Vertical Stratification Reduces Microbial Network Complexity and Disrupts Nitrogen Balance in Seasonally Frozen Ground at Qinghai Lake in Tibet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
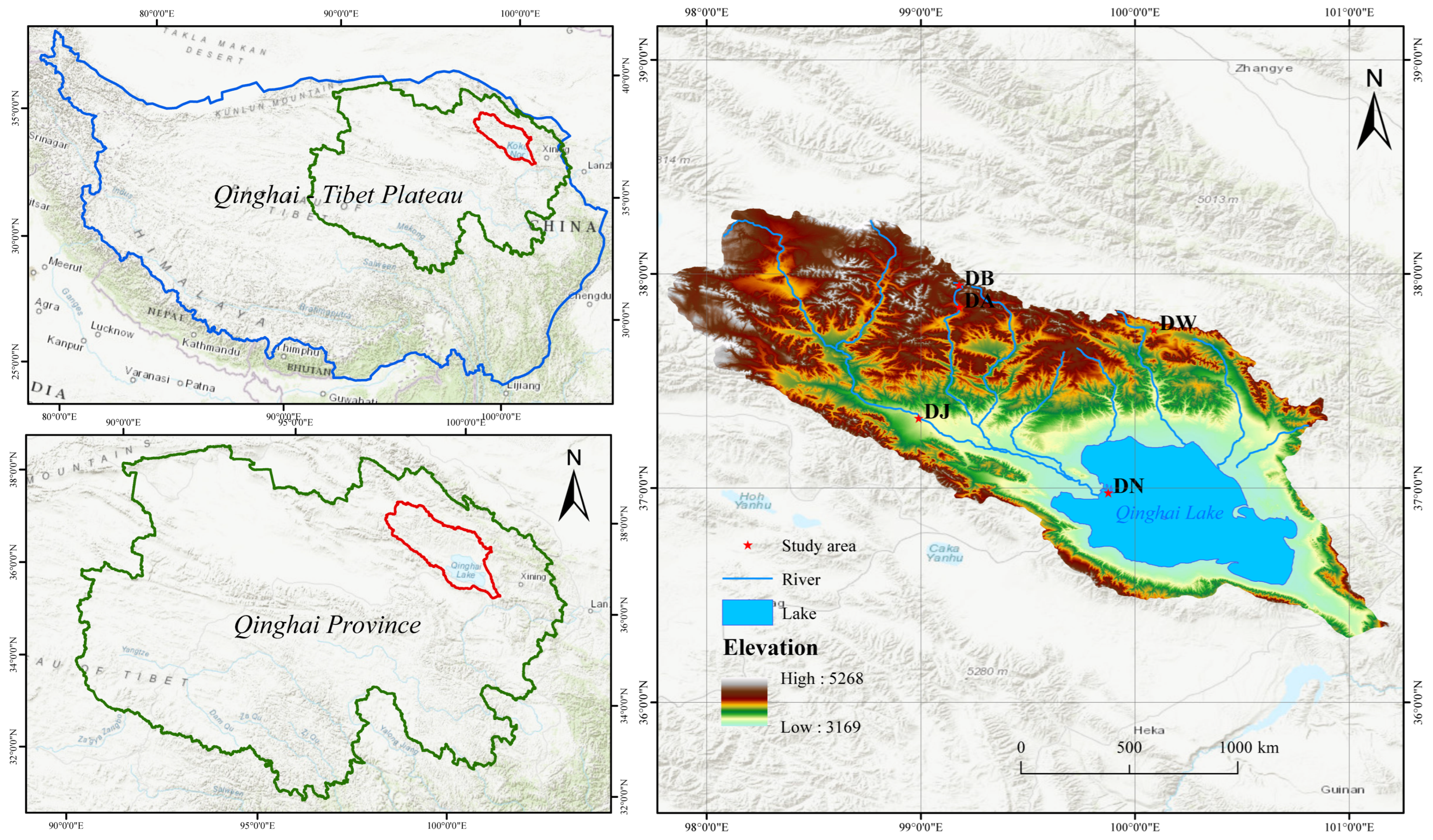
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of Soil Biogeochemical Properties
2.4. DNA Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification
2.5. Metabolite Extraction and UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
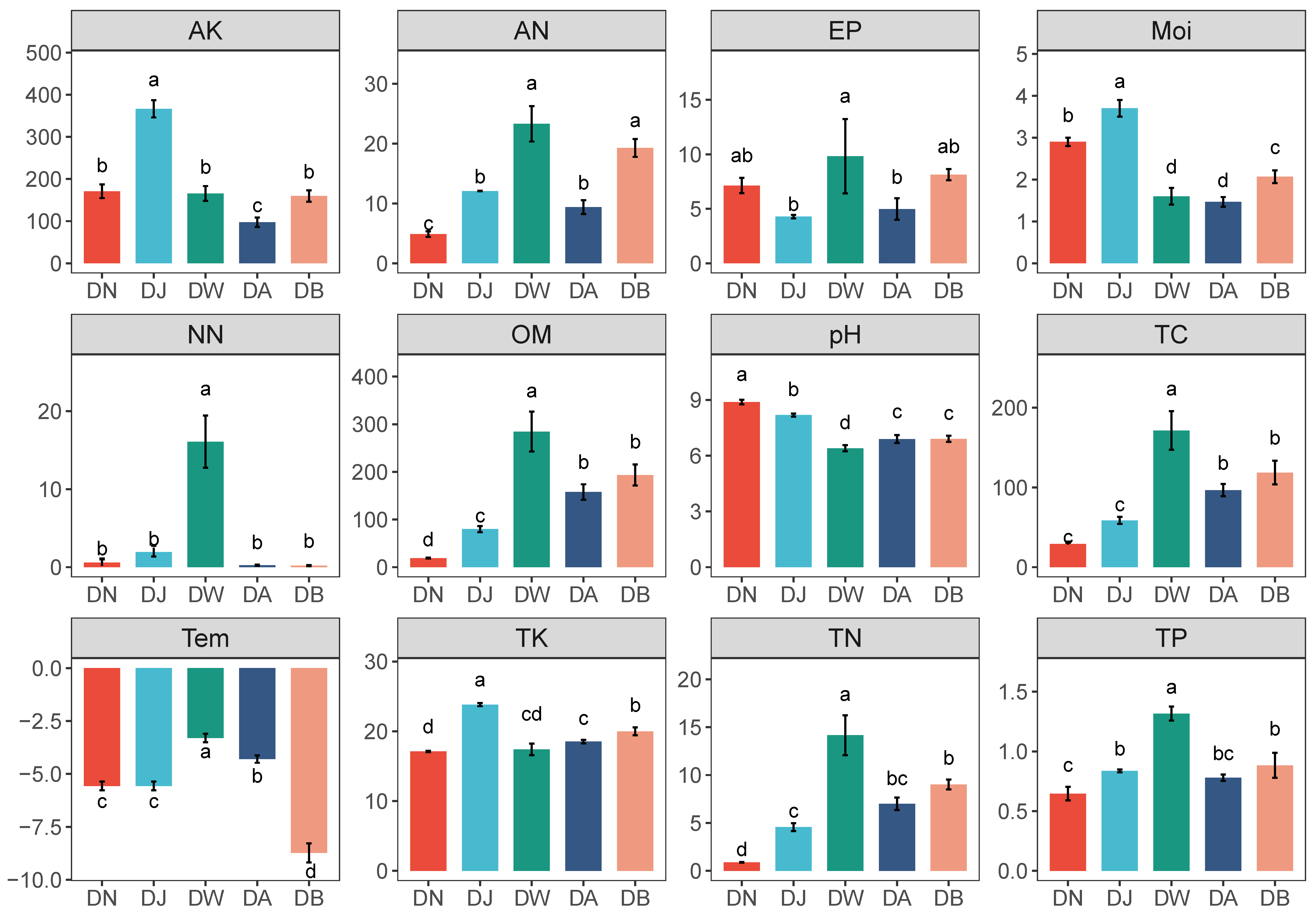
3.1. Environmental Factors
3.2. Bacterial Diversity
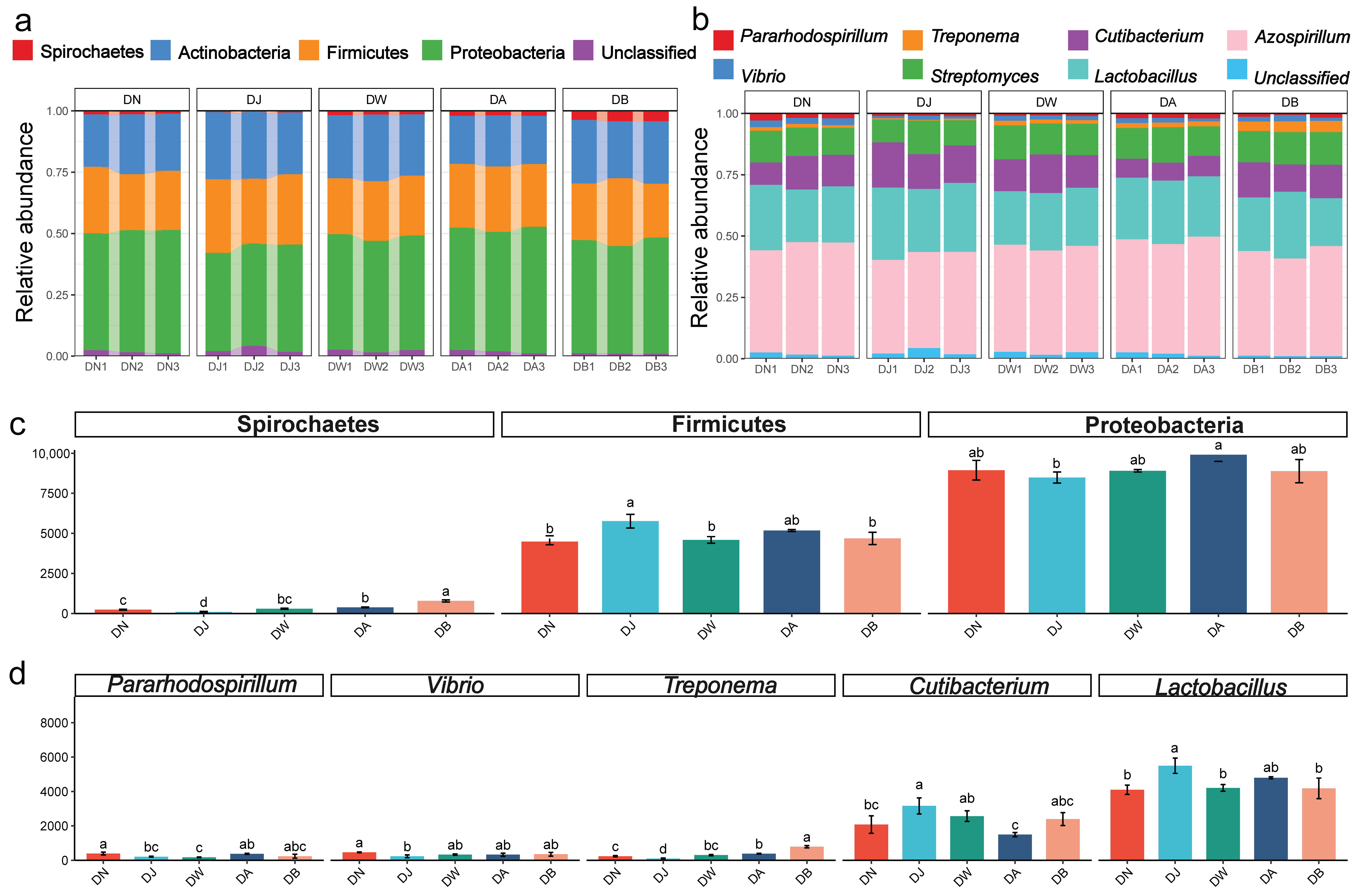
3.3. Bacterial Community Structure
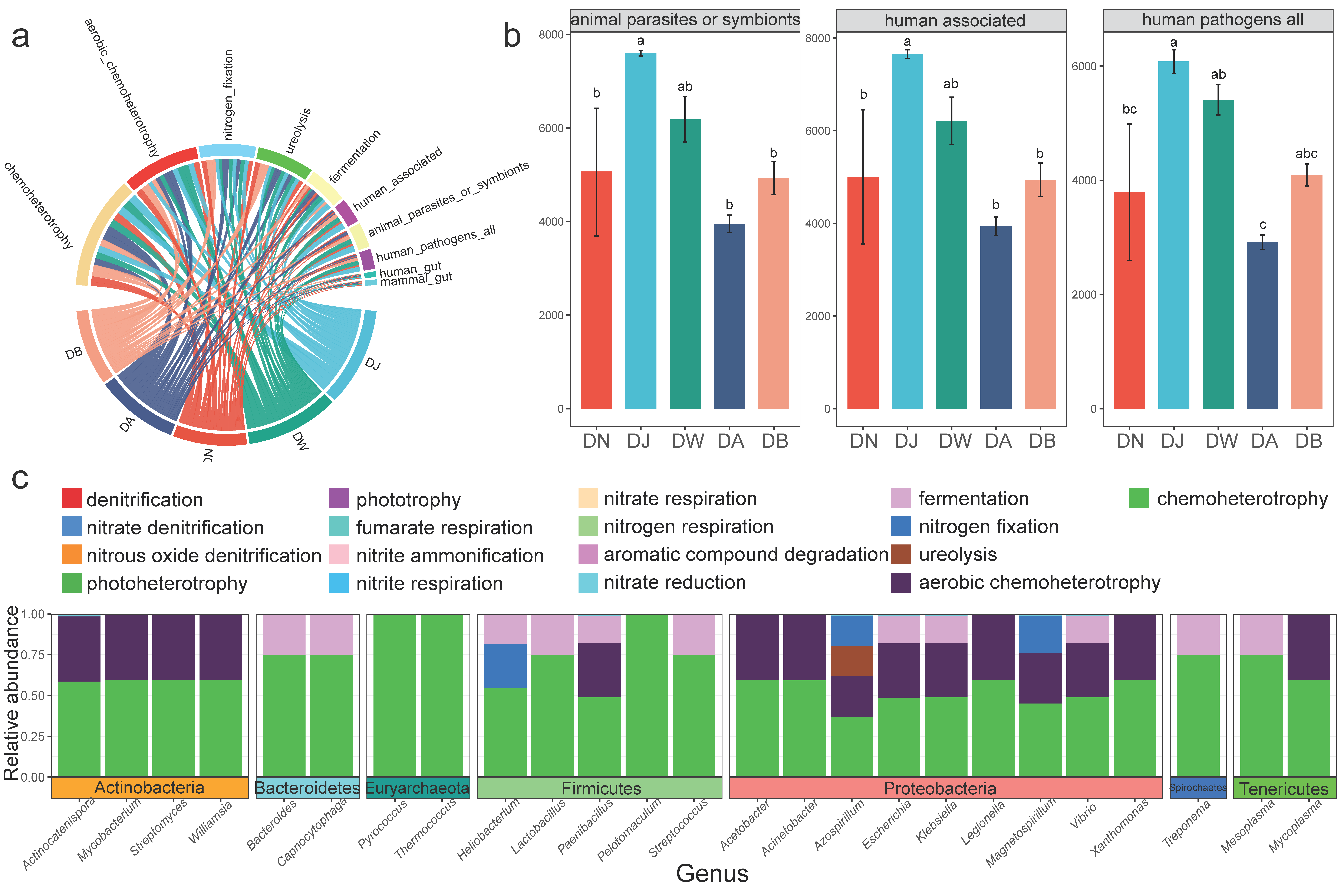
3.4. Bacterial Community Function
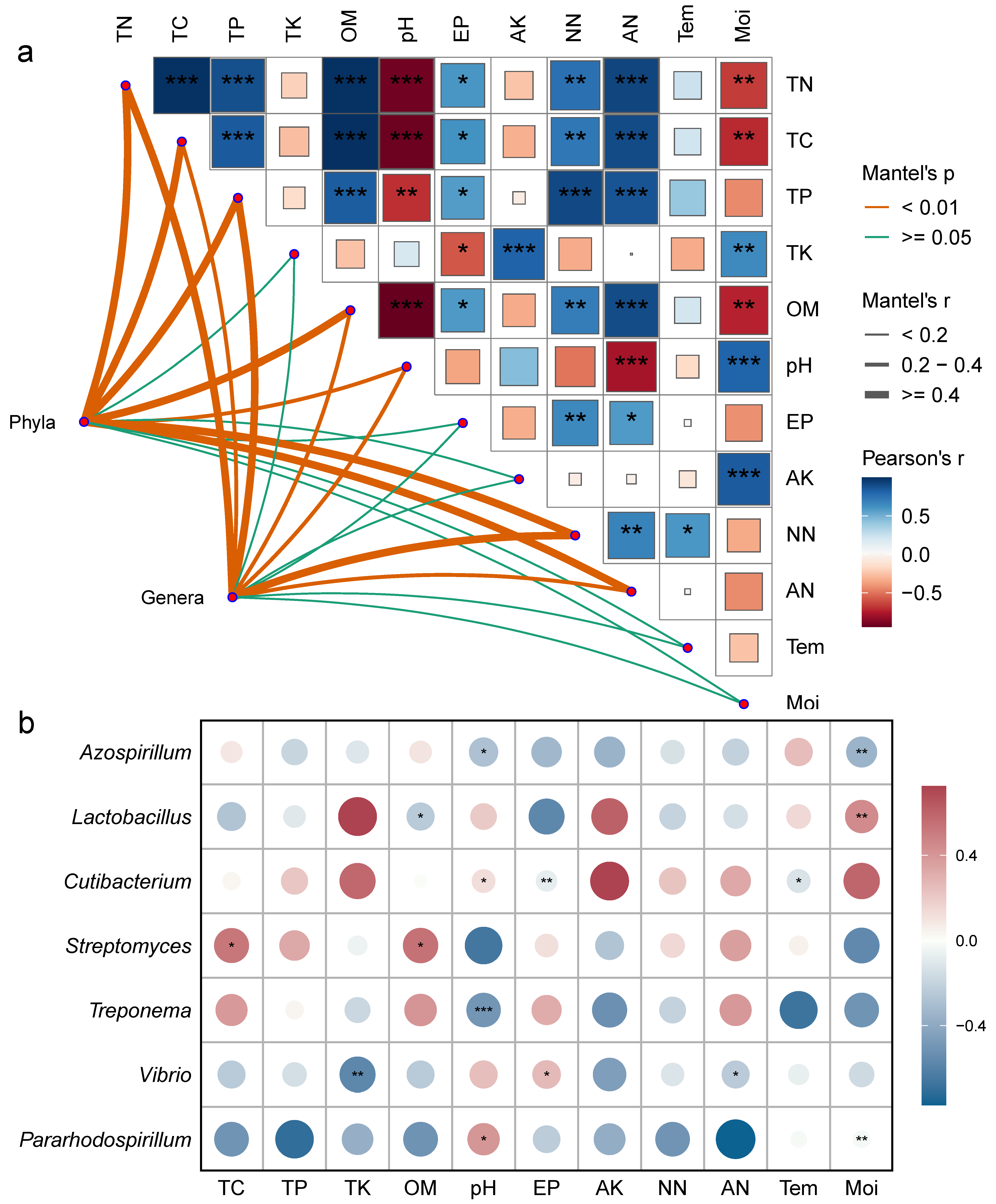
3.5. Correlation Analysis
3.6. Bacterial Community Construction
3.7. Soil Metabolites
3.8. Correlation Analysis Between Soil Metabolites and Dominant Bacterial Communities
3.9. Bacterial Interaction Networks
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Microbial Community Structure to Altitudinal Gradients During the Freezing Period
4.2. Soil Metabolites at Different Altitudinal Gradients During the Freezing Period and Their Interactions with Microorganisms
4.3. Response of Soil Microbial Community Diversity to Altitudinal Gradients During the Freezing Period
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, D.; Qiu, G. China Permafrost; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Ping, C.L.; Yang, D.; Cheng, G.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S. Changes of climate and seasonally frozen ground over the past 30 years in Qinghai–Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau, China. Glob. Planet Change 2004, 43, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, L.; Ji, C.; Hugelius, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Qin, S.; Zhang, B.; Yang, G.; Li, F.; et al. Decadal soil carbon accumulation across Tibetan permafrost regions. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Bai, E.; Yang, Y.; Zong, S.; Hagedorn, F. A global meta-analysis on freeze-thaw effects on soil carbon and phosphorus cycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 108283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lai, C.T.; Mayes, M.A.; Murayama, S.; Xu, X. Microbial seasonality promotes soil respiratory carbon emission in natural ecosystems: A modeling study. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 3035–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Song, C.C.; Wang, X.W.; Ma, X.Y.; Gao, J.L.; Gao, S.Q.; Wang, L.L. Linking soil organic carbon mineralization with soil microbial and substrate properties under warming in permafrost peatlands of Northeastern China. Catena 2021, 203, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.L.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y.T.; Hu, N.L.; Wang, G.D.; Jiang, M. Variations in microbial carbon metabolic activities in sedge peatlands along an altitudinal gradient in the Changbai Mountain, China. Catena 2023, 220, 106722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Jeffries, T.C.; Trivedi, C.; Anderson, I.C.; Lai, K.; McNee, M.; Flower, K.; Singh, B.P.; Minkey, D.; et al. Soil aggregation and associated microbial communities modify the impact of agricultural management on carbon content. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3070–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemergut, D.R.; Costello, E.K.; Meyer, A.F.; Pescador, M.Y.; Weintraub, M.N.; Schmidt, S.K. Structure and function of alpine and arctic soil microbial communities. Res. Microbiol. 2005, 156, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Paredes, C.; T’ajmel, D.; Rousk, J. Can moisture affect temperature dependences of microbial growth and respiration? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, Y.; Qin, W.; Xu, T.