Resistance Genes and Virulence Factor Genes in Coagulase-Negative and Positive Staphylococci of the Staphylococcus intermedius Group (SIG) Isolated from the Dog Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. References Strains
2.2. Sampling, Culture, and Identification
2.3. MALDI-TOF MS
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Gene Detection Using PCR and Gel Electrophoresis
2.6. Disk Diffusion Method
2.7. MIC Determination (Miditech System)
2.8. Biofilm Activity Assay
2.9. Statistical Evaluation of Biofilm Activity
3. Results
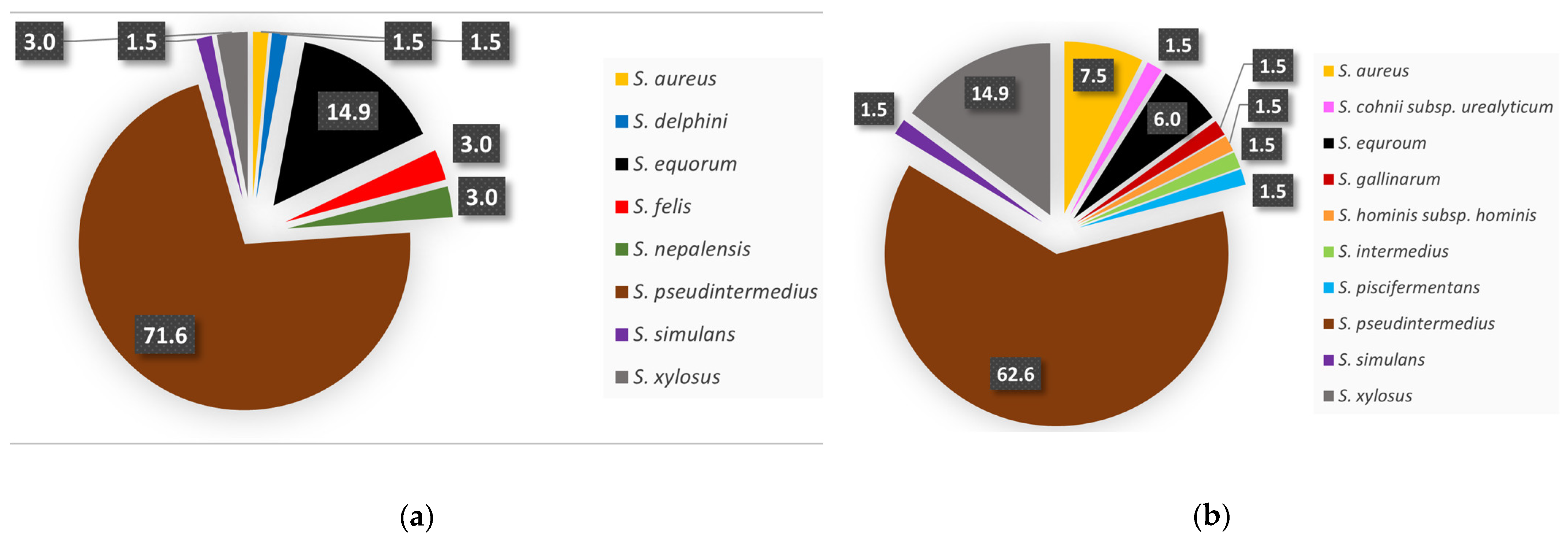
3.1. Isolate Identification
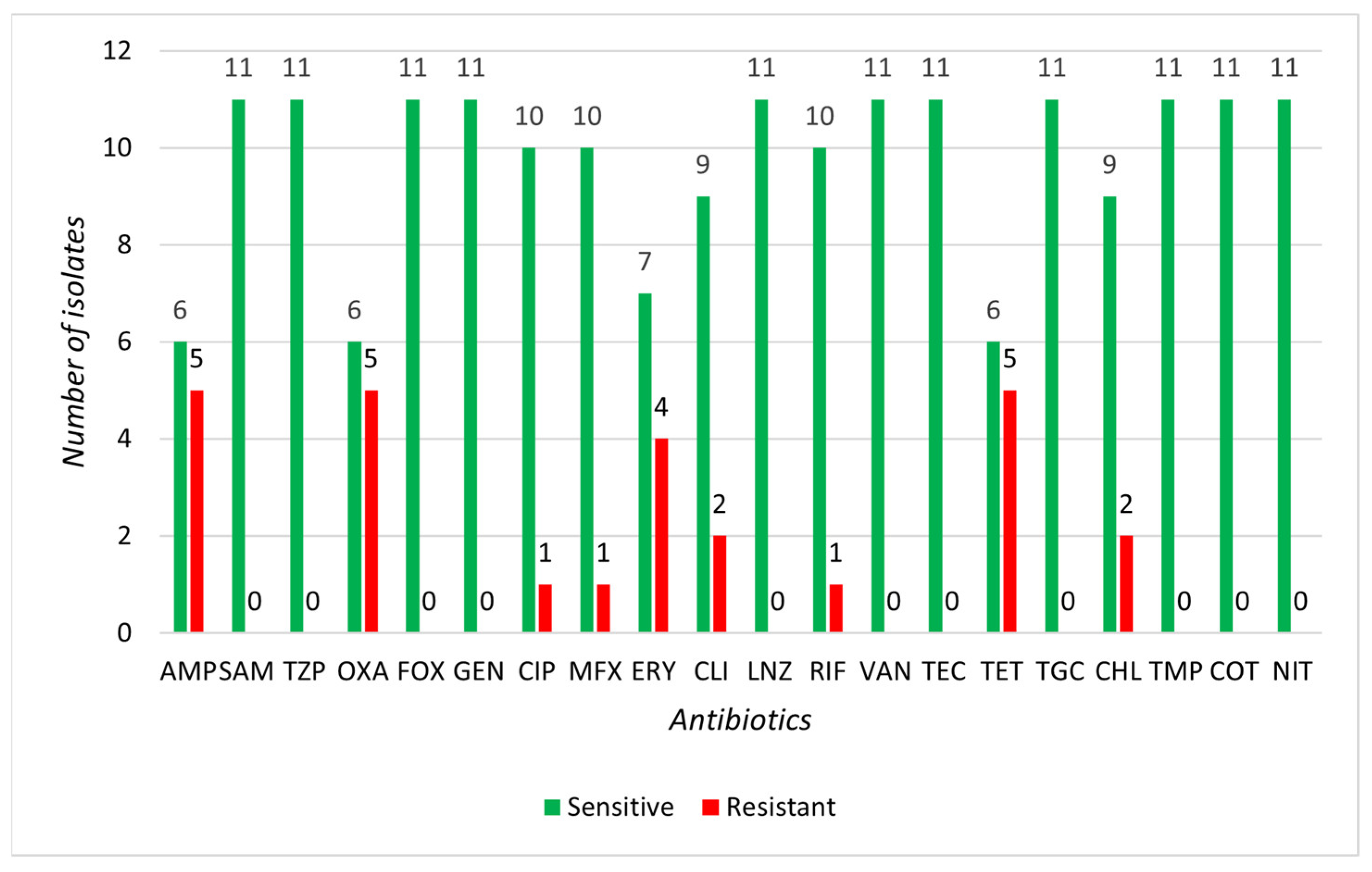
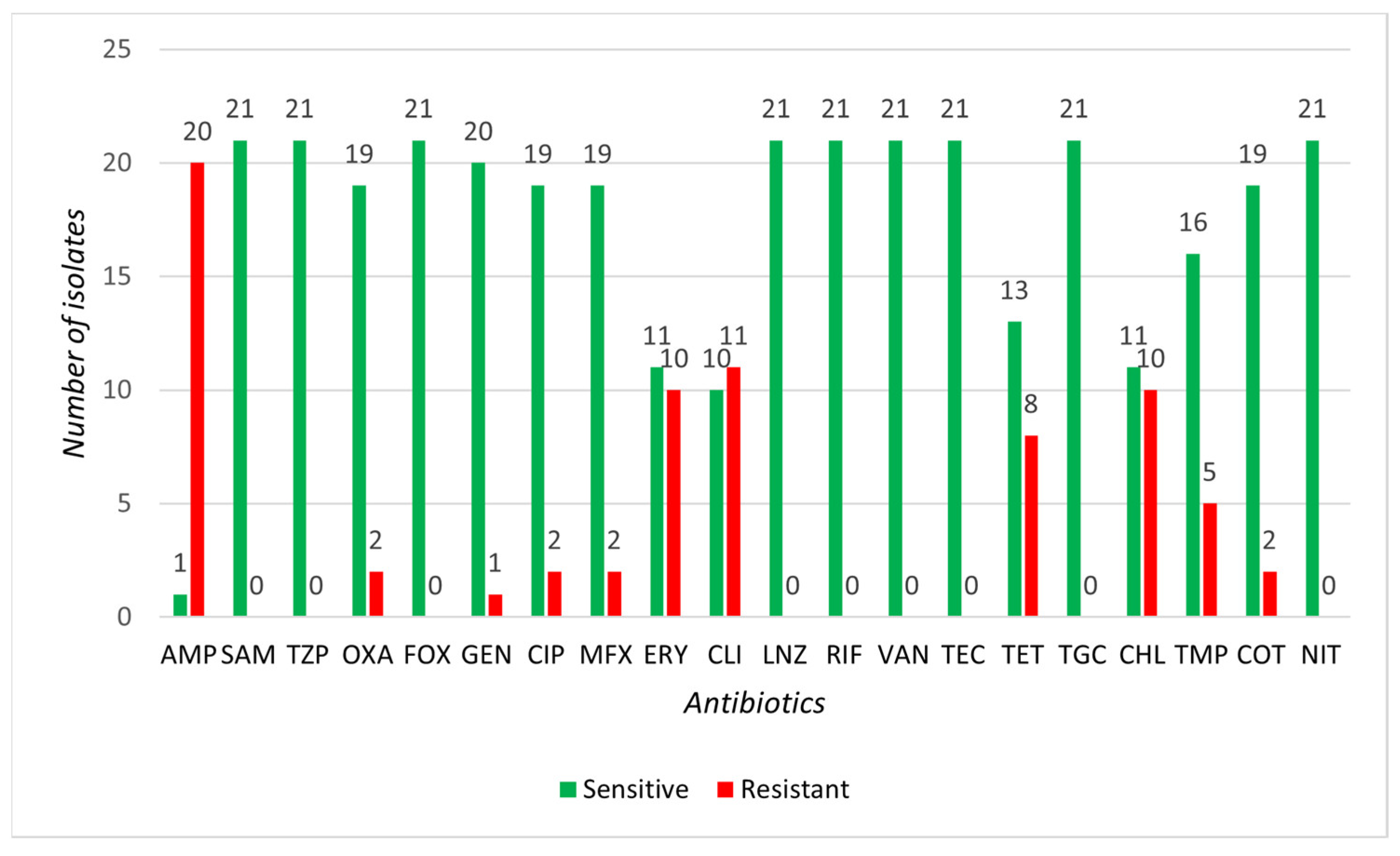
3.2. Determination of Susceptibility to Selected Antibiotics
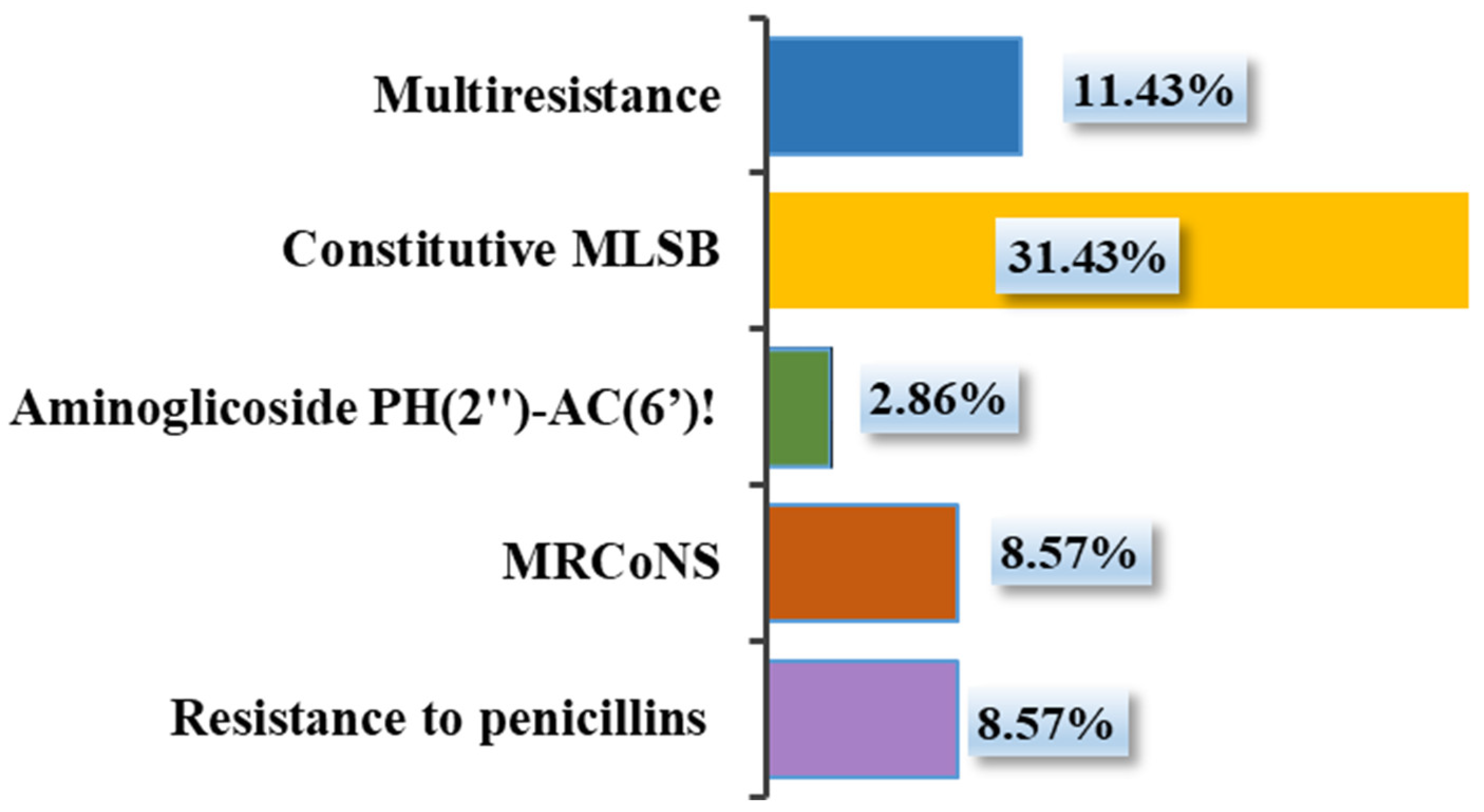
3.3. Gene Resistance Detection of Selected SIG and CoNS Isolates
3.4. Biofilm Activity Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIP | auto-inducting peptide |
| AK | amikacin |
| AMC | amoxicillin/clavulanate |
| AMP | ampicillin |
| BPA | Baird-Parker agar |
| CIP | ciprofloxacin |
| CLI, CLN | clindamycin |
| CN | cephalexin |
| CoNS | coagulase-negative staphylococci |
| CoPS | coagulase-positive staphylococci |
| COT | co-trimoxazole |
| CVN | cefovecin |
| CWAPs | cell wall-anchored proteins |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DOX | doxycycline |
| EPS | extracellular polymeric substance |
| ENR | enrofloxacin |
| ERY | erythromycin |
| ESBL | extended-spectrum beta-lactamase |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
| FOX | cefoxitin |
| GEN | gentamicin |
| CHL | chloramphenicol |
| LNZ | linezolid |
| MALDI-TOF MS | matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry |
| MDR | multidrug-resistant |
| mBHI | modified brain heart infusion |
| MFX | moxifloxacin |
| MGE | mobile genetic element |
| MHA | Mueller–Hinton agar |
| MIC | minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MRCoNS | Multi-resistant CoNS |
| MRSA | methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| MSA | mannitol salt agar |
| MSCRAMM | microbial surface components recognizing |
| NIT | nitrofurantoin |
| OD | optical density |
| OXA | oxacillin |
| PBP | penicillin-binding protein |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PIA | polysaccharide intercellular adhesin |
| QS | quorum sensing |
| RIF | rifampicin |
| rRNA | ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| SAM | ampicillin/sulbactam |
| SCCmec | staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec |
| SIG | Staphylococcus intermedius group |
| TEC | teicoplanin |
| TGC | tigecycline |
| TET | tetracycline |
| TMP | trimethoprim |
| TZP | piperacillin/tazobactam |
| VAN | vancomycin |
| VRSA | vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
Appendix A
| Species | AK 25 µg | AMC 30 µg | CLN 2 µg | CN 30 µg | COT 25 µg | CVN 30 µg | DOX 30 µg | ENR 5 µg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoNS | |||||||||
| 2 | S. felis * | S | S | I | S | S | S | R | S |
| 23 | S. xylosus * | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 30 | S. felis * | S | R | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 32 | S. simulans | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 35 | S. xylosus * | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 39 | S. equorum | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 41 | S. equorum | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S |
| 43 | S. equorum * | S | S | R | S | S | R | R | S |
| 44 | S. equorum * | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | I |
| 45 | S. equorum * | S | S | R | S | S | R | S | I |
| 50 | S. equorum * | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 60 | S. equorum * | S | S | I | R | S | R | R | S |
| 75 | S. equorum * | S | S | R | R | R | R | R | S |
| 76 | S. equorum | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 91 | S. nepalensis | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 93 | S. nepalensis * | S | S | I | S | R | S | R | R |
| SIG | |||||||||
| 3 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 4 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | I | S | S | S | R | R |
| 5 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | I | S | S | S | S | S |
| 6 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | R | S | S | S | R | S |
