Abstract
Pathogenic infections can reshape the intestinal microbiota of aquatic animals, thereby impacting their health status. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection induces dysbiosis in the intestinal bacterial community of Penaeus vannamei and to assess the associated ecological risks. Our findings revealed the deterministic processes in intestinal bacterial community assembly during bacterial infections, indicating that host selection, i.e., host immune response post-infection, has a significant influence on intestinal microbes. More importantly, we found that bacterial infection reshaped the intestinal community by reducing the relative abundance of probiotic Ruegeria species (e.g., R. atlantica, R. lacuscaerulensis, R. conchae, R. profundi, R. arenilitoris, R. pomeroyi) and increasing the relative abundance of Vibrio species (V. harveyi, V. sinaloensis, V. coralliilyticus, and V. brasiliensis). Significant negative correlations were observed between the relative abundance of these Ruegeria species and the relative abundance of Vibrio species. Moreover, the control P. vannamei contained a substantially higher number of keystone species belonging to Ruegeria in the bacterial community network, whereas bacterial infection individuals had few or no keystone species belonging to Ruegeria, with keystone species belonging to Vibrio becoming more prominent. Thus, the significant increase in Vibrio species abundance in the P. vannamei intestine following bacterial infection was associated with the marked reduction in Ruegeria species. Our findings will provide valuable insights into the complex interactions among bacterial infection, intestinal microbiota, and host health, and they provide guidance for the development of probiotics in promoting the healthy culture of P. vannamei.
1. Introduction
Penaeus vannamei, commonly known as the Pacific white shrimp, is the most extensively farmed shrimp species globally, accounting for over 50% of total shrimp production [1]. Currently, the global aquaculture of P. vannamei faces a significant threat from bacterial diseases. Vibrio parahaemolyticus, one of the most prevalent bacterial pathogens affecting crustaceans, fish, and shellfish, particularly harboring a virulence plasmid encoding PirA/B, can cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in shrimp [2,3]. This disease can lead to 100% mortality among infected shrimp populations, resulting in substantial economic losses for the shrimp-farming industry [4,5]. Consequently, the prevention and control of vibriosis in shrimp pose a critical challenge for both scientific research and industrial practices.
The intestinal microbiota plays crucial roles in resisting pathogen invasion and maintaining host health [6,7,8,9,10]. Thus, a stable intestinal microbiota is vital for host health, and disruptions to this equilibrium can adversely affect the host [11]. Pathogenic infections can significantly alter the composition of intestinal microbiota in aquatic animals, characterized by reduced community diversity and pronounced shifts in specific bacterial taxa within the host intestines. For instance, high-dose infections with Vibrio vulnificus and V. parahaemolyticus lead to a marked decrease in the diversity index of the intestinal bacterial community in Cynoglossus semilaevis and Penaeus vannamei [12,13]. Similarly, viral infections induce significant alterations in the intestinal microbiota of aquatic animals; for example, grass carp reovirus infection in Ctenopharyngodon idellus resulted in decreased community diversity and the dysbiosis of intestinal microbiota, leading to a substantial expansion of Cetobacterium in the host’s intestine [14]. These findings have substantially advanced our understanding of the relationship between pathogenic infections and intestinal microbiota homeostasis in aquatic animals. However, further research is needed to fully comprehend how pathogenic infections impact host health through disruption of intestinal microbiota.
Multiple studies have provided compelling evidence that the disruption of the intestinal bacterial community can contribute to the Vibrio infection and the development of bacterial diseases in P. vannamei [15,16,17,18]. Additionally, a study by Zhang et al. [13] highlighted significant alterations in both the composition and function of the intestinal bacterial community following V. parahaemolyticus infection. These changes included an increase in the abundance of potential pathogenic bacteria and a decrease in beneficial bacteria, which were closely associated with metabolic disorders of nucleotides, lipids, amino acids, and carbohydrates within the host’s intestine. This research offers novel insights into the pathogenesis of vibriosis induced by the V. parahaemolyticus infection in P. vannamei. However, the mechanisms by which V. parahaemolyticus infection modulates the intestinal microbiota to affect its preventive function against V. parahaemolyticus and the subsequent disease progression remain unclear.
