Abstract
Background: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections in children, and the antibiotic susceptibility in the youngest patients remains poorly understood. This study aimed to describe the distribution of uropathogens and their antibiotic susceptibility, focusing on oral formulations. Methods: Data from the first microbiological isolation, between January 2007 and December 2023, at Istituto Gaslini, in young infants (aged <6 months), were analyzed. Results: We isolated 2473 infants’ first pathogen, with a median age in the sample of 2.8 months and 62.6% male. A total of 2498 bacterial isolates were identified, of which 88.8% were Gram-negative and 11.2% were Gram-positive. Escherichia coli (53%) was the most frequent isolate, followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae (12.3%) and Enterococcus spp. (9.6%). No significant differences were observed between males and females, but infants younger than 3 months exhibited a significantly different pathogen distribution compared to older infants. The pathogen distribution showed significant changes before and after 2015, with a marked increase in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates post-2015. Escherichia coli showed increases in resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate and ciprofloxacin after 2015. Conclusions: Escherichia coli remains the most common uropathogen; however, Klebsiella pneumoniae has not only shown a high prevalence but also significant resistance, particularly in recent years.
1. Introduction
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections in pediatrics, with infants in the first few months of life being at a particularly high risk [1]. This susceptibility has been attributed to an incompletely developed adaptive immune system, but congenital malformations of the urinary tract also play a pivotal role, especially in males [2,3,4].
Gram-negative bacteria from the Enterobacterales family are the predominant cause, with Escherichia coli accounting for over 70% of UTIs. Other common pathogens include Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., and Proteus spp., while Pseudomonas aeruginosa is less frequent but associated with severe infections [5]. Among Gram-positive bacteria, Enterococcus spp. are the most prevalent UTI pathogens. However, there is significant geographical variability in the prevalence of microorganisms and the patterns of antimicrobial resistance [6].
The increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance also complicates the management of UTIs in the pediatric population, with resistance to orally administrable first-line antibiotics such as amoxicillin-clavulanate documented worldwide. Recent reports from different countries have highlighted a concerning prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing and multidrug-resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella in children, underscoring the need for updated local data to guide empirical treatment approaches [5,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. However, the antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria isolated from the urinary tract in the youngest subjects remains poorly explored, particularly for those suitable for oral administration.
It is well-documented that both the prevalence of microorganisms and antibiotic susceptibility exhibit geographical variability [6,15]. Such variability can manifest on a local scale over time, and these temporal changes can be effectively monitored through longitudinal studies. Accordingly, this 17-year retrospective study aimed to describe and analyze the etiology and antibiotic susceptibility patterns associated with the first bacterial isolation from urine cultures in young infants aged 0–6 months, observed at a pediatric tertiary care center in northwest Italy.
2. Materials and Methods
Data on microbiological isolation from urine cultures sampled between January 2007 and December 2023 in young infants, aged 0–6 months, were extracted from the Microbiology Laboratory database at the IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini (IGG), Genoa, Italy and analyzed anonymously. The IGG is a tertiary care pediatric hospital in northwest Italy, admitting patients from Italy and other countries. For each episode, data on sex, age in months at the time of the first isolation, and the department of admission, where the patient was sampled, were retrieved.
All positive urinary cultures were considered, independently of a diagnosis of upper (pyelonephritis) or lower (cystitis) UTI or asymptomatic bacteriuria [8,16]. All urine samples were obtained by midstream clean-catch, catheterization, or urine bags, as determined by the patient’s age, according to international recommendations [17,18]. Urine samples were cultured on Columbia agar with 5% sheep blood (bioMérieux SA, Marcy-l’Etoile, France) and MacConkey agar (bioMérieux SA, Marcy-l’Etoile, France), then incubated at 37 °C overnight. Bacterial growth was considered significant if it reached ≥105 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL of urine. Antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed using automated systems (BD Phoenix, Becton, Dickinson and Company, Sparks, MD, USA), following the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines from 2007 to 2010. After 2011, the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) guidelines were used. Due to this major shift and annual updates to EUCAST breakpoints, we chose to report antibiotic susceptibility or resistance based on the criteria set by the system used each year, reflecting the protocols followed in routine practice over time.
The isolated pathogens were divided into Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Within the Gram-positive group, pathogens were further categorized as Enterococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., and Staphylococcus spp. In the Gram-negative group, pathogens were classified as Enterobacterales and glucose non-fermenting bacteria. Antibiotic susceptibility was analyzed for bacterial pathogens accounting for >3% of all isolates. For the Gram-negative strains, antibiotic susceptibility was assessed against amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefixime, cefuroxime, ciprofloxacin, fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, cotrimoxazole, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime. In the case of Enterococcus spp., susceptibility was evaluated for nitrofurantoin and ampicillin. It is important to note that amoxicillin shares the same spectrum of activity as ampicillin and can therefore be used for oral therapy of ampicillin-sensitive Enterococcus strains. Due to differences in the antibiotics available in different periods for automated systems, nitrofurantoin and cefixime were tested from 2011 to 2015, cefuroxime from 2007 to 2015, and cotrimoxazole from 2007 to 2021.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics were reported in terms of absolute frequencies and percentages for categorical data, and Pearson’s chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test, when appropriate, was applied to compare proportions. Continuous data were described in terms of median values and IQRs, due to their non-normal (Gaussian) distribution.
