Occurrence of Vibrio spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Isolates of Nodipecten nodosus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Water from a Mariculture Farm in Angra dos Reis, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
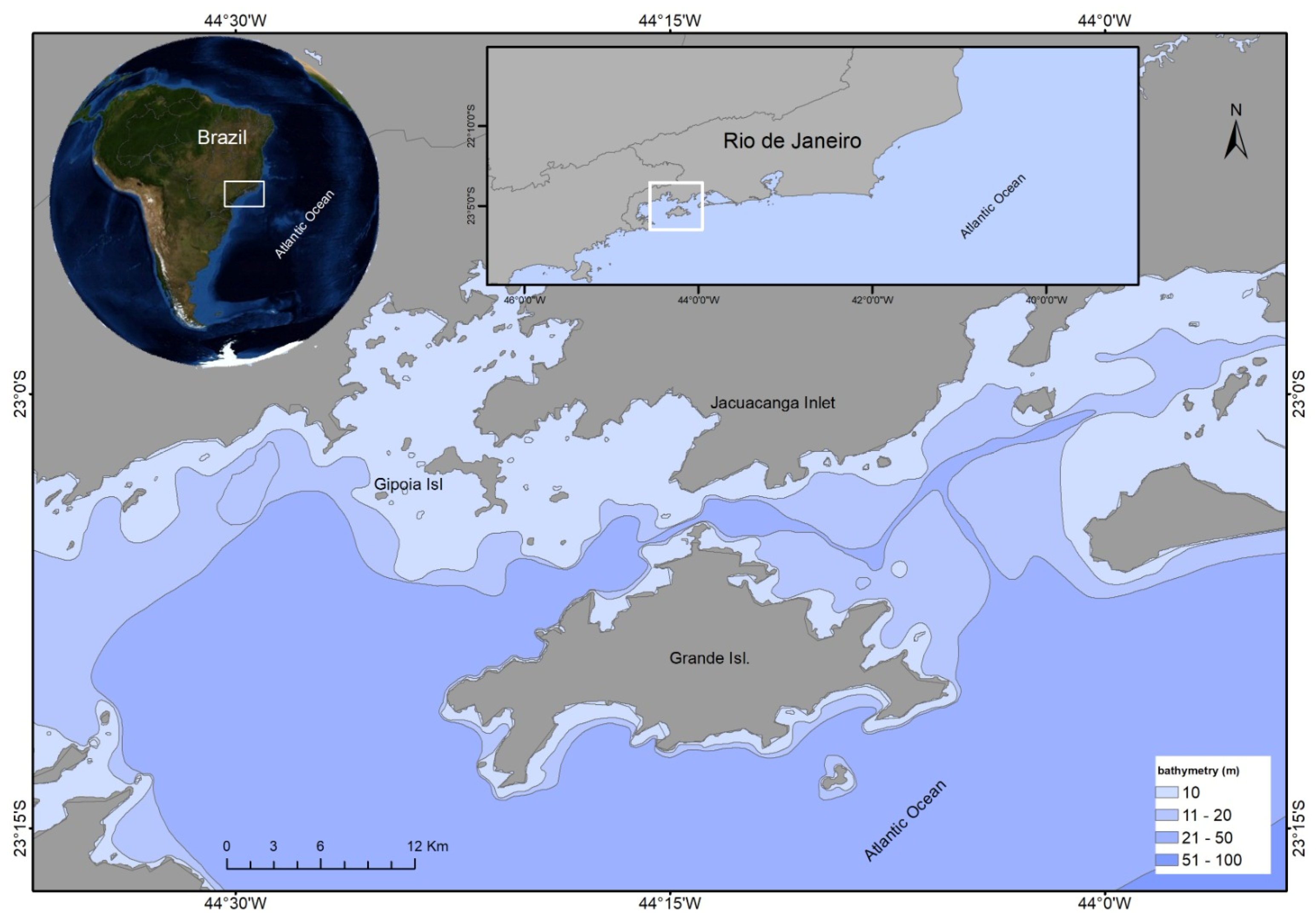
2.1. Collection Study Area
2.2. Sample Processing and Bacterial Isolation
2.3. MALDI-TOF Analysis
2.4. Criteria for Classifying Samples
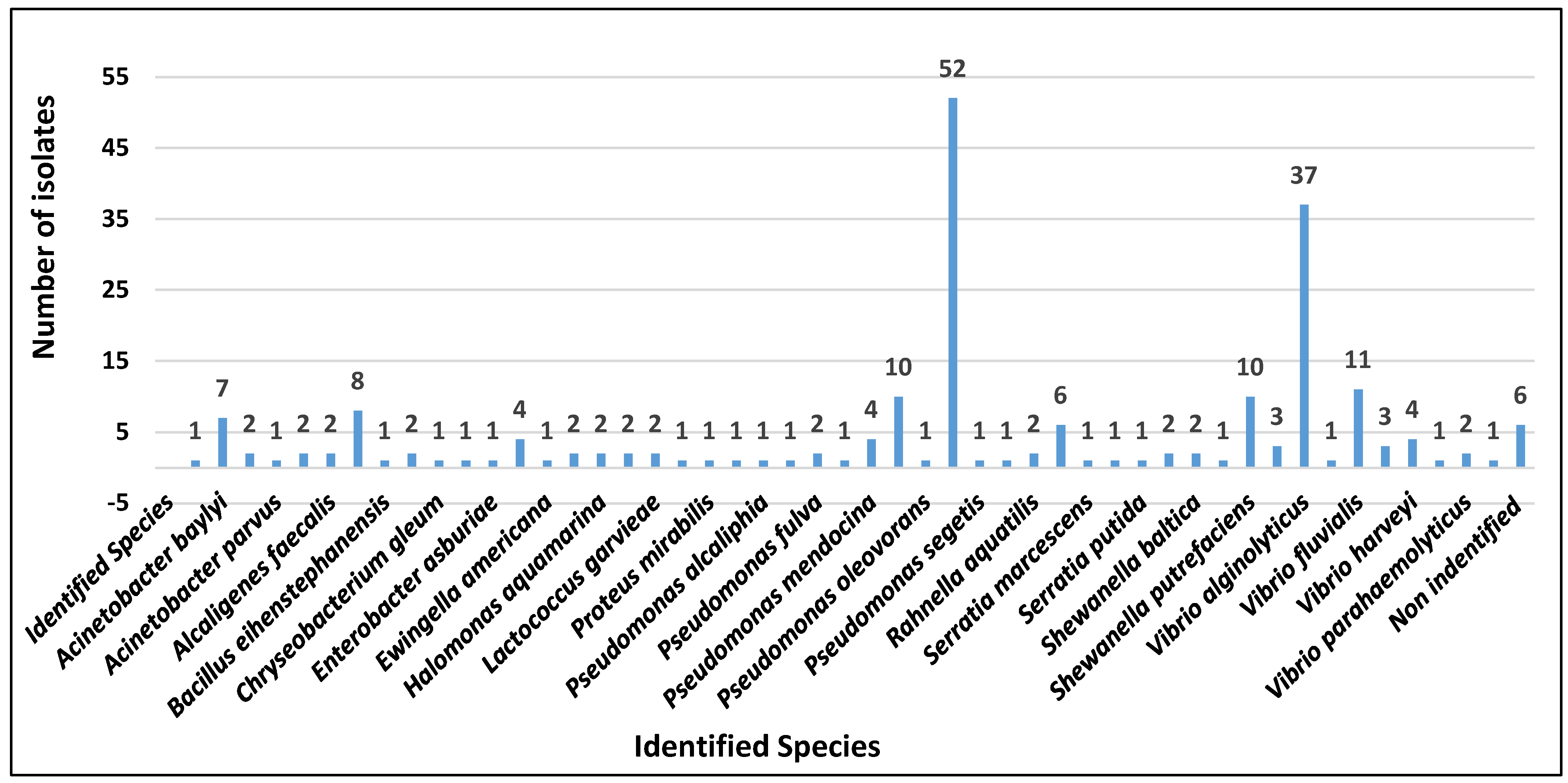
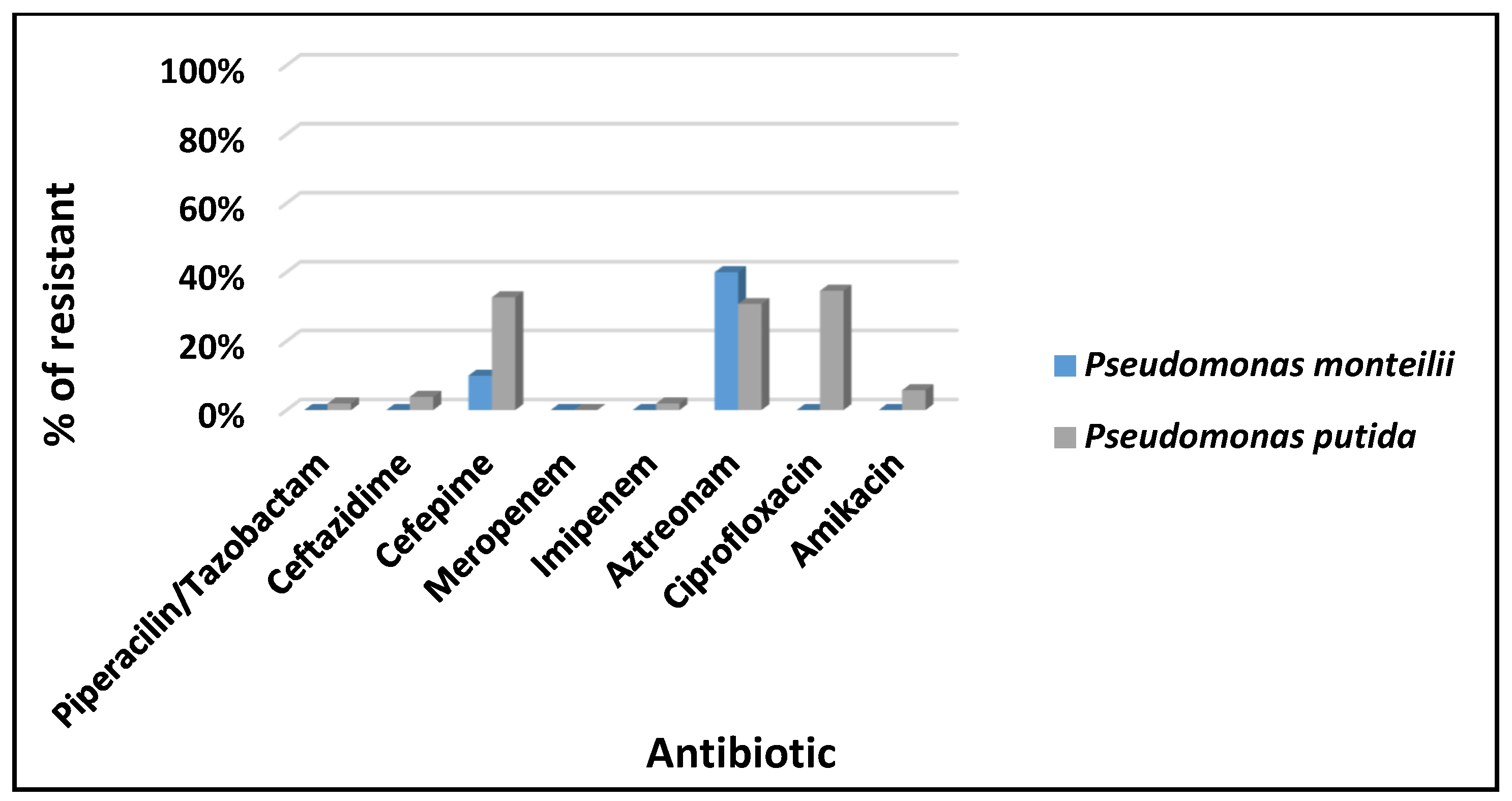
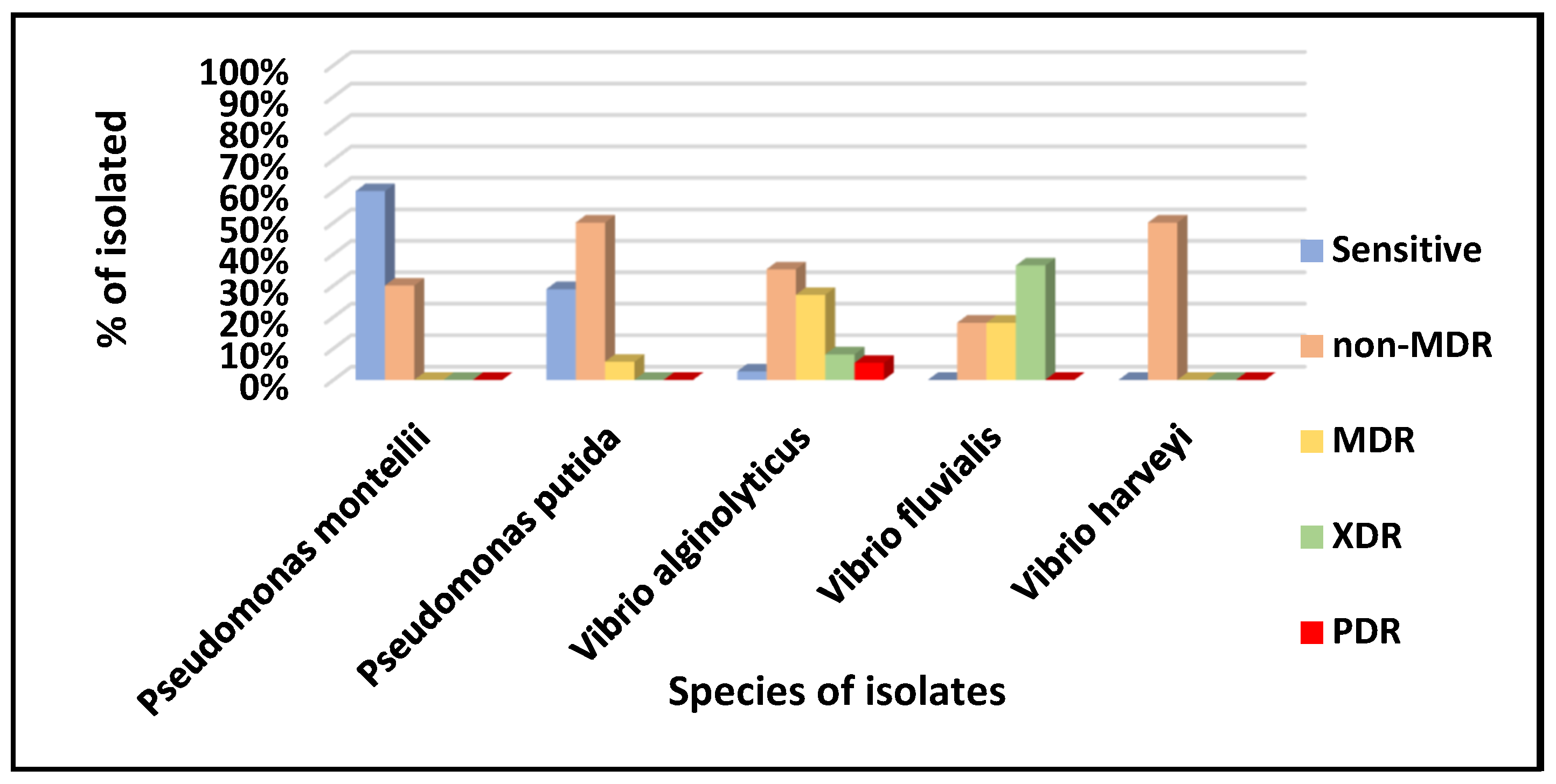
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563, Erratum in Nature 2021, 593, E12, Erratum in Nature 2021, 595, E36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human Health and Ocean Pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022: Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; p. 236. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/a2090042-8cda-4f35-9881-16f6302ce757/content (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. GLOBEFISH—Quarterly Bivalves Analysis 2025. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/items/35095eb1-fb01-4b88-82c5-f864b6f8f988 (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Tan, K.; Zheng, H. Ocean acidification and adaptive bivalve farming. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lino, A.S.; Galvão, P.M.A.; Longo, R.T.L.; Azevedo-Silva, C.E.; Dorneles, P.R.; Torres, J.P.M.; Malm, O. Metal bioaccumulation in consumed marine bivalves in Southeast Brazilian coast. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 34, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu Corrêa, A.; Huaman, M.E.D.; Siciliano, G.M.; Silva, R.R.E.; Zaganelli, J.L.; Pinto, A.M.V.; Dos Santos, A.L.; Vieira, C.B. First investigation of Ostreid herpesvirus-1 and human enteric viruses in a major scallop production area in Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, Y.D.; Fogaça, F.H.D.S.; Andrade, A.O.; da Silva, L.K.S.; Lima, J.P.; da Silva, J.L.; Vieira, B.S.; Cunha Neto, A.; Figueiredo, E.E.S.; Tassinari, W.S. Salmonella spp. in Aquaculture: An exploratory analysis (Integrative Review) of microbiological diagnoses between 2000 and 2020. Animals 2022, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.L.; Li, Y.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Thompson, C.C.; Hoste, B.; Vandemeulebroecke, K.; Rupp, G.S.; Pereira, A.; De Bem, M.M.; Sorgeloos, P.; et al. Vibrio neptunius sp. nov., Vibrio brasiliensis sp. nov. and Vibrio xuii sp. nov., isolated from the marine aquaculture environment (bivalves, fish, rotifers and shrimps). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães Filho, C.E.; Calixto, F.A.; Kasnowski, M.C.; Mesquita, E.D. Depuration of bivalve mollusks: A literature review. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e06622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.M.; Soares, H.K.S.S.; Souza, A.M.; Bezerra, N.P.C.; Cantanhede, S.P.D.; Souza Serra, I.M.R. Mapping of the world scientific production on bacterial and fungal microbiota in mollusks. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2023, 51, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, D.A.G.; Franco, R.M.B. Bivalve mollusks intended for human consumption with vectors of pathogenic protozoa: Detection methodologies and control standards. Rev. Panam. Infectol. 2018, 10, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gagne, N.; Cochennec, N.; Stephenson, M.; McGladdery, S.; Meyer, G.R.; Bower, S.M. First report of a Mikrocytos-like parasite in European oysters Ostrea edulis from Canada after transport and quarantine in France. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2008, 80, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallenave-Namont, C.; Pouchus, Y.F.; Du Pont, R.T.; Lassus, P.; Verbist, J.F. Toxigenic saprophytic fungi in marine shellfish farming areas. Mycopathologia 2000, 149, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.A.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Santos, M.J.; De Simone, S.G. Potentially toxic filamentous fungi associated to the economically important Nodipecten nodosus (Linnaeus, 1758) scallop farmed in southeastern Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bul. 2016, 115, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.E.; Thériault, I.; Mallet, A.L. Infection of cultured eastern oysters Crassostrea virginica by the boring sponge Cliona celata, with emphasis on sponge life history and mitigation strategies. J. Shellfish Res. 2010, 29, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, G.S.; Parsons, G.J. Aquaculture of the Scallop Nodipecten nodosus in Brazil. Develop. Aquacult. Fish. Sci. 2016, 40, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schets, F.M.; van den Berg, H.H.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Determination of the recovery efficiency of cryptosporidium oocysts and giardia cysts from seeded bivalve mollusks. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado-García, R.L.; Kraffe, E.; Tripp-Valdez, M.A.; Ramírez-Arce, J.L.; Artigaud, S.; Flye-Sainte-Marie, J.; Mathieu-Resuge, M.; Sicard, M.T.; Arellano-Martínez, M.; Racotta, I.S. Energy metabolism of juvenile scallops Nodipecten subnodosus under acute increased temperature and low oxygen availability. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2023, 278, 111373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, E.; Santos, C.; Rosa, I.C.; Ferreira, V.; Portner, H.O.; Duarte, C.M.; Levin, L.A.; Rosa, R. Impacts of hypoxic events surpass those of future ocean warming and acidification. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, T.K.; Zheng, H. Climate change and bivalve mass mortality in temperate regions. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 251, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, A.F.O.; Lima, C.; Bacha, L.; Oliveira, M.A.P.; Leomil, L.; Rezende, C.E.; Wasserman, J.C.F.A.; Costa, P.M.S.; Costa, S.R.; Siegle, E.; et al. Large polluted river plumes threats sustainable mariculture in the Baia da Ilha Grande. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 83, 104049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbossa, L.H.; Souza, R.V.; Campos, C.J.; Vanz, A.; Vianna, L.F.; Rupp, G.S. Thermotolerant coliform loadings to coastal areas of Santa Catarina (Brazil) evidence the effect of growing urbanization and insufficient provision of sewerage infrastructure. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizan, A.; Venter, L.; Zhang, J.; Young, T.; Ericson, J.A.; Delorme, N.J.; Ragg, N.L.C.; Alfaro, A.C. Interactive effects of elevated temperature and Photobacterium swingsii infection on the survival and immune response of marine mussels (Perna canaliculus): A summer mortality scenario. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 196, 106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FIPERJ. Boletim Informativo Sobre os Dados de Produção da Maricultura no Município de Angra dos Reis. Fundação Instituto de Pesca do Estado do Rio de Janeiro. 2022. Available online: https://portal.angra.rj.gov.br/spe-estatistica-maricultura.asp?IndexSigla=SAAP&vNomeLink=Produ%E7%E3o%20-%20Maricultura (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Thompson, C.; Bacha, L.; Paz, P.H.C.; Oliveira, M.d.A.P.; Oliveira, B.C.V.; Chueke, C.O.C.; Hilário, M.d.L.; Lima, M.; Leomil, L.; Felix-Cordeiro, T.; et al. Collapse of scallop Nodipecten nodosus production in the tropical Southeast Brazil as a possible consequence of global warming and water pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO. World Heritage Convention. Paraty and Ilha Grande—Culture and Biodiversity. 2019. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1308 (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- ISO 194558:2006; Water Quality. Sampling for Microbiological Analysis. International Standard (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/sist/4ada84a7-687c-45c6-90e5-ea5837c66fb3/iso-19458-2006 (accessed on 5 February 2023).
