Abstract
Alterations in both oral and gut microbiomes have been associated with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementia (ADRD). While extensive research has focused on the role of gut dysbiosis in ADRD, the contribution of the oral microbiome remains relatively understudied. This study aims to evaluate distinct patterns and potential synergistic effects of oral and gut microbiomes in a cohort of predominantly Hispanic individuals with cognitive impairment (CI) and without cognitive impairment (NC). We conducted 16S rRNA gene sequencing on stool and saliva samples from 32 participants (17 CI, 15 NC; 62.5% female, mean age = 70.4 ± 6.2 years) recruited in San Antonio, Texas, USA. Differential abundance analysis evaluated taxa with significant differences between both groups. While diversity metrics showed no significant differences between CI and NC groups, differential abundance analysis revealed an increased presence of oral genera such as Dialister, Fretibacterium, and Mycoplasma in CI participants. Conversely, CI individuals exhibited a decreased abundance of gut genera, including Shuttleworthia, Holdemania, and Subdoligranulum, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. No evidence was found for synergistic contributions between oral and gut microbiomes in the context of CI. Our findings suggest that like the gut microbiome, the oral microbiome of CI participants undergoes significant modifications. Notably, the identified oral microbes have been previously associated with periodontal diseases and gingivitis. These results underscore the necessity for further investigations with larger sample sizes to validate our findings and elucidate the complex interplay between oral and gut microbiomes in ADRD pathogenesis.
1. Background
The intricate interplay between the human microbiome and health has garnered significant attention, with emerging research elucidating its profound influence on physiological functions and disease states [1,2,3]. The gut microbiome stands out as a pivotal player among the myriad microbial ecosystems inhabiting the human body [4,5,6]. The concept of the gut–brain axis has emerged as a fundamental framework elucidating the bidirectional communication between the gut microbiota and the central nervous system, implicating its involvement in various neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14].
While gut dysbiosis has been extensively studied in the context of ADRD, the role of the oral microbiome, particularly the saliva microbiome, remains elusive despite its potential significance. The oral cavity harbors a diverse microbiota, second only to the gut, comprising over 770 bacterial species [15,16]. Emerging evidence suggests that the effects of oral dysbiosis could extend beyond oral health, impacting brain health through mechanisms such as the production of inflammatory factors like lipopolysaccharides (LPS), which may enter the bloodstream through compromised oral tissue barriers and facilitate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration [17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28].
Environmental factors and cardiovascular disease risk factors have been implicated in shaping the oral microbiome, potentially affecting inflammatory responses [29,30,31,32,33,34]. Additionally, oral-to-gut and gut-to-oral microbial transmissions can modulate the microbial ecosystems in both habitats, influencing disease pathogenesis. Recent research has begun to shed light on the oral microbiome’s involvement in neurological health, proposing the concept of an oral–brain axis [19,20,21,35,36,37]. For instance, previous research have indicated that dysbiosis in the oral cavity can lead to periodontitis which is linked with the development of ADRD [38,39]. Additionally, oral dysbiosis in individuals with poor cardiovascular health and/or cognitive impairment is associated with an increase in bacterial genera such as Tannerella, Porphyromonas, Dialister, Treponema, Fretibacterium, and Fusobacterium [21,22,23,40]. Moreover, oral dysbiosis has been shown to induce inflammatory responses through elevated levels of cytokines, C-reactive protein, white blood cells, and intercellular adhesion molecules [40,41,42,43,44].
Although a direct correlation between oral microbiota and intestinal microbiota is not yet in depth enough, synergistic interactions between both have been reported, underscoring their collective impact on neurological function and disease processes. Indeed, evidence indicates that saliva microbes entering the gastrointestinal tract may disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota and disturb the homeostasis of the immune response in the intestine [21,35,45,46].
This study aims to investigate the differential patterns of the gut and saliva microbiomes in a cohort of predominantly Hispanic/Latino participants comprising cognitively normal individuals and those with cognitive impairment in San Antonio, Texas, USA. By examining the intricate relationships between the gut–brain axis, the oral–brain axis, and cognitive status, this research seeks to contribute to our understanding of the roles of the human oral and gut microbiomes in neurodegenerative diseases.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Sample Collection
This study was conducted at the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UTHSCSA). Questionnaires were used to collect demographic details such as age and sex, as well as pertinent medical history, current medication usage, dietary patterns, and alcohol consumption habits. Participants were excluded if they had used antibiotics in the last 30 days or were younger than 55. Only participants who provided both stool and saliva samples and had recently undergone a comprehensive physical/neurological exam and cognitive assessment using the Uniform Data Set version 3 (USD-3 [46,47,48]) were included in this analysis. Participants with MCI or dementia were clinically diagnosed using the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association criteria [49] and had a Global Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) [50] Scale score of 0.5 or 1. Stool and saliva samples were collected by participants at home using OMNIgene ORAL and OMNIgene GUT collection tubes (DNAgenotek, Ottawa, ON, Canada). Saliva samples were collected in the morning, on an empty stomach without drinking any fluids. Samples were shipped to the South Texas Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center (STAC) Biomarker laboratory in San Antonio, TX, and processed/stored according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the UTHSCSA, ensuring adherence to ethical principles and guidelines governing human research participants. All procedures involving human participants were conducted in accordance with the ethical standards outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments. Prior to enrollment, participants provided signed, written informed consent indicating their willingness to participate.
