Characterization and Pathogenicity of Mannheimia glucosida Isolated from Sheep
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Clinical Samples
2.2. Isolation and Cultivation of Strains
2.3. Extraction of Total DNA
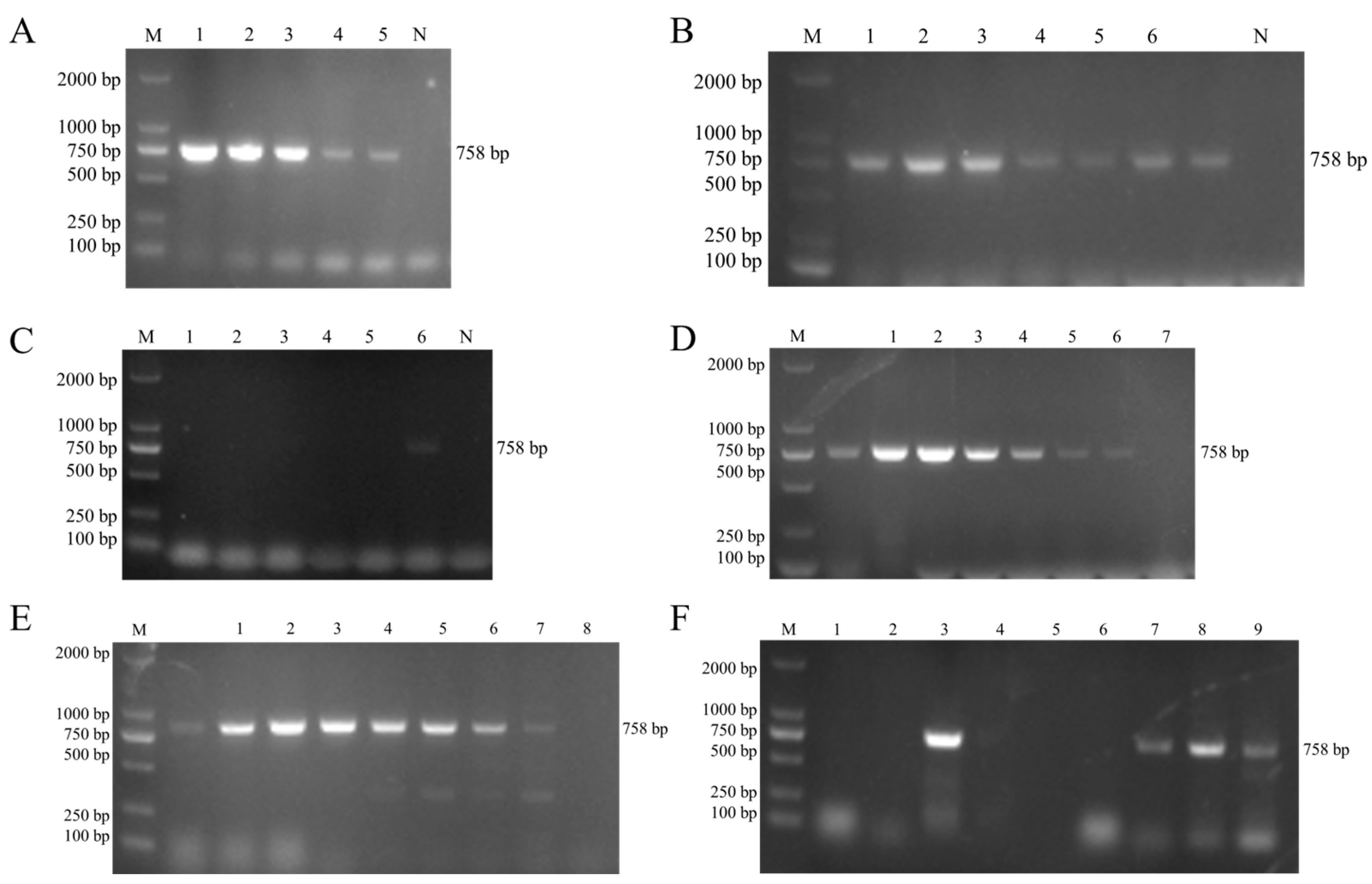
2.4. PCR Identification of Mannheimia
2.5. Biochemical Test of Isolated Strains
2.6. Virulence Gene Detection
2.7. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.8. Analysis of the Pathogenicity of M. glucosida in Mice
2.9. Sequence Analysis of the lktA Gene
2.10. Whole Genome Sequencing, Splicing and Assembly
2.11. Establishment of Species-Specific PCR for M. glucosida
2.12. Sensitivity and Specificity Analysis of Species-Specific PCR
2.13. Identification of Clinical Samples by Species-Specific PCR
3. Results
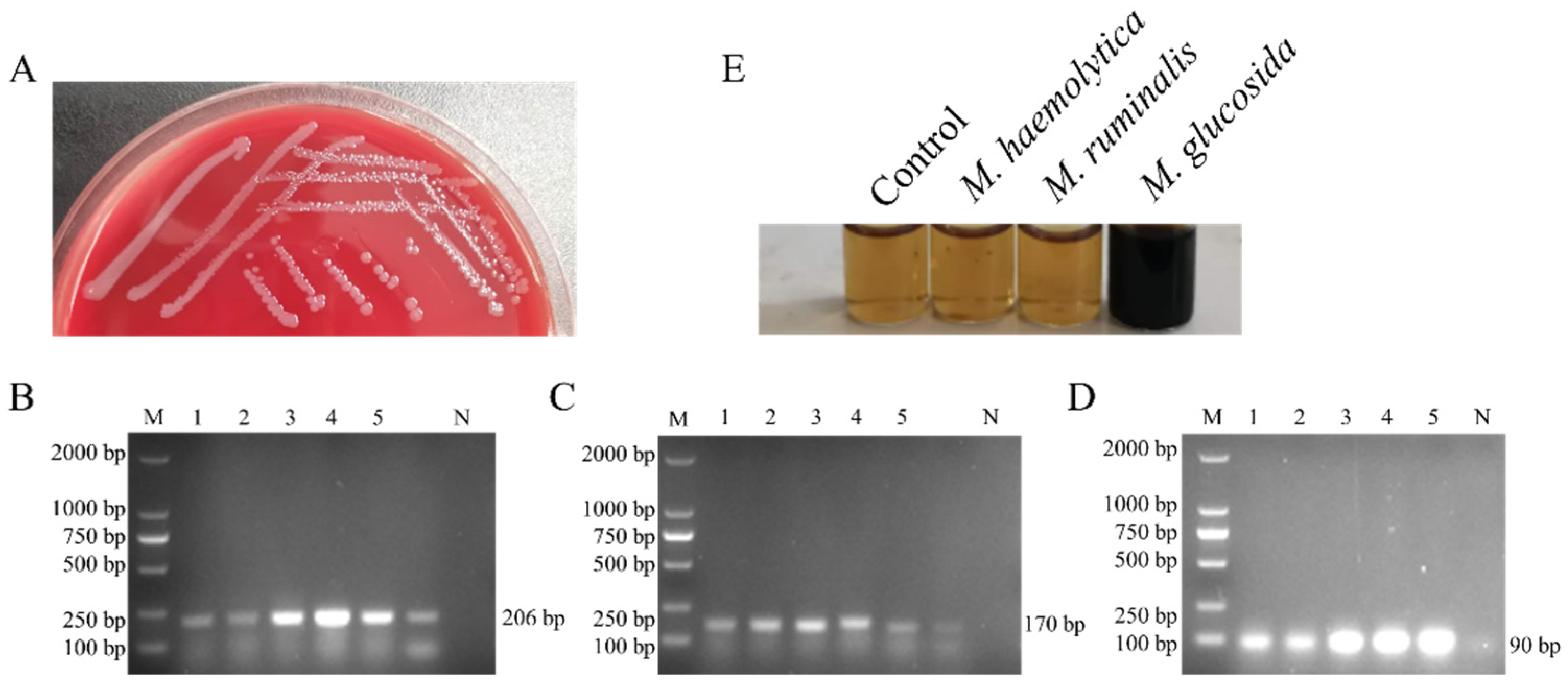
3.1. Isolation and Identification of M. glucosida
3.2. Biochemical Characteristics of M. glucosida
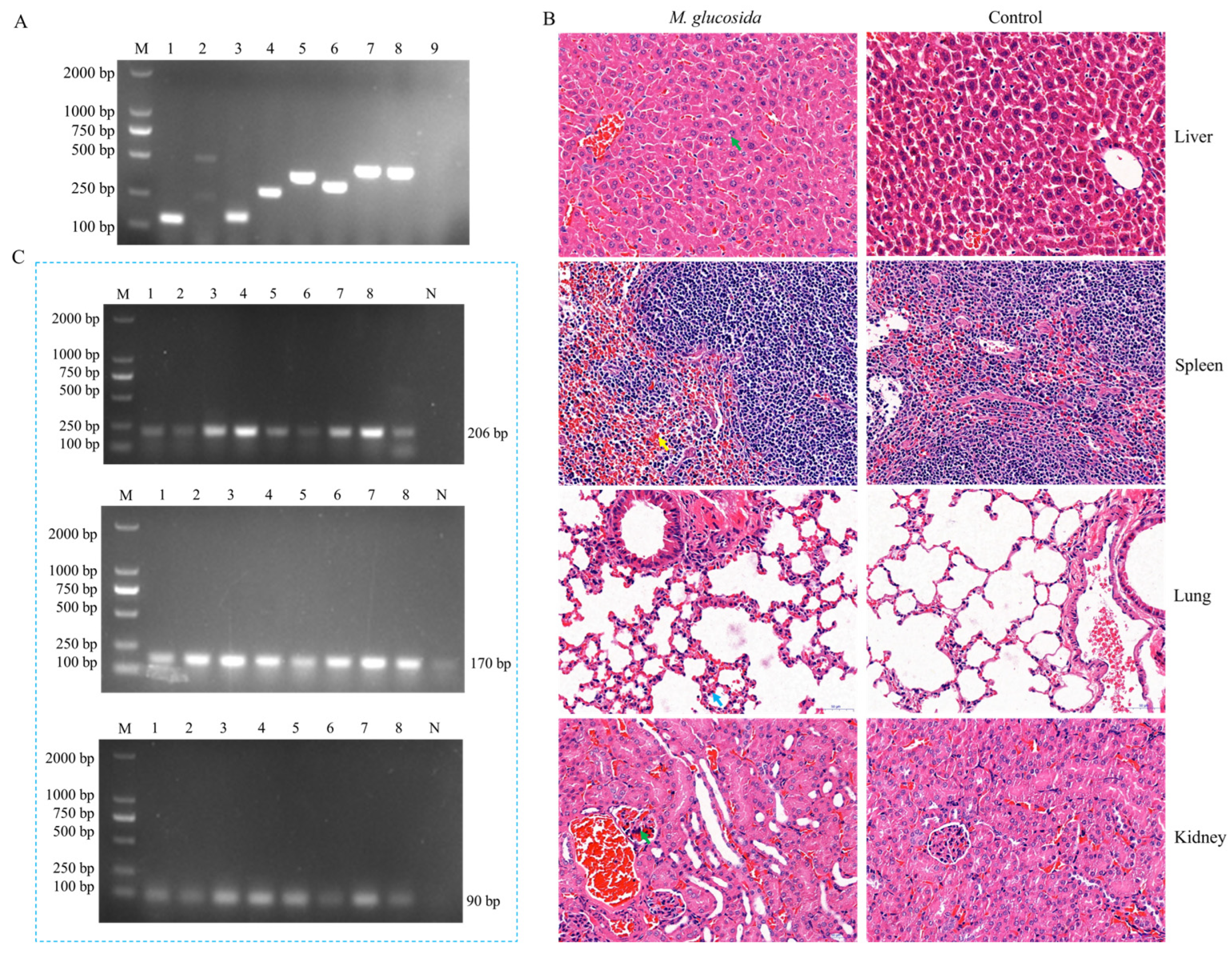
3.3. Pathogenicity Assays of M. glucosida in Mice
3.4. Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis of M. glucosida
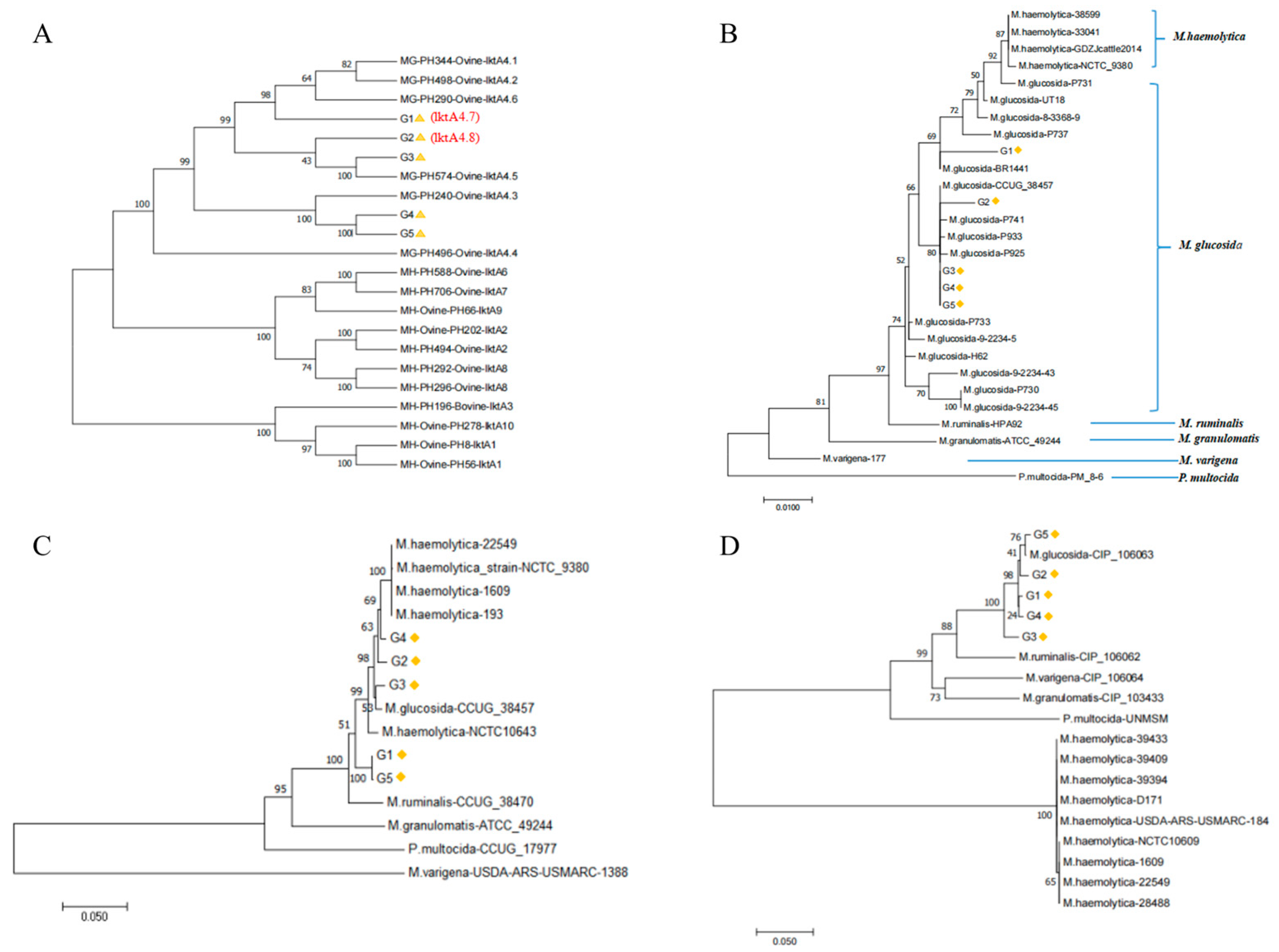
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of M. glucosida
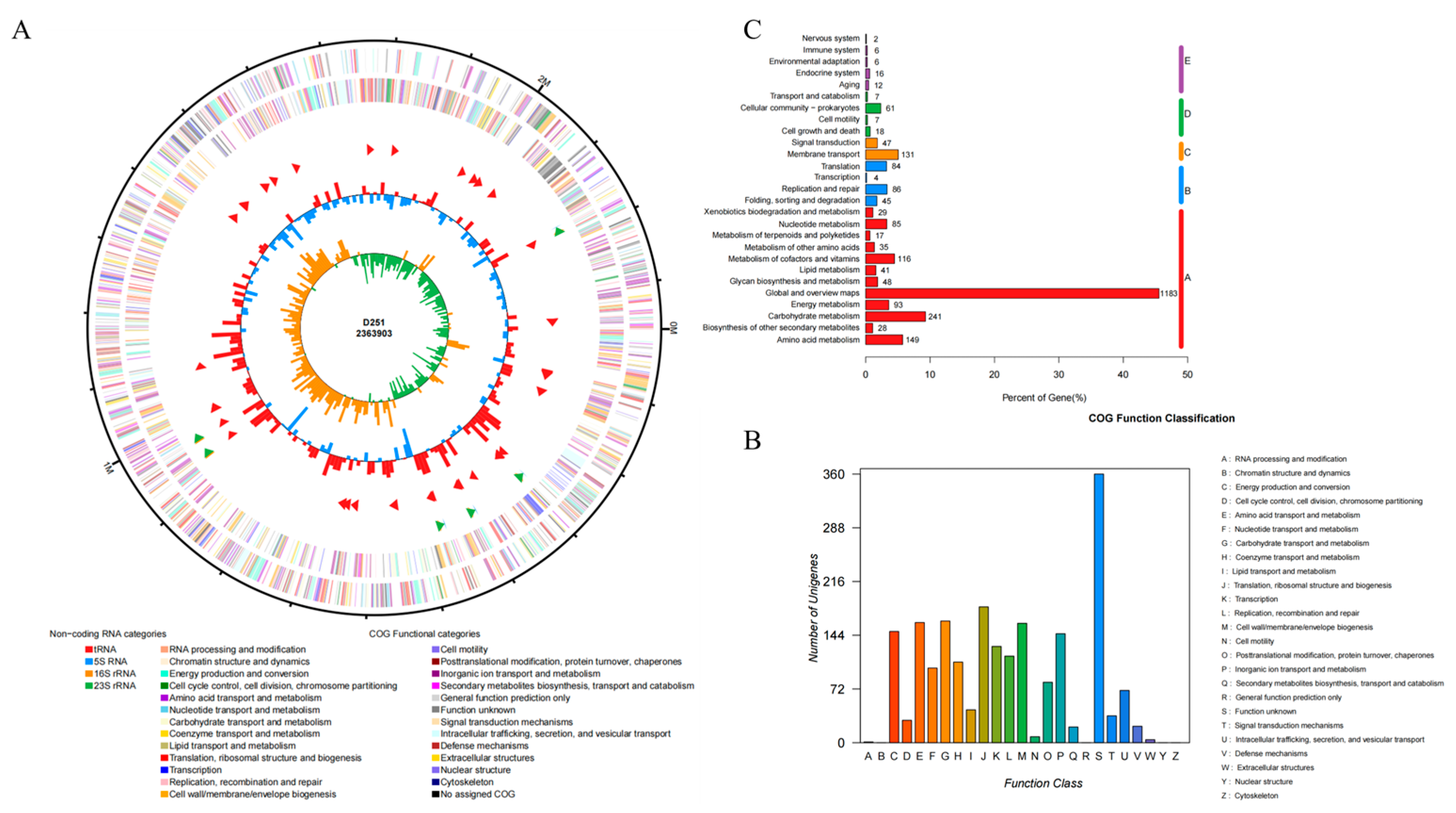
3.6. Whole-Genome Sequencing Analysis of M. glucosida
3.7. Prediction of Virulence and Resistance Genes in M. glucosida
3.8. Establishment of the Specific Detection for M. glucosida
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katsarou, E.I.; Lianou, D.T.; Michael, C.K.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Papadopoulos, E.