Highly Alkaline-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis Induces Compromised M1 Polarization and Phagocytosis of Macrophage via Z-DNA Binding Protein 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. E. faecalis Culture
2.3. Screening of HAR E. faecalis
2.4. Cell Infection
2.5. Cellular Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)-Mediated Gene Silencing
2.7. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Confocal Microscopy Imaging Analysis
2.10. Phagocytosis Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
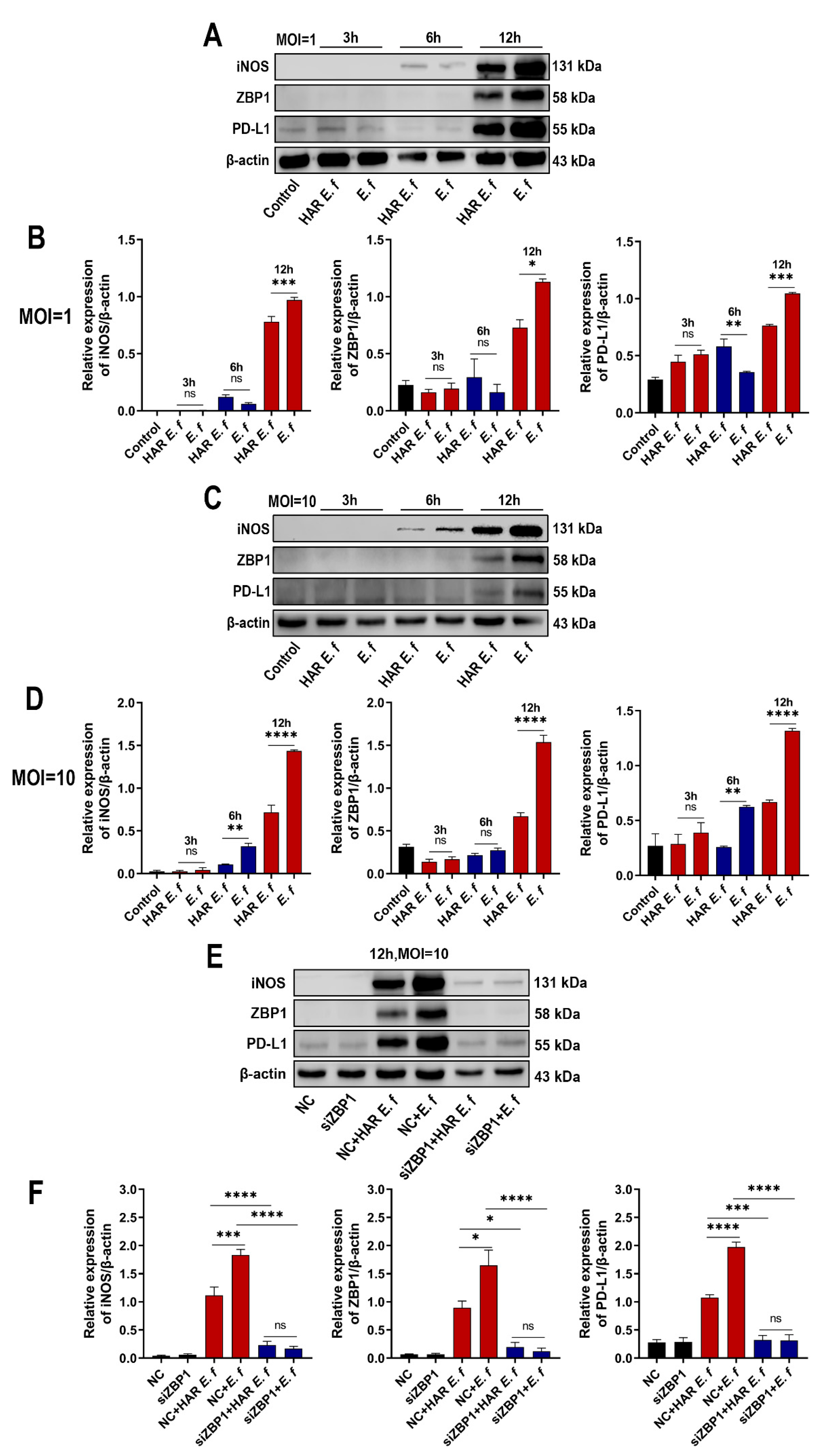
3.1. HAR E. faecalis Induced Lower ZBP1 Expression in Macrophages than Standard Strain
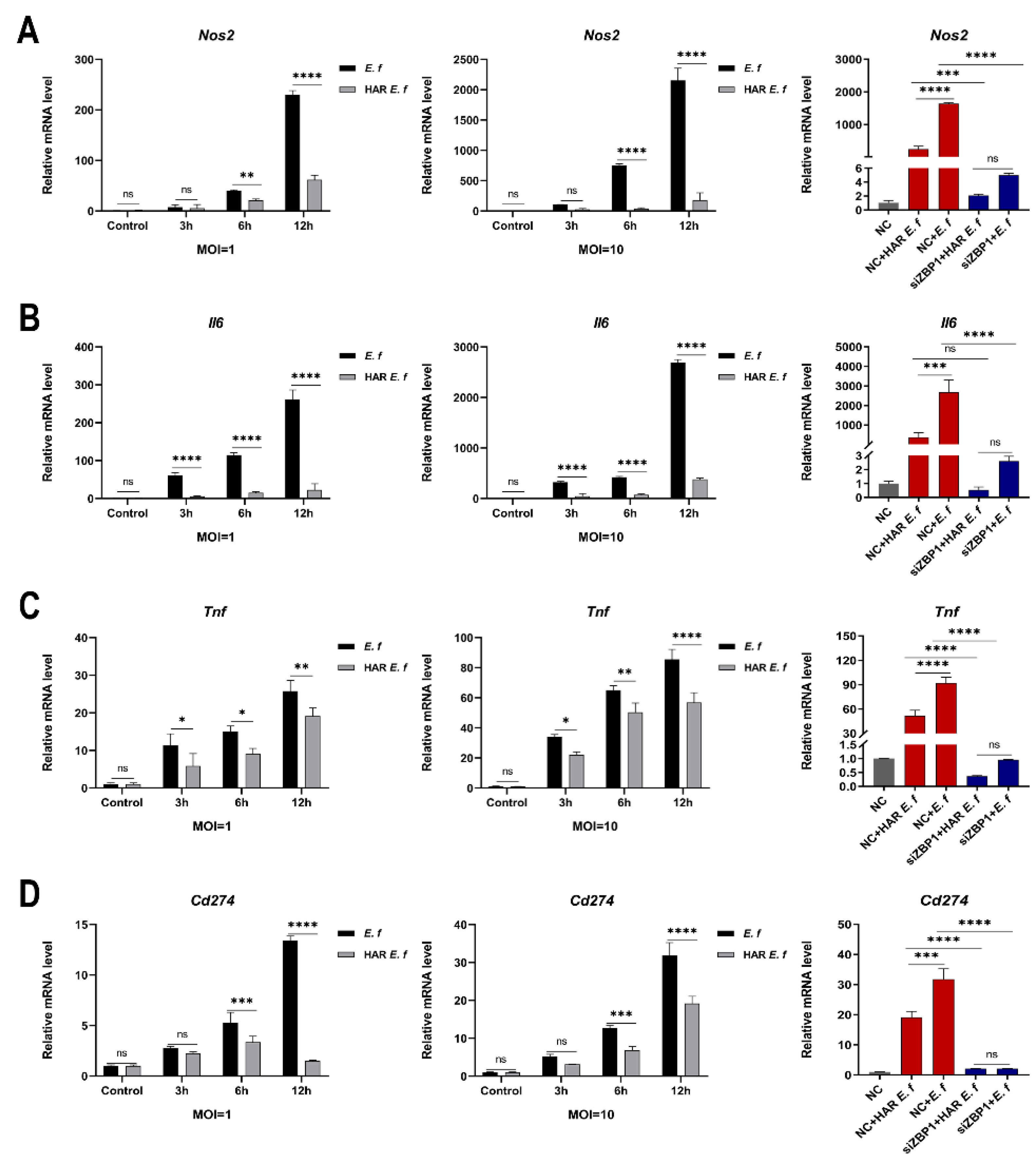
3.2. HAR E. faecalis Showed Compromised M1 Polarization Expression and Cd274(PD-L1) in Macrophages Through ZBP1
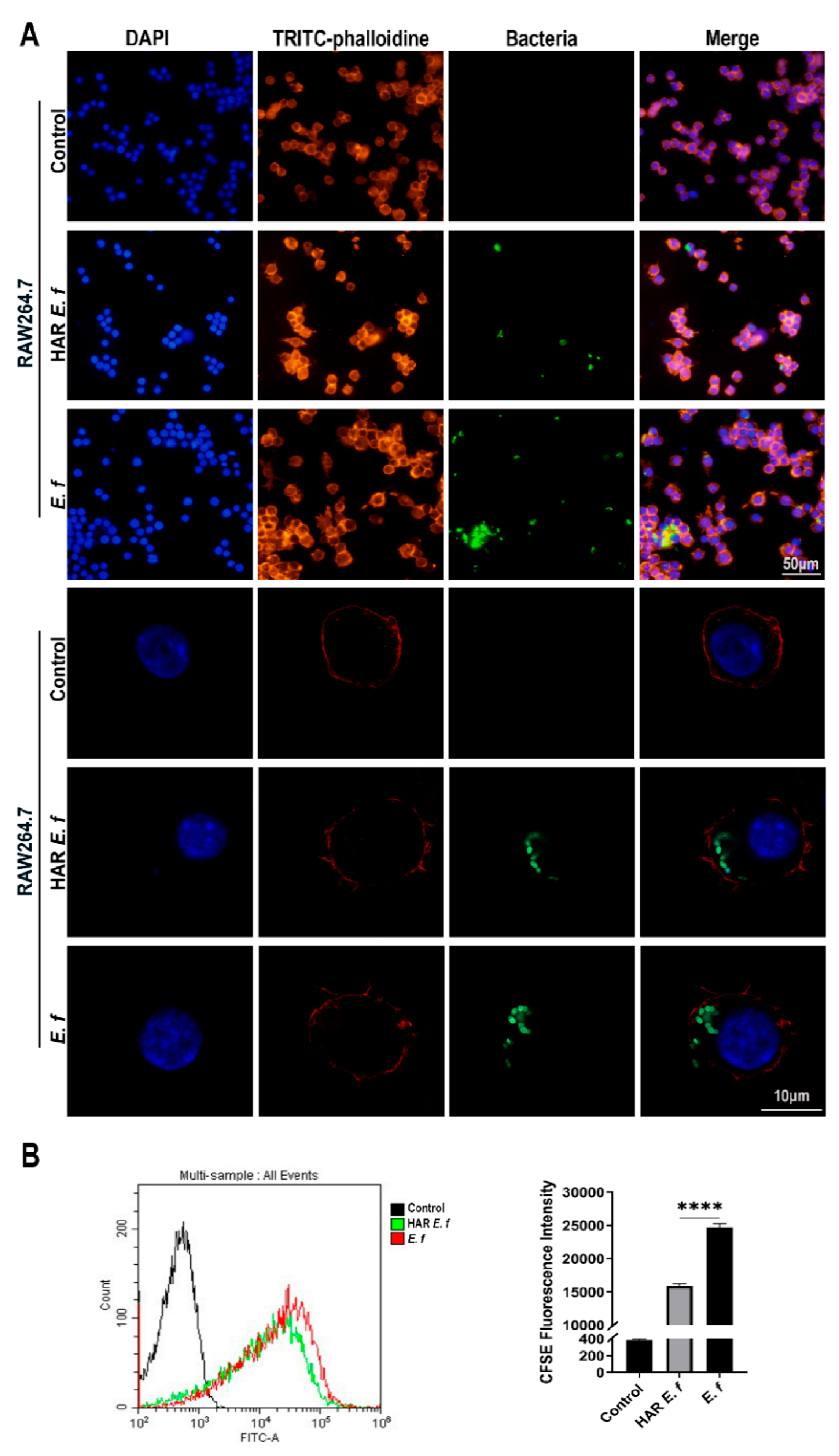
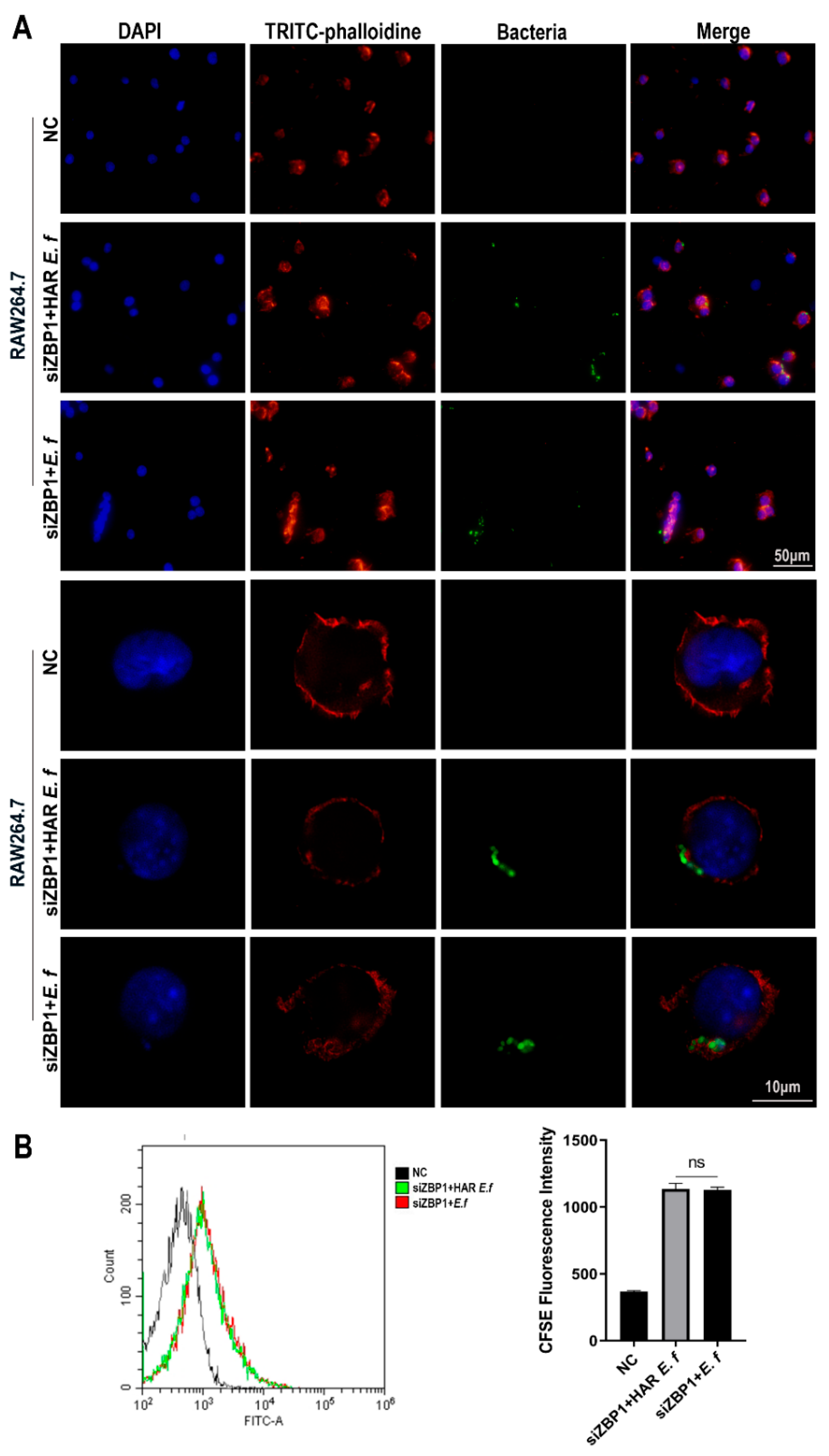
3.3. HAR E. faecalis Compromised Macrophage Phagocytosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| CFDA-SE | Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate Succinimidyl Ester |
| CFU | Colony-Forming Unit |
| CH | Calcium Hydroxide |
| CLSM | Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| E. faecalis | Enterococcus faecalis |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| HAR | Highly Alkaline-Resistant |
| HRP | Horseradish Peroxidase |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| IRE1α/ERN1 | Inositol-Requiring Enzyme 1α |
| MOI | Multiplicity of Infection |
| PAP | Persistent Apical Periodontitis |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
| RT-qPCR | Reverse Transcription Quantitative real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| siRNA | Small Interfering RNA |
| TBST | Tris-Buffered Saline with Tween 20 |
| UPR | Unfolded Protein Response |
| ZBP1 | Z-DNA Binding Protein 1 |
References
- Bergenholtz, G. Assessment of treatment failure in endodontic therapy. J. Oral Rehabil. 2016, 43, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, G.; Ren, B.; Gao, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, M.; Xu, H.H.K.; Han, Q.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; et al. Effect of Antibacterial Root Canal Sealer on Persistent Apical Periodontitis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, A.S.; Tompkins, G.R.; Cathro, P.R. Alkaline Tolerance and Biofilm Formation of Root Canal Isolates of Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 542–547.