The year and age at the first isolation were categorized based on the median values of 2015 and 2.8 months, respectively, with the latter being approximated to 3 months. Percentages of antibiotic-resistant pathogen were calculated as the ratio of the number of resistant to the number of tested strains. The analysis and presentation were based on the available data, i.e., no imputation of missing data was performed.
All tests were 2-tailed and a p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using Stata (Stata Corp. Stata Statistical Software, Release 18.0, College Station, TX, USA, Stata Corporation, 2023).
This study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration. According to Italian legislation, this study did not need ethical approval, as it was a purely observational, retrospective study on routinely collected anonymous data. Moreover, informed consent for participation in this study was not required since retrospective data were obtained by an anonymous microbiology database. In any case, consent for the completely anonymous use of one’s clinical data for research/epidemiological purposes is requested as part of the clinical routine at the time of admission/during the diagnostic procedure.
3. Results
During the study period, 2473 young infants had their first isolation of pathogens from urinary samples at a median age of 2.8 months (IQR 1.2–4.7). The majority (62.6%) were male, and 25% of them subsequently had other episodes (Table 1). For more than half of the cases (55.2%), the department of first sampling was the Emergency Unit.

Table 1.
Characteristics of young infants, aged 0–6 months, at the first isolation of pathogens from urinary samples.
A total of 2473 positive cultures yielded 2498 bacterial isolates; 281 (11.2%) were Gram-positives, and 2217 (88.8%) were Gram-negatives (Table 2). Among the 2498 isolates, the most frequent pathogen was Escherichia coli (53%), followed by Klebsiella pneumoniae (12.3%) and Enterococcus spp. (9.6%). In the Gram-positives, the most frequent were enterococci (241, 85.8%), with E. faecalis being the most common species (n = 209). Among the Gram-negatives, 2116 (95.4%) were Enterobacterales, with Escherichia coli being the most frequent (n = 1324, 62.6%). Non- glucose fermenting bacteria totaled 101 (4.6%), with the majority (n = 90) being Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

