Anaerobic Digestion of High-Solid Chicken Manure (CM) at Different Temperature: Intestinal Microbiome Efficiency, Inhibition, and Microbial Community Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock, Inoculum and Operating Procedure
2.2. Chemical and Physiological Analysis Procedures
2.3. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) Extraction and Analysis
2.4. Kinetic Analysis
2.5. Free VFA (FVFA) and Free Ammonia (FA) Calculation
2.6. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.7. Statistical Analysis and Functional Prediction
3. Results and Discussion
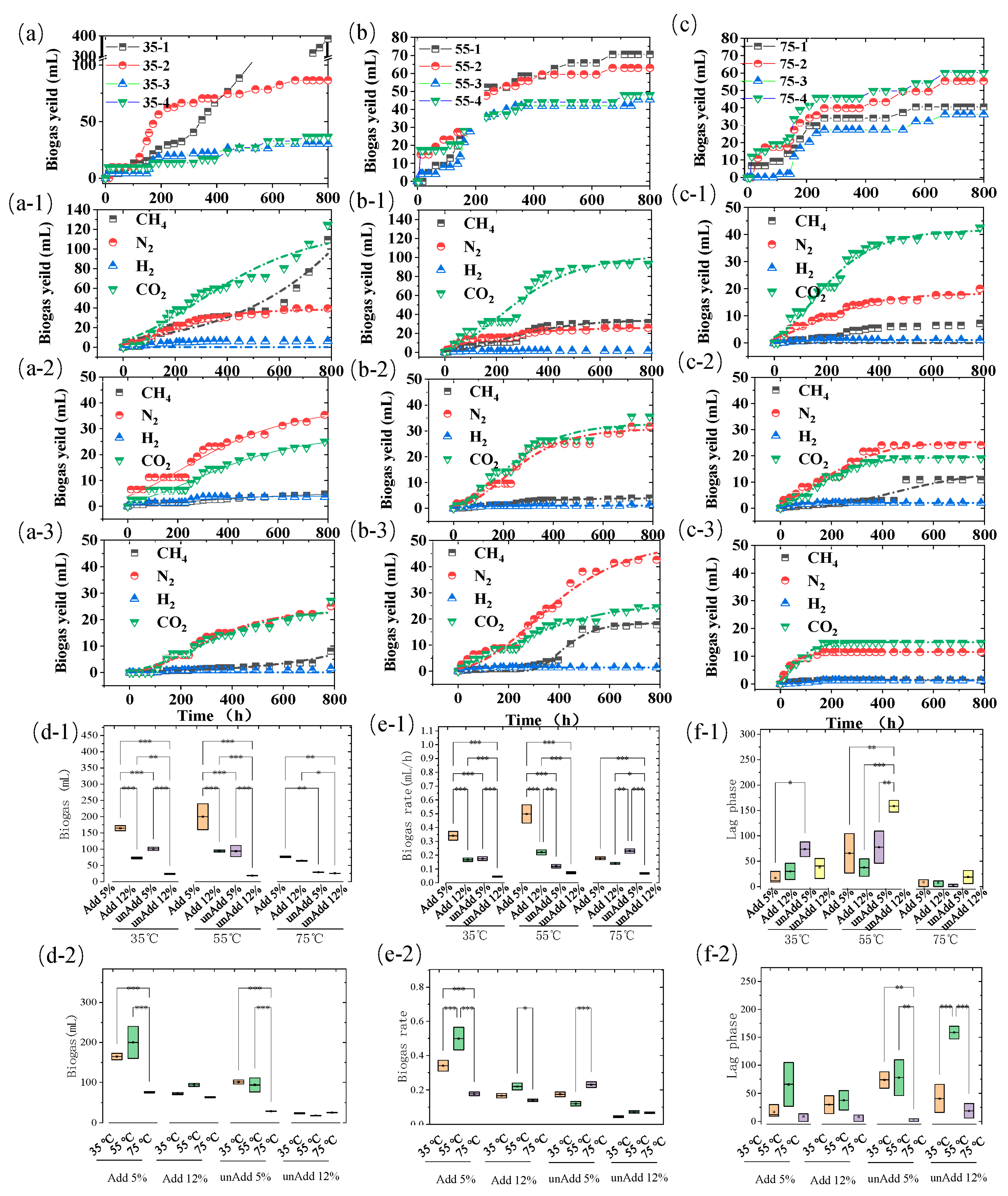
3.1. Biogas Performance Response to TS and Temperature Variation
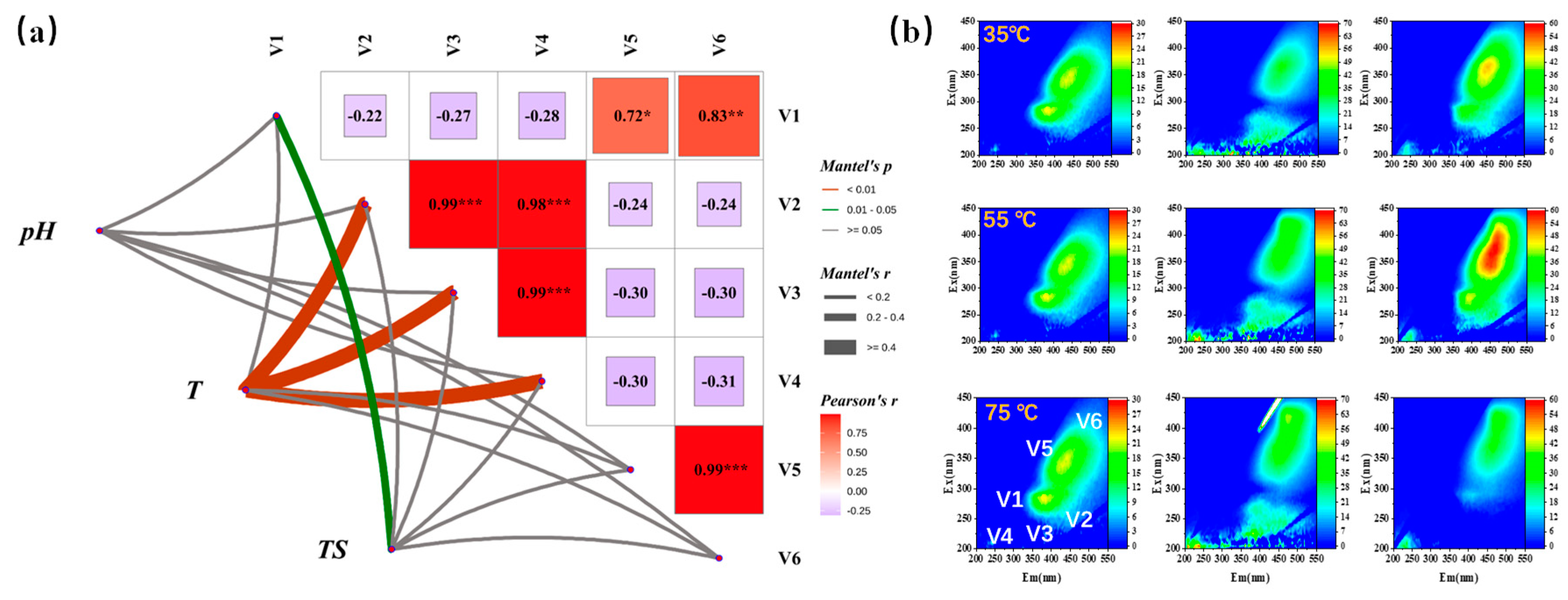
3.2. The Influence of TS and Temperature on Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM)
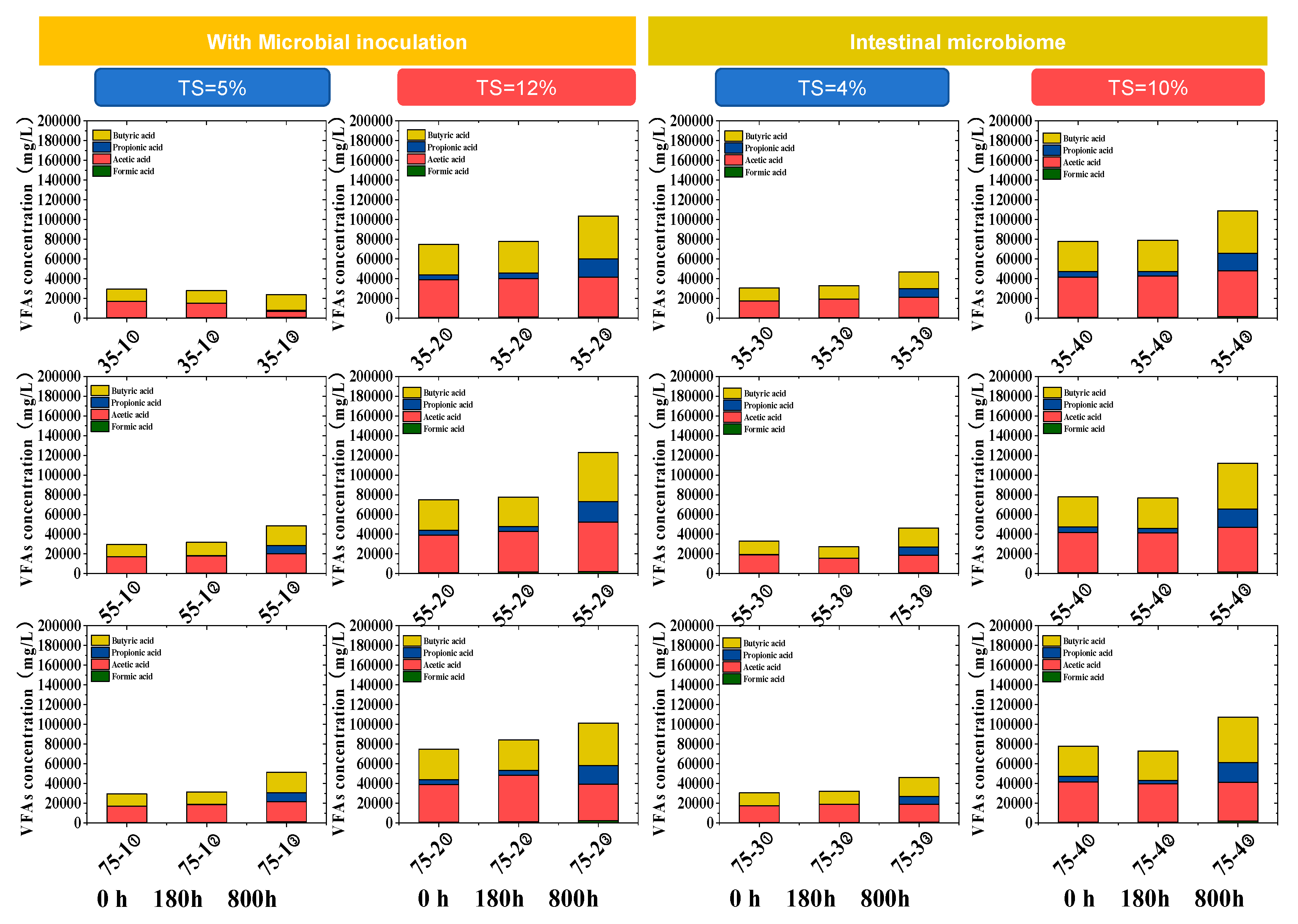
3.3. The Influence of TS and Temperature on VFAs
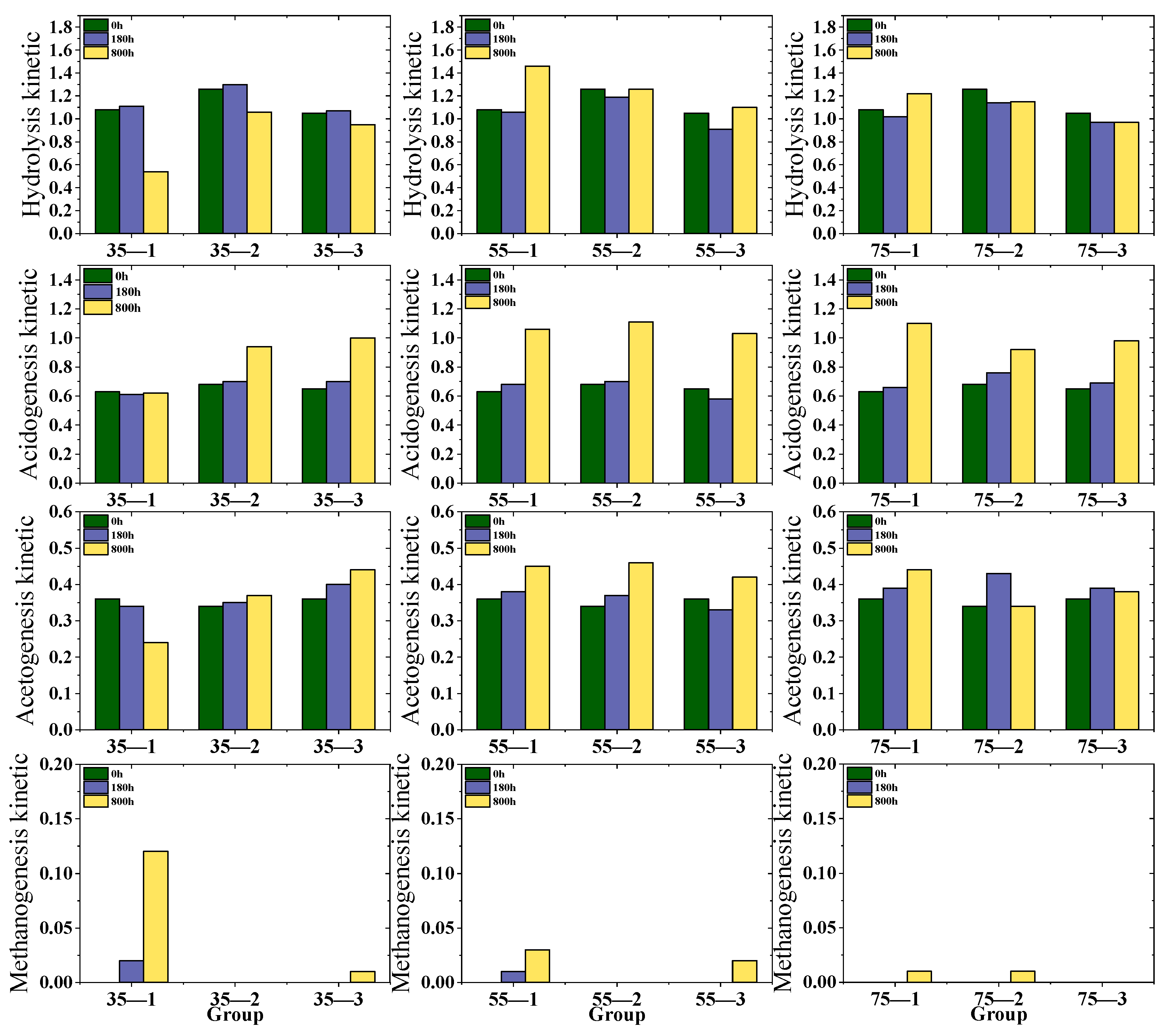
3.4. Organic Matter Transformation via the Four Classical AD Stages
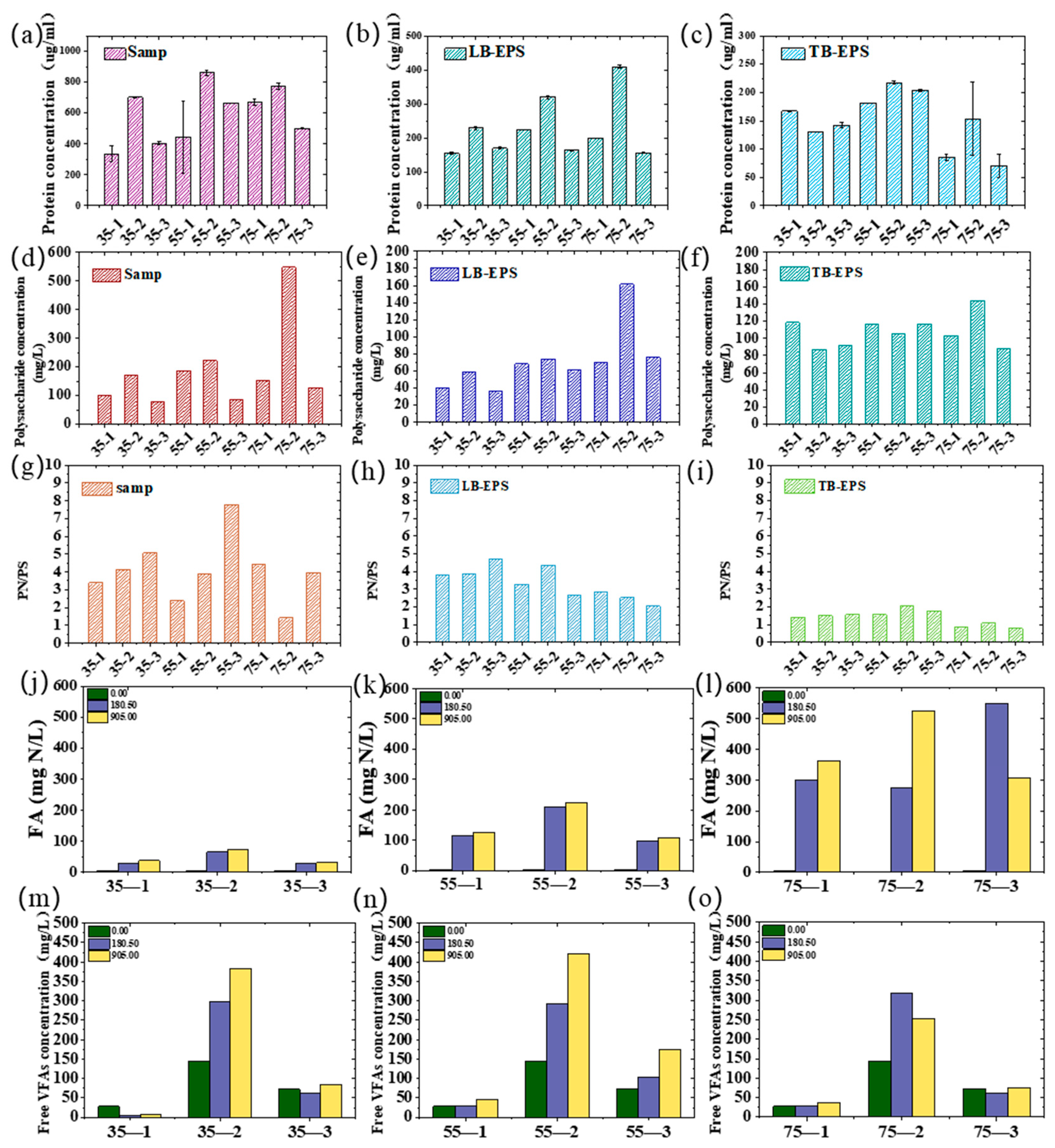
3.5. EPS Changes Response to the Key Inhibitors of FA and FVFA
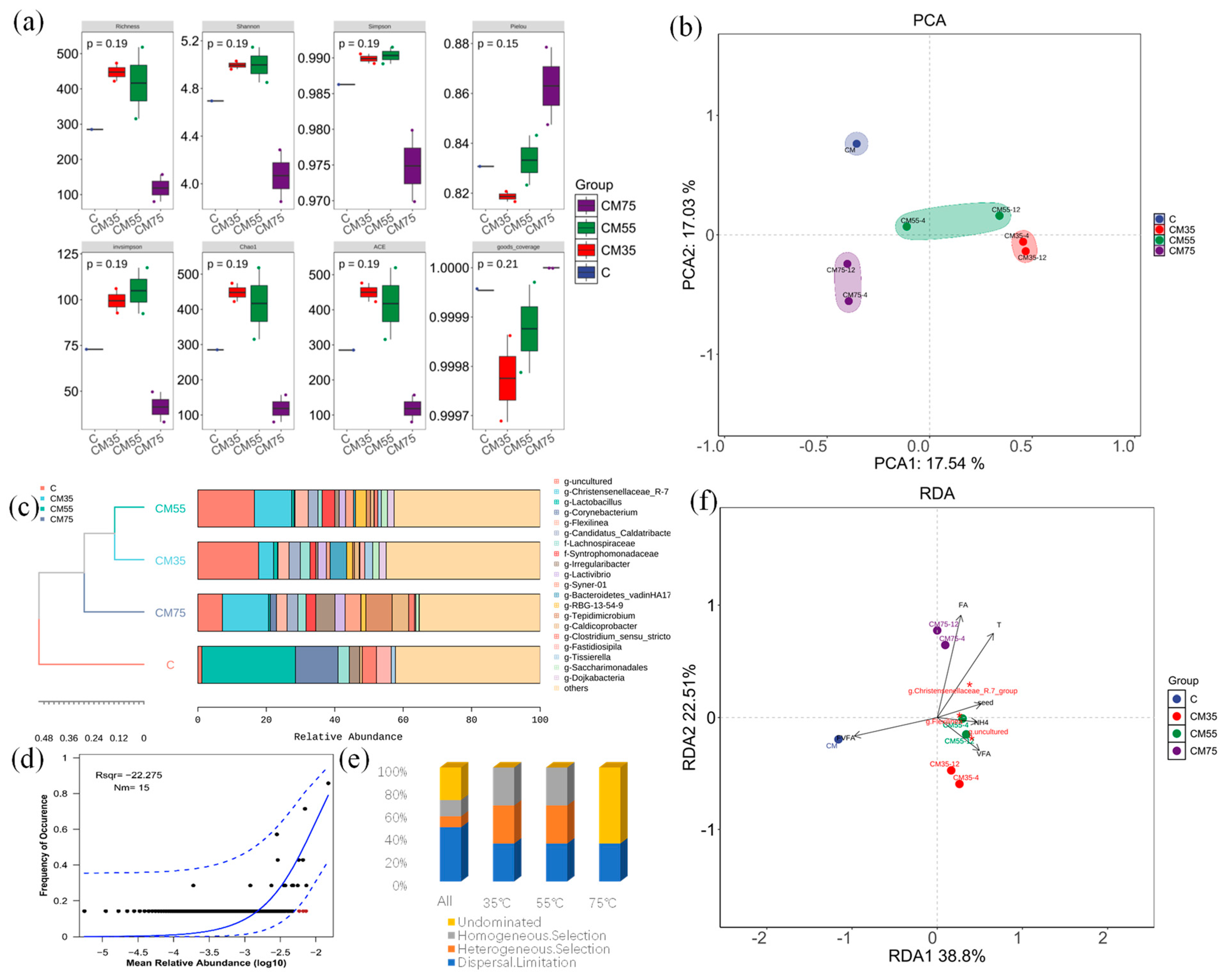
3.6. Microbial Community Succession and Self-Assembly
3.7. Microbial Community Metabolism Functional Prediction
3.8. Environmental Implications of the Present Work
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakadevan, K.; Nguyen, M.L. Livestock Production and Its Impact on Nutrient Pollution and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Adv. Agron. 2017, 141, 147–184. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Liu, R.H.; Yu, Q.; Ma, R.J. Removal of nitrogen from chicken manure anaerobic digestion for enhanced biomethanization. Fuel 2018, 232, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, G.K.; Xu, J.Y.; Xu, H.; Yuan, Q.X.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Sarma, J.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, J.; et al. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal carbonization of dairy manure: Chemical and structural properties of the products. Energy 2018, 165, 662–672. [Google Scholar]