A previous study has indicated that the shrimp infection rate following injection was 40.4 times greater than that following immersion by V. parahaemolyticus [19]. Research reported signaling events induced by lipopolysaccharide-activated Toll in response to V. parahaemolyticus injection in shrimp, and this further induced antimicrobial peptides [20]. The shrimp’s antibacterial activities (PO and T-NOS) and the expression of the antibacterial genes (proPO, ALF, Toll, and Imd) and pathogen pattern recognition genes (LGBP and Lec) increased at first and then decreased after LPS injection [21]. Here, our objective was to investigate whether bacterial infection induces dysbiosis in the intestinal bacterial community of P. vannamei and to assess the associated ecological risks. Specifically, we evaluated the changes in bacterial community diversity and compositions within the P. vannamei intestines during infection by V. parahaemolyticus and lipopolysaccharides. We also focused on identifying probiotics from P. vannamei intestines that significantly decrease in response to infections. Our findings will provide valuable insights into the complex interactions among pathogens, intestinal microbiota, and host health and provide guidance for the development of the probiotics of healthy P. vannamei culture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
We conducted a controlled experiment to address our research questions. In this experiment, shrimp seedlings were free from specific pathogens. All foreign substances, including seawater and feed, were disinfected and tested for pathogens. We further determined that the experimental shrimp were not infected by examining each individual shrimp, ensuring that they met the following criteria: no macroscopic signs of disease; a complete hepatopancreas with clear margins; and a full intestine. During the experiment, the shrimp culture’s water temperature varied with indoor natural temperatures, and salinity was set at 30‰; each aquarium had the same breeding density, with 30 shrimp per aquarium. The shrimps were given commercial feeds 4 times (7:00, 11:00, 15:00, and 20:00) every day (approximately 1 g feed for each aquarium); residual feed and feces in the aquarium were cleaned 90 min after feeding. Initially, P. vannamei (8.73 ± 0.66 cm length and 5.14 ± 1.11 g weight) were randomly allocated to aquariums for acclimatization. After three days of acclimatization, the shrimp were divided into three groups: the V. parahaemolyticus (Vpa) group, the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) group, and the control group. Each group comprised 30 shrimp. We conducted intramuscular examinations in the experiment. The V. parahaemolyticus used in the experiment was isolated from hepatopancreatic necrosis shrimp, harboring a virulence plasmid encoding PirA/B [18]. V. parahaemolyticus was cultured in a Luria-Broth medium for more than 12 h and then diluted in PBS to achieve a concentration of approximately 103 CFU per 50 μL. Each shrimp in the Vpa group was injected with 50 μL of this bacterial suspension. Each shrimp in the LPS group was injected with 5 μg of LPS dissolved in 50 μL of PBS, while each shrimp in the control group received 50 μL of PBS alone [22]. Intestinal samples were collected at 72 h post-injection. For each group, five randomly selected shrimp served as individual samples. During sampling, the shrimp surfaces were disinfected using a 70% ethanol solution. The intestines were carefully dissected using sterile scissors, and their contents were gently scraped off. The collected intestinal contents were transferred into 2 mL centrifuge tubes containing 1.5 mL of a PBS buffer. All samples were stored at −80 °C prior to DNA extraction.
