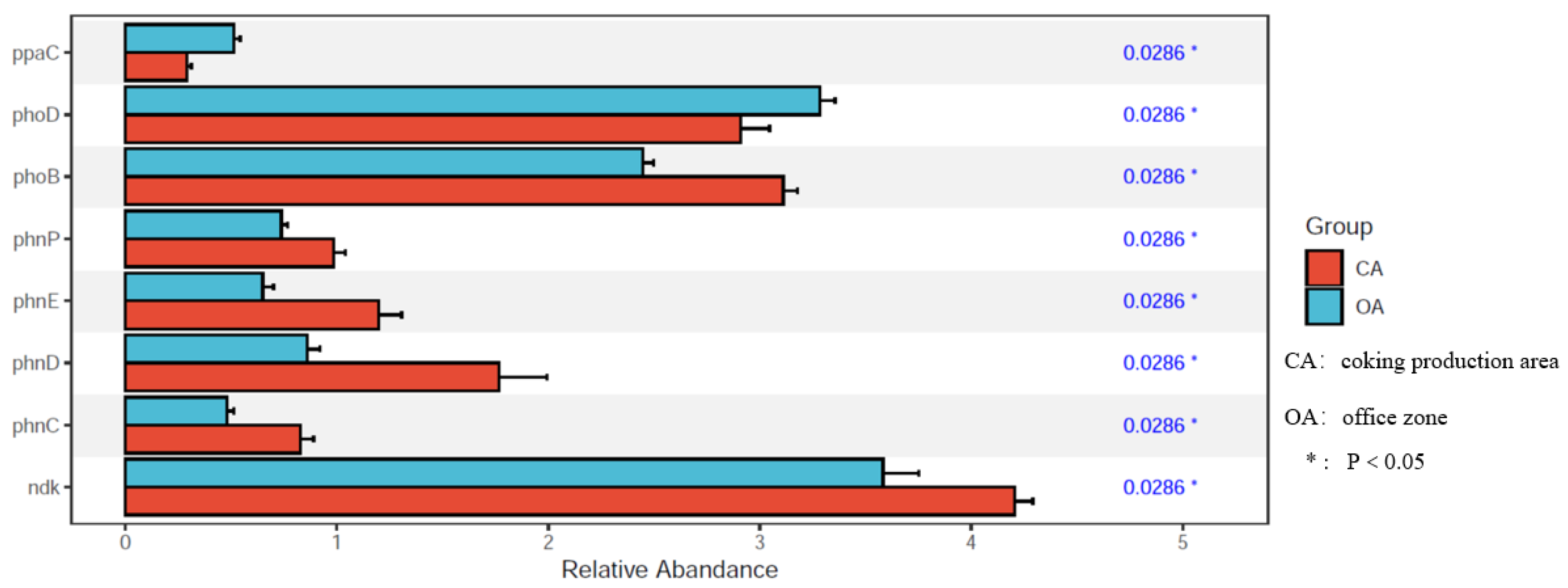
3.4. Functional Gene of Soil Phosphorus Cycling and PAH Degradation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, W.; Geng, S.; Zou, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, J. Post relocation of industrial sites for decades: Ascertain sources and human risk assessment of soil polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 198, 110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.S.; Liu, W.X.; Tao, S. Emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Wei, G. Bacterial communities in oil contaminated soils: Biogeography and co-occurrence patterns. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Tao, S. Global atmospheric emission inventory of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) for 2004. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S.; Keum, Y.S.; Li, Q.X. Bacterial degradation of aromatic compounds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 278–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockne, K.J.; Strand, S.E. Anaerobic biodegradation of naphthalene, phenanthrene, and biphenyl by a denitrifying enrichment culture. Water Res. 2001, 35, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 166-2004; The Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- HJ 834-2017; Soil and Sediment-Determination of Semivolatile Organic Compounds- Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Li, X.; Qu, C.S.; Bian, Y.R.; Gu, C.G.; Jiang, X.; Song, Y. New insights into the responses of soil microorganisms to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon stress by combining enzyme activity and sequencing analysis with metabolomics. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gudda, F.; Wang, Y.; Ling, W. Distribution of bound-PAH residues and their correlations with the bacterial community at different depths of soil from an abandoned chemical plant site. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Metagenomic analysis exhibited the co-metabolism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacterial community from estuarine sediment. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Metagenomics of the Effect of Long-Term Straw Return on the Phosphorus Cycle in Meadow Black Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, F. Critical review on soil phosphorus migration and transformation under freezing-thawing cycles and typical regulatory measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.L.; Lambers, H.; Condron, L.M.; Cramer, M.D.; Leake, J.R.; Richardson, A.E.; Smith, S.E. Soil microbial biomass and the fate of phosphorus during long-term ecosystem development. Plant Soil 2012, 367, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hy’sek, J.; Sˇarapatka, B. Relationship between phosphatase active bacteria and phosphatase activities in forest soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 26, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Sivabalan, S.; Shanmuganathan, R.; Thanigaivelan, K.; Dakshina, B.; Rajkumar, P.; Sivanesan, D. Biocatalytic Potential of Pseudomonas Species in the Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. J. Basic Microbiol. 2024, 29, 2400448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurie, A.D.; Lloyd-Jones, G. The phn Genes of Burkholderia sp. Strain RP007 Constitute a Divergent Gene Cluster for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Catabolism. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbera’n, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2011, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, W.J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, J. The phn Island: A New Genomic Island Encoding Catabolism of Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 3, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lors, C.; Ryngaert, A.; Perie, F.; Diels, L.; Damidot, D. Evolution of bacterial community during bioremediation of PAHs in a coal tar contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Cao, W.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ding, A.; Zhu, Y.; Dou, J. Microbial diversity and co-occurrence patterns in deep soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokul, J.K.; Hodson, A.J.; Saetnan, E.R.; Irvine-Fynn, T.D.; Westall, P.J.; Detheridge, A.P.; Takeuchi, N.; Bussell, J.; Mur, L.A.; Edwards, A. Taxon interactions control the distributions of cryoconite bacteria colonizing a high Arctic ice cap. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 3752–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, A.; Ju, F.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Mulla, S.; Sun, Q.; Helmut, B.; Yu, C. Strong impact of anthropogenic contamination on the co-occurrence patterns of a riverine microbial community. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4993–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Ji, G. Biotic factors drive distinct DNRA potential rates and contributions in typical Chinese shallow lake sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, B.D.; Fu, W. Research frontiers in soil ecology. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2020, 40, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Distribution of bacterial polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases genes in oilfield soils and mangrove sediments explored by gene-targeted metagenomics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2427–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Duan, F.A.; Cui, Z.; Hong, J.; Ni, S.Q. Insights into the vertical distribution of the microbiota in steel plant soils with potentially toxic elements and PAHs contamination after 60 years operation: Abundance, structure, co-occurrence network and functionality. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakshi; Haritash, A.K. A comprehensive review of metabolic and genomic aspects of PAH-degradation. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2033–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, L.K.; Bao, S.Y.; Yu, X.; Mao, X.; Chen, C. Research progress on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degrading bacteria and their applications. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1663–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Imam, A.; Suman, S.K.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Anjan, R. Biological machinery for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harayama, S.; Rekik, M.; Wasserfallen, A.; Bairoch, A. Evolutionary relationships between catabolic pathways for aromatics: Conservation of gene order and nucleotide sequences of catechol oxidation genes of pWW0 and NAH7 plasmids. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1987, 210, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Liang, X.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Pyrene degradation by Mycobacterium gilvum: Metabolites and proteins involved. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, R.P. Soil health paradigms and implications for disease management. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2015, 53, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moebius-Clune, B.N.; Moebius-Clune, D.J.; Gugino, B.K.; Idowu, O.J.; Schindelbeck, R.R.; Ristow, A.J.; van Es, H.M.; Thies, J.E.; Dhayler, H.A.; Mcbride, M.B.; et al. Comprehensive Assessment of Soil Health: The Cornell Framework; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Cai, Z.C. Frotiers in Soil Health Reach; Zhejiang University Press: Hangzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Hong, Y.; Odinga, E.S.; Liu, J.; Tsang, D.C.; Gao, Y. Bacterial community and PAH-degrading genes in paddy soil and rice grain from PAH-contaminated area. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 158, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Malla, M.A.; Khan, F.; Chowdhary, K.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, A.; Khan, M.L. Soil microbiome: A key player for conservation of soil health under changing climate. Biodivers. Conserv. 2019, 28, 2405–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Soil microbiomes and one health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, S. Assessing the ecological impacts of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons petroleum pollutants using a network toxicity model. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Luo, R.; Liu, C.M.; Leung, C.M.; Ting, H.F.; Sadakane, K.; Yamashita, H.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT v1. 0: A fast and scalable metagenome assembler driven by advanced methodologies and community practices. Methods 2016, 102, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Du, J.; Lu, X.; Xu, L.; Xie, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, B. Microbial Diversity, Co-Occurrence Patterns, and Functional Genes of Bacteria in Aged Coking Contaminated Soils by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Implications to Soil Health and Bioremediation. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040869
Zheng L, Yan Y, Li Q, Du J, Lu X, Xu L, Xie Q, Chen Y, Zhang A, Zhao B. Microbial Diversity, Co-Occurrence Patterns, and Functional Genes of Bacteria in Aged Coking Contaminated Soils by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Implications to Soil Health and Bioremediation. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040869
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Liping, Yifan Yan, Qun Li, Junyang Du, Xiaosong Lu, Li Xu, Qunhui Xie, Yangsheng Chen, Aiguo Zhang, and Bin Zhao. 2025. "Microbial Diversity, Co-Occurrence Patterns, and Functional Genes of Bacteria in Aged Coking Contaminated Soils by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Implications to Soil Health and Bioremediation" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040869
APA StyleZheng, L., Yan, Y., Li, Q., Du, J., Lu, X., Xu, L., Xie, Q., Chen, Y., Zhang, A., & Zhao, B. (2025). Microbial Diversity, Co-Occurrence Patterns, and Functional Genes of Bacteria in Aged Coking Contaminated Soils by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Implications to Soil Health and Bioremediation. Microorganisms, 13(4), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040869





