Saponin Improves Recovery of Bacteria from Orthopaedic Implants for Enhanced Diagnosis Ex Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. In Vitro PJI Biofilm
2.3. Biofilm Detachment
2.4. Novel In Vitro 3D PJI Soft Tissue Model
2.5. Infection and Processing of the Novel 3D PJI Soft Tissue Model
2.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.7. Moleculight i:XTM Imaging
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
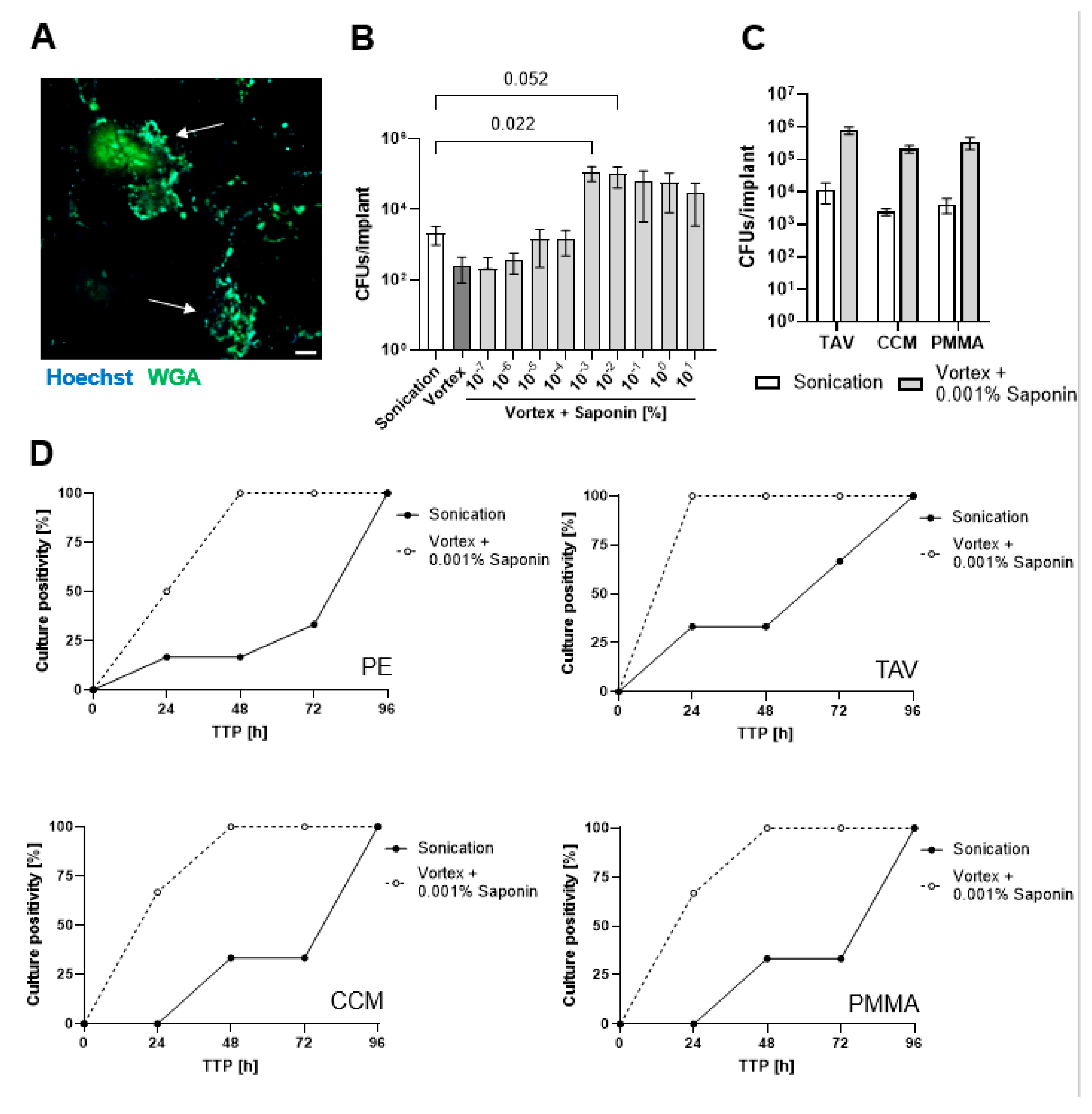
3.1. Finding the Optimum Saponin Concentration for Bacterial Recovery from Biofilms on Implant Discs
3.2. Saponin Effectively Reduces Time-to-Positivity (TTP)
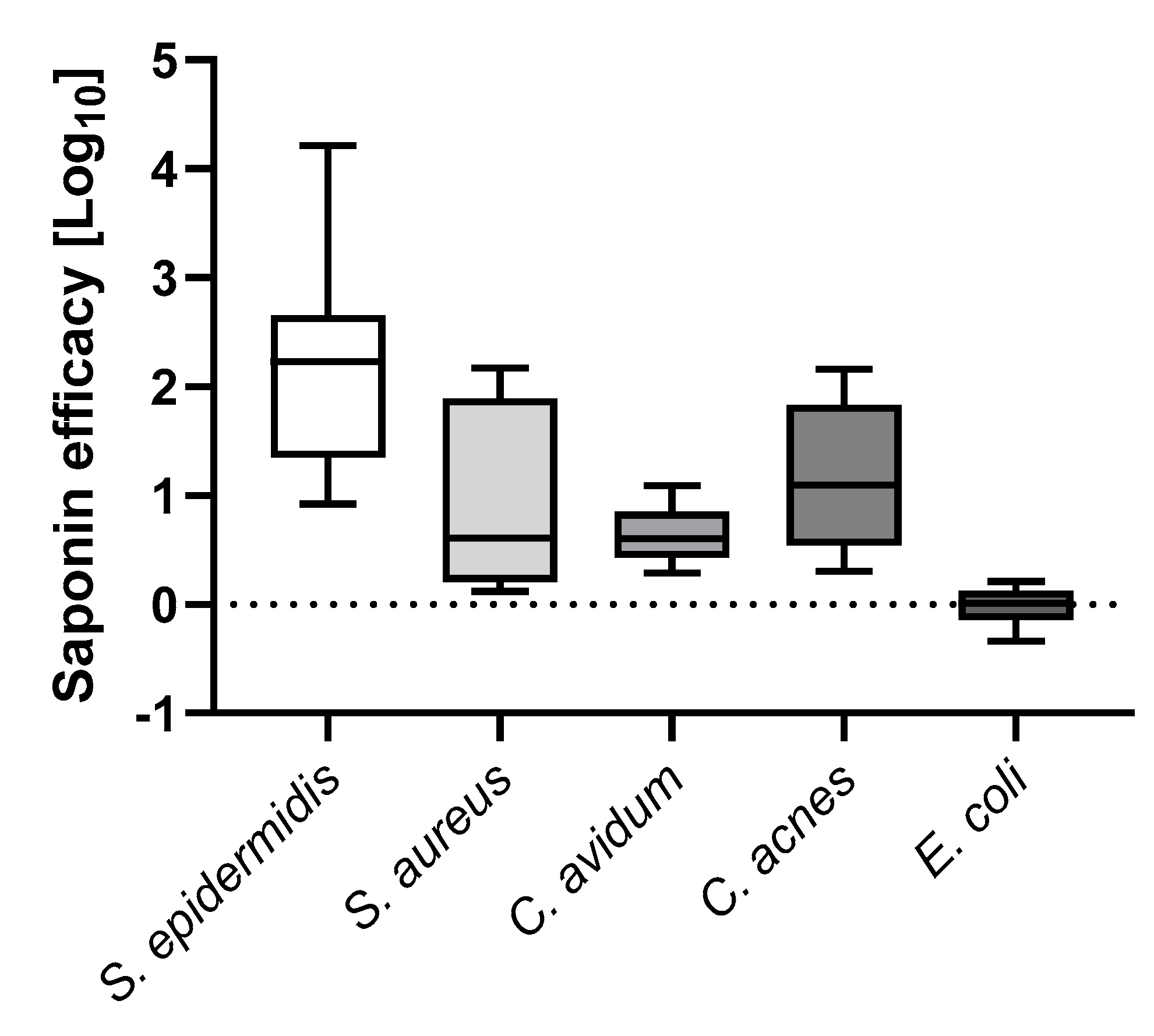
3.3. Saponin Enhances Recovery of the Most Prevalent PJI-Causing Bacteria from Orthopedic Material
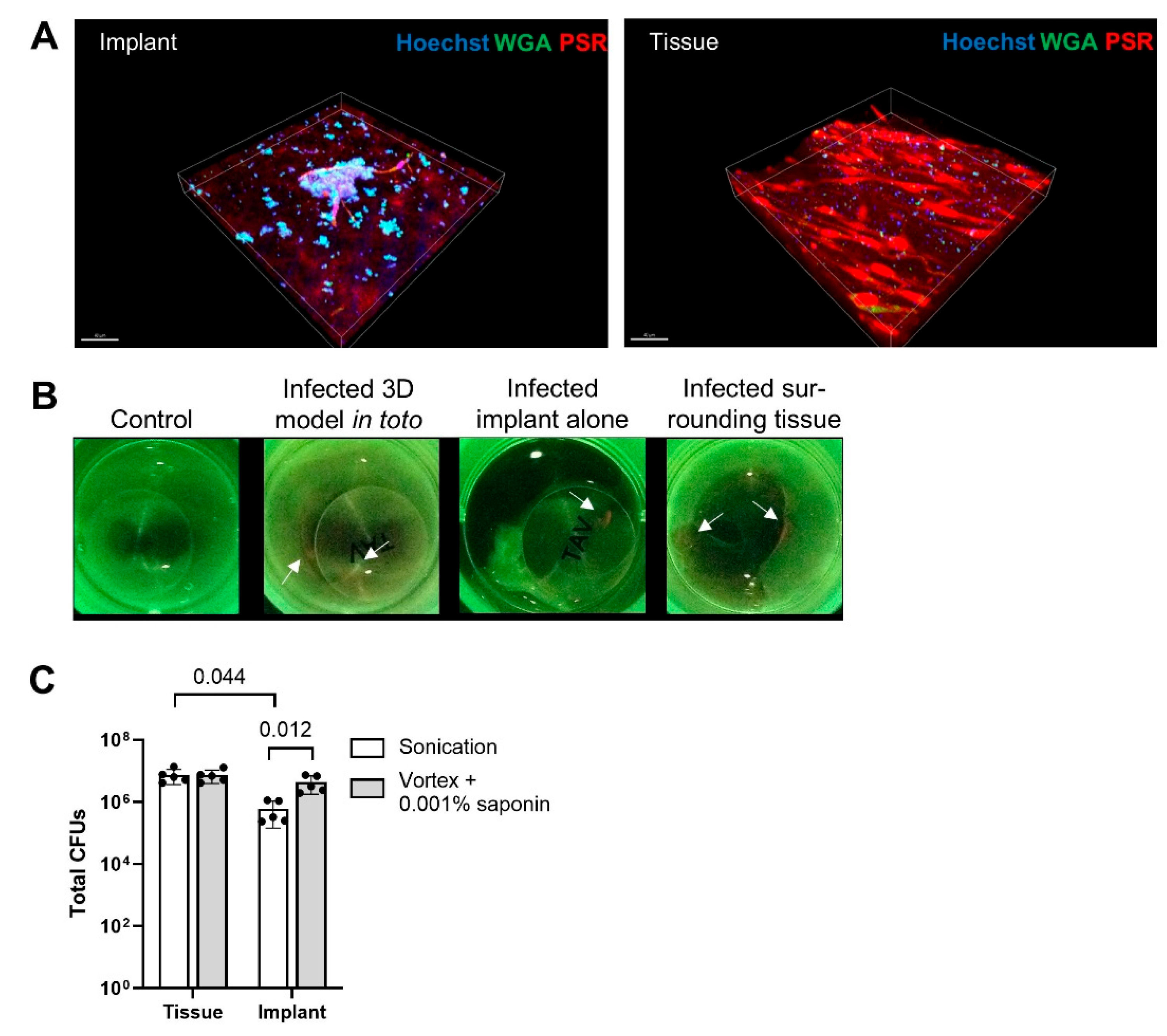
3.4. Saponin Enhances Recovery of S. epidermidis from Orthopedic Implant Material in a Novel 3D PJI Soft Tissue Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, R. Periprosthetic joint infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, S.M.; Kursawe, L.; Rahm, S.; Prinz, J.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Moter, A.; Kuster, S.P.; Zbinden, R.; Zingg, P.O.; Achermann, Y. Cutibacterium avidum resists surgical skin antisepsis in the groin-a potential risk factor for periprosthetic joint infection: A quality control study. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachalios, T.; Komnos, G.A. Management strategies for prosthetic joint infection: Long-term infection control rates, overall survival rates, functional and quality of life outcomes. EFORT Open Rev. 2021, 6, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Hanssen, A.D.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Low sensitivity of periprosthetic tissue pcr for prosthetic knee infection diagnosis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 79, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsma, D.T.; Ploegmakers, J.J.W.; Jutte, P.C.; Kampinga, G.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M. Time to positivity of acute and chronic periprosthetic joint infection cultures. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 99, 115178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Karau, M.J.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Osmon, D.R.; Abdel, M.P.; Patel, R. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of periprosthetic tissue culture in blood culture bottles to that of prosthesis sonication fluid culture for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection (pji) by use of bayesian latent class modeling and idsa pji criteria for classification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00319-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, T.N.; Spelman, T.; Dylla, B.L.; Hughes, J.G.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Cheng, A.C.