| 7 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| 9 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | I |
| 10 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | I | S | S | S | S | S |
| 11 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 13 | S. pseudintermedius | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 14 | S. pseudintermedius | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 16 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | I | S | S | S | R | R |
| 17 | S. delphini | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 18 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 19 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 20 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 21 | S. pseudintermedius | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 22 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 24 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 25 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 27 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 31 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 33 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | R | S | R | S | S | S |
| 36 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | I |
| 37 | S. pseudintermedius | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 42 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | R | S | S | S | R | S |
| 46 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | I | I | S | R | I | S |
| 48 | S. pseudintermedius * | R | R | R | R | S | R | R | S |
| 52 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | R | S | S | S | R | S |
| 53 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 55 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 56 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 57 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | I | R | I | S | S | R |
| 58 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 65 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 66 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 67 | S. pseudintermedius | I | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 73 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | I | S | S | S | S | S |
| 80 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | I | S | S | S | R | S |
| 81 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| 82 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | S | S | R | S | R | S |
| 85 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | I | S | R | S | R | I |
| 88 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | S |
| 90 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S |
| 92 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 96 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | I | S | S | S | S | S |
| 99 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | R | S | S | I | S | S | S |
| 100 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| 103 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 104 | S. pseudintermedius | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | S |
| 105 | S. pseudintermedius * | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Other CoPS | |||||||||
| 71 | S. aureus* | S | S | I | S | S | I | I | S |
| AMP | SAM | TZP | OXA | FOX | GEN | CIP | MFX | ERY | CLI | LNZ | RIF | VAN | TEC | TET | TGC | CHL | TMP | COT | NIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoNS | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 23 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 30 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | R | S | S | S |
| 35 | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 43 * | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 44 | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 45 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 50 | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 60 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 75 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 93 * | S | S | S | R | S | S | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | R | S | S | S |
| SIG | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | R | S | S | S |
| 6 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S |
| 11 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 16 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | R | S | S | S |
