Abstract
Due to the increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance, the efficacy of standard triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection has declined, with eradication rates now falling below 80% in most countries. Although bismuth quadruple therapy and concomitant therapy are advised in regions with high clarithromycin resistance, these treatments commonly cause frequent adverse events and require the use of two or three antibiotics. This review article evaluates the effectiveness of 14-day mono-antibiotic therapies for H. pylori infection through randomized controlled trials conducted from 1 October 2014 to 1 October 2024. The pooled eradication rates for 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/proton pump inhibitor (PPI) dual therapies were 86.1% (3335/3875; 95% confidence interval (CI): 85.1–87.2%) by intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis and 87.3% (3232/3702; 95% CI: 86.2–88.4%) by per-protocol (PP) analysis. For 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapies, the rates were 87.4% (1085/1241; 95% CI: 85.5–89.2%) by ITT and 93.0% (1044/1124; 95% CI: 91.5–94.5%) by PP. In the penicillin-allergic population, 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy showed eradication rates of 92.0% (138/150) by ITT and 95.1% (135/142) by PP. In conclusion, 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy presents an effective option for eradicating H. pylori in patients allergic to penicillin. For those without a penicillin allergy, first-line treatments can include 14-day mono-antibiotic regimens, such as high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual, high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual, and tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapies.
1. Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is the primary cause of chronic gastritis, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, gastric adenocarcinoma, and gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma (MALToma) [1,2,3]. Recent guidelines recommend considering eradication therapy for all individuals with confirmed H. pylori infections [4,5]. In the treatment of H. pylori infection, antibiotic resistance significantly influences eradication outcomes. Recent data indicate that primary resistance to clarithromycin, metronidazole, and levofloxacin in H. pylori is on the rise [6,7]. Currently, the resistance rates for clarithromycin, amoxicillin, metronidazole, tetracycline, and levofloxacin are 56–71%, 0–8%, 35–74%, 0–4%, and 21–43%, respectively [7]. Due to increasing clarithromycin resistance, the effectiveness of standard triple therapy has diminished, with eradication rates now below 80% in most countries. Consequently, several strategies including bismuth quadruple therapy and non-bismuth quadruple therapy (such as sequential therapy, concomitant therapy, and hybrid therapy) have been proposed to enhance the eradication rate of first-line anti-H. pylori treatments [8,9,10]. While most international guidelines or consensuses favor bismuth quadruple therapy (BQT) as the first-line treatment in areas with high clarithromycin resistance [8,9,10], this approach presents challenges, such as its complex regimen and the relatively high occurrence of adverse events observed in extensive randomized studies [11,12,13,14]. In two large-scale randomized controlled trials [13,14], the frequencies of adverse events of BQT were 48% and 56%, respectively. The most frequently observed adverse events were taste distortion, darkened tongue, darkened stool, nausea, and abdominal discomfort [15,16,17,18,19].
Concomitant therapy is an effective regimen with proven success regardless of clarithromycin resistance in several studies [10]. It is a four-drug regimen containing proton pump inhibitor (PPI), clarithromycin, amoxicillin, and metronidazole, which are all administered for the entire duration of therapy. A meta-analysis demonstrated that concomitant therapy is more effective than standard triple therapy. Hybrid therapy is another non-bismuth quadruple therapy developed by our group [8]. It consists of a dual therapy with a PPI and amoxicillin for 7 days, followed by a quadruple regimen with a PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole for 7 days. A pilot study of hybrid therapy showed that it achieved an eradication rate of 97.4% by intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis and 99.1% by per-protocol (PP) analysis in Taiwan [8]. A recent large multicenter randomized controlled trial documented that 14-day hybrid therapy and 14-day BQT had comparable efficacy in the treatment of H. pylori infection, and both could cure more than 90% of patients with H. pylori infections in areas of moderate clarithromycin resistance (17%) [14]. In addition, 14-day hybrid therapy had fewer adverse events than 14-day BQT. However, hybrid therapy requires an additional two antibiotics in the last 7 days, which can confuse patients and may dampen enthusiasm for its use in clinical practice. Reversing the sequence of drug administration (a quadruple regimen followed by a dual regimen) can simplify hybrid therapy; patients do not need to take additional medications during the course of treatment. A multicenter randomized trial demonstrated that 14-day reverse hybrid therapy had comparable eradication rate as 14-day BQT [13]. The novel therapy also had a lower frequency of adverse events than 14-day BQT. Nonetheless, all the bismuth quadruple, concomitant, hybrid, and reverse hybrid therapies require two to three antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori.
Currently, resistance rates to amoxicillin and tetracycline remain extremely low (<3%) in most countries [20,21]. An alternative dual therapy, combining a high-dose PPI with amoxicillin, maintains intragastric pH above 6.5, irrespective of the CYP2C19 genotype, and ensures a constant plasma concentration of amoxicillin or tetracycline that exceeds the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) required to combat H. pylori. A randomized controlled trial in Taiwan demonstrated that the intention-to-treat eradication rate for mono-antibiotic therapy with high-dose amoxicillin and rabeprazole exceeded that of standard triple therapy (95% vs. 81%) [22]. Additional benefits include simplicity, fewer adverse events, and the avoidance of unnecessary antibiotics. However, growing evidence indicates that the effectiveness of high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual therapy varies across countries.