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Optimal periprosthetic tissue specimen number for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achermann, Y.; Vogt, M.; Leunig, M.; Wust, J.; Trampuz, A. Improved diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection by multiplex pcr of sonication fluid from removed implants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Piper, K.E.; Hanssen, A.D.; Osmon, D.R.; Cockerill, F.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. Sonication of explanted prosthetic components in bags for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection is associated with risk of contamination. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Piper, K.E.; Jacobson, M.J.; Hanssen, A.D.; Unni, K.K.; Osmon, D.R.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Cockerill, F.R.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Greenleaf, J.F.; et al. Sonication of removed hip and knee prostheses for diagnosis of infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbakken, E.T.; Witso, E.; Sporsheim, B.; Egeberg, K.W.; Foss, O.A.; Hoang, L.; Bjerkan, G.; Loseth, K.; Bergh, K. Highly variable effect of sonication to dislodge biofilm-embedded staphylococcus epidermidis directly quantified by epifluorescence microscopy: An in vitro model study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.; Fidanza, A.; Giannetti, A.; Ciuffoletti, A.; Logroscino, G.; Romano, C.L. Bacteria living in biofilms in fluids: Could chemical antibiofilm pretreatment of culture represent a paradigm shift in diagnostics? Microorganisms 2024, 12, 259, Erratum in Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2577. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dudareva, M.; Barrett, L.; Figtree, M.; Scarborough, M.; Watanabe, M.; Newnham, R.; Wallis, R.; Oakley, S.; Kendrick, B.; Stubbs, D.; et al. Sonication versus tissue sampling for diagnosis of prosthetic joint and other orthopedic device-related infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00688-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, T.C.; Honda, E.K.; Daniachi, D.; Cury, R.P.L.; da Silva, C.B.; Klautau, G.B.; Salles, M.J. The impact of sonication cultures when the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection is inconclusive. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago, L.; Signori, V.; De Vecchi, E.; Vassena, C.; Palazzi, E.; Cappelletti, L.; Romano, D.; Romano, C.L. Use of dithiothreitol to improve the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infections. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbakken, E.T.; Hoyer, E.; Witso, E.; Sogaard, C.K.; Diez-Sanchez, A.; Hoang, L.; Wik, T.S.; Bergh, K. Biofilm and the effect of sonication in a chronic staphylococcus epidermidis orthopedic in vivo implant infection model. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, K.N.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Lichtenberg, M. The non-attached biofilm aggregate. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Otero, J.; Karau, M.J.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Abdel, M.P.; Mandrekar, J.; Patel, R. Evaluation of sonicate fluid culture cutoff points for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, L.; Martin, C.; Echeverz, M.; Lasa, I.; Ezpeleta, C.; Portillo, M.E. Evaluation of the use of sonication combined with enzymatic treatment for biofilm removal in the microbiological diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0002024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.; Romano, C.L.; Mattina, R.; Signori, V.; De Vecchi, E. Does dithiothreitol improve bacterial detection from infected prostheses? A pilot study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Calori, G.M.; Colombo, M.; Navone, P.; Nobile, M.; Auxilia, F.; Toscano, M.; Drago, L. Comparative evaluation of microdttect device and flocked swabs in the diagnosis of prosthetic and orthopaedic infections. Injury 2016, 47 (Suppl. S4), S17–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolenda, C.; Josse, J.; Batailler, C.; Faure, A.; Monteix, A.; Lustig, S.; Ferry, T.; Laurent, F.; Dupieux, C. Experience with the use of the microdttect device for the diagnosis of low-grade chronic prosthetic joint infections in a routine setting. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 565555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbysheva, S.; Cabric, S.; Koliszak, A.; Bervar, M.; Kirschbaum, S.; Hardt, S.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Clinical evaluation of dithiothreitol in comparison with sonication for biofilm dislodgement in the microbiological diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 103, 115679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbysheva, S.; Di Luca, M.; Butini, M.E.; Winkler, T.; Schutz, M.; Trampuz, A. Comparison of sonication with chemical biofilm dislodgement methods using chelating and reducing agents: Implications for the microbiological diagnosis of implant associated infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambri, A.; Cadossi, M.; Giannini, S.; Pignatti, G.; Marcacci, M.; Neri, M.P.; Maso, A.; Storni, E.; Gamberini, S.; Naldi, S.; et al. Is treatment with dithiothreitol more effective than sonication for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2018, 476, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Ren, H.; Geng, J.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, L. Towards physicochemical and biological effects on detachment and activity recovery of aging biofilm by enzyme and surfactant treatments. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, S.L.; Mayer, D.; Kirsner, R.S.; Schultz, G.; Weir, D.; Roy, S.; Alavi, A.; Romanelli, M. Surfactants: Role in biofilm management and cellular behaviour. Int. Wound J. 2019, 16, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koley, D.; Bard, A.J. Triton x-100 concentration effects on membrane permeability of a single hela cell by scanning electrochemical microscopy (secm). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16783–16787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutormin, O.S.; Kolosova, E.M.; Torgashina, I.G.; Kratasyuk, V.A.; Kudryasheva, N.S.; Kinstler, J.S.; Stom, D.I. Toxicity of different types of surfactants via cellular and enzymatic assay systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.J. Legal status and toxicity of saponins. Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 1965, 3, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, P.; Demeyer, M.; Decroo, C.; Colson, E.; Gerbaux, P. Mass spectrometry analysis of saponins. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2023, 42, 954–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Cao, Y.; Jørgensen, L.V.G.; Strobel, B.W.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Cedergreen, N. Where does the toxicity come from in saponin extract? Chemosphere 2018, 204, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Strobel, B.W.; Cedergreen, N.; Cao, Y.; Hansen, H.C.B. Stability of saponin biopesticides: Hydrolysis in aqueous solutions and lake waters. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2019, 21, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, J.; Schmid, B.; Zbinden, R.; Zingg, P.O.; Uckay, I.; Achermann, Y.; Bosshard, P.P. Fast and sensitive multiplex real-time quantitative pcr to detect cutibacterium periprosthetic joint infections. J. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 24, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, J.; Wink, M.; Neuhaus, S.; Grob, M.C.; Walt, H.; Bosshard, P.P.; Achermann, Y. Effective biofilm eradication on orthopedic implants with methylene blue based antimicrobial photodynamic therapy in vitro. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.A.; Keikhosravi, A.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Vezina, C.M. Fluorescence of picrosirius red multiplexed with immunohistochemistry for the quantitative assessment of collagen in tissue sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2017, 65, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.M.; Dunham, D.; Rennie, M.Y.; Kirman, J.; Lopez, A.J.; Keim, K.C.; Little, W.; Gomez, A.; Bourke, J.; Ng, H.; et al. In vitro detection of porphyrin-producing wound bacteria with real-time fluorescence imaging. Future Microbiol. 