| 24 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 33 * | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 36 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 42 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | R | R | R | S |
| 46 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 48 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 52 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 56 * | R | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S |
| 57 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 58 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 65 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 80 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| 82 * | R | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S |
| 85 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S | S | S |
| 88 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S |
| 99 * | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S | S | S |
| 105 | R | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| S. aureus | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 71 | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
References
- Kasela, M.; Ossowski, M.; Dzikoń, E.; Ignatiuk, K.; Wlazło, Ł.; Malm, A. The Epidemiology of Animal-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawhney, S.S.; Vargas, R.C.; Wallace, M.A.; Muenks, C.E.; Lubbers, B.V.; Fritz, S.A.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Dantas, G. Diagnostic and commensal Staphylococcus pseudintermedius genomes reveal niche adaptation through parallel selection of defense mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Martín, M.; Corbera, J.A.; Suárez-Bonnet, A.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T. Virulence factors in coagulase-positive staphylococci of veterinary interest other than Staphylococcus aureus. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, I.B.; Santos, F.F.; Gales, A.C. Human Colonization and Infection by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: An Emerging and Underestimated Zoonotic Pathogen. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prévost, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Mitra, S.; Mondal, A.H.; Kumari, H.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Prevalence and molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant coagulase negative staphylococci from urban wastewater in Delhi-NCR, India. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Sobkowich, K.E.; Hui, A.Y.; Poljak, Z.; Szlosek, D.; Plum, A.; Weese, J.S. Nationwide analysis of methicillin-resistant staphylococci in cats and dogs: Resistance patterns and geographic distribution. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2025, 86, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caddey, B.; Fisher, S.; Barkema, H.W.; Nobrega, D.B. Companions in antimicrobial resistance: Examining transmission of common antimicrobial-resistant organisms between people and their dogs, cats, and horses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 38, e0014622. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, C.I.; Lin, C.Y.; Teng, K.T.-Y. Prevalent and Severe Conditions That Compromise the Welfare of Shelter Dogs: Opinions from the Taiwanese Experts. Animals 2025, 15, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelloni, F.; Cagnoli, G.; Ebani, V.V. Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance in Canine Staphylococcus spp. Isolates. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naziri, Z.; Majlesi, M. Comparison of the prevalence, antibiotic resistance patterns, and biofilm formation ability of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in healthy dogs and dogs with skin infections. Vet. Res. Commun. 2023, 47, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Su, C.; He, Z. Isolation, characterization, and fermentation potential of coagulase-negative Staphylococci with taste-enhancing properties from Chinese traditional bacon. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolska-Gębarzewska, M.; Międzobrodzki, J.; Kosecka-Strojek, M. Current types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) in clinically relevant coagulase-negative staphylococcal (CoNS) species. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 50, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelwahab, M.A.; Amer, W.H.; Elsharawy, D.; Elkolaly, R.M.; Helal RA, E.F.; El Malla, D.A.; Elfeky, Y.G.; Bedair, H.A.; Amer, R.S.; Abd-Elmonsef, M.E.; et al. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococci Isolated from an Egyptian University Hospital. Pathogens 2023, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretto, E.; Visiello, R.; Nardini, P. Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. In Pet-To-Man Travelling Staphylococci, 1st ed.; Savini, V., Ed.; Elsevier Saunders: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.-Q.; Shi, Y.-F. Exploring PBP2a resistance in MRSA by comparison between molecular covalent docking and non-covalent docking. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafourian, S.; Sadeghifard, N.; Soheili, S.; Sekawi, Z. Extended Spectrum Beta-lactamases: Definition, Classification and Epidemiology. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2015, 17, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husna, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Badruzzaman, A.T.M.; Sikder, M.H.; Islam, M.R.; Rahman, M.T.; Alam, J.; Ashour, H.M. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases (ESBL): Challenges and Opportunities. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, N.K.; Mazaitis, M.J.; Costerton, J.W.; Leid, J.G.; Powers, M.E.; Shirtliff, M.E. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Properties, regulation, and roles in human disease. Virulence 2011, 2, 445–459. [Google Scholar]
- Hajiagha, M.N.; Kafil, H.S. Efflux pumps and microbial biofilm formation. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2023, 112, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouiller, K.; David, M.Z. Staphylococcus aureus Genomic Analysis and Outcomes in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilcher, K.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcal Biofilm Development: Structure, Regulation, and Treatment Strategies. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, 1128. [Google Scholar]
- Alorabi, M.; Ejaz, U.; Khoso, B.K.; Uddin, F.; Mahmoud, S.F.; Sohail, M.; Youssef, M. Detection of Genes Encoding Microbial Surface Component Recognizing Adhesive Matrix Molecules in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Pyoderma Patients. Genes 2023, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, A.; Soteyome, T.; Yuan, L.; Ma, Q.; Seneviratne, G.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Cell-wall-anchored proteins affect invasive host colonization and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 285, 127782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato’o, Y. Staphylococcus aureus Pathogenesis Based on Genetic Background. In Staphylococcus Aureus; Nakane, A., Asano, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 119–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Pan, J.; Dong, J.; Zhou, X.; Niu, X.; Deng, X. Oligopeptide Targeting Sortase A as Potential Anti-infective Therapy for Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 245. [Google Scholar]
- Lower, S.K.; Lamlertthon, S.; Casillas-Ituarte, N.N.; Lins, R.D.; Yongsunthon, R.; Taylor, E.S.; DiBartola, A.C.; Edmonson, C.; McIntyre, L.M.; Reller, L.B.; et al. Polymorphisms in fibronectin binding protein A of Staphylococcus aureus are associated with infection of cardiovascular devices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18372–18377. [Google Scholar]
- Herman-Bausier, P.; Labate, C.; Towell, A.M.; Derclaye, S.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor A is a force-sensitive molecular switch that activates bacterial adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5564–5569. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, J.; Pérez-Tanoira, R.; Pérez-Jorge-Peremarch, C.; Gómez-Barrena, E. Bacterial Adherence to Biomaterials Used in Surgical Procedures. In Microbiology for Surgical Infections: Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment; Elsevier Saunders: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Király, J.; Hajdučková, V.; Gregová, G.; Szabóová, T.; Pilipčinec, E. Resistant S. aureus Isolates Capable of Producing Biofilm from the Milk of Dairy Cows with Subclinical Mastitis in Slovakia. Agriculture 2024, 14, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, M.; Ardebili, A.; Jamalan, M.; Jahanbakhsh, R.; Behnampour, N.; Ghaemi, E.A. Evaluation of Biofilm Formation and Presence of Ica Genes in Staphylococcus epidermidis Clinical Isolates. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2018, 9, 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartbeck, B.; Rumpf, C.H.; Hait, R.J.; Janssen, T.; Deiwick, S.; Schwierzeck, V.; Mellmann, A.; Kahl, B.C. Various mutations in icaR, the repressor of the icaADBC locus, occur in mucoid Staphylococcus aureus isolates recovered from the airways of people with cystic fibrosis. Microbes Infect. 2024, 26, 105306. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.; Wigneshweraraj, S. Molecular insights into the control of transcription initiation at the Staphylococcus aureus agr operon. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 412, 862–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliard, G.M.; Wilkinson, T.S.; Harris, L.G.; Jenkins, R.E.; Shornick, L.P. PCL-gelatin honey scaffolds promote Staphylococcus aureus agrA expression in biofilms with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1440658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Cuellar, E.; Tsuchiya, K.; Valle-Ríos, R.; Medina-Contreras, O. Differences in Biofilm Formation by Methicillin-Resistant and Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Diseases 2023, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czech Collection of Microorganisms. Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus CCM 4223. Department of Experimental Biology of Masaryk University. Available online: https://ccm.sci.muni.cz/en/catalogue-of-cultures/bacteria-and-archaea/bakterie/htmlb/T526 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Czech Collection of Microorganisms. Staphylococcus epidermidis CCM 4418. Department of Experimental Biology of Masaryk University. Available online: https://ccm.sci.muni.cz/en/catalogue-of-cultures/bacteria-and-archaea/bakterie/htmlb/T535 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Czech Collection of Microorganisms. Staphylococcus edaphicus CCM 8731. Department of Experimental Biology of Masaryk University. Available online: https://ccm.sci.muni.cz/en/catalogue-of-cultures/bacteria-and-archaea/bakterie/htmlb/T2167 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Lovayová, V.; Čurová, K.; Hrabovský, V.; Nagyová, M.; Siegfried, L.; Toporová, A.; Rimárová, K.; Andraščíková, Š. Antibiotic resistance in the invasive bacteria Escherichia coli. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2022, 30, S75–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUCAST. EUCAST Clinical Breakpoint Tables, Version 15.0; European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST): Växjö, Sweden, 2025.
- CLSI. Part B. CLSI vs. FDA Breakpoints (CLSI M100-Ed33), Version 1.0; Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI): Wayne, PA, USA, 2023.
- Dančová, N.; Gregová, G.; Szabóová, T.; Regecová, I.; Király, J.; Hajdučková, V.; Hudecová, P. Quinolone and Tetracycline-Resistant Biofilm-Forming Escherichia coli Isolates from Slovak Broiler Chicken Farms and Chicken Meat. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Pratt, L.A.; Watnick, P.I.; Newman, D.K.; Weaver, V.B.K.R. Genetic approaches to study of biofilms. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 310, 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Djukić, S.; Cirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. APMIS 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, G.M.; Saggin, B.F.; de Carli, S.; da Silva, M.E.R.J.; da Costa, M.M.; Brenig, B.; Siqueira, F.M. Virulent potential of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in dogs. Acta Trop. 2023, 242, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsman, S.; Meler, E.; Mikkelsen, D.; Mallyon, J.; Yao, H.; Magalhães, R.J.S.; Gibson, J.S. Nasal microbiota profiles in shelter dogs with dermatological conditions carrying methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus species. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarbrough, M.L.; Lainhart, W.; Burnham, C.D. Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profiles of Human Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus intermedius Group. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigudu, T.T.; Oguttu, J.W.; Qekwana, D.N. Prevalence of Staphylococcus spp. from human specimens submitted to diagnostic laboratories in South Africa, 2012–2017. S. Afr. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 38, 477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miszczak, M.; Korzeniowska-Kowal, A.; Wzorek, A.; Gamian, A.; Rypuła, K.; Bierowiec, K. Colonization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus species in healthy and sick pets: Prevalence and risk factors. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, V.M.; Williams, N.J.; Pinchbeck, G.; E Corless, C.; Shaw, S.; McEwan, N.; Dawson, S.; Nuttall, T. Antimicrobial resistance and characterisation of staphylococci isolated from healthy Labrador retrievers in the United Kingdom. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Priyantha, R.; Gaunt, M.C.; Rubin, J.E. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius colonizing healthy dogs in Saskatoon, Canada. Can. Vet. J. 2016, 57, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuny, C.; Layer-Nicolaou, F.; Weber, R.; Köck, R.; Witte, W. Colonization of Dogs and Their Owners with Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Households, Veterinary Practices, and Healthcare Facilities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanecka, A.; Król, J.; Twardoń, J.; Mrowiec, J.; Korzeniowska-Kowal, A.; Wzorek, A. Efficacy of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry as well as genotypic and phenotypic methods in identification of staphylococci other than Staphylococcus aureus isolated from intramammary infections in dairy cows in Poland. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2019, 31, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Asbell, P.A.; Sanfilippo, C.M.; DeCory, H.H. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial pathogens isolated from the conjunctiva in the Antibiotic Resistance Monitoring in Ocular micRoorganisms (ARMOR) surveillance study (2009–2021). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 108, 116069. [Google Scholar]
- Dopelt, K.; Amar, A.; Yonatan, N.; Davidovitch, N. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding Antibiotic Use and Resistance: A Cross-Sectional Study among Students in Israel. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khinchi, R.K.; Abhishek Gaurav Manju, S.K. Sharma, and Sudeep Solanki. Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern of Bacterial Pathogens Isolated from Canine Superficial Pyoderma. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2022, 41, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler, A.; Beever, L.; Chang, Y.M.; Klein, B.; Kostka, V.; Meyer, C.; Müller, E.; Weis, J.; Wildermuth, B.; Fishwick, J.; et al. Intervention with impact: Reduced isolation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from dogs following the introduction of antimicrobial prescribing legislation in Germany. Vet. Rec. 2024, 194, e3714. [Google Scholar]
- Mack, C.; Gibson, J.S.; Meler, E.; Woldeyohannes, S.; Yuen, N.; Herndon, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of aerobic bacteria isolated from canine urinary samples in South East Queensland, 2013 to 2018. Aust. Vet. J. 2024, 102, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Domínguez, M.S.; Carvajal, H.D.; Calle-Echeverri, D.A.; Chinchilla-Cárdenas, D. Molecular Detection and Characterization of the mecA and nuc Genes From Staphylococcus Species (S. aureus, S. pseudintermedius, and S. schleiferi) Isolated From Dogs Suffering Superficial Pyoderma and Their Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 376. [Google Scholar]
- Yudhanto, S.; Hung, C.C.; Maddox, C.W.; Varga, C. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria Isolated From Canine Urine Samples Submitted to a Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, Illinois, United States. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 867784. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, A.F.A.G. Coagulase Negative Staphylococci from Companion Dogs in Angola: A Pilot Study. Master’s Thesis, FMV-Universidade de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Horsman, S.; Zaugg, J.; Meler, E.; Mikkelsen, D.; Soares Magalhães, R.J.; Gibson, J.S. Molecular Epidemiological Characteristics of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, Staphylococcus coagulans, and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Cultured from Clinical Canine Skin and Ear Samples in Queensland. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2022, Trends from 2010 to 2022; Thirteenth ESVAC Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023.
