Comparison of the Presence of Heavy Metal Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica and Their Association with Antibiotic Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Data Processing
2.3. Analysis of HMRG Prevalence in Salmonella Isolates
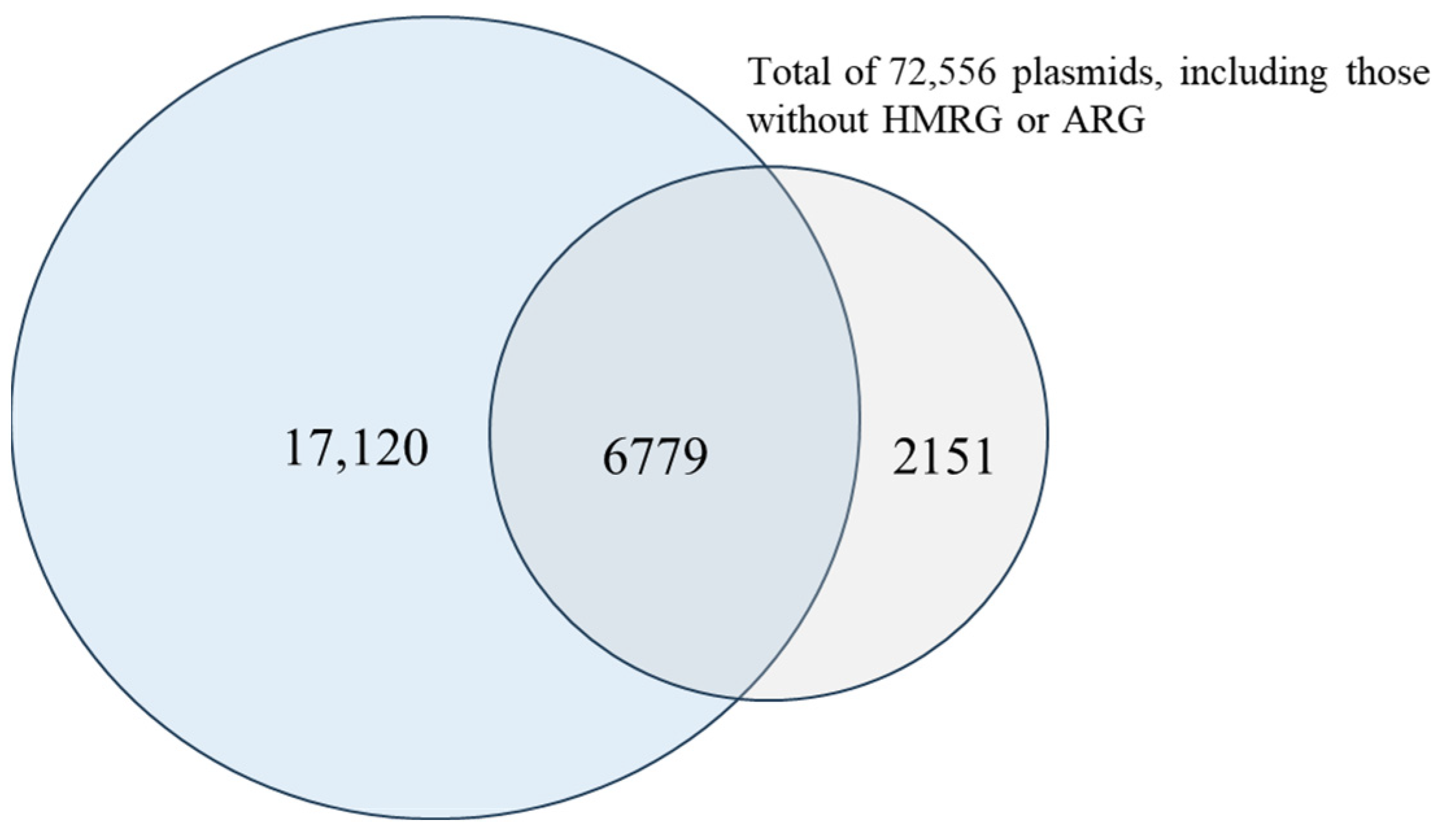
2.4. Screening of Plasmids for ARGs and HMRGs
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
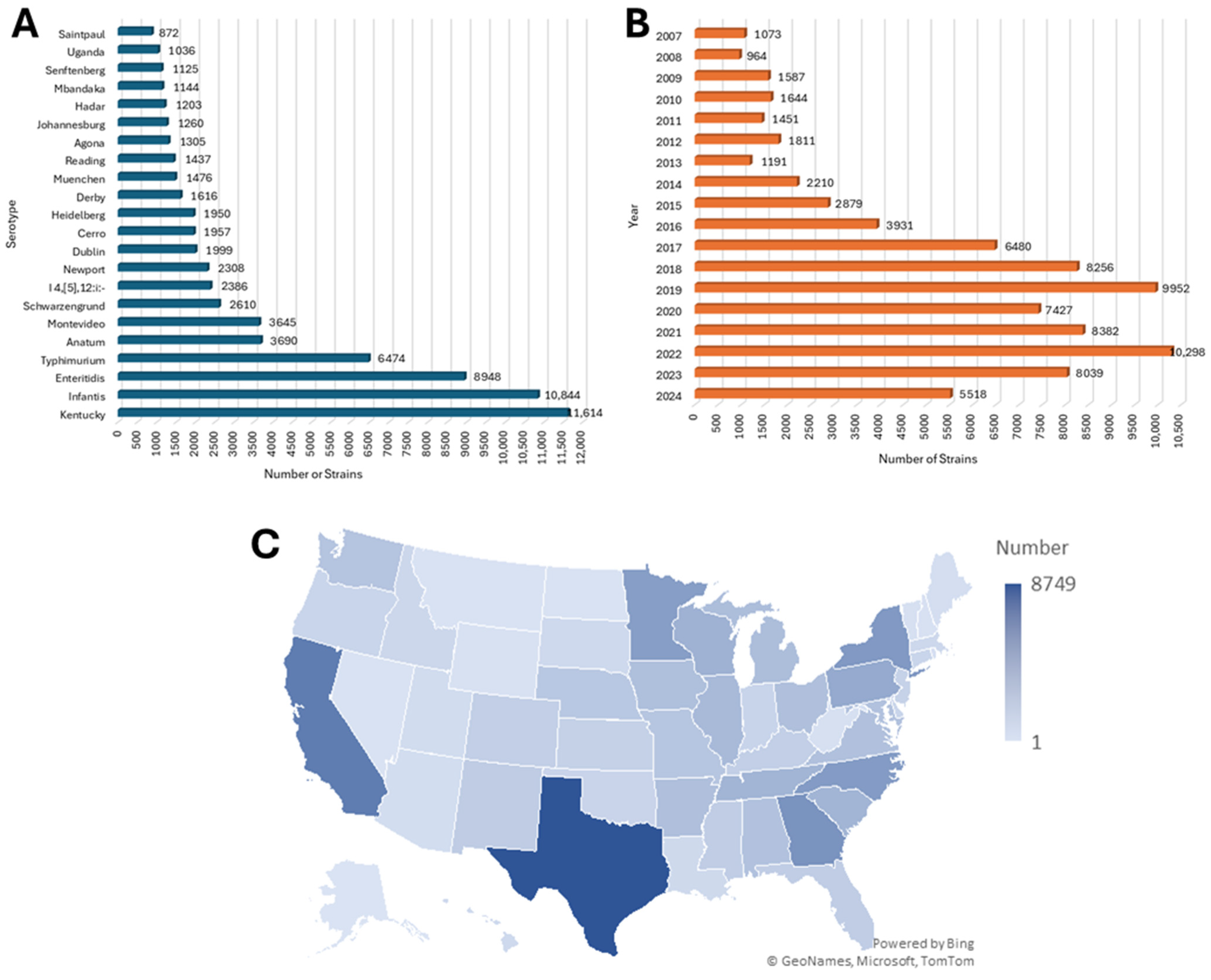
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of Salmonella Isolates
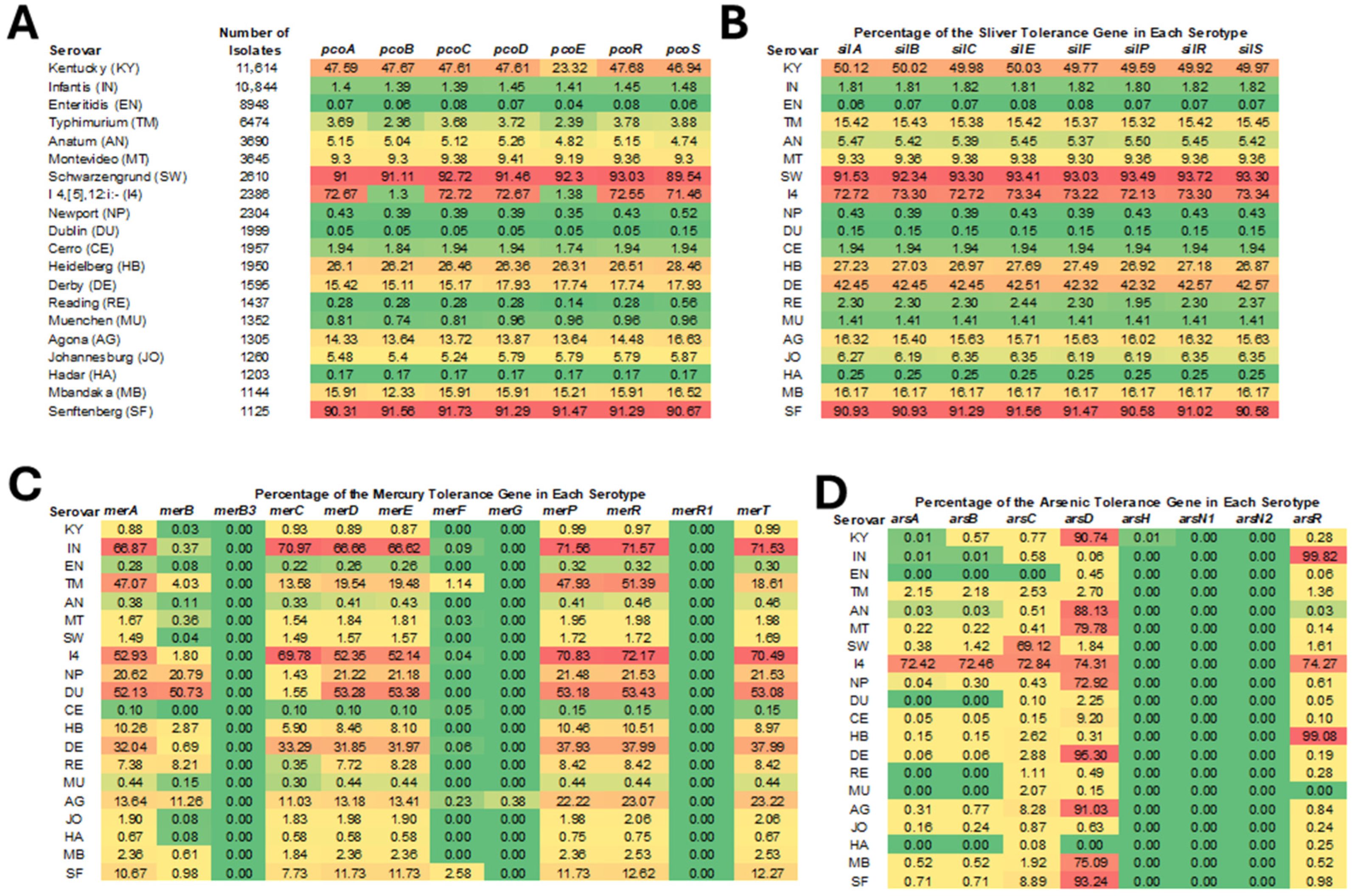
3.2. Prevalence of HMRGs Across Different Serotypes of Salmonella
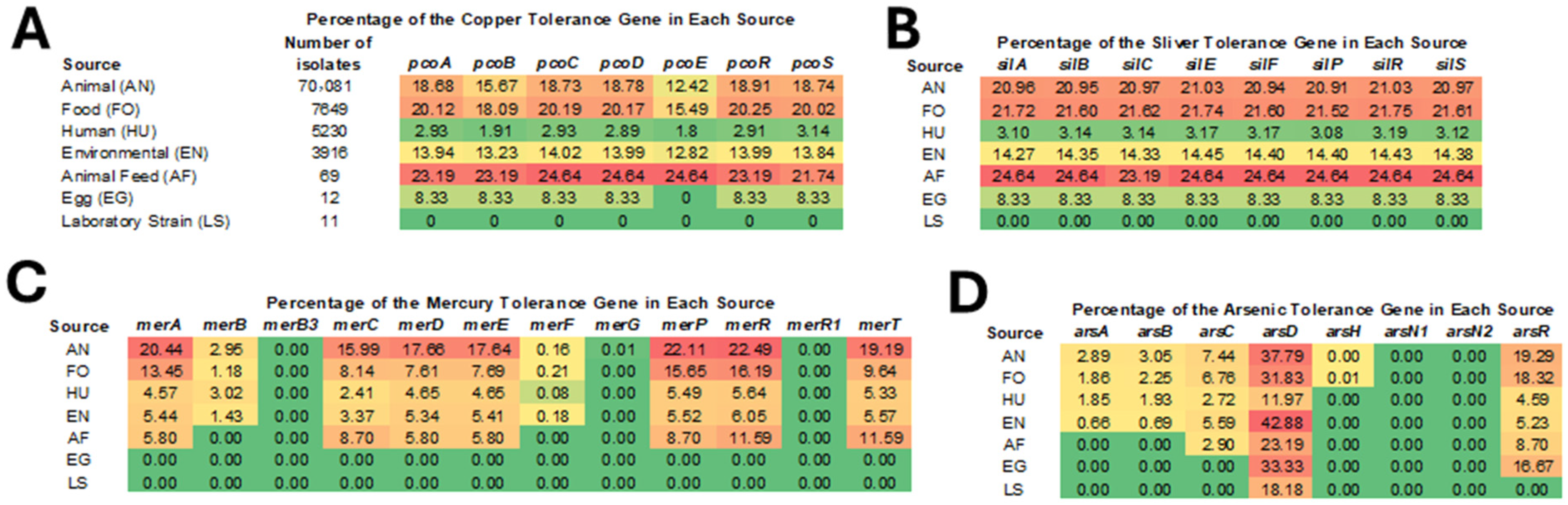
3.3. Prevalence of HMRGs Across Different Isolation Sources
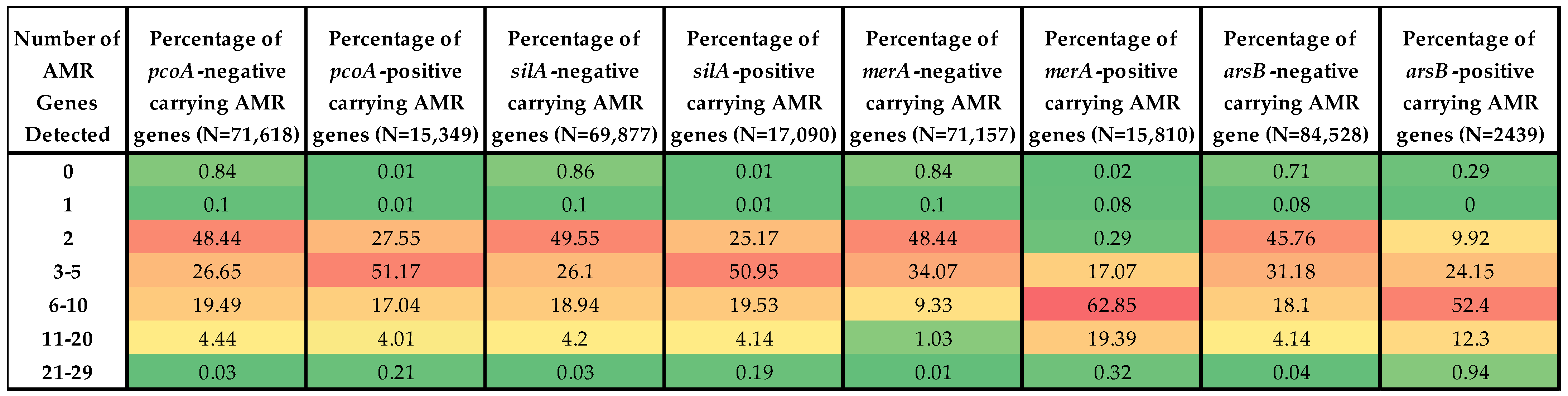
3.4. Prevalence of ARGs in HMRG-Positive vs. -Negative Isolates
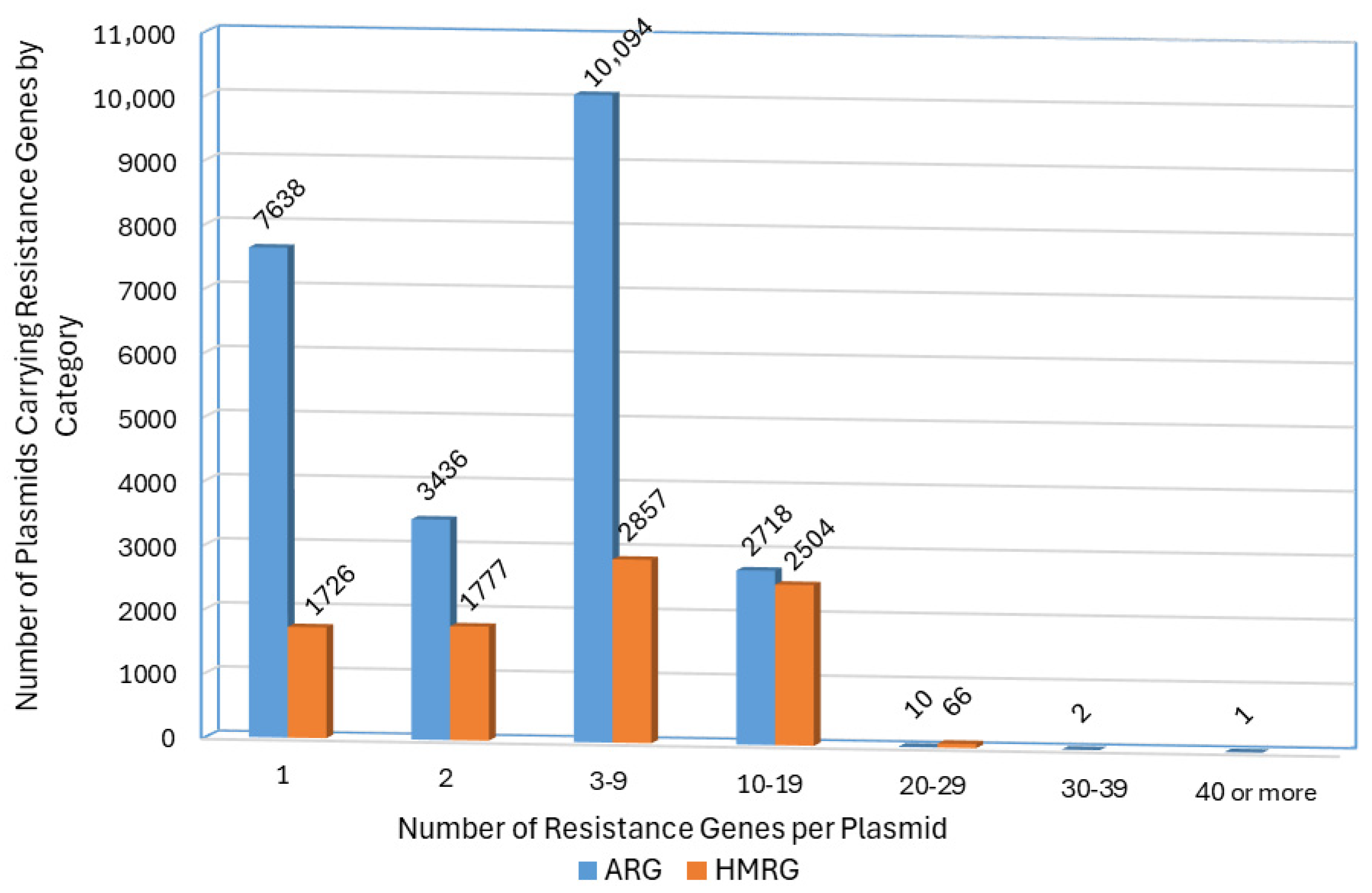
3.5. Co-Localization of ARGs and HMRGs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, Y.J.; Cowling, B.J. Reducing antibiotic use in livestock, China. Bull. World Health Organ. 2020, 98, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.R.; Zhao, K.; He, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Mustafa, A.; He, L.; Yang, Y.; Yu, X.; Penttinen, P.; et al. Heavy Metal Resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium and Its Association with Disinfectant and Antibiotic Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 702725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argudin, M.A.; Lauzat, B.; Kraushaar, B.; Alba, P.; Agerso, Y.; Cavaco, L.; Butaye, P.; Porrero, M.C.; Battisti, A.; Tenhagen, B.A.; et al. Heavy metal and disinfectant resistance genes among livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 191, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, B.; Jiang, J.; Fitzgerald, M.; Huang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Yang, C.; et al. Heavy Metal Contaminations in Herbal Medicines: Determination, Comprehensive Risk Assessments, and Solutions. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 595335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Kim, J.E.; Islam, A.; Bilal, M.