Virulence and Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Poultry in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. DNA Extraction and PCR Assay
2.3. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PCR Assay
3.2. Genomic Characterization
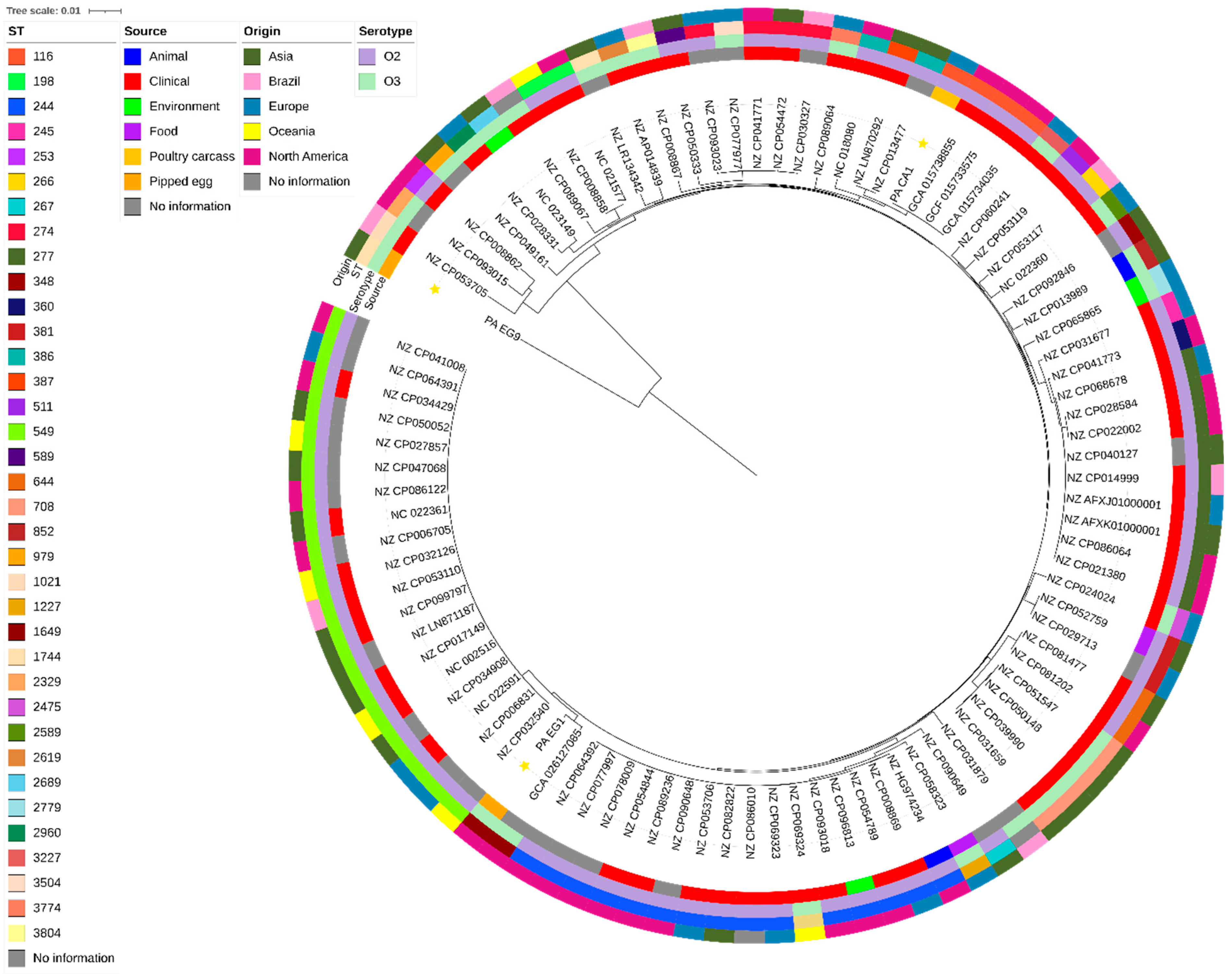
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mena, K.D.; Gerba, C.P. Risk Assessment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in water. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 201, 71–115. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Ghany, W.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of avian origin: Zoonosis and one health implications. Vet. World 2021, 14, 2155–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marouf, S.; Li, X.; Salem, H.M.; Ahmed, Z.S.; Nader, S.M.; Shaalan, M.; Awad, F.H.; Zhou, H.; Cheang, T. Molecular detection of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa of different avian sources with pathogenicity testing and in vitro evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Biomed. Res Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, S.M.; Lavenir, R.; Colinon-Dupuich, C.; Boukerb, A.M.; Cholley, P.; Bertrand, X.; Freney, J.; Doléans-Jordheim, A.; Nazaret, S.; Laurent, F.; et al. Lagooning of wastewaters favors dissemination of clinically relevant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitondo-Silva, A.; Gonçalves, G.B.; Stehling, E.G. Heavy metal resistance and virulence profile in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from Brazilian soils. APMIS 2016, 124, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesudason, T. WHO publishes updated list of bacterial priority pathogens. Lancet Microbe. 2024, 5, 100940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, R.A.; Szabo, D. Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Acinetobacter Species and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43 (Suppl. 2), 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Mulet, X.; López-Causapé, C.; Juan, C. The increasing threat of Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk clones. Drug Resist. Updates 2015, 21–22, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahat, H.S.; Mohamed, H.; Abd Al-Azeem, M.W.; Nasef, S.A. Molecular detection of some virulence genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from chicken embryos and broilers with regard to disinfectant resistance. SVU-Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 2, 52–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Shao, B. Spread of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in animal-derived foods in Beijing, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 403, 110296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, A.M.; Elsayed, M.M.; Abd El Tawab, A.A.; Elhofy, F.I.; Soliman, E.A.; Kozytska, T.; Brangsch, H.; Sprague, L.D.; Neubauer, H.; Wareth, G. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of resistance and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from poultry farms in Egypt using whole genome sequencing. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 292, 110063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algammal, A.M.; Eidaroos, N.H.; Alfifi, K.J.; Alatawy, M.; Al-Harbi, A.I.; Alanazi, Y.F.; Ghobashy, M.O.; Khafagy, A.R.; Esawy, A.M.; El-Sadaa, S.S.; et al. oprL gene sequencing, resistance patterns, virulence genes, quorum sensing and antibiotic resistance genes of XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from broiler chickens. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 853–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, K.; Kot, B.; Jakubczak, A.; Rymuza, K. BOX-PCR is an adequate tool for typing of clinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2011, 49, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nageeb, W.; Amin, D.H.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; Makharita, R.R. Novel Molecular Markers Linked to Pseudomonas aeruginosa Epidemic High-Risk Clones. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; et al. Epidemiology and molecular characterization of the antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Chinese mink infected by hemorrhagic pneumonia. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 83, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infection. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabot, G.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.A.; Domínguez, M.A.; Gago, J.F.; Juan, C.; Tubau, F.; Rodríguez, C.; Moyà, B.; Peña, C.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; et al. Genetic markers of widespread extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk clones. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 6349–6357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, M.; Wolf, P. Pseudomonas Exotoxin A: Optimized by evolution for effective killing. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Malakar, P.K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. New insights into the mediation of biofilm formation by three core extracellular polysaccharide biosynthesis pathways in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogiel, T.; Prażyńska, M.; Kwiecińska-Piróg, J.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E.; Mikucka, A. Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains-distribution of the essential enzymatic virulence factors genes. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet, X.; Cabot, G.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.A.; Domínguez, M.A.; Zamorano, L.; Juan, C.; Tubau, F.; Rodríguez, C.; Moyà, B.; Peña, C.; et al. Biological markers of Pseudomonas aeruginosa epidemic high-risk clones. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5527–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, S.; Hegerle, N.; Sen, S.; Nkeze, J.; Sen, S.; Permala-Booth, J.; Choi, M.; Sinclair, J.; Tapia, M.D.; Johnson, J.K.; et al. Distribution of serotypes and antibiotic resistance of invasive Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a multi-country collection. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klockgether, J.; Cramer, N.; Wiehlmann, L.; Davenport, C.F.; Tümmler, B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa genomic structure and diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picão, R.C.; Poirel, L.; Gales, A.C.; Nordmann, P. Further Identification of CTX-M-2 Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 2225–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Ai, Q.; Dong, Y.; Yu, J. Autoinducer-2 regulates Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm formation and virulence production in a dose-dependent manner. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
