A Microbial Inoculum (PLC-8) Improves Composting of Spent Mushroom Substrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Composting Materials and Ratio
2.2. Composting Methods and Sampling
2.3. Measurement of Compost Pile Temperature
2.4. Determination of Chemical Indicators
2.5. Determination of Microbial Indicators
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
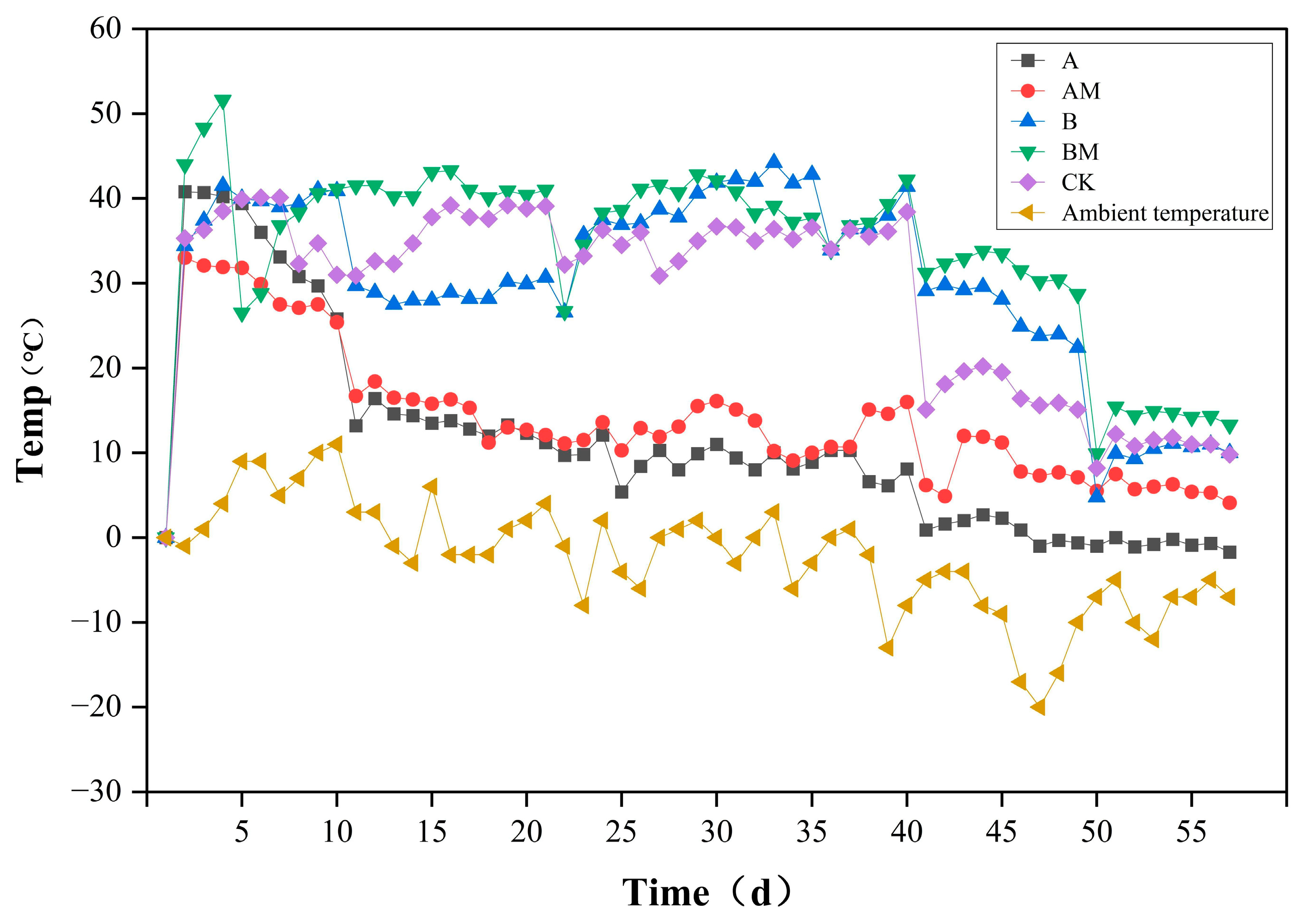
3.1. Temperature Change During Composting
3.2. Changes in Physicochemical Properties During Composting
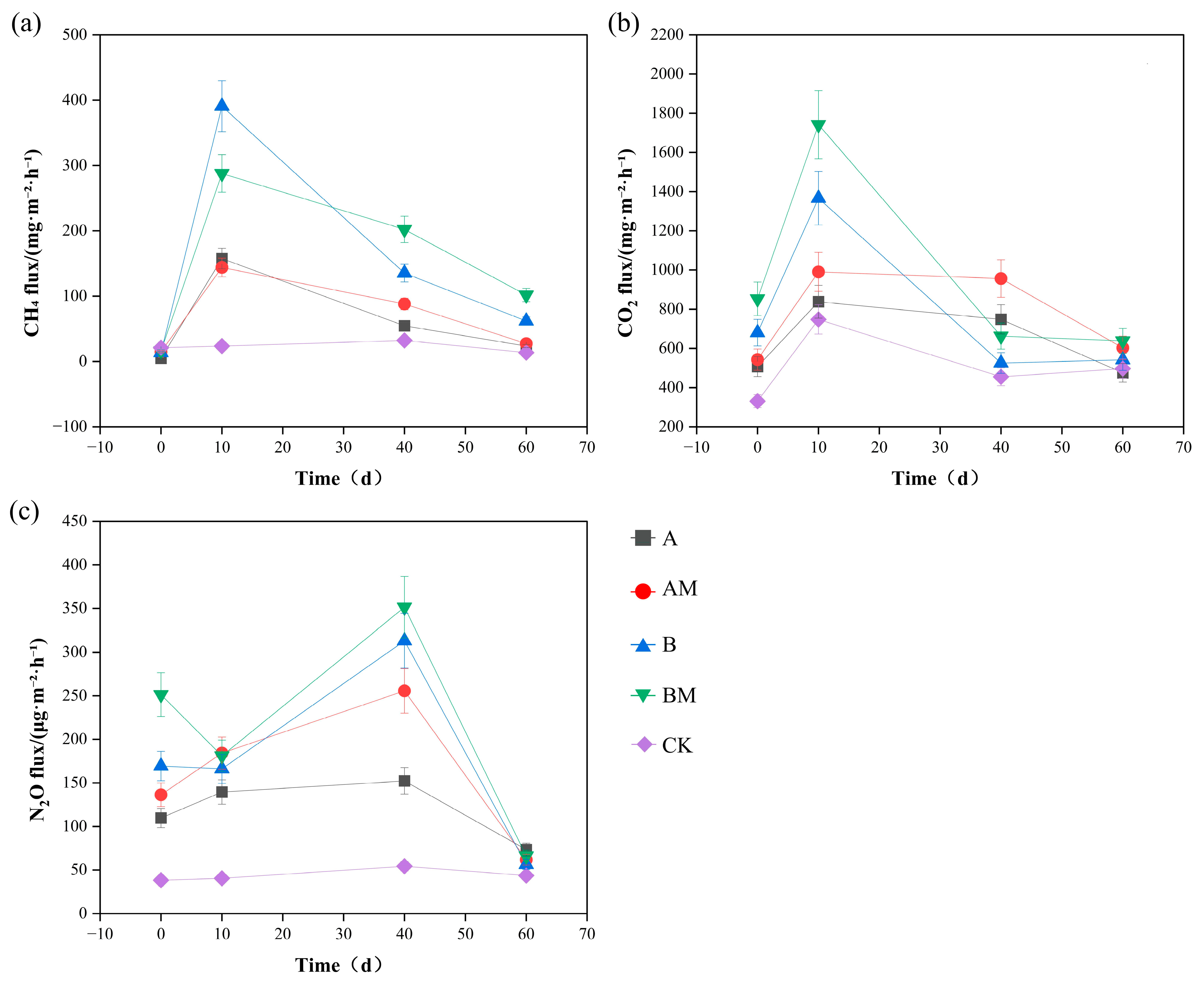
3.3. Changes in Gas Emissions During Composting
3.4. Changes in Microbial Community Composition During Composting
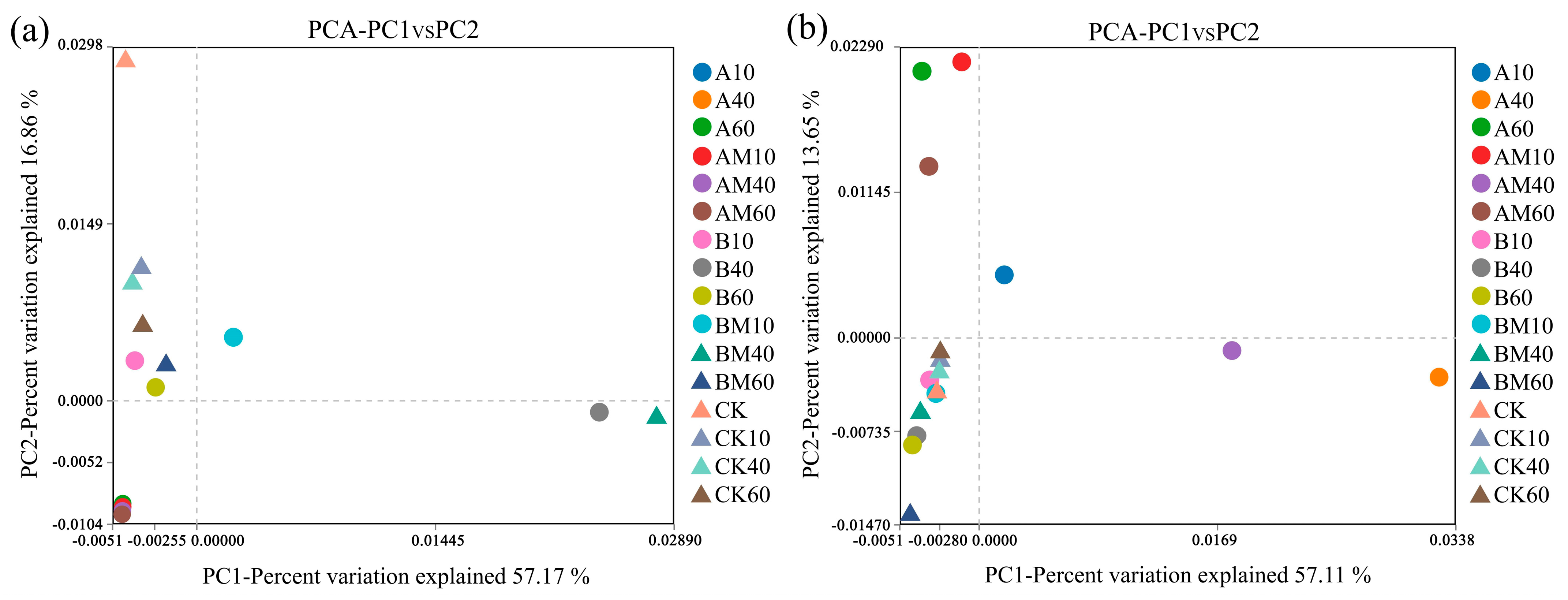
3.4.1. Principal Component Analysis
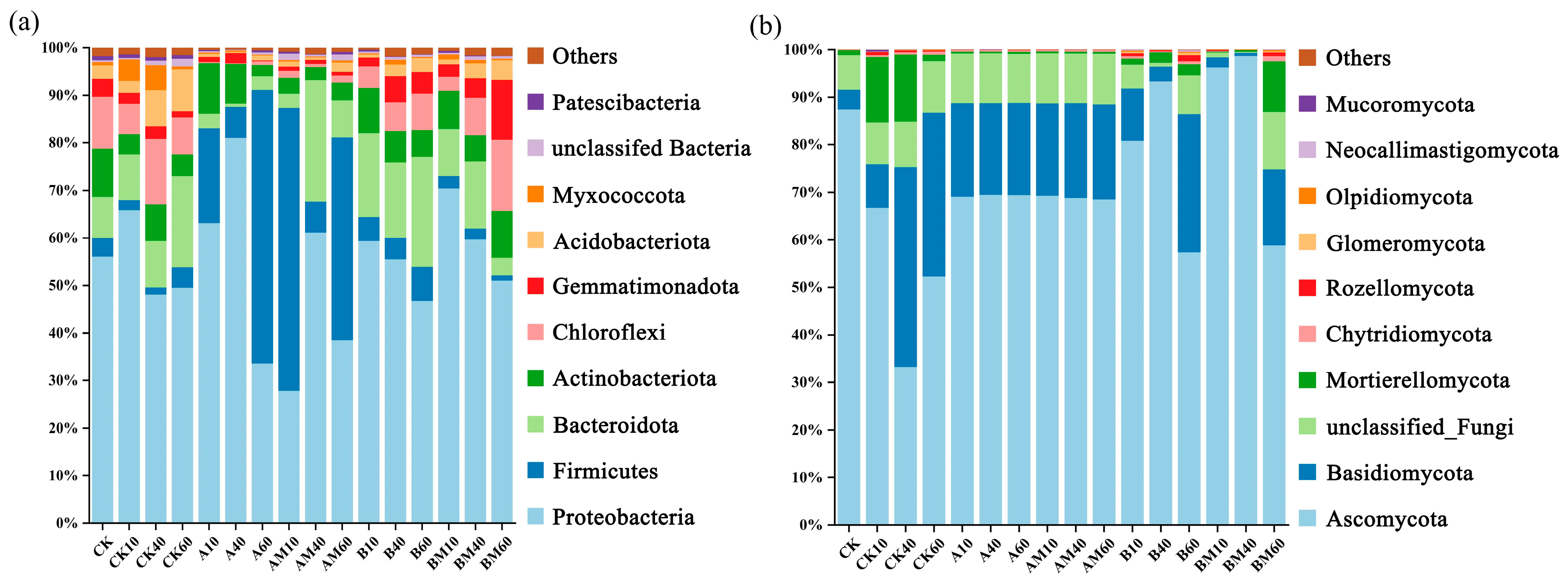
3.4.2. Microbial Community Phylum-Level Composition Analysis
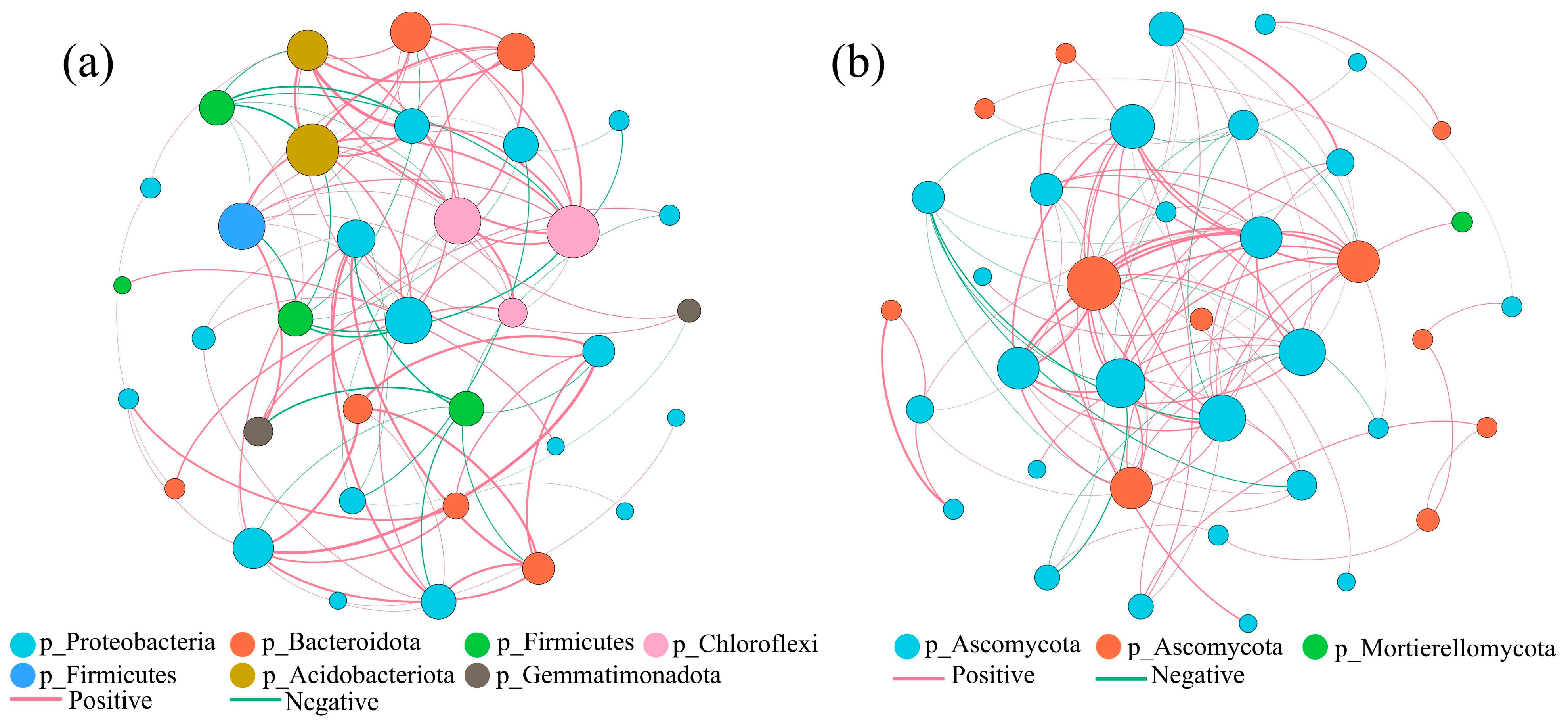
3.4.3. Microbial Community Correlation Network Analysis at the Genus Level
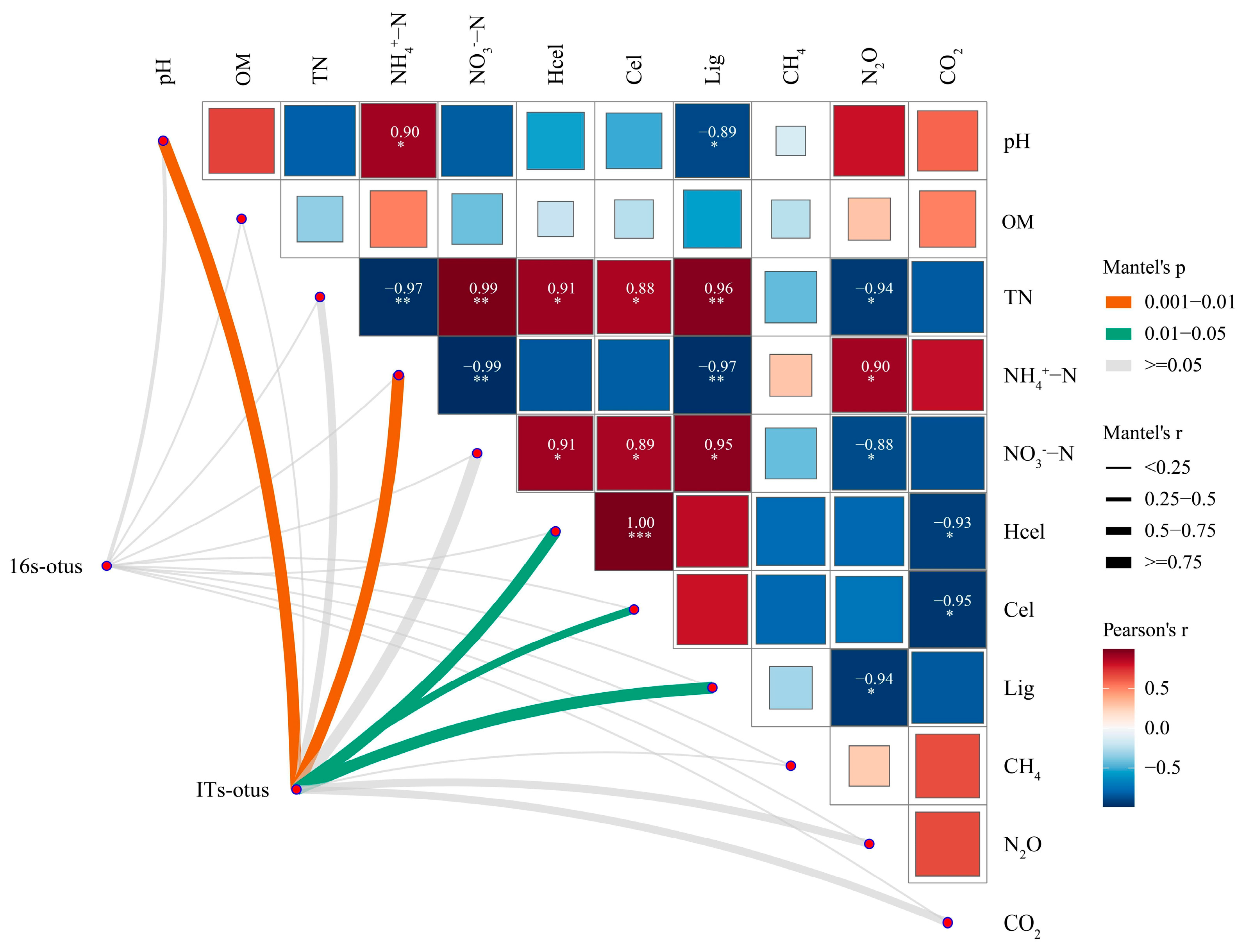
3.4.4. Microbial Community Association Heatmap
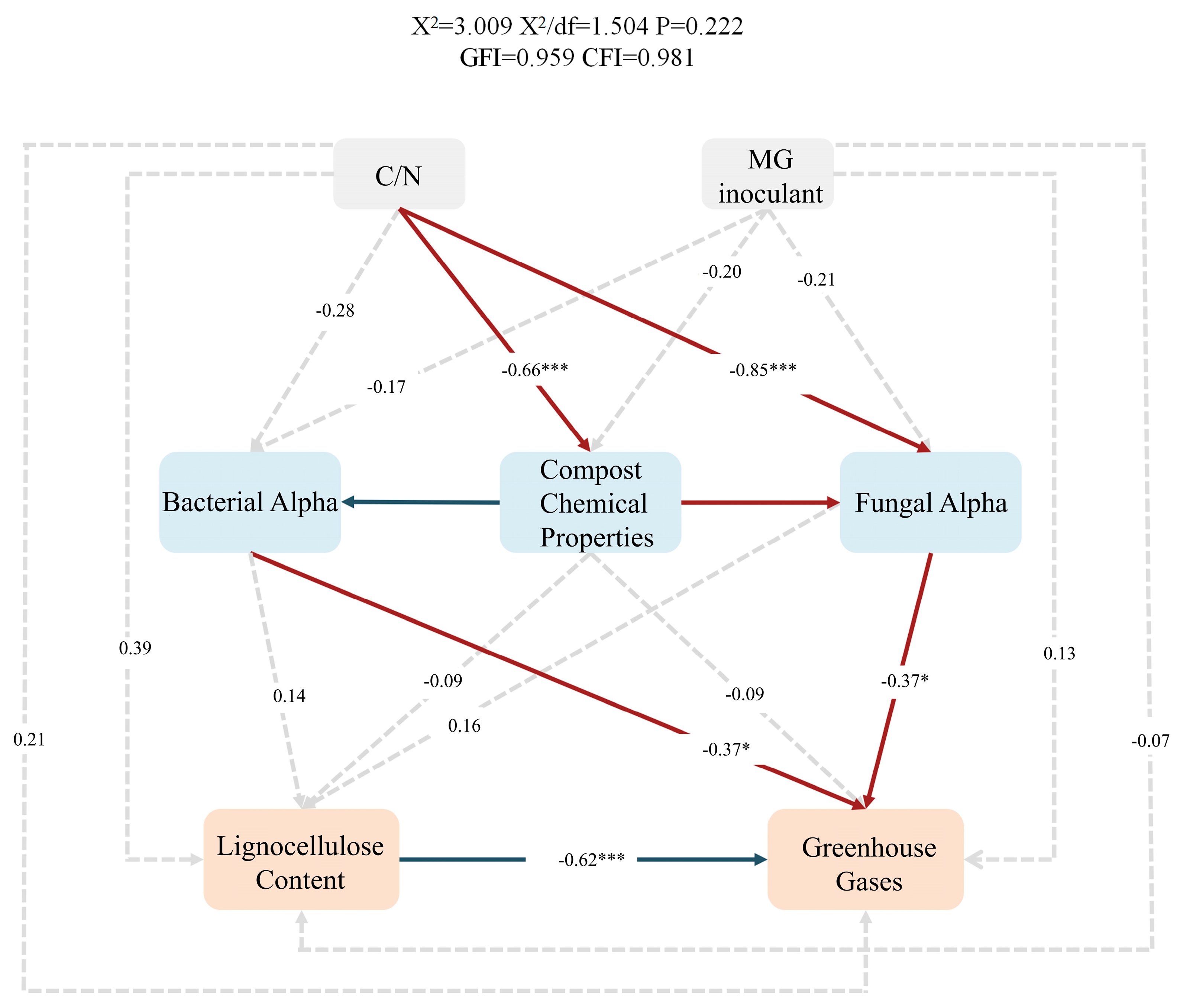
3.4.5. Structural Equation Model (SEM)
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Physicochemical Properties During Composting
4.2. Changes in Lignocellulose During Composting
4.3. Changes in Gas Emissions During Composting
4.4. Changes in Microbial Community During Composting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jahedi, A.; Safaie, N.; Goltapeh, E.M.; Ahmadifar, S. Auricularia (wood ear mushroom) genus: A contribution to classification and new species records for Iran and world. Plant Fung. Syst. 2024, 69, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Kong, X.H.; Zhang, P.Q.; Liu, J.N.; Ma, Y.P.; Dai, X.D.; Han, Z.H.; Ma, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yu, L.P. Identification of a New Fungal Pathogen Causing White Villous Disease on the Fruiting Body of the Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom Auricularia auricula-judae (Agaricomycetes) in China. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2017, 19, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, L. Status and development of spent mushroom substrate recycling: A review. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2024, 74, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Wu, P.; Zheng, J.; Xing, Y.; Qu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X. Aerobic composting of Auricularia auricula (L.) residues: Investigating nutrient dynamics and microbial interactions with different substrate compositions. Diversity 2025, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harindintwali, J.D.; Wang, F.; Yang, W.; Zhou, J.; Muhoza, B.; Mugabowindekwe, M.; Yu, X. Harnessing the power of cellulolytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria for biovalorization of lignocellulosic biomass. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 186, 115235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Qin, X.; Jia, X.; Lyu, Q.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; Huang, J. Lignocellulose degradation and temperature adaptation mechanisms during composting of mushroom residue and wood chips at low temperature with inoculation of psychrotolerant microbial agent. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Ding, B.; Ali, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Dong, H.; Divvela, P.K.; Juan, Y. Screening and isolation of cold-adapted cellulose degrading bacterium: A candidate for straw degradation and De novo genome sequencing analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1098723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chang, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Han, J.; Shi, P.; Wu, Z. Biochar-microbial inoculum co-application prolongs the thermophilic phase and enhances lignocellulose degradation in mushroom residue composting. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 201, 107546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, N.; Jamuda, M.; Panda, A.K.; Samal, K.; Nayak, J.K. Emission of greenhouse gases (GHGs) during composting and vermicomposting: Measurement, mitigation, and perspectives. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Harahap, I.A.; Osei-Owusu, J.; Saikia, T.; Wu, Y.S.; Fernando, I.; Perestrelo, R.; Câmara, J.S. Bioconversion of organic waste by insects—A comprehensive review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 187, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Bai, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Qi, Z.; Zhou, W. Phytotoxicity Removal Technologies for Agricultural Waste as a Growing Media Component: A Review. Agronomy 2024, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Ma, Y.; Bao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Niu, X.; Meng, Q.; Qin, D.; Wang, Y.; Wan, J.; Guo, X. The Impacts of the C/N Ratio on Hydrogen Sulfide Emission and Microbial Community Characteristics during Chicken Manure Composting with Wheat Straw. Agriculture 2024, 14, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, R.; Li, L.; Zheng, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Bao, Z.; Yin, Z.; Li, G.; Yuan, J. A global meta-analysis of greenhouse gas emissions and carbon and nitrogen losses during livestock manure composting: Influencing factors and mitigation strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Ge, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, H. Optimization of manure-based substrate preparation to reduce nutrients losses and improve quality for growth of Agaricus bisporus. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.M.; Chen, L.P.; Chen, S.; Chu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Effects of Soil Microbes on Methane Emissions from Paddy Fields under Varying Soil Oxygen Conditions. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, F.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Mohyuddin, A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Aziz, F.; Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Goh, H.H.; Anouzla, A. Environmental impacts of food waste management technologies: A critical review of life cycle assessment (LCA) studies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Cao, H.; Qi, C.; Hu, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, Z. Straw management in paddy fields can reduce greenhouse gas emissions: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2024, 306, 109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yan, F.; Yan, M.; Wang, H.; Piao, R.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, H. Decomposition characteristics of corn stover by microbial consortiumplc-8 with lignocellulose-degradation at low temperature. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, D. Synthetic microbial community enhances lignocellulose degradation at the composting thermophilic phase: Metagenomic and metabolic pathway insights. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 520, 165847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasta, C.S.; Hlavac, N.; Marcondes, N.A.; de Almeida Lacerda, L.; de Faria Valle, S.; González, F.H.D. Blood bank quality control: pH assessment methods in platelet concentrates. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 4129–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáez-Plaza, P.; Michałowski, T.; Navas, M.J.; Asuero, A.G.; Wybraniec, S. An overview of the kjeldahl method of nitrogen determination. Part I. early history, chemistry of the procedure, and titrimetric finish. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 178–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafner, E.V. Segmented continuous-flow analyses of nutrient in seawater: Intralaboratory comparison of Technicon AutoAnalyzer II and Bran+ luebbe continuous flow autoanalyzer III. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2015, 13, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffrenato, E.; Van Amburgh, M.E. Technical note: Improved methodology for analyses of acid detergent fiber and acid detergent lignin. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3613–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavifar, A.; Navaei, M.; Hesketh, P.J.; Findlay, M.; Stetter, J.R.; Hunter, G.W. Transient thermal response of micro-thermal conductivity detector (µTCD) for the identification of gas mixtures: An ultra-fast and low power method. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2015, 1, 15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, X. Optimizing green waste composting with Bacillus siamensis inoculant: Impacts on decomposition and microbial dynamics. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 388, 126017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, R.; Tang, D.K.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Quan, F. Enhancing nitrogen transformation and humification in cow manure composting through psychrophilic and thermophilic nitrifying bacterial consortium inoculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 413, 131507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.; Goufo, P.; Fonseca, J.; Pereira, J.L.S.; Ferreira, L.; Coutinho, J.; Trindade, H. Effect of lignocellulosic and phenolic compounds on ammonia, nitric oxide and greenhouse gas emissions during composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannett, M.; DiTommaso, A.; Sparks, J.P.; Kao-Kniffin, J. Microbial nitrogen immobilization as a tool to manage weeds in agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 366, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yue, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, F.; Qu, F.; Song, C.; Wei, Z. Functional genes are the key factors driving the Fenton-like reactions to promote the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass during composting. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yue, K.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Fan, Y. Keystone bacterial functional module activates P-mineralizing genes to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of organic P in a subtropical forest soil with 5-year N addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, D.; Nan, J.; Feng, Y. Aeration intensity drives dissolved organic matter transformation and humification during composting by regulating the organics metabolic functions of microbiome. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 476, 146645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Paredes, A.; Valdés, G.; Araneda, N.; Valdebenito, E.; Hansen, F.; Nuti, M. Microbial community in the composting process and its positive impact on the soil biota in sustainable agriculture. Agronomy 2023, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, B.; Shen, J.; Xu, F.; Li, N.; Jia, P.; Jia, Y.; An, S.; Amoah, I.D.; Huang, Y. Shifts in C-degradation genes and microbial metabolic activity with vegetation types affected the surface soil organic carbon pool. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Lin, P.P.; Magnusson, L.; Warner, L.; Liao, J.C.; Maness, P.