Table 2.
Distribution of 2498 bacterial pathogens isolated in 2473 UTIs.
3.1. Distribution of the Most Frequently Isolated Bacteria
The distribution of the most frequently isolated bacteria (n = 2201), including Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella oxytoca, Enterobacter cloacae, Enterococcus faecalis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, was not statistically significant different between males and females (Table 3). However, statistically significant differences (p < 0.001) were observed between infants younger than 3 months and those aged 3 months or older (Table 3).

Table 3.
Distribution of the most frequently bacterial pathogens isolated (n = 2201) with respect to sex, age (<3 months, ≥3 months), and period (<2015, ≥2015) of the first isolate.
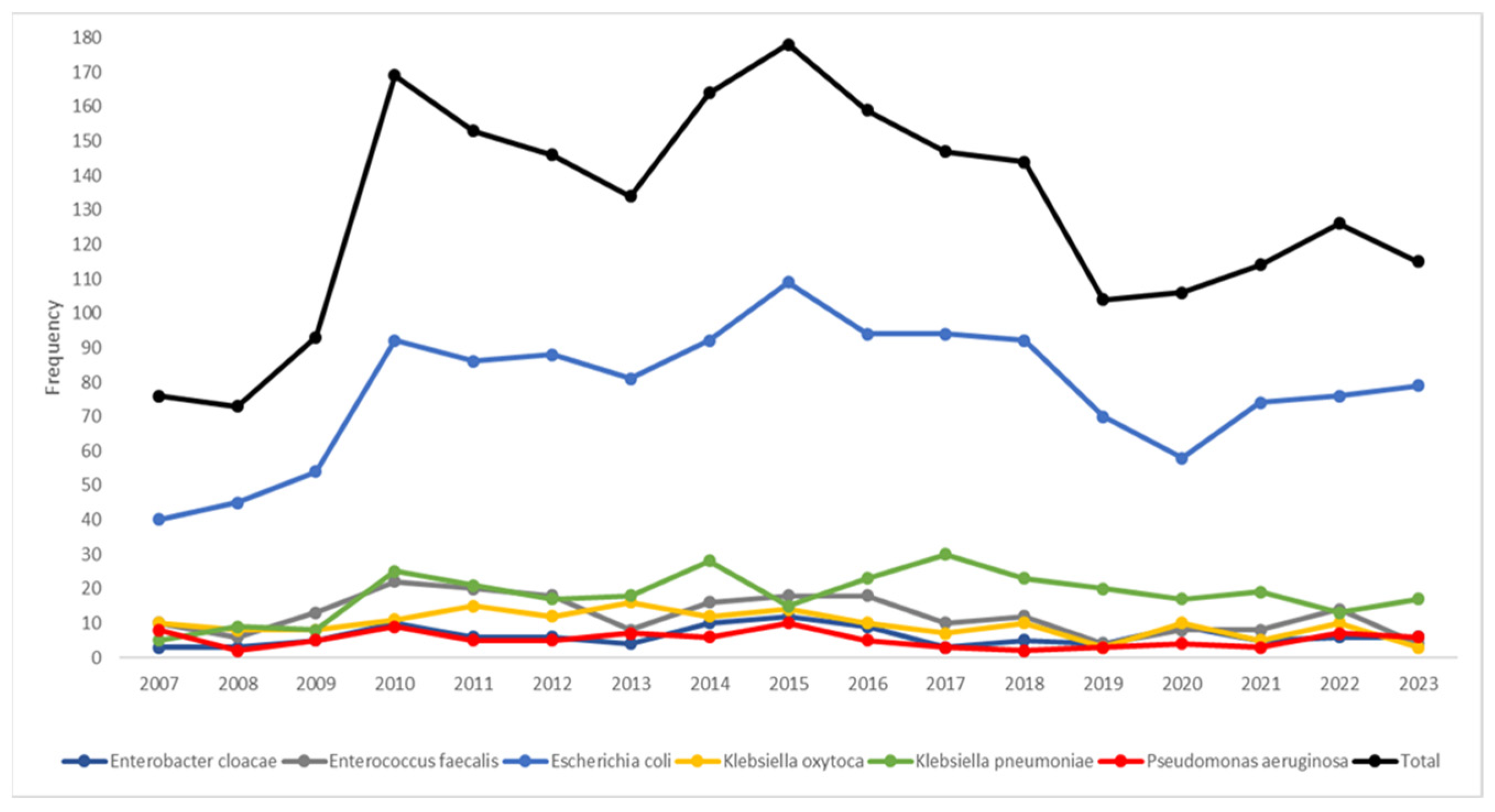
The temporal trends (Figure 1) highlighted Escherichia coli as the dominant species; its frequency showed a sharp increase, starting in 2008, peaking in 2015, and then gradually declining. Klebsiella pneumoniae emerged as the second most prevalent species, displaying a steady rise in frequency from 2010 onward. If the median year (2015) of the study period was considered (Table 3), the pathogen distribution displayed statistically significant patterns (p < 0.001); Klebsiella oxytoca, Enterobacter cloacae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterococcus faecalis were most frequently isolated before 2015, while there was almost an equal distribution for Escherichia coli in the two periods. After 2015, there was a higher frequency of Klebsiella pneumoniae.
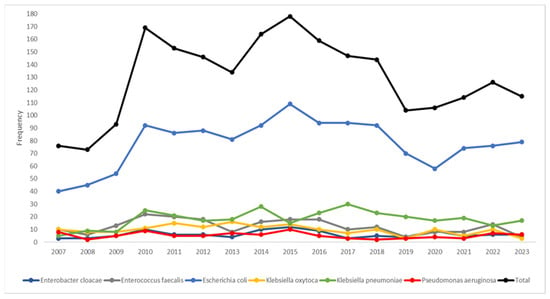
Figure 1.
Temporal trends of the most frequent bacterial pathogens isolated (n = 2201) during the study period.