2.2. Clinical Labs
Standard biological, clinical lab measurements, such as HbA1c, fasting glucose, lipid panels, homocysteine, hsCRP, and creatinine, were performed by Labcorp (Burlington, NC). Measurements were not available for all participants. HbA1c (n = 32), fasting glucose (n = 32), lipid panels (n = 32), homocysteine (n = 27), hsCRP (n = 27), and creatinine (n = 31) and were collected on average within 25.6 days (SD = 39.7, Min = 0, Max = 196) of the stool and saliva samples used for microbiome sequencing.
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis and Microbial Profiling
Stool and saliva samples were collected and shipped as described above. Bacterial DNA was extracted using the Maxwell RSC Fecal Microbiome kit (Madison, WI, USA). The UTHSCSA Genomic Sequencing Facility performed 16S rRNA (V4 region) gene sequencing (primer 515F:5′-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACTATGGTAATTGTGTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′) and unique reverse barcode primers from the Golay primer set [51,52,53]. After amplification, sample replicates were pooled, cleaned to remove residual contaminants, and sequenced at the UTHSCSA Genomic Sequencing Facility using the Illumina HiSeq 3000 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The reads generated from the 16S rRNA gene sequencing were processed and analyzed using the Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology 2 (QIIME2) software version 2024.10 [54]. Sequencing reads were clustered into Amplicon Sequencing Variants (ASVs) to delineate individual bacterial taxa present within the samples. To ensure robust and reliable analysis, ASVs with less than four reads in less than 10% of samples were removed to minimize the impact of low representation and sequencing depth variations across samples. Taxonomic classification was performed on the clustered ASVs to assign taxonomy to the sequences, enabling the identification of bacterial taxa at various levels of phylogenetic resolution. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the MAFFT algorithm implemented within the QIIME2 (version 2024.10) pipeline.
2.4. Predictive Functional Content of Microbial Communities
To explore the potential functional attributes of the microbial communities within the cohort, we used the Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved State (PICRUSt v2.5.0) [55]. Functional prediction was performed using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) orthologs (KO), Enzyme Commission (EC) classifications, and MetaCyc metabolic pathways (MePath) enrichments. Differences between the predicted functional contents of cognitively normal (NC) and impaired (CI) participants were conducted using the MaAslin2 package (version 1.8.0) [56].
2.5. Differential Abundance Analysis of Microbial Communities
We analyzed the association between clinical laboratory measures and gut/oral microbial genera using univariable linear regression via MaAsLin2. The following model was employed to identify genera associated with clinical laboratory measures: Genera~clinical labs measurements, where “Genera” denotes the relative abundance counts at the genus level. For MaAslin2 processing, thresholds were set with a minimum relative abundance of >10−3 and a minimum detection threshold of 10% of samples for each feature. Associations were considered significant if the Benjamini–Hochberg (BH)-adjusted p-value was less than 0.05.
Sample α-diversity was assessed using Chao1, ACE, Observed, Shannon, and Simpson indices. At the same time, β-diversity was visualized through principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) based on Bray–Curtis distances to evaluate group separation in compositional data. Differences in community composition between cognitively impaired and cognitively normal groups were tested using permutational analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) implemented in the vegan package [57].
Differential abundance (DA) analysis, performed with the R package MicrobiotaProcess version 1.10.2, identified gut and saliva microbial features that differed between NC and CI groups. DA results were considered significant if they had adjusted p-values < 0.05 and a logarithmic linear discriminant analysis (LDA) score > 2. We used to perform differential Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Orthology (KOs) representations between NC and CI participants. Statistically significant KOs (adjusted p-value < 0.05) were subsequently subjected to pathway enrichment analysis using the ClusterProfiler package version 4.6.2 in R and visualized using EnrichPlot version 1.18.4 [58].
3. Results
This study included 32 predominantly Hispanic/Latino (%Hispanic = 90.6) participants (%Female = 62.5, mean age = 70.4 ± 6.2), of which 17 were classified as CI and 15 were classified as NC. Two participants in CI group were diagnosed with gum disease while one individual in NC group had gum disease. There were no statistically significant differences in demographic and clinical characteristics between CI and NC participants (p > 0.05). Detailed information on the study cohort’s characteristics is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Demographic, BMI, fasting blood glucose and lipids, and markers inflammation, diabetes, and metabolism of cognitively normal and impaired Hispanic participants (%Hispanics/Latinos = 90.6).
3.1. Participants’ Oral and Gut Microbial Contents Differ Between the Cognitively Impaired and Normal Groups
We assessed the association between participants’ clinical laboratory measurements and their gut and saliva microbial compositions, operating under the hypothesis that there exists a correlation between physiological parameters and the gut microbiome (Figure 1A,B). Through regression analyses, we identified multiple oral and gut bacterial genera significantly associated with two or more clinical laboratory measures (BH-adjusted p-value < 0.05) (Figure 1A,B). These findings suggest distinct patterns of association between the participants’ physiological states and their gut and oral microbial compositions.