2.2. The 16S rRNA Sequencings and Bioinformatic Analysis
Intestinal genomic DNA was extracted using the PowerFecal DNA Isolation Kit (Qiagen, Düsseldorf, Germany). The DNA quality control and PCR amplification were performed according to our previous study [23]. Sequencing libraries were constructed as previously described [24]. A qualified library was sequenced on a PacBio Sequel II platform (Pacific Biosciences, Menlo Park, CA, USA) by Biomarker Technologies Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China), generating single-end reads. Raw data (PRJNA1234576) were deposited in the SRA maintained by NCBI. Raw sequences were filtered and demultiplexed using SMRT Link (version 8.0) to obtain circular consensus sequencing (CCS) reads with minPasses ≥ 5 and minPredictedAccuracy ≥ 0.9, which were further processed with Lima (version 1.7.0). The forward and reverse primers on these reads were identified via cutadapt (version 2.7); if the error rate in primer identification exceeded 20%, the sequence was discarded. CCS reads lacking primer sequences were removed, and the remaining CCS reads were filtered based on a length threshold of 1200–1650 bp. Each sample yielded more than 5000 CCS reads. The UCHIME algorithm (V8.1) [25] was used for chimera detection and removal, resulting in a set of clean reads. Sequences with 100% similarity were clustered into amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) using USEARCH (V10.0). Taxonomy annotation was performed based on SILVA SSU NR99 database version 138. Alpha-diversity (the diversity index reached a plateau; see Figure S1a) and beta-diversity were calculated using QIIME2 [26], and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGAN analysis [27].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Venn analysis was conducted to compare the differences in bacterial OTU numbers among the three groups. Student’s t-test was used to evaluate the differences in bacterial diversity indices between any two groups. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS), permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA), and heatmap analyses were performed to assess the dissimilarities in community structure between the groups based on the Bray–Curtis distance [18]. LEfSe analysis was employed to identify bacterial indicators at the genus and species levels in the control, Vpa, and LPS groups. Spearman’s correlation analysis was utilized to examine the relationships between different bacterial taxa. SparCC analysis [28] was applied to assess the complexity of bacterial community interactions within each group at the species level over time, with a significance threshold of |r| > 0.5 and p < 0.05. The mean nearest taxon distance measure was then used to determine the processes governing community assembly in P. vannamei intestines across the three groups [29,30].
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Intestinal Bacterial Diversity of the Control, Vpa, and LPS Groups
The number of OTUs in the intestine of the Vpa group showed a slight decrease compared to the control group, whereas the LPS group exhibited a substantial increase relative to both the control and Vpa groups (Figure 1a). Student’s t-test results indicated that the Chao1 (Figure 1b) and Shannon (Figure 1c) indices of the Vpa group (243 ± 29 and 6.05 ± 0.46) were numerically lower than those of the control group (255 ± 57, 6.16 ± 0.31), although they were not statistically significant (p > 0.05). In contrast, the LPS group had significantly (p = 0.006 and = 0.018; p = 0.005 and = 0.017) higher Chao1 (449 ± 120) and Shannon (7.36 ± 0.58) indices compared to both the control group and the Vpa group. Regarding β-diversity, the NMDS analysis (stress = 0.136) (Figure 1d) and heatmap results (Figure S1b) demonstrated significant variations in community structures within P. vannamei intestines across all pairwise comparisons, as supported by PERMANOVA analysis (r = 0.729, p = 0.001) (Figure 1e). Notably, the intestinal bacterial community structure of P. vannamei in the Vpa and LPS groups (87.40 ± 4.97% distance) was more similar to each other than to that of the control group (90.07 ± 4.35% distance, p < 0.05. Figure 1d,e and Figure S1b). These findings suggested that bacterial infection significantly altered the diversity of the intestinal bacterial communities in P. vannamei.
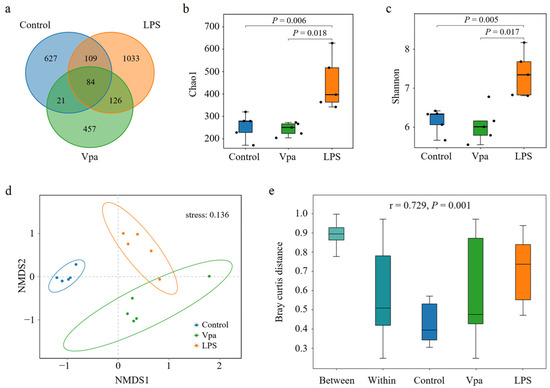
Figure 1.
