Diversity of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes in Sanya Haitang Bay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
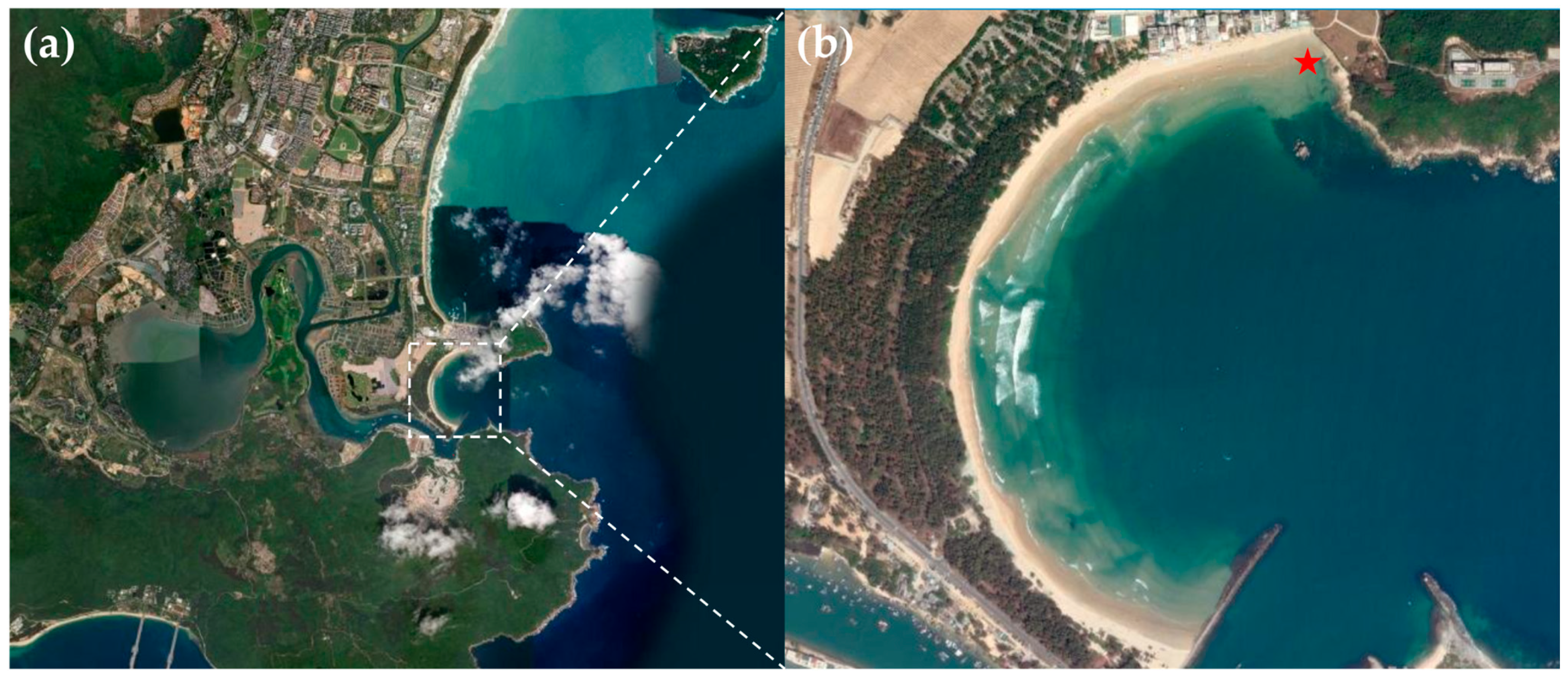
2.1. Sample Collection, Enrichment, and Observation
2.2. Morphological Analysis of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes
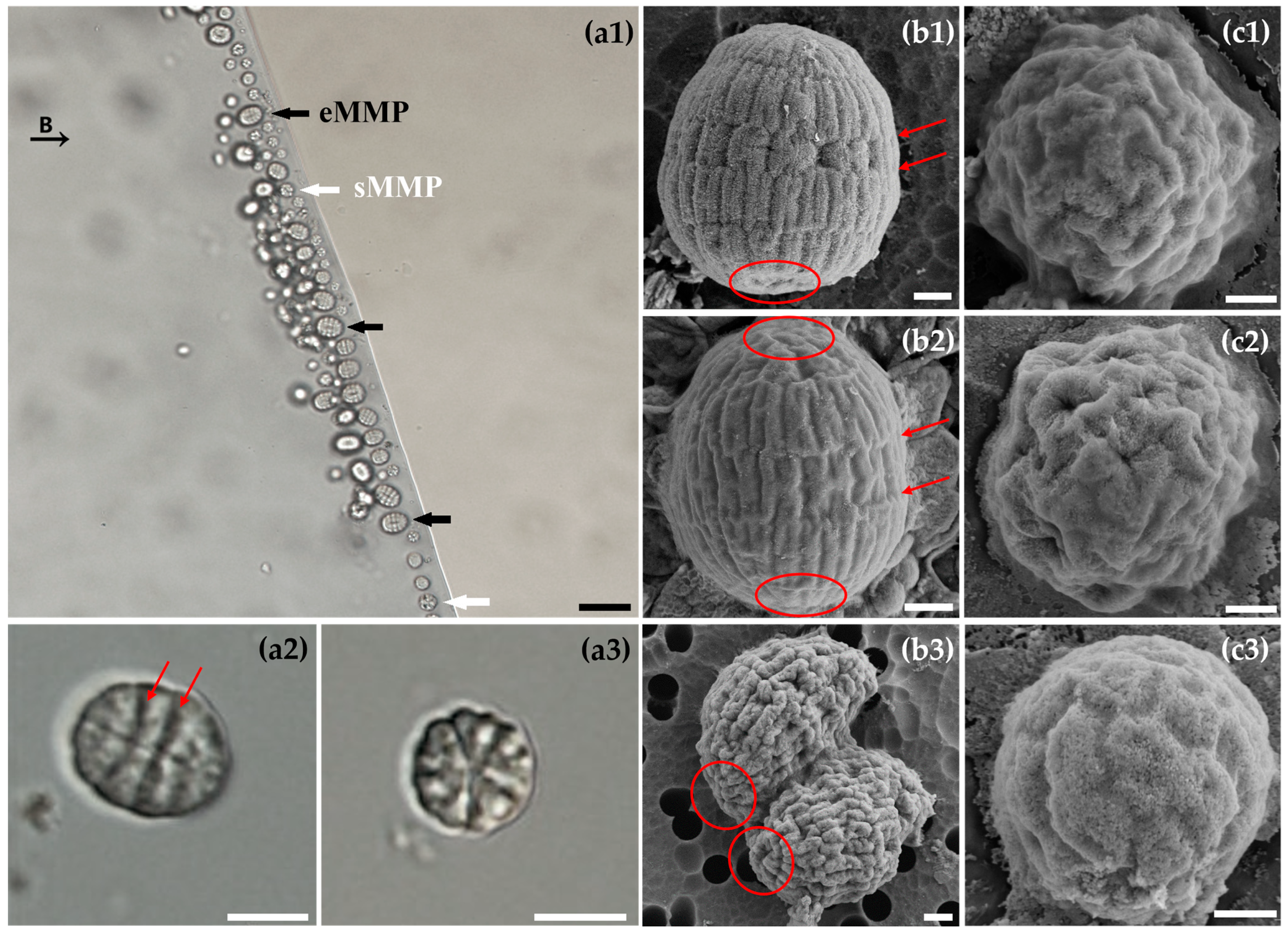
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
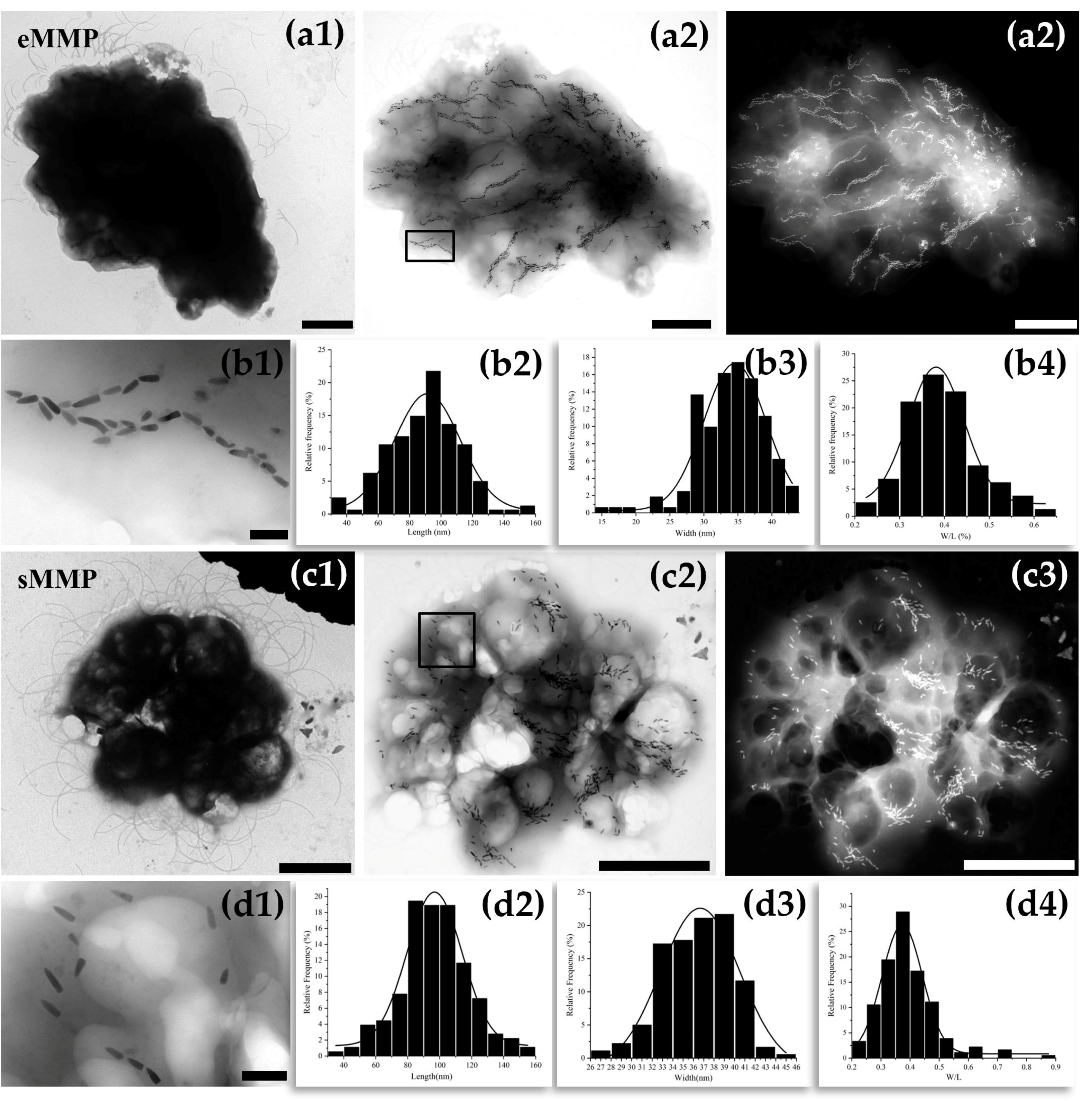
2.2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis of MulticellularMagnetotactic Prokaryotes
3. Results
3.1. Abundance and Motility Behaviors of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes
3.2. Morphology of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes
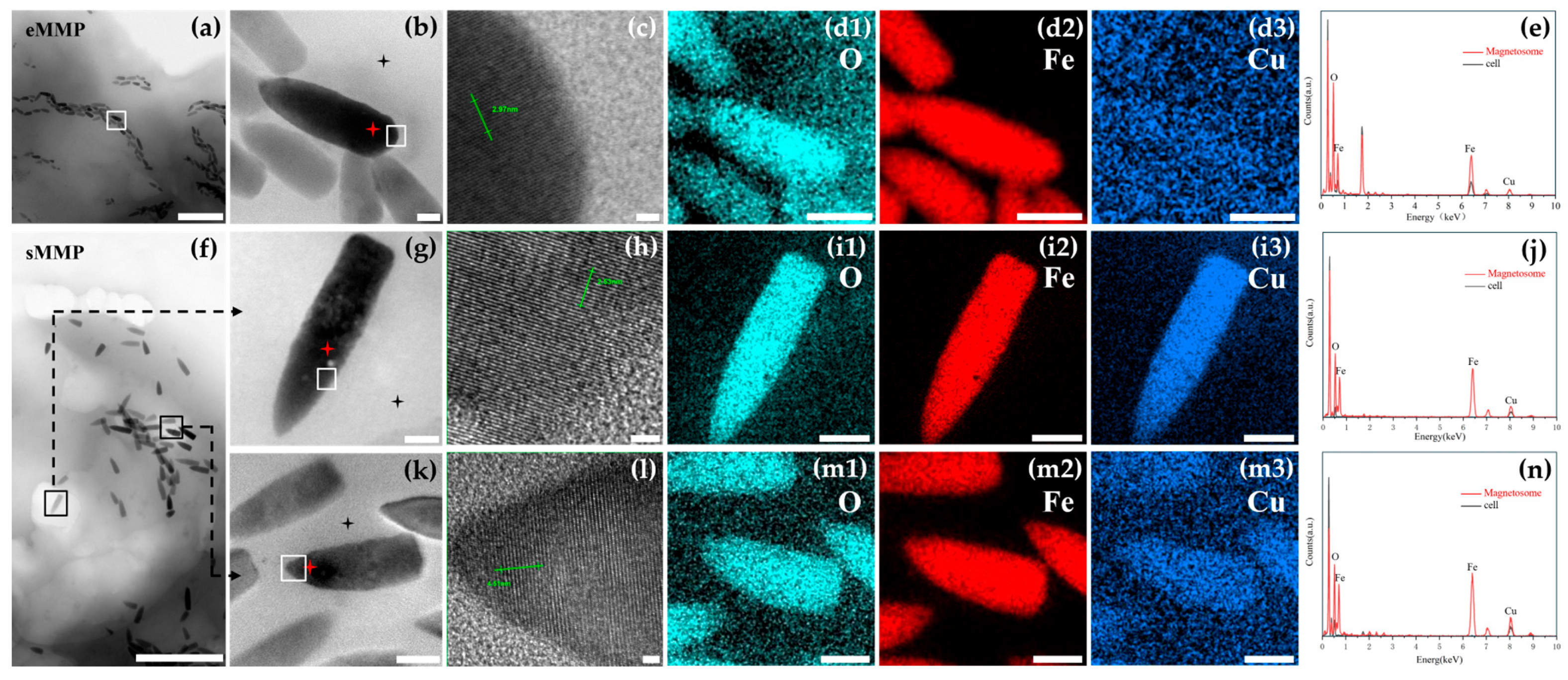
3.3. Magnetosome Characteristics of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes
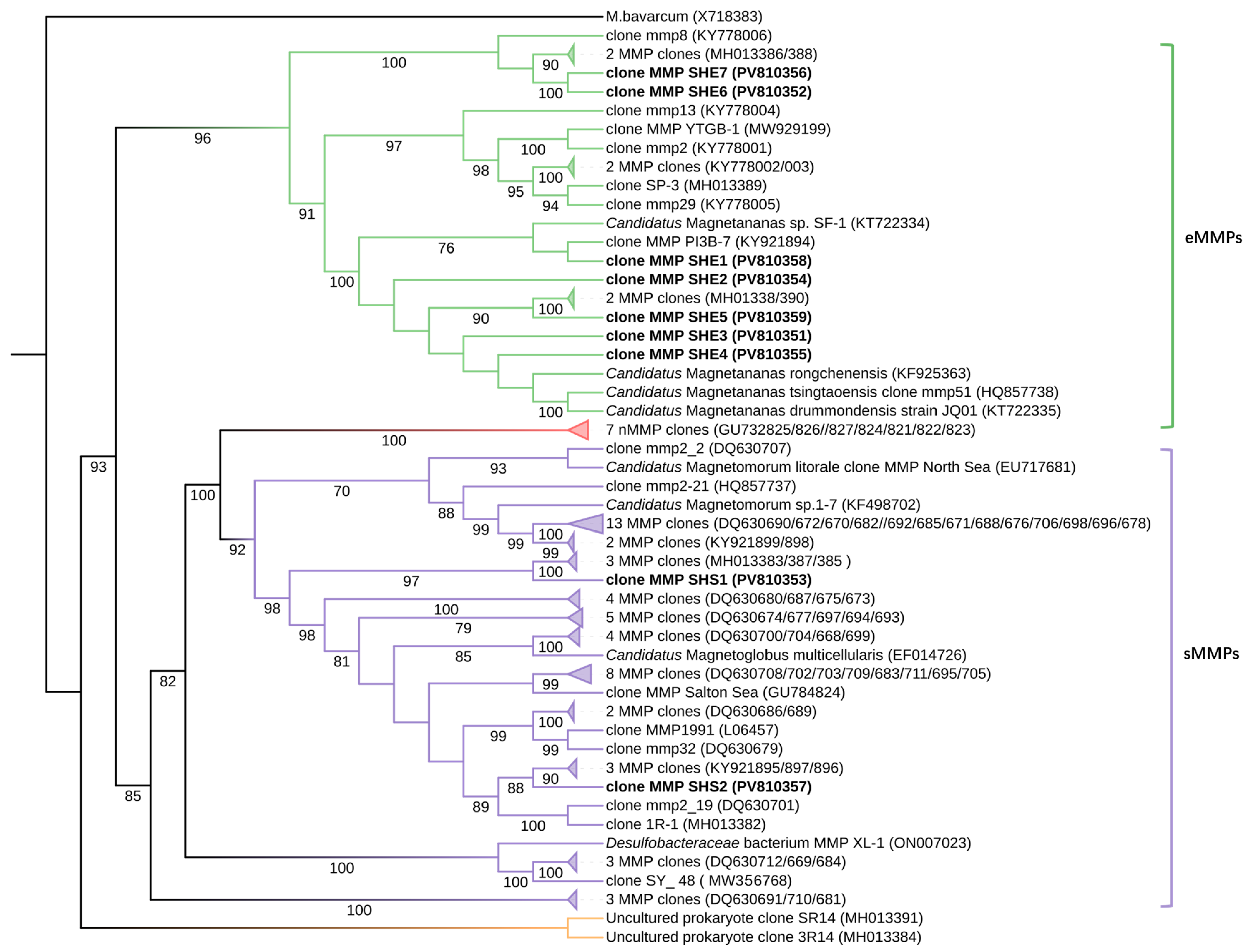
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of 16S rRNA Genes in Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes
4. Discussion
4.1. Magnetosome Characteristics of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes
| Type | Sampling Site | Size (µm) | Magnetosome | Ecological Environment | NCBI Accepted Sequences | NCBI Accepted Sequences | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Shape | Composition | Size (nm) | |||||||
| eMMPs | Sanya, China | (9.74 ± 1.52) µm × (8.15 ± 1.54) µm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 90.1 ± 22.8 (L), 34.0 ± 4.9 (W) | Intertidal zone | Tropical Monsoon Climate | PV810351–PV810352, PV810354–PV810356, PV810358–PV810359 | This study |
| Qingdao, China | (9.6 ± 1.2) μm × (7.8 ± 0.9) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 102 ± 24 (L), 38 ± 6 (W) | Intertidal zone | Temperate Monsoon Climate | HQ857738 (Candidatus Magnetananas tsingtaoensis) | [12] | |
| Rongcheng, China | (9.18 ± 1.01) μm × (7.41 ± 0.76) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 115 ± 27 (L), 39 ± 5 (W) | Intertidal zone | Temperate Monsoon Climate | KF925363 (Candidatus Magnetananas rongchenensis) | [14] | |
| II | Bullet-shaped Irregularly shaped | Fe3O4 | — | |||||||
| Fe3S4 | 102 ± 14 (L), 78 ± 13 (W) | |||||||||
| Marseille, France | (8.1 ± 1.2) μm × (6.5 ± 1.1) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 119 ± 29 (L), 40 ± 4 (W) | Sediment | Mediterranean Climate | KT722334 (Candidatus Magnetananas sp. SF-1) | [37] | |
| Drummond Island, China | (10.3 ± 1.4) μm × (8.2 ± 1.2) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 115 ± 24 (L), 44 ± 6 (W) | Sediment | Tropical Monsoon Climate | KT722335 (Candidatus Magnetananas drummondensis) | [37] | |
| Marseille, France | (6.93 ± 1.58) μm × (5.53 1.29) μm | — | — | — | — | Sediment | Mediterranean Climate | KY778001–KY778006, MH013381, MH013386, MH013388-MH013390 | [16] | |
| Xisha Islands, China | (7.47 ± 1.6) µm × (6.04 ± 1.21) µm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 134 ± 23 (L), 40 ± 4 (W) | Coral Reef | Tropical Monsoon Climate | KY921894 | [15] | |