- Lord, J.; Millis, N.; Jones, R.D.; Johnson, B.; Kania, S.A.; Odoi, A. Patterns of antimicrobial, multidrug and methicillin resistance among Staphylococcus spp. isolated from canine specimens submitted to a diagnostic laboratory in Tennessee, USA: A descriptive study. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Chah, K.F.; Gómez-Sanz, E.; Nwanta, J.A.; Asadu, B.; Agbo, I.C.; Lozano, C.; Zarazaga, M.; Torres, C. Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Healthy Dogs in Nsukka, Nigeria. Brazil. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. AWaRe Classification of Antibiotics for Evaluation and Monitoring of Use; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Grönthal, T.; Eklund, M.; Thomson, K.; Piiparinen, H.; Sironen, T.; Rantala, M. Antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and the molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant S. pseudintermedius in small animals in Finland. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Ganiere, J.P.; Medaille, C.; Mangion, C. Antimicrobial drug susceptibility of Staphylococcus intermedius clinical isolates from canine pyoderma. J. Vet. Med. 2005, 52, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, H.; Keane, C.T. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. Lancet 1997, 350, 737–738. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, M.; Santoro, D. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant coagulase-positive staphylococci in canine and feline dermatological patients over a 10-year period: A retrospective study. Microbiology 2023, 169, 001300. [Google Scholar]
- Siugzdaite, J.; Gabinaitiene, A. Methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci in healthy dogs. Veterinární Medicína 2017, 62, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, M.; Joshi, P.R.; Paudel, S.; Acharya, M.; Rijal, K.R.; Ghimire, P.; Banjara, M.R. Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase Negative Staphylococci and Their Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern from Healthy Dogs and Their Owners from Kathmandu Valley. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feßler, A.T.; Billerbeck, C.; Kadlec, K.; Schwarz, S. Identification and characterization of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from bovine mastitis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, F.; Ruppé, E.; Hernandez, D.; Lebeaux, D.; Francois, P.; Felix, B.; Desprez, A.; Maiga, A.; Woerther, P.-L.; Gaillard, K.; et al. Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in the Community: High Homology of SCCmec IVa between Staphylococcus epidermidis and Major Clones of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, J.; Shimizu, A.; Saitoh, Y.; Yagi, M.; Saito, T.; Okamoto, R. Isolation of methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci from chickens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platenik, M.O.; Archer, L.; Kher, L.; Santoro, D. Prevalence of mecA, mecC and Panton-Valentine-Leukocidin Genes in Clinical Isolates of Coagulase Positive Staphylococci from Dermatological Canine Patients. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.; Ramalheira, E.; Afreixo, V.; Gago, B. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the new mecC gene—A meta-analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 84, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacinti, G.; Carfora, V.; Caprioli, A.; Sagrafoli, D.; Marri, N.; Giangolini, G.; Amoruso, R.; Iurescia, M.; Stravino, F.; Dottarelli, S.; et al. Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecA or mecC and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in dairy sheep farms in central Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E.; Nuttall, T.J.; Gkekas, G.; Mellanby, R.J.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Paterson, G.K. Not just in man’s best friend: A review of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius host range and human zoonosis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2024, 174, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, L.; Teixeira, I.M.; da Silva, I.T.; Antunes, M.; Pesset, C.; Fonseca, C.; Santos, A.L.; Côrtes, M.F.; Penna, B. Epidemiologic case investigation on the zoonotic transmission of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius among dogs and their owners. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Jantorn, P.; Heemmamad, H.; Soimala, T.; Indoung, S.; Saising, J.; Chokpaisarn, J.; Wanna, W.; Tipmanee, V.; Saeloh, D. Antibiotic Resistance Profile and Biofilm Production of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius Isolated from Dogs in Thailand. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Zhi, Z.; Zhong, T.; Lin, S.; Ye, J.; Qian, X.; Chen, F.; Yuan, W. Carvacrol inhibits bacterial polysaccharide intracellular adhesin synthesis and biofilm formation of mucoid Staphylococcus aureus: An in vitro and in vivo study. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Cui, L.; Dong, J.; Meng, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, H. Antibiotic resistance, biofilm formation, and virulence factors of isolates of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from healthy dogs and dogs with keratitis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 903633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Correia, E.; Pereira, J.E.; González-Machado, C.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Exploring the Biofilm Formation Capacity in S. pseudintermedius and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Species. Pathogens 2022, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.; Oliveira, K.; Morais, C.; Abrantes, P.; Pomba, C.; Rosato, A.E.; Couto, I.; Costa, S.S. Virulence Potential of Biofilm-Producing Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus coagulans Causing Skin Infections in Companion Animals. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Isolate with mecA Gene | MHA | MIC |
|---|---|---|
| S. equorum no. 43 | CLN, CVN, DOX | AMP, OXA, ERY, TET |
| S. equorum no. 45 | CLN, CVN | ERY, CLN |
| S. equorum no. 50 | AMC, CLN | AMP, OXA |
| S. equorum no. 75 | CLN, CN, COT, CVN, DOX | - |
| CoNS | Isolate | Diameter | Biofilm |
| 2 | 3.657 | strong | |
| 23 | 3.620 | strong | |
| 30 | 3.637 | strong | |
| 35 | 3.661 | strong | |
| 43 | 2.605 | strong | |
| 44 | 2.55 | strong | |
| 45 | 1.563 | moderate | |
| 50 | 3.117 | strong | |
| 60 | 3.543 | strong | |
| 75 | 0.873 | weak | |
| 93 | 2.731 | strong | |
| SIG | 4 | 3.687 | strong |
| 6 | 3.525 | strong | |
| 11 | 3.637 | strong | |
| 16 | 3.722 | strong | |
| 24 | 3.536 | strong | |
| 33 | 3.677 | strong | |
| 36 | 3.608 | strong | |
| 42 | 3.435 | strong | |
| 46 | 3.528 | strong | |
| 48 | 0.566 | weak | |
| 52 | 3.629 | strong | |
| 56 | 3.574 | strong | |
| 57 | 3.561 | strong | |
| 58 | 3.300 | strong | |
| 65 | 3.495 | strong | |
| 80 | 3.304 | strong | |
| 82 | 2.143 | strong | |
| 85 | 3.557 | strong | |
| 88 | 3.670 | strong | |
| 99 | 3.525 | strong | |
| 105 | 1.303 | moderate | |
| SA | 71 | 2.444 | strong |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hisirová, S.; Koščová, J.; Király, J.; Hajdučková, V.; Hudecová, P.; Lauko, S.; Gregová, G.; Dančová, N.; Koreneková, J.; Lovayová, V. Resistance Genes and Virulence Factor Genes in Coagulase-Negative and Positive Staphylococci of the Staphylococcus intermedius Group (SIG) Isolated from the Dog Skin. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040735
Hisirová S, Koščová J, Király J, Hajdučková V, Hudecová P, Lauko S, Gregová G, Dančová N, Koreneková J, Lovayová V. Resistance Genes and Virulence Factor Genes in Coagulase-Negative and Positive Staphylococci of the Staphylococcus intermedius Group (SIG) Isolated from the Dog Skin. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040735
Chicago/Turabian StyleHisirová, Simona, Jana Koščová, Ján Király, Vanda Hajdučková, Patrícia Hudecová, Stanislav Lauko, Gabriela Gregová, Nikola Dančová, Júlia Koreneková, and Viera Lovayová. 2025. "Resistance Genes and Virulence Factor Genes in Coagulase-Negative and Positive Staphylococci of the Staphylococcus intermedius Group (SIG) Isolated from the Dog Skin" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040735
APA StyleHisirová, S., Koščová, J., Király, J., Hajdučková, V., Hudecová, P., Lauko, S., Gregová, G., Dančová, N., Koreneková, J., & Lovayová, V. (2025). Resistance Genes and Virulence Factor Genes in Coagulase-Negative and Positive Staphylococci of the Staphylococcus intermedius Group (SIG) Isolated from the Dog Skin. Microorganisms, 13(4), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040735





