Infection-Mediated Shifts in the Microbial Communities of Deer-Fed Ixodes scapularis Ticks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tick Collection and Sample Preparation
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.3. Pathogen Testing
2.4. Microbial Community Amplification and Sequencing
2.4.1. Bacterial 16S Library Construction
2.4.2. Fungal Internal Transcribed Spacer Region Library Construction
2.5. Sequencing
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. 16S Sequence Processing
2.6.2. ITS Sequence Processing
2.6.3. Community and Network Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Natural Infection of Ticks Harvested from Deer in Wisconsin
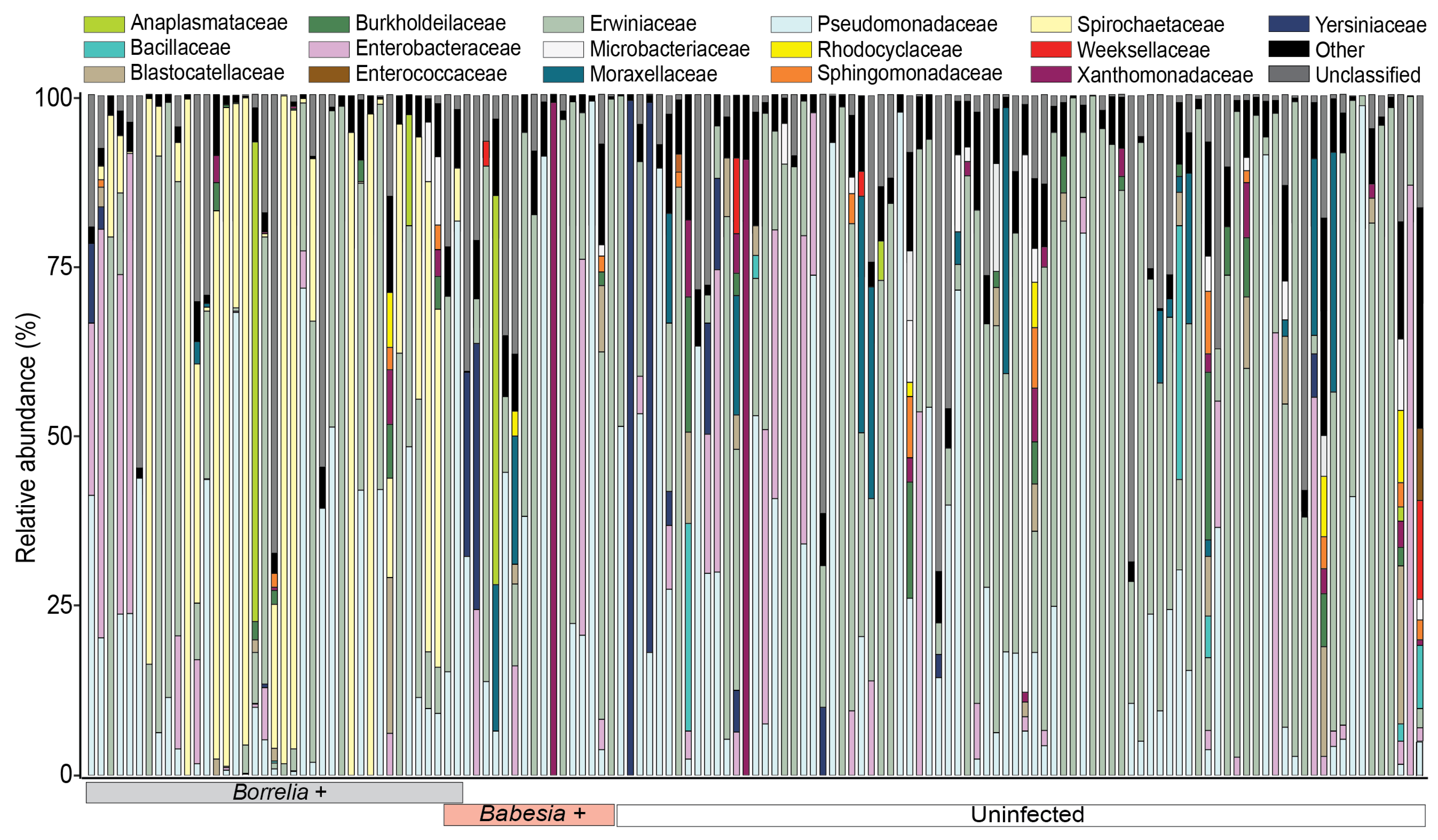
3.2. Microbial Community Composition of Deer-Fed Ixodes Scapularis Ticks
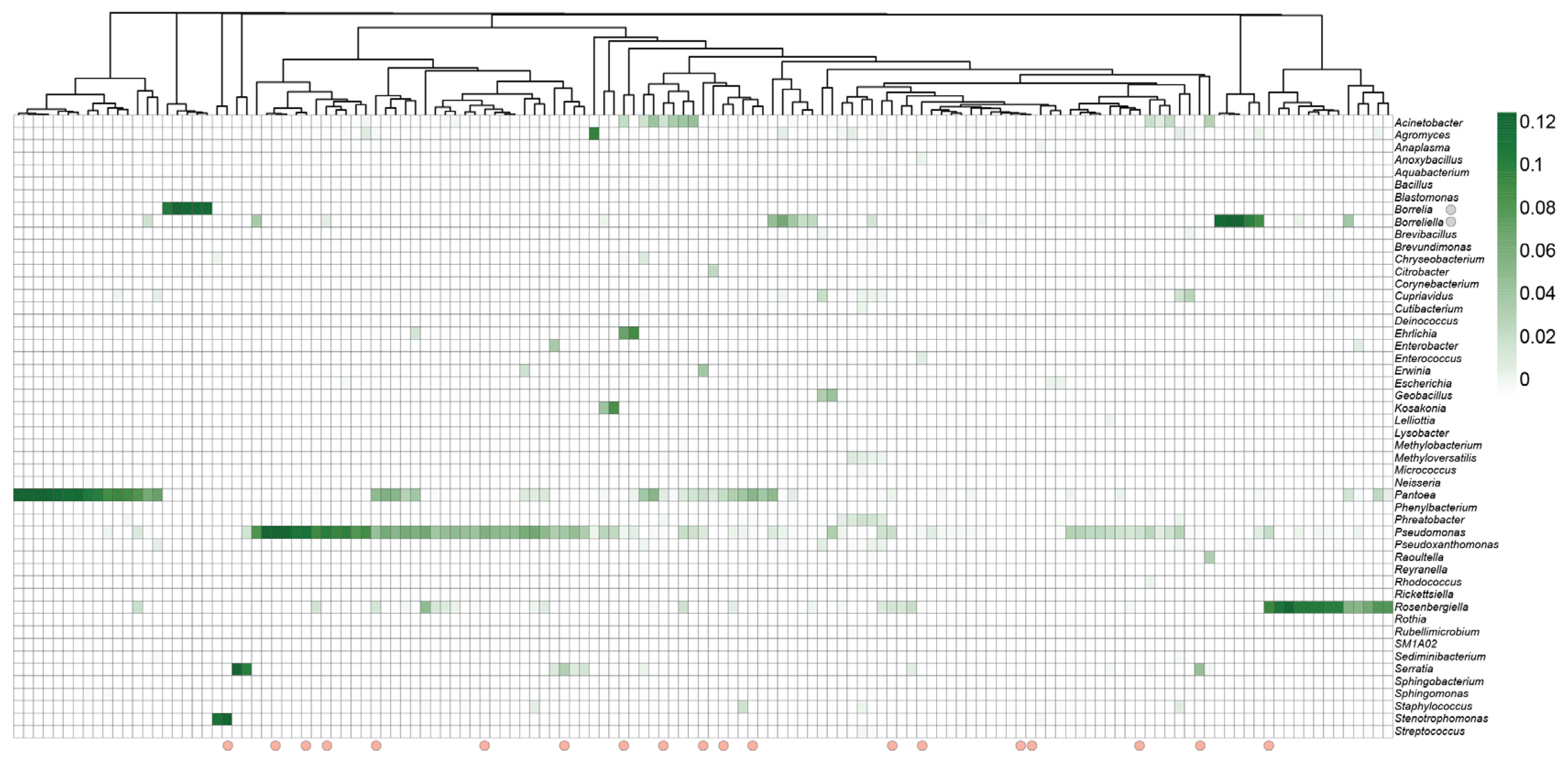
3.2.1. Microbiota Composition of Ixodes Scapularis Ticks
3.2.2. Mycobiota Composition of Ixodes Scapularis Ticks
3.3. Shift in Relative Abundance of Bacterial and Fungal Genera in Response to Infection
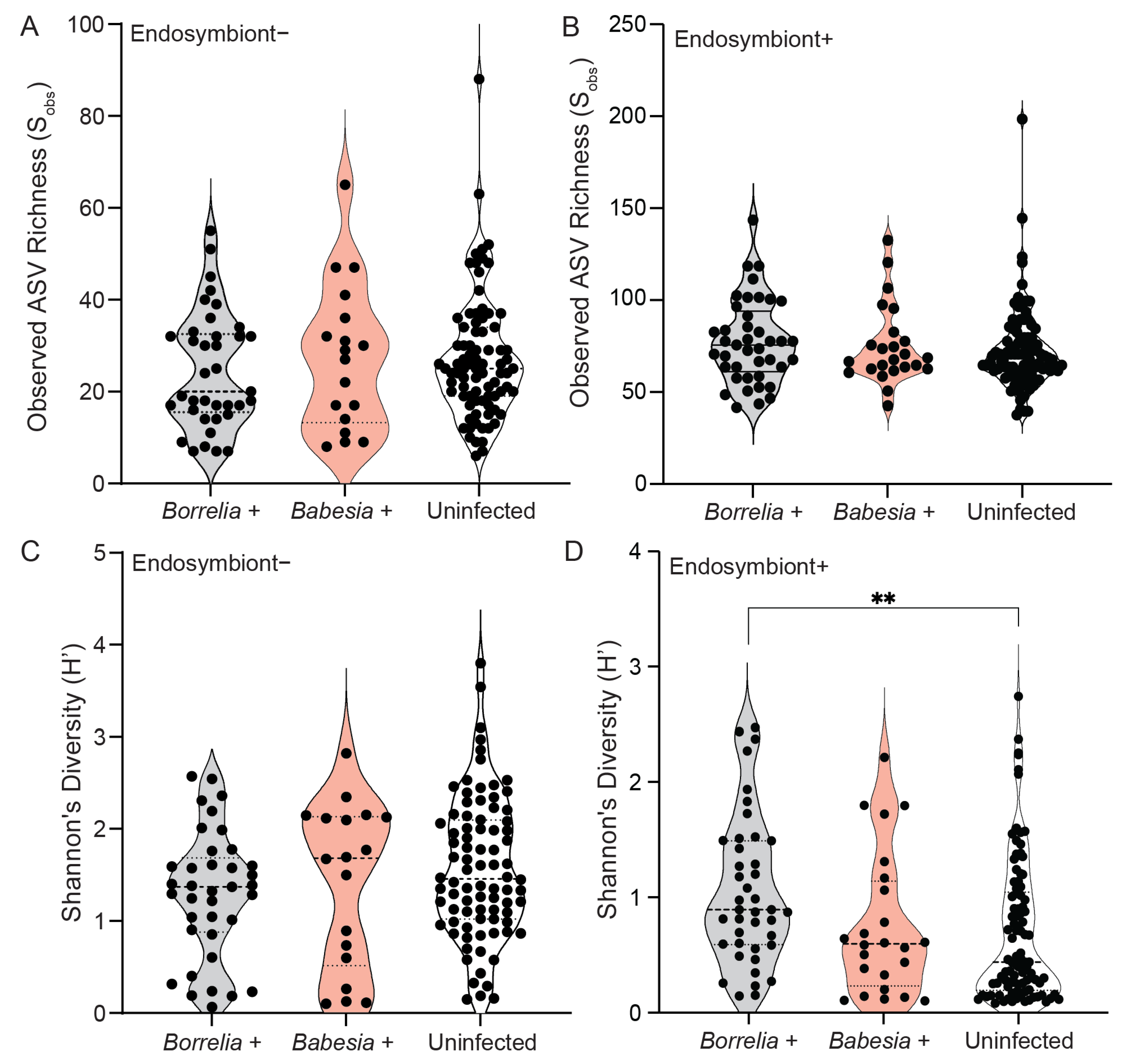
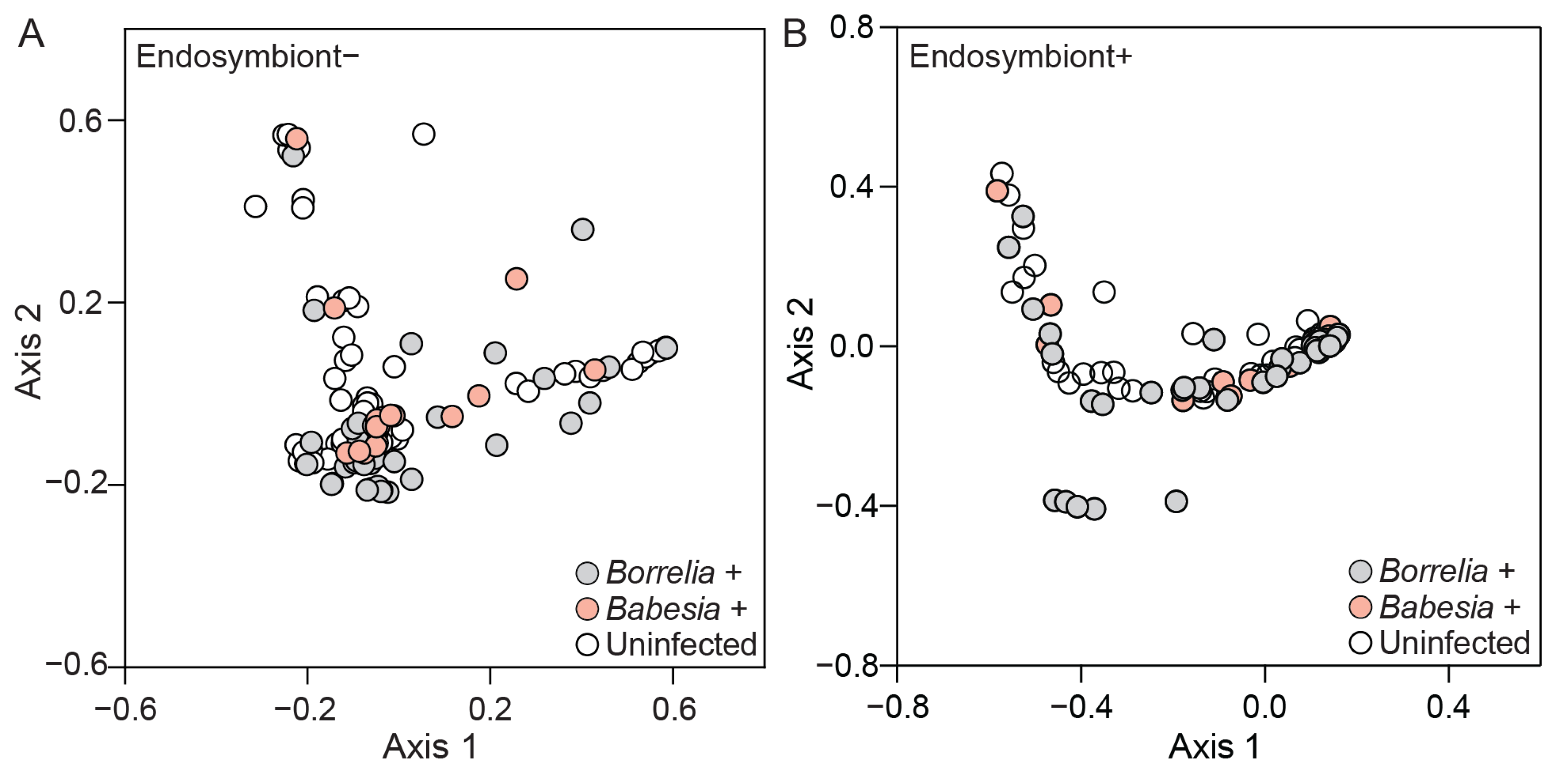
3.4. Bacterial Community Composition and Diversity Differ Between Infected and Uninfected Ticks
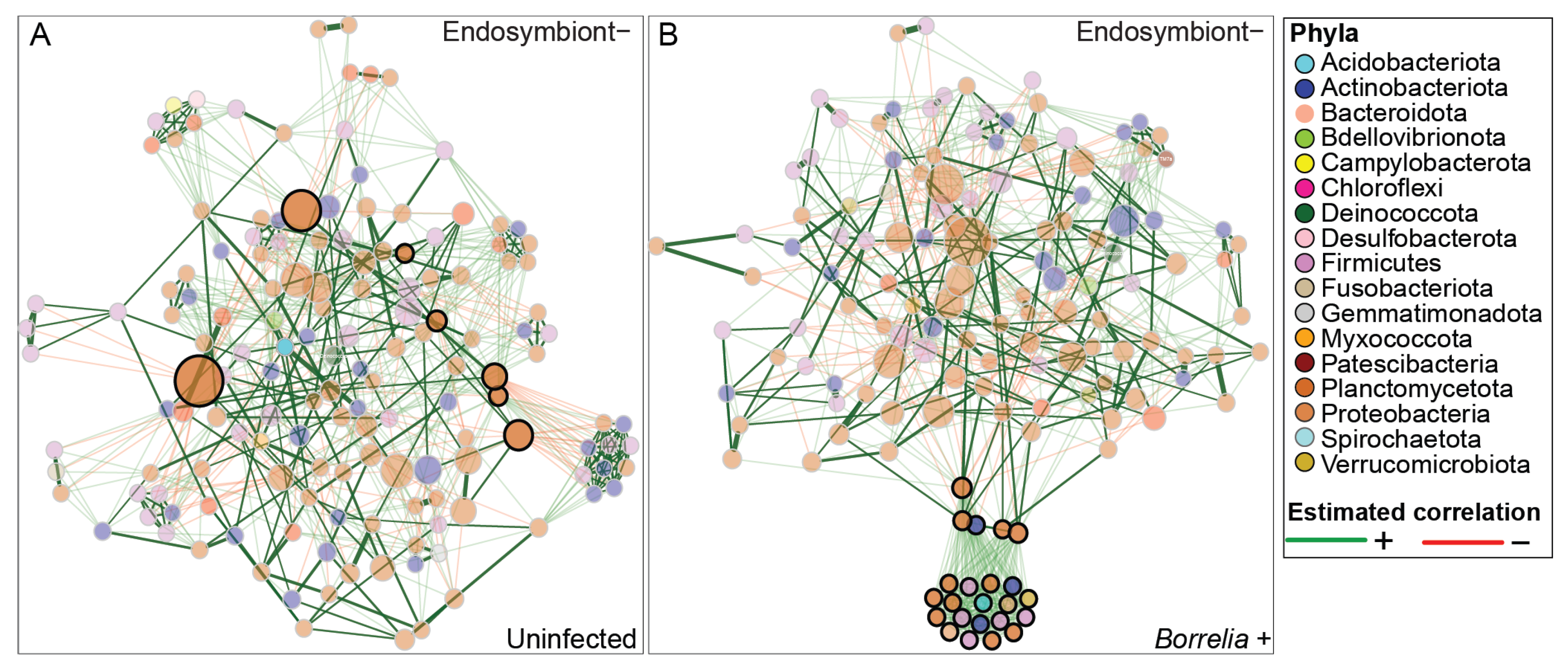
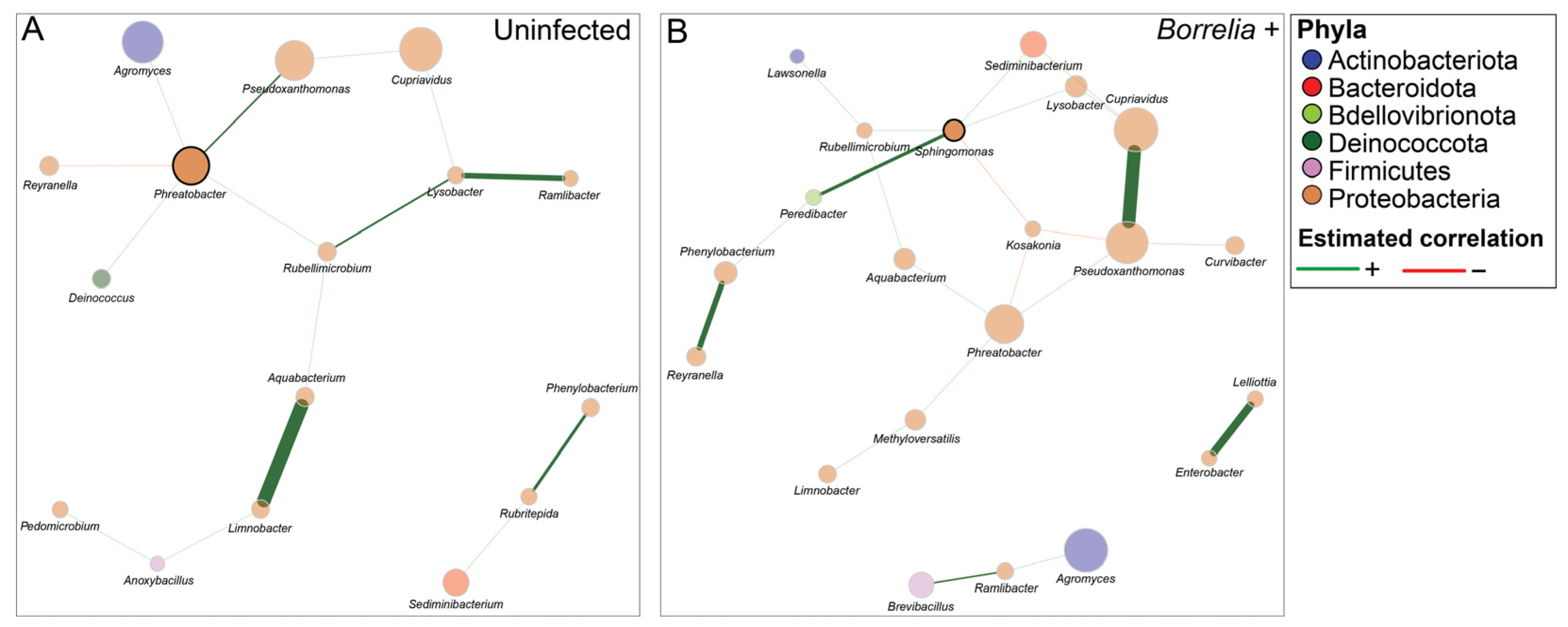
3.5. Borrelia Infection Alters the Bacterial Network Structure in Ixodes Scapularis Ticks
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eisen, R.J.; Eisen, L. The Blacklegged Tick, Ixodes scapularis: An Increasing Public Health Concern. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelder, M.P.; Russell, C.B.; Sheehan, N.J.; Sander, B.; Moore, S.; Li, Y.; Johnson, S.; Patel, S.N.; Sider, D. Human Pathogens Associated with the Blacklegged Tick Ixodes scapularis: A Systematic Review. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugeler, K.J.; Schwartz, A.M.; Delorey, M.J.; Mead, P.S.; Hinckley, A.F. Estimating the Frequency of Lyme Disease Diagnoses, United States, 2010–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Fikrig, E. Tick Microbiome: The Force Within. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Ruiz, P. The Tick Microbiome: The “Other Bacterial Players” in Tick Biocontrol. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cull, B.; Burkhardt, N.Y.; Wang, X.-R.; Thorpe, C.J.; Oliver, J.D.; Kurtti, T.J.; Munderloh, U.G. The Ixodes scapularis Symbiont Rickettsia buchneri Inhibits Growth of Pathogenic Rickettsiaceae in Tick Cells: Implications for Vector Competence. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 748427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duron, O. Nutritional Symbiosis in Ticks: Singularities of the Genus Ixodes. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Torkelson, J.L.; Bodnar, J.; Mortazavi, B.; Laurent, T.; Deason, J.; Thephavongsa, K.; Zhong, J. The Rickettsia Endosymbiont of Ixodes pacificus Contains All the Genes of De Novo Folate Biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greay, T.L.; Gofton, A.W.; Paparini, A.; Ryan, U.M.; Oskam, C.L.; Irwin, P.J. Recent Insights into the Tick Microbiome Gained through Next-Generation Sequencing. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.E.; Bloom, M.E. Sharing the Ride: Ixodes scapularis Symbionts and Their Interactions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Zhang, Y.; Allen, M.S. Bacterial Microbiomes of Ixodes scapularis Ticks Collected from Massachusetts and Texas, USA. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landesman, W.J.; Mulder, K.; Fredericks, L.P.; Allan, B.F. Cross-Kingdom Analysis of Nymphal-Stage Ixodes scapularis Microbial Communities in Relation to Borrelia burgdorferi Infection and Load. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.C.; Helal, Z.H.; Risatti, G.; Hird, S.M. Ixodes scapularis Microbiome Correlates with Life Stage, Not the Presence of Human Pathogens, in Ticks Submitted for Diagnostic Testing. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, J.L.H.; Fitzgerald, D.; Sperling, F.A.H.; Magor, K.E. Microbiome Composition and Borrelia Detection in Ixodes scapularis Ticks at the Northwestern Edge of Their Range. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolnik, C.P.; Falco, R.C.; Daniels, T.J.; Kolokotronis, S.O. Transient Influence of Blood Meal and Natural Environment on Blacklegged Tick Bacterial Communities. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, T.; Shifflett, S.A.; Kennedy, A.C.; Maestas, L.P.; Ellis, V.A. Microbiome Compositions of Nymphal Blacklegged Ticks (Ixodes scapularis) Infected and Uninfected with Borrelia burgdorferi in Delaware. J. Vector Ecol. 2024, 49, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Treuren, W.; Ponnusamy, L.; Brinkerhoff, R.J.; Gonzalez, A.; Parobek, C.M.; Juliano, J.J.; Andreadis, T.G.; Falco, R.C.; Ziegler, L.B.; Hathaway, N.; et al. Variation in the Microbiota of Ixodes Ticks with Regard to Geography, Species, and Sex. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6200–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolnik, C.P.; Prill, R.J.; Falco, R.C.; Daniels, T.J.; Kolokotronis, S.O. Microbiome Changes through Ontogeny of a Tick Pathogen Vector. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 4963–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkerhoff, R.J.; Clark, C.; Ocasio, K.; Gauthier, D.T.; Hynes, W.L. Factors Affecting the Microbiome of Ixodes scapularis and Amblyomma americanum. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Rajeevan, N.; Graham, M.; Wu, M.-J.; DePonte, K.; Marion, S.; Masson, O.; O’Neal, A.J.; Pedra, J.H.F.; Sonenshine, D.E.; et al. Tick Transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi to the Murine Host Is Not Influenced by Environmentally Acquired Midgut Microbiota. Microbiome 2022, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.; Rajeevan, N.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.O.; Heisig, J.; Pan, J.; Eppler-Epstein, R.; DePonte, K.; Fish, D.; Fikrig, E. Gut Microbiota of the Tick Vector Ixodes scapularis Modulate Colonization of the Lyme Disease Spirochete. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuininga, A.R.; Miller, J.L.; Morath, S.U.; Daniels, T.J.; Falco, R.C.; Marchese, M.; Sahabi, S.; Rosa, D.; Stafford, K.C. Isolation of Entomopathogenic Fungi From Soils and Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) Ticks: Prevalence and Methods. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.B.; Yoder, J.A.; Ark, J.T.; Rellinger, E.J. Fungal Fauna of Ixodes scapularis Say and Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Latreille) (Acari: Ixodida) with Special Reference to Species-Associated Internal Mycoflora. Int. J. Acarol. 2005, 31, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greengarten, P.J.; Tuininga, A.R.; Morath, S.U.; Falco, R.C.; Norelus, H.; Daniels, T.J. Occurrence of Soil- and Tick-Borne Fungi and Related Virulence Tests for Pathogenicity to Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Lin, Y.; Han, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Shao, Z. Revealing the Diversity of the Mycobiome in Different Phases of Ticks: ITS Gene-Based Analysis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 8814592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, M.T.; Mandli, J.; Pritt, B.S.; Stauffer, W.; Sloan, L.M.; Zembsch, T.; Lee, X.; Paskewitz, S.M. Detection