- MAPA 2012. Brazil. Ministry of Fisheries and Aquaculture. Interministerial Normative Instruction MPA/MAPA No. 7, May 8, 2012. Institutes the National Program for Hygienic-Sanitary Control of Bivalve Molluscs (PNCMB) Establishes the Procedures for Its Implementation and Contains Other Provisions. Official Gazette [of the] Federative Republic of Brazil. Brasília. 2012. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/sanidade-animal-e-vegetal/saude-animal/programas-de-saude-animal/arquivos-programas-sanitarios/in_inter_mpa_mapa_07_2012_programanacionalcontrolehigienicosanitariomoluscosbivalves_retificada.pdf (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária—ANVISA. Dispõe Sobre os Padrões Microbiológicos de Alimentos e Sua Aplicação (RDC nº 331, de 23 de Dezembro de 2019). Diário Oficial da República Federativa do Brasil, n° 249. Available online: https://cvs.saude.sp.gov.br/zip/U_IN-MS-ANVISA-60_231219.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; 724p. [Google Scholar]
- Kahlmeter, G.; Giske, C.G.; Kirn, T.J.; Sharp, S.E. Point-counterpoint: Differences between the European committee on antimicrobial susceptibility testing and clinical and laboratory standards institute recommendations for reporting antimicrobial susceptibility results. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pan drug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.P.; De Souza-Carneiro, C.; Saraiva, M.A.F.; De Oliveira, T.A.S.; De Sousa, O.V.; Evangelista Barreto, N.S. Antimicrobial resistance and potential virulence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from water and bivalve mollusks from Bahia, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, E.; Orso, M.; Cozzolino, F.; Sacchini, L.; Leoni, F.; Magistrali, C.F. A systematic review and meta-analysis on antimicrobial resistance in marine bivalves. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1040568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetti, S.J.; Hallinan, B.D.; Tettelbach, S.T.; Volkenborn, N.; Doherty, O.W.; Allam, B.; Gobler, C.J. Warming and hypoxia reduce the performance and survival of northern bay scallops (Argopecten irradians irradians) amid a fishery collapse. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotze, S.; Bock, C.; Eymann, C.; Steffen, J.B.M.; Portner, H.O. Single and combined effects of the “Deadly trio” hypoxia, hypercapnia and warming on the cellular metabolism of the great scallop Pecten maximus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 243–244, 110438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanes, E.; Byrne, M. Warming and hypoxia threaten a valuable scallop fishery: A warning for commercial bivalve ventures in climate change hotspots. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 2043–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Cui, C.; Qin, B.; Ding, K.; Zhou, J. Climate change intensifies algal biomass resurgence in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, D.; Horta, P.; Flores, A.A.V.; Turra, A.; Berchez, F.A.S.; Batista, M.B.; Lopes Filho, E.S.; Melo, M.S.; Ignacio, B.L.; Carneiro, I.M.; et al. Decadal losses of canopy-forming algae along the, warm temperate coastline of Brazil. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, C.B. Viruses as pathogens of marine organisms—From bacteria to whales. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2006, 86, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging strategies to combat ESKAPE pathogens in the era of antimicrobial resistance: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Jiang, F.; He, M.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, H.; Chen, M.; Pang, R.U.; Wei, L.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; et al. Prevalence, virulence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of fluoroquinolone resistance of Vibrio paraemolyticus from different types of food samples in China. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2020, 317, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.E.; Hamid, O.M.; Ali, S.S.; Allam, M.; Elhussein, A.M. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pan drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates in Khartoum State, Sudan. Am. J. Infect. Dis. Microbiol. 2023, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO 2021. The FAO Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance 2021–2025. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/dd6c0ba1-fd85-4a3e-b398-53b610c35318/content (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- Ulug, M.; Gedik, E.; Girgin, S.; Celen, M.K.; Ayaz, C. Pyogenic liver abscess caused by community-acquired multidrug resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntema, V.M.; Potgieter, N.; Barnard, T.G. Detection of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus by molecular and culture-based methods from source water to household container-stored water at the point-of-use in South African rural communities. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 3091–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: Final report and recommendations. Review on antimicrobial resistance. Welcome Trust and HM Government. Arch. Pharm. Practice. 2016, 7, 110. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/references papers?referenceid=2618400 (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- WHO. Cholera. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cholera (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Canellas, A.L.B. Isolation and Characterization of Bacteria of the Genus Vibrio from the Waters of Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; Pós-Graduation Couse of Microbiology, Paulo de Goés Institute of Microbiology, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020; 150p, Available online: https://pantheon.ufrj.br/bitstream/11422/17503/1/ALBCanellas.