Postlarval Shrimp-Associated Microbiota and Underlying Ecological Processes over AHPND Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Sampling
2.2. PCR Amplification and Amplicons Sequencing
2.3. Amplicon Data Processing
2.4. Construction of Diagnosis Model
2.5. Microbial Community Assembly Analysis
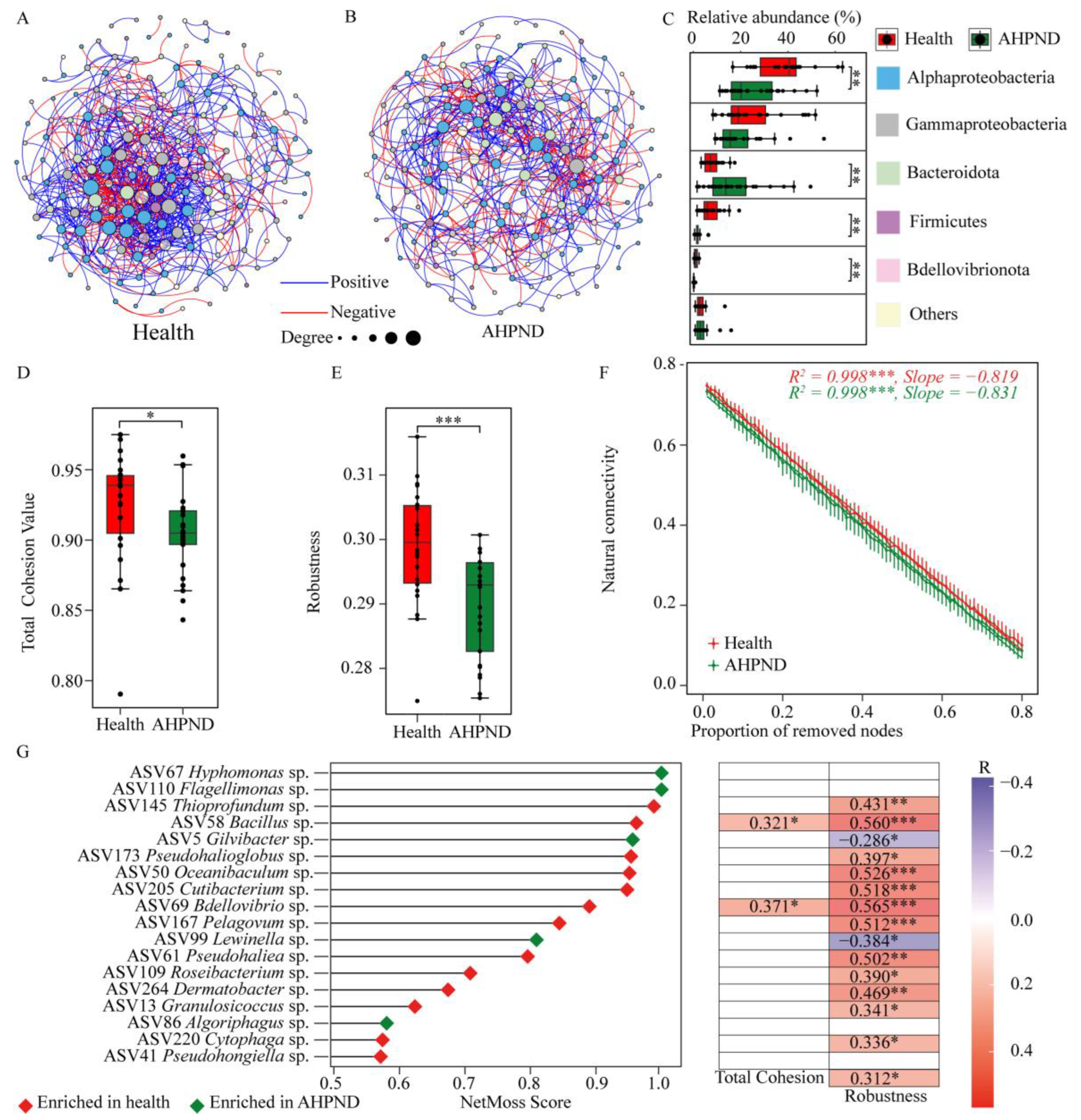
2.6. Interspecies Interactions of Postlarvae-Associated Microbiota Between Health Status
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Shrimp Mortality over AHPND Progression
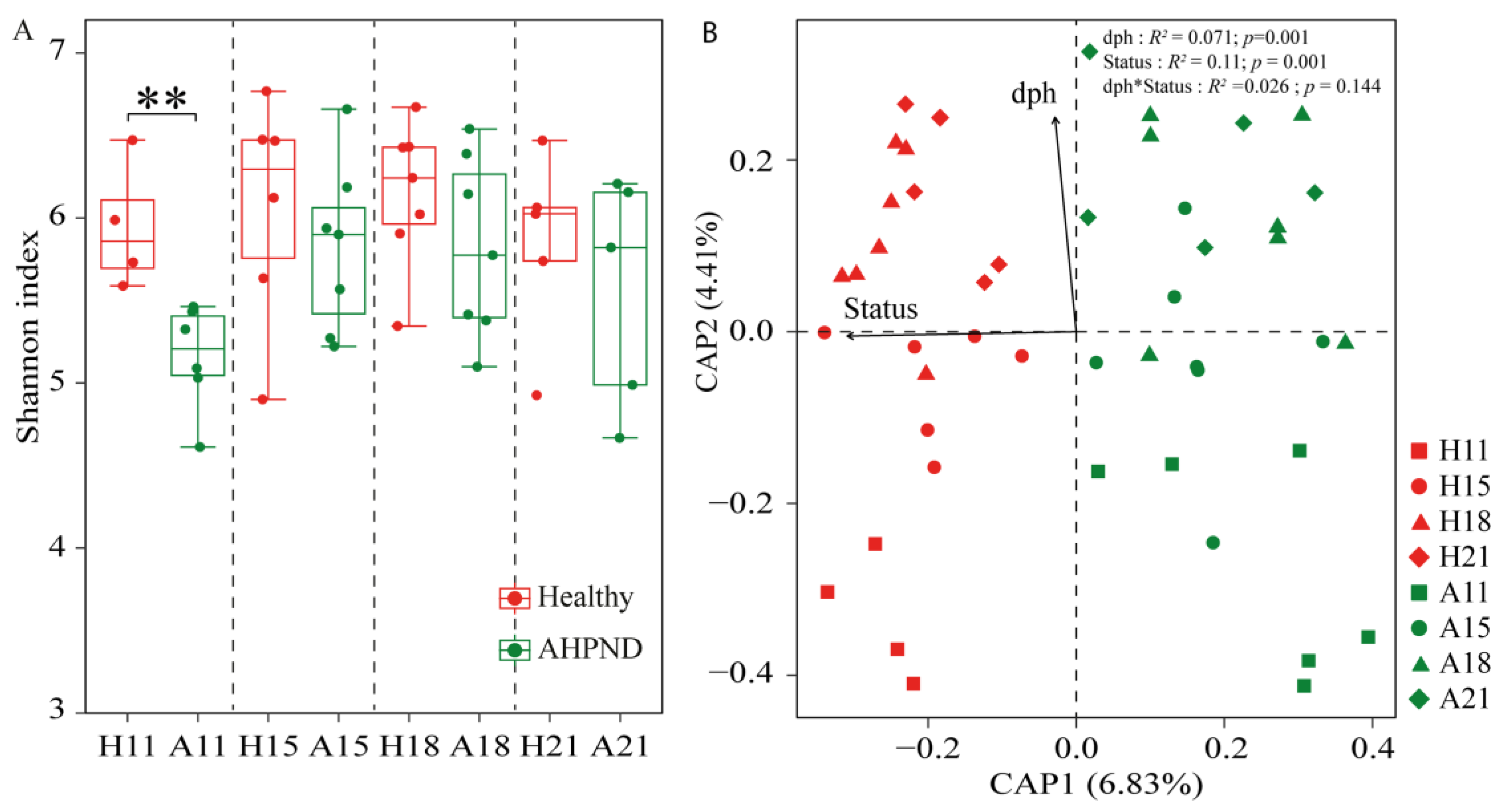
3.2. Responses of Postlarvae-Associated Bacteria Community to AHPND
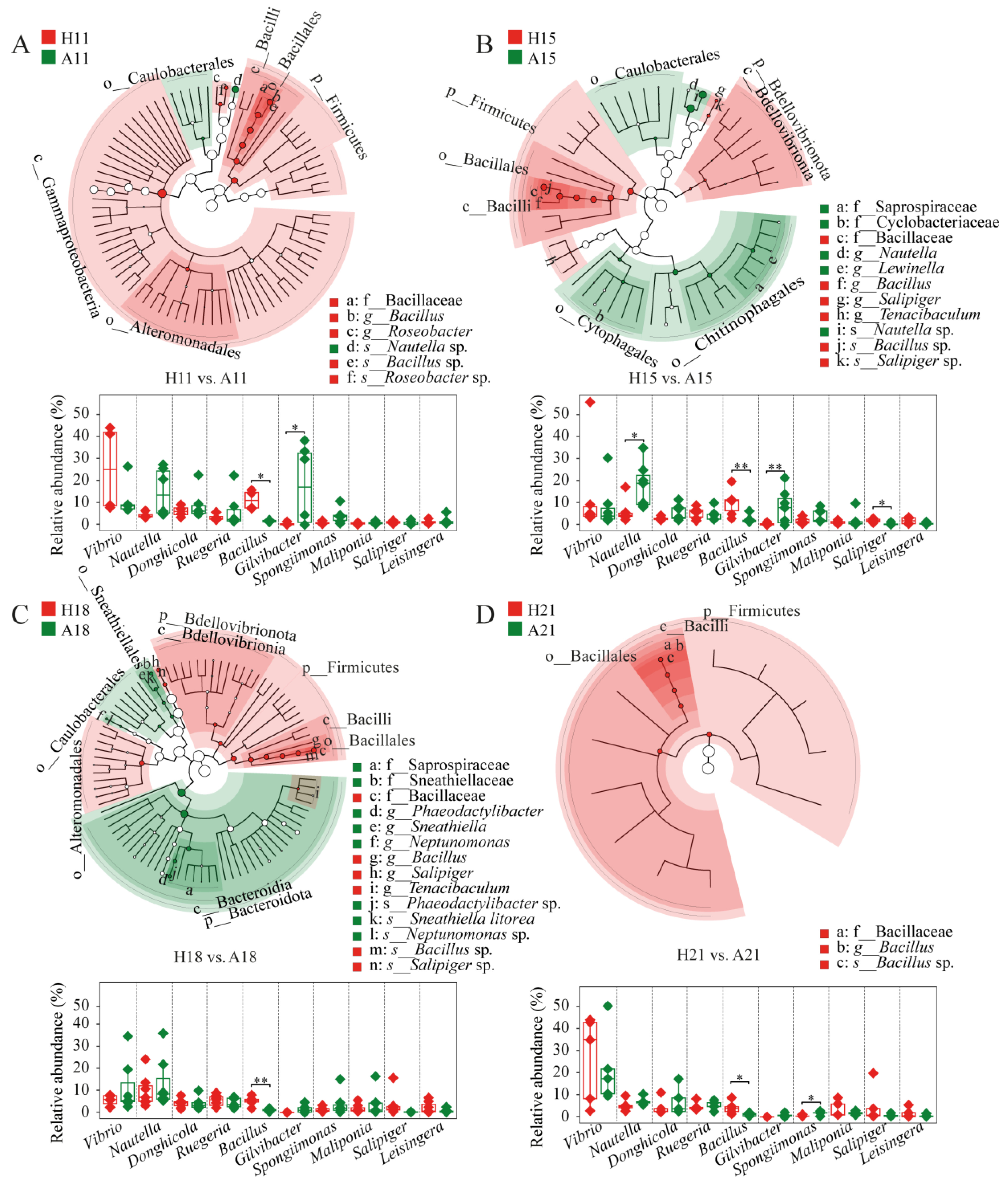
3.3. Bacterial Lineages Featured Shrimp Health Status
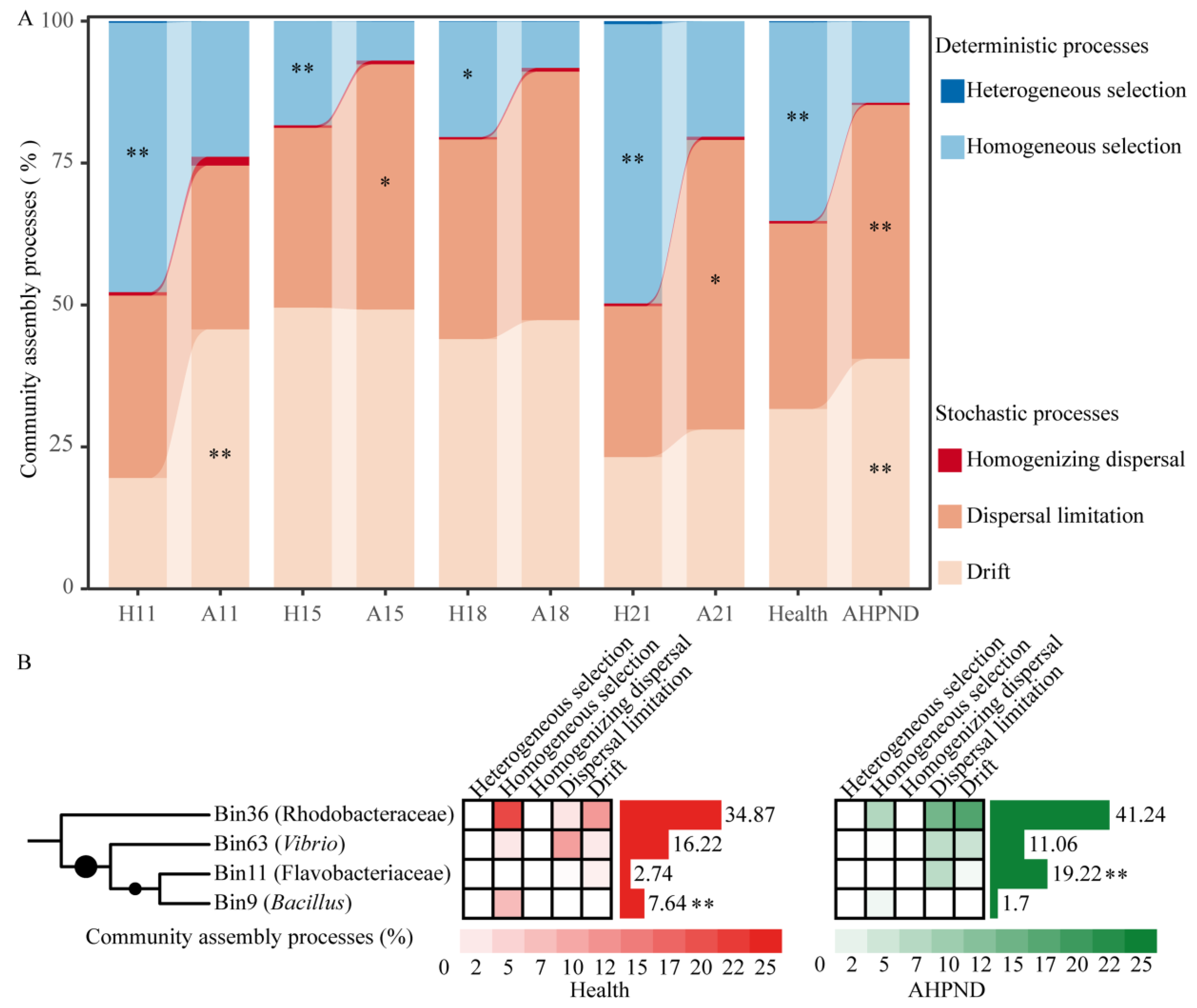
3.4. Ecological Processes Governing the Postlarval-Associated Microbiota
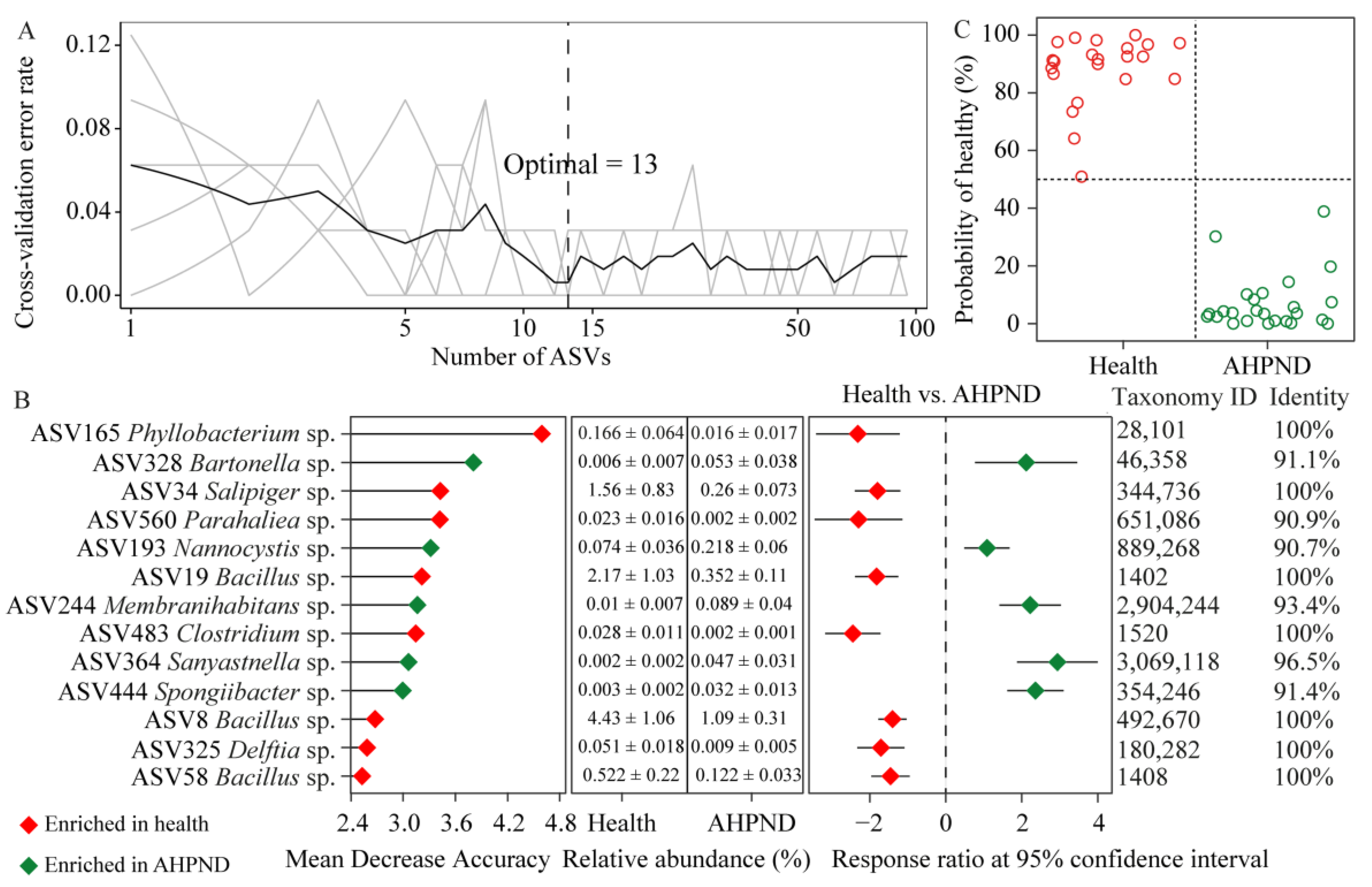
3.5. Identifying AHPND-Discriminatory Taxa Diagnosing Shrimp Health Status
3.6. Interspecies Interaction Between Healthy and AHPND Postlarvae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Sun, D.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Tan, H. Stocking density effects on pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei hatchery performance in algal-bacterial biofloc systems. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2023, 85, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen Thi Ngoc, A.; Bui Nguyen Thu, A.; Lam My, L.; Tran Ngoc, H. Integrating different densities of white leg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and red seaweed Gracilaria tenuistipitata in the nursery phase: Effects on water quality and shrimp performance. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3223–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Vidya, R.; Kumar, S.; Alavandi, S.V.; Vijayan, K.K. Zoea-2 syndrome of Penaeus vannamei in shrimp hatcheries. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 759–767. [Google Scholar]
- Intriago, P.; Medina, A.; Espinoza, J.; Enriquez, X.; Arteaga, K.; Aranguren, L.F.; Shinn, A.P.P.; Romero, X. Acute mortality of Penaeus vannamei larvae in farm hatcheries associated with the presence of Vibrio sp. carrying the VpPirAB toxin genes. Aquac. Int. 2023, 31, 3363–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Sha, H.; Chen, J. Updated roles of the gut microbiota in exploring shrimp etiology, polymicrobial pathogens, and disease incidence. Zool. Res. 2024, 45, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Ko, T.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, M.F.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.S.; et al. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Van, P.T.; Dang, L.T.; Hirono, I. Draft genome sequence of non-Vibrio parahaemolyticus acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease strain KC13.17.5, isolated from diseased shrimp in Vietnam. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00978-15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.; Xia, X.; Dai, X.; Pan, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y. A Vibrio owensii strain as the causative agent of AHPND in cultured shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 153, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.E.; Tang, K.J.; Aranguren, L.F.; Piamsomboon, P. Characterization and pathogenicity of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease natural mutants, pirABvp(−) V. parahaemolyticus, and pirABvp(+) V. campbellii strains. Aquaculture 2017, 470, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Ng, T.H.; Wang, H. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in penaeid shrimp. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ng, T.H.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. Microbiome dynamics in a shrimp grow-out pond with possible outbreak of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J.; Yang, W.; Ni, S.; Xiong, J. Starvation stress affects the interplay among shrimp gut microbiota, digestion and immune activities. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Li, Z.; Ou, M.; Wu, X.; Qiao, X.; Wei, W.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, W. Hypoimmunity and intestinal bacterial imbalance are closely associated with blue body syndrome in cultured Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2020, 522, 735118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angthong, P.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Rungrassamee, W. Shrimp microbiome and immune development in the early life stages. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2023, 147, 104765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, L.; Dong, P.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Lu, Z.; Hou, D.; Zhang, D. Fine-scale succession patterns and assembly mechanisms of bacterial community of Litopenaeus vannamei larvae across the developmental cycle. Microbiome 2020, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.; Domínguez-Borbor, C.; Salazar, L.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K.; Sonnenholzner, S.; Alexis, F.; Rodríguez, J. The probiotics Vibrio diabolicus (Ili), Vibrio hepatarius (P62), and Bacillus cereus sensu stricto (P64) colonize internal and external surfaces of Penaeus vannamei shrimp larvae and protect it against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angthong, P.; Uengwetwanit, T.; Arayamethakorn, S.; Chaitongsakul, P.