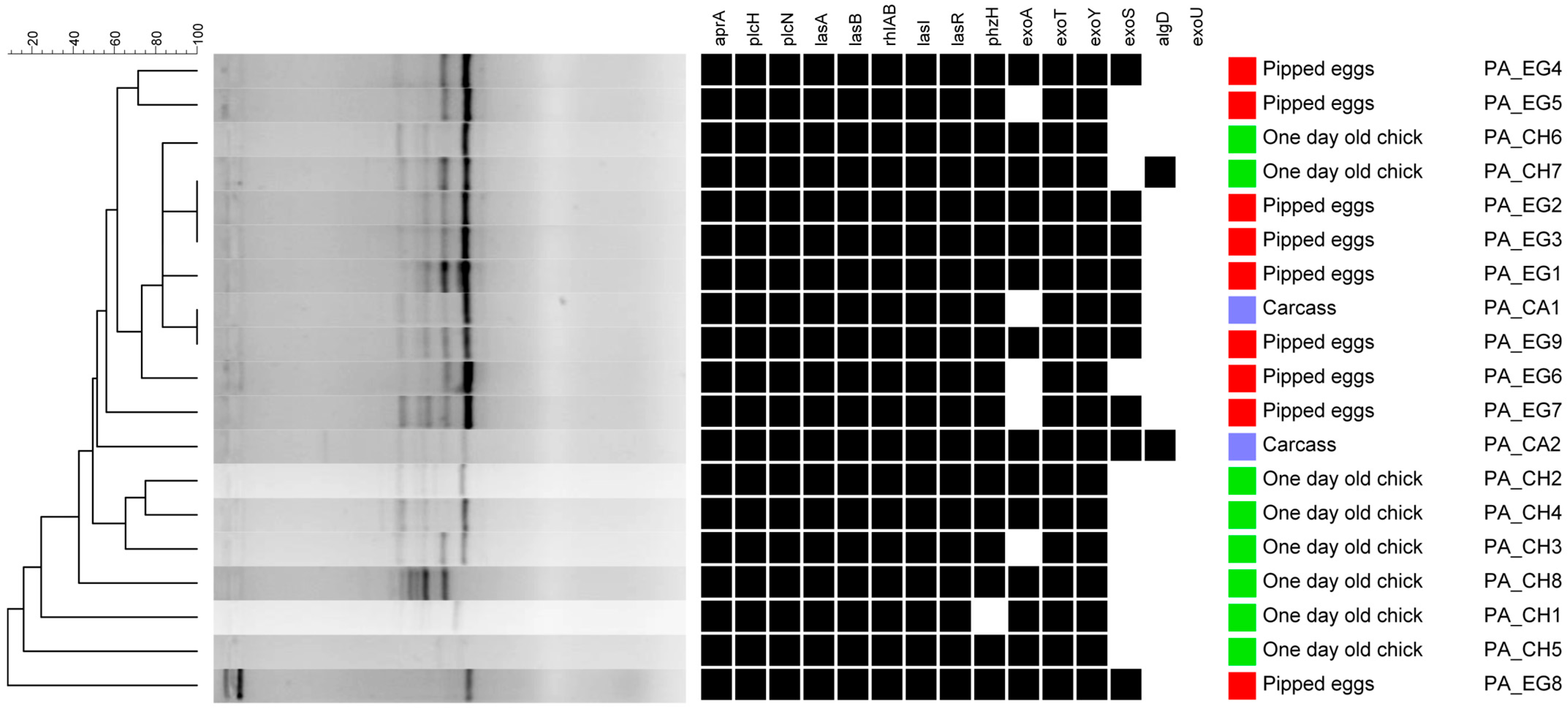
| Virulence Genes | Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipped Eggs (%) n = 9 | One-Day-Old-Chicken (%) n = 8 | Carcass (%) n = 2 | Total | |
| algD | 11.1% (1) | 12.5% (1) | 100% (2) | 21.1% (4) |
| plcH, | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| aprA | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| plcN | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| exoU | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 0% (0) |
| exoS | 77.7% (7) | 0% (0) | 100% (2) | 47.3% (9) |
| exoY | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| exoT | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| exoA | 66.6% (6) | 87.5% (7) | 100% (2) | 78.9% (15) |
| lasA | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| lasB | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| rhlAB | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| phzH | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| lasI | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| lasR | 100% (9) | 100% (8) | 100% (2) | 100% (19) |
| In Silico Characterization | P. aeruginosa Isolated from Carcass (PA_CA1) | P. aeruginosa Isolated from Pipped Eggs (PA_EG1) | P. aeruginosa Isolated from Pipped Eggs (PA_EG9) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serotype | O3 | O2 | O3 |
| MLST | 116 | 1649 | 1744 |
| Plasmid | None | Col3M_1 and ColRNAI_1 | None |
| Resistance genes | blaOXA-396, blaPAO, aph(3′)-IIb, catB7, and fosA | blaCTX-M-2, blaOXA-50, blaPAO, aadA, aph(3′)-IIb, aac(3)-VIa, aac(6′)-IIc, cat, catB7, crpP, fosA, sul1, and qacE | blaOXA-395, blaPAO, aph(3′)-IIb, catB7, fosA, and crpP |
| Virulence genes | |||
| Phospholipases C | plcH, plcN | plcH, plcN | plcH |
| Alkaline protease | aprA | aprA | aprA |
| Rhamnolipid | rhlAB, rhlI, rhlR | rhlAB, rhlR | rhlAB, rhlI, rhlR |
| Mucoid related alginate | algD | algD | algD |
| Pyocyanin biosynthesis | phzH | phzH | |
| Type III System-Secreted effectors | exoA, exoY, exoT, exoS | exoA, exoY, exoT, exoS | exoA |
| Quorum sensing | lasA, lasB, lasI, lasR | lasA, lasB, lasI, lasR | lasA, lasB, lasI |
| GenBank accession number | SAMN47217368 | SAMN47217369 | SAMN47217370 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, F.B.; Pons, M.J.; Ruiz, J.; Sáenz, Y.; Christensen, H.; Knöbl, T. Virulence and Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Poultry in Brazil. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102402
Barbosa FB, Pons MJ, Ruiz J, Sáenz Y, Christensen H, Knöbl T. Virulence and Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Poultry in Brazil. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102402
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, Fernanda Borges, Maria J. Pons, Joaquim Ruiz, Yolanda Sáenz, Henrik Christensen, and Terezinha Knöbl. 2025. "Virulence and Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Poultry in Brazil" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102402
APA StyleBarbosa, F. B., Pons, M. J., Ruiz, J., Sáenz, Y., Christensen, H., & Knöbl, T. (2025). Virulence and Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Poultry in Brazil. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102402