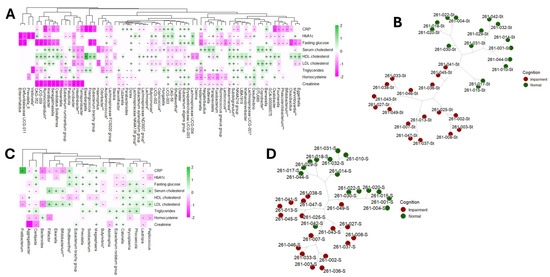
Figure 1.
Univariable association analysis using MaAslin2 displaying the positive (+) and negative (-) correlations (BH-adjusted p-value < 0.05) between participants’ CRP, hbA1c, fasting blood glucose, blood lipids, homocysteine and creatinine and gut (A) and oral (B) microbiomes. The genera known to be able to produce short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) are marked with an asterisk (*) and those that are probiotics for SCFA are marked with two asterisks (**). Unsupervised phylogenic clustering of gut (C) and oral microbiomes (D) distinguished normal participants from cognitively impaired.
Fasting glucose and the microbiome: We observed a general negative correlation trend between gut bacterial genera and fasting glucose levels. Specifically, genera such as Marvinbryantia, Bifidobacterium, Phascolarctobacterium, Oxalobacter, Subdoligranulum, Butyricimonas, and Lachnospira exhibited these negative associations. Among the 45 correlations examined between bacterial genera and fasting glucose, only 9 bacterial genera showed positive correlations, notably including Barnesiella, Dialister, Dorea, and members of the Eubacterium eligens group (refer to Figure 1A and Table 2 for details). The comprehensive list of gut bacterial genera associated with fasting blood glucose levels is provided in Table 2. Additionally, our analysis revealed 13 correlations between saliva microbiome composition and fasting glucose levels. Of these, 5 correlations were negative, involving oral bacterial genera such as Aggregatibacter, Butyrivibrio, and Lautropia. Conversely, 8 correlations were positive, including genera such as Mycoplasma, Prevotella, and Megasphaera (see Figure 1B).

Table 2.
Univariable association of gut bacterial genera and clinical labs measures using MaAslin2. Gut genera showing significant (BH-adjusted p-value < 0.05) positive or negative correlation with fasting blood glucose, blood lipids and a marker of systemic inflammation (CRP).
Implications of the microbiome on diabetes (hemoglobin A1c): Our analysis revealed that the majority of gut bacterial genera exhibited negative correlations with hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels. Specifically, out of 41 statistically significant correlations, 26 gut genera demonstrated significant associations with HbA1c. Notable genera among these include Barnesiella, Phascolarctobacterium, Oxalobacter, Subdoligranulum, Akkermansia, Methanobrevibacter, Veillonella, and Prevotella_9 (Figure 1A and Table 3). In contrast, only 11 oral bacterial genera were found to be significantly correlated with HbA1c levels. The comprehensive list of these correlations is detailed in Table S1.

Table 3.
Univariable association of gut bacterial genera and clinical labs measures using MaAslin2. Gut genera showing significant (BH-adjusted p-value < 0.05) positive or negative correlation with a marker of diabetes (hbA1c) and overall metabolism (homocysteine).
Fasting blood cholesterol and microbiome: We observed statistically significant correlations between gut bacterial genera and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, as illustrated in Figure 1A and detailed in Table 2. Notably, the genera Oxalobacter, Subdoligranulum, Akkermansia, Barnesiella, and Lachnospira demonstrated positive associations with HDL cholesterol levels. In contrast, oral bacterial genera showed predominantly negative correlations (63.6% of negative correlations) with HDL cholesterol, with fewer instances of positive associations. Furthermore, serum cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol also exhibited correlations with gut microbiota. Most correlations were negative (60.5% of negative correlations), although some positive associations were observed. The gut bacterial genera showing significant negative correlations with both serum cholesterol and LDL cholesterol included Marvinbryantia, Shuttleworthia, Coprococcus, Butyricimonas, Lachnospira, and Acidaminococcus. Conversely, oral bacterial genera exhibited mostly positive correlations (67.7% of positive correlations) with serum cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels, with notable genera including Bifidobacterium, Peptococcus, Mycoplasma, Prevotella, and Megasphaera. A comprehensive summary of these correlations is presented in Table 2 and Table S1.
Implications of the microbiome on inflammation (C-reactive protein) and oxidation (homocysteine): No statistically significant differences in C-reactive protein (CRP) or homocysteine levels were observed between cognitively normal (NC) and cognitively impaired (CI) older adults. However, several gut bacterial genera demonstrated notable correlations with CRP and homocysteine. Specifically, CRP levels were predominantly negatively (66.7% of negative correlations) correlated with various gut genera, including Coprococcus, Acidaminococcus, Bifidobacterium, Oxalobacter, Marvinbryantia, and Subdoligranulum. In contrast, the correlations between homocysteine levels and gut genera were more evenly distributed, with both positive and negative associations observed. A comprehensive summary of these associations is presented in Table 3. Additionally, only a limited number of associations were identified between oral bacterial genera and CRP and homocysteine levels (Figure 1B and Table S1).