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Nandi, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, T. Heavy metals contamination and associated health risks in food webs-a review focuses on food safety and environmental sustainability in Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 3230–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Meng, J.; Sweetman, A.J.; Jenkins, A.; Ferrier, R.C.; Li, H.; Luo, W.; et al. Impacts of soil and water pollution on food safety and health risks in China. Environ. Int. 2015, 77, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deemy, M.; Benjamin, L. CVM CY15-17 Report on Heavy Metals in Animal Food; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vats, P.; Kaur, U.J.; Rishi, P. Heavy metal-induced selection and proliferation of antibiotic resistance: A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 4058–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Deng, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Mustafa, G.R.; Chen, S.; He, L.; Ao, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, K.; et al. Presence of heavy metal resistance genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella isolates and analysis of resistance gene structure in E. coli E308. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A challenge for the food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Hu, K.; Liu, S.; Ma, M.; et al. Insights into antibiotic and heavy metal resistance interactions in Escherichia coli isolated from livestock manure and fertilized soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; International Collaboration on Enteric Disease “Burden of Illness” Studies. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Aljahdali, N.; Zhao, S.; Tang, H.; Harbottle, H.; Hoffmann, M.; Frye, J.G.; Foley, S.L. Infection biology of Salmonella enterica. EcoSal Plus 2024, 12, eesp00012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report; United States Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.; Schonfeld, J.; Bessonov, K.; Bastedo, P.; Nash, J.H.E. A global survey of Salmonella plasmids and their associations with antimicrobial resistance. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A. Plasmid-mediated antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2003, 5, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Wang, Y.W.; Chen, B.H.; Hong, Y.P.; Teng, R.H.; Liu, P.Y.; Chiou, C.S. Carbapenem resistance in extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Agona and AmpC beta-lactamase-producing S. Infantis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0292223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillieatt, B.F.; Coleman, N.V. Unravelling