Biochemical Features of the Cry3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis and Its Toxicity to the Red Imported Fire Ant Solenopsis invicta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of and Culture Conditions for Btt
2.2. Purification of Native Cry3A Toxin
2.3. Cloning and Expression of the cry3a Gene
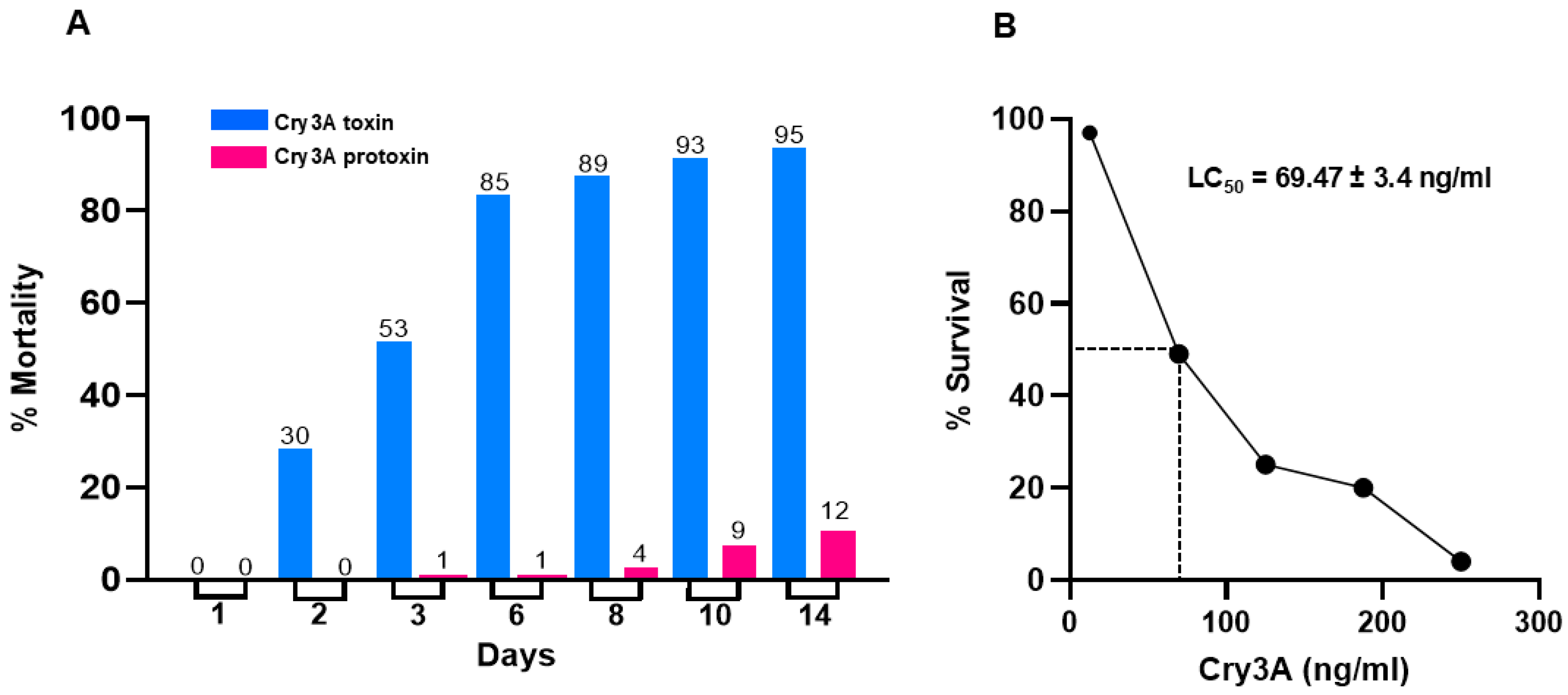
2.4. Fire Ant Maintenance and Bioassays
3. Results
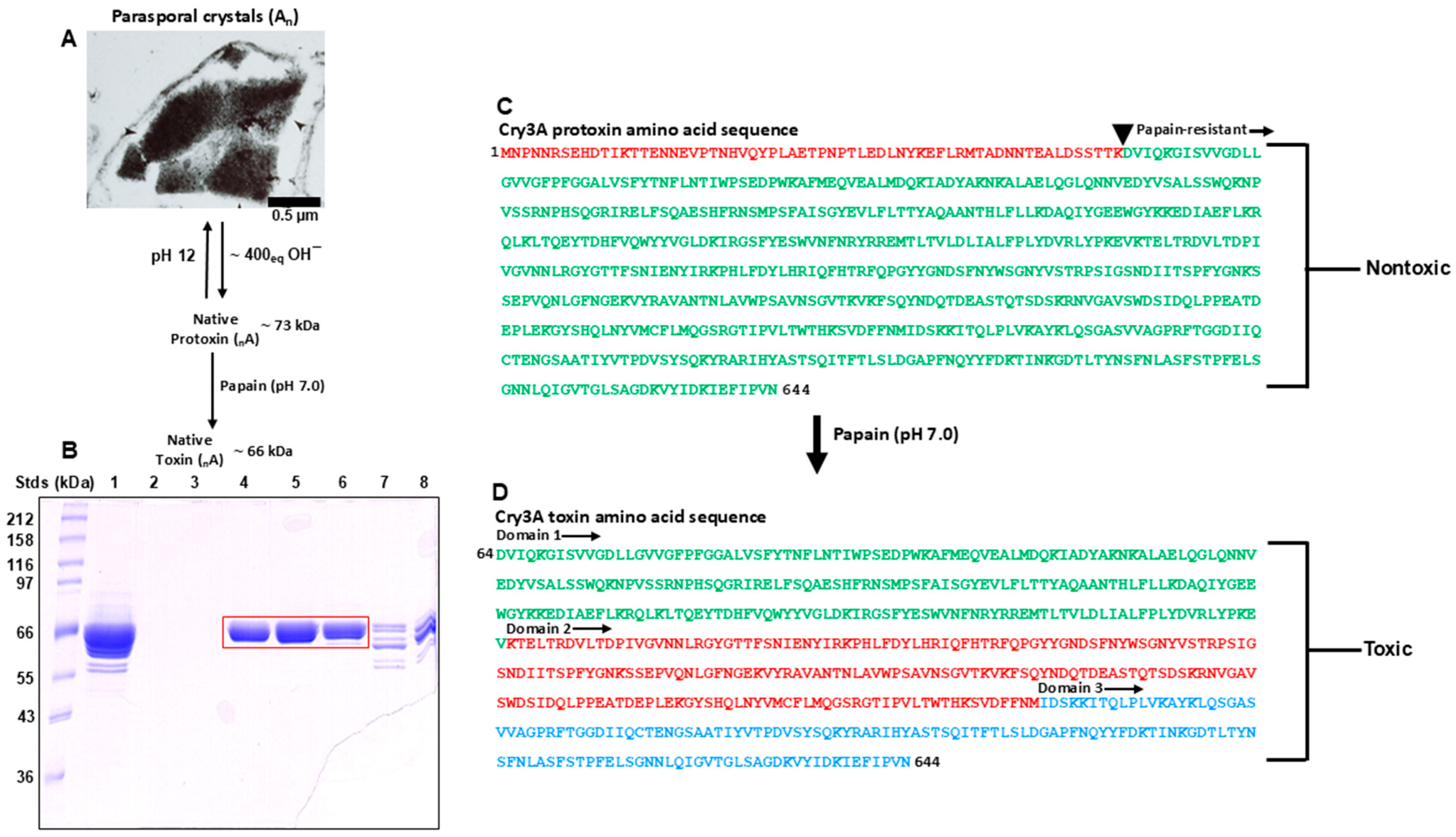
3.1. Domain Structure of the Cry3A Toxin
3.2. Cloning and Expression of the cry3a Gene
3.3. Toxicity of Recombinant Cry3A Toxin to Worker Ants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krieg, A.; Huger, A.M.; Langenbruch, G.A.; Schnetter, W. Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis: Ein neuer, gegenuber Larven von Coleoptern wirksamer Pathotyp. Z. Agnew. Entomol. 1983, 96, 500–508. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.; Ji, X.; Yang, J.; Liang, L.; Si, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, D. Transgenic potato plants expressing cry3A gene confer resistance to Colorado potato beetle. Comptes Rendus Biol. 2015, 338, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehian, H.; Rahnama, H.; Dezhsetan, S.; Babaei, S. Constitutive expression of cry3A gene in transgenic potato plants for resistance to Colorado potato beetle (CPB). Potato Res. 2021, 64, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.-C.; Zhao, L.-H. Pyridine alkaloids in the venom of imported fire ants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11388–11395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potiwat, R.; Sitcharungsi, R. Ant allergens and hypersensitivity reactions in response to ant stings. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 33, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Meléndez, S.; Miranda, A.; García-González, J.J.; Barber, D.; Lombardero, M. Anaphylaxis caused by imported red fire ant stings in Málaga, Spain. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 17, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- More, D.R.; Kohlmeier, R.E.; Hoffman, D.R. Fatal anaphylaxis to indoor native fire ant stings in an infant. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2008, 29, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu-Sheng, L.; Huang, S.