-C.; Chou, K.J. CO2-fixing one-carbon metabolism in a cellulose-degrading bacterium Clostridium thermocellum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13180–13185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Yi, J.; Zhen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhao, C. An integrated analysis of the rice transcriptome and metabolome reveals differential regulation of carbon and nitrogen metabolism in response to nitrogen availability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, C.J.; Taha, K.; Kenney, I.; Yeh, D.H. The role of carbon to nitrogen ratio on the performance of denitrifying biocathodes for decentralized wastewater treatment. Water 2022, 14, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q. A novel carbon-nitrogen coupled metabolic pathway promotes the recyclability of nitrogen in composting habitats. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 381, 129134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, H.H.P.; Jin, T.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, T. Thermophilic microbial cellulose decomposition and methanogenesis pathways recharacterized by metatranscriptomic and metagenomic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z. Effect of thermo-tolerant actinomycetes inoculation on cellulose degradation and the formation of humic substances during composting. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Tang, J.; Sun, H.; Yao, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, S. Straw waste promotes microbial functional diversity and lignocellulose degradation during the aerobic process of pig manure in an ectopic fermentation system via metagenomic analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | C/N | PLC-8 |
|---|---|---|
| A | 25:1 | Not added |
| AM | 25:1 | Added |
| B | 30:1 | Not added |
| BM | 30:1 | Added |
| CK | Untreated | |