| III | octahedral | Fe3O4 | 40 | |||||||
| Yitong Ansha Reef, China | — | — | — | — | — | Coral Reef | Tropical Monsoon Climate | MW929199 | — | |
| sMMPs | Sanya, China | (5.64 ± 0.8) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 97.2 ± 21.4 (L), 36.3 ± 3.4 (W) | Intertidal zone | Tropical Monsoon Climate | PV810353, V810357 | This study |
| Little Sippewissett Salt Marsh, USA | (6.54 ± 0.93) μm | — | — | — | — | salt marsh | Temperate Oceanic Climate | DQ630668–DQ630712 | [36] | |
| Araruama Lagoon, Brazil | (6.0–9.5) μm | III | Irregularly shaped | Fe3S4 | 88 (L), 71 (W) | salt marsh | Tropical Marine Climate | EF014726 (Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis) | [17] | |
| Wadden Sea, Germany | 5.7 μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3S4 | 90 ± 21 (L), 40 ± 6 (W) | sandy sediments | Temperate Oceanic Climate | EU717681 (Candidatus Magnetomorum littorale) | [24] | |
| Pyramid Lake, USA | — | — | — | — | — | Sediment | Subtropical Arid Climate | GU784824 | — | |
| Qingdao, China | (5.5 ± 0.8) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 92 ± 20 (L), 35 ± 4 (W) | Intertidal zone | Temperate Monsoon Climate | HQ857737 (Candidatus Magnetomorum tsingtaoroseum) | [30] | |
| Rongcheng, China | (5.6 ± 0.9) μm | II | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 80.1 ± 16.1 (L), 33.6 ± 3.5 (W) | Intertidal zone | Temperate Monsoon Climate | KF498702 (Candidatus Magnetomorum rongchengroseum) | [19] | |
| Irregularly shaped | Fe3S4 | 63.9 ± 9.3 (L), 52.5 ± 7.5 (W) | ||||||||
| Xisha Islands, China | (5.87 ± 1.37) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 139.4 ± 36.3 (L), 39.2 ± 3.5 (W) | Coral Reef | Tropical Monsoon Climate | KY921895–KY921899 | [15] | |
| Little Sippewissett Salt Marsh, USA | (4.33 ± 0.20) μm | — | — | Fe3S4/FeS2 | — | salt marsh | Temperate Oceanic Climate | L06457 | [54] | |
| Marseille, France | — | — | — | — | — | Sediment | Mediterranean Climate | MH013382, MH013383, MH013385, MH013387 | — | |
| Sanya, China | (4.6 ± 0.2) μm | III | Irregularly shaped | Fe3S4 | 77 ± 11 | mangrove | Tropical Monsoon Climate | MW356768 | [40] | |
| II | Irregularly shaped Bullet-shaped | Fe3S4 | 80 ± 19 | |||||||
| Fe3O4 | 88 ± 19 (L), 34 ± 5 (W) | |||||||||
| I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 78 ± 18 (L), 34 ± 4 (W) | |||||||
| Jinsha Bay, China | (4.78 ± 0.6) μm | I | Bullet-shaped | Fe3O4 | 87.0 ± 20.3 (L), 35.2 ± 3.5 (W) | Intertidal zone | Subtropical Monsoon Climate | ON007023 (Candidatus Magnetoradiorum zhanjiangense XL-1) | [20] | |
| III | Irregularly shaped | Fe3S4 | 72.8 ± 8.7 (L), 55.2 ± 7.3 (W) | |||||||
| nMMPs | Pyramid Lake, USA | (7.5 ± 1.0) μm | — | — | — | — | Sediment | Subtropical Arid Climate | GU732821–GU732827 | [21] |
| — | Marseille, France | — | — | — | — | — | Sediment | Mediterranean Climate | MH013384, MH013391 | — |
4.2. Distribution Patterns of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MTB | Magnetotactic bacteria |
| GTDB | Genome Taxonomy Database |
| MMPs | multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes |
| eMMPs | ellipsoidal multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes |
| sMMPs | spherical multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes |
| nMMPs | non-magnetosome-forming multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes |
| WGA | whole-genome amplification |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| HRTEM | High-resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| EDXS | energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| MDA | multiple displacement amplification |
| OTUs | Operational Taxonomic Units |
| MGC | magnetosome gene clusters |
References
- Bellini, S. Further studies on “magnetosensitive bacteria”. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakemore, R. Magnetotactic bacteria. Science 1975, 190, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Ji, R.J.; Liu, J.; Ma, K.; Pan, Y.X.; Lin, W. Biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria: From diversity to molecular discovery-based applications. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, C.T.; Bernadac, A.; Yu-Zhang, K.; Pradel, N.; Wu, L.F. Isolation and characterization of a magnetotactic bacterial culture from the Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isambert, A.; Menguy, N.; Larquet, E.; Guyot, F.; Valet, J.P. Transmission electron microscopy study of magnetites in a freshwater population of magnetotactic bacteria. Am. Miner. 2007, 92, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, J.H.; Schüler, D.; Jogler, C.; Pan, Y.X. Diversity analysis of magnetotactic bacteria in Lake Miyun, northern China, by restriction fragment length polymorphism. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 32, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.L.; Pan, H.M.; Li, J.H.; Yu-Zhang, K.; Zhang, S.D.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhou, K.; Yue, H.D.; Pan, Y.X.; Xiao, T.A.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a marine magnetotactic spirillum axenic culture QH-2 from an intertidal zone of the China Sea. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, C.T.; Schmidt, M.L.; Viloria, N.; Trubitsyn, D.; Schüler, D.; Bazylinski, D.A. Insight into the Evolution of Magnetotaxis in Magnetospirillum spp., Based on mam Gene Phylogeny. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, C.T.; Viloria, N.; Schmidt, M.L.; Pósfai, M.; Frankel, R.B.; Bazylinski, D.A. Novel magnetite-producing magnetotactic bacteria belonging to the Gammaproteobacteria. Isme J. 2012, 6, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, M.; Debarros, H.L.; Esquivel, D.M.S.; Danon, J. Ultrastructure of A Magnetotactic microorganism. Biol. Cell 1983, 48, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, F.G.; Blakemore, R.P.; Blakemore, N.A.; Frankel, R.B.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Maratea, D.; Rodgers, C. Intercellular structure in a many-celled magnetotactic prokaryote. Arch. Microbiol. 1990, 154, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Kui, Y.