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Associations of Climatic Variables with Health Problems in Dairy Sheep Farms in Greece. Climate 2024, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.R.; Brogden, K.A. Response of the ruminant respiratory tract to Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrenberg, C.; Schulzetanzil, G.; Martel, J.L.; Chaslus-Dancla, E.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial resistance in Pasteurella and Mannheimia: Epidemiology and genetic basis. Vet. Res. 2001, 32, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deressa, A.; Asfaw, Y.; Lubke, B.; Kyule, M.W.; Zessin, K.H. Molecular detection of Pasteurella multocida and Mannheimia haemolytica in sheep respiratory infections in Ethiopia. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2010, 8, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Harhay, G.P.; Murray, R.W.; Lubbers, B.; Griffin, D.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M.; Harhay, D.M.; Bono, J.; Clawson, M.L.; Heaton, M.P.; et al. Complete closed genome sequences of four Mannheimia varigena isolates from cattle with shipping fever. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00088-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angen, O.; Mutters, R.; Caugant, D.A.; Olsen, J.E.; Bisgaard, M. Taxonomic relationships of the (Pasteurella) haemolytica complex as evaluated by DNA-DNA hybridizations and 16S rRNA sequencing with proposal of Mannheimia haemolytica gen. nov. comb. nov. Mannheimia granulomatis comb. nov. Mannheimia glucosida sp. nov. glucosida sp. nov. Mannheimia ruminalis sp. nov. and Mannheimia varigena sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Ritchey, J.W.; Confer, A.W. Mannheimia haemolytica: Bacterial-host interactions in bovine pneumonia. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, M.M.; van Schaik, G.; Meertens, N.M.; Peperkamp, N.H.; van Engelen, E.; van Garderen, E. Emergence of fatal Mannheimia haemolytica infections in cattle in the Netherlands. Vet. J. 2021, 268, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo-Arango, C.J.; Hernández-Castro, R.; Suárez-Güemes, F.; Martínez-Maya, J.J.; Aguilar-Romero, F.; Jaramillo-Meza, L.; Trigo, F.J. Characterisation of Mannheimia spp. strains isolated from bovine nasal exudate and factors associated to isolates, in dairy farms in the Central Valley of Mexico. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 84, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angen, O.; Quirie, M.; Donachie, W.; Bisgaard, M. Investigations on the species specificity of Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica serotyping. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angen, O.; Ahrens, P.; Bisgaard, M. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica-like strains isolated from diseased animals in Denmark. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 84, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omaleki, L.; Barber, S.R.; Allen, J.L.; Browning, G.F. Mannheimia species associated with ovine mastitis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3419–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, K.; Zaheer, R.; Klima, C.; McAllister, T.; Peters, D.; Niu, Y.D.; Ralston, B. Antimicrobial Resistance in Members of the Bacterial Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex Isolated from Lung Tissue of Cattle Mortalities Managed with or without the Use of Antimicrobials. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, W.; Tucker, J.; Fritz, H.; Bross, C.; Adams, J.; Silva, M.; Lorenz, C.; Marshall, E. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiles among commensal Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolated from apparently healthy sheep processed in California: Results from a cross-sectional pilot study. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 233, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klima, C.L.; Zaheer, R.; Cook, S.R.; Booker, C.W.; Hendrick, S.; Alexander, T.W.; McAllister, T.A. Pathogens of bovine respiratory disease in North American feedlots conferring multidrug resistance via integrative conjugative elements. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.; Dixit, S.K.; Kumar, R. Rapid detection of Mannheimia haemolytica in lung tissues of sheep and from bacterial culture. Vet. World 2015, 8, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, S.; Schierack, P.; Grobbel, M.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Wieler, L.H.; Ewers, C. Real-time PCR assay for the detection of species of the genus Mannheimia. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 75, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.C.; Daher, R.K.; Stanford, K.; Amoako, K.K.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G.; Alexander, T.; Cook, S.; Ralston, B.; Zaheer, R.; et al. A Sensitive and Accurate Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Detection of the Primary Bacterial Pathogens Causing Bovine Respiratory Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, T.W.; Cook, S.R.; Yanke, L.J.; Booker, C.W.; Morley, P.S.; Read, R.R.; Gow, S.P.; McAllister, T.A. A multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay for the identification of Mannheimia haemolytica, Mannheimia glucosida and Mannheimia ruminalis. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 130, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klima, C.L.; Alexander, T.W.; Hendrick, S.; McAllister, T.A. Characterization of Mannheimia haemolytica isolated from feedlot cattle that were healthy or treated for bovine respiratory disease. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 78, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- García-Alvarez, A.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F.; Chaves, F.; Pinto, C.; Cid, D. Ovine Mannheimia haemolytica isolates from lungs with and without pneumonic lesions belong to similar genotypes. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Supplement M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 31st ed. CLSI: Malvern, PA, USA, 2022.
- Gioia, J.; Qin, X.; Jiang, H.; Clinkenbeard, K.; Lo, R.; Liu, Y.; Fox, G.E.; Yerrapragada, S.; McLeod, M.P.; McNeill, T.Z.; et al. The genome sequence of Mannheimia haemolytica A1: Insights into virulence, natural competence, and Pasteurellaceae phylogeny. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7257–7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albelda, S.M.; Buck, C.A. Integrins and other cell adhesion molecules. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1990, 4, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswaran, S.K.; Kannan, M.S.; Weiss, D.J.; Reddy, K.R.; Townsend, E.L.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, B.W.; Whiteley, L.O. Enhancement of neutrophil-mediated injury to bovine pulmonary endothelial cells by Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapattu, D.N.; Czuprynski, C.J. Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin induces apoptosis of bovine lymphoblastoid cells (BL-3) via a caspase-9-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5504–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumbikat, P.; Dileepan, T.; Kannan, M.S.; Maheswaran, S.K. Mechanisms underlying Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin-induced oncosis and apoptosis of bovine alveolar macrophages. Microb. Pathog. 2005, 38, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchinon, L.; Fett, T.; Desmecht, D. How Mannheimia haemolytica defeats host defence through a kiss of death mechanism. Vet. Res. 2005, 36, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, R.L.; Whittam, T.S.; Selander, R.K. Sequence diversity and molecular evolution of the leukotoxin (lktA) gene in bovine and ovine strains of Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clawson, M.L.; Murray, R.W.; Sweeney, M.T.; Apley, M.D.; DeDonder, K.D.; Capik, S.F.; Larson, R.L.; Lubbers, B.V.; White, B.J.; Kalbfleisch, T.S.; et al. Genomic signatures of Mannheimia haemolytica that associate with the lungs of cattle with respiratory disease, an integrative conjugative element, and antibiotic resistance genes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Lasheras, S.; Zaheer, R.; Klima, C.; Sanderson, H.; Ortega Polo, R.; Milani, M.R.M.; Vertenten, G.; McAllister, T.A. Serotyping and antimicrobial resistance of Mannheimia haemolytica strains from European cattle with bovine respiratory disease. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 124, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klima, C.L.; Zaheer, R.; Briggs, R.E.; McAllister, T.A. A multiplex PCR assay for molecular capsular serotyping of Mannheimia haemolytica serotypes 1, 2, and 6. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 139, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Test | Isolates | M. glucosida | M. haemolytica | M. ruminalis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D251 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | ||||
| β-Glucosidase (NPG) | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| β-Xylosidase | − | − | − | − | + | +/− | − | − |
| L-Arabitol | + | − | − | − | + | +/− | − | + |
| D-Maltose | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + |
| D-Sorbitol | − | + | − | + | + | +/− | + | +/− |
| D-trehalose | + | + | + | + | − | +/− | UN | UN |
| Ornithine decarboxylase | − | − | − | − | − | +/− | − | − |
| Esculin | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| Virulence Genes | Isolates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D251 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | |
| gcp | + | + | + | + | − |
| gs60 | + | + | + | + | − |
| tpbA | + | + | + | + | − |
| tpbB | + | + | + | + | − |
| lktC | + | + | + | + | − |
| nmaA | − | − | − | − | − |
| adh | + | + | + | + | + |
| plpD | + | + | + | + | + |
| Dose (CFU/mL) | Deaths |
|---|---|
| 1.0 × 104 | 0 |
| 1.0 × 105 | 0 |
| 1.0 × 106 | 1 |
| 1.0 × 107 | 4 |
| 1.0 × 108 | 5 |
| 1.0 × 109 | 5 |
| Antimicrobial | Disk Diffusion Breakpoints (mm) | R | I | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | S | ||||
| Florfenicol | ≤12 | ≥18 | 0 | 0 | 100% (5/5) |
| Cephalothin | ≤14 | ≥18 | 0 | 0 | 100% (5/5) |