the mechanisms of antibiotic and heavy metal resistance co-selection in environmental bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Frye, J.G.; Haendiges, J.; Haft, D.H.; Hoffmann, M.; Pettengill, J.B.; Prasad, A.B.; Tillman, G.E.; et al. AMRFinderPlus and the Reference Gene Catalog facilitate examination of the genomic links among antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galata, V.; Fehlmann, T.; Backes, C.; Keller, A. PLSDB: A resource of complete bacterial plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D195–D202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, W. Pandas: A Foundational Python Library for Data Analysis and Statistics. Python High. Perform. Sci. Comput. 2011, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, E.; Oliphant, T.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open Source Scientific Tools for Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference (SciPy 2010), Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mourao, J.; Marcal, S.; Ramos, P.; Campos, J.; Machado, J.; Peixe, L.; Novais, C.; Antunes, P. Tolerance to multiple metal stressors in emerging non-typhoidal MDR Salmonella serotypes: A relevant role for copper in anaerobic conditions. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R.; Morgan, A.G.; Rouch, D.A.; Brown, N.L.; Lee, B.T. Copper-resistant enteric bacteria from United Kingdom and Australian piggeries. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2531–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehlin, B.M.; Gibbons, J.G.; Rokas, A.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Slot, J.C. Evolution of a Heavy Metal Homeostasis/Resistance Island Reflects Increasing Copper Stress in Enterobacteria. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikal, A.F.; Hasan, S.; Gudeta, D.; Zhao, S.; Foley, S.; Khan, A.A. The acquired pco gene cluster in Salmonella enterica mediates resistance to copper. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1454763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Montes, G.; Arguello, J.M.; Valderrama, B. Evolution and diversity of periplasmic proteins involved in copper homeostasis in gamma proteobacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Nayeri, N.; Gorecki, K.; Becares, E.R.; Wang, K.; Mahato, D.R.; Andersson, M.; Abeyrathna, S.S.; Lindkvist-Petersson, K.; Meloni, G.; et al. PcoB is a defense outer membrane protein that facilitates cellular uptake of copper. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, e4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, K.; Tang, A.; Tang, A.; Chen, A.; Huang, Z. Investigation of the Genes Involved in the Outbreaks of Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. in the United States. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.M.; Chartone-Souza, E. Operon mer: Bacterial resistance to mercury and potential for bioremediation of contaminated environments. Genet. Mol. Res. 2003, 2, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Naguib, M.M.; El-Gendy, A.O.; Khairalla, A.S. Microbial Diversity of Operon Genes and Their Potential Rules in Mercury Bioremediation and Resistance. Open Biotechnol. J. 2018, 12, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, E.S.; Barkay, T. The mercury resistance operon: From an origin in a geothermal environment to an efficient detoxification machine. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, C.Y.; Liu, M.Q.; Guo, Y. Synthetic bacteria designed using ars operons: A promising solution for arsenic biosensing and bioremediation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, S.S.R.; Turcotte, M.R.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wolfe, K.L.; Gao, F.; Benton, C.S.; Andam, C.P. Population analysis of heavy metal and biocide resistance genes in Salmonella enterica from human clinical cases in New Hampshire, United States. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 983083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.C.; Rosen, B.P. New mechanisms of bacterial arsenic resistance. Biomed. J. 2016, 39, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, S.L.; Johnson, T.J.; Ricke, S.C.; Nayak, R.; Danzeisen, J. Salmonella pathogenicity and host adaptation in chicken-associated serovars. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 582–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algarni, S.; Ricke, S.C.; Foley, S.L.; Han, J. The dynamics of the antimicrobial resistance mobilome of Salmonella enterica and related enteric bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 859854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, S.; Han, J.; Gudeta, D.D.; Khajanchi, B.K.; Ricke, S.C.; Kwon, Y.M.; Rhoads, D.D.; Foley, S. In silico analyses of diversity