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Rungrassamee, W. Bacterial analysis in the early developmental stages of the black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, G.; Andrade, B.; Betancourt, I.; Panchana, F.; Preciado, C.; Bayot, B. Bacterial communities and signatures in the stomach and intestine of juvenile Penaeus (litopenaeus) vannamei shrimp affected by acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Song, T.; Lu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Shrimp AHPND causing Vibrio anguillarum infection: Quantitative diagnosis and identifying antagonistic bacteria. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, L.; Domínguez-Borbor, C.; Bajaña, L.; Betancourt, I.; Rodríguez, J.; Bayot, B.; Reyes, A. Microbial community characterization of shrimp survivors to AHPND challenge test treated with an effective shrimp probiotic (Vibrio diabolicus). Microbiome 2021, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Consistent features of the gut microbiota in response to diverse shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei diseases: A meta-analysis. Fish Fish. 2023, 24, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Mao, J.; Qi, X.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. The assembly of gut microbiota implicates shrimp acute hepatopancreas necrosis disease progression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 7489–7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibay-Valdez, E.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Calderón, K.; Vargas-Albores, F.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Martínez-Córdova, L. Taxonomic and functional changes in the microbiota of the white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) associated with postlarval ontogenetic development. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, M. Bacterial community associated with healthy and diseased pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) larvae and rearing water across different growth stages. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, G.; Betancourt, I.; Andrade, B.; Panchana, F.; Román, R.; Sorroza, L.; Trujillo, L.E.; Bayot, B. Microbiome of Penaeus vannamei larvae and potential biomarkers associated with high and low survival in shrimp hatchery tanks affected by acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 838640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, C.; Wellband, K.; Perreault, A.; Bernatchez, L.; Derome, N. Artificial rearing of Atlantic Salmon juveniles for supportive breeding programs induces long-term effects on gut microbiota after stocking. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; De Bels, L.; Couck, L.; Baruah, K.; Bossier, P.; Van den Broeck, W. PirABVP toxin binds to epithelial cells of the digestive tract and produce pathognomonic AHPND lesions in germ-free brine shrimp. Toxins 2019, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Roy, S.; Behera, B.K.; Bossier, P.; Das, B.K. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND): Virulence, pathogenesis and mitigation strategies in shrimp aquaculture. Toxins 2021, 13, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J. Progress in the gut microbiota in exploring shrimp disease pathogenesis and incidence. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7343–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. A meta-analysis study of the robustness and universality of gut microbiota-shrimp diseases relationship. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 3924–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ning, D.; Yu, W.; Chen, G.; Tao, X.; Zhou, J.; Du, Z.; Mu, D. Niche modification by sulfate-reducing bacteria drives microbial community assembly in anoxic marine sediments. mBio 2023, 14, e0353522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, D.; Yuan, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Arkin, A.P.; Firestone, M.K.; Zhou, J. A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Dai, W.; Qiu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, C. Response of host-bacterial colonization in shrimp to developmental stage, environment and disease. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Rationally designed probiotics prevent shrimp white feces syndrome via the probiotics–gut microbiome–immunity axis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Xiong, J.; Hou, D.; Zhou, R.; Xing, C.; Wei, D.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Microecological Koch’s postulates reveal that intestinal microbiota dysbiosis contributes to shrimp white feces syndrome. Microbiome 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D. Gastrointestinal microbiota imbalance is triggered by the enrichment of Vibrio in subadult Litopenaeus vannamei with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Aquaculture 2021, 533, 736199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawinkel, S.; Mattiello, F.; Bijnens, L.; Thas, O. A broken promise: Microbiome differential abundance methods do not control the false discovery rate. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, K. WSGMB: Weight signed graph neural network for microbial biomarker identification. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbad448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Chen, J.; Xiong, J. Concept of microbial gatekeepers: Positive guys? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhan, P.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Qiu, Q.; Xiong, J. Consistent responses of the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei gut microbiota to Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei infection across spatially distant farms. Aquaculture 2025, 594, 741447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.G.