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Liu, P.; Luo, Y.; Fan, W.; Fan, B. Metformin reduced the alkaline resistance of Enterococcus faecalis against calcium hydroxide via Man-PTS EII: In vitro and in vivo studies. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascale, C.; Geaman, J.; Mendoza, C.; Gao, F.; Kaminski, A.; Cuevas-Nunez, M.; Darvishan, B.; Mitchell, J.C.; Carrilho, M.R.; Sigar, I. In vitro assessment of antimicrobial potential of low molecular weight chitosan and its ability to mechanically reinforce and control endogenous proteolytic activity of dentine. Int. Endod. J. 2023, 56, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sandoval, E.M.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, R.; Torres-Monjarás, A.P.; Alvarado-Hernández, D.L.; Méndez-González, V.; Hernández-Castro, B.; Bernal-Silva, S.; Comas-García, A.; Martínez-Rider, R.; González-Amaro, R.; et al. α-IRAK-4 Suppresses the Activation of RANK/RANKL Pathway on Macrophages Exposed to Endodontic Microorganisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Dey, A.A.; Kesavardhana, S. Z-Nucleic Acid Sensing and Activation of ZBP1 in Cellular Physiology and Disease Pathogenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2025, 329, e13437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xie, J.; Chen, Z.; Ye, K.; Wu, C.; Dai, X.; Yuan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Role of Z-DNA Binding Protein 1 Sensing Mitochondrial Z-DNA and Triggering Necroptosis in Oxalate-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2025, 36, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, D.; Cao, W.; Guo, L.; Liu, K.; Bai, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, P.; Liu, X. Suppression of ZBP1-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome by the tegument protein VP22 facilitates pseudorabies virus infection. mBio 2024, 15, e0194524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z.; Xie, D.; Huang, Z.; Ouyang, S. ZBP1 promotes hepatocyte pyroptosis in acute liver injury by regulating the PGAM5/ROS pathway. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Lu, F.; Hou, L.; Zhang, X.; Pan, C.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Hou, Y.; et al. IRF1 regulation of ZBP1 links mitochondrial DNA and chondrocyte damage in osteoarthritis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.T.R.; Guimarães, E.S.; Oliveira, S.C. ZBP1 senses Brucella abortus DNA triggering type I interferon signaling pathway and unfolded protein response activation. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1511949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Thevkar Nagesh, P.; Joshi, R.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zivny, A.; Mehta, J.; Parikh, S.M.; Szabo, G. Bile acid-induced IRF3 phosphorylation mediates cell death, inflammatory responses, and fibrosis in cholestasis-induced liver and kidney injury via regulation of ZBP1. Hepatology 2024, 79, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Liu, M.; Gao, A.; Fu, W.; Lu, F.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, R.; et al. ZBP1 senses spliceosome stress through Z-RNA:DNA hybrid recognition. Mol. Cell 2025, 85, 1790–1805.e1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.H.; Wu, P.; Zhang, B.X.; Yang, C.R.; Huang, J.; Wu, L.; Guo, S.H.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, Y.; Yin, Y.; et al. ZBP1 senses splicing aberration through Z-RNA to promote cell death. Mol. Cell 2025, 85, 1775–1789.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, G.; Lü, K. Overexpression of lncRNA HEM2M alleviates liver injury in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2024, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Lin, J.; Zhu, W.; Huang, D.; Tan, X.P. Gingivalis induce macrophage polarization by regulating hepcidin expression in chronic apical periodontitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Mo, C.; Li, S.; Zeng, J.; Chai, Y.; Yao, M.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, P.; Ni, J.; Xu, S. High concentrations of NaF aggravate periodontitis by promoting M1 polarization in macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 140, 112830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesbats, J.; Brillac, A.; Reisz, J.A.; Mukherjee, P.; Lhuissier, C.; Fernández-Monreal, M.; Dupuy, J.W.; Sequeira, A.; Tioli, G.; De La Calle Arregui, C.; et al. Macrophages recycle phagocytosed bacteria to fuel immunometabolic responses. Nature 2025, 640, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qin, K.; Li, N.; Han, C.; Cao, X. An endosomal LAPF is required for macrophage endocytosis and elimination of bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12958–12963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, L.C. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and rheumatoid arthritis: All roads lead to PD-1? Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2025, 70s, 152582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonds, E.F.; Lu, E.D.; Badillo, O.; Karimi, S.; Liu, E.V.; Tamaki, W.; Rancan, C.; Downey, K.M.; Stultz, J.; Sinha, M.; et al. Deep immune profiling reveals targetable mechanisms of immune evasion in immune checkpoint inhibitor-refractory glioblastoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, D.; Wang, J.; Du, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Dong, Q. PD-L1 in plasmacytoid dendritic cells promote HBV persistence through disrupting humoral immune response. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1545667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Pan, N.; Sun, X.; Chen, B.; Zheng, S.; Wei, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Tumor cell-released autophagosomes (TRAPs) induce PD-L1-decorated NETs that suppress T-cell function to promote breast cancer pulmonary metastasis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e009082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-de la Cruz, M.L.; Salinas-Carmona, M.C. The immune exhaustion paradox: Activated functionality during chronic bacterial infections. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2024, 18, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Guo, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Xu, M.; Zhu, X.D.; et al. ACE2 Enhances Sensitivity to PD-L1 Blockade by Inhibiting Macrophage-Induced Immunosuppression and Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2025, 85, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Nie, F.; Yin, Q.; Tian, H.; Gong, P.; Ju, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, C. Periodontitis promotes tumor growth and immune evasion via PD-1/PD-L1. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2024, 74, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Sitosari, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shiotsu, N.; Fukuhara, Y.; Ikegame, M.; Okamura, H. Gingipain regulates isoform switches of PD-L1 in macrophages infected with Porphyromonas gingivalis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, S.; Wu, F.; Wagenlehner, F.; Dansranjav, T.; Ruf, S.; Denter, F.; Meyle, J. PD-L1 Up-Regulation in Prostate Cancer Cells by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 935806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel-Khattab, D.; Groeger, S.; Domann, E.; Chakraborty, T.; Lochnit, G.; Meyle, J. Porphyromonas gingivalis induced up-regulation of PD-L1 in colon carcinoma cells. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2021, 36, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2015, 10, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Chen, J.; Du, J.; Tian, Y.; Ma, J.; et al. SIRT7 orchestrates melanoma progression by simultaneously promoting cell survival and immune evasion via UPR activation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Cohen, J.M.; Reglinski, M.; Jose, R.J.; Chan, W.Y.; Marshall, H.; de Vogel, C.; Gordon, S.; Goldblatt, D.; Petersen, F.C.; et al. Naturally Acquired Human Immunity to Pneumococcus Is Dependent on Antibody to Protein Antigens. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006137, Erratum in PLOS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006259. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, P.N. On the causes of persistent apical periodontitis: A review. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 249–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Luo, Y.; Liu, P.; Xiao, S.; Fan, W.; Fan, B. The potential regulatory role of mannose phosphotransferase system EII in alkaline resistance of Enterococcus faecalis. J. Oral Microbiol. 2025, 17, 2487944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Lv, X.; Liao, C.; Liang, A.; Luo, C.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tong, Z. Single-cell RNA sequencing combined with proteomics of infected macrophages reveals prothymosin-α as a target for treatment of apical periodontitis. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 66, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.Y.; Deng, Z.L.; Du, Q.Y.; Dai, M.Q.; Luo, Y.Y.; Liang, Y.E.; Dai, X.Z.; Guo, S.M.; Zhao, W.H. Enterococcus faecalis Extracellular Vesicles Promote Apical Periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2024, 103, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißelberg, S.; Both, A.; Failla, A.V.; Huang, J.; Linder, S.; Ohnezeit, D.; Bartsch, P.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Rohde, H. Staphylococcus epidermidis alters macrophage polarization and phagocytic uptake by extracellular DNA release in vitro. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N. Z-DNA binding protein 1 orchestrates innate immunity and inflammatory cell death. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 77, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Fan, W.; Fan, B. Fusobacterium nucleatum triggers proinflammatory cell death via Z-DNA binding protein 1 in apical periodontitis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Lee, S.; Mall, R.; Pandian, N.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, B.R.; Malireddi, R.S.; Yang, D.; Trifkovic, S.; Steele, J.A.; et al. ZBP1-dependent inflammatory cell death, PANoptosis, and cytokine storm disrupt IFN therapeutic efficacy during coronavirus infection. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabo6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udawatte, D.J.; Rothman, A.L. Viral Suppression of RIPK1-Mediated Signaling. mBio 2021, 12, e0172321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, U.; Sabu, M.K.; Rajmani, R.S.; Chaudhary, A.D.; Gupta, S.K.; Chakravortty, D. Salmonella Effector SseL Induces Programmed Death Ligand 1 Upregulation and T-Cell Inactivation via the β-Catenin Signaling Axis. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, 232, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.Z.; Bai, L.A.; Luo, Y.; Liu, P.; Hua, F.; Fan, W.; Fan, B. The presence of Enterococcus in root canal infections based on next-generation sequencing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Endod. J. 2025, 58, 1331–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, R.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Z.; Fan, W. Enterococcus faecalis and lipoteichoic acid up-regulated PD-L1 of macrophage through TLR and IRE1 α/XBP1 signaling axis. Odontology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Danenberg, E.; Huang, C.S.; Egle, D.; Callari, M.; Bermejo, B.; Dugo, M.; Zamagni, C.; Thill, M.; Anton, A.; et al. Spatial predictors of immunotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer. Nature 2023, 621, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Wu, S.; Yan, Z. Candida albicans induces upregulation of programmed death ligand 1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuzzi, G.; Vasciaveo, A.; Taglialatela, A.; Chen, X.; Firestone, T.M.; Hickman, A.R.; Mao, W.; Thakar, T.; Vaitsiankova, A.; Huang, J.W.; et al. SMARCAL1 is a dual regulator of innate immune signaling and PD-L1 expression that promotes tumor immune evasion. Cell 2024, 187, 861–881.e832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Heng, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, G.; Peng, M.; Chan, E.