Epstein–Barr Virus Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Modulating m6A-Dependent YTHDF1–TSC22D1 Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
2.2. Clinical Tissue Samples
2.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Transcriptomic Analysis
2.6. Microarray Analysis
2.7. Transfection of siRNA and Overexpression Vector
2.8. MTT Assay (Cell Viability Assay)
2.9. Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay
2.10. Wound Healing Assay
2.11. Apoptosis Assay
2.12. m6A RNA Methylation Quantification (ELISA-Based Method)
2.13. m6A RNA Immunoprecipitation (MeRIP) and m6A Sequencing
2.14. RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP)
2.15. UZH1a Treatment
2.16. RNA Stability Assay
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
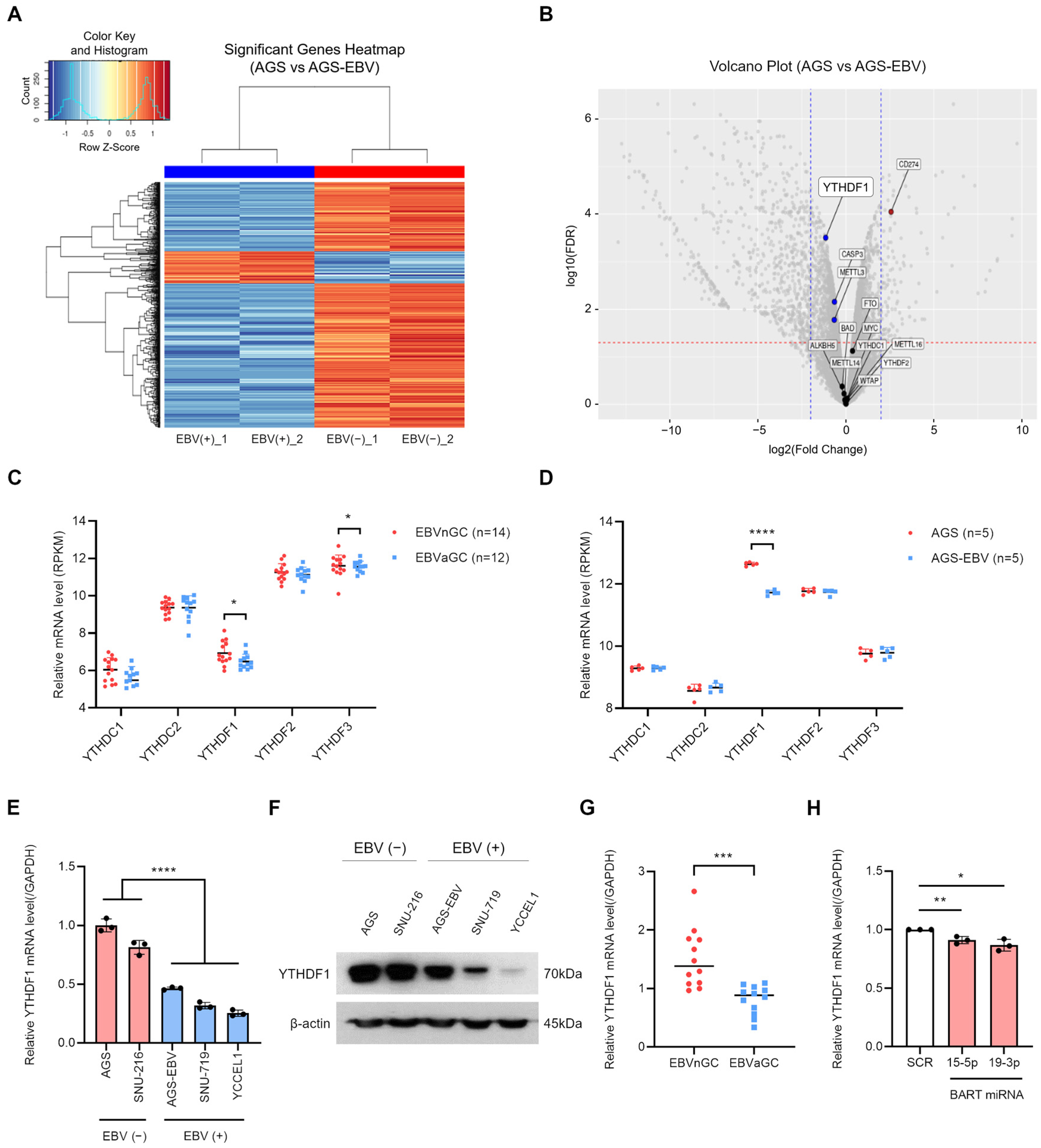
3.1. EBV Infection Suppresses YTHDF1 Expression in Gastric Cancer
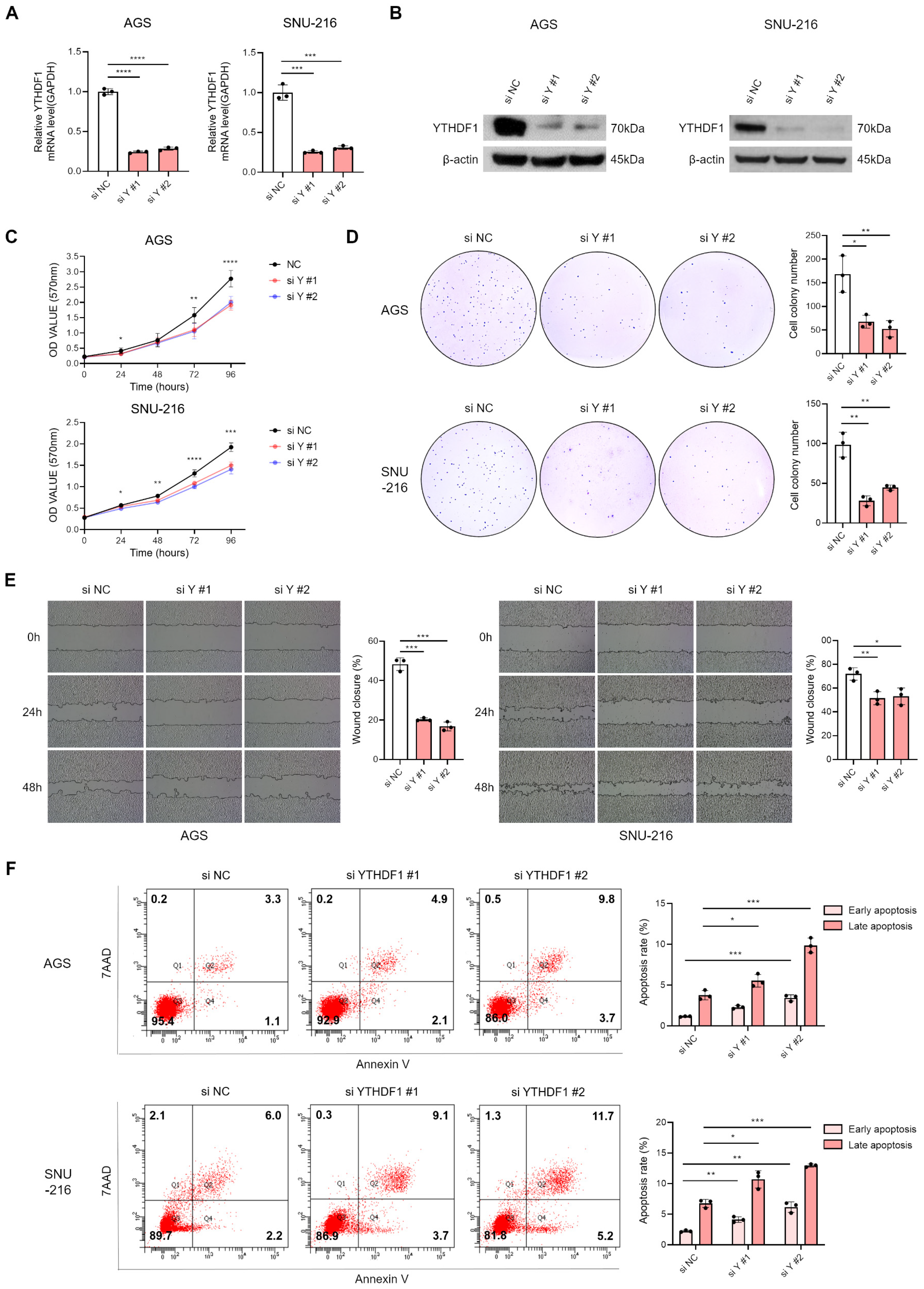
3.2. Suppression of YTHDF1 Expression Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells
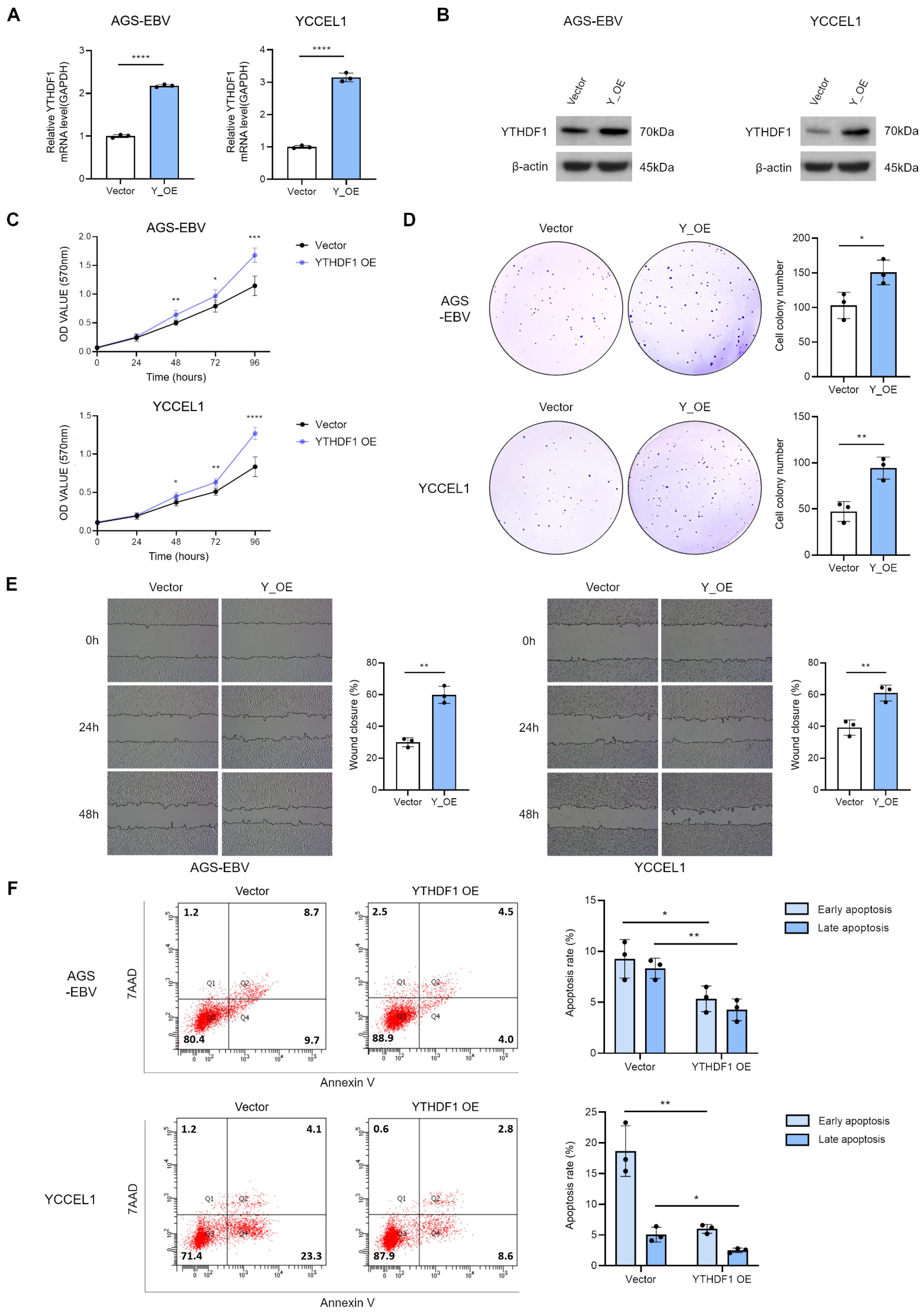
3.3. Overexpression of YTHDF1 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells
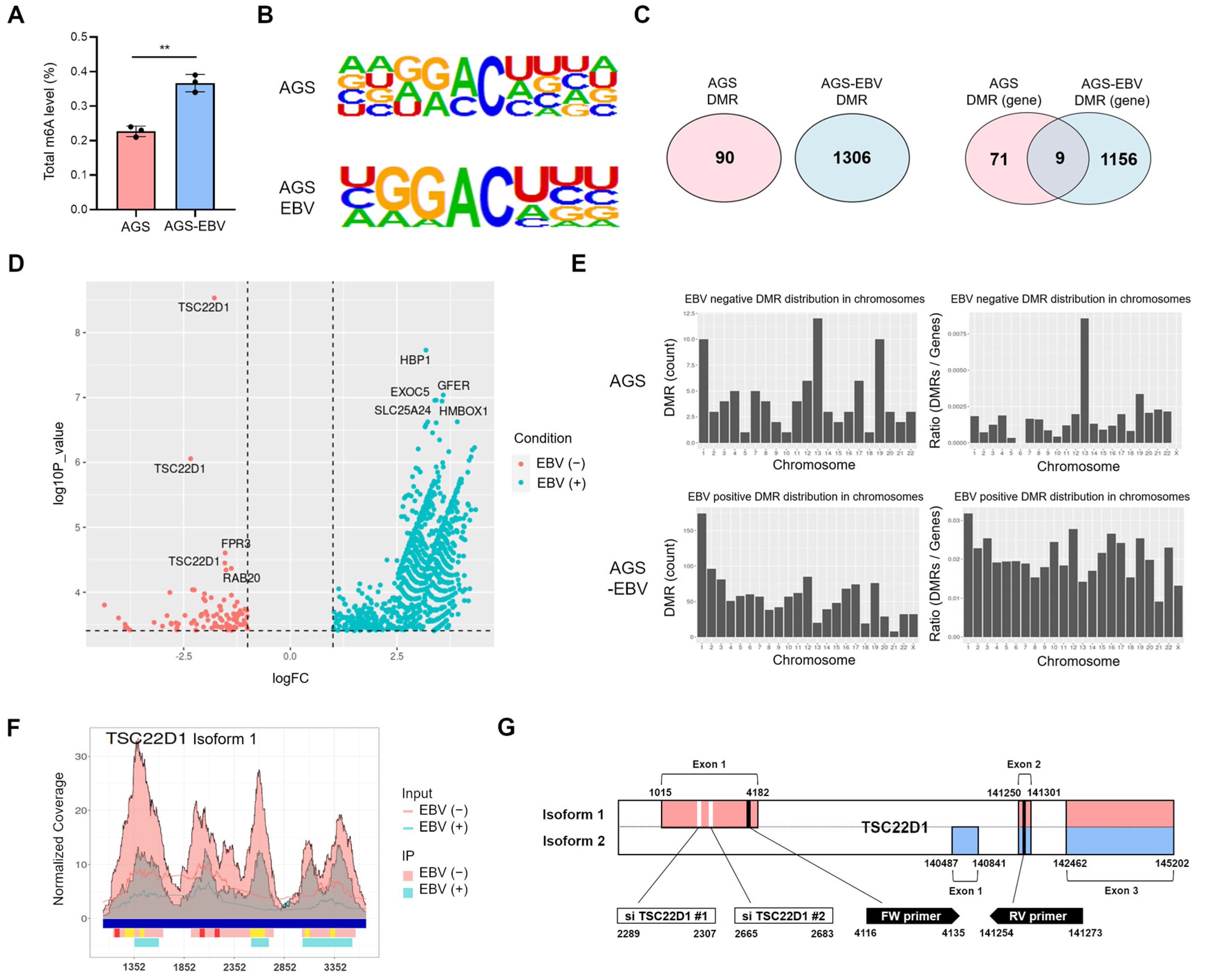
3.4. EBV Infection Modulates the m6A Methylation Pattern of TSC22D1 in Gastric Cancer Cells
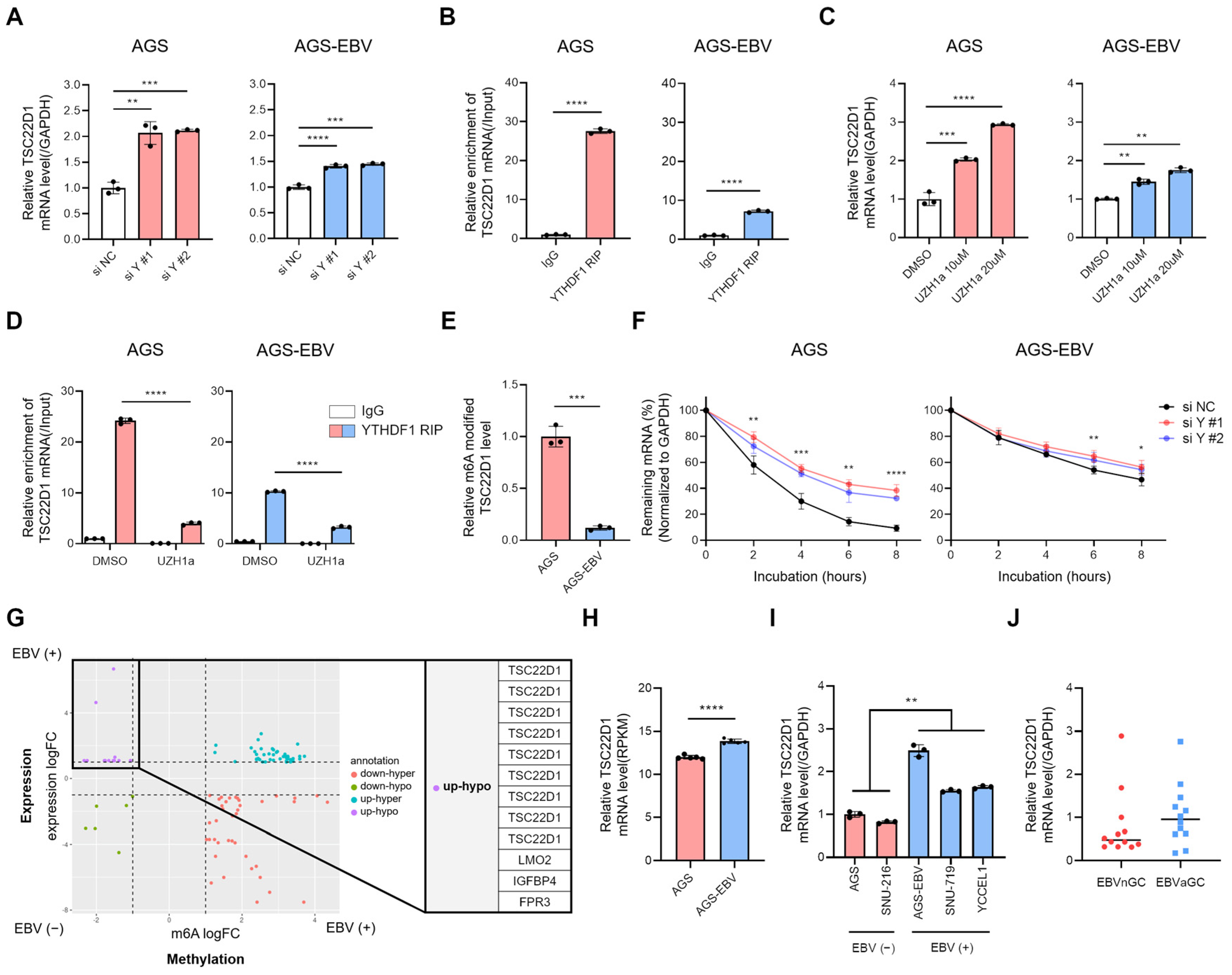
3.5. YTHDF1 Binds to TSC22D1 mRNA and Regulates Its Stability in an m6A-Dependent Manner
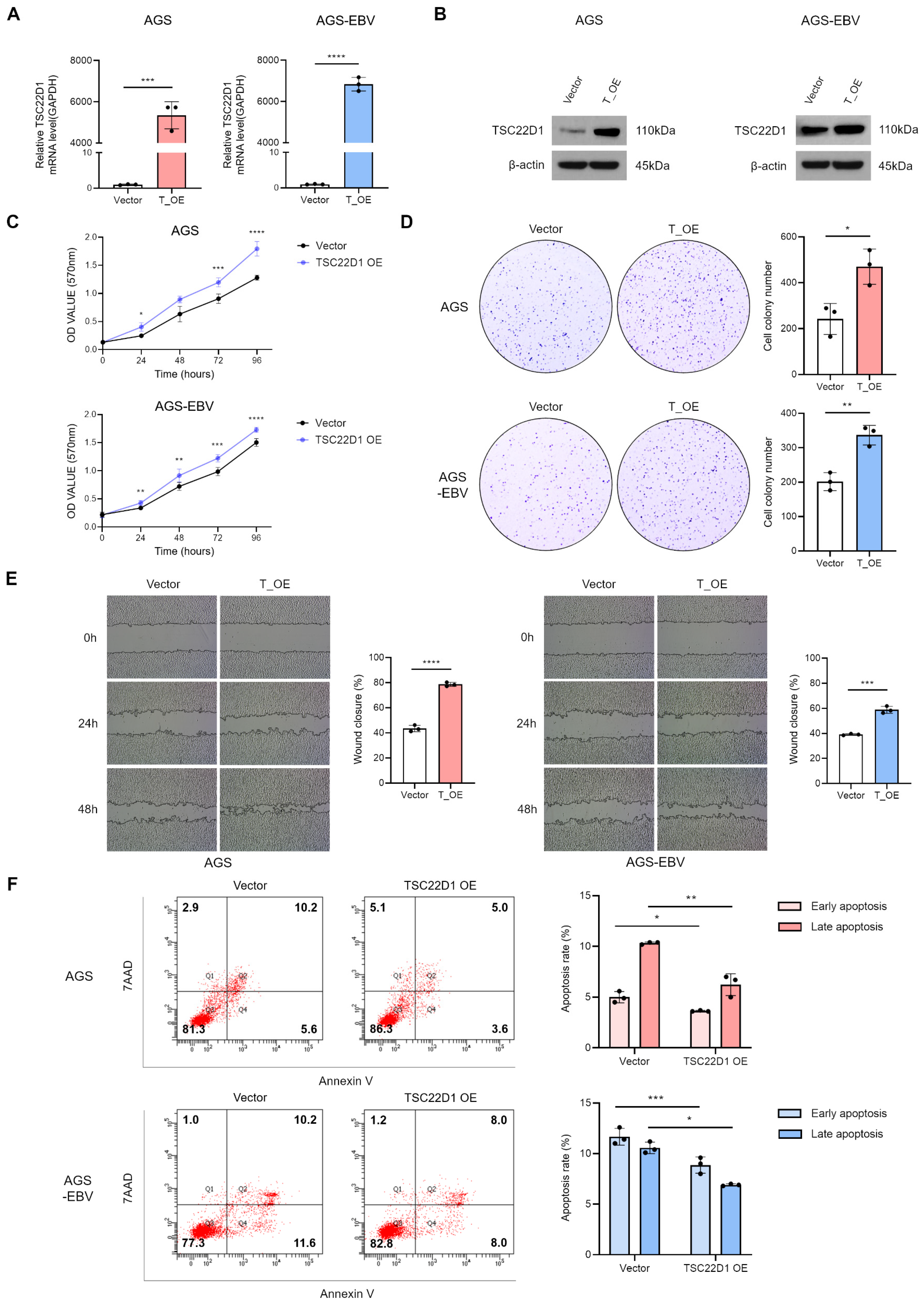
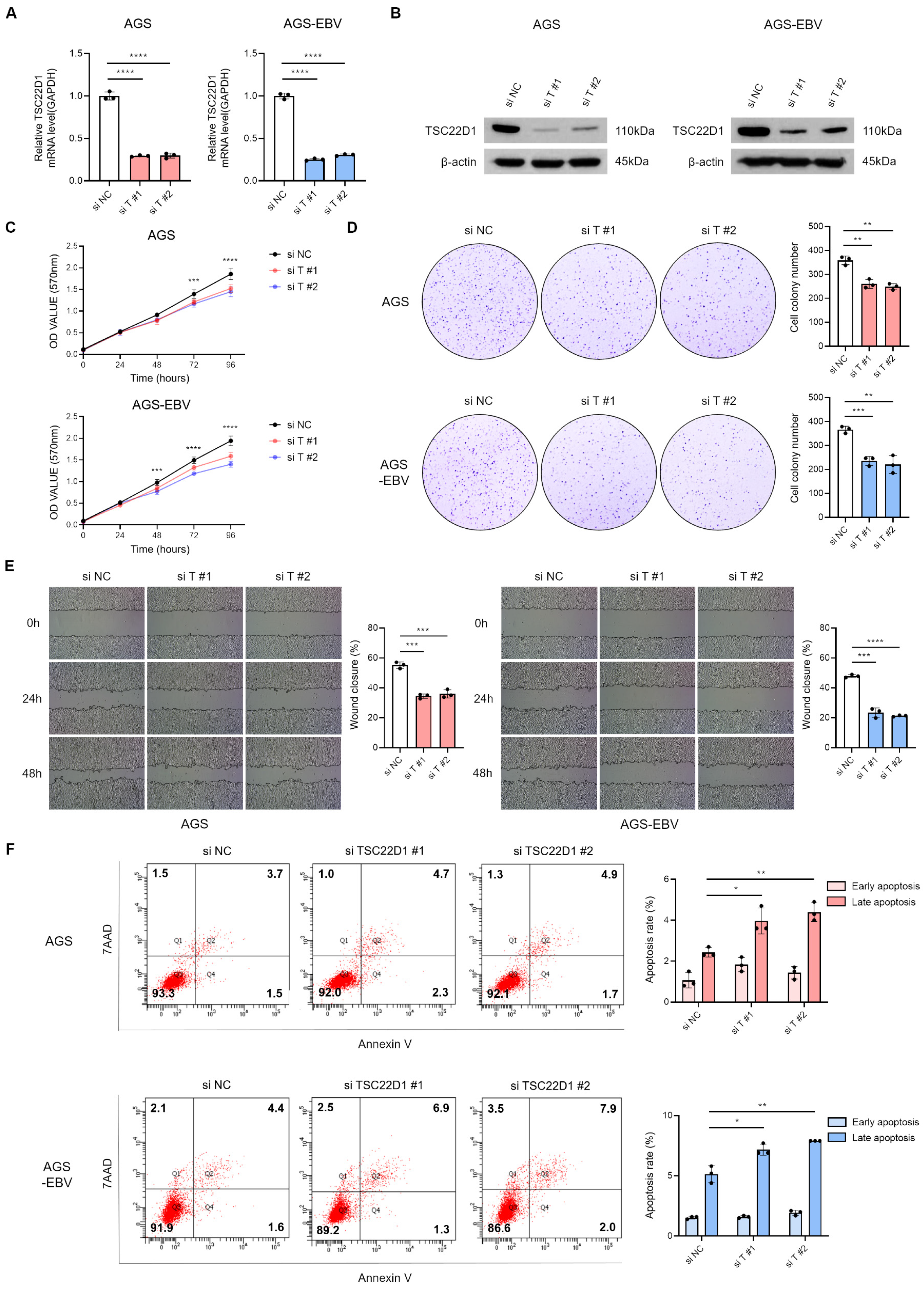
3.6. Silencing of TSC22D1 Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells
3.7. Overexpression of TSC22D1 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells
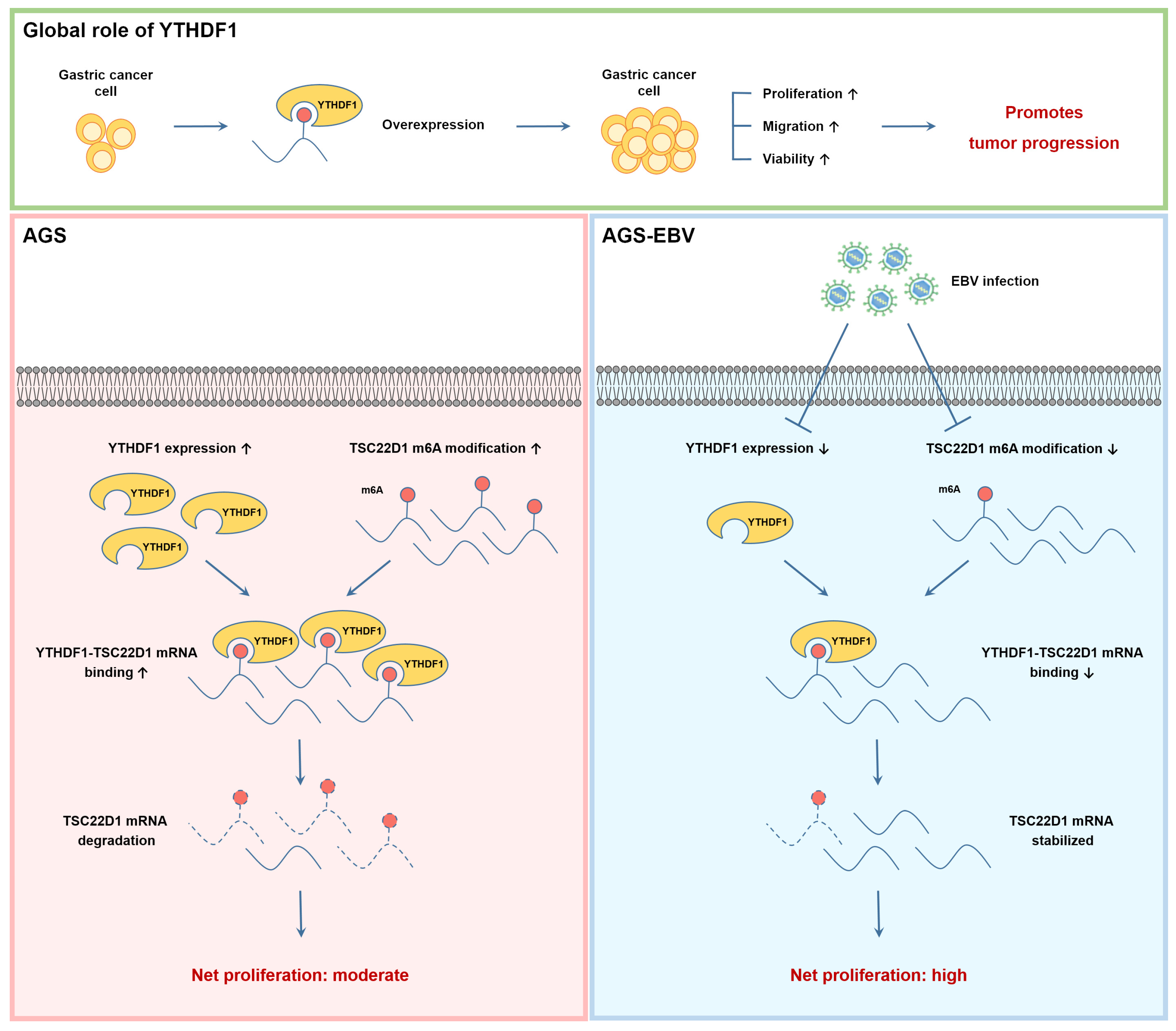