-Z.; Pan, H.-M.; Zhang, S.-D.; Zhang, W.-J.; Yue, H.-D.; Li, Y.; Xiao, T.; Wu, L.-F. A novel genus of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes from the Yellow Sea. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Dai, J.; Zhu, S.; Guenno, H.L.; Kosta, A.; Pan, H.; Qian, X.-X.; Santini, C.-L.; Menguy, N.; et al. Membrane-remodeling protein ESCRT-III homologs incarnate the evolution and morphogenesis of multicellular magnetotactic bacteria. bioRxiv 2022, 2022, 2022-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Zhang, R.; Du, H.J.; Pan, H.M.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.H.; Xiao, T.; Wu, L.F. A novel species of ellipsoidal multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes from Lake Yuehu in China. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Pan, H.M.; Xu, J.H.; Huang, H.; Xiao, T.; Wu, L.F. Diversity and Characterization of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes from Coral Reef Habitats of the Paracel Islands, South China Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.X.; Santini, C.L.; Kosta, A.; Menguy, N.; Le Guenno, H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Li, J.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Liu, J.; Alberto, F.; et al. Juxtaposed membranes underpin cellular adhesion and display unilateral cell division of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, F.; Lopes Martins, J.; Souza Silveira, T.; Neumann Keim, C.; Lins De Barros, H.G.P.; Gueiros, F.J.; Lins, U. ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’, a multicellular, magnetotactic prokaryote from a hypersallne environment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Pan, H.M.; Zhang, S.D.; Yue, H.D.; Xiao, T.A.; Wu, L.F. Occurrence and microscopic analyses of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes from coastal sediments in the Yellow Sea. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.R.; Du, H.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Pan, H.M.; Xiao, T.; Wu, L.F. Characterization and phylogenetic identification of a species of spherical multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes that produces both magnetite and greigite crystals. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.X.; Pan, H.M.; Chen, J.W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.Y.; Xiao, T.; Wu, L.F. A Novel Isolate of Spherical Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes Has Two Magnetosome Gene Clusters and Synthesizes Both Magnetite and Greigite Crystals. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, C.T.; Abreu, F.; Lins, U.; Bazylinski, D.A. Nonmagnetotactic Multicellular Prokaryotes from Low-Saline, Nonmarine Aquatic Environments and Their Unusual Negative Phototactic Behavior. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3220–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.D.; Schüler, D.; Pfeiffer, D. A Compass to Boost Navigation: Cell Biology of Bacterial Magnetotaxis. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, 10–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, U.; Keim, C.N.; Evans, F.F.; Farina, M.; Buseck, P.R. Magnetite (Fe3O4) and greigite (Fe3S4) crystals in multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes. Geomicrobiol. J. 2007, 24, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenter, R.; Wanner, G.; Schüler, D.; Overmann, J. Ultrastructure, tactic behaviour and potential for sulfate reduction of a novel multicellular magnetotactic prokaryote from North Sea sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, R.D.; Acosta-Avalos, D. The swimming polarity of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes can change during an isolation process employing magnets: Evidence of a relation between swimming polarity and magnetic moment intensity. Eur. Biophys. J. Biophys. Lett. 2017, 46, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.D.; Petersen, N.; Zhang, W.J.; Cargou, S.; Ruan, J.F.; Murat, D.; Santini, C.L.; Song, T.; Kato, T.; Notareschi, P.; et al. Swimming behaviour and magnetotaxis function of the marine bacterium strain MO-1. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulchro, A.G.V.; de Barros, H.L.; de Mota, H.O.L.; Berbereia, K.S.; Huamani, K.P.T.; Lopes, L.C.D.; Sudbrack, V.; Acosta-Avalos, D. Magnetoreception in multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes: A new analysis of escape motility trajectories in different magnetic fields. Eur. Biophys. J. Biophys. Lett. 2020, 49, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.Y.; Prakash, M.; Brumley, D.R. Escape motility of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes. J. R. Soc. Interface 2024, 21, 20240310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, C.N.; Farina, M. On the backward excursions in the free-swimming magnetotactic multicellular prokaryote ‘Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis’. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, O.H.; Hatzenpichler, R.; Buckley, D.H.; Zinder, S.H.; Orphan, V.J. Multicellular photo-magnetotactic bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, W.Y.; Pan, H.M.; Li, J.H.; Yue, H.D.; Xiao, T.; Wu, L.F. Adaptation of spherical multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes to the geochemically variable habitat of an intertidal zone. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, F.; Morillo, V.; Nascimento, F.F.; Werneck, C.; Cantao, M.E.; Ciapina, L.P.; de Almeida, L.G.P.; Lefèvre, C.T.; Bazylinski, D.A.; de Vasconcelos, A.T.R.; et al. Deciphering unusual uncultured magnetotactic multicellular prokaryotes through genomics. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.X.; Zhao, Y.C.; Santini, C.L.; Pan, H.M.; Xiao, T.; Chen, H.T.; Song, T.; Li, J.H.; Alberto, F.; Brustlein, S.; et al. How light affect the magnetotactic behavior and reproduction of ellipsoidal multicellular magnetoglobules? J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, S.L.; Edwards, K.J. Unexpected diversity in populations of the many-celled magnetotactic prokaryote. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.L.; Silveira, T.S.; Silva, K.T.; Lins, U. Salinity dependence of the distribution of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes in a hypersaline lagoon. Int. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, F.; Silva, K.T.; Leao, P.; Guedes, I.A.; Keim, C.N.; Farina, M.; Lins, U. Cell Adhesion, Multicellular Morphology, and Magnetosome Distribution in the Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryote Candidatus Magnetoglobus multicellularis. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Zhang, R.; Pan, H.M.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhou, K.; Wu, L.F.; Xiao, T. Temporal distributions and environmental adaptations of two types of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryote in the sediments of Lake Yuehu, China. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.R.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhou, K.; Pan, H.M.; Du, H.J.; Xu, C.; Xu, J.H.; Pradel, N.; Santini, C.L.; Li, J.H.; et al. Novel species and expanded distribution of ellipsoidal multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Du, H.J.; Leng, X.Y.; Li, J.H.; Pan, H.M.; Xu, J.H.; Wu, L.F.; Xiao, T. Seasonal changes in the vertical distribution of two types of multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes in the sediment of Lake Yuehu, China. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 10, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.T.; Li, J.H.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, W.J. Morphological and phylogenetic diversity of magnetotactic bacteria and multicellular magnetotactic prokaryotes from a mangrove ecosystem in the Sanya River, South China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Chen, S.Q. Health status and influencing factors of the coral reef ecosystems in Houhai water, Sanya, Hainan Province. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 1105–1112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Department of Ecology and Environment of Hainan Province. New Discoveries! New Records! Sanya Completely Documents Its Biodiversity Inventory. Available online: https://hain.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202309/12/WS64ffb745a310936092f2159a.html?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 19 June 2025). (In Chinese)
- Wu, Z.J.; Chen, S.Q.; Cai, Z.F.; Shen, J.; Luo, L.Z.; Wang, D.R. Analysis of distribution change and restoration suggestion of the seagrass beds in Hainan Island. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 542–549. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schüler, D. The biomineralization of magnetosomes in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. Int. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, R.S.; Thauer, R.K.; Pfennig, N. A Capillary Racetrack Method for Isolation of Magnetotactic Bacteria. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 1987, 45, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.A.; Reich, C.I.; Sharma, S.; Weisbaum, J.S.; Wilson, B.A.; Olsen, G.J. Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Updating the 97% identity threshold for 16S ribosomal RNA OTUs. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, B.J.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Busse, H.J.; Ludwig, W.; Kämpfer, P. Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, C.T.; Menguy, N.; Abreu, F.; Lins, U.; Posfai, M.; Prozorov, T.; Pignol, D.; Frankel, R.B.; Bazylinski, D.A. A Cultured Greigite-Producing Magnetotactic Bacterium in a Novel Group of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Science 2011, 334, 1720–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, M.; Mathon, F.P.; Monteil, C.L.; Busigny, V.; Lefevre, C.T. Iron-biomineralizing organelle in magnetotactic bacteria: Function, synthesis and preservation in ancient rock samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3611–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylinski, D.A.; Garrattreed, A.J.; Abedi, A.; Frankel, R.B. Copper Association with Iron Sulfide Magnetosomes in a Magnetotactic Bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 1993, 160, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pósfai, M.; Buseck, P.R.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Frankel, R.B. Iron sulfides from magnetotactic bacteria: Structure, composition, and phase transitions. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Samusawa, I.; Tachibana, S.; Shiotani, K.; Hase, K. Influence of Cu on nanostructure of Fe3O4 particles. Mater. Corros.-Werkst. Und Korros. 2019, 70, 1872–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Kulkarni, G.R. Enhancement of magnetotactic bacterial yield in a modified MSGM medium without alteration of magnetosomes properties. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 48, 518–523. [Google Scholar]
- Jogler, C.; Wanner, G.; Kolinko, S.; Niebler, M.; Amann, R.; Petersen, N.; Kube, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Schüler, D. Conservation of proteobacterial magnetosome genes and structures in an uncultivated member of the deep-branching Nitrospira phylum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.Q.; Huang, X.L.; Li, J.H.; Li, L.; Pan, Y.X.; Li, Y. MamX encoded by the mamXY operon is involved in control of magnetosome maturation in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1. Bmc Microbiol. 2013, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Pan, Y.X. Diversity of magnetotactic bacteria and its implications for environments. Quat. Sci. 2012, 32, 567–575. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre, C.T.; Trubitsyn, D.; Abreu, F.; Kolinko, S.; de Almeida, L.G.P.; de Vasconcelos, A.T.R.; Lins, U.; Schüler, D.; Ginet, N.; Pignol, D.; et al. Monophyletic origin of magnetotaxis and the first magnetosomes. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pósfai, M.; Lefèvre, C.T.; Trubitsyn, D.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Frankel, R.B. Phylogenetic significance of composition and crystal morphology of magnetosome minerals. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, R.R.; Bai, J.L.; Zhu, K.L.; Benzerara, K.; Menguy, N.; Zhao, X.; Roberts, A.P.; Pan, Y.X.; et al. Key gene networks that control magnetosome biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