-C.; Chen, S. Capsular polysaccharide enables Klebsiella pneumoniae to evade phagocytosis by blocking host-bacteria interactions. mBio 2025, 16, e0383824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zierke, L.; Mourad, R.; Kohler, T.P.; Müsken, M.; Hammerschmidt, S. Influence of the polysaccharide capsule on virulence and fitness of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1450984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B.; Zhang, B.; Qin, X.J.; Li, H. Preadsorption of Serum Proteins Regulates Bacterial Infections and Subsequent Macrophage Phagocytosis on Biomaterial Surfaces. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5957–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschalidi, S.; Ravichandran, K.S. Phagocytosis: Sweet Repulsions via the Glycocalyx. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R20–R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, N.; Derré-Bobillot, A.; Gaubert, S.; Herry, J.M.; Deschamps, J.; Wei, Y.; Baranek, T.; Si-Tahar, M.; Briandet, R.; Serror, P.; et al. Exploration of the role of the virulence factor ElrA during Enterococcus faecalis cell infection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amuasi, G.R.; Dsani, E.; Owusu-Nyantakyi, C.; Owusu, F.A.; Mohktar, Q.; Nilsson, P.; Adu, B.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Egyir, B. Enterococcus species: Insights into antimicrobial resistance and whole-genome features of isolates recovered from livestock and raw meat in Ghana. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1254896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, V.; Theruvath, J.; Pauck, D.; Picard, D.; Qin, N.; Blümel, L.; Maue, M.; Bartl, J.; Ahmadov, U.; Langini, M.; et al. Tacedinaline (CI-994), a class I HDAC inhibitor, targets intrinsic tumor growth and leptomeningeal dissemination in MYC-driven medulloblastoma while making them susceptible to anti-CD47-induced macrophage phagocytosis via NF-kB-TGM2 driven tumor inflammation. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e005871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Mao, C.; Liu, G.; Li, S.; Wen, L. Chemerin 15 enhances microglial phagocytosis to attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the ChemR23/p38 MAPK pathway. iScience 2025, 28, 113396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Wen, X.; Li, B.; Hu, R.; Yang, J.; Yu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Feng, H.; Zhu, F.; Cai, Z.