Multi-Omics Insights into Microbial Interactions and Fermented Food Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microbial Community Structural Characteristics in Fermented Foods
2.1. Major Microbial Groups and Their Functions
2.2. Community Dynamics
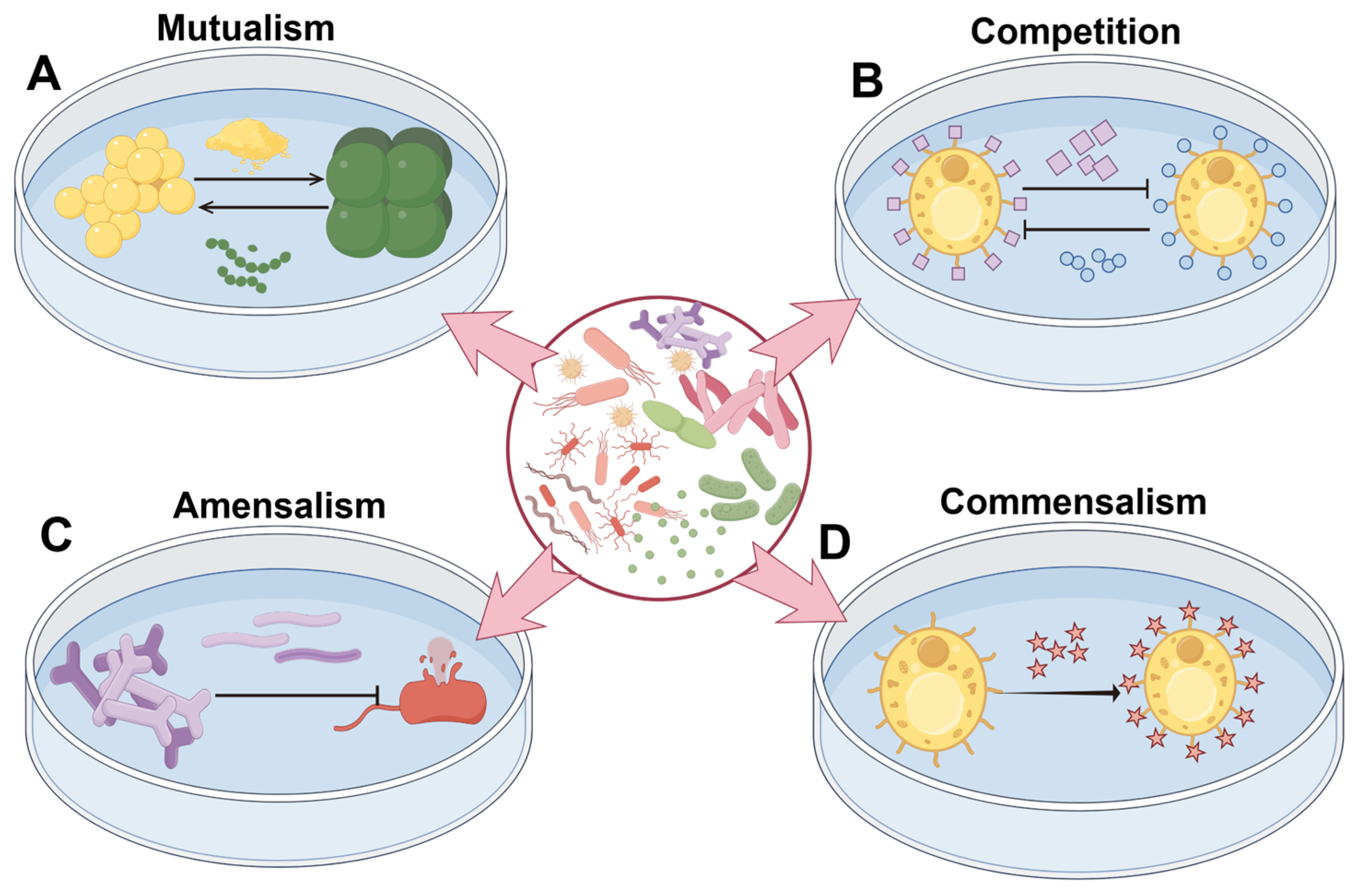
3. Metabolite Synthesis Mediated by Microbial Interactions
3.1. Mutualism
3.2. Competition
3.3. Amensalism
3.4. Commensalism
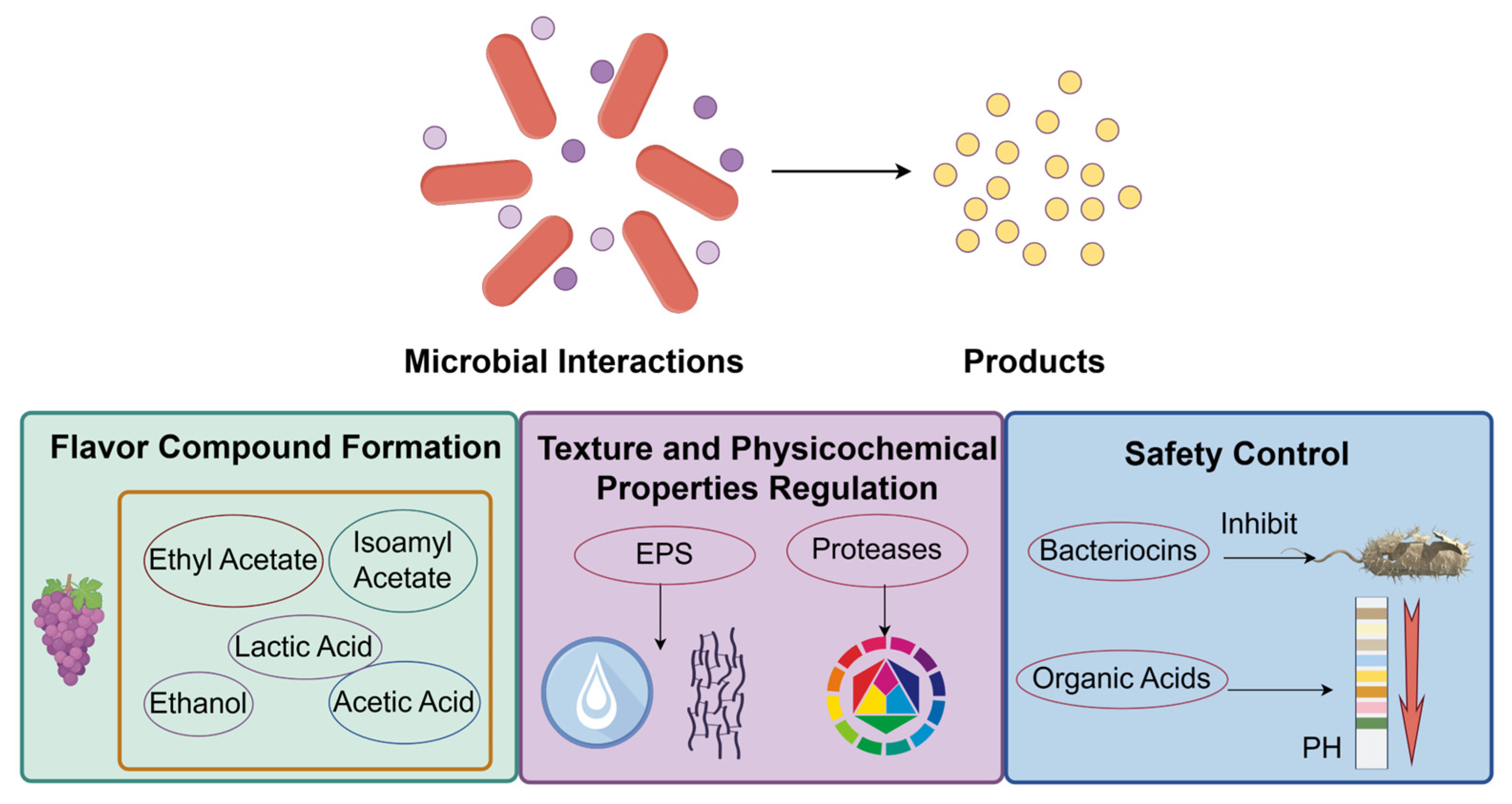
4. Quality Regulation in Fermented Foods Driven by Microbial Interactions
4.1. Formation of Flavor Compounds
4.1.1. Typical Flavor Compounds
4.1.2. Multi-Pathway Collaborative Flavor Orientation Regulation Strategy
4.2. Extracellular Polysaccharides Precisely Modulate
4.3. Safety Control
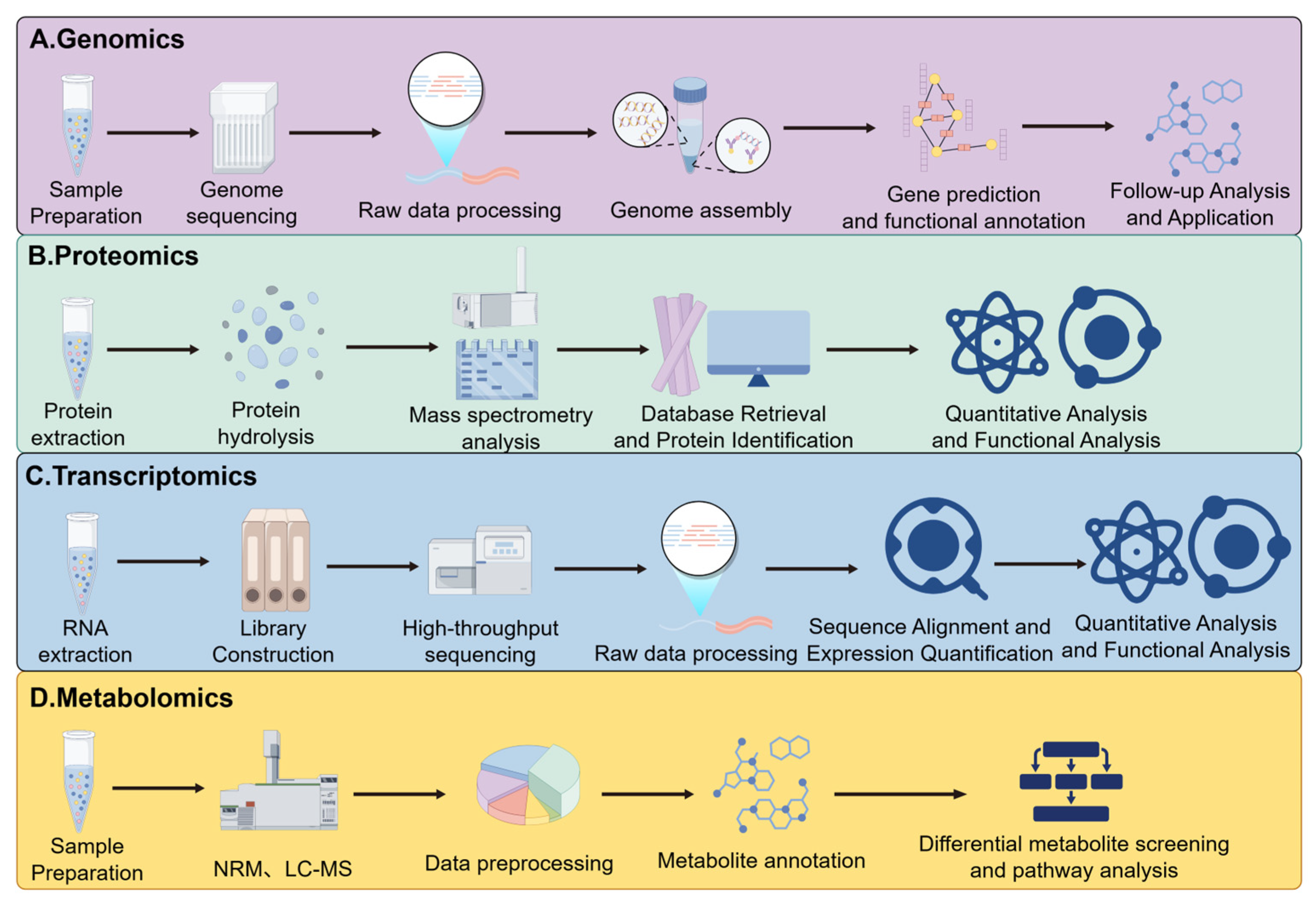
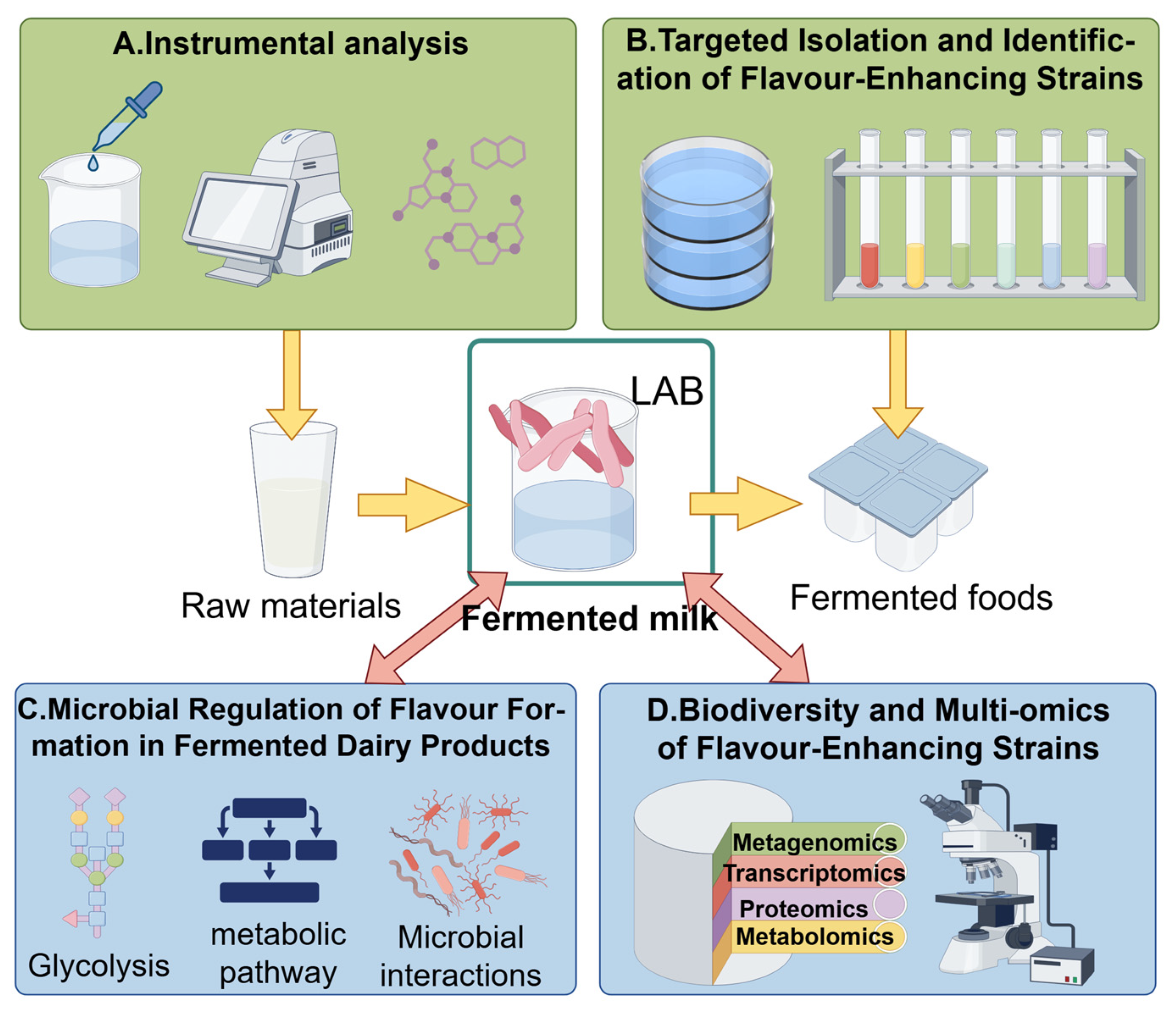
5. Utilizing Multi-Omics Research to Explore the Relationship Between Fermented Foods Composed of Complex Microorganisms and Their Functionality, Flavor, and Quality
5.1. Flavor
5.2. Quality
5.3. Functionality
5.4. Industrial Applications
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chuah, W.W.; Tan, J.S.; Hazwani Oslan, S.N.; Bothi Raja, P. Enhancing Food Preservation with Postbiotic Metabolites γ-Aninobutyric Acid (GABA) and Bacteriocin-Like Inhibitory Substances (BLIS) Produced by Lactobacillus brevis C23 Co-Cultures in Plant-Based Medium. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 54, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koistinen, V.M.; Hedberg, M.; Shi, L.; Johansson, A.; Savolainen, O.; Lehtonen, M.; Aura, A.M.; Hanhineva, K.; Landberg, R. Metabolite Pattern Derived from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-Fermented Rye Foods and In Vitro Gut Fermentation Synergistically Inhibits Bacterial Growth. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, H.-P.; Yin, X.-J.; Dong, Z.-H.; Wang, S.-R.; Li, J.-F.; Shao, T. Dynamics of Phyllosphere Microbiota and Chemical Parameters at Various Growth Stages and Their Contribution to Anaerobic Fermentation of Pennisetum giganteum. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0228822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.N.; McDonald, M.J. Microbial interspecies interactions constrain community adaptation but maintain ecological stability. ISME J. 2022, 16, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapp, C.; Dijamentiuk, A.; Mangavel, C.; Callon, C.; Theil, S.; Revol-Junelles, A.-M.; Chassard, C.; Borges, F. Serial fermentation in milk generates functionally diverse community lineages with different degrees of structure stabilization. mSystems 2024, 9, e0044524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Courty, P.E.; Varoquaux, N.; Cole, B.; Montoya, L.; Xu, L.; Purdom, E.; Vogel, J.; Hutmacher, R.B.; Dahlberg, J.A.; et al. Successional Adaptive Strategies Revealed by Correlating Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Abundance with Host Plant Gene Expression. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 2674–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, C.; Tong, X.; Ou, S. Effect of Sequential Inoculation of Tetragenococcus halophilus and Wickerhamomyces anomalus on the Flavour Formation of Early-Stage Moromi Fermented at a Lower Temperature. Foods 2023, 12, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspitasari, C.; Pinsirodom, P.; Wattanachaisaereekul, S. Effect of solid-state fermentation using Aspergillus oryzae and Aspergillus niger on bitter and bioactive compounds of Moringa oleifera seed flour. LWT 2024, 207, 116616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Li, X.; Datta, R.; Chen, J.; Du, Y.; Du, D.-L.J.A.S.E. Key factors shaping prokaryotic communities in subtropical forest soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Ngea, G.L.N.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H. Changes of the microbial community in kiwifruit during storage after postharvest application of Wickerhamomyces anomalus. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Kilcawley, K.; O’Sullivan, O.