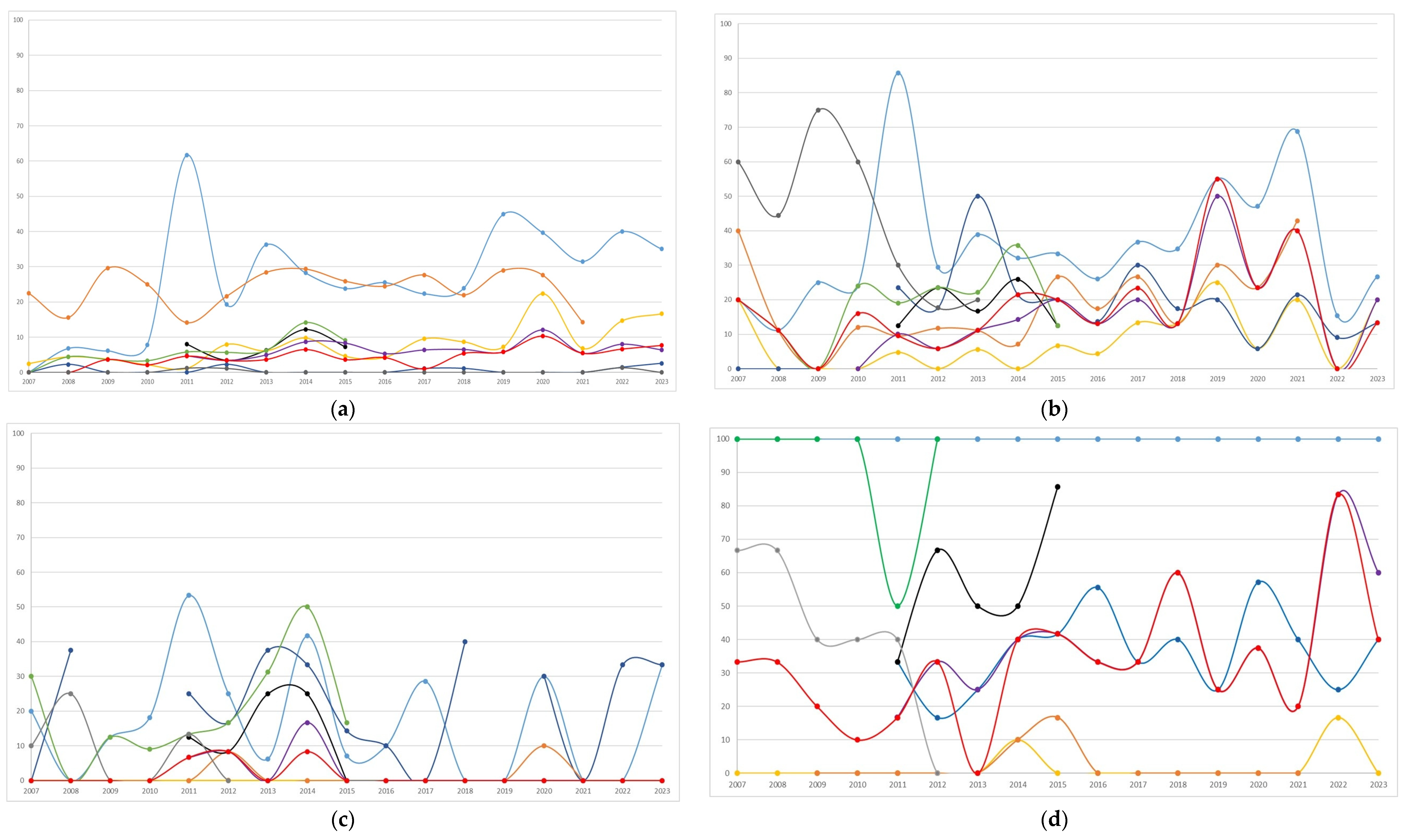
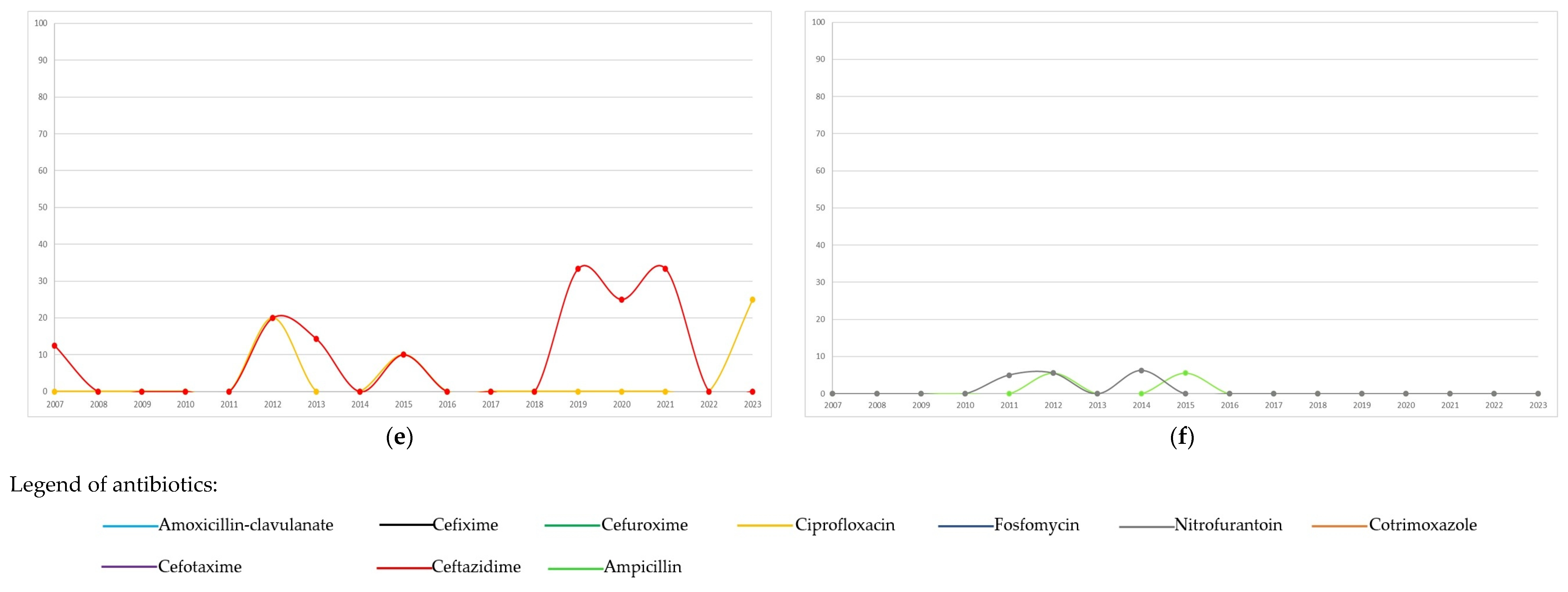
3.2. Temporal Trends in Antibiotic Resistance by Pathogen
The distribution of antibiotic resistance overall, and by period (<2015 or ≥2015) of the first isolate, is summarized in Table 4. Annual trends in antibiotic resistance are shown in Figure 2. In Escherichia coli, the highest resistance was observed for amoxicillin-clavulanate (27.9%), followed by cotrimoxazole, with resistance trends exhibiting variability over the study period. Starting from 2015, resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate and ciprofloxacin increased significantly (from 24.1% to 31.8%, p = 0.002; and from 5% to 10.7%, <0.001, respectively, Table 4) compared to the previous period. Both nitrofurantoin and fosfomycin showed minimal resistance. In Klebsiella pneumoniae, frequent resistance was observed to nitrofurantoin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, and third-generation cephalosporins. Resistance significantly increased from 2015 compared to the prior period for ciprofloxacin (from 2.7% to 12.8%), cotrimoxazole (from 12.3% to 23.3%), cefotaxime (from 11.9% to 22.4%), and ceftazidime (from 13.7% to 23.1%). Klebsiella oxytoca showed infrequent resistance to ciprofloxacin, cotrimoxazole, and ceftazidime, while maintaining high resistance to cefuroxime, during the period in which it was tested, and exhibited fluctuating resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate, with notable peaks throughout the study period. Enterobacter cloacae displayed high resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate and substantial resistance to cefixime and cefuroxime. Ciprofloxacin exhibited minimal resistance. Although Pseudomonas aeruginosa was less frequently isolated, it showed a variation in resistance over time, with peaks especially for ceftazidime compared to ciprofloxacin. Enterococcus faecalis exhibited excellent susceptibility to ampicillin and nitrofurantoin, which followed similar temporal trends.

Table 4.
Distribution of antibiotic resistance overall and by period (<2015 or ≥2015) of the first isolate.