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirabayashi, M.; Georges, D.; Clifford, G.M.; De Martel, C. Estimating the Global Burden of Epstein-Barr Virus–Associated Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 922–930.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.; Groen-van Schooten, T.S.; Brugman, C.P.; Jamaludin, F.S.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Derks, S. The Tumor Immune Composition of Mismatch Repair Deficient and Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 127, 102737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, B.; Hu, G.; Gan, R. Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer: A Distinct Subtype. Cancer Lett. 2020, 495, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, M.; Barzi, A.; Brezden-Masley, C.; Puccini, A.; Berger, M.D.; Tokunaga, R.; Battaglin, F.; Soni, S.; McSkane, M.; Zhang, W.; et al. Outlooks on Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Gastric Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 66, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempera, I.; Lieberman, P.M. Epigenetic Regulation of EBV Persistence and Oncogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 26, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, J.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Nakamura, M.; Saito, M.; Sasaki, S.; Shimokuri, K.; Yanagihara, M.; Sakai, K.; Suehiro, Y.; et al. The Role of Epigenetic Regulation in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.C.; He, C. m6A RNA Methylation: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Potential. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, B.; Nie, Z.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y. The Role of m6A Modification in the Biological Functions and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Laurent, B.; Hsu, C.-H.; Nachtergaele, S.; Lu, Z.; Sheng, W.; Xu, C.; Chen, H.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. RNA m6A Methylation Regulates the Ultraviolet-Induced DNA Damage Response. Nature 2017, 543, 573–576, Erratum in Nature 2017, 552, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.