-A.; Lin, I.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Lai, H.-K.; Yang, C.-H.; Huang, R.-N. Establishment and social impacts of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta, (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, R.; Zeng, L.; Du, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y. Mental health effects caused by red imported fire ant attacks (Solenopsis invicta). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petralia, R.S.; Vinson, B. Internal anatomy of the fourth instar larva of the imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta Buren (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 1980, 9, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wilcox, X.E.; Fisher, A.J.; Boyd, S.D.; Zhi, J.; Winkler, D.D.; Bulla, L.A., Jr. Functional and structural analysis of the toxin-binding site of the cadherin G-protein-coupled receptor, BT-R1, for Cry1A toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Bulla, L.A., Jr. Cell death signaling in Anopheles gambiae initiated by Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4B toxin involves Na+/K+ ATPase. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfiore, C.J.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Osman, Y.A.; Bulla, L.A., Jr. A specific binding protein from Tenebrio molitor for the insecticidal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 200, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Chemical Safety: Pesticides, World Health Organization (2020). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/chemical-safety-pesticides (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Bertani, G. Lysogeny at mid-twentieth century: P1, P2, and other experimental systems. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Carroll, J.; Ellar, D.J. Crystal structure of insecticidal δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 1991, 353, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Lofgren, C.S.; Jouvenaz, D.P.; Stringer, C.E.; Bishop, P.M.; Williams, D.F.; Wojcik, D.P.; Glancey, B.M. Techniques for Collecting, Rearing, and Handling Imported Fire Ants; USDA, SEA, AATS-S-21: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; 9p.
