Autochthonous Leishmaniasis in the United States of America
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Identification
2.1. Identification of Leishmania spp.
2.2. Criteria for Autochthonous Leishmaniasis
3. Autochthonous Leishmaniasis
| Year | State | Age | Sex | Clinical Signs and Symptoms | Diagnostic Methods * | Leishmania spp. | Treatment (/F/H/LTF/NR) ‡ | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1942 | TX | 6 | M | Chronic ulcers on the dorsum of both feet, right knee, and right buttock | M | [10] | ||
| 1967 | TX | 64 | F | Numerous nodules and plaques over extremities and buttocks for years | C, M | Camolar (F) | [14] | |
| 1972 | TX | 74 | F | Hard plaque on right eyelid, left cheek, and left earlobe | AI, M | Surgery (H) | [15] € | |
| 1974 | TX | 56 | M | Crusting and superficial ulceration of the left cartilaginous septum | AI, C, M, S, VI | Pentostam (F) | ||
| 1980 | TX | 11 | M | Red papule on the left cheek | C, IP, M | L. mexicana | Sodium stibogluconate (H) | [16,17] |
| 1982 | TX | 56 | F | Crusted plaque on left earlobe | M, S | Antimony potassium tartrate (H) | ||
| 1982 | TX | 5 | M | Papule on left front thigh | M, S | Surgery (H) | ||
| 1983 | TX | 10 | M | Papules on face | C, M, S | No treatment (H) | ||
| 1986 | TX | 46 | F | Nodules on right arm and wrist | M, C, IP | L. mexicana | Ketoconazole (H) | [18] |
| 1986 | TX | 13 | M | Ulcer on right ear | M | Antimony tartrate (H) | [19] | |
| 1986 | TX | 28 | F | Ulcerating papule on right cheek | M | Unknown (LTF) | ||
| 1988 | TX | 52 | M | Crusted lesion on right ear | M | Isoniazid (H) | ||
| 1988 | TX | 37 | F | Ulcerating nodule on right lower leg | M | No treatment (H) | ||
| 1988 | TX | 3 | M | Papule on nose | M, C | Cryotheropy (LTF) | ||
| 1988 | TX | 4 | M | Nodule on left lower eyelid | M, C | No treatment (H) | ||
| 1988 | TX | 50 | F | Ulcerating papule on nose | M | No treatment (H) | ||
| 1988 | TX | 2 | M | Plaque on left cheek | M, C | No treatment (LTF) | ||
| 1989 | TX | 28 | F | Ulcerating nodule on right cheek | M, C | Ketoconazole (H) | ||
| 1989 | TX | 20 | F | Ulcerating nodule on right angle | M | Antimony tartrate (H) | ||
| 1989 | TX | 86 | F | Ulcer on right cheek | M | Ketoconazole (H) | ||
| 1989 | TX | 2 | M | Ulcer on right ear | M | Antimony tartrate (H) | ||
| 1989 | TX | 62 | M | Nodule on right ear, right cheek, forehead and right elbow; plaque on right thigh | M, C | Sodium stibogluconate (F); Sodium stibogluconate + Ketoconazole (H) | ||
| 1989 | TX | 67 | M | Ulcer on left ear | M | No treatment (H) | ||
| 1990 | TX | 81 | F | Ulcerating papule on right cheek | M | Electrodesiccation + curettage (H) | ||
| 1992 | TX | 15 | M | Lesion on face | M | Isoniazid + Rifampin (H) | ||
| 1993 | TX | 51 | F | Ulcerating nodule on left wrist | M, C | Ketoconazole (H) | ||
| 1987 | TX | 62 | M | Cutaneous lesions on the extremities | M, C | [20] | ||
| 2002 + | TX | 78 | F | Erythematous plaque on right forearm | M | No treatment (LTF) | [21] | |
| 2003 | OK | 26 | M | Skin lesion on right cheek | M | No treatment (H) | [22] | |
| 2005 | OK | 73 | M | Skin lesions on right forearm | M | Heat (LTF) | ||
| 2005 | TX | 74 | F | Nodule on left eyelid | M | No treatment (LTF) | ||
| 2005 | TX | 70 | M | Skin lesion on right arm | M | Amphotericin + Fluconazole (NR) | [11,22] # | |
| 2005 | TX | 8 | F | Skin lesions on face and left upper arm | M, C, PCR # | L. mexicana | Amphotericin B + Fluconazole (NR) | |
| 2006 | TX | 60 | F | Skin lesion on nose | M | Ketoconazole + Cryotherapy (NR) | ||
| 2006 | TX | 76 | F | Skin lesion on forehead | M | Cryotherapy (NR) | ||
| 2006 | TX | 80 | M | Skin lesion on left arm | M | |||
| 2006 | TX | 64 | M | Skin lesion on right abdomen | M | |||
| 2007 | TX | 57 | M | Skin lesion on left back | M | Diflucan + Surgery (NR) | ||
| 2007 | TX | 82 | F | Skin lesion on left cheek | M | Fluconazole (NR) | ||
| 2007 | TX | 64 | F | Skin lesion on right chest | M | |||
| 2006 | TX | M | Skin lesion on right abdomen | M | [23] | |||
| 2007 | TX | F | Skin lesion on upper arm | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2007 | TX | F | Skin lesions on chin and neck | M | ||||
| 2007 | TX | F | Skin lesions on forearm and wrist | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2010 | TX | M | Skin lesion on left wrist | M | ||||