Subsequently, we performed phylogenetic clustering of the samples to evaluate whether microbial abundance could independently differentiate CI participants from NC (refer to Figure 1C,D). Our analyses demonstrated distinct clustering patterns based on the compositions of both the gut (Figure 1C) and saliva (Figure 1D) microbiomes among the participants.
Altogether, these findings underscore the potential importance of gut microbiota in metabolic health, particularly in the context of glucose metabolism, among individuals with cognitive impairment.
3.2. No Difference in Alpha and Beta Diversity Metrics
To evaluate the diversity of gut and oral microbiomes in NC and CI participants, we utilized Chao1, Observed Species, and Abundance-based Coverage Estimator (ACE) indices to assess species richness, while the Shannon diversity index was employed to estimate both species evenness and richness. Our analysis revealed no significant differences in gut alpha diversity between the NC and CI groups, as depicted in Figure 2A,B. Additionally, gut beta diversity, analyzed using Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) with Bray–Curtis distances, showed no significant differences in species composition between the two groups after performing PERMANOVA. Similarly, alpha and beta diversity analyses of saliva samples indicated no significant differences between the NC and CI groups, as shown in Figure 2C,D.
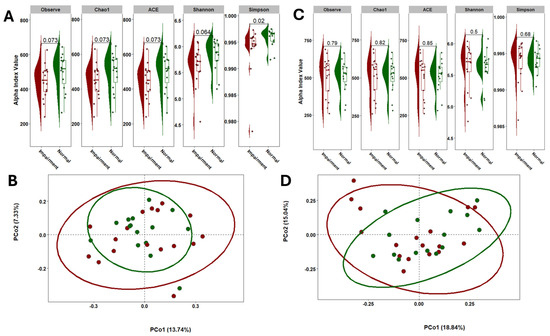
Figure 2.
Comparison of the microbial community diversity of samples collected in individuals with CI and NC. Alpha diversity of stool (A) and saliva (C) samples based on 16S rRNA sequencing. The tests of difference in microbial diversity (Chao1, ACE, Observe, and Shannon indexes) at the OTU level between CI and NC were based on Wilcoxon test. Beta diversity on stool (B) and saliva (D) samples represented by PCoA with Bray–Curtis distances. No differences were observed between groups based on the PERMANOVA test (p = 0.83).
3.3. Oral Genera Are Differentially Abundant Between NC and CI Participants
The differential abundance analysis of oral microbiome composition revealed notable shifts in several genera among CI individuals. Specifically, there was a marked decrease in the relative abundance of Neisseria and an increase in Streptococcus and Fusobacterium in CI participants compared to those who were cognitively normal (Figure 3A). For biomarker discovery, we employed Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) to assess the effect sizes and relative abundances driving these differences. LDA effect sizes indicate the magnitude of consistent differences in relative abundance between features (bacterial taxa) in CI and NC individuals. Using this approach, we identified 13 taxonomic biomarkers that were significantly overrepresented in CI cases (adjusted p-value < 0.05, with LDA effect sizes > 2; Figure 3B and Table S2).
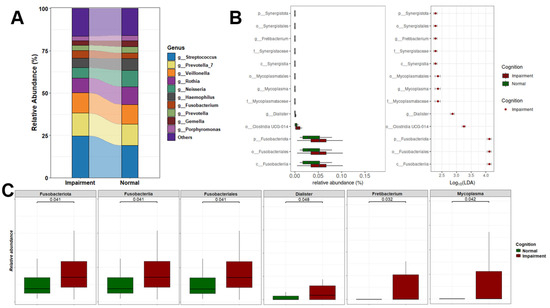
Figure 3.
Oral microbial composition and alterations related to cognition status. (A) Stacked plot illustrating the microbiome profiles of predominant taxa in the oral microbiomes of CI and NC participants at the genus level. (B) LDA results on saliva microbiome detected 13 bacterial taxa showing statistically significant and biologically consistent differences in CI at the phylum (p-), class (c-), order (o-), family (f-), and genus (g-) levels. (C) Relative abundance of the most differential taxa and identified oral genera between CI and NC participants.
Among the top differentially abundant taxa were Fusobacteriia, Fusobacteriota, and Fusobacteriales. We also observed a significant increase in the abundance of several genera in CI participants, including Fretibacterium, a Gram-negative bacterium previously linked to periodontitis; Mycoplasma, a Gram-negative species prevalent in individuals with gingivitis and periodontitis; and Dialister [59,60]. These bacteria are commonly associated with oral and systemic diseases, particularly periodontitis, gingivitis, and advanced periodontal conditions [61,62]. Furthermore, the phyla Synergistota and Fusobacteria were significantly increased in CI participants. Figure 3C highlights the top statistically significant taxa, underscoring their varying abundance between NC and CI groups.