- Drózdz, D.; Wystalska, K.; Malinska, K.; Grosser, A.; Grobelak, A.; Kacprzak, M. Management of poultry manure in Poland—Current state and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110327. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.Y.; Song, Y.; Li, D.J.; Liu, R.T.; Niu, Q.G. The auto fluorescence characteristics, specific activity, and microbial community structure in batch tests of mono-chicken manure digestion. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.N.; Chen, W.H.; Luo, W.D.; Fang, H.L.; Lv, H.Y.; Liu, R.T.; Niu, Q.G. Anaerobic co-digestion of chicken manure and cardboard waste: Focusing on methane production, microbial community analysis and energy evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 321, 124429. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.L.; Shi, Y.S.; Li, D.J.; Song, L.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, R.T.; Yuan, D.; Niu, Q.G. Synergistic co-digestion of waste commercial yeast and chicken manure: Kinetic simulation, DOM variation and microbial community assessment. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 2272–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.G.; Qiao, W.; Qiang, H.; Hojo, T.; Li, Y.Y. Mesophilic methane fermentation of chicken manure at a wide range of ammonia concentration: Stability, inhibition and recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 358–367. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.D.; Fang, Y.S.; Song, L.Y.; Niu, Q.G. Production of struvite by magnesium anode constant voltage electrolytic crystallisation from anaerobically digested chicken manure slurry. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113991. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Zhou, L.; Arhin, S.G.; Papadakis, V.G.; Goula, M.A.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Bioaugmentation with well-constructed consortia can effectively alleviate ammonia inhibition of practical manure anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118244. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, L.C.; Van Hengel, M.; Kroeze, C.; Medema, G.; Spanier, J.E.; Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Hofstra, N. concentrations in rivers worldwide. Water Res. 2019, 149, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jurgutis, L.; Slepetiene, A.; Volungevicius, J.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K. Biogas production from chicken manure at different organic loading rates in a mesophilic full scale anaerobic digestion plant. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 141, 105693. [Google Scholar]
- Yellezuome, D.; Zhu, X.P.; Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, R.H. Mitigation of ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion of nitrogen-rich substrates for biogas production by ammonia stripping: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112043. [Google Scholar]
- Cea-Barcia, G.; Pérez, J.; Buitrón, G. Co-digestion of microalga-bacteria biomass with papaya waste for methane production. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, S.H.; Abdelaziz, K.; Spahany, H.; Astill, J.; Trott, D.; Wang, B.; Wang, A.; Parkinson, J.; Sharif, S. Intestinal microbiome profiles in broiler chickens raised without antibiotics exhibit altered microbiome dynamics relative to conventionally raised chickens. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301110. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.T.; Peng, Z.Y.; Hu, Z.G.; Xue, H.H.; Qiao, J.P.; Niu, Q.G. Fe/Co-modified bio-hydrochar enhanced anaerobic digestion of chicken manure with sulfadimethazine: Focusing on synergistic mechanism and microbial community succession. Biochar 2024, 6, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Y.; Zhuang, W.E.; Chen, C.T.A.; Wang, B.J.; Kuo, F.W. Unveiling the transformation and bioavailability of dissolved organic matter in contrasting hydrothermal vents using fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC. Water Res. 2017, 111, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Dev, S.; Saha, S.; Kurade, M.B.; Salama, E.S.; El-Dalatony, M.M.; Ha, G.S.; Chang, S.W.; Jeon, B.H. Perspective on anaerobic digestion for biomethanation in cold environments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo-Reyes, J.; Buitrón, G.; Arcila, J.S.; Lopez-Gomez, M.O. Thermophilic biogas production from microalgae-bacteria aggregates: Biogas yield, community variation and energy balance. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129898. [Google Scholar]
- Dalkilic, K.; Ugurlu, A. Biogas production from chicken manure at different organic loading rates in a mesophilic-thermopilic two stage anaerobic system. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Li, W.G.; Gong, X.J.; Li, Y.B.; Wu, C.D.; Ren, N.Q. Spectral study of dissolved organic matter in biosolid during the composting process using inorganic bulking agent: UV-vis, GPC, FTIR and EEM. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 617–623. [Google Scholar]