and dissemination of antimicrobial resistance genes and mobile genetics elements, for plasmids of enteric pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1095128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Lynne, A.M.; E David, D.; Tang, H.; Xu, J.; Nayak, R.; Kaldhone, P.; Logue, C.M.; Foley, S.L. DNA sequence analysis of plasmids from multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Heidelberg isolates. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, D.; Hou, Q.; Li, G.; Han, H. Epidemiological and biological characteristics of IncR plasmids as multihost antibiotic resistance carriers. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1622352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Pendleton, S.J.; Deck, J.; Singh, R.; Gilbert, J.; Johnson, T.J.; Sanad, Y.M.; Nayak, R.; Foley, S.L. Impact of co-carriage of IncA/C plasmids with additional plasmids on the transfer of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica isolates. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 271, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Metal Resistance | Metal Resistance Genes | Products |
|---|---|---|
| Mercury | merA | mercury(II) reductase |
| merB | organomercurial lyase MerB | |
| merC | organomercurial transporter MerC | |
| merD | mercury resistance co-regulator MerD | |
| merE | broad-spectrum mercury transporter MerE | |
| merP | mercury resistance system periplasmic binding protein MerP | |
| merR | mercury resistance transcriptional regulator MerR | |
| merT | mercuric transport protein MerT | |
| Arsenic | arsA | arsenite efflux transporter ATPase subunit ArsA |
| arsB | arsenite efflux transporter membrane subunit ArsB | |
| arsC | glutaredoxin-dependent arsenate reductase | |
| arsD | arsenite efflux transporter metallochaperone ArsD | |
| arsH | organoarsenical oxidase ArsH | |
| arsR | arsenite efflux transporter ATPase subunit ArsA | |
| Sliver | silA | Cu(+)/Ag(+) efflux RND transporter permease subunit SilA |
| silB | Cu(+)/Ag(+) efflux RND transporter periplasmic adaptor subunit SilB | |
| silC | Cu(+)/Ag(+) efflux RND transporter outer membrane channel SilC | |
| silE | silver-binding protein SilE | |
| silF | Cu(+)/Ag(+) efflux RND transporter periplasmic metallochaperone SilF | |
| silP | Ag(+)-translocating P-type ATPase SilP | |
| silR | copper/silver response regulator transcription factor SilR | |