3.4. Differential Abundance Analysis of the Gut Microbiome in CI and NC Participants
Significant differences emerged in the gut microbiome composition between individuals with normal cognition and those with cognitive impairment. As depicted in Figure 4A, the relative abundances of gut genera varied markedly between the two groups. Specifically, individuals with CI exhibited an increased abundance of Bacteroides and Escherichia-Shigella, and a decreased abundance of Ruminococcus and Subdoligranulum. Further analysis utilizing Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) identified several taxonomic biomarkers with significantly lower abundances in the CI group (Figure 4B and Table S1). Notably, genera known for their anti-inflammatory functions, such as Subdoligranulum, Holdemania, Shuttleworthia, UGC-005, and the Eubacterium brachy group, were found to be reduced in CI individuals. Additionally, Clostridia, Firmicutes, and Oscillospirales were the most differentially abundant gut bacteria, with effect sizes of 4.61, 4.54, and 4.49, respectively. Moreover, a significant reduction in the overall abundance of the Firmicutes phylum was observed in CI participants (Figure 4C). This depletion further underscores the complex dysbiosis present in individuals with cognitive impairment, highlighting the potential functional implications of these microbial alterations on cognitive function.
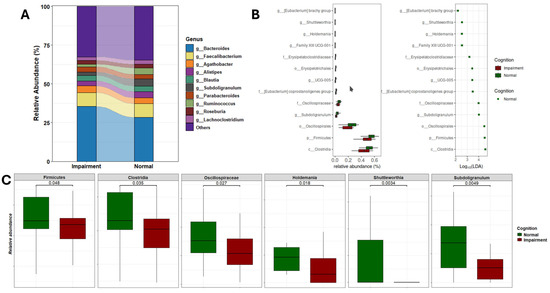
Figure 4.
Gut microbial composition and alteration related to cognition status. (A) Stacked plot illustrating the microbiome profiles of predominant taxa in the gut microbiome of CI and NC participants at the genus level. (B) LDA results on gut microbiome detected 13 bacterial taxa showing statistically significant and biologically consistent differences in CI at the phylum (p-), class (c-), order (o-), family (f-), and genus (g-) levels. (C) Relative abundance of the most differential taxa and identified gut genera between CI and NC participants.
3.5. Functional Potential of the Gut and Oral Microbial Communities Associated with Cognitive Health
We employed Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt) analysis to assess the functional potential of the gut microbiota differentially represented in CI and NC individuals. This analysis revealed 487 predicted metabolic pathways (MePath), 2913 predicted enzyme commission numbers (ECs), and 10,543 predicted Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes orthologs (KOs). Subsequent differential analysis identified 33 MePath that exhibited significant differences (BH-adjusted p-value < 0.05) between CI participants and NC individuals. Among these differential pathways, several are known to play crucial roles in host metabolism, including glucose degradation, glycol metabolism and degradation, glycolysis, pyruvate dehydrogenase, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, glyoxylate bypass, glyoxylate cycle, phospholipases, TCA cycle IV (2-oxoglutarate decarboxylase), photorespiration, fatty acid biosynthesis (E. coli), and L-glutamate degradation VIII (to propanoate). Notably, with the exception of glutamate degradation VIII, these pathways were enriched in CI participants compared to NC individuals (see Figure S1A).
In our analysis, we identified 14 oral metabolic pathways (MePath) that were significantly altered between CI and NC participants (see Figure S1B). Notably, pathways such as ketogluconate metabolism, enterobacterial common antigen biosynthesis, 4-hydroxyphenylacetate degradation, and aerobactin biosynthesis were found to be significantly reduced in CI participants. Conversely, the pathways involved in L-glutamate degradation VIII and L-tryptophan biosynthesis were elevated in CI participants. Further examination of enzyme commission (EC) terms revealed 160 distinct gut EC terms and 120 oral EC terms with significant differences between CI and NC participants (see Table S3). Additionally, our analysis of gene orthologs (KOs) indicated that 1025 KOs were differentially expressed in the gut microbiome between NC and CI participants, while 616 KOs showed differential expression in saliva samples (see Table S4). To elucidate the biological relevance of these findings, we employed a pathway enrichment analysis using the differentially expressed KOs to map the activated KEGG pathways associated with the transition from NC to CI. This approach provides a more nuanced understanding of the functional roles of the gut and saliva microbiomes in cognitive health.
3.6. KEGG Pathways Associated with Gut Microbiome Profiles in Cognitive Health
We aimed to explore the biological pathways associated with the differentially expressed KEGG Orthologs (KOs) identified between CI and NC individuals. We identified 28 KEGG pathways that were significantly enriched (Benjamini–Hochberg-adjusted p-value < 0.05) in the differential KOs between NC and CI participants. These pathways include lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis, bacterial chemotaxis, beta-alanine metabolism, propanoate metabolism, methane metabolism, and bacterial secretion systems. Figure 5A illustrates the number of differential gut KOs associated with each enriched pathway, and a comprehensive summary of these pathways is provided in Table S5. Remarkably, many of these KEGG pathways have been previously implicated in cognitive deficits and Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias (ADRD) in both animal models and clinical studies [63,64,65]. To further elucidate these associations, we constructed a network diagram (Figure 5B) depicting the relationships between differential gut KOs and KEGG pathways. In this network, blue and red nodes represent gut KOs that were upregulated and downregulated in CI individuals, respectively. For example, differential gut KOs such as K02848 (waaP), K03275 (waaO), K03276 (waaR), K07264 (arnT), K11211 (kdkA), K12973 (pagP), K12975 (eptB), K12981 (waaZ), and K12985 (waaW), which are involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis, were found to be upregulated in CI participants. Analysis of these enriched KEGG pathways revealed several notable associations. Methane metabolism was found to correlate with propanoate metabolism, and glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism showed associations with carbon metabolism as well as glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism (see Figure S2). Additionally, beta-alanine metabolism demonstrated a connection with propanoate metabolism. However, no direct associations were observed between lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and bacterial chemotaxis with other pathways. To provide a spatial representation, we mapped the identified gut KOs involved in beta-alanine metabolism onto a KEGG metabolic map (Figure S3), highlighting these KOs in red.