Vonoprazan is a novel gastric acid suppression agent that functions as a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB) [23,24]. It exerts its acid-suppressive effect by reversibly inhibiting the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme [23,24]. Research has demonstrated that vonoprazan’s capacity to suppress gastric acid secretion exceeds that of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). Additionally, it may enhance H. pylori therapy by optimizing gastric acid suppression and antimicrobial activity compared to PPIs. The primary metabolic pathway for vonoprazan involves cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) in the liver, with additional metabolism by SULT2A1, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, and CYP2D6. Evidence, including several randomized controlled trials and non-randomized studies, has shown that a 7-day vonoprazan-based triple therapy is more effective than a 7-day PPI-based triple therapy as a first-line treatment for H. pylori infection [23,24]. Moreover, vonoprazan dual therapy has shown similar efficacy to vonoprazan triple therapy in clinical trials [25]. Recently, there has been growing interest in using a single sensitive antibiotic with potent acid suppression for H. pylori infection. These new mono-antibiotic regimens are simpler to administer; have fewer adverse events than standard triple, bismuth quadruple, and concomitant therapies; and may potentially become standard therapies for H. pylori infection in the future.
This article aims to assess the efficacy of 14-day mono-antibiotic therapies for the first-line treatment of H. pylori infection through recent randomized controlled trials and to develop a new algorithm for the treatment of H. pylori infection.
2. Article Search
This systematic review was conducted following the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines to enhance the organization of its methodology. The central question addressed was, “In patients with H. pylori infection, can 14-day mono-antibiotic therapies achieve an eradication rate ≥ 90% according to per-protocol analysis in first-line treatment?” The bibliographic search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library electronic databases. The search terms included (“Helicobacter pylori” [MeSH] OR “H. pylori” [MeSH]) AND (“Therapy” [MeSH] OR “Treatment” [MeSH]), focusing on the publication’s abstract and/or title. The research was limited to clinical trials published in English from 1 October 2014 to 1 October 2024. Two investigators (C.A.S. and C.B.S.) independently carried out the search and study selection, with a third author (P.I.H.) assisting in cases of disagreement over article selection.
The inclusion criteria were (1) human studies on 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual, 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual, and 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapies for first-line H. pylori treatment; (2) participants over the age of 18; (3) randomized controlled trials; (4) articles reporting treatment efficacy; and (5) publications in English. The exclusion criteria included (1) treatments shorter than 14 days; (2) amoxicillin doses below 3 g/day; (3) unconfirmed H. pylori status pre- and post-treatment via at least one of the following tests: rapid urease test, histology, culture, or urea breath test; (4) assessment of H. pylori post-treatment status less than four weeks after treatment completion; (5) studies not reporting results for both ITT and PP analyses; and (6) studies published only in abstract form.
All relevant data matching the study’s objectives were collected. Two authors (C.A.S. and C.B.S.) performed this task; in cases of disagreement, a third author (P.I.H.) was consulted. Specifically retrieved were the author’s name, year of publication, study country, sample size, and eradication rates by ITT and PP analyses. Initially, 1484 articles were found; 1444 were excluded during the initial screening due to irrelevance for being meta-analyses, review articles, or not clinical trials. After removing these articles, the remaining articles were screened by reading their titles and abstracts. Subsequently, one additional article was excluded due to duplication, leaving 40 for full-text evaluation. The previously defined eligibility criteria led to the final selection of 30 studies. For data analysis, the MedCalc v23.0.2 statistical software package (MedCalc Software Ltd., Ostend, Belgium) was used. Figure 1 presents the flow diagram of the literature search.
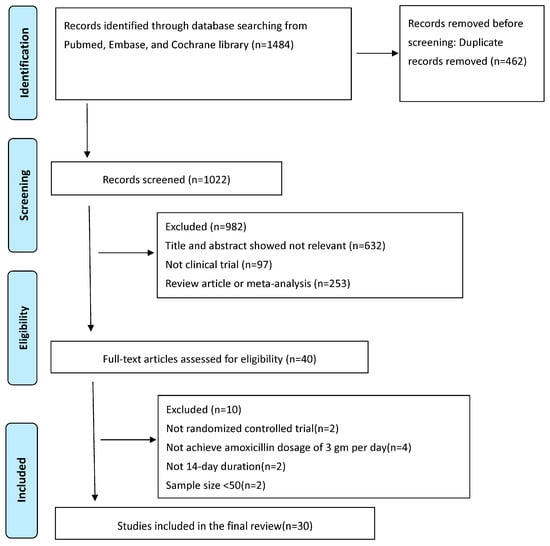
Figure 1.
PRISMA diagram of the literature search.
3. High-Dose Amoxicillin/PPI Dual Therapy
Table 1 summarizes the ITT and PP eradication rates of high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual therapy for the first-line treatment of H. pylori infection in randomized control trials conducted between 2014 and 2024 [15,16,17,18,19,22,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. The eradication rates from ITT analysis range from 65.7% to 95.3%, and from PP analysis, they range from 71.0% to 96.6%. The pooled eradication rates for 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual therapies were 86.1% (3335/3875; 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 85.1–87.2%) by ITT analysis and 87.3% (3232/3702; 95% CI: 86.2–88.4%) by PP analysis. These data suggest that the eradication rates of high-dose amoxicillin/PPI vary across countries and do not consistently achieve an eradication rate of ≥ 90%. For instance, a regimen comprising 750 mg of amoxicillin four times daily and 40 mg of esomeprazole three times daily for 14 days achieved a PP eradication rate of 95.7% (110/115) in Taiwan [27], whereas the PP eradication rate for the same regimen in a study from China was only 71.0% (71/100) [15,16,17,18,19,22,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
The variable efficacies of high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual therapy for H. pylori treatment may be attributed to differences in the prevalence of amoxicillin-resistant strains, the potencies and dosages of PPIs, ethnic differences in PPI metabolism, patient drug adherence, body surface area (BSA), and the amount of acidic food intake. A large multicenter randomized controlled trial conducted by our group indicated that amoxicillin-resistant strains and poor drug adherence were independent risk factors predicting eradication failure in high-dose amoxicillin/rabeprazole dual therapy, with odds ratios of 8.2 and 8.6, respectively [19]. In this study, the eradication rate for patients receiving high-dose amoxicillin/rabeprazole dual therapy was significantly lower in those with amoxicillin-resistant strains compared to those with susceptible strains (50% vs. 88%). Similarly, patients with poor drug adherence had a lower eradication rate than those with good adherence (40% vs. 87%). Another clinical study from China found that a BSA ≥1.69 m2 was the only independent predictor of eradication failure for high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual therapy [39].