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from alveolar macrophages harboring phagocytosed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus induce necroptosis. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, A.; Ahmed, F.; Okuno, A.; Peng, Z.; Cao, D.Y.; Saito, S. Neutrophils Expressing Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Play an Indispensable Role in Effective Bacterial Elimination and Resolving Inflammation in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection. Pathogens 2024, 13, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| siZBP1 | GGACAUAGAAAGCUCUCAATT | UUGAGAGCUUUCUAUGUCCTT |
| Negative control | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | ACGUAGCACGUUCGGAGAATT |
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Zbp1 | AAGAGTCCCCTGCGATTATTTG | TCTGGATGGCGTTTGAATTGG |
| Nos2 | TCAATGGGACTGCATATCTGCC | GCCAAAATACTACCAGCTCACT |
| Il6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| Tnf | TATGGCCCAGACCCTCACA | GGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCCATC |
| Cd274 | TCAGCTACGGTGGTGCGGACT | AGCTTCTGGATAACCCTCGGCCT |
| Gapdh | TGTGTCCGTCGTGGATCTGA | TTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCAGGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Min, Y.; Fan, W. Highly Alkaline-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis Induces Compromised M1 Polarization and Phagocytosis of Macrophage via Z-DNA Binding Protein 1. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122647
Xiao Y, Liu R, Yang Y, Li X, Min Y, Fan W. Highly Alkaline-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis Induces Compromised M1 Polarization and Phagocytosis of Macrophage via Z-DNA Binding Protein 1. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122647
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yifang, Runze Liu, Yanling Yang, Xinlu Li, Yi Min, and Wei Fan. 2025. "Highly Alkaline-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis Induces Compromised M1 Polarization and Phagocytosis of Macrophage via Z-DNA Binding Protein 1" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122647
APA StyleXiao, Y., Liu, R., Yang, Y., Li, X., Min, Y., & Fan, W. (2025). Highly Alkaline-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis Induces Compromised M1 Polarization and Phagocytosis of Macrophage via Z-DNA Binding Protein 1. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122647