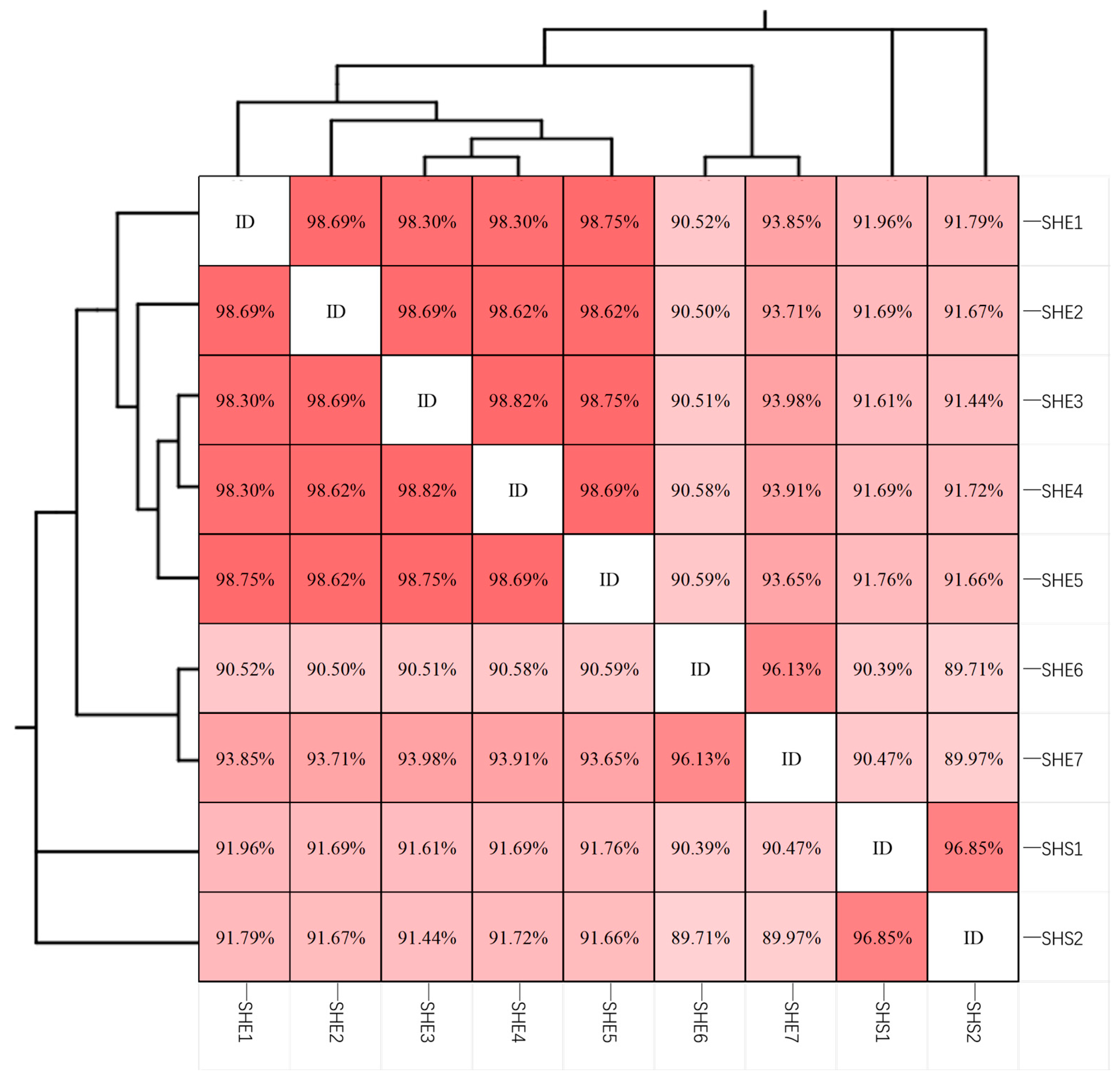
| Type | OTUs | Number of Sequences | Most Similar MMPs Sequences (Accession Numbers) | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eMMPs | SHE1 | 8 | uncultured delta proteobacterium clone MMP PI3B-7 (KY921894) | 99.28% |
| SHE2 | 7 | uncultured delta proteobacterium clone MMP PI3B-7 (KY921894) | 98.82% | |
| SHE3 | 2 | Candidatus Magnetananas rongchenensis (KF925363) | 99.15% | |
| SHE4 | 2 | Candidatus Magnetananas rongchenensis (KF925363) | 99.41% | |
| SHE5 | 8 | uncultured prokaryote clone SP-6 (MH013390) | 99.28% | |
| SHE6 | 1 | uncultured prokaryote R3-34 (MH013388) | 94.50% | |
| SHE7 | 1 | Candidatus Magnetananas sp. SF-1 (KT722334) | 94.03% | |
| sMMPs | SHS1 | 2 | uncultured delta proteobacterium clone MMP PI7B-6 (KY921895) | 96.99% |
| SHS2 | 5 | uncultured delta proteobacterium clone MMP PI7B-6 (KY921895) | 99.54% |
| Type | Point | O (%) | Fe (%) | Cu (%) | (Fe + Cu)/O | Cu/Fe | Cu/Fe (Averege) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eMMP | BC1 | 90.21 | 0.20 | 4.35 | 0.05 | 21.75 | 21.75 |
| MS1 | 84.41 | 7.70 | 3.47 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 0.27 | |
| * | 76.04 | 18.52 | 2.91 | 0.28 | 0.16 | ||
| * | 75.70 | 17.37 | 3.75 | 0.28 | 0.22 | ||
| * | 80.30 | 12.60 | 3.35 | 0.20 | 0.27 | ||
| sMMP | BC2 | 68.20 | 0.26 | 27.18 | 0.40 | 104.54 | 104.54 |
| MS2 | 62.77 | 22.71 | 11.62 | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.38 | |
| * | 57.61 | 31.57 | 9.20 | 0.71 | 0.29 | ||
| * | 58.12 | 28.34 | 10.90 | 0.68 | 0.38 | ||
| * | 60.02 | 28.66 | 9.24 | 0.63 | 0.32 | ||
| BC3 | 65.46 | 1.06 | 27.92 | 0.44 | 26.34 | 26.34 | |
| MS3 | 54.41 | 33.55 | 9.85 | 0.80 | 0.29 | 0.34 | |
| * | 54.52 | 31.39 | 10.82 | 0.77 | 0.34 | ||
| * | 53.81 | 30.87 | 11.83 | 0.79 | 0.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiao, T.; Wu, L.-F.; Pan, H. Diversity of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes in Sanya Haitang Bay. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112624
Shi J, Zhang W, Dong Y, Liu Y, Liu M, Xiao T, Wu L-F, Pan H. Diversity of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes in Sanya Haitang Bay. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112624
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jiangxue, Wenyan Zhang, Yi Dong, Yao Liu, Min Liu, Tian Xiao, Long-Fei Wu, and Hongmiao Pan. 2025. "Diversity of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes in Sanya Haitang Bay" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112624
APA StyleShi, J., Zhang, W., Dong, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, M., Xiao, T., Wu, L.-F., & Pan, H. (2025). Diversity of Multicellular Magnetotactic Prokaryotes in Sanya Haitang Bay. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112624