| Doxycycline | ≤12 | ≥16 | 0 | 20% (1/5) | 80% (4/5) |
| Cephalexin | ≤14 | ≥18 | 0 | 20% (1/5) | 80% (4/5) |
| Streptomycin | ≤11 | ≥15 | 100% (5/5) | 0 | 0 |
| Kanamycin | ≤13 | ≥18 | 40% (2/5) | 60% (3/5) | 0 |
| Gentamicin | ≤12 | ≥15 | 20% (1/5) | 80% (4/5) | 0 |
| Cefoxitin | ≤14 | ≥18 | 0 | 0 | 100% (5/5) |
| Antimicrobial | Number of Resistance Genes | Antimicrobial | Number of Resistance Genes | Antimicrobial | Number of Resistance Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-lactams | 1 | Vancomycin | 1 | Nitrofurantoin | 1 |
| Sulfonamides | 1 | Rifampicin | 1 | Isoniazid | 1 |
| Fluoroquinolones | 3 | Fosfomycin | 5 | Pyrazinamide | 1 |
| Neomycin | 2 | Spectinomycin | 1 | Daptomycin | 1 |
| Fusidic acid | 1 | Mupirocin | 1 | Streptomycin | 1 |
| Dicyclomycin | 1 | Coumarin | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Q.; Gao, M.; Gao, T.; Yang, Y.; Sha, X.; Yang, F. Characterization and Pathogenicity of Mannheimia glucosida Isolated from Sheep. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122676
Gu Q, Gao M, Gao T, Yang Y, Sha X, Yang F. Characterization and Pathogenicity of Mannheimia glucosida Isolated from Sheep. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122676
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Qibing, Min Gao, Taichun Gao, Youwen Yang, Xue Sha, and Falong Yang. 2025. "Characterization and Pathogenicity of Mannheimia glucosida Isolated from Sheep" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122676
APA StyleGu, Q., Gao, M., Gao, T., Yang, Y., Sha, X., & Yang, F. (2025). Characterization and Pathogenicity of Mannheimia glucosida Isolated from Sheep. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122676