- Ney, B.; Ahmed, F.H.; Carere, C.R.; Biswas, A.; Warden, A.C.; Morales, S.E.; Pandey, G.; Watt, S.J.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Taylor, M.C.; et al. The methanogenic redox cofactor F is widely synthesized by aerobic soil bacteria. ISME J. 2017, 11, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Srisowmeya, G.; Chakravarthy, M.; Devi, G.N. Critical considerations in two-stage anaerobic digestion of food waste—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 119, 109587. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.P.; Yellezuome, D.; Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, X.W.; Liu, R.H. Comprehensive insights into the effects of acidogenic off-gas utilization on successive biogas production, microbial community structure and metabolite distribution during two-stage anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2024, 258, 121740. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Dennehy, C.; Lawlor, P.G.; Hu, Z.H.; Yang, Q.F.; Mccarthy, G.; Tan, S.P.; Zhan, X.M.; Gardiner, G.E. Inactivation of during dry co-digestion of food waste and pig for manure. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 231–240. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.R.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Li, Y. Bioaugmentation improves batch psychrophilic anaerobic co-digestion of cattle manure and corn straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126118. [Google Scholar]
- Elsamadony, M.; Mostafa, A.; Fujii, M.; Tawfik, A.; Pant, D. Advances towards understanding long chain fatty acids-induced inhibition and overcoming strategies for efficient anaerobic digestion process. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116732. [Google Scholar]
- Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B.K. Anaerobic Thermophilic Digestion of Manure at Different Ammonia Loads—Effect of Temperature. Water Res. 1994, 28, 727–731. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.N.; Chen, W.H.; Liu, M.L.; Lv, H.Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Niu, Q.G. Biogas production, DOM performance and microbial community changes in anaerobic co-digestion of chicken manure with and green waste. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 158, 106359. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Mcadam, E.; Zhang, Y.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Longhurst, P. Ammonia inhibition and toxicity in anaerobic digestion: A critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100899. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, C.; Zeng, A.P.; Deckwer, W.D. Growth inhibition by ammonia and use of a pH controlled feeding strategy for the effective cultivation of Mycobacterium chlorophenolicum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1995, 44, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; He, F.; Sun, N.; Hu, S.; Zhao, X. Sodium dodecyl sulfate rearranges the conformation of transferrin and attenuates its iron-binding capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketsub, N.; Whatmore, P.; Abbasabadi, M.; Doherty, W.O.S.; Kaparaju, P.; O’hara, I.M.; Zhang, Z.Y. Effects of pretreatment methods on biomethane production kinetics and microbial community by solid state anaerobic digestion of sugarcane trash. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 352, 127112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhajeri, N.S.; Eraky, M.; Qyyum, M.A.; Tawfik, A. Eco-friendly fermentation module for maximization of hydrogen harvesting from fatty restaurant waste diluted with grey water. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 26461–26474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.G.; Takemura, Y.; Kubota, K.; Li, Y.Y. Comparing mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of chicken manure: Microbial community dynamics and process resilience. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.Y.; An, Z.G.; Li, C.Y.; Cui, X.J.; Li, K.