Impact of Nisin on Proliferation of Background Microbiota, Pressure-Stressed and Wild-Type Listeria monocytogenes, and Listeria innocua During a Real-Time Shelf-Life Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Listeria Strains and Inocula
2.2. Sample Preparation and Inoculation
2.3. Preparation of Pressure-Stressed Microbial Cells
2.4. Microbiological and Physiochemical Analysis
2.5. Design and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
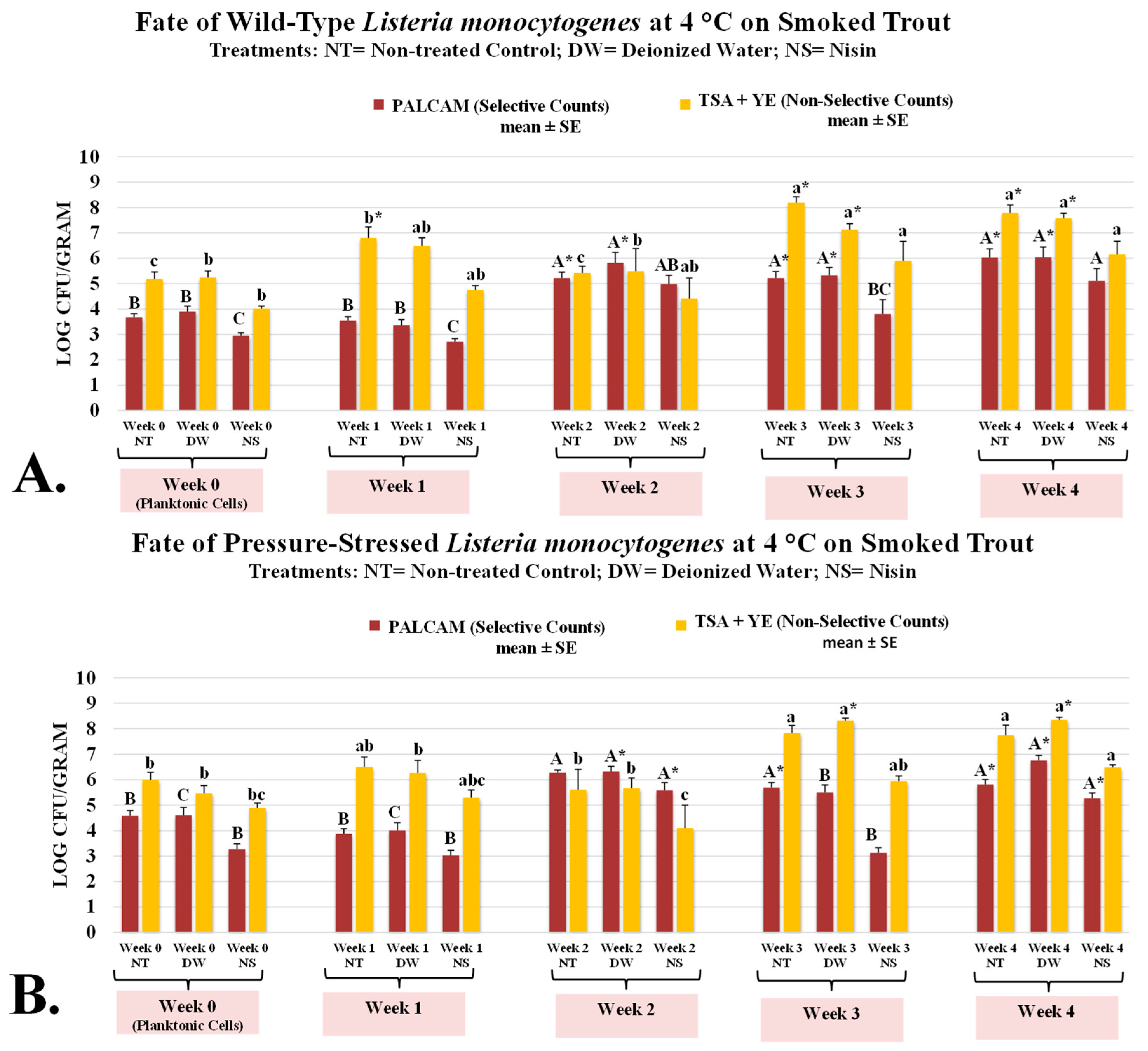
3.1. Fate of Wild-Type and Pressure-Stressed Listeria monocytogenes and Background Microbiota of Smoked Trout During 4-Week Aerobic Refrigerated Storage as Affected by Nisin
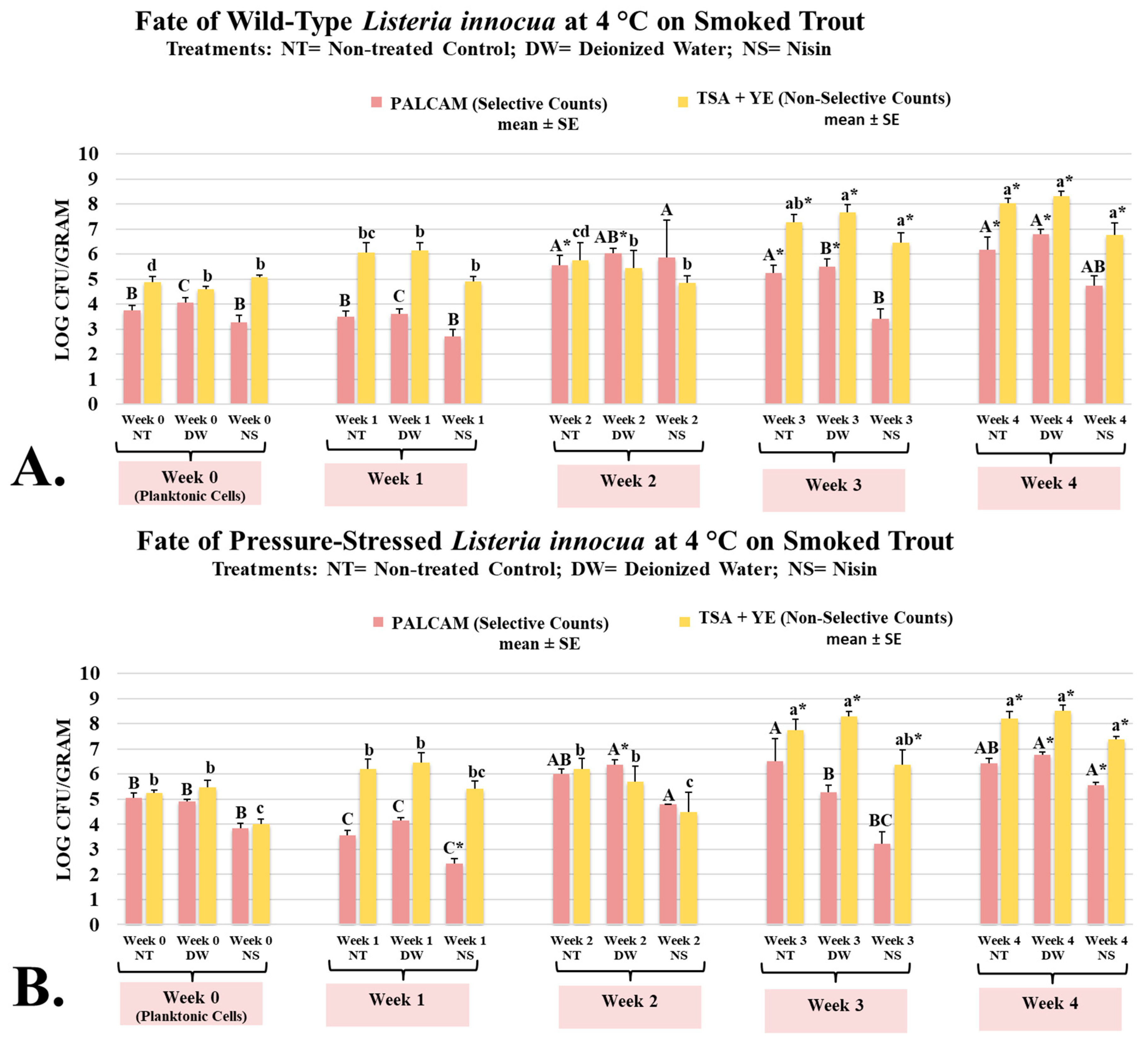
3.2. Fate of Wild-Type and Pressure-Stressed Listeria innocua on Smoked Trout During 4-Week Aerobic Refrigerated Storage as Affected by Nisin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hof, H. History and Epidemiology of Listeriosis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 35, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, A.; Linke, K.; Wagner, M.; Stessl, B. The Saprophytic Lifestyle of Listeria monocytogenes and Entry into the Food-Processing Environment. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 789801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Get the Facts About Listeria. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/animal-health-literacy/get-facts-about-listeria (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. J. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Cresence, V.M.; Rejitha, J.S.; Lekshmi, M.U.; Dharsana, K.S.; Prasad, S.P.; Vijila, H.M. Listeria—Review of Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2007, 40, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osek, J.; Wieczorek, K. Listeria monocytogenes—How This Pathogen Uses Its Virulence Mechanisms to Infect the Hosts. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, R.G.; Kalinowski, R.M.; Bodnaruk, P.W.; Eifert, J.D.; Boyer, R.R.; Duncan, S.E.; Bailey, R.H. Incidence of Listeria spp. in Ready-to-Eat Food Processing Plant Environments Regulated by the US Food Safety and Inspection Service and the US Food and Drug Administration. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Public Health Notice: Outbreak of Listeria Infections Linked to Recalled Plant-Based Refrigerated Beverages; Public Health Agency of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2024. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/public-health-notices/2024/outbreak-listeria-infections-recalled-refrigerated-plant-based-beverages.html (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Listeria Outbreaks; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/outbreaks/ (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Hamidiyan, N.; Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Rezaei, Z.; Dehghani-Tafti, R.; Akrami-Mohajeri, F. The Prevalence of Listeria spp. Food Contamination in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, B.; Szymczak, M.; Trafiałek, J. Prevalence of Listeria Species and L. monocytogenes in Ready-to-Eat Foods in the West Pomeranian Region of Poland: Correlations Between the Contamination Level, Serogroups, Ingredients, and Producers. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrica, M.; Andoni, E.; Intraina, I.; Curone, G.; Copelotti, E.; Massacci, F.R.; Terio, V.; Colombo, S.; Balzaretti, C.M. Prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. in Different Ready-to-Eat Foods from Large Retailers and Canteens Over a 2-Year Period in Northern Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpundu, P.; Mbewe, A.; Muma, J.; Mwasinga, W.; Mukumbuta, N.; Munyeme, M. A Global Perspective of Antibiotic-Resistant Listeria monocytogenes Prevalence in Assorted Ready-to-Eat Foods: A Systematic Review. Vet. World 2021, 14, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, K.; Rip, D. Listeria monocytogenes in the Seafood Industry: Exploring Contamination Sources, Outbreaks, Antibiotic Susceptibility and Genetic Diversity. MicrobiologyOpen 2024, 13, e70003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericsson, H.; Eklöw, A.; Danielsson-Tham, M.L.; Loncarevic, S.; Mentzing, L.O.; Persson, I.; Unnerstad, H.; Tham, W. An Outbreak of Listeriosis Suspected to Have Been Caused by Rainbow Trout. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2904–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocmo, R.; Krizman, K.; Khoo, W.J.; Phua, L.K.; Kim, M.; Yuk, H. Listeria monocytogenes in Vacuum-Packed Smoked Fish Products: Occurrence, Routes of Contamination, and Potential Intervention Measures. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbedel, S.; Sperle, I.; Lachmann, R.; Kleta, S.; Fischer, M.A.; Wamp, S.; Holzer, A.; Lüth, S.; Murr, L.; Freitag, C.; et al. Large Multicountry Outbreak of Invasive Listeriosis by a Listeria monocytogenes ST394 Clone Linked to Smoked Rainbow Trout, 2020 to 2021. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e03520-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hwang, C.A.; Sheen, S. Shelf-Life Boundaries of Listeria monocytogenes in Cold-Smoked Salmon During Refrigerated Storage and Temperature Abuse. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shineman, T.L.; Harrison, M.A. Growth of Listeria monocytogenes on Different Muscle Tissues. J. Food Prot. 1994, 57, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotopoulou, E.T.; Jenkins, C.; Painset, A.; Amar, C. Listeria monocytogenes: The Silent Assassin. J. Med. Microbiol. 