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, K.; Zhu, B. Plant and microbial regulations of soil carbon dynamics under warming in two alpine swamp meadow ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Morrissey, E.M.; Mau, R.L.; Hayer, M.; Pĩneiro, J.; Mack, M.C.; Marks, J.C.; Bell, S.L.; Miller, S.N.; Schwartz, E.; et al. The temperature sensitivity of soil: Microbial biodiversity, growth, and carbon mineralization. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, T.; Frauenfeld, O.W.; Wang, K.; Cao, B.; Zhong, X.; Su, H.; Mu, C. Response of seasonal soil freeze depth to climate change across China. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.D.; Wu, T.H. Responses of permafrost to climate change and their environmental significance, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, F02S03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A.G.; McGuire, A.D.; Schadel, C.; Grosse, G.; Harden, J.W.; Hayes, D.J.; Hugelius, G.; Koven, C.D.; Kuhry, P.; Lawrence, D.M.; et al. Climate change and the permafrost carbon feedback. Nature 2015, 520, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, A.K.; Daanen, R.; Anthony, P.; Thomas, S.V.D.; Ping, C.L.; Chanton, J.P.; Grosse, G. Methane emissions proportional to permafrost carbon thawed in Arctic lakes since the 1950s. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.Z.; Li, L.; Wang, X.L.; You, J.; Li, J.N.; Chen, X. Elevational is the main factor controlling the soil microbial community structure in alpine tundra of the Changbai Mountain. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hou, E.; Liu, Y.; Wen, D. Altitudinal patterns and controls of plant and soil nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry in subtropical China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottingham, A.T.; Turner, B.L.; Whitaker, J.; Ostle, N.J.; McNamara, N.P.; Bardgett, R.D.; Salinas, N.; Meir, P. Soil microbial nutrient constraints along a tropical forest elevation gradient: A belowground test of a biogeochemical paradigm. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 6071–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, T.; Tian, P.C.; Gao, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.Q. Effects of microbial agent and microbial fertilizer input on soil microbial community structure and diversity in a peanut continuous cropping system. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 64, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ware, I.; Franke, K.; Frolov, A.; Bureiko, K.; Kysil, E.; Yahayu, M.; El Enshasy, H.A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Comparative metabolite analysis of Piper sarmentosum organs approached by LC-MS-based metabolic profiling. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2024, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, J. Elevational characteristics of soil bacterial community and their responses to soil translocation at a mountainside in northwest Sichuan, China. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 17906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Huang, P.; Zhu, K.; Gao, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Ran, Y.; Chen, S.; Ma, M.; Wu, S. Zonation of bulk and rhizosphere soil bacterial communities and their covariation patterns along the elevation gradient in riparian zones of three Gorges reservoir, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, D. Water level fluctuations influence microbial communities and mercury methylation in soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 68, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, J.; Cong, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y. Distinct Elevational Patterns and Their Linkages of Soil Bacteria and Plant Community in An Alpine Meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Sui, Y.; Xu, Q.; Geisen, F.; Sun, B. Organism body size structures the soil microbial and nematode community assembly at a continental and global scale. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Jeffries, T.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Encinar, D.; Berdugo, M.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Palacios, P.; Vandegehuchte, M.L.; Shaw, E.A.; Dam, M.; Post, K.H.; Ramirez, K.S.; Sylvain, Z.A.; de Tomasel, C.M.; Wall, D.H. Are there links between responses of soil microbes and ecosystem functioning to elevated CO2, N deposition and warming? A global perspective. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 1590–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shen, C.; Jiang, L.; Feng, Z.; Fang, J. Difference in soil bacterial community composition depends on forest type rather than nitrogen and phosphorus additions in tropical montane rainforests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Yang, X. Discrepant diversity patterns and function of bacterial and fungal communities on an earthquake-prone mountain gradient in Northwest Sichuan, China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1217925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, X. Elevation rather than season determines the assembly and co-occurrence patterns of soil bacterial communities in forest ecosystems of Mount Gongga. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7589–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Shi, Y.; Fan, K.; He, J.S.; Adams, J.M.; Ge, Y.; Chu, H. Soil pH dominates elevational diversity pattern for bacteria in high elevation alkaline soils on the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz0033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; He, M.; Adams, J.M.; Chu, H. Strong partitioning of soil bacterial community composition and co-occurrence networks along a small-scale elevational gradient on Zijin Mountain. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 3, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Wei, G. Co-occurrence patterns of soybean rhizosphere microbiome at a continental scale. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 118, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; McCormack, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, G.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Linkages between the soil organic matter fractions and the microbial metabolic functional diversity within a broad-leaved Korean pine forest. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2015, 66, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Purahong, W.; Yang, L. Contrasting altitudinal patterns and co-occurrence networs of soil bacterial and fungal communities along soil depths in the cold-temperate montane forests of China. Catena 2021, 209, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L. Seasonal variations in soil fungal communities and cooccurrence networks along an altitudinal gradient in the cold temperate zone of China: A case study on Oakley Mountain. Catena 2021, 204, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, J.; Suárez-Estrella, F.; Vargas-García, M.; López, M.; Jurado, M.; Moreno, J. Dynamics of bacterial microbiota during lignocellulosic waste composting: Studies upon its structure, functionality and biodiversity. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trovato, M.; Funck, D.; Forlani, G.; Okumoto, S.; Amir, R. Amino acids in plants: Regulation and functions in development and stress defense. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 772810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Feng, Y.; Dang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Qi, H.; Feng, B. Linkages of microbial community structure and root exudates: Evidence from microbial nitrogen limitation in soils of crop families. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikoyi, I.; Fowler, A.; Schmalenberger, A. One-time phosphate fertilizer application to grassland columns modifies the soil microbiota and limits its role in ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, R.C.I.; Newsham, K.K.; Hill, P.W.; Stott, A.; Jones, D.L. Differential acquisition of amino acid and peptide enantiomers within the soil microbial community and its implications for carbon and nitrogen cycling in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yuan, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, F.; Hou, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhai, L.; Cui, Z.; Zou, Y. Methane