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. Microbial Succession and Flavor Production in the Fermented Dairy Beverage Kefir. mSystems 2016, 1, e0005216, Erratum in mSystems 2017, 2, e00003-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Laaksonen, O.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Battino, M.; Yang, B.; Gu, Q.J. Aroma characteristics of volatile compounds brought by variations in microbes in winemaking. Food Chem. 2023, 420, 136075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Alenyorege, E.A.; Ouyang, N.; Zhou, A.; Ma, H. Simulated natural and high temperature solid-state fermentation of soybean meal: A comparative study regarding microorganisms, functional properties and structural characteristics. LWT 2022, 159, 113125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanou, C.-R.; Bartodziejska, B.; Gajewska, M.; Szosland-Fałtyn, A. Microbiological Quality and Safety of Traditional Raw Milk Cheeses Manufactured on a Small Scale by Polish Dairy Farms. Foods 2022, 11, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Bianba, C.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, H. Exploring microbial dynamics associated with flavours production during highland barley wine fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 130, 108971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D. Microbiome Multi-Omics Network Analysis: Statistical Considerations, Limitations, and Opportunities. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, e00995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Baltar, F.; Herndl, G.J. Decoupling between the Genetic Potential and the Metabolic Regulation and Expression in Microbial Organic Matter Cleavage across Microbiomes. mBio 2024, 15, e0303623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Z.; Chen, K.; Cao, W.; Meng, L.; Yang, B.; Xu, M.; Xing, Y.; Li, P.; Freilich, S.; Chen, C.; et al. Engineering natural microbiomes toward enhanced bioremediation by microbiome modeling. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, T.; Wu, X.; Hou, R.; Tian, L.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, S.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, J. Application of Clostridium butyricum, rummeliibacillus suwonensis, and Issatchenkia orientalis for Nongxiangxing baijiu fermentation: Improves the microbial communities and flavor of upper fermented grain. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.T.H.; Huang, M.B.; Liu, F.Y.; Huang, W.L.; Tran, H.T.; Hsu, T.W.; Huang, C.L.; Chiang, T.Y. Deciphering Microbial Community Dynamics along the Fermentation Course of Soy Sauce under Different Temperatures Using Metagenomic Analysis. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2023, 42, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Yu, L.; Huang, L.; Xia, N.; Teng, J.; Wei, B. Isolation, Identification, and Community Diversity of Microorganisms during Tank Fermentation of Liupao Tea. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 4230–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Pan, Z.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z. Microbial community and metabolite dynamics during soy sauce koji making. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 841529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Cao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Shen, C.; Li, Q. Chinese Baijiu: The perfect works of microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 919044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, C.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y. Exploring the flavor formation mechanism under osmotic conditions during soy sauce fermentation in Aspergillus oryzae by proteomic analysis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, C.; Shan, W.; Zheng, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Physicochemical, flavor and microbial dynamic changes during low-salt doubanjiang (broad bean paste) fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 128454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Fujimoto, J.; Tomii, Y.; Sasamoto, M.; Makino, H.; Kudo, Y.; Okada, S. Lactobacillus kisonensis sp. nov., Lactobacillus otakiensis sp. nov., Lactobacillus rapi sp. nov. and Lactobacillus sunkii sp. nov., heterofermentative species isolated from sunki, a traditional Japanese pickle. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Carg, P.; Kumar, P.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kulshrestha, S. Microbial fermentation and its role in quality improvement of fermented foods. Fermentation 2020, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Huang, J. Contribution of Latilactobacillus sakei to Metabolite Changes and Microbiome Composition during Fermented Sausage Processing. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2022, 4, 100089. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Li, R.; Hu, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.-X.; Han, B.-Z. Microbial Interactions in Mixed-Species Biofilms on the Surfaces of Baijiu Brewing Environments. Food Res. Int. 2024, 191, 114698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, B.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, W.; Yang, Q.; Chen, S. Effects of ultra-long fermentation time on the microbial community and flavor components of light-flavor Xiaoqu Baijiu based on fermentation tanks. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.N.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.N.; Yan, Y.Z.; Chen, J.Y.; Han, B.Z. Influence of indigenous lactic acid bacteria on the volatile flavor profile of light-flavor Baijiu. LWT 2021, 147, 111540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tso, N.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, R. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Microbial Synergistic Metabolic Mechanisms and Health Benefits in Kombucha Fermentation: A Review. Biology 2025, 14, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Brasiel, P.G.; Dutra Medeiros, J.; Barbosa Ferreira Machado, A.; Ferreira, M.S.; Peluzio, M.D.C.G.; Luquetti, S.C.P.D. Microbial community dynamics of fermented kefir beverages changes over time. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2021, 74, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korena, K.; Krzyzankova, M.; Florianova, M.; Karasova, D.; Babak, V.; Strakova, N.; Juricova, H. Microbial succession in the cheese ripening process—Competition of the starter cultures and the microbiota of the cheese plant environment. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Choi, E.J.; Jeon, C.O. Microbial succession and metabolite changes during long-term storage of Kimchi. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, M763–M769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.; Narayanan, S.; Alcock, J.; Varsani, A.; Maley, C.; Aktipis, A. Kombucha: A Novel Model System for Cooperation and Conflict in a Complex Multi-Species Microbial Ecosystem. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Dong, Y.; Shi, L.; Xu, T.; Wu, F. The anti-obesity effect of fermented barley extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum dy-1 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in diet-induced obese rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Toit, S.C.; Rossouw, D.; du Toit, M.; Bauer, F.F. Enforced Mutualism Leads to Improved Cooperative Behavior between Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus plantarum. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Wang, B.; Bai, Y.; Miao, Z.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, B. Interactive mechanism-guided microbial interaction dynamics in food fermentations: Lactic acid bacteria and yeasts as a case example. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Maistrenko, O.M.; Andrejev, S.; Kim, Y.; Bork, P.; Patil, K.R.; Patil, K.R. Polarization of microbial communities between competitive and cooperative metabolism. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 5, 195–203. [Google Scholar]