The pooled incidence of adverse events in these studies of high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual therapy was 13.0% (484 out of 3804). The most frequently observed adverse events were diarrhea, abdominal distension, and nausea, which were generally mild.

Table 1.
Eradication rates of 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual, high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual, and tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapies for the first-line treatment of H. pylori infection in randomized controlled trials from 2014 to 2024.
Table 1.
Eradication rates of 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual, high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual, and tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapies for the first-line treatment of H. pylori infection in randomized controlled trials from 2014 to 2024.
| Author (Year) | Country | No. of Cases | Regimen | Test to Conform Eradication | Eradication Rate | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITT PP | ||||||
| 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual therapy | ||||||
| Yang et al. [22] (2015) | Taiwan | 150 | rabeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 95.3% (143/150) 96.6% (143/148) | 23.0% (34/148) |
| Hu et al. [26] (2017) | China | 87 | rabeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 81.6% (71/87) 83.5% (71/85) | 3.4% (3/87) |
| Tai et al. [27] (2019) | Taiwan | 120 | esomeprazole 40 mg tid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 91.7% (110/120) 95.7% (110/115) | 9.6% (11/115) |
| Yang et al. [15] (2019) | China | 116 | esomeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 87.9% (102/116) 91.1% (102/112) | 6.3% (7/112) |
| Yu et al. [28] (2019) | China | 80 | esomeprazole 40 mg bid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | 13C-UBT | 92.5% (74/80) 96.1% (73/76) | 7.5% (6/80) |
| Song et al. [29] (2020) | China | 380 | esomeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 87.1% (331/380) 92.4% (329/356) | 17.6% (66/375) |
| Hwong-Ruey et al. [30] (2020) | Malaysia | 97 | rabeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 1 gm qid | 13C-UBT | 92.8% (90/97) 93.8% (90/96) | 20.5% (20/97) |
| Shen et al. [31] (2022) | China | 496 | esomeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C/14C-UBT | 88.31% (438/496) 91.63% (438/478) | 13.3% (66/496) |
| Guan et al. [16] (2022) | China | 350 | esomeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | 13C/14C-UBT | 89.4% (313/350) 90.6% (308/340) | 12.9% (45/349) |
| Han et al. [32] (2022) | China | 315 | esomeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C/14C-UBT | 88.6% (279/315) 90.4% (274/303) | 13.7% (43/314) |
| Shao et al. [17] (2022) | China | 120 | rabeprazole 20 mg tid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | 13C-UBT | 85.8% (103/120) 89.6% (103/115) | 13.0% (15/115) |
| Bi et al. [33] (2022) | China | 329 | esomeprazole 40 mg tid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | 13C/14C-UBT | 75.4% (248/329) 81.3% (248/305) | 11.1% (34/305) |
| Liu et al. [18] (2023) | China | 422 | esomeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | 13C-UBT | 90.3% (381/422) 93.6% (381/407) | 13.5% (55/407) |
| Hsu et al. [19] (2023) | Taiwan | 306 | rabeprazole 20 mg qid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 83% (255/306) 87% (253/291) | 13.0% (40/305) |
| Ding et al. [34] (2023) | China | 134 | esomeprazole 40 mg bid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | 13C-UBT | 73.1% (98/134) 83.1% (98/118) | 6.0% (8/134) |
| Yun et al. [35] (2023) | China | 108 | esomeprazole 40 mg tid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 65.7% (71/108) 71.0% (71/100) | 2.0% (2/100) |
| Zhang et al. [36] (2023) | China | 101 | ilaprazole 5 mg bid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | 13C-UBT | 92.1% (93/101) 94.9% (93/98) | 13.9% (14/101) |
| Macedo et al. [37] (2023) | Portugal | 50 | esomeprazole 40 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg alternating with amoxicillin 500 mg qid | SAT | 96.2% (48/50) 95.9% (47/49) | 2.0% (1/50) |
| Valizadeh et al. [38] (2024) | Iran | 114 | esomeprazole 40 mg bid, amoxicillin 1 gm tid | SAT | 76.3% (87/114) 79.1% (87/110) | 12.2% (14/114) |
| All | 86.1% (3335/3875) 87.3% (3232/3702) | 13.0% (484/3804) | ||||
| 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy | ||||||
| Chey et al. [40] (2022) | USA | 324 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 13C-UBT | 78.5% (208/265) 81.2% (177/218) | 29.9% (104/348) |
| Yang et al. [41] (2023) | China | 200 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 13C/14C-UBT | 86% (172/200) 92.5% (172/186) | 9.5% (17/200) |
| Peng et al. [42] (2023) | China | 158 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 750 mg qid | 13C-UBT | 89.9% (142/158) 97.9% (142/145) | 19.0% (30/158) |
| Hu et al. [43] (2023) | China | 97 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 13C-UBT | 88.6% (86/97) 95.5% (86/90) | 16.67% (15/90) |
| Hu et al. [44] (2023) | China | 55 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 13C-UBT | 87.3% (48/55) 95.9% (47/49) | 20.0% (11/55) |
| Jiang et al. [45] (2024) | China | 200 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 14C-UBT | 94.0% (188/200) 97.9% (188/192) | 19.0% (38/200) |