| Time | Treatment | C/N | pH | OM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/kg) | Hcel (%) | Cel (%) | Lig (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | CK | 20.1 | 7.7 ± 0.4 c | 319.9 ± 0.2 e | 24.0 ± 2.7 a | 6.1 ± 0.8 c | 141.0 ± 0.3 a | 11.1 ± 0.5 a | 33.3 ± 0.2 a | 41.8 ± 0.8 a |
| 60 d | CK | 18.5 | 8.0 ± 0.1 b | 335.3 ± 0.5 e | 9.1 ± 0.9 d | 18.2 ± 0.5 b | 11.5 ± 0.5 b | 8.3 ± 0.2 b | 22.5 ± 0.9 b | 27.8 ± 0.6 d |
| A | 21.1 | 8.1 ± 0.7 a | 357.1 ± 0.2 b | 10.2 ± 1.2 c | 24.1 ± 0.7 a | 7.8 ± 0.2 c | 5.4 ± 0.1 c | 21.1 ± 2.1 b | 30.8 ± 3.4 c | |
| AM | 27.3 | 8.2 ± 0.2 ab | 514.5 ± 0.5 a | 12.2 ± 1.3 b | 24.7 ± 0.6 a | 6.7 ± 0.1 d | 5.3 ± 0.2 c | 17.8 ± 0.2 bc | 30.9 ± 0.2 c | |
| B | 15.4 | 8.0 ± 0.1 b | 342.6 ± 0.6 d | 12.4 ± 4.5 b | 22.0 ± 0.8 a | 6.7 ± 0.3 d | 4.2 ± 0.7 d | 15.8 ± 0.2 c | 33.9 ± 0.2 b | |
| BM | 17.5 | 7.9 ± 0.1 b | 353.5 ± 0.9 c | 10.6 ± 1.6 c | 21.9 ± 1.1 a | 6.5 ± 0.6 d | 1.8 ± 0.6 e | 9.3 ± 0.9 d | 31.4 ± 0.3 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, J.; Yu, H.; Qi, S.; Hu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhao, H.; Cui, Z. A Microbial Inoculum (PLC-8) Improves Composting of Spent Mushroom Substrate. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112627
Yin J, Yu H, Qi S, Hu Y, Chen D, Zhao H, Cui Z. A Microbial Inoculum (PLC-8) Improves Composting of Spent Mushroom Substrate. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112627
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Jiamin, Hairu Yu, Sen Qi, Yufu Hu, Di Chen, Hongyan Zhao, and Zongjun Cui. 2025. "A Microbial Inoculum (PLC-8) Improves Composting of Spent Mushroom Substrate" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112627
APA StyleYin, J., Yu, H., Qi, S., Hu, Y., Chen, D., Zhao, H., & Cui, Z. (2025). A Microbial Inoculum (PLC-8) Improves Composting of Spent Mushroom Substrate. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2627. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112627