| 2011 | TX | F | Skin lesions on face, left elbow, and buttock | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2011 | TX | F | Skin lesion on upper arm | M | ||||
| 2012 | TX | M | Skin lesion on face | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on right wrist | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on upper arm | M | ||||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on right forehead | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on forehead | M | ||||
| 2013 | TX | M | Skin lesion on forearm | M | ||||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on upper arm | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on shoulder | M | ||||
| 2013 | TX | M | Skin lesion on left arm | M | ||||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on right lower eyelid | M | ||||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on left eyelid | M | ||||
| 2013 | TX | F | Skin lesion on upper shoulder | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2014 | TX | M | Skin lesion on upper eyelid | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2014 | TX | F | Skin lesion on face | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2014 | TX | F | Skin lesion on left temple | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2014 | TX | M | Skin lesions on arm | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2014 | TX | F | Skin lesions on face and eyelid | M | ||||
| 2014 | TX | F | Skin lesion on right forehead | M | ||||
| 2014 | TX | F | Skin lesion on left cheek | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2014 | TX | M | Skin lesion on right ear | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2014 | TX | F | Skin lesion on left upper arm | M | ||||
| 2015 | TX | F | Skin lesion on left upper arm | M | ||||
| 2015 | TX | M | Skin lesions on face and cheek | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2015 | TX | F | Skin lesion on right dorsal hand | M | ||||
| 2015 | TX | F | Skin lesion on forearm | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2015 | TX | F | Skin lesion on left earlobe | M | ||||
| 2015 | TX | M | Skin lesions on elbows | M | ||||
| 2015 | TX | M | Skin lesion on left forearm | M | ||||
| 2015 | TX | F | Skin lesion on face | M | ||||
| 2015 | TX | M | Skin lesions on ear and back | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2016 | TX | F | Skin lesion on right anterior upper neck | M | ||||
| 2016 | TX | M | Skin lesion on right upper arm | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2016 | TX | F | Skin lesion on left forehead | M, PCR | L. mexicana | |||
| 2016 | TX | F | Skin lesion on right face | M | ||||
| 2012 | ND | 2 | M | Single lesion each on the upper and lower eyelid of right eye | PCR | L. donovani complex | No treatment (H) | [24] |
| 2016 | TX | 67 | M | Multiple painless and non-pruritic papules at the anterior surface of the right leg | M, C, PCR, D | L. mexicana | Miltefosine + Ketoconazole (F) | [25] |
| 2017 | AZ | 72 | F | Two discrete, edematous, violaceous papules on the low back | M, C, PCR, D | L. ellisi | No treatment (H) | [26,27] |
| 2018–2019 | TX | 2 | F | Non-healing nodular lesion on right jawline | ¥ | L. mexicana | Fluconazole (H) | [28] |
| TX | 3 | M | Non-healing nodular lesion on left arm | M, PCR, D | L. mexicana | Fluconazole (H) | ||
| TX | 0 £ | M | Nodular lesion on face | M, PCR, D | L. mexicana | Fluconazole (F); Paromomycin (F) | ||
| 2020 + | TX | 65 | M | Three erythematous lesions on the left lateral shoulder | M | Cryotherapy (H) | [29] | |
| 2023 + | AZ | 34 | M | Single ulcerated verruous plague on lower left leg | M, I | Surgery (H) | [30] |

4. Leishmania spp. in the USA
5. Transmission Routes
5.1. Sand Fly Vector
5.2. Vertical Transmission—Congenital Transmission
5.3. Horizontal Transmission—Blood Transfusion
6. Risks of Leishmania spp. Transmission in the USA