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, B.X.; Hao, P.; Kulyar, M.F.; Yin, W.; et al. Salt-contaminated water exposure induces gut microbial dysbiosis in chickens. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114731. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.G.; Hojo, T.; Qiao, W.; Qiang, H.; Li, Y.Y. Characterization of methanogenesis, acidogenesis and hydrolysis in thermophilic methane fermentation of chicken manure. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 244, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, M.; Yan, Y.; Nie, C.; Yu, K.; Tu, Z.; Xia, Y. Micron-scale heterogeneity reduction leads to increased interspecies competition in thermophilic digestion microbiome. Water Res. 2025, 279, 123419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detman, A.; Laubitz, D.; Chojnacka, A.; Kiela, P.R.; Salamon, A.; Barberan, A.; Chen, Y.J.; Yang, F.; Blaszczyk, M.K.; Sikora, A. Dynamics of dark fermentation microbial communities in the light of lactate and butyrate production. Microbiome 2021, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessione, E. Lactic acid bacteria contribution to gut microbiota complexity: Lights and shadows. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhurdina, S.; Zhuravleva, E.; Kovalev, A.; Andreev, E.; Kryukov, E.; Loiko, N.; Laikova, A.; Popova, N.; Kovalev, D.; Vivekanand, V.; et al. Comparative effect of conductive and dielectric materials on methanogenesis from highly concentrated volatile fatty acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 377, 128966. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.Q.; Li, P.F.; Pan, X.H.; Yuan, Y.K.; Li, G.; Jiao, Y.Z.; Petracchini, F.; Hou, T.T.; He, C. Achieving synergistic enhancement in the anaerobic digestion of corn straw by (CH4+CO2) nanobubbles in conjunction with optimized particle sizes. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 418, 131997. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Xue, Y.G.; Chen, S.S.; Takahashi, J.; Dai, L.L.; Dai, X.H. Methanogenic population dynamics regulated by bacterial community responses to protein-rich organic wastes in a high solid anaerobic digester. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 444–453. [Google Scholar]
- Nobu, M.K.; Narihiro, T.; Kuroda, K.; Mei, R.; Liu, W.T. Chasing the elusive Euryarchaeota class WSA2: Genomes reveal a uniquely fastidious methylreducing methanogen. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Niu, Q.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Y.; Song, G.; Liu, R. Anaerobic Digestion of High-Solid Chicken Manure (CM) at Different Temperature: Intestinal Microbiome Efficiency, Inhibition, and Microbial Community Evolution. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040724
Chen X, Niu Q, Li J, Zhou Z, Wu Y, Song G, Liu R. Anaerobic Digestion of High-Solid Chicken Manure (CM) at Different Temperature: Intestinal Microbiome Efficiency, Inhibition, and Microbial Community Evolution. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040724
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xujing, Qigui Niu, Jingyi Li, Zijing Zhou, Yue Wu, Guixue Song, and Rutao Liu. 2025. "Anaerobic Digestion of High-Solid Chicken Manure (CM) at Different Temperature: Intestinal Microbiome Efficiency, Inhibition, and Microbial Community Evolution" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040724
APA StyleChen, X., Niu, Q., Li, J., Zhou, Z., Wu, Y., Song, G., & Liu, R. (2025). Anaerobic Digestion of High-Solid Chicken Manure (CM) at Different Temperature: Intestinal Microbiome Efficiency, Inhibition, and Microbial Community Evolution. Microorganisms, 13(4), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040724