(a) Venn analysis results of bacterial ASV numbers in the Penaeus vannamei intestine of the control, Vpa, and LPS groups. (b,c) Comparative analysis of the Chao1 and Shannon indices in the bacterial community within P. vannamei intestines among the control, Vpa, and LPS groups. (d,e) NMDS and PERMANOVA results of community structure within the P. vannamei intestines among the control, Vpa, and LPS groups. Vpa: Vibrio parahaemolyticus; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.
3.2. Differences in Bacterial Composition of the Control, Vpa and LPS Groups
Obviously, alterations in the bacterial taxonomic composition of host intestines were observed in the Vpa and LPS groups compared to the control group. Specifically, the relative abundances of Ruegeria, Marinovum, and Nautella decreased in the Vpa and LPS groups, while Vibrio and Pseudoalteromonas showed the opposite trends (Figure 2a). At the species level, R. atlantica abundance decreased in the Vpa and LPS groups, but Vibrio brasiliensis and Pseudoalteromonas spongiae increased (Figure 2b). LEfSe analysis revealed that Ruegeria, Marinovum, Nautella, and Formosa were key biomarkers of the control P. vannamei, while Lysobacter and Vibrio were dominant in the Vpa group (Figure 3a), and Vibrio, Marinovum, Tenacibaculum, and Pseudoalteromonas were prominent in the LPS group (Figure 3b). At the species level, 28 indicator species were identified in the control group compared to the Vpa group, 7 of which belonged to Ruegeria (R. atlantica, R. lacuscaerulensis, R. conchae, R. profundi, R. arenilitoris, R. pomeroyi, and Rugeria_bacterium_1D703); only 2 indicator species were found in the Vpa group, with 1 being V. brasiliensis (Figure 4a). Similarly, 23 indicator species were identified in the control group compared to the LPS group, with 7 belonging to Ruegeria (also R. atlantica, R. lacuscaerulensis, R. pomeroyi, R. profundi, R. arenilitoris, R. conchae, and Rugeria_bacterium_1D703); 5 indicator species were found in the LPS group, 4 of which belonged to Vibrio (V. harveyi, V. sinaloensis, V. coralliilyticus, and V. brasiliensis) (Figure 4b). Therefore, bacterial infection reshaped the intestinal community by reducing the relative abundance of Ruegeria and increasing the relative abundance of Vibrio. We further observed that the relative abundance of 17 Ruegeria species was markedly reduced in both the Vpa and LPS groups, with some species, particularly R. atlantica and R. lacuscaerulensis, decreasing to nearly 0% in the Vpa group (Figure 4c). Spearman’s correlation analysis revealed significant (p < 0.05) negative correlations between the relative abundance of all seven Ruegeria indicator species and V. brasiliensis (Figure 4d). Additionally, there were significant (p < 0.05) negative correlations between R. lacuscaerulensis and unclassified_Vibrio, as well as between Rugeria_bacterium_1D703 and V. sinaloensis (Figure 4d). These suggested that the significant increase in Vibrio abundance in P. vannamei intestines following bacterial infection was associated with the marked reduction in Ruegeria.
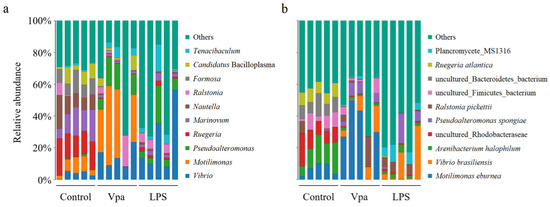
Figure 2.
Relative abundances of top ten bacterial taxa within the P. vannamei intestines in the control, Vpa, and LPS groups at the (a) genus and (b) species levels. Vpa: Vibrio parahaemolyticus; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.