2024, 73, 001800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.; Wibisono, R.; De Hoop, L.; Summers, G.; Fletcher, G.C. Identifying Suitable Listeria innocua Strains as Surrogates for Listeria monocytogenes for Horticultural Products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allerberger, F. Listeria: Growth, Phenotypic Differentiation and Molecular Microbiology. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 35, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, G.; Zufía, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Food-Preservation Technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 28, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, B.G.; Mukhtar, K.; Arshad, R.N.; Radicetti, E.; Tedeschi, P.; Shahbaz, M.U.; Walayat, N.; Nawaz, A.; Inam-Ur-Raheem, M.; Aadil, R.M. High-Pressure Processing for Sustainable Food Supply. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, R.; Kaur, B.P.; Nema, P.K.; Tewari, S.; Kumar, L. Microbial Inactivation by High Pressure Processing: Principle, Mechanism and Factors Responsible. Foods 2021, 30, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, C.; Grimaud, G.M.; Coakley, M.; O’Connor, P.M.; Mathur, H.; Peterson, V.L.; O’Donovan, C.M.; Lawlor, P.G.; Cotter, P.D.; Stanton, C.; et al. Modulation of the Gut Microbiome with Nisin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 34586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santativongchai, P.; Tulayakul, P.; Jeon, B. Enhancement of the Antibiofilm Activity of Nisin against Listeria monocytogenes Using Food Plant Extracts. Pathogens 2023, 12, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, D.; De Ullivarri, M.F.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. After a Century of Nisin Research—Where Are We Now? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, S.; Kabir, M.N.; Chowdhury, S.; Fouladkhah, A.C. Augmenting the Pressure-Based Pasteurization of Listeria monocytogenes by Synergism with Nisin and Mild Heat. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.N.; Aras, S.; George, J.; Wadood, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Fouladkhah, A.C. High-Pressure and Thermal-Assisted Pasteurization of Habituated, Wild-Type, and Pressure-Stressed Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria innocua, and Staphylococcus aureus. LWT. 2021, 137, 110445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Bacteriological Analytical Manual (BAM); FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food/bacteriological-analytical-manual-bam (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Fouladkhah, A.; Geornaras, I.; Sofos, J.N. Effects of Reheating Against Listeria monocytogenes Inoculated on Cooked Chicken Breast Meat Stored Aerobically at 7 °C. Food Prot. Trends 2012, 32, 697–704. [Google Scholar]