of Zoonotic Human Pathogens in Ixodes scapularis in Wisconsin-2017. J. Vector Ecol. 2020, 45, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritt, B.S.; Mead, P.S.; Johnson, D.K.H.; Neitzel, D.F.; Respicio-Kingry, L.B.; Davis, J.P.; Schiffman, E.; Sloan, L.M.; Schriefer, M.E.; Replogle, A.J.; et al. Identification of a Novel Pathogenic Borrelia Species Causing Lyme Borreliosis with Unusually High Spirochaetaemia: A Descriptive Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, M.J.; Rosenbaum, E.R.; Pritt, B.S.; Haselow, D.T.; Ferren, K.M.; Alzghoul, B.N.; Rico, J.C.; Sloan, L.M.; Ramanan, P.; Purushothaman, R.; et al. Possible Transfusion-Transmitted Babesia divergens–like/MO-1 Infection in an Arkansas Patient. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, G.D.; Campbell, E.N.; Goethert, H.K.; Spielman, A.; Telford, S.R. Enzootic Transmission of Deer Tick Virus in New England and Wisconsin Sites. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 63, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS Primers with Enhanced Specificity for Basidiomycetes-Application to the Identification of Mycorrhizae and Rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and Direct Sequencing of Fungal Ribosomal RNA Genes for Phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 315–322. ISBN 978-0-12-372180-8. [Google Scholar]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing Mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open-Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarenkov, K.; Henrik Nilsson, R.; Larsson, K.-H.; Alexander, I.J.; Eberhardt, U.; Erland, S.; Høiland, K.; Kjøller, R.; Larsson, E.; Pennanen, T.; et al. The UNITE Database for Molecular Identification of Fungi–Recent Updates and Future Perspectives. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- The Galaxy Community The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible, and Collaborative Data Analyses: 2024 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W83–W94. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peschel, S.; Müller, C.L.; von Mutius, E.; Boulesteix, A.L.; Depner, M. NetCoMi: Network Construction and Comparison for Microbiome Data in R. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtinen, L.W.; Kruger, A.N.; Hacker, M.M. Prevalence of Borrelia burgdorferi in Adult Female Ticks (Ixodes Scapularis), Wisconsin 2010–2013. J. Vector Ecol. 2015, 40, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paskewitz, S.M.; Vandermause, M.; Belongia, E.A.; Kazmierczak, J.J. Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae): Abundance and Rate of Infection with Borrelia burgdorferi in Four State Parks in Wisconsin. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembsch, T.E.; Lee, X.; Bron, G.M.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Paskewitz, S.M. Coinfection of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) Nymphs With Babesia spp. (Piroplasmida: Babesiidae) and Borrelia burgdorferi (Spirochaetales: Spirochaetaceae) in Wisconsin. J. Med. Entomol. 2021, 58, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoles, G.A.; Papero, M.; Beati, L.; Fish, D. A Relapsing Fever Group Spirochete Transmitted by Ixodes scapularis Ticks. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2001, 1, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, C.D.; Carolan, H.E.; Rounds, M.A.; Honig, V.; Mothes, B.; Haag, H.; Nolte, O.; Luft, B.J.; Grubhoffer, L.; Ecker, D.J.; et al. Prevalence of Borrelia miyamotoi in Ixodes Ticks in Europe and the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1678–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Hickling, G.J.; Ogden, N.H.; Ginsberg, H.S.; Kobbekaduwa, V.; Rulison, E.L.; Beati, L.; Tsao, J.I. Seasonality of Acarological Risk of Exposure to Borrelia miyamotoi from Questing Life Stages of Ixodes scapularis Collected from Wisconsin and Massachusetts, USA. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, A.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D. The Specificity of Babesia-Tick Vector Interactions: Recent Advances and Pitfalls in Molecular and Field Studies. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackney, D.E.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Fitzpatrick, K.A.; Brown, I.K.; Ebel, G.D. Short Report: Stable Prevalence of Powassan Virus in Ixodes scapularis in a Northern Wisconsin Focus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 79, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, A.R.; Lougheed, S.C.; Huang, D.; Colautti, R.I. Multiomics Reveals Symbionts, Pathogens, and Tissue-Specific Microbiome of Blacklegged Ticks (Ixodes scapularis) from a Lyme Disease Hot Spot in Southeastern Ontario, Canada. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01404-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.D.; Hayes, B.; Radey, M.C.; Lee, X.; Josek, T.; Bjork, J.; Neitzel, D.; Paskewitz, S.; Chou, S.; Mougous, J.D. Ixodes scapularis Does Not Harbor a Stable Midgut Microbiome. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The Changing Face of the Family Enterobacteriaceae (Order: “Enterobacterales”): New Members, Taxonomic Issues, Geographic Expansion, and New Diseases and Disease Syndromes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e00174-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiers, A.J.; Buckling, A.; Rainey, P.B. The Causes of Pseudomonas Diversity. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2345–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruley, M.; Pasternicki, C.; Fattar, N.; Amoros, J.; Duhayon, M.; McCoy, K.; Duron, O. Culturable Bacteria and Fungi in Ixodes, Dermacentor, Amblyomma and Ornithodoros Ticks. Parasite 2025, 32, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Ji, Y.; Sun, S.; Yue, X.; Wang, C.; Luo, T.; Moming, A.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R. Bacterial Microbiota in Unfed Ticks (Dermacentor nuttalli) From Xinjiang Detected Through 16S rDNA Amplicon Sequencing and Culturomics. Zoonoses 2021, 1, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizzo, M.G.; Dolezelikova, K.; Neupane, S.; Frantova, H.; Hrbatova, A.; Pafco, B.; Fiorotti, J.; Kopacek, P.; Zurek, L. Characterization and Manipulation of the Bacterial Community in the Midgut of Ixodes ricinus. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawidian, P.; Jumpponen, A.; Michel, K. Patterns of Fungal Community Assembly Across Two Culex Mosquito Species. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 911085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawidian, P.; Coon, K.L.; Jumpponen, A.; Cohnstaedt, L.W.; Michel, K. Host-Environment Interplay Shapes Fungal Diversity in Mosquitoes. mSphere 2021, 6, e00646-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellemain, E.; Carlsen, T.; Brochmann, C.; Coissac, E.; Taberlet, P.; Kauserud, H. ITS as an Environmental DNA Barcode for Fungi: An in Silico Approach Reveals Potential PCR Biases. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, K.; Braun, U.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. The Genus Cladosporium. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 72, 1–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, R.; Russo, E.; Becchimanzi, A. Cladosporium—Insect Relationships. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swett, C.L.; Hamby, K.A.; Hellman, E.M.; Carignan, C.; Bourret, T.B.; Koivunen, E.E. Characterizing Members of the Cladosporium cladosporioides Species Complex as Fruit Rot Pathogens of Red Raspberries in the Mid-Atlantic and Co-Occurrence with Drosophila suzukii (Spotted Wing Drosophila). Phytoparasitica 2019, 47, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.D. Control of the Molds Aspergillus sydowi and Penicillium citrinum in Laboratory Colonies of the Lone-Star Tick, Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1989, 6, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, N.V.; Mitkovets, P.V.; Mitina, G.V.; Movila, A.; Tokarev, Y.S.; Leclerque, A. Prevalence of Beauveria pseudobassiana among Entomopathogenic Fungi Isolated from the Hard Tick, Ixodes ricinus. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkovets, P.V.; Munteanu, N.V.; Mitina, G.V.; Tokarev, Y.S.; Movila, A.A.; Toderas, I.; Kleespies, R.G.; Leclerque, A. Prevalence of the Species Beauveria pseudobassiana among Tick-Associated Fungal Isolates from the Republic of Moldova. In Proceedings of the IOPC/WPRS Working Group “Insect Pathogens and Entomopathogenic Nematodes”, Innsbruck, Austria, 19–23 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Landesman, W.J.; Mulder, K.; Allan, B.F.; Bashor, L.A.; Keesing, F.; LoGiudice, K.; Ostfeld, R.S. Potential Effects of Blood Meal Host on Bacterial Community Composition in Ixodes scapularis Nymphs. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Cao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J. The Tick Microbiota Dysbiosis Promote Tick-Borne Pathogen Transstadial Transmission in a Babesia microti–Infected Mouse Model. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 713466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratou, M.; Maitre, A.; Abuin-Denis, L.; Piloto-Sardiñas, E.; Corona-Guerrero, I.; Cano-Argüelles, A.L.; Wu-Chuang, A.; Bamgbose, T.; Almazan, C.; Mosqueda, J.; et al. Disruption of Bacterial Interactions and Community Assembly in Babesia-Infected Haemaphysalis longicornis Following Antibiotic Treatment. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, S.; Schuijt, T.J.; Abraham, N.M.; Rajeevan, N.; Coumou, J.; Graham, M.; Robson, A.; Wu, M.-J.; Daffre, S.; Hovius, J.W.; et al. Modulation of the Tick Gut Milieu by a Secreted Tick Protein Favors Borrelia burgdorferi Colonization. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primers and Probes | Organism | Gene | Sequence (5′–3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bor2F | Borrelia burgdorferi | oppA1 | GAA GCG ACT ATT ACT CAT C | [27] |