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic Community Assembly: Does It Matter in Microbial Ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.C.; Ritchie, S.C.; Inouye, M.; Holt, K.E. FastSpar: Rapid and scalable correlation estimation for compositional data. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1064–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, F. Large-scale microbiome data integration enables robust biomarker identification. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2022, 2, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Nature 2009, 535, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Xue, K.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Kang, S.; Rui, J.; Thies, J.; et al. Reduced microbial stability in the active layer is associated with carbon loss under alpine permafrost degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025321118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Willis, T.J. Canonical analysis of principal coordinates: A useful method of constrained ordination for ecology. Ecology 2003, 84, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Granados, F.; Gallardo-Becerra, L.; Leonardo-Reza, M.; Ochoa-Romo, J.P.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. A meta-analysis reveals the environmental and host factors shaping the structure and function of the shrimp microbiota. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Lopez, R.; Cornejo-Granados, F.; Lopez-Zavala, A.A.; Sanchez-Lopez, F.; Cota-Huizar, A.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Guerrero, A.; Mendoza-Vargas, A.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. Doing More with Less: A comparison of 16S hypervariable regions in search of defining the shrimp microbiota. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schryver, P.; Vadstein, O. Ecological theory as a foundation to control pathogenic invasion in aquaculture. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranguren Caro, L.F.; Mai, H.N.; Noble, B.; Dhar, A.K. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (VPAHPND), a chronic disease in shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) population raised in latin America. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 174, 107424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungrassamee, W.; Klanchui, A.; Maibunkaew, S.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Bacterial dynamics in intestines of the black tiger shrimp and the Pacific white shrimp during Vibrio harveyi exposure. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 133, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, E.K.; Gordon, J.I.; Secor, S.M.; Knight, R. Postprandial remodeling of the gut microbiota in Burmese pythons. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1375–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Song, W.; Tan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, S. The effects of dietary protein level on the growth performance, body composition, intestinal digestion and microbiota of Litopenaeus vannamei fed Chlorella sorokiniana as the main protein source. Animals 2023, 13, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.T.; Ko, H.T.; Wu, P.L.; Kumar, R.; Wang, H.C.; Lu, H.P. Gut microbiota of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) exhibits distinct responses to pathogenic and non-pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0118023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, F. Transcriptome analysis on hepatopancreas reveals the metabolic dysregulation caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in Litopenaeus vannamei. Biology 2023, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, B.J.; Jiang, K.Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, L. Comparative analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics provides insights into the mechanisms of VP AHPND invasion and hepatopancreatic damage in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 154, 109920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Xi, C.; Gong, J.; Zhu, M.; Shui, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, G.; Shen, H. 16S rRNA gene sequencing analysis reveals an imbalance in the intestinal flora of Eriocheir sinensis with hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2022, 42, 100988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ai, C.; Cheng, W.; Huang, H.; Hou, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, P.; Mao, Y. Impact of dietary variations on Kuruma shrimp (Penaeus japonicus) assessed through individual-based rearing and insights into individual differences. Animals 2024, 14, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Dong, C.; Qiu, Q.; Li, C. Integrating gut microbiota immaturity and disease-discriminatory taxa to diagnose the initiation and severity of shrimp disease. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, Q.; Xiong, J. Quantifying the importance of abiotic and biotic factors governing the succession of gut microbiota over shrimp ontogeny. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 752750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Shao, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Q. Supplementation of dietary crude lentinan Improves the Intestinal Microbiota and Immune Barrier in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Infected by Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 920065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Tan, B.; Dong, X.; Chi, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Fan, D.; Hu, Y. The isolation, identification, whole-genome sequencing of Clostridium butyricum LV1 and its effects on growth performance, immune response, and disease-resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 272, 127384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B.; Park, S.Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Kim, B.; Kwon, M.G.; Kim, S.M.; Han, J.E.; Kim, J.H. Genomic and pathological characterization of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND)-associated natural mutant Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from Penaeus vannamei cultured in Korea. Animals 2024, 14, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñan-Vidriales, M.A.; Peña-Rodríguez, A.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Elizondo-González, R.; Barajas-Sandoval, D.R.; Ponce-Gracía, E.I.; Rodríguez-Jaramillo, C.; Balcázar, J.L.; Quiroz-Guzmán, E. Effect of rice bran fermented with Bacillus and Lysinibacillus species on dynamic microbial activity of Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasyimi, W.; Widanarni, W.; Yuhana, M. Growth performance and intestinal microbiota diversity in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei fed with a probiotic bacterium, honey prebiotic, and synbiotic. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2982–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Liao, M.; Qin, Y.; He, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Hemocyanin-derived antimicrobial peptide PvL1 defense against AHPND infection by regulating the hepatopancreatic microbiota of Penaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 161, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhan, P.; Chen, J.; Qiu, Q.; Xiong, J. Beneficial effects of probiotics on Litopenaeus vannamei growth and immunity via the recruitment of gut Rhodobacteraceae symbionts. Zool. Res. 2025, 46, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Guo, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K. Glucose addition improves the culture performance of Pacific white shrimp by regulating the assembly of Rhodobacteraceae taxa in gut bacterial community. Aquaculture 2023, 567, 739254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Gao, J. Attribution of dispersal limitation can better explain the assembly patterns of plant microbiota. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1168760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, G.; Chai, X.; Chen, J. Bacterial community dynamics during nursery rearing of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) revealed via high-throughput sequencing. Indian J. Microbiol. 2020, 60, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Winter, M.G.; Byndloss, M.X.; Spiga, L.; Duerkop, B.A.; Hughes, E.R.; Büttner, L.; de Lima Romão, R.; Behrendt, C.L.; Lopez, C.A.; et al. Precision editing of the gut microbiota ameliorates colitis. Nature 2018, 553, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolanchinathan, P.; Kumari, P.R.; Raja, K.; John, G.; Balasundaram, A. Analysis of feed composition and growth parameters of Penaeus monodon supplemented with two probiotic species and formulated diet. Aquaculture 2022, 549, 737740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Zhou, Q.J.