| Huang et al. [46] (2024) | China | 102 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 13C/14C-UBT | 92.2% (94/102) 93.9% (93/99) | 13.7% (14/102) |
| Cheung et al. [47] (2024) | China | 100 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 13C-UBT | 96.0% (96/100) 96.7% (89/92) | 39.0% (39/100) |
| Liu et al. [48] (2024) | China | 64 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, amoxicillin 1000 mg tid | 13C/14C-UBT | 79.7% (51/64) 94.3% (50/53) | 7.8% (5/64) |
| All | 87.4% (1085/1241) 93.0% (1044/1124) | 20.7% (273/1317) | ||||
| 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy | ||||||
| Gao et al. [49] (2024) | China | 150 | vonoprazan 20 mg bid, tetracycline 500 mg tid | 13C-UBT | 92.0% (138/150) 95.1% (135/142) | 14.0% (21/150) |
Abbreviations: UBT, urea breath test; SAT, stool antigen test; bid, twice a day; tid, three times a day; qid, four times a day.
4. High-Dose Amoxicillin/Vonoprazan Dual Therapy
Table 1 lists the ITT and PP eradication rates of high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy for the first-line treatment of H. pylori infection in randomized control trials from 2014 to 2024 [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. The ITT analysis shows eradication rates ranging from 78.5% to 96.0%, and PP analysis shows rates from 81.2% to 97.9%. The pooled eradication rates for 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapies were 87.4% (1085/1241; 95% CI: 85.5–89.2%) by ITT and 93.0% (1044/1124; 95% CI: 91.5–94.5%) by PP. The efficacy of high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy also varies across countries and does not consistently achieve an eradication rate of ≥ 90%. In China, nearly all randomized controlled trials reported PP eradication rates of ≥ 90% for this therapy. However, in the USA and Taiwan, PP eradication rates were only 81.2% [40] and 87.2% [50], respectively. Thus, optimizing high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy is essential before it can be established as a standard first-line treatment for H. pylori.
Currently, the risk factors predicting eradication failure of 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy remain unclear. In a randomized controlled trial from Taiwan [50], poor drug adherence was identified as an independent risk factor predicting eradication failure, with an odds ratio of 8.4. Patients with poor drug adherence had a significantly lower eradication rate compared to those with good adherence (60.0% vs. 87.7%). A clinical study from Japan showed that a high BSA was a risk factor for eradication failure with 7-day regular-dose vonoprazan dual therapy (vonoprazan twice daily plus amoxicillin 750 mg twice daily) [51]. Failure of high-dose vonoprazan dual therapy for H. pylori eradication was associated with higher BSA (eradication rate: 79.6% in those with BSA ≥1.723 vs. 90.8% in patients with BSA <1.723).
The pooled incidence of adverse events in these studies of high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy was 20.7% (273 out of 1317). No serious adverse reactions were reported with high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy. The main adverse events included nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal distension. Among them, two important studies by Chey et al. [40] and Cheung et al. [47] reported adverse event incidences of 29.9% and 39%, respectively. The most common adverse events identified in the analysis of the two studies were diarrhea, with rates of 5.2% and 12.0%, respectively.
Bismuth salts enhance the effectiveness of antibiotics, yielding synergistic effects that boost eradication efficacy in anti-H. pylori therapy. Evidence shows that bismuth can inactivate bacterial urease, respiratory enzymes (such as F1-ATPase), and alcohol dehydrogenase. Additionally, bismuth drugs disrupted several essential pathways of pathogens, including oxidative defense systems and bacterial pH-buffering ability, and bacterium–host cell adhesion. Adding bismuth to the standard 14-day triple therapy can improve cure rates [52]. Specifically, the major effect of bismuth is to increase the cure rate by an additional 30–40% in the treatment of resistant strains [52]. A single randomized controlled trial by Liang et al. has reported on the efficacy of amoxicillin/vonoprazan/bismuth triple therapy [53]. This regimen, consisting of vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 750 mg three times daily, and bismuth 220 mg twice daily for 14 days, achieved an ITT eradication rate of 83.7% and a PP eradication rate of 90.9%. The study found no differences in eradication efficacy between this 14-day triple therapy and a quadruple regimen that includes esomeprazole, bismuth, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin for H. pylori eradication [53]. Recently, we conducted a pilot study to assess the efficacy and safety of high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan/bismuth triple therapy. The regimen included tripotassium dicitrato bismuthate (300 mg four times daily), high-dose amoxicillin (750 mg four times daily), and vonoprazan (20 mg twice daily) for 14 days. The eradication rates of this novel therapy as a first-line treatment were 95.6% (43/45) by ITT analysis and 100.0% (43/43) by PP analysis [54]. Further research is warranted to determine whether high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan/bismuth triple therapy can achieve higher eradication rates than the regular-dose regimen.