| silS | copper/silver sensor histidine kinase SilS | |
| Copper | pcoA | multicopper oxidase PcoA |
| pcoB | copper-binding protein PcoB | |
| pcoC | copper resistance system metallochaperone PcoC | |
| pcoD | copper resistance inner membrane protein PcoD | |
| pcoE | copper resistance system metallochaperone PcoE | |
| pcoR | copper response regulator transcription factor PcoR | |
| pcoS | copper resistance membrane spanning protein PcoS | |
| Gold | golS | gold-responsive transcriptional regulator GolS |
| golT | gold-exporting ATPase GolT |
| AMR Gene | pcoA | χ2 Value | silA | χ2 Value | merA | χ2 Value | arsB | χ2 Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tet(A) | −17.93 | 2322.81 | −12.85 | 1293.79 | 78.51 | 45,529.57 | −17.84 | 429.93 |
| aph(3′’)-Ib | 38.26 | 10,915.40 | 35.31 | 10,092.07 | 3.39 | 87.63 | 44.32 | 2744.77 |
| aph(6)-Id | 38.3 | 11,063.08 | 35.43 | 10,283.84 | 3.33 | 85.56 | 44.45 | 2793.32 |
| sul1 | −9.36 | 881.17 | −5.29 | 304.62 | 58.48 | 35,273.56 | −5.05 | 47.64 |
| tet(B) | 25.4 | 7122.68 | 26.21 | 8231.89 | −2.65 | 79.20 | 67.64 | 9467.24 |
| sul2 | 1.97 | 46.55 | 5.41 | 382.57 | 37.37 | 17,223.18 | 51.79 | 6058.76 |
| gyrA_D87Y | −14.32 | 2477.14 | −14.68 | 2833.31 | 42.45 | 22,300.25 | −12.16 | 334.12 |
| aadA1 | −8.01 | 776.69 | −4.88 | 312.39 | 52.17 | 33,742.17 | −7.29 | 119.83 |
| floR | −9.99 | 1409.29 | −9.63 | 1425.33 | 30.94 | 13,835.70 | −5.16 | 69.95 |
| fosA7 | −1.25 | 33.05 | −1.76 | 71.34 | −5.9 | 757.21 | −6.01 | 143.55 |
| aac(3)-IVa | −4.69 | 473.42 | −4.88 | 553.33 | 25.51 | 14,315.98 | −3.37 | 45.19 |
| aph(4)-Ia | −4.73 | 483.26 | −4.92 | 569.14 | 25.51 | 14,367.89 | −3.56 | 50.74 |
| blaCMY-2 | −3.26 | 247.38 | −3.38 | 291.70 | 15.04 | 5433.14 | −3.12 | 42.47 |
| blaTEM-1 | 9.06 | 1971.50 | 9.1 | 2160.76 | 8.18 | 1644.41 | 59.06 | 15,722.66 |
| blaCTX-M-65 | −4.14 | 622.11 | −4.27 | 719.19 | 16.25 | 9782.97 | −3.56 | 85.16 |
| dfrA14 | −3.46 | 448.97 | −3.58 | 522.57 | 13.94 | 7493.32 | −1.97 | 26.90 |
| aadA2 | 0.06 | 0.09 (p = 0.77) | 1.15 | 65.84 | 5.64 | 1506.24 | 5.21 | 234.30 |
| aac(3)-VIa | 0.74 | 35.07 | 4.37 | 1348.27 | 5.75 | 2183.20 | −0.15 | 0.22 |
| fosA7.3 | −0.68 | 33.34 | 2.3 | 418.68 | 1.83 | 251.72 | −1.42 | 27.02 |
| tet(C) | −0.37 | 10.84 (p = 0.001) | 3.19 | 840.32 | 2.73 | 568.85 | −0.4 | 2.01 |
| fosA7.2 | −0.4 | 13.12 (p = 0.0003) | −0.37 | 12.53 (p = 0.0004) | −0.42 | 14.06 | −1.18 | 21.34 |