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Hackbusch, S.; Wichels, A.; Gimenez, L.; Döpke, H.; Gerdts, G. Potentially human pathogenic Vibrio spp. in a coastal transect: Occurrence and multiple virulence factors. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 707, 136113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechri, B.; Monastiri, A.; Medhioub, A.; Medhioub, M.N.; Aouni, M. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of highly pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus strains isolated during mortality outbreaks in cultured Ruditapes decussatus juvenile. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches-Fernandes, G.M.M.; Sá-Correia, I.; Costa, R. Vibriosis outbreaks in aquaculture: Addressing environmental and public health concerns and preventive therapies using gilthead seabream farming as a model system. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 904815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehlet-Delgado, H.; Häse, C.C.; Mueller, R.S. Comparative genomic analysis of Vibrios yields insights into genes associated with virulence towards C. gigas larvae. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Yan, P. Haemocyte protein expression profiling of scallop Chlamys farreri response to acute viral necrosis virus (AVNV) infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.H.; Mutabilib, N.S.A.; Law, J.W.F.; Wong, S.H.; Letchumanan, V. Discovery on antibiotic resistance patterns of V. parahaemolyticus in Selangor reveals carbapenemase-producing V. parahaemolyticus in marine and freshwater fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, K.-Y.; Letchumanan, V.; Law, J.W.-F.; Pusparajah, P.; Goh, B.-H.; AB Mutalib, N.-S.; He, Y.-W.; Lee, L.-H. Incidence of antibiotic resistance in Vibrio spp. Rev. Aquacult. 2020, 12, 2590–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, M.; Rong, X.; LI, B.; Wang, C.; Ge, J.; Zhang, X. Antibiotic resistance, virulence and genetic characteristics of Vibrio alginolyticus isolates from the aquatic environment in coastal mariculture areas in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa Solomieu, V.; Renault, T.; Travers, M.A. Mass mortality in bivalves and the intricate case of the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 131, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jun, J.W.; Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, J.W.; Han, S.J.; Kwon, J.; Oh, W.T.; et al. Mass mortality in Korean bay scallops (Argopecten irradians) associated with Ostreid herpesvirus-1 μVar. Transb. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petton, B.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Pernet, F.; Toulza, E.; de Lorgeril, J.; Degremont, L.; Mitta, G. The Pacific Oyster mortality syndrome, a polymicrobial and multifactorial disease: State of knowledge and future directions. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 630343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.; Kiffney, T.; Tanaka, K.R.; Morse, D.; Brady, D.C. Meta-analysis of growth and mortality rates of net cultured sea scallops across the North Atlantic. Aquaculture 2022, 546, 737392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirella da Silva, P.; Ramos Queiroga, F.; Dantas Farias, N.; Tubino Vianna, R.; Costa Sabry, R. Perkinsus spp. Occurrence in South America: A review. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2024, 204, 108108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Gong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, C. Pathogenic analysis of Vibrio alginolyticus infection in a mouse model. Folia Microbiol. 2014, 59, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Ortmann, A.C.; Bolhuis, H.; Makhalanyane, T.; Thompson, F. Harnessing marine microbiomes to develop a sustainable, all-Atlantic bioeconomy. mLife 2024, 3, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, A.L.d.; De-Simone, S.G.; Carvalho, G.S.L.; Fernandes, K.C.B.; Clementino, M.B.M. Occurrence of Vibrio spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Isolates of Nodipecten nodosus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Water from a Mariculture Farm in Angra dos Reis, Brazil. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040752
Santos ALd, De-Simone SG, Carvalho GSL, Fernandes KCB, Clementino MBM. Occurrence of Vibrio spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Isolates of Nodipecten nodosus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Water from a Mariculture Farm in Angra dos Reis, Brazil. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040752
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Antônia L. dos, Salvatore G. De-Simone, Guilherme S. L. Carvalho, Kayo C. B. Fernandes, and Maysa B. M. Clementino. 2025. "Occurrence of Vibrio spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Isolates of Nodipecten nodosus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Water from a Mariculture Farm in Angra dos Reis, Brazil" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040752
APA StyleSantos, A. L. d., De-Simone, S. G., Carvalho, G. S. L., Fernandes, K. C. B., & Clementino, M. B. M. (2025). Occurrence of Vibrio spp. and Pseudomonas spp. Isolates of Nodipecten nodosus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Water from a Mariculture Farm in Angra dos Reis, Brazil. Microorganisms, 13(4), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040752