5. Tetracyline/Vonoprazan Dual Therapy
Dual therapy using high-dose PPI or standard-dose vonoprazan plus high-dose amoxicillin has been proven effective and safe for treating H. pylori in Asia [55,56]. However, this amoxicillin-based dual therapy may not be suitable for individuals allergic to penicillin or those infected with amoxicillin-resistant H. pylori strains. Tetracycline, one of the most effective antibacterial drugs against H. pylori, has a resistance rate generally between 1.2% and 3.3% [57]. Table 1 presents the ITT and PP eradication rates of 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy for the first-line treatment of H. pylori infection in randomized controlled trials conducted between 2014 and 2024 [49]. There was only one randomized controlled trial that assessed this novel regimen for H. pylori eradication. In this study, Gao et al. [49] evaluated the efficacy of vonoprazan/tetracycline dual therapy, which included vonoprazan 20 mg twice daily and tetracycline 500 mg three times daily for 14 days, in patients with a history of penicillin allergy. This regimen achieved an ITT eradication rate of 92.0% and a PP eradication rate of 95.1%. The study found no significant differences in eradication rates between the 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy and standard bismuth quadruple therapy, although the former resulted in fewer adverse events. Further research is essential to explore the efficacy of 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy in patients without a history of penicillin allergy.
6. Advantages of High-Dose Dual Therapy Versus Standard Triple and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies
Dual therapies combining an antibiotic with a PPI or potassium competitive acid blocker (PCAB) for H. pylori infection offer simplicity, minimal adverse effects, and the reduction of unnecessary antibiotic use. Dual therapies were associated with fewer adverse events, primarily including nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. However, these were mild and did not significantly disrupt the patients’ daily activities. An initial trial in Taiwan of high-dose rabeprazole/amoxicillin dual therapy showed that the intention-to-treat eradication rate was superior to that of standard triple therapy (95% vs. 81%) [22]. However, current reviews indicate that eradication rates for high-dose amoxicillin/PPI therapy vary internationally and do not consistently exceed 90%. Eradication rates by PP analysis range from 71.0% to 96.6% in randomized controlled trials (Table 1). A recent large-scale trial demonstrated that bismuth quadruple therapy achieved higher eradication rates than high-dose dual therapy (PP analysis: 95% vs. 87%), albeit with more adverse events [19]. Vonoprazan, a potent acid inhibitor, has shown superior acid suppression compared to PPIs. A significant study from the United States and Europe found that 14-day vonoprazan triple therapy was more effective than 14-day PPI triple therapy [40]. No significant differences in eradication rates were observed between 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy and 14-day amoxicillin/clarithromycin/vonoprazan triple therapy. Moreover, a recent trial revealed that 10-day high-dose vonoprazan–amoxicillin dual therapy in China achieved similar eradication rates to bismuth quadruple therapy, but with fewer adverse events, as a first-line treatment [58]. However, the efficacy of high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual therapy still varies by country, with PP analysis showing eradication rates between 81% and 98% (Table 1). Only one randomized controlled trial has evaluated vonoprazan/tetracycline dual therapy [49], finding no significant differences in eradication rates compared to standard bismuth quadruple therapy, but with fewer adverse events.
The bactericidal effect of amoxicillin against H. pylori is both time- and pH-dependent, as amoxicillin is more stable at higher intragastric pH levels. Dual therapies involving a PPI and amoxicillin administered twice daily have not achieved satisfactory outcomes [59]. Instead, their effectiveness can be enhanced by administering both drugs at higher doses and frequencies [60]. It has been observed that eradication rates are generally higher with four-times-daily dosing compared to three times daily, as maintaining a steady plasma concentration of amoxicillin above the minimum inhibitory concentration is crucial for its bactericidal effect against H. pylori [61]. This is because it is critical to maintain a steady plasma concentration of amoxicillin above the MIC with more frequent dosing for its bactericidal effect against H. pylori.
This systematic review has several limitations. First, the majority of the included studies originate from China, potentially limiting the applicability of the findings in other regions. Second, the number of included articles is small, particularly those addressing tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy. Third, only two studies are from Western countries (USA and Portugal). Therefore, the applicability of the therapies recommended in this review should be further validated in Western contexts.
7. Conclusions
Although most international consensuses and guidelines recommend anti-H. pylori therapy based on local rates of clarithromycin resistance, there is growing interest in using a single sensitive antibiotic in combination with potent acid suppression for H. pylori infection. This systemic review shows that 14-day dual therapies combining an antibiotic with a PPI or vonoprazan can achieve a high eradication rate for H. pylori infection and have fewer adverse effects than bismuth quadruple therapy. These encouraging results suggest the potential for developing simple and effective mono-antibiotic regimens for H. pylori treatment. In Figure 2, we propose a new algorithm of mono-antibiotic therapies for H. pylori infection based on the history of penicillin allergy. In patients with a penicillin allergy, 14-day tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapy is a viable option for eradicating H. pylori. For those without a penicillin allergy, first-line treatments such as 14-day high-dose amoxicillin/PPI dual, high-dose amoxicillin/vonoprazan dual, and tetracycline/vonoprazan dual therapies are potentially effective mono-antibiotic options for H. pylori eradication. However, current dual therapies based on amoxicillin or tetracycline require taking antibiotics three to four times daily. A significant drawback of this regimen is poor adherence to treatment. Therefore, optimizing the dosage, administration, and duration of these novel dual therapies is essential before they can be established as a standard first-line treatment.