- Melkonian, C.; Zorrilla, F.; Kjærbølling, I.; Blasche, S.; Machado, D.; Junge, M.; Sørensen, K.I.; Andersen, L.T.; Patil, K.R.; Zeidan, A.A. Microbial interactions shape cheese flavour formation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montel, M.-C.; Buchin, S.; Mallet, A.; Delbes-Paus, C.; Vuitton, D.A.; Desmasures, N.; Berthier, F. Traditional cheeses: Rich and diverse microbiota with associated benefits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Y.; Wu, Q.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Biocontrol of geosmin-producing Streptomyces spp. by two Bacillus strains from Chinese liquor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 231, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.C.C.P.; Bover-Cid, S.; Bolívar, A.; Zurera, G.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F. Modelling the Interaction of the Sakacin-Producing Lactobacillus sakei CTC494 and Listeria monocytogenes in Filleted Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) under Modified Atmosphere Packaging at Isothermal and Non-Isothermal Conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 297, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, J. Effects of Kimchi-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria on Reducing Biological Hazards in Kimchi. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S.; Imtiaz, A.; Awan, K.A.; Murtaza, M.S.; Mubeen, B.; Yinka, A.A.; Boasiako, T.A.; Alsulami, T.; Rehman, A.; Khalifa, I.; et al. Impact of fermentation through synergistic effect of different lactic acid bacteria (mono and co-cultures) on metabolic and sensorial profile of mulberry juice. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 9364–9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Yang, S.Y.; Yoon, K.S. Lactic acid bacteria starter in combination with sodium chloride controls pathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC, ETEC, and EHEC) in kimchi. Food Microbiol. 2021, 100, 103868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, H.; Costello, P.J.; Remize, F.; Guzzo, J.; Guilloux-Benatier, M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae–Oenococcus oeni interactions in wine: Current knowledge and perspectives. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 93, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zabed, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yun, J.; Zhang, G.; Yang, M.; Sun, W.; Qi, X. Optimization of fermentation medium for a newly isolated yeast strain (Zygosaccharomyces rouxii JM-C46) and evaluation of factors affecting biosynthesis of D-arabitol. LWT 2019, 99, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Sun, W.; Zhao, M.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Su, G. Effects of Fermentation with Tetragenococcus halophilus and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii on the Volatile Profiles of Soybean Protein Hydrolysates. Foods 2023, 12, 4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. Effect of autochthonous starter cultures on the volatile flavour compounds of Chinese traditional fermented fish (Suan yu). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Dong, J.; Yin, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wan, X.; Chen, P.; Hou, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, L. Wort composition and its impact on the flavour-active higher alcohol and ester formation of beer—A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, M. Dendritic Mesoporous Silica-Supported Lipase for Efficient and Sustainable Synthesis of Food-Grade Flavor Esters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 12434–12444. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, J. An insight into specific flavor sensation in fermented milk: Linalool and mushroom alcohol. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 5741–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Su, G. Volatile Profile and Esterification Mechanisms in Traditional Chinese Fermented Soy Sauce. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126724. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, H.S.; Ball, J.C.; Doll, K.M.; Anderson, J.E.; Vermillion, K. Investigation of polymers and alcohols produced in oxidized soybean oil at frying temperatures. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Gao, P.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Q. Effect of commercial starter cultures on the quality characteristics of fermented fish-chili paste. LWT 2020, 122, 109016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, H.; Poupard, P.; Legoahec, L.; Millet, M.; Bauduin, R.; Le Quéré, J.-M. Brettanomyces anomalus, a double drawback for cider aroma. LWT 2019, 102, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.L.; Balcão, V.M.; Malcata, F.X. Kinetics and mechanisms of reactions catalyzed by immobilized lipases. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 27, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, S.; Behrens, M.; Dunkel, A.; Hofmann, T.; Meyerhof, W. Amino acids and peptides activate at least five members of the human bitter taste receptor family. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hu, W.; Xiu, Z.; Jiang, A.; Yang, X.; Ji, Y.; Guan, Y.; Feng, K. Comparison of northeast sauerkraut fermentation between single lactic acid bacteria strains and traditional fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozer, B.; Demirci, F. Determination of Microbial Dynamics and Some Metabolite Formation of Semi-Dried Tarhana Produced from Home-Made Yoghurt. Food Chem. 2025, 378, 131932. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, T.; Wang, D.; Jin, R.L.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhou, T.T.; Sun, T.S. Characterization of volatile compounds in fermented milk using solid-phase microextraction methods coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 2488–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, T.; Wang, D.; Wu, S.; Jin, R.; Ren, W.; Sun, T. Profiles of volatile flavor compounds in milk fermented with different proportional combinations of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. Molecules 2017, 22, 1633. [Google Scholar]
- Kapp, J.M.; Sikora, A.E. Komagataeibacter fermentation of winemaking byproducts to produce kombucha vinegar: Chemical composition and bioactivity. LWT 2024, 203, 116370. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, M.; de Oliveira, H.L.; de Almeida, P.Z.; de Almeida, R.A.; de Almeida, R.B.; Teixeira, J.A.; Silva, R. Unraveling microbial succession and metabolic pathways in artisanal kombucha fermentations. Food Res. Int. 2025, 191, 114678. [Google Scholar]
- Neffe-Skocinska, K.; Sionek, B.; Scibisz, I.; Kolozyn-Krajewska, D. Acid contents and the effect of fermentation condition of Kombucha tea beverages on physicochemical, microbiological and sensory properties. CyTA J. Food. 2017, 15, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Ferrocino, I.; Reale, A.; Sabbatini, R.; Milanović, V.; Alkić-Subašić, M.; Boscaino, F.; Aquilanti, L.; Pasquini, M.; Trombetta, M.F.; et al. Study of kefir drinks produced by backslopping method using kefir grains from Bosnia and Herzegovina: Microbial dynamics and volatilome profile. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Shah, N.P. Other Fermented Dairy Products: Kefir and Koumiss; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128052723. [Google Scholar]
- Anfiteatro, D.N. Dom’s all about Kefir in-site. Electron. J. Food Ferment. 2020, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Karaoğlan, S.Y.; Jung, R.; Jelínek, L.; Karabín, M.; Kinčl, T.; Dostálek, P. Aroma Potential of a New Maltose-Negative Yeast Isolate. Foods 2025, 14, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Cho, I.H.; Lee, S.R.; Choi, H.-K.; Kwon, D.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S. Metabolite profiling of Cheonggukjang, a fermented soybean paste, during fermentation by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and principal component analysis. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, S.; Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, P. Volatile Metabolomics and Metagenomics Reveal the Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Alfalfa Silage Quality, Microbial Communities, and Volatile Organic Compounds. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; Peng, B. Analysis of the Formation of Characteristic Aroma Compounds by Amino Acid Metabolic Pathways during Fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecules 2023, 28, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.N.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.P.; Dong, X.; Zhu, B.; Qin, L. Analysis of lipid molecule profiling and conversion pathway in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) during fermentation via untargeted lipidomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8673–8684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Niu, J.; Lin, M.; Zhu, H.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Sun, B. Characteristics and Correlation of the Microbial Communities and Flavor Compounds during the First Three Rounds of Fermentation in Chinese Sauce-Flavor Baijiu. Foods 2023, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.-T.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Bui, D.-C.; Hong, P.-T.; Hoang, Q.-K.; Nguyen, H.-T. Exopolysaccharide Production by Lactic Acid Bacteria: The Manipulation of Environmental Stresses for Industrial Applications. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Ju, X.; Wang, L. Impact of Exopolysaccharides-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria on the Chemical, Rheological Properties of Buckwheat Sourdough and the Quality of Buckwheat Bread. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, S.; Tang, H.; Evivie, S.E.; Guo, Z.; Li, B. Effect of Exopolysaccharides Yield and Addition Concentration of Lactobacillus helveticus on the Processing Characteristics of Fermented Milk and Its Mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Liu, L. Biological Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides and Their Applications in the Food and Pharmaceutical Industries. Foods 2024, 13, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentès, M.-C.; St-Gelais, D.; Turgeon, S.L. Gel Formation and Rheological Properties of Fermented Milk with in Situ Exopolysaccharide Production by Lactic Acid Bacteria. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2011, 91, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; Ye, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Safety Evaluation of Weissella confusa SY628 and the Effect of Its Fermentation on the Taste and Quality of Soy Yogurt. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1567399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ding, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, G.; Deng, S.; Gao, M.; Liu, H.; Lv, W.; Zeng, X.; Xin, B.; et al. Mycoidesin, a novel lantibiotic, exhibits potent bacteriostatic activity against Listeria monocytogenes and effectively controls its growth in beef. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e00067-25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Mutanda, T.; Olaniran, A.O. Perspectives on the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria from African traditional fermented foods and beverages. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 29630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yu, S.; Han, B.; Chen, J. Bacterial community succession and metabolite changes during sufu fermentation. LWT 2018, 97, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, X. Multi-omics Analysis Reveals the Microbial Interactions of S. cerevisiae and L. plantarum on Suanyu, Chinese Traditional Fermented Fish. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Gu, Q. Multi-omics Analyses of the Mechanism for Formation of Key Aroma-Active Compounds in Blood Orange Wine Fermented by Pichia kudriavzevii. Food Res. Int. 2024, 198, 115321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X.; Wu, Q. Gut Microbiota-Mediated Antihypertensive Effects of Probiotic Fermented Milk: A Multi-Omics Study. J. Food Sci. 2025, 90, e70654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Jin, J.; Tong, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. Multi-omics analyses of the mechanism for the formation of soy sauce-like and soybean flavor in Bacillus subtilis BJ3-2. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D. Changes of fungal community and non-volatile metabolites during pile-fermentation of dark green tea. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Luo, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Crabbe, M.J.C.; Qiao, Q.; Li, G.; Zhang, T. Integrative Analysis of the Metabolome and Transcriptome Reveals the Potential Mechanism of Fruit Flavor Formation in Wild Hawthorn (Crataegus chungtienensis). Plant Divers. 2023, 45, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Shemirani, P.; Sood, T.; Pare, G. From ‘Omics to multi-omics technologies: The discovery of novel causal mediators. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2023, 25, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Xue, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, B.Z. Integrated multi-omics approaches to understand microbiome assembly in Jiuqu, a mixed-culture starter. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 4076–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.M.; Huang, Z.R.; Wu, L.; Wu, Q.; Guo, W.L.; Zhao, W.H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Rao, P.F.; Lv, X.C.; et al. Microbial diversity and flavour of Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu): An overview of current research and future prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.S.; Whon, T.W.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Choi, H.J.; Rhee, J.K.; Roh, S.W. Microbial niches in raw ingredients determine microbial community assembly during kimchi fermentation. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E.; Ruiz-Bellido, M.A.; Romero-Gil, V.; Rodríguez-Gómez, F.; Montes-Borrego, M.; Landa, B.B.; Arroyo-López, F.N. Assessment of the bacterial community in directly brined Aloreña de Málaga table olive fermentations by metagenetic analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 236, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chu, H.; Padmanabhan, A.; Shah, N.P. Functional genomic analyses of exopolysaccharide-producing Streptococcus thermophilus ASCC 1275 in response to milk fermentation conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gong, S.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.L.; Li, N. Soybean fermentation drives the production of native neuroprotective peptides based on a peptidomics strategy. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 10, 101082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, S.; Dong, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Y.; Xu, D.; Yang, R.; Zeng, B.; Hu, Y.; et al. Fermentation-driven microbial and metabolic shifts in filler tobacco leaves of different grades. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1651289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.E.; Tandon, K.; Verbruggen, H.; Nikoloski, Z. Integration of Metatranscriptomics Data Improves the Predictive Capacity of Microbial Community Metabolic Models. mSystems 2025, 10, wraf109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocolin, L.; Mataragas, M.; Bourdichon, F.; Doulgeraki, A.; Pilet, M.F.; Jagadeesan, B.; Rantsiou, K.; Phister, T. Next generation microbiological risk assessment meta-omics: The next need for integration. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 287, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Whon, T.W.; Roh, S.W.; Jeon, C.O. Unraveling microbial fermentation features in kimchi: From classical to meta-omics approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7731–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.-K.; Tang, Y.-M.; Guo, X.-J.; Zhao, K.; Penttinen, P.; Tian, X.-H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, D.-Q.; Zhang, X.-P. Structural and functional changes in prokaryotic communities in artificial pit mud during Chinese baijiu production. mSystems 2020, 5, e0082919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Barrangou, R. Combining omics technologies with CRISPR-based genome editing to study food microbes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, B.; Baidoo, E.E.K. Omics-driven biotechnology for industrial applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 613307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Metabolic Type | Specific Metabolic Pathways | Metabolic Microorganism |