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, J. Interplay between the gut microbiota and immune responses of ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) during Vibrio anguillarum infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Maistrenko, O.M.; Andrejev, S.; Kim, Y.; Bork, P.; Patil, K.R.; Patil, K.R. Polarization of microbial communities between competitive and cooperative metabolism. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunny, G.M.; Brickman, T.J.; Dworkin, M. Multicellular behavior in bacteria: Communication, cooperation, competition and cheating. Bioessays 2008, 30, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Han, Z.; Chen, F.; Lv, A.; Hu, X.; Sun, X.; Qi, H.; Guo, Y. Vibrio parahaemolyticus alters the community composition and function of intestinal microbiota in Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Healthy | AHPND | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H11 | H15 | H18 | H21 | A11 | A15 | A18 | A21 | |
| H11 | - | 0.179 | 0.524 | 0.213 | 0.528 | 0.836 | 0.817 | 0.55 |
| H15 | 0.159 | - | −0.021 | 0.133 | 0.631 | 0.487 | 0.431 | 0.365 |
| H18 | 0.004 | 0.491 | - | 0.144 | 0.609 | 0.457 | 0.272 | 0.344 |
| H21 | 0.128 | 0.155 | 0.127 | - | 0.581 | 0.642 | 0.355 | 0.072 |
| A11 | 0.012 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.002 | - | 0.139 | 0.447 | 0.323 |
| A15 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.115 | - | 0.082 | 0.464 |
| A18 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.024 | 0.004 | 0.21 | - | 0.025 |
| A21 | 0.016 | 0.015 | 0.022 | 0.249 | 0.027 | 0.005 | 0.335 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhan, P.; Xiong, J. Postlarval Shrimp-Associated Microbiota and Underlying Ecological Processes over AHPND Progression. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040720
Zhou Z, Lu J, Zhan P, Xiong J. Postlarval Shrimp-Associated Microbiota and Underlying Ecological Processes over AHPND Progression. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040720
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhongjiang, Jiaqi Lu, Pingping Zhan, and Jinbo Xiong. 2025. "Postlarval Shrimp-Associated Microbiota and Underlying Ecological Processes over AHPND Progression" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040720
APA StyleZhou, Z., Lu, J., Zhan, P., & Xiong, J. (2025). Postlarval Shrimp-Associated Microbiota and Underlying Ecological Processes over AHPND Progression. Microorganisms, 13(4), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040720