- Kafle, R.; Fouladkhah, A.C. Effects of Thermally-Assisted and High-Pressure Processing on Background Microbiota and the Listeria monocytogenes Load of a Minimally Processed Commodity. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekonomou, S.I.; Bulut, S.; Karatzas, K.A.G.; Boziaris, I.S. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in Raw and Hot Smoked Trout Fillets by High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Combined with Liquid Smoke and Freezing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 64, 102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimothe, J.; Nightingale, K.K.; Gall, K.; Scott, V.N.; Wiedmann, M. Tracking of Listeria monocytogenes in Smoked Fish Processing Plants. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Prevalence, Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Fresh and Smoked Fish in Poland. Food Microbiol. 2017, 64, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, L. Basic Aspects of Food Preservation by Hurdle Technology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 55, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Shalini, R. Effect of Hurdle Technology in Food Preservation: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Tango, C.N.; Miskeen, S.; Lee, B.H.; Oh, D.H. Hurdle Technology: A Novel Approach for Enhanced Food Quality and Safety—A Review. Food Control 2017, 73, 1426–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, S.; Kabir, N.; Wadood, S.; George, J.; Chowdhury, S.; Fouladkhah, A.C. Synergistic Effects of Nisin, Lysozyme, Lactic Acid, and Citricidal™ for Enhancing Pressure-Based Inactivation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Geobacillus stearothermophilus, and Bacillus atrophaeus Endospores. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.N.; Aras, S.; Wadood, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Fouladkhah, A.C. Fate and Biofilm Formation of Wild-Type and Pressure-Stressed Pathogens of Public Health Concern in Surface Water and on Abiotic Surfaces. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.C.M.; de Oliveira Pena, P.; Júnior, S.B.P.; do Nascimento, M.D.S. Effect of Different Dry Aging Temperatures on Listeria innocua as Surrogate for Listeria monocytogenes. Meat Sci. 2019, 157, 107884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, S.R.; Friedly, E.C.; Saldivar, J.C.; Muthaiyan, A.; O’bryan, C.; Crandall, P.G.; Johnson, M.G.; Ricke, S.C. A Review of the Ecology, Genomics, and Stress Response of Listeria innocua and Listeria monocytogenes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Angulo, A.B.; Zanini, S.F.; Rosenthal, A.; Rodrigo, D.; Klein, G.; Martínez, A. Comparative Study of the Effects of Citral on the Growth and Injury of Listeria innocua and Listeria monocytogenes Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Stasiewicz, M.J.; Murray, D.; Boor, K.J.; Wiedmann, M.; Bergholz, T.M. Optimization of combinations of bactericidal and bacteriostatic treatments to control Listeria monocytogenes on cold-smoked salmon. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 179, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heir, E.; Jensen, M.R.; Aasli, A.W.; Berget, I.; Holck, A.L. Reduction and growth inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes by use of anti-listerial nisin, P100 phages and buffered dry vinegar fermentates in standard and sodium-reduced cold-smoked salmon. Foods 2023, 12, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Stasiewicz, M.J.; Wiedmann, M.; Boor, K.J.; Bergholz, T.M. Efficacy of different antimicrobials on inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes growth in laboratory medium and on cold-smoked salmon. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 165, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Skeens, J.W.; Wiedmann, M.; Guariglia-Oropeza, V. The efficacy of nisin against Listeria monocytogenes on cold-smoked salmon at natural contamination levels is concentration-dependent and varies by serotype. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 930400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leistner, L.; Gorris, L.G. Food preservation by hurdle technology. Trends Food Sci Technol. 1995, 6, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, J.; Kafle, R.; Chowdhury, S.; Fouladkhah, A.C. Synergetic Effect of Elevated Hydrostatic Pressure, Mild Heat, and Carvacrol on Inactivation of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Serovars in Buffered Environment. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kafle, R.; Fouladkhah, A.C. Impact of Nisin on Proliferation of Background Microbiota, Pressure-Stressed and Wild-Type Listeria monocytogenes, and Listeria innocua During a Real-Time Shelf-Life Study. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030668
Kafle R, Fouladkhah AC. Impact of Nisin on Proliferation of Background Microbiota, Pressure-Stressed and Wild-Type Listeria monocytogenes, and Listeria innocua During a Real-Time Shelf-Life Study. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(3):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030668
Chicago/Turabian StyleKafle, Ranju, and Aliyar Cyrus Fouladkhah. 2025. "Impact of Nisin on Proliferation of Background Microbiota, Pressure-Stressed and Wild-Type Listeria monocytogenes, and Listeria innocua During a Real-Time Shelf-Life Study" Microorganisms 13, no. 3: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030668
APA StyleKafle, R., & Fouladkhah, A. C. (2025). Impact of Nisin on Proliferation of Background Microbiota, Pressure-Stressed and Wild-Type Listeria monocytogenes, and Listeria innocua During a Real-Time Shelf-Life Study. Microorganisms, 13(3), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13030668