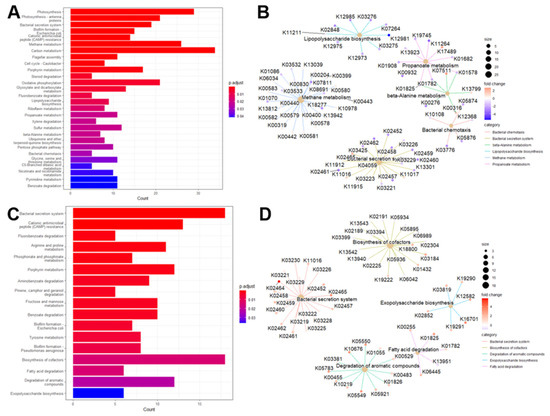
Figure 5.
Enriched KEGG pathways in the connection between gut/oral microbiome and cognition. Barplot of enriched KEGG pathways for stool (A) and saliva (C). Network plot of some enriched KEGG pathways displaying the linkages with differential gut KOs for stool (B) and saliva (D).
3.7. KEGG Pathways Associated with Oral Microbiome Profiles in Cognitive Health
We performed a differential representation analysis of KEGG pathways to elucidate the biological pathways associated with oral KOs and their implications for cognitive health. Our analysis identified 17 KEGG pathways with significant enrichment, including critical pathways such as fatty acid degradation, biosynthesis of cofactors, degradation of aromatic compounds, exopolysaccharide biosynthesis, and the bacterial secretion system. The relationship between these differential oral KOs and the enriched KEGG pathways is depicted in Figure 5, with a comprehensive summary provided in Table S6. Notably, Figure 5D details the differential oral KOs associated with each enriched KEGG pathway. Among the identified pathways, the bacterial secretion system, biosynthesis of cofactors, cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) resistance, and degradation of aromatic compounds emerged as the top four pathways with the highest counts of differential oral KOs. These findings are consistent with previous research highlighting associations between enriched KEGG pathways and cognitive function, as well as alterations in microbiome composition [66,67,68,69,70]. Further analysis of the interactions among the identified KEGG pathways (see Figure S4) revealed a strong correlation between Benzoate degradation and the degradation of aromatic compounds, as well as Fluorobenzoate degradation. The degradation of aromatic compounds also exhibited associations with Tyrosine metabolism and Fluorobenzoate degradation. Additionally, connections were observed between Porphyrin metabolism and the biosynthesis of cofactors, and between biofilm formation and the bacterial secretion system. Fatty acid degradation was linked to Pinene, Camphor, and Geraniol degradation. To illustrate these relationships, we mapped the identified oral KOs involved in fatty acid degradation onto a KEGG metabolic map, underscoring their relevance to cognitive health (see Figure S5).
3.8. On the Synergistic Contribution of Oral and Gut Microbiomes to Brain Health
Previous studies have highlighted a synergistic association between oral and gut microbiomes and brain health [22,71]. To further elucidate this relationship, we conducted a detailed examination of the overlap in microbiome taxa and potential functional profiles across these two habitats. Our analysis identified no overlapping differentially abundant taxa between the oral and gut microbiomes in our sampled population. This finding suggests that, within our cohort, there is no apparent synergistic effect in microbial composition between these two sites. To extend our investigation into potential functional synergies, we analyzed KEGG pathways associated with each microbiome. We identified 22 KEGG pathways unique to the gut microbiome, 11 unique to the oral cavity, and 6 pathways that were shared between the two environments (see Figure 6 and Table 4). The shared pathways included essential functions such as Benzoate degradation, Fluorobenzoate degradation, Porphyrin metabolism, Cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) resistance, biofilm formation in Escherichia coli, and bacterial secretion systems. These findings highlight specific functional overlaps that may be relevant to understanding the interactions between the gut and oral microbiomes in relation to cognitive health. Further research is necessary to elucidate the mechanisms underlying these pathways and their potential impacts on cognitive processes, which will advance our understanding of their roles in brain health.
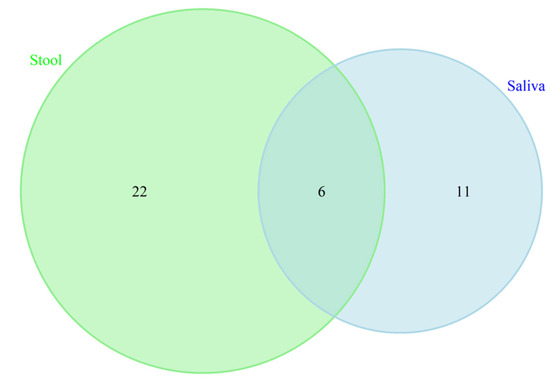
Figure 6.