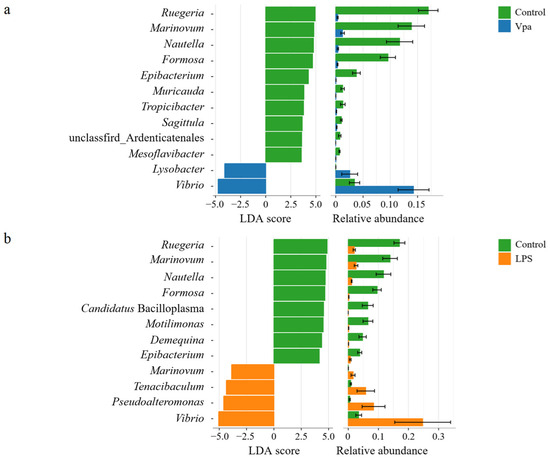
Figure 3.
(a) LEfSe results of bacterial indicator genera within the P. vannamei intestines in the control and Vpa groups. (b) LEfSe results of bacterial indicator genera between the control and LPS groups. Vpa: Vibrio parahaemolyticus; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.
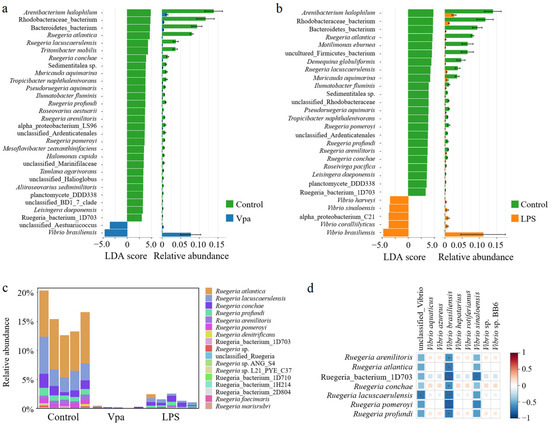
Figure 4.
(a) LEfSe results of the bacterial indicator species within P. vannamei intestines in the control and Vpa LPS groups and (b) between the control and LPS groups. (c) Relative abundances of Ruegeria species within the P. vannamei intestines in the control, Vpa, and LPS groups. (d) Spearman’s correlation analysis was utilized to examine the relationships between Ruegeria species and Vibrio species; * means p < 0.05. Vpa: Vibrio parahaemolyticus; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.
3.3. Differences in Bacterial Co-Association Networks and Ecological Processes on the Intestinal Community Assembly Among the Control, Vpa, and LPS Groups
We utilized SparCC analysis to examine the impact of bacterial infection on the co-association networks of bacterial species in P. vannamei intestines. Our results demonstrated that both the number of nodes and number of edges in the bacterial networks were significantly higher in the Vpa (130 nodes and 512 edges) and LPS (210 nodes and 2502 edges) groups compared to the control group (113 nodes and 343 edges) (Figure 5a). Notably, the control group contained a substantially higher number of keystone species belonging to the Ruegeria species, whereas the Vpa and LPS groups had few or no keystone species from this genus, with the Vibrio species becoming more prominent (Figure 5b). Consequently, under the conditions of bacterial infection, there was a marked increase in the complexity of the bacterial networks within P. vannamei intestines, which may be associated with the significant reduction in Ruegeria and concurrent rise in Vibrio. We further quantified the relative contributions of major ecological processes to evaluate bacterial assembly in P. vannamei intestines across three groups (Figure 5c). Overall, approximately half of the observed variation was attributed to stochastic processes: drift (49.11%, 34.49%, and 29.84%), dispersal limitation (12.71%, 15.06%, and 31.59%), and homogenizing dispersal (15.77%, 9.09%, and 7.19%) in the control, Vpa, and LPS groups, respectively. This indicates that stochastic factors play a significant role in shaping the bacterial community in P. vannamei intestines. However, deterministic processes such as heterogeneous selection and homogeneous selection were notably higher in the Vpa (1.30% and 40.06%) and LPS (0.81% and 30.57%) groups compared to the control group (0.09% and 22.32%). This suggested that deterministic factors have a greater influence on intestinal bacterial community assembly in Vpa and LPS P. vannamei. Consequently, bacterial infection might result in strong selective pressure on the intestinal bacterial community, potentially leading to a decline in the native dominant bacteria Ruegeria in P. vannamei intestines.