- Schesser, J.H.; Bulla, L.A., Jr. Toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis spores to the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grochulski, P.; Masson, L.; Borisova, S.; Pusztai-Carey, M.; Schwartz, J.L.; Prousseau, R.; Cygler, M. Bacillus thuringiensis CryIA(a) insecticidal toxin crystal structure and channel formation. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonserm, P.; Davis, P.; Ellar, D.J.; Li, J. Crystal structure of the mosquito-larvicidal toxin Cry4Ba and its biological implications. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, S.A.; Perlak, F.J.; Fuchs, R.L.; Marrone, P.G.; Lavrik, P.B.; Fischhoff, D.A. Characterization of the coleopteran-specific protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis. Nat. Biotechnol. 1988, 6, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschinkel, W.R. The Fire Ants; Belknap Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; 752p. [Google Scholar]
- Tschinkel, W.R. The Wonder, Beauty, and Science of Underground Nests; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2021; 248p. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulla, L.A., Jr. Biochemical Features of the Cry3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis and Its Toxicity to the Red Imported Fire Ant Solenopsis invicta. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020371
Bulla LA Jr. Biochemical Features of the Cry3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis and Its Toxicity to the Red Imported Fire Ant Solenopsis invicta. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(2):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020371
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulla, Lee A., Jr. 2025. "Biochemical Features of the Cry3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis and Its Toxicity to the Red Imported Fire Ant Solenopsis invicta" Microorganisms 13, no. 2: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020371
APA StyleBulla, L. A., Jr. (2025). Biochemical Features of the Cry3A Toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tenebrionis and Its Toxicity to the Red Imported Fire Ant Solenopsis invicta. Microorganisms, 13(2), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13020371