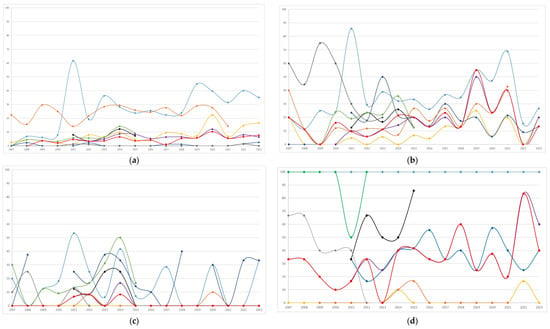
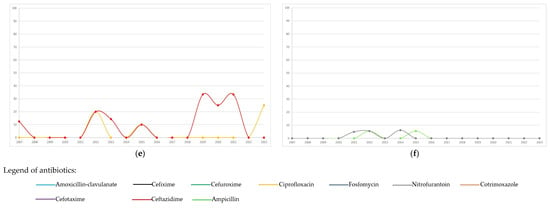
Figure 2.
Temporal trends (percentages of resistant/tested) of antibiotic resistance to the most frequent bacterial pathogens isolated (n = 2201) during the study period: (a) Escherichia coli, n = 1324; (b) Klebsiella pneumoniae, n = 308; (c) Klebsiella oxytoca, n = 164; (d) Enterobacter cloacae, n = 106; (e) Pseudomonas aeruginosa, n = 90; (f) Enterococcus faecalis, n = 209.
4. Discussion
This study investigates the etiology and antibiotic resistance profiles of the first bacterial isolates from UTIs in young infants, under six months of age. We specifically focused on this age group because, in our previous study [8], we observed a concerning prevalence of resistance among infants. As the first single-center study to specifically examine bacterial profiles and antibiotic resistance in this population, it offers important insights into the evolving patterns of UTI pathogens and the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance. However, this study primarily addresses the epidemiology of bacterial isolates, independent of symptom presence to confirm UTIs, due to the lack of clinical data. While this constitutes a notable limitation, it still provides valuable information regarding antibiotic efficacy.
Another important consideration is the shift in the methodology used for antibiotic susceptibility testing in our center. From 2007 to 2010, testing was conducted according to the CLSI guidelines. However, starting in 2011, the EUCAST guidelines were adopted. This transition to EUCAST, which publishes annual updates to breakpoint values, required that antibiotic susceptibility be reported in accordance with the criteria defined by the guidelines in effect for each respective year. For instance, recently, EUCAST revised the breakpoints for amoxicillin-clavulanate, particularly for Enterobacterales associated with UTIs, highlighting the importance of adhering to the latest guidelines for accurate susceptibility reporting.