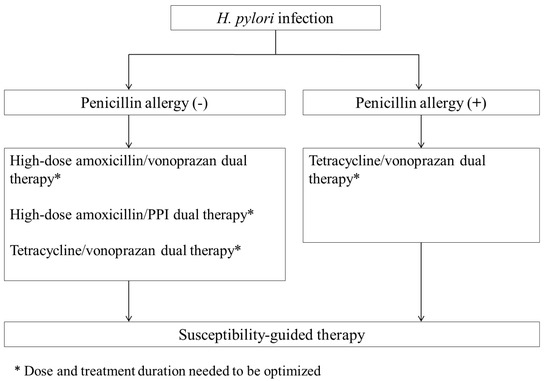
Figure 2.
Algorithm for mono-antibiotic anti-H. pylori therapy of Helicobacter pylori infection.
Author Contributions
P.-I.H. and C.-B.S. designed the research, reviewed the literature, and critically revised the manuscript. C.-A.S. and D.-C.W. reviewed the literature and drafted the initial manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Research Foundation of An Nan Hospital (Grant Numbers: ANHRF112-45, ANHRF113-21, and ANHRF113-22).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Suerbaum, S.; Michetti, P. Helicobacter pylori infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graham, D.Y.; Lew, G.M.; Klein, P.D.; Evans, D.G.; Evans, D.J., Jr.; Saeed, Z.A.; Malaty, H.M. Effect of treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection on the long-term recurrence of gastric or duodenal ulcer. A randomized, controlled study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 116, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.J.; Chung, S.C.; Ling, T.K.; Yung, M.Y.; Leung, V.K.; Ng, E.K.; Li, M.K.; Cheng, A.F.; Li, A.K. Antibacterial treatment of gastric ulcers associated with Helicobacter pylori. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asaka, M.; Kato, M.; Takahashi, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Ota, H.; Uemura, N.; Murakami, K.; Satoh, K.; Sugano, K.; et al. Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: 2009 revised edition. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, J.M.; Malfertheiner, P.; Lee, Y.C.; Sheu, B.S.; Sugano, K.; Cheng, H.C.; Yeoh, K.G.; Hsu, P.I.; Goh, K.L.; Mahachai, V.; et al. Screening and eradication of Helicobacter pylori for gastric cancer prevention: The Taipei global consensus. Gut 2020, 69, 2093–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.M.; Tai, W.C.; Hsu, P.I.; Wu, D.C.; Kuo, C.H.; Tsay, F.W.; Lee, C.L.; Chen, K.Y.; Chuah, S.K. Trend of changes in antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori from 2013 to 2019: A multicentre report from Taiwan. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820976990. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, C.A.; Shie, C.B.; Hsu, P.I. Update on the first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in areas with high and low clarithromycin resistances. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221138168. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, P.I.; Wu, D.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Graham, D.Y. Modified sequential Helicobacter pylori therapy: Proton pump inhibitor and amoxicillin for 14 days with clarithromycin and metronidazole added as a quadruple (hybrid) therapy for the final 7 days. Helicobacter 2011, 16, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Fallone, C.A.; Chiba, N.; van Zanten, S.V.; Fischbach, L.; Gisbert, J.P.; Hunt, R.H.; Jones, N.L.; Render, C.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Moayyedi, P.; et al. The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 51–69. [Google Scholar]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.M.; Schulz, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Hunt, R.H.; Leja, M.; O’Morain, C.; et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut 2022, 71, 1724–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, J.M.; Fang, Y.J.; Chen, C.C.; Bair, M.J.; Chang, C.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, C.C.; Tseng, C.H.; Hsu, Y.C.; et al. Concomitant, bismuth quadruple, and 14-day triple therapy in the first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori: A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Bazzoli, F.; Delchier, J.C.; Celiñski, K.; Giguère, M.; Rivière, M.; Mégraud, F.; Pylera Study Group. Helicobacter pylori eradication with a capsule containing bismuth subcitrate potassium, metronidazole, and tetracycline given with omeprazole versus clarithromycin-based triple therapy: A randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.I.; Tsay, F.W.; Graham, D.Y.; Tsai, T.J.; Tsai, K.W.; Kao, J.Y.; Peng, N.J.; Kuo, C.H.; Kao, S.S.; Wang, H.M.; et al. Equivalent Efficacies of Reverse Hybrid and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies in Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsay, F.W.; Wu, D.C.; Yu, H.C.; Kao, S.S.; Lin, K.H.; Cheng, J.S.; Wang, H.M.; Chen, W.C.; Sun, W.C.; Tsai, K.W.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Shows that both 14-Day Hybrid and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies Cure Most Patients with Helicobacter pylori Infection in Populations with Moderate Antibiotic Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00140-17. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, T.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, D.F.; Lan, C.H. Eradication Efficacy of Modified Dual Therapy Compared with Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy as a First-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, J.L.; Hu, Y.L.; An, P.; He, Q.; Long, H.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.F.; Xiong, J.G.; Wu, S.S.; Ding, X.W.; et al. Comparison of high-dose dual therapy with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in Helicobacter pylori-infected treatment-naive patients: An open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Pharmacotherapy 2022, 42, 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Q.Q.; Yu, X.C.; Yu, M.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J.B.; Yuan, L.; Qi, Y.B.; Hu, R.B.; Wei, P.R.; Xiao, W.; et al. Rabeprazole plus amoxicillin dual therapy is equally effective to bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication in central China: A single-center, prospective, open-label, randomized-controlled trial. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12876. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.N.; Wang, Q.Y.; Li, P.Y.; Wu, D.H.; Pan, J.; Chen, Z.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Han, X.Y.; Lan, C.; Tang, J.; et al. Comparing high-dose dual therapy with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for the initial eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection on Hainan Island: A randomized, multicenter clinical trial. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2023, 47, 102125. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, P.I.; Chen, K.Y.; Tai, W.C.; Yang, J.C.; Tsay, F.W.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, C.L.; Lee, C.L.; Yeh, H.Z.; Kuo, C.H.; et al. Hybrid, High-Dose Dual and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies for First-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Taiwan: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Randomized Trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.M.; O’Morain, C.; McNamara, D. Helicobacter pylori resistance to current therapies. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, Y.T.; Liou, J.M.; El-Omar, E.M.; Wu, J.Y.; Leow, A.H.R.; Goh, K.L.; Das, R.; Lu, H.; Lin, J.T.; Tu, Y.K.; et al. Primary antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori in the Asia-Pacific region: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.C.; Lin, C.J.; Wang, H.L.; Chen, J.D.; Kao, J.Y.; Shun, C.T.; Lu, C.W.; Lin, B.R.; Shieh, M.J.; Chang, M.C.; et al. High-dose dual therapy is superior to standard first-line or rescue therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 895–905. [Google Scholar]