-S.; Li, M.-M.; Wang, X.-J.; Yang, Y.-G. N6-Methyl-Adenosine (m6A) in RNA: An Old Modification with a Novel Epigenetic Function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2013, 11, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Wu, R.; Ming, L. The Role of m6A RNA Methylation in Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Mutti, L.; Peng, J.; Jiang, X. The Function and Clinical Implication of YTHDF1 in the Human System Development and Cancer. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Jaffrey, S.R. A Unified Model for the Function of YTHDF Proteins in Regulating m6A-Modified mRNA. Cell 2020, 181, 1582–1595.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, V.; Selberg, S.; Lalowski, M.; Karelson, M.; Kankuri, E. The Structure and Function of YTHDF Epitranscriptomic m6A Readers. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-X.; Li, L.-M.; Sun, H.-L.; Liu, S.-M. Link Between m6A Modification and Cancers. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, X.; Xia, M.; Zhong, J. The Roles and Mechanisms of the m6A Reader Protein YTHDF1 in Tumor Biology and Human Diseases. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, D.; Zeng, X.; Luo, Z. YTHDF1 Upregulation Mediates Hypoxia-Dependent Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis through Regulating PKM2 to Affect Glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lin, C.; Lin, X.; Lin, P.; He, R.; Pan, X.; Lin, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhu, G. NAT10 Phase Separation Regulates YTHDF1 Splicing to Promote Gastric Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 3207–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, G. The Functions of N-Methyladenosine (m6A) Modification on HIV-1 mRNA. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. Regulation of Virus Replication and T Cell Homeostasis by N6-Methyladenosine. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, W.; Chen, M.; Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-binding Protein YTHDF1 Suppresses EBV Replication and Promotes EBV RNA Decay. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e50128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Long, N.P.; Min, J.E.; Kim, H.M.; Yoon, J.H.; Anh, N.H.; Park, M.C.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, S.K. Comprehensive Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Aberrant Metabolism of Epstein-Barr-Virus-Associated Gastric Carcinoma. Cells 2019, 8, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map Format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Meyer, C.A.; Eeckhoute, J.; Johnson, D.S.; Bernstein, B.E.; Nusbaum, C.; Myers, R.M.; Brown, M.; Li, W.; et al. Model-Based Analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhan, Q.; Eckert, M.; Zhu, A.; Chryplewicz, A.; De Jesus, D.F.; Ren, D.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Lengyel, E.; He, C.; et al. RADAR: Differential Analysis of MeRIP-Seq Data with a Random Effect Model. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Amariglio, N.; Rechavi, G. Transcriptome-Wide Mapping of N6-Methyladenosine by m6A-Seq Based on Immunocapturing and Massively Parallel Sequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Lin, P.; Chen, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.E.; Wu, C.-I. Direct Measurement of Pervasive Weak Repression by microRNAs and Their Role at the Network Level. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; He, C.; Parisien, M.; Pan, T. N6-Methyladenosine-Dependent RNA Structural Switches Regulate RNA-Protein Interactions. Nature 2015, 518, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesser, C.R.; Karijolich, J.; Dominissini, D.; He, C.; Glaunsinger, B.A. N6-Methyladenosine Modification and the YTHDF2 Reader Protein Play Cell Type Specific Roles in Lytic Viral Gene Expression during Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; da Silva, S.R.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J.; Cui, X.; Yuan, H.; Sorel, O.; Zhang, S.; et al. Viral and Cellular N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) and N6, 2’-O-Dimethyladenosine (m6Am) Epitranscriptomes in KSHV Life Cycle. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, N.S.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Mattocks, M.D.; Holley, C.L.; Lazear, H.M.; Mason, C.E.; Horner, S.M. Altered m6A Modification of Specific Cellular Transcripts Affects Flaviviridae Infection. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 542–555.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Su, T.; Wu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, C.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Li, X.-X.; Peng, S.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Reader YTHDF1 Promotes Stemness and Therapeutic Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Enhancing NOTCH1 Expression. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, R.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Pu, L.; Tang, J.; et al. HIF-1α-Induced Expression of m6A Reader YTHDF1 Drives Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy and Malignancy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Promoting ATG2A and ATG14 Translation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Yang, M.; Huang, H.; Ma, S.; Hu, J.; Xi, Z.; Guo, H.; Yao, G.; Yang, L.; et al. YTHDF1 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression by Facilitating FOXM1 Translation in an m6A-Dependent Manner. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wei, Q.; Jin, J.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Li, L.; Pi, J.; Si, Y.; et al. The m6A Reader YTHDF1 Promotes Ovarian Cancer Progression via Augmenting EIF3C Translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 3816–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Pu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, J.; Song, Q.; Ji, Q. YTHDF1 Regulates GID8-Mediated Glutamine Metabolism to Promote Colorectal Cancer Progression in m6A-Dependent Manner. Cancer Lett. 2024, 601, 217186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.-G.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wu, G.-C.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Wen, R.; et al. The RNA m6A Reader YTHDF1 Is Required for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Progression. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wong, C.C.; Pan, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Zhai, J.; Kang, W.; Shi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; et al. Loss of YTHDF1 in Gastric Tumors Restores Sensitivity to Antitumor Immunity by Recruiting Mature Dendritic Cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, K.; Dong, X.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, R.; Yang, Z.; et al. YTHDF1 Promotes mRNA Degradation via YTHDF1-AGO2 Interaction and Phase Separation. Cell Prolif. 2021, 55, e13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. METTL3 Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tumorigenesis by Enhancing C-Myc Stability via YTHDF1-Mediated m6A Modification. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Gao, Z.; Su, X.; Ji, M.; Liu, J. N6-Methyladenosine METTL3 Promotes Cervical Cancer Tumorigenesis and Warburg Effect through YTHDF1/HK2 Modification. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, I.; Kang, S.K.; Kwon, W.