| fosA3 | −1.77 | 274.54 | −1.81 | 312.69 | 6.76 | 4104.97 | −1.5 | 36.09 |
| qnrB19 | 2.79 | 724.29 | 2.83 | 808.80 | 0.85 | 68.09 | 11.58 | 2334.25 |
| blaTEM | −1.07 | 114.21 | −1.11 | 132.26 | 5.03 | 2579.47 | −0.09 | 0.09 (p = 0.76) |
| blaCARB-2 | −1.21 | 172.27 | −0.93 | 109.44 | −0.52 | 33.63 | −1.05 | 23.86 |
| tet(G) | −1.11 | 170.73 | −0.93 | 129.84 | −0.42 | 24.77 | −0.94 | 22.12 |
| HMRG Classes on Plasmid | AG | BL | BLE | CHL | EP | FOF | LNC | ML | MUP | OXL | PMB | QAC | QL | RIF | STP | SUL | TET | TMP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arsenic | 14.46 | 12.85 | 0.68 | 9.51 | 0.43 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 5.68 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 7.35 | 6.25 | 1.00 | 0.04 | 12.70 | 7.23 | 10.95 |
| Copper | 22.98 | 18.65 | 1.25 | 14.80 | 0.99 | 0.28 | 0.81 | 9.66 | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 12.60 | 9.78 | 3.08 | 0.83 | 18.94 | 12.13 | 16.48 |
| Mercury | 44.41 | 44.92 | 4.84 | 24.28 | 1.96 | 3.27 | 0.89 | 17.42 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 2.45 | 31.24 | 12.18 | 7.69 | 0.18 | 37.82 | 23.48 | 24.03 |
| Silver | 21.68 | 18.51 | 1.77 | 14.25 | 1.34 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 8.73 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 12.23 | 9.74 | 1.77 | 0.01 | 18.82 | 12.55 | 15.49 |
| Cadmium | 4.99 | 13.54 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 5.24 | 0.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.91 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 0.43 |
| Tellurium | 22.33 | 20.17 | 5.83 | 14.74 | 4.41 | 2.77 | 1.83 | 10.75 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.86 | 16.46 | 10.71 | 7.64 | 0.12 | 20.27 | 12.49 | 14.04 |
| Plasmid Replicon Type | Co-Localized Mercury and Beta-Lactam ARGs (N = 2729) | Co-Localized Mercury and Aminoglycoside ARGs (N = 2584) | Mercury Resistance Genes, but not Aminoglycoside or Beta-Lactam ARGs (N = 785) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percent | Number | Percent | Number | Percent | |
| IncFIB | 870 | 31.88 | 843 | 32.62 | 223 | 28.41 |
| IncFII | 690 | 25.28 | 666 | 25.77 | 168 | 21.4 |
| IncFIA | 638 | 23.38 | 597 | 23.1 | 184 | 23.44 |
| IncR | 504 | 18.47 | 461 | 17.84 | 159 | 20.25 |
| IncHI2A | 420 | 15.39 | 383 | 14.82 | 119 | 15.16 |
| IncU | 382 | 14 | 355 | 13.74 | 123 | 15.67 |
| IncC | 364 | 13.34 | 358 | 13.85 | 111 | 14.14 |