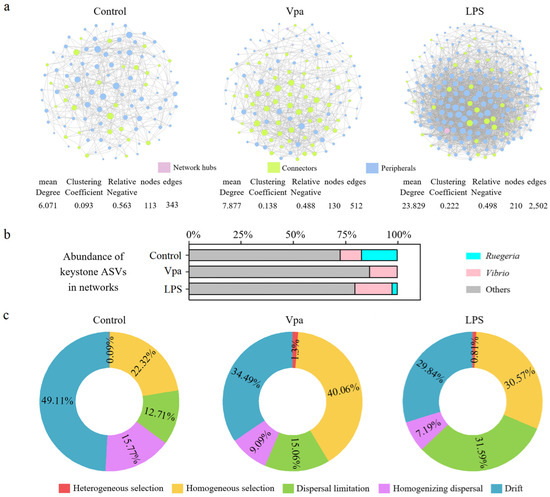
Figure 5.
(a) Distinctions in co-association networks of the bacterial community within the P. vannamei intestines were observed among the control, Vpa, and LPS groups. (b) A substantially higher number of keystone species belonging to the Ruegeria species in the control group, but more Vibrio keystone species in the Vpa and LPS groups. (c) Differences in ecological processes affecting the bacterial community assembly in the intestine of P. vannamei among the control, Vpa, and LPS groups. Vpa: Vibrio parahaemolyticus; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.
4. Discussion
Host response to pathogen infection modulates the intestinal microbial community composition, which in turn adversely affects the host’s health. This study specifically investigated the effects of bacterial infection on the intestinal microbiota of P. vannamei and its interaction with host health. It is evident that pathogen infection can elicit an extensive immune response against host microbes, as demonstrated in previous studies showing the upregulation of immune-related genes in P. vannamei [2,31] under the conditions of V. parahaemolyticus infection. These immune responses further interact with commensal bacteria in hosts, thereby altering the bacterial community composition in the host intestine. This observation is supported by a pronounced deterministic process in intestinal community assembly under bacterial infection, indicating that the host immune response, i.e., host selection post-infection, has a significant influence on the intestinal microbes. More precisely, our study found that the intestinal bacterial community of infected individuals exhibited obvious dysbiosis compared to the control P. vannamei, characterized by a marked decrease in Ruegeria (e.g., R. atlantica, R. lacuscaerulensis, R. conchae, R. profundi, R. arenilitoris, R. pomeroyi) abundance and significant enrichment of pathogens (e.g., V. harveyi, V. brasiliensis). The excessive expansion of pathogens is likely associated with intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, characterized by a disruption in the microecological balance and a diminished host defense against pathogen invasion [32,33].