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, A.; Lee, S.K.; Bogenrieder, T.; Chung, H.C.; et al. Regulation of Proliferation and Invasion by the IGF Signalling Pathway in Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Gastric Cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5899–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, R.; Uchida, D.; Kanno, S.; Shiraishi, R.; Hyodo, T.; Sawatani, Y.; Shimura, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Tsubura-Okubo, M.; Yaguchi, E.; et al. Identification of Binding Proteins for TSC22D1 Family Proteins Using Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hömig-Hölzel, C.; van Doorn, R.; Vogel, C.; Germann, M.; Cecchini, M.G.; Verdegaal, E.; Peeper, D.S. Antagonistic TSC22D1 Variants Control BRAFE600-Induced Senescence. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1753–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Kitaura, J.; Enomoto, Y.; Lu, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Isobe, M.; Ozaki, K.; Komeno, Y.; Nakahara, F.; Oki, T.; et al. Transforming Growth Factor-β-Stimulated Clone-22 Is a Negative-Feedback Regulator of Ras/Raf Signaling: Implications for Tumorigenesis. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragotto, J.; Canterini, S.; Del Porto, P.; Bevilacqua, A.; Fiorenza, M.T. The Interplay between TGF-β-Stimulated TSC22 Domain Family Proteins Regulates Cell-Cycle Dynamics in Medulloblastoma Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18349–18360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huser, C.A.; Pringle, M.A.; Heath, V.J.; Bell, A.K.; Kendrick, H.; Smalley, M.J.; Crighton, D.; Ryan, K.M.; Gusterson, B.A.; Stein, T. TSC-22D1 Isoforms Have Opposing Roles in Mammary Epithelial Cell Survival. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Forward (5′ → 3′) | Reverse (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | ATGGGGAAGGTGAAGGTCG | GGGGTCATTGATGGCAACAATA |