Venn diagram displaying the similarity and overlapping KEGG pathways between saliva and gut microbiotas in cognition. These 6 overlapped KEGG pathways included Benzoate degradation, Fluorobenzoate degradation, Porphyrin metabolism, Cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) resistance, biofilm formation in Escherichia coli, and bacterial secretion system.

Table 4.
List complete of 22 KEGG pathways unique to the gut microbiome, 11 unique to the oral cavity.
4. Discussion
The human microbiome plays a critical role in maintaining brain health; however, the specific interactions between alterations in the oral and gut microbiomes within underrepresented populations, particularly Hispanics, are not well elucidated. To address this gap, we examined the shifts in composition and functional profiles of the oral and gut microbiota in individuals with cognitive impairment compared to those with normal cognitive function in a diverse sample. Our analysis revealed significant differences in microbial composition at the genus level. Notably, there was an increase in the abundance of taxa with known pathogenic potential in the oral cavity, alongside a reduction in beneficial taxa within the gut microbiota of CI participants. Despite these observed alterations in microbial communities within each habitat, we found no evidence of a synergistic interaction between oral and gut microbiota in relation to brain health.
Although alpha and beta diversity metrics did not reveal statistically significant differences, differential abundance analysis identified notable changes in taxa among participants with cognitive impairment. Specifically, the oral microbiome exhibited a predominance of Gram-negative taxa, such as Dialister, Fretibacterium, and Mycoplasma. These taxa have been implicated in inflammatory responses associated with oral diseases, including periodontitis and gingivitis [72,73,74,75]. Recent studies of microbiome data from Hispanic adults have shown that the proliferation of genera like Dialister, Fretibacterium, and Mycoplasma correlates with severe periodontal disease, a known risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease [76]. Our results align with a previous meta-analysis that examined European and American cohorts, which reported that binge drinking induces a shift in the oral microbiome, characterized by an increased abundance of Dialister and Fretibacterium, and associates these genera with AD [77]. Additionally, the enrichment of genera associated with bacteremia in CI participants supports prior research suggesting a potential pathway for bacterial dissemination from the oral cavity to the systemic circulation, possibly affecting brain function [78]. This hypothesis is corroborated by recent studies demonstrating significant alterations in the oral microbiota profiles of individuals with AD, highlighting the importance of oral microbiota in neurodegenerative conditions [23,79]. Clinical findings have also linked poor oral hygiene to the proliferation of invasive Dialister species, suggesting a potential relationship between oral health and cognitive impairment [80]. Furthermore, our data reveal positive correlations between Fretibacterium and Mycoplasma and C-reactive protein levels, a marker of systemic inflammation, indicating a possible overlap between oral microbiota, inflammation, and cognitive health. These findings emphasize the critical role of the oral microbiome in both health and disease, particularly its association with cognitive function.
The analysis of the gut microbiome in individuals with CI revealed a significant decrease in the abundance of beneficial bacteria, particularly within the Firmicutes phylum, which includes key short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) producers [81]. Notably, Subdoligranulum, a Gram-positive bacterium closely related to the Faecalibacterium genus, known for its butyrate production, exhibited reduced abundance in CI participants. Butyrate, an SCFA, is increasingly recognized for its potential probiotic effects and its role in improving metabolic health [82]. Additionally, Holdemania, an acetate-producing bacterium involved in SCFA metabolism, was found to be less prevalent among CI individuals. Higher levels of Holdemania have been associated with anti-inflammatory effects and maintenance of gut barrier integrity in both rodent models and humans [83,84].
Recent investigations have also highlighted the role of Shuttleworthia, a Gram-positive, saccharolytic bacterium capable of producing acetate, butyrate, and lactate [85]. Shuttleworthia is essential for sustaining gut health. The observed dysbiosis, characterized by a reduced abundance of these beneficial bacteria, suggests a compromised protective mechanism crucial for maintaining gut barrier integrity. This dysbiosis may contribute to increased gut permeability and subsequent systemic inflammation. Furthermore, the absence of overlapping taxonomic biomarkers between oral and gut microbiomes emphasizes the distinct microbial profiles of these environments. The activation of immune responses and cytokine production in CI could facilitate the translocation of inflammatory agents to the intestine, thereby compromising gut barrier function and potentially exacerbating neuroinflammation and cognitive decline [11,86,87].
Despite the lack of significant differences in C-reactive protein levels between cognitively impaired and normal cognition groups, we observed notable correlations between CRP levels and gut microbiota. Specifically, CRP levels were negatively correlated with several gut bacterial genera, including Bifidobacterium, Subdoligranulum, Marvinbryantia, Acidaminococcus, and Coprococcus. In contrast, associations with oral bacterial genera were less pronounced; however, Mycoplasma, Fretibacterium, and Megasphaera were positively correlated with CRP levels, whereas Bifidobacterium, Aggregatibacter, and Bacteroides exhibited negative correlations.