Ruegeria is a symbiotic bacterium in the intestine of P. vannamei that plays a crucial role in enhancing the host’s resistance to bacterial infections and maintaining intestinal homeostasis [34]. Our results demonstrated that bacterial infection reshaped the intestinal community by reducing the abundance of Ruegeria species and increasing the abundance of Vibrio species, and significant negative correlations between the abundance of all seven Ruegeria indicator species and Vibrio species were observed. Moreover, the control P. vannamei contained a substantially higher number of keystone species belonging to the Ruegeria species, whereas bacterial infection individuals had few or no keystone species from the Ruegeria genus, with Vibrio species becoming more prominent. Thus, the significant increase in Vibrio species abundance in P. vannamei intestines following bacterial infection was associated with the marked reduction in Ruegeria species. In fact, several studies have confirmed that the enrichment of Ruegeria in the P. vannamei intestine enhances the host’s antagonistic response to V. parahaemolyticus [35], thereby reducing the likelihood of bacterial digestive tract diseases, including white feces syndrome [2,3]. Therefore, the secondary expansion of opportunistic pathogens such as Vibrio in the P. vannamei intestine following bacterial infection may be associated with a significant reduction in Ruegeria populations. Since LPS could trigger the host’s antimicrobial peptide pathway [20], we hypothesized that Ruegeria might be more susceptible to antimicrobial peptides induced by LPS injection in comparison to Vibrio as Gram-negative bacteria [36] according to our results. Consequently, bacterial infection can disrupt the intestinal bacterial community of P. vannamei, particularly leading to the depletion of native intestinal bacteria such as Ruegeria species, thereby promoting the proliferation of bacterial opportunistic pathogens and increasing the risk of bacterial disease in the host.
In addition, R. arenilitoris, an indigenous intestinal bacterium of P. vannamei, holds significant potential as a probiotic in aquaculture, which aids in enhancing resistance against Vibrio infections. A study meticulously formulated a probiotic mixture comprising four strains, Ruegeria lacuscaerulensis, Nioella nitratireducens, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptomyces euryhalinus, in a specific ratio; moreover, dietary supplementation with these probiotic blends promoted beneficial intestinal bacteria, enhanced short-chain fatty acid production, boosted taurine metabolism potential, and improved bacterial network stability while it reduced the turnover rate and average variation degree of intestinal community, thereby reinforcing both ecological and mechanical barriers against Vibrio pathogens in P. vannamei [37]. Thus, Ruegeria species may exert an antagonistic effect against Vibrio pathogens in the intestine of P. vannamei through the aforementioned functions, yet the precise anti-Vibrio mechanism requires further investigation.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study specifically investigated the effects of bacterial infection on the intestinal bacterial community of P. vannamei and its interaction with the host’s health. We mainly found that bacterial infection reshaped the intestinal bacterial community by reducing the relative abundance of probiotic Ruegeria species and increasing the relative abundance of pathogenic Vibrio species, and the significant increase in Vibrio was associated with the marked reduction in Ruegeria. Our findings enhance the comprehension of the complex interactions among bacterial infection, intestinal microbiota, and host health, and they provide guidance for the development of probiotics for the healthy culture of P. vannamei.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13040864/s1, Figure S1: (a) The α-diversity indices in all samples were calculated using rarefaction curves at the ASV level at a sequencing depth of 3885 with 1000 iterations, where the indices had stabilized. (b) Heatmap results of bacterial community structure within the P. vannamei intestines among the control, Vpa, and LPS groups.
Author Contributions
R.Z.: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, visualization, and writing—original draft preparation; S.W.: supervision and writing—review and editing; J.H.: funding acquisition, project administration, and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China Grant (2022YFF1000304) and the Earmarked Fund for CARS-48.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- FAO. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Ko, T.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, M.F.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.S.; et al. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, A.; Priya, P.S.; Meenatchi, R.; Vaishnavi, S.; Pavithra, V.; Kumar, T.T.A.; Arockiaraj, J. Insights into molecular aspects of pathogenesis and disease management in acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND): An updated review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 142, 109138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.C.; Ng, T.H.; Ando, M.; Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Chuang, J.C.; Mavichak, R.; Chang, S.H.; Yeh, M.D.; Chiang, Y.A. Pathogenesis of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Lu, L.; Xu, D. Progress in research on acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). Aquacult. Int. 2016, 24, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Gordon, J.I. Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 2001, 292, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, J.F.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I. Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4596–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.M.; Finlay, B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, J.; Britton, R.A.; Roos, S. Host-microbial symbiosis in the vertebrate gastrointestinal tract and the Lactobacillus reuteri paradigm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Hayatsu, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Nagayama, A.; Tago, K.; Fukatsu, T. Symbiont-mediated insecticide resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; An, B.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Immune response and intestinal microbial succession of half-smooth tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis) infected with Vibrio vulnificus. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, F.; Lv, A.; Hu, X.; Sun, X.; Qi, H.; Guo, Y. Vibrio parahaemolyticus alters the community composition and function of intestinal microbiota in Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Liao, L.; Xu, Q.; He, Z.; Xiao, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Wu, B.; Yan, Q. Host-microbiota interactions and responses to grass carp reovirus infection in Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Dong, C.; Qiu, Q.; Li, C. Integrating gut microbiota immaturity and disease-discriminatory taxa to diagnose the initiation and severity of shrimp disease. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Dai, W.; Qiu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, C. Response of host-bacterial colonization in shrimp to developmental stage, environment and disease. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Xiong, J.; Hou, D.; Zhou, R.; Xing, C.; Wei, D.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Microecological Koch’s postulates reveal that intestinal microbiota dysbiosis contributes to shrimp white feces syndrome. Microbiome 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Weng, S.; He, J. Ammonia nitrogen stress induces dysbiosis of the intestinal bacterial community and facilitates the enrichment of pathogenic bacteria in intestines of shrimp. Aquaculture 2024, 595, 741510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Jiang, K.; Wang, L. A new method to evaluate the effects of bacterial dosage, infection route and Vibrio strain in experimental challenges of Litopenaeus vannamei, based on the Cox proportional hazard model. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Yin, B.; Li, S.; He, J.; Li, C. Signaling events induced by lipopolysaccharide-activated Toll in response to bacterial infection in shrimp. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1119879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Ding, X. Morphologic, digestive enzymes and immunological responses of intestine from Litopenaeus vannamei after lipopolysaccharide injection. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 153, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Li, H.; Wei, E.; Su, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xu, X. Identification and functional analysis of a Hemolin like protein from Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 43, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Weng, S.; He, J. Nitrite nitrogen stress disrupts the intestine bacterial community by altering host-community interactions in shrimp. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 925, 171536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, P.; Shen, W.; Wan, F.; He, J.; Tang, S.; Tan, Z.; et al. Fermented soybean meal replacement in the diet of lactating Holstein dairy cows: Modulated rumen fermentation and ruminal microflora. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 625857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Auch, A.F.; Qi, J.; Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Gen. Res. 2007, 17, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J.; Mering, C.V. Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; He, J.; Li, C. Ammonia nitrogen stress increases susceptibility to bacterial infection via blocking IL-1R–Relish axis mediated antimicrobial peptides expression in shrimp. Aquaculture 2022, 170, 38934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizário, J.E.; Faintuch, J. Microbiome and gut dysbiosis. Exp. Suppl. 2018, 109, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeevi, D.; Korem, T.; Godneva, A.; Bar, N.; Kurilshikov, A.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Weinberger, A.; Fu, J.; Wijmenga, C.; Zhernakova, A.; et al. Structural variation in the gut microbiome associates with host health. Nature 2019, 568, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepaamorndech, S.; Nookaew, I.; Higdon, S.M.; Santiyanont, P.; Phromson, M.; Chantarasakha, K.; Mhuantong, W.; Plengvidhya, V.; Visessanguan, W. Metagenomics in bioflocs and their effects on gut microbiome and immune responses in Pacific white shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 106, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Fu, X.; He, J.; Wang, R.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, P.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. Gut bacterial consortium enriched in a biofloc system protects shrimp against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Microbiome 2023, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, E.; Nielsen, K.; D’Alvise, P.; Porsby, C.H.; Melchiorsen, J.; Heilmann, J.; Kalatzis, P.G.; López-Pérez, M.; Bunk, B.; Spröer, C.; et al. Global occurrence and heterogeneity of the Roseobacter-clade species Ruegeria mobilis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Rationally designed probiotics prevent shrimp white feces syndrome via the probiotics-gut microbiome-immunity axis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).