| YTHDF1 | CGACGACTTTGCTCACTACGA | CTGGTTCGCCCTCATTGTTT |
| TSC22D1 | TTCCTAGTGCTGCTGGTGTG | TTCCTAGTGCTGCTGGTGTG |
| siRNA | Sense (5′ → 3′) | Antisense (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGU | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAA |
| si YTHDF1 #1 | CCGAAAGAGUUUGAGUGGA | UCCACUCAAACUCUUUCGG |
| si YTHDF1 #2 | GCUCCAUUAAGUACUCCAU | AUGGAGUACUUAAUGGAGC |
| si TSC22D1 #1 | GAGCAGGAACAACAGUGAUTT | AUCACUGUUGUUCCUGCUCTT |
| si TSC22D1 #2 | ACAAGGAGUAGAACCAGUATT | UACUGGUUCUACUCCUUGUTT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, Y.R.; Jung, J.; Kwon, K.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.; Lee, S.K. Epstein–Barr Virus Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Modulating m6A-Dependent YTHDF1–TSC22D1 Axis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122820
An YR, Jung J, Kwon KM, Kim JY, Lee M-H, Lee JY, Lee M, Lee SK. Epstein–Barr Virus Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Modulating m6A-Dependent YTHDF1–TSC22D1 Axis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122820
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Yea Rim, Jaehun Jung, Kyeong Min Kwon, Jun Yeob Kim, Min-Hyeok Lee, Ju Yeon Lee, Minho Lee, and Suk Kyeong Lee. 2025. "Epstein–Barr Virus Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Modulating m6A-Dependent YTHDF1–TSC22D1 Axis" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122820
APA StyleAn, Y. R., Jung, J., Kwon, K. M., Kim, J. Y., Lee, M.-H., Lee, J. Y., Lee, M., & Lee, S. K. (2025). Epstein–Barr Virus Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression by Modulating m6A-Dependent YTHDF1–TSC22D1 Axis. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2820. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122820