- Inatomi, N.; Matsukawa, J.; Sakurai, Y.; Otake, K. Potassium-competitive acid blockers: Advanced therapeutic option for acid-related diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 168, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, Y.; Mori, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Nishimura, A.; Komura, E.; Araki, T.; Shiramoto, M. Acid-inhibitory effects of vonoprazan 20 mg compared with esomeprazole 20 mg or rabeprazole 10 mg in healthy adult male subjects--a randomised open-label cross-over study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Gotoda, T.; Kusano, C.; Ikehara, H.; Ichijima, R.; Ohyauchi, M.; Ito, H.; Kawamura, M.; Ogata, Y.; Ohtaka, M.; et al. Seven-day vonoprazan and low-dose amoxicillin dual therapy as first-line Helicobacter pylori treatment: A multicentre randomised trial in Japan. Gut 2020, 69, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Li, P.; Han, R.; Fang, D.C. Optimized high-dose amoxicillin-proton-pump inhibitor dual therapies fail to achieve high cure rates in China. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, W.C.; Liang, C.M.; Kuo, C.M.; Huang, P.Y.; Wu, C.K.; Yang, S.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Lin, M.T.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, C.N.; et al. A 14 day esomeprazole- and amoxicillin-containing high-dose dual therapy regimen achieves a high eradication rate as first-line anti-Helicobacter pylori treatment in Taiwan: A prospective randomized trial. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Luo, L.; Long, X.; Liang, X.; Ji, Y.; Graham, D.Y.; Lu, H. High-dose PPI-amoxicillin dual therapy with or without bismuth for first-line Helicobacter pylori therapy: A randomized trial. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12596. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xue, Y.; Suo, B.; Tian, X.; Niu, Z. A comparative study of 14-day dual therapy (esomeprazole and amoxicillin four times daily) and triple plus bismuth therapy for first-line Helicobacter pylori infection eradication: A randomized trial. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12762. [Google Scholar]
- Hwong-Ruey, L.A.; Chang, J.V.; Goh, K.L. Searching for an optimal therapy for H pylori eradication: High-dose proton-pump inhibitor dual therapy with amoxicillin vs. standard triple therapy for 14 days. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12723. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Li, C.; Lv, M.; Dai, X.; Gao, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, W.; Liu, C.; Han, S.; et al. The prospective multiple-centre randomized controlled clinical study of high-dose amoxicillin-proton pump inhibitor dual therapy for H. pylori infection in Sichuan areas. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.Y.; Long, H.; Lin, Y.; He, Q.; Chen, W.G.; Ding, X.W.; Zhou, L.; An, P.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Optimized dual therapy for treatment-naive patients of Helicobacter pylori infection: A large-scale prospective, multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled study. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Lyu, T.; Han, S.; Lin, T.; Li, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of high-dose esomeprazole-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori rescue treatment: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.N.; Luo, L.S.; Zhang, W.; Liang, X.; Lu, H. A randomized superiority clinical trial: Metronidazole improved the efficacy of high-dose dual therapy in Helicobacter pylori rescue treatment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.W.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H.M.; Gou, L.Z.; Li, X.L.; Yi, G.R.; Lin, Y.M.; Han, T.Y.; Zhang, D.K. High-dose amoxicillin-proton pump inhibitor dual therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection in Northwest China: A prospective, randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 89, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Zhang, D.Y.; Chen, R.X.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, C.; Zeng, F.; Huang, S.M.; Li, D.; Bai, F.H. Ilaprazole-amoxicillin dual therapy at high dose as a first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection in Hainan: A single-center, open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, S.V.; Lima, C.T.; Freitas, M.; Boal, C.P.; Magalhães, J.; Cotter, J. A “new” option in Helicobacter pylori eradication: High-dose amoxicillin dual therapy outperforms bismuth quadruple therapy in a high dual resistance setting. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e12962. [Google Scholar]