7. Conclusion Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, C. Leishmania spp. and leishmaniasis on the Caribbean islands. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 114, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Donelson, J.E.; Wilson, M.E. The major surface protease (MSP or GP63) of Leishmania sp. Biosynthesis, regulation of expression, and function. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2003, 132, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.D. Human leishmaniasis: Clinical, diagnostic, and chemotherapeutic developments in the last 10 years. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 24, 684–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kone, A.K.; Niaré, D.S.; Piarroux, M.; Izri, A.; Marty, P.; Laurens, M.B.; Piarroux, R.; Thera, M.A.; Doumbo, O.K. Visceral Leishmaniasis in West Africa: Clinical Characteristics, Vectors, and Reservoirs. J. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 2019, 9282690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burza, S.; Croft, S.L.; Boelaert, M. Leishmaniasis. Lancet 2018, 392, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azami-Conesa, I.; Gomez-Munoz, M.T.; Martinez-Diaz, R.A. A Systematic Review (1990–2021) of Wild Animals Infected with Zoonotic Leishmania. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, J.M.; Aronson, N.E. Leishmaniasis in the United States: Emerging Issues in a Region of Low Endemicity. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens-Riha, N.; Fleischmann, E.; Pratlong, F.; Bretzel, G.; von Sonnenburg, F.; Loscher, T. Cutaneous leishmaniasis (Leishmania tropica) in a German tourist after travel to Greece. J. Travel. Med. 2009, 16, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, A.; Slavin, J.; Stark, D.; Aboltins, C. A case of imported Leishmania infantum cutaneous leishmaniasis; an unusual presentation occurring 19 years after travel. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.D.; Pilcher, J.F. American leishmaniasis: Report of an autochthonous case. Arch. Dermatol. Syphilol. 1945, 51, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, N.A.; Davis, L.E.; Aftergut, K.S.; Parrish, C.A.; Cockerell, C.J. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Texas: A northern spread of endemic areas. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 650–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Che, G.; Yang, Q.; Lai, S.; Teng, J.; Duan, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, F. Leishmania donovani visceral leishmaniasis diagnosed by metagenomics next-generation sequencing in an infant with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A case report. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1197149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Q.; He, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Chen, E.Q. Fever of unknown origin and splenomegaly: A case report of visceral leishmaniasis diagnosed by metagenomic next-generation sequencing. Future Microbiol. 2023, 18, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.H.; Mullins, J.F.; Stone, O.J. Disseminated anergic cutaneous leishmaniasis. An autochthonous case in Texas and the Mexican states of Tamaulipas and Nuevo Leon. Arch Dermatol. 1968, 97, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.K.; Quigg, L.T.; Allain, D.S.; Juranek, D.D.; Healy, G.R. Autochthonous dermal leishmaniasis in Texas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1976, 25, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, T.L.; Reed, C.M.; McGreevy, P.B.; Pappas, M.G.; Fox, J.C.; Lawyer, P.G. Human cutaneous leishmaniasis acquired in Texas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 34, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.A.; Gustafson, T.L.; Spielvogel, R.L. Clinical aspects of cutaneous leishmaniasis acquired in Texas. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1985, 12, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furner, B.B. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Texas: Report of a case and review of the literature. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1990, 23 Pt 2, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, C.P.; Melby, P.C.; LaFon, S.G. Leishmaniasis in Texas: Epidemiology and clinical aspects of human cases. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1996, 55, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golino, A.; Duncan, J.M.; Zeluff, B.; DePriest, J.; McAllister, H.A.; Radovancevic, B.; Frazier, O.H. Leishmaniasis in a heart transplant patient. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 1992, 11 Pt 1, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maloney, D.M.; Maloney, J.E.; Dotson, D.; Popov, V.L.; Sanchez, R.L. Cutaneous leishmaniasis: Texas case diagnosed by electron microscopy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 47, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.F.; Bradley, K.K.; Wright, J.H.; Glowicz, J. Case report: Emergence of autochthonous cutaneous leishmaniasis in northeastern Texas and southeastern Oklahoma. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwee, B.E.; Weis, S.E.; Hosler, G.A. Incidence of Endemic Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douvoyiannis, M.; Khromachou, T.; Byers, N.; Hargreaves, J.; Murray, H.W. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in North Dakota. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, e73–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, E.J.; de Almeida, M.; Marcet, P.L.; Bradbury, R.S.; Benedict, T.K.; Lin, W.; Dotson, E.M.; Hergert, M. An Atypical Case of Autochthonous Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Associated with Naturally Infected Phlebotomine Sand Flies in Texas, United States. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapp, S.G.H.; Low, R.; Nine, G.; Nascimento, F.S.; Qvarnstrom, Y.; Barratt, J.L.N. Genetic characterization and description of Leishmania (Leishmania) ellisi sp. nov.: A new human-infecting species from the USA. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.; Zheng, Y.; Nascimento, F.S.; Bishop, H.; Cama, V.A.; Batra, D.; Unoarumhi, Y.; Afghan, A.K.; Shi, V.Y.; LeBoit, P.E.; et al. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by an Unknown Leishmania Strain, Arizona, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1714–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, B.; McCormick-Baw, C.; Patel, K.; Firmani, S.; Wetzel, D.M. Cutaneous Leishmania mexicana infections in the United States: Defining strains through endemic human pediatric cases in northern Texas. mSphere 2024, 9, e0081423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.A.; Charles, J.E.M.; Worrell, J.T.; Wilkes, D.V. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in a 65-year-old North Texas male, treated with cryotherapy: A case report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2050313X20904593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenet, C.B.; Davis, M.S.; Murphy, S.; Thiede, R.; Culpepper, K.S.; Fazel, M. Limited Cutaneous Leishmaniasis as Ulcerated Verrucous Plaque on Leg, Tucson, Arizona, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1268–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, B.C.; Intermill, R.W.; Hajduk, M.E. Differences in biological characteristics of three Leishmania isolates from patients with espundia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1977, 26 Pt 1, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcover, M.M.; Rocamora, V.; Ribas, A.; Fisa, R.; Riera, C. Underestimation of Human Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum in an Endemic Area of the Mediterranean Basin (Balearic Islands). Microorganisms 2023, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mazini, S.; Ejghal, R.; Bekhti, K.; Lemrani, M. The Sporadic cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania infantum in Morocco: A presumably trend towards endemicity. Acta Trop. 2022, 227, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piyasiri, S.B.; Dewasurendra, R.; Samaranayake, N.; Karunaweera, N. Diagnostic Tools for Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania donovani: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, S.; Gouba, A.; Drabo, M.K.; Nezien, D.; Bougoum, M.; Guiguemde, T.R. Epidemiological profile of cutaneous leishmaniasis: Retrospective analysis of 7444 cases reported from 1999 to 2005 at Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2013, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravani, M.; Moemenbellah-Fard, M.D.; Sharafi, M.; Rafat-Panah, A. Epidemiologic profile of oriental sore caused by Leishmania parasites in a new endemic focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis, southern Iran. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimo, S.M.; Duggal, P.; Braz, R.F.; Cheng, C.; Monteiro, G.R.; Nascimento, E.T.; Martins, D.R.A.; Karplus, T.M.; Ximenes, M.F.F.M.; Oliveira, C.C.G.; et al. An emerging peri-urban pattern of infection with Leishmania chagasi, the protozoan causing visceral leishmaniasis in northeast Brazil. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 36, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, N.E.; Lima, I.D.; Gaur Dixit, U.; Turcotte, E.A.; Lockard, R.D.; Batra-Sharma, H.; Nascimento, E.L.; Jeronimo, S.M.B.; Wilson, M.E. Epidemiological and Experimental Evidence for Sex-Dependent Differences in the Outcome of Leishmania infantum Infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Giudice, P.; Marty, P.; Lacour, J.P.; Perrin, C.; Pratlong, F.; Haas, H.; Dellamonica, P.; Le Fichoux, Y. Cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania infantum: Case reports and literature review. Arch Dermatol. 1998, 134, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.B.; Banjara, M.R.; Chuke, S.; Kroeger, A.; Jain, S.; Aseffa, A.; Reeder, J.C. Assessment of the impact of implementation research on the Visceral Leishmaniasis (VL) elimination efforts in Nepal. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.E.; Spann, D.R.; Bradbury, R.S. Leishmania infantum in US-Born Dog. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1882–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.C.; Campos, M.P.; Popielarczyk, M.; Kiupel, M. Cutaneous Leishmaniosis caused by Leishmania martiniquensis in a Horse in Florida. J. Comp. Pathol. 2019, 173, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuss, S.M.; Dunbar, M.D.; Calderwood Mays, M.B.; Owen, J.L.; Mallicote, M.F.; Archer, L.L.; Wellehan, J.F.X., Jr. Autochthonous Leishmania siamensis in horse, Florida, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1545–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, E.A.; Mahachi, K.G.; Petersen, C.A. Possibility of Leishmania Transmission via Lutzomyia spp. Sand Flies Within the USA and Implications for Human and Canine Autochthonous Infection. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2022, 9, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, S.F.; McHugh, C.P.; Merkelz, R. Short report: A focus of Leishmania mexicana near Tucson, Arizona. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 61, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzer, R.D. Genetic analysis of Leishmania mexicana populations from Texas, Latin America, and the Caribbean. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990, 43, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.E.; Steurer, F.J.; Koru, O.; Herwaldt, B.L.; Pieniazek, N.J.; da Silva, A.J. Identification of Leishmania spp. by molecular amplification and DNA sequencing analysis of a fragment of rRNA internal transcribed spacer 2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C. Major Surface Protease (MSP, or GP63) of Trypanosomatids, One Size Fits All? Infect Immun. 2010, 78, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Wilson, M.E. Dynamics of sterol synthesis during development of Leishmania spp. parasites to their virulent form. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinnage-Pulley, T.; Scott, B.; Petersen, C.A. A Mother’s Gift: Congenital Transmission of Trypanosoma and Leishmania Species. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, C.P.; Grogl, M.; Kreutzer, R.D. Isolation of Leishmania mexicana (Kinetoplastida: Trypanosomatidae) from Lutzomyia anthophora (Diptera: Psychodidae) collected in Texas. J. Med. Entomol. 1993, 30, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, C.P.; Ostrander, B.F.; Raymond, R.W.; Kerr, S.F. Population dynamics of sand flies (diptera: Psychodidae) at two foci of leishmaniasis in Texas. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaut, R.G.; Robles-Murguia, M.; Juelsgaard, R.; Esch, K.J.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Ramalho-Ortigao, M.; Petersen, C.A. Vectorborne Transmission of Leishmania infantum from Hounds, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2209–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakundi, P.M.; Muigai, R.; Were, J.B.; Oster, C.N.; Gachihi, G.S.; Kirigi, G. Congenital visceral leishmaniasis: Case report. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1988, 82, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinchuk, A.; Nadraga, A. Congenital visceral leishmaniasis in Ukraine: Case report. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2010, 30, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinecke, C.K.; Schottelius, J.; Oskam, L.; Fleischer, B. Congenital transmission of visceral leishmaniasis (Kala Azar) from an asymptomatic mother to her child. Pediatrics 1999, 104, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, C.C.; Hain, U.; Novosel, A.; Eichenlaub, S.; Fleischmann, E.; Loscher, T. Congenital visceral leishmaniasis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, S.D.; Oakley, D.A.; Marryott, K.; Hatchett, W.; Walton, R.; Nolan, T.J.; Newton, A.; Steurer, F.; Schantz, P.; Giger, U. Transmission of visceral leishmaniasis through blood transfusions from infected English foxhounds to anemic dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 219, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, S.; Fakhar, M.; Soosaraei, M.; Hosseini Teshnizi, S.; Mardani, A.; Banimostafavi, E.S.; Hezarjaribi, H.Z. Global status of visceral leishmanial infection among blood donors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2017, 56, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.P.; Montenegro, S.; Werkauser, R.; Sales, K.; Soares, F.C.S.; Costa, V.M.A.; Bezerra, A.C.; Pinto, M.B.D.A.; Ferreira, S.M.; Neitzke-Abreu, H.C.; et al. Asymptomatic Leishmania infection in blood donors from a major blood bank in Northeastern Brazil: A cross-sectional study. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2020, 62, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaram, S.; Fakhar, M.; Mohebali, M.; Ziaei Hezarjaribi, H.; Mardani, A.; Ghezelbash, B.; Akhoundi, B.; Zarei, Z.; Moazeni, M. A Convenient and Sensitive kDNA-PCR for Screening of Leishmania infantum Latent Infection Among Blood Donors in a Highly Endemic Focus, Northwestern Iran. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengyi, Z.; Yuhui, L.; Zhan, G.; Anqing, L.; Yujia, L.; Shilin, L.; Lei, G.; Yue, L.; Mei, H.; Jianhua, W.; et al. Plasma metagenomics reveals regional variations of emerging and re-emerging pathogens in Chinese blood donors with an emphasis on human parvovirus B19. One Health 2023, 17, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grogl, M.; Daugirda, J.L.; Hoover, D.L.; Magill, A.J.; Berman, J.D. Survivability and infectivity of viscerotropic Leishmania tropica from Operation Desert Storm participants in human blood products maintained under blood bank conditions. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 49, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Silva, M.M.; Teixeira, L.A.S.; Tibúrcio, M.S.; Pereira, G.A.; Rodrigues, V.; Palis, M.; Afonso, P.; Alves, M.; Feitosa, J.M.; Urias, E.; et al. Socio-epidemiological characterisation of blood donors with asymptomatic Leishmania infantum infection from three Brazilian endemic regions and analysis of the transfusional transmission risk of visceral leishmaniasis. Transfus. Med. 2018, 28, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freitas, E.; Melo, M.N.; da Costa-Val, A.P.; Michalick, M.S. Transmission of Leishmania infantum via blood transfusion in dogs: Potential for infection and importance of clinical factors. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, C.; Wang, O.; Strutz, S.E.; Gonzalez-Salazar, C.; Sanchez-Cordero, V.; Sarkar, S. Climate change and risk of leishmaniasis in north america: Predictions from ecological niche models of vector and reservoir species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 ; L. infantum:
; L. infantum:  ; L. donovani:
; L. donovani:  ; L. ellisi:
; L. ellisi:  ; L. martiniquensis:
; L. martiniquensis:  ; Sand fly species: Lu. anthophora:
; Sand fly species: Lu. anthophora:  ; Lu. cruciate:
; Lu. cruciate:  ; Lu. diabolica:
; Lu. diabolica:  ; Lu. shannoni:
; Lu. shannoni:  . Super Teacher Worksheets—www.superteacherworksheets.com.
. Super Teacher Worksheets—www.superteacherworksheets.com.
 ; L. infantum:
; L. infantum:  ; L. donovani:
; L. donovani:  ; L. ellisi:
; L. ellisi:  ; L. martiniquensis:
; L. martiniquensis:  ; Sand fly species: Lu. anthophora:
; Sand fly species: Lu. anthophora:  ; Lu. cruciate:
; Lu. cruciate:  ; Lu. diabolica:
; Lu. diabolica:  ; Lu. shannoni:
; Lu. shannoni:  . Super Teacher Worksheets—www.superteacherworksheets.com.