|---|---|---|
| Glycometabolic pathway | Glycolysis (EMP pathway) | Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Lactobacillus |
| Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) | Aerobic/Facultative aerobic microorganisms (Escherichia coli, yeast, Acetobacter) | |
| Pentose phosphate pathway | Yeast, Escherichia coli, cyanobacteria, actinomycetes | |
| Acetaldehyde cycle | Escherichia coli, rhizobia, certain fungi (such as Aspergillus niger) | |
| Lipid and Fatty Acid Metabolism | Fatty acid synthesis | Yeast, Escherichia coli, Actinomycetes, plant pathogenic fungi (such as Fusarium) |
| Fatty acid β-oxidation | Aerobic microorganisms (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas) Facultative anaerobic microorganisms (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | |
| Glycerol metabolism | Escherichia coli, yeast, lactic acid bacteria | |
| Polysaccharide degradation | Starch hydrolysis | Bacillus subtilis, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, Rhizopus |
| Cellulose decomposition | Mucor, cellulose-degrading bacteria (such as Clostridium thermofibrinolyticum), certain actinomycetes (such as Streptomyces), and the gut microbiota of termites | |
| Pectinase | Aspergillus niger, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus pectoralis | |
| glycogenolysis | Escherichia coli, yeast, certain bacteria (such as streptococci) |
| Fermented Foods | Multi-Omics Approaches | Significant Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fermented soybeans | Transcriptome analysis and proteome analysis | Main metabolic pathways involved carbohydrates, proteins, and amino acids. | [64] |
| Fermented fish | Transcriptomics and Metabolomics analyses | During microbial interactions, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Lactobacillus plantarum produce antibiotics that influence carbohydrate and energy metabolism. | [86] |
| Light-flavor Baijiu | Metagenomics and Metabolomics | alcohols and esters were the most abundant metabolites. | [65] |
| Blood orange wine | volatilomics, genomics, and transcriptomics | Enhanced the complexity and appeal of the aroma; a substantial portion of the P. kudriavzevii BP15 genome is dedicated to carbohydrate, amino acid, and energy metabolism. | [87] |
| Fermented Milk | Metagenomics and Metabolomics | Potential Mechanism Underlying the Hypotensive Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum SR37-3 (PFM-SR37-3) Fermented Milk in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats (SHR) | [88] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, J.; Jiang, X.; Song, P.; Yang, Q.; Sun, M.; Dong, Z.; Lu, Y.; Dou, S.; Dong, L. Multi-Omics Insights into Microbial Interactions and Fermented Food Quality. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122679
Ji J, Jiang X, Song P, Yang Q, Sun M, Dong Z, Lu Y, Dou S, Dong L. Multi-Omics Insights into Microbial Interactions and Fermented Food Quality. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122679
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Jiayi, Xinyue Jiang, Panpan Song, Qi Yang, Mengying Sun, Zhihui Dong, Yi Lu, Shaohua Dou, and Liang Dong. 2025. "Multi-Omics Insights into Microbial Interactions and Fermented Food Quality" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122679
APA StyleJi, J., Jiang, X., Song, P., Yang, Q., Sun, M., Dong, Z., Lu, Y., Dou, S., & Dong, L. (2025). Multi-Omics Insights into Microbial Interactions and Fermented Food Quality. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2679. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122679