| IncQ1 | 207 | 7.59 | 220 | 8.51 | 57 | 7.26 |
| IncFIC | 155 | 5.68 | 149 | 5.77 | 39 | 4.97 |
| IncHI1B | 153 | 5.61 | 145 | 5.61 | 58 | 7.39 |
| IncN | 86 | 3.15 | 72 | 2.79 | 29 | 3.69 |
| IncP | 82 | 3 | 77 | 2.98 | 23 | 2.93 |
| IncL/M | 55 | 2.02 | 54 | 2.09 | 16 | 2.04 |
| IncK2/Z | 48 | 1.76 | 46 | 1.78 | 9 | 1.15 |
| IncI-gamma/K1 | 41 | 1.5 | 34 | 1.32 | 14 | 1.78 |
| IncHI1A | 37 | 1.36 | 41 | 1.59 | 9 | 1.15 |
| IncX1 | 34 | 1.25 | 33 | 1.28 | 10 | 1.27 |
| IncY | 26 | 0.95 | 26 | 1.01 | 9 | 1.15 |
| IncA | 23 | 0.84 | 21 | 0.81 | 11 | 1.4 |
| IncX3 | 11 | 0.4 | 10 | 0.39 | 1 | 0.13 |
| Col(VCM04) | 10 | 0.37 | 10 | 0.39 | 3 | 0.38 |
| IncT | 6 | 0.22 | 8 | 0.31 | 1 | 0.13 |
| Col3M | 3 | 0.11 | 3 | 0.12 | 1 | 0.13 |
| Col156 | 2 | 0.07 | 2 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.13 |
| Inc18 | 2 | 0.07 | 2 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 |
| IncQ2 | 2 | 0.07 | 1 | 0.04 | 1 | 0.13 |
| ColE10 | 1 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.13 |
| IncI1 | 1 | 0.04 | 1 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| IncI1/B/O | 1 | 0.04 | 1 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| IncW | 1 | 0.04 | 1 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| IncX4 | 1 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.13 |
| IncX3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, E.; Khan, A.; Foley, S.L. Comparison of the Presence of Heavy Metal Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica and Their Association with Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122696
Tang E, Khan A, Foley SL. Comparison of the Presence of Heavy Metal Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica and Their Association with Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122696
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Eric, Ashraf Khan, and Steven L. Foley. 2025. "Comparison of the Presence of Heavy Metal Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica and Their Association with Antibiotic Resistance" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122696
APA StyleTang, E., Khan, A., & Foley, S. L. (2025). Comparison of the Presence of Heavy Metal Resistance Genes in Salmonella enterica and Their Association with Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2696. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122696