- Valizadeh, T.S.M.; Feyzi, S.; Kazemi, A. Comparison of the Efficacy of 12-day Concomitant Quadruple Therapy versus 14-day High dose Dual Therapy as a First-line H. pylori Eradication Regimen. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 83, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.L.; Han, Y.Y.; Wang, M.R.; Xia, S.H.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhao, K.; Feng, L.N.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, R.N.; et al. Impact of body size on efficacy of high-dose dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e12953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Mégraud, F.; Laine, L.; López, L.J.; Hunt, B.J.; Howden, C.W. Vonoprazan Triple and Dual Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection in the United States and Europe: Randomized Clinical Trial. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yu, B.; Qin, L.; Dai, X. A randomized clinical study on the efficacy of vonoprazan combined with amoxicillin duo regimen for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Medicine 2023, 102, e35610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Chen, H.W.; Wan, Y.; Su, P.Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yao, J.Y.; Zhi, M. Combination of vonoprazan and amoxicillin as the first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: A multicenter, prospective, randomized, parallel-controlled study. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Mei, H.; Su, N.Y.; Sun, W.J.; Zhang, D.K.; Fan, L.L.; He, P.; Pan, J.; Wang, X.W.; Zou, P.Y.; et al. Eradication rates of Helicobacter pylori in treatment-naive patients following 14-day vonoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy: A multicenter randomized controlled trial in China. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.S.; He, C.; Ouyang, Y.B.; Li, N.S.; Xie, C.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Z.H.; Xie, Y.; et al. Fourteen-day vonoprazan and low- or high-dose amoxicillin dual therapy for eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection: A prospective, open-labeled, randomized non-inferiority clinical study. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1049908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Luo, M.; Zheng, P.; Cong, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, F. Eradication rate and safety of vonoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.P.; Liu, Y.J.; Lin, S.W.; Shao, Y.F.; Qiu, F.; Qiu, Q.W.; Xu, Z.K.; Chen, J.X.; Chen, L.H.; Lin, Z.Q.; et al. Vonoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication in Chinese population: A prospective, multicenter, randomized, two-stage study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 3304–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.S.; Lyu, T.; Deng, Z.; Han, S.; Ni, L.; Wu, J.; Tan, J.T.; Qin, J.; Ng, H.Y.; Leung, W.K.; et al. Vonoprazan Dual or Triple Therapy Versus Bismuth-Quadruple Therapy as First-Line Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Three-Arm, Randomized Clinical Trial. Helicobacter 2024, 29, e13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, D.; Kou, L.; Jia, L.; Hao, J.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, W.; Gao, F.; Chen, X. Vonoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy with different amoxicillin dosages for treatment-naive patients of Helicobacter pylori infection in China: A prospective, randomized controlled study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Ye, H.; Li, J.; Dong, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.; et al. Simplified Helicobacter pylori therapy for patients with penicillin allergy: A randomised controlled trial of vonoprazan-tetracycline dual therapy. Gut 2024, 73, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.I.; Shih, C.A.; Chen, C.L.; Chuah, S.K.; Yang, J.C.; Wu, D.C. Both 14-day vonoprazan triple therapy and 14-day rabeprazole reverse hybrid therapy are superior to 14-day vonoprazan high-dose dual therapy for the first-line anti-H. pylori treatment in populations with high rates of antibiotic resistance. Gastroenterology 2024, 166, S-431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eto, H.; Suzuki, S.; Kusano, C.; Ikehara, H.; Ichijima, R.; Ito, H.; Kawabe, K.; Kawamura, M.; Yoda, Y.; Nakahara, M.; et al. Impact of body size on first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication success using vonoprazan and amoxicillin dual therapy. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, M.P.; Lu, H.; Graham, D.Y. Role of bismuth in improving Helicobacter pylori eradication with triple therapy. Gut 2016, 65, 870–878. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.W.; Xiong, S.; Jia, Y.G.; Xiao, D.; Tan, S.Y.; Cao, J.W.; Sun, J.; Tian, X.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, R.H.; et al. Comparison of vonoprazan bismuth-containing triple therapy with quadruple therapy in Helicobacter pylori-infected treatment-naive patients: A prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, P.I.; Wu, D.C.; Chuah, S.K.; Yang, K.C.; Kuo, C.H.; Lee, C.L.; Shih, C.A.; Wu, I.T.; Shie, C.B.; Tsay, F.W. The Efficacy and Safety of High-dose Amoxicillin-Bismuth-Potassium Competitive Acid Blocker Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection—A Pilot Study. Adv. Dig. Med. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.P.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.X.; Han, S.X.; Graham, D.Y.; Lu, H. PPI-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: An update based on a systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12692. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Teng, G.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H. Eradication rate and safety of a “simplified rescue therapy”: 14-day vonoprazan and amoxicillin dual regimen as rescue therapy on treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection previously failed in eradication: A real-world, retrospective clinical study in China. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12918. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Mi, Y.; He, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Huang, H.; et al. A retrospective study of the antibiotic-resistant phenotypes and genotypes of Helicobacter pylori strains in China. Am. J. Cancer. Res. 2021, 11, 5027–5037. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, H.S.; Li, W.J.; Dang, Y.N.; Li, L.R.; Xu, X.B.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, W.F.; Yang, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Ten-Day Vonoprazan-Amoxicillin Dual Therapy as a First-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection Compared with Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, R.H. pH and Hp--gastric acid secretion and Helicobacter pylori: Implications for ulcer healing and eradication of the organism. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 88, 481–483. [Google Scholar]
- Bayerdörffer, E.; Miehlke, S.; Mannes, G.A.; Sommer, A.; Höchter, W.; Weingart, J.; Heldwein, W.; Klann, H.; Simon, T.; Schmitt, W.; et al. Double-blind trial of omeprazole and amoxicillin to cure Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcers. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.C.; Lu, C.W.; Lin, C.J. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Current status and future concepts. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).