In line with previous findings [2,3,4,19,20], this study observed a higher prevalence of isolates in males. This is consistent with anatomical and physiological factors that predispose male infants to UTIs, while females typically show a higher incidence of UTIs starting from the second year of life, due to hormonal and anatomical changes. However, in this study, the distribution of the most commonly isolated pathogens did not show statistically significant differences between males and females. The present study also highlighted that the first bacterial isolation typically occurred within the first few months of life, with a median age of approximately 3 months. This early onset, combined with significant levels of antibiotic resistance, might be at least partially attributed to the acquisition of nosocomial microorganisms during birth, as previously reported in the literature [21,22,23]. Indeed, the significant differences in pathogen distribution between infants younger than 3 months and those older than 3 months suggest that microbial exposure and resistance acquisition may differ as infants mature. In fact, as another study [24] showed, positive urine cultures were most common in infants with a postnatal age of 8–30 days and a very low birth weight (<1500 g).
Our data confirm that UTIs in young infants are predominantly diagnosed in emergency settings. Clear criteria are needed to assist clinicians in deciding whether to test a patient’s urine and how to manage the case. Due to the necessary delay in obtaining urine culture results, clinicians must make decisions on whether to prescribe antibiotics for a suspected UTI prior to receiving culture results [25].
A further important observation is that recurrent UTIs were observed in 25% of young infants after their first isolation, which is consistent with other studies [26,27]. Recurrent infections are more common in the presence of urinary tract abnormalities [28], particularly those with vesicoureteral reflux, which often requires repeated antibiotic courses. This repeated exposure to antibiotics is a well-established risk factor for the development of antibiotic resistance. As already mentioned, a limitation of this study is the lack of detailed clinical data, such as data on the presence of urinary tract malformations, which would help better contextualize these findings.
Gram-negative bacteria were the predominant pathogens, with Escherichia coli being the most commonly isolated pathogen, though at a lower frequency (53%, among all isolates) compared to the >70% reported in the literature. The second most frequently isolated pathogen was Klebsiella pneumoniae (12.3%, among all isolates). However, there is considerable variability in the prevalence of pathogens, driven both by geographical differences and by the specific study populations and time periods. For instance, a single-center study conducted in Portugal [29] between 2017 and 2019, which included patients up to 18 years of age, found that Escherichia coli was the most commonly isolated microorganism (71.5%), followed by Proteus mirabilis (14.9%) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (5.1%). A study of a specific multicenter cohort in the United States [24] involving infants with very low birth weight, who were discharged from the neonatal intensive care unit, found that Enterococcus spp. (20%) was the most common pathogen, followed by Escherichia coli (19%) and Klebsiella spp. (18%).
The data further revealed a notable shift in pathogen distribution over time. A greater number of pathogens were isolated prior to 2015, particularly Klebsiella oxytoca and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, while Escherichia coli was almost equally distributed across the time period. After 2015, an increased frequency of Klebsiella pneumoniae was observed. This temporal shift in pathogen profiles highlights the importance of ongoing surveillance to understand local epidemiology and the necessity of adjusting empirical antibiotic treatment regimens accordingly. In fact, the selection of empirical antibiotics for pediatric UTIs is strongly influenced by local bacterial profiles and resistance patterns within specific populations [23]. Accurate knowledge of the responsible pathogens and their antibiotic susceptibility is essential, particularly in light of the dynamic nature of UTI etiology and the evolving resistance patterns of uropathogens. This is even more critical in very young infants, who are particularly vulnerable to severe infections and present unique bacterial profiles compared to older children or adults.
Our data on temporal trends in antibiotic resistance revealed that certain antibiotics (nitrofurantoin, cefixime, cefuroxime, and cotrimoxazole) were tested intermittently, limiting the generalizability of the findings across the entire study period. Amoxicillin-clavulanate and ciprofloxacin were the most commonly tested oral antibiotics, while ceftazidime was primarily tested for intravenous administration. High rates of antibiotic resistance were documented for commonly prescribed oral antibiotics in infants with their first bacterial isolates. This may be linked to pre- or peri-partum maternal antibiotic exposure, which can increase the risk of colonization by resistant bacteria in neonates [28]. Maternal–child transmission through colonization of the fecal microbiota or genital tract may represent an underrecognized risk factor for acquiring ESBL-producing Enterobacterales [27]. The observed high rates of antibiotic resistance, particularly to commonly used oral antibiotics like amoxicillin-clavulanate, raise concerns about the feasibility of adhering to national treatment guidelines, which recommend amoxicillin-clavulanate or cefixime as first-line therapies for pediatric UTIs [30]. The increasing resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate, especially in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, underscores the need for more cautious use of these antibiotics, particularly in neonates and infants under one year of age [23]. Ciprofloxacin consistently exhibited the lowest resistance rates across most pathogens. However, for Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, resistance significantly increased from 2015 onwards compared to the previous period. Notably, Escherichia coli showed a significant rise in resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate, from 24% to 32%. These findings are consistent with a previous study in which E. coli strains demonstrated an increase in resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate over time, from 16% (2000–2004) to 36% (2015–2019) [31]. In our earlier study [8], male infants aged <6 months, admitted to the Neonatal or Pediatric ICU with a history of previous infections, were found to have an estimated risk of over 60% for resistance to amoxicillin-clavulanate for Escherichia coli and other Enterobacteriales.