production and characteristics of the microbial community in the co-digestion of spent mushroom substrate with dairy manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 32, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.G.; Takagi, H. Microbial alkaline proteases: From a bioindustrial viewpoint. Biotechnol. Adv. 1999, 17, 561–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wan, S.; Hua, K.; Yin, Y.; Chu, H.; Wang, D.; Guo, X. Fertilization regime has a greater effect on soil microbial community structure than crop rotation and growth stage in an agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 149, 103510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Gunina, A.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Hemp, A.; Classen, A.T.; Ge, Y. Contrasting patterns and drivers of soil bacterial and fungal diversity across a mountain gradient. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottingham, A.T.; Fierer, N.; Turner, B.L.; Whitaker, J.; Ostle, N.J.; McNamara, N.P. Microbes follow Humboldt: Temperature drives plant and soil microbial diversity patterns from the Amazon to the Andes. Ecology 2018, 99, 2455–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Huang, R.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.L. A monotonically declining elevational pattern of bacterial diversity in freshwater lake sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 5175–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Yang, T.; Xia, S.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Sun, R.; Gao, H.; Chu, H.; Ma, C. Soil depth exerts stronger impact on bacterial community than elevation in subtropical forests of Huangshan Mountain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Ni, Y.Y.; Liang, W.J.; Wang, J.J.; Chu, H.Y. Distinct soil bacterial communities along a small-scale elevational gradient in alpine tundra. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.X.; Bing, H.J.; Fang, L.