| Bor2R | GGC TTT TCT AAT TTT AAC GTT | |||
| Bor2-Bb-P | Red640-TTC AAT ACA CAC ATC AAA CCA C-FL | |||
| GlpQ-F | Borrelia miyamotoi | GlpQ | TCC AGA ACA TAC CTT AGA AGC | [26] |
| GlpQ-R | ATC AAA TCT TTC ACT GAG ACT TA | |||
| GlpQ-P | GAC AAT GTT CCT ATT ATA ATG CAC GAC CC-FL Red640-GAA ATT GAC ACA ACC ACA AAT GTT GCA C-PH | |||
| BAB 1 | Babesia spp. | 18S | TTC AAC GAG TTT TTC CTT | [28] |
| BAB 1-1 | TTC ATC GAG TTT TAT CCC T | |||
| BAB 2 | CAG TCC GAA TAA TTC ACC | |||
| BAB 3 | GTG ATG GGG ATA GAT TAT TGC AA-FL | |||
| BAB 4 | Red640-TAT TAA TCT TGA ACG AGG AAT GCC-PO | |||
| Env-1 | Powassan virus | Envelope | GAG AAG CTT ACG AGG TGC ACG CAT CTT GA | [29] |
| Env-2 | GTG CTC GAG TGC GCC TAC TGA GCC TTT GTC CCA |
| Pathogen | No. Positive | Positive (%) | County |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borrelia burgdorferi | 38/163 | 23.3% | Columbia Dane Dunn La Crosse Monroe Sauk Unknown |
| Borrelia miyamotoi | 7/163 | 4.29% | Monroe |
| Babesia odocoilei | 24/163 | 14.7% | Dane Monroe Richland Unknown |
| Babesia microti | 1/163 | 0.613% | Monroe |
| Powassan virus | 1/163 | 0.613% | Unknown |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tawidian, P.; Tucker, B.J.; Zembsch, T.E.; Ip, H.S.; Bartholomay, L.C. Infection-Mediated Shifts in the Microbial Communities of Deer-Fed Ixodes scapularis Ticks. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112635
Tawidian P, Tucker BJ, Zembsch TE, Ip HS, Bartholomay LC. Infection-Mediated Shifts in the Microbial Communities of Deer-Fed Ixodes scapularis Ticks. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112635
Chicago/Turabian StyleTawidian, Patil, Bradley J. Tucker, Tela E. Zembsch, Hon S. Ip, and Lyric C. Bartholomay. 2025. "Infection-Mediated Shifts in the Microbial Communities of Deer-Fed Ixodes scapularis Ticks" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112635
APA StyleTawidian, P., Tucker, B. J., Zembsch, T. E., Ip, H. S., & Bartholomay, L. C. (2025). Infection-Mediated Shifts in the Microbial Communities of Deer-Fed Ixodes scapularis Ticks. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2635. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112635