Klebsiella pneumoniae was most frequently isolated since 2015, particularly in young infants under 3 months of age, with an increase in resistance during the more recent period, both to oral and intravenous antibiotics. In a study in Poland [32], non-E. coli UTIs were significantly more common in patients with congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract, neurogenic bladder, or those receiving antibiotic prophylaxis. Infections caused by non-E. coli and multidrug-resistant bacteria may be associated with prior hospitalizations and patient colonization by pathogens acquired in the hospital environment. Specifically, Devrim et al. [33] reported that nosocomial UTIs were most often caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae (34.1%).
5. Limitations
This study had several limitations, including its retrospective design and the fact that it was conducted within a specific local epidemiological context, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, certain antibiotics were tested only intermittently, which restricts the applicability of the results across the entire study period. Furthermore, the data for this study were extracted from a microbiology database, and as such, detailed clinical data were not available for analysis.
6. Conclusions
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of bacterial pathogens and their susceptibility profiles in young infants, under 6 months of age, over a 17-year period. Escherichia coli remains the most common uropathogen, with a notable increase in amoxicillin-clavulanate resistance in recent years. However, it is important to highlight that Klebsiella pneumoniae has not only shown a high prevalence but also significant resistance, particularly in recent years, to both oral and intravenous antibiotics. These findings underscore the need for more personalized and targeted antibiotic therapies, contributing to the optimization of empirical antibiotic treatment and supporting antimicrobial stewardship initiatives. Ultimately, this may improve clinical outcomes in this vulnerable population, reduce the time required for managing UTIs, and help minimize healthcare workloads and associated costs.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to this article. Conceptualization, E.C. (Elio Castagnola) and F.B.; methodology, E.C. (Elio Castagnola) and F.B.; formal analysis, F.B.; investigation, E.U., E.C. (Emanuela Caci), D.C., E.T. and A.C.; data curation, F.B.; writing—original draft preparation, E.C. (Elio Castagnola), F.B. and F.L.C.; writing—review and editing, A.M., C.S., E.R., C.R., M.M., G.P., E.V. and R.B.; visualization, F.B.; supervision, E.C. (Elio Castagnola); project administration, E.C. (Elio Castagnola); funding acquisition, E.C. (Elio Castagnola). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by grants from the Ministero della Salute—Ricerca Corrente.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Since this study was based only on anonymized laboratory and administrative data and no clinical records were analyzed, this study did not need Internal Review Board approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent to participate in this study was not required since retrospective data were obtained from an anonymous microbiology database.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| UTI | Urinary tract infections |
| IGG | Istituto Giannina Gaslini |
| ESBL | Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| CFU | Colony-forming units |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| EUCAST | European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing |
References
- Greenhow, T.L.; Hung, Y.Y.; Herz, A.M.; Losada, E.; Pantell, R.H. The changing epidemiology of serious bacterial infections in young infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2014, 33, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.M.; Akers, S.; Nguyen, H.; Woxland, H. Evaluation and management of urinary tract infections in the school-aged child. Prim. Care 2015, 42, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbel, L.; Howell, M.; Spencer, J.D. The clinical diagnosis and management of urinary tract infections in children and adolescents. Paediatr. Int. Child. Health. 2017, 37, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balighian, E.; Burke, M. Urinary Tract Infections in Children. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 39, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, S.; Maglietta, G.; Di Costanzo, M.; Ceccoli, M.; Vergine, G.; La Scola, C.; Malaventura, C.; Falcioni, A.; Iacono, A.; Crisafi, A.; et al. Retrospective 8-Year Study on the Antibiotic Resistance of Uropathogens in Children Hospitalised for Urinary Tract Infection in the Emilia-Romagna Region, Italy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990–2021: A systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkalim Zemer, V.; Ashkenazi, S.; Levinsky, Y.; Richenberg, Y.; Jacobson, E.; Nathanson, S.; Shochat, T.; Kushnir, S.; Cohen, M.; Cohen, A.H. Pathogens Causing Pediatric Community Acquired Urinary Tract Infections and Their Increasing Antimicrobial Resistance: A Nationwide Study. Pathogens 2024, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnasco, F.; Piaggio, G.; Mesini, A.; Mariani, M.; Russo, C.; Saffioti, C.; Losurdo, G.; Palmero, C.; Castagnola, E. Epidemiology of Antibiotic Resistant Pathogens in Pediatric Urinary Tract Infections as a Tool to Develop a Prediction Model for Early Detection of Drug-Specific Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierantoni, L.; Andreozzi, L.; Ambretti, S.; Dondi, A.; Biagi, C.; Baccelli, F.; Lanari, M. Three-Year Trend in Escherichia coli Antimicrobial Resistance among Children’s Urine Cultures in an Italian Metropolitan Area. Children 2021, 8, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chao, M. A retrospective study of uropathogen and its antibiotic resistance among children with urinary tract infection from a single center in