2020, 15, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, S.; Lewis, C.J.; Rowe, S.; Raby, E.; Rea, S. The use of moleculight for early detection of colonisation in dermal templates. Burns 2019, 45, 1940–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizman, R.; Dunham, D.; Lindvere-Teene, L.; Jones, L.M.; Tapang, K.; Linden, R.; Rennie, M.Y. Use of a bacterial fluorescence imaging device: Wound measurement, bacterial detection and targeted debridement. J. Wound Care 2019, 28, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, Y.; Roschke, E.; Dietze, N.; Dahse, A.J.; Chaberny, I.F.; Ranft, D.; Pempe, C.; Goralski, S.; Ghanem, M.; Kluge, R.; et al. Early-outcome differences between acute and chronic periprosthetic joint infections-a retrospective single-center study. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Alam, S.; Rathore, A.S.; Khare, S.K. Stability of therapeutic enzymes: Challenges and recent advances. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1148, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, Z.K.; McQuivey, K.S.; Deckey, D.G.; Haglin, J.; Spangehl, M.J.; Bingham, J.S. Acute or chronic periprosthetic joint infection? Using the esr ∕ crp ratio to aid in determining the acuity of periprosthetic joint infections. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2021, 6, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, J.; Gomez-Barrena, E.; Cordero, J.; Martin-de-Hijas, N.Z.; Kinnari, T.J.; Fernandez-Roblas, R. Evaluation of quantitative analysis of cultures from sonicated retrieved orthopedic implants in diagnosis of orthopedic infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloin, C.; Roux, A.; Ghigo, J.M. Escherichia coli biofilms. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 322, 249–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrate, O.A.; Zhou, X.; Reichhardt, C.; Cegelski, L. Sum of the parts: Composition and architecture of the bacterial extracellular matrix. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 4286–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Buys, M.; Moodley, K.; Cakic, J.N.; Pietrzak, J.R.T. Staphylococcus aureus colonization and periprosthetic joint infection in patients undergoing elective total joint arthroplasty: A narrative review. EFORT Open Rev. 2023, 8, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Gallego, I.; Melendez-Carmona, M.A.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Garrido-Allepuz, C.; Chaves, F.; Sebastian, V.; Viedma, E. Microbiological and molecular features associated with persistent and relapsing staphylococcus aureus prosthetic joint infection. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisrenoult, P. Cutibacterium acnes prosthetic joint infection: Diagnosis and treatment. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2018, 104, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.D.S.; De Melo, B.S.T.; Oliva, A.; de Araujo, P.S.R. Sonication protocols and their contributions to the microbiological diagnosis of implant-associated infections: A review of the current scenario. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1398461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bori, G.; Munoz-Mahamud, E.; Garcia, S.; Mallofre, C.; Gallart, X.; Bosch, J.; Garcia, E.; Riba, J.; Mensa, J.; Soriano, A. Interface membrane is the best sample for histological study to diagnose prosthetic joint infection. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; Morawietz, L.; Hasart, O.; Strube, P.; Perka, C.; Tohtz, S. Histopathological diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection following total hip arthroplasty: Use of a standardized classification system of the periprosthetic interface membrane. Orthopade 2009, 38, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoodley, P.; Nistico, L.; Johnson, S.; Lasko, L.A.; Baratz, M.; Gahlot, V.; Ehrlich, G.D.; Kathju, S. Direct demonstration of viable staphylococcus aureus biofilms in an infected total joint arthroplasty. A case report. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.R.; Chonko, D.J.; Pigott, M.; Sullivan, A.C.; Moore, K.; Stoodley, P. Mapping bacterial biofilm on explanted orthopedic hardware: An analysis of 14 consecutive cases. APMIS 2023, 131, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moley, J.P.; McGrath, M.S.; Granger, J.F.; Sullivan, A.C.; Stoodley, P.; Dusane, D.H. Mapping bacterial biofilms on recovered orthopaedic implants by a novel agar candle dip method. APMIS 2019, 127, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.; Gupta, N.; Gupta, T.T.; Patel, K.; Brooks, J.R.; Sullivan, A.; Litsky, A.S.; Stoodley, P. Mapping bacterial biofilm on features of orthopedic implants in vitro. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schweizer, T.A.; Egli, A.; Bosshard, P.P.; Achermann, Y. Saponin Improves Recovery of Bacteria from Orthopaedic Implants for Enhanced Diagnosis Ex Vivo. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040836
Schweizer TA, Egli A, Bosshard PP, Achermann Y. Saponin Improves Recovery of Bacteria from Orthopaedic Implants for Enhanced Diagnosis Ex Vivo. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):836. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040836
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchweizer, Tiziano Angelo, Adrian Egli, Philipp P. Bosshard, and Yvonne Achermann. 2025. "Saponin Improves Recovery of Bacteria from Orthopaedic Implants for Enhanced Diagnosis Ex Vivo" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040836
APA StyleSchweizer, T. A., Egli, A., Bosshard, P. P., & Achermann, Y. (2025). Saponin Improves Recovery of Bacteria from Orthopaedic Implants for Enhanced Diagnosis Ex Vivo. Microorganisms, 13(4), 836. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040836