. Super Teacher Worksheets—www.superteacherworksheets.com.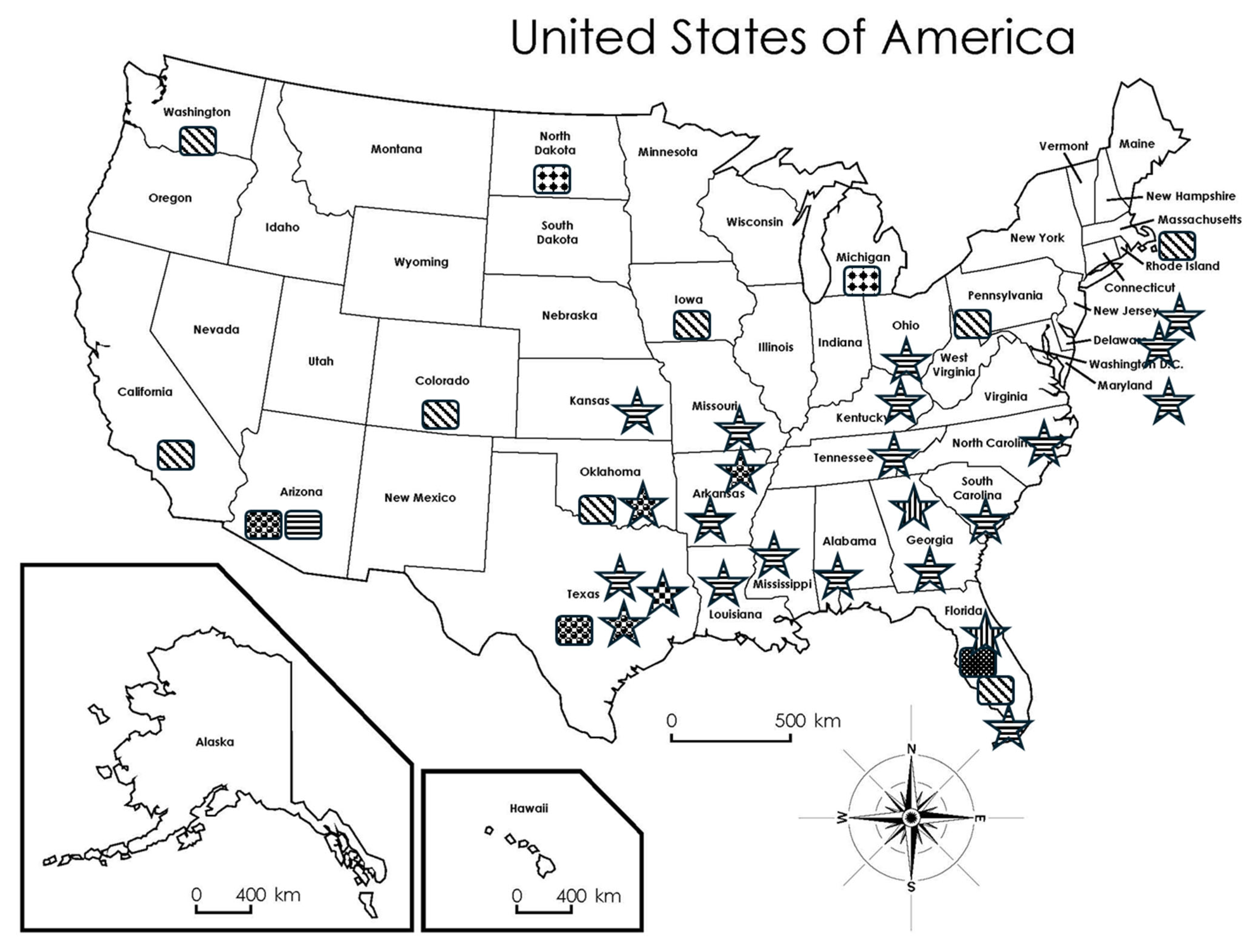
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, C.; Yang, Y.; Du, A. Autochthonous Leishmaniasis in the United States of America. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112485
Yao C, Yang Y, Du A. Autochthonous Leishmaniasis in the United States of America. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112485
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Chaoqun, Yi Yang, and Aifang Du. 2025. "Autochthonous Leishmaniasis in the United States of America" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112485
APA StyleYao, C., Yang, Y., & Du, A. (2025). Autochthonous Leishmaniasis in the United States of America. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112485