China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Bastug, Y.; Senol, C.; Kassim, M.M.; Yusuf, A.A.; Mohamed, A.H. Antimicrobial resistance pattern and uropathogens distribution in children visiting a referral hospital in Mogadishu. Future Sci. OA 2024, 10, FSO978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Thänert, R.; Reske, K.A.; Nickel, K.B.; Olsen, M.A.; Hink, T.; Thänert, A.; Wallace, M.A.; Wang, B.; Cass, C.; et al. Gut microbiome correlates of recurrent urinary tract infection: A longitudinal, multi-center study. EClinicalMedicine 2024, 71, 102490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washahi, M.; Miron, D.; Steinberg Ben Zeev, Z.; Chayen, G.; Jacob, R. High Rates of ESBL-producing and Gentamycin-resistant Gram-negative Bacteria During the First Week of Life: A Multicenter Cross-sectional Study Among Infants Younger Than 2 Months With Urinary Tract Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flokas, M.E.; Karanika, S.; Alevizakos, M.; Mylonakis, E. Prevalence of ESBL-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Pediatric Bloodstream Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubes, J.N.; Fridkin, S.K. Factors affecting the geographic variability of antibiotic-resistant healthcare-associated infections in the United States using the CDC Antibiotic Resistance Patient Safety Atlas. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullus, K.; Shaikh, N. Urinary tract infections in children. Lancet 2020, 395, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandström, P.; Hansson, S. Urinary Tract Infection in Children. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 69, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro Pérez, R.; Cilleruelo Ortega, M.J.; Ares Álvarez, J.; Baquero-Artigao, F.; Silva Rico, J.C.; Velasco Zúñiga, R.; Martínez Campos, L.; Carazo Gallego, B.; Conejo Fernández, A.J.; Calvo, C.; et al. Recomendaciones sobre el diagnóstico y tratamiento de la infección urinaria [Recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infection]. An. Pediatría (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 90, e1–e400. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belko, N.A.; Pohl, H.G. Pediatric Urinary Tract Infections. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 51, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaili, K.; Lolin, K.; Damry, N.; Alexander, M.; Lepage, P.; Hall, M. Febrile urinary tract infections in 0- to 3-month-old infants: A prospective follow-up study. J. Pediatr. 2011, 158, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, J.A.; Downs, S.M.; Dudley, S.; Donowitz, L.G. Hospital-acquired urinary tract infections in the pediatric patient: A prospective study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1994, 13, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Shetty, N. Healthcare-associated infections in neonatal units: Lessons from contrasting worlds. J. Hosp. Infect. 2007, 65, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnani, C.; Tersigni, C.; D’Arienzo, S.; Miftode, A.; Venturini, E.; Bortone, B.; Bianchi, L.; Chiappini, E.; Forni, S.; Gemmi, F.; et al. Resistance Patterns from Urine Cultures in Children Aged 0 to 6 Years: Implications for Empirical Antibiotic Choice. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpatrick, R.; Boutzoukas, A.E.; Chan, E.; Girgis, V.; Kinduelo, V.; Kwabia, S.A.; Yan, J.; Clark, R.H.; Zimmerman, K.O.; Greenberg, R.G. Urinary Tract Infection Epidemiology in NICUs in the United States. Am. J. Perinatol. 2024, 41 (Suppl. S1), e2202–e2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tishberg, L.M.; Kusulas, M.P. Management of pediatric urinary tract infections in the emergency department. Pediatr. Emerg. Med. Pract. 2024, 21, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nuutinen, M.; Uhari, M. Recurrence and follow-up after urinary tract infection under the age of 1 year. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2001, 16, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.T.; Chang, C.N.; Yu, C.H.; Wang, C.C. The risk factors, antimicrobial resistance patterns, and outcomes associated with extended-spectrum β-lactamases-Producing pathogens in pediatric urinary tract infection. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2024, 65, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabih, A.; Leslie, S.W. Complicated Urinary Tract Infections. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK436013/ (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Fernandes, A.; Oliveira, Í.; Pereira, M.; Mendes, P.; Virtuoso, M.J.; Pereira, A. Local Antimicrobial Resistance Trends in Pediatric Urinary Tract Infection: The Importance of Local Surveillance of a Global Problem. Cureus 2024, 16, e54700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammenti, A.; Alberici, I.; Brugnara, M.; Chimenz, R.; Guarino, S.; La Manna, A.; La Scola, C.; Maringhini, S.; Marra, G.; Materassi, M.; et al. Updated Italian recommendations for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of the first febrile urinary tract infection in young children. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejonckheere, Y.; Desmet, S.; Knops, N. A study of the 20-year evolution of antimicrobial resistance patterns of pediatric urinary tract infections in a single center. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 3271–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalec, A.; Józefiak, J.; Kiliś-Pstrusińska, K. Urinary Tract Infection and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns: 5-Year Experience in a Tertiary Pediatric Nephrology Center in the Southwestern Region of Poland. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devrim, F.; Serdaroğlu, E.; Çağlar, İ.; Oruç, Y.; Demiray, N.; Bayram, N.; Ağın, H.; Çalkavur, S.; Sorguç, Y.; Dinçel, N.; et al. The Emerging Resistance in Nosocomial Urinary Tract Infections: From the Pediatrics Perspective. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 10, e2018055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).