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Yu, J.L.; Shen, G.T.; Jiang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.C. Diversity patterns of the rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial communities along an altitudinal gradient in an alpine ecosystem of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2019, 338, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




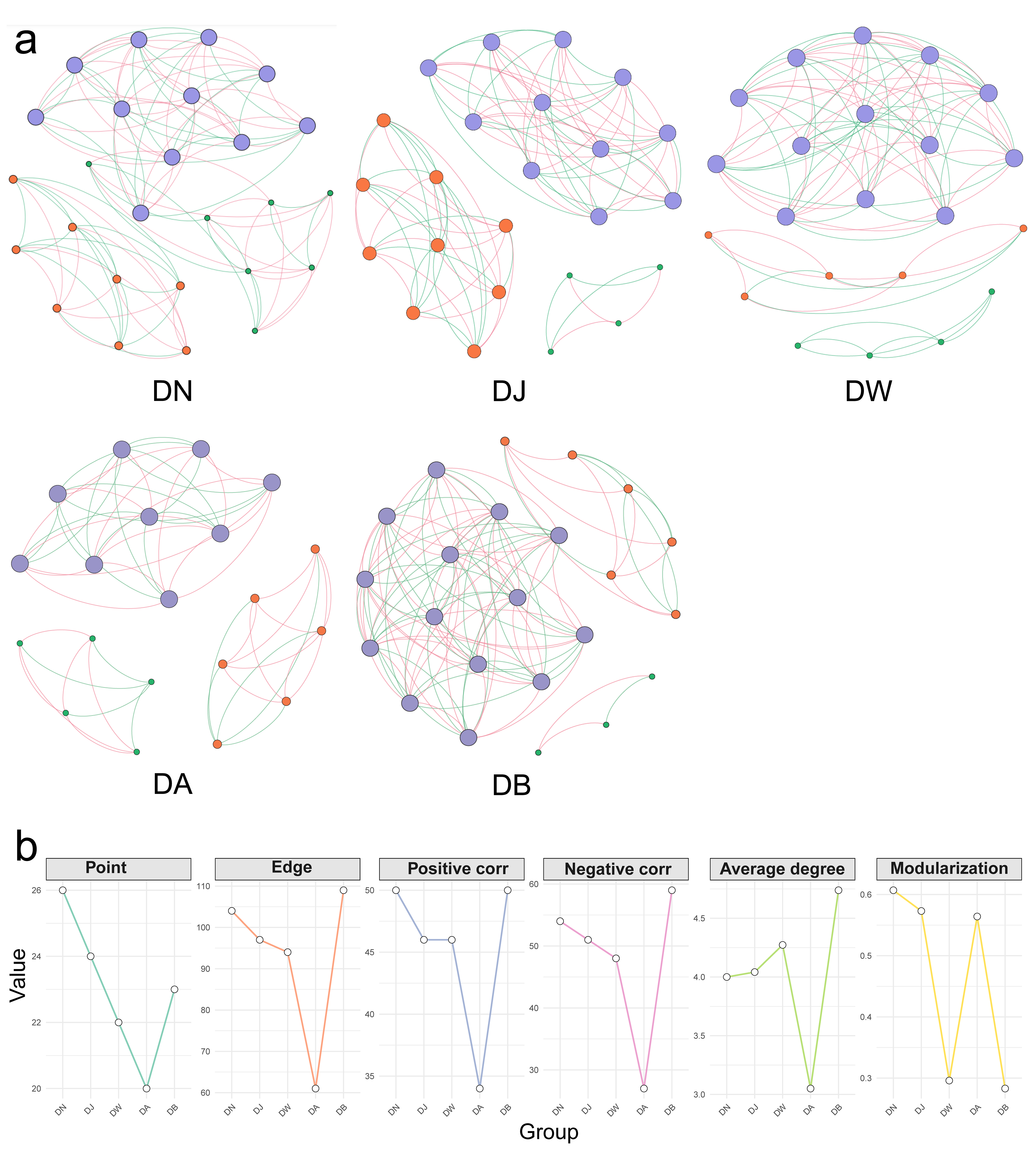
| Group | Average Degree | Modularization | Edge | Negative Correlation | Positive Correlation | Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN | 4.000 | 0.607 | 104 | 54 | 50 | 26 |
| DJ | 4.042 | 0.573 | 97 | 51 | 46 | 24 |
| DW | 4.273 | 0.296 | 94 | 48 | 46 | 22 |
| DA | 3.050 | 0.564 | 61 | 27 | 34 | 20 |
| DB | 4.739 | 0.283 | 109 | 59 | 50 | 23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Ma, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, K. Vertical Stratification Reduces Microbial Network Complexity and Disrupts Nitrogen Balance in Seasonally Frozen Ground at Qinghai Lake in Tibet. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020459
Zhang N, Zhou Z, Wang Y, Zhou S, Ma J, Sun J, Chen K. Vertical Stratification Reduces Microbial Network Complexity and Disrupts Nitrogen Balance in Seasonally Frozen Ground at Qinghai Lake in Tibet. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(2):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020459
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ni, Zhiyun Zhou, Yijun Wang, Shijia Zhou, Jing Ma, Jianqing Sun, and Kelong Chen. 2025. "Vertical Stratification Reduces Microbial Network Complexity and Disrupts Nitrogen Balance in Seasonally Frozen Ground at Qinghai Lake in Tibet" Microorganisms 13, no. 2: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020459
APA StyleZhang, N., Zhou, Z., Wang, Y., Zhou, S., Ma, J., Sun, J., & Chen, K. (2025). Vertical Stratification Reduces Microbial Network Complexity and Disrupts Nitrogen Balance in Seasonally Frozen Ground at Qinghai Lake in Tibet. Microorganisms, 13(2), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020459