Hemoglobin A1c and fasting glucose, both critical for diagnosing diabetes, showed distinct correlations with gut microbiota. Negative correlations were observed with genera such as Subdoligranulum, Akkermansia, Oxalobacter, and Ruminiclostridium. Conversely, positive correlations were noted with Dorea, Dialister, and CAG-56. Additionally, HbA1c and fasting glucose levels exhibited positive correlations with oral bacterial genera Shuttleworthia, Centipeda, Prevotella, and Megasphaera, while negative correlations were observed with Catonella and the Eubacterium nodatum group. The relative abundance of Barnesiella showed negative correlation with HbA1c and positive correlation with fasting glucose. Regarding homocysteine, a marker of oxidative stress, no significant differences were found between NC and CI groups. However, homocysteine levels were positively correlated with gut bacterial genera Acidaminococcus, Coprobacter, Subdoligranulum, and Oxalobacter. Homocysteine also showed positive associations with oral genera Bacteroides and the Eubacterium nodatum group, and a negative correlation with Mycoplasma. We did not observe significant differences in lipid profiles or serum metabolites between NC and CI participants. Nonetheless, HDL cholesterol levels demonstrated positive correlations with gut bacterial genera such as Subdoligranulum, Marvinbryantia, Barnesiella, Butyricimonas, Lachnospira, and Oxalobacter. Serum metabolites exhibited more negative correlations with gut genera, including Shuttleworthia, Acidaminococcus, Odoribacter, Marvinbryantia, Coprococcus, Butyricimonas, and Lachnospira. Few associations were found between HDL cholesterol levels and oral bacterial genera, with Fretibacterium negatively correlated with HDL cholesterol and Mycoplasma positively correlated with both serum metabolites and HDL cholesterol. Overall, these findings suggest that gut and oral microbial populations may have distinct functional roles, influencing different physiological and biochemical pathways.
The functional roles of microbial communities were further elucidated through PICRUSt analysis, identifying enriched pathways associated with cognitive dysfunction. Notably, lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation was found to be associated with cognitive impairment through mechanisms that enhance beta-amyloid generation [63]. Additionally, bacterial chemotaxis may contribute to or exacerbate cognitive impairment, highlighting the adaptive responses of gut microbiota to environmental changes [64,88]. Furthermore, beta-alanine metabolism was identified as a significant pathway related to cognitive performance, with evidence suggesting that beta-alanine supplementation may improve cognitive function, particularly among older adults with borderline to suboptimal cognitive levels [63,89,90]. Propanoate metabolism, which has been closely associated with Alzheimer’s disease, was also implicated in disease progression. Elevated propionate levels, potentially resulting from the activity of the Bacteroidetes phylum—the primary producer of propionate in the human gut—could play a role in this process [64,91]. In contrast, methane metabolism has been recognized for its potential to mitigate spatial memory deficits, likely through the modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and microglial activation within the hippocampus [65,92,93].
Our pathway analysis identified several KEGG pathways relevant to the interaction between the saliva microbiome and cognitive function, as well as alterations in microbiome composition. Notably, perturbations in fatty acid homeostasis and associated pathways have been linked to cognitive impairment and dementia [94]. The biosynthesis of cofactors pathway has been specifically associated with cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease [66,67]. Additionally, cathelicidins, which are key components of the innate immune response, play a critical role in host defense against microbial infections [68,69,70]. The pathway related to exopolysaccharide biosynthesis has been associated with cognitive function enhancement in Alzheimer’s disease, potentially due to its anti-inflammatory effects. Furthermore, our analysis revealed KEGG orthologs involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in the gut and fatty acid degradation in the oral cavity, suggesting a potential synergistic contribution of both oral and gut microbiome pathways to cognitive impairment. However, it is important to note that the mere overlap of these pathways between the oral and gut microbiomes may not be sufficient to fully support the hypothesized synergistic effects, as previously described [22,71].
Figure 7 illustrates a proposed interaction between gut microbiome metabolism and the regulation of fasting blood glucose. Complex plant-derived fibers, which are resistant to human digestive enzymes, undergo bacterial fermentation within the gut. This fermentation process converts these complex carbohydrates into hexoses (e.g., glucose) and pentoses, which can then be utilized for energy production through pyruvate and the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Short-chain fatty acids, produced by gut microbiome metabolism, play a significant role in colonocyte energy metabolism, contributing approximately 70% of their energy needs. SCFAs diffuse into the bloodstream, where they provide roughly 10% of the total caloric requirement and influence health by modulating various pathways, including immune, endocrine, vagal, and other humoral pathways, such as neurotransmitter regulation. This modulation is a crucial component of the complex gut–brain axis. We hypothesize that dietary fibers and specific gut bacterial genera that regulate glucose levels and support SCFA production are more likely to be associated with cognitive health. Additionally, our findings reveal that gut bacterial genera associated with both fasting glucose and HDL cholesterol levels exhibit opposing directional associations. Overall, distinct bacterial taxa combinations were identified in association with fasting glucose, lipid levels, and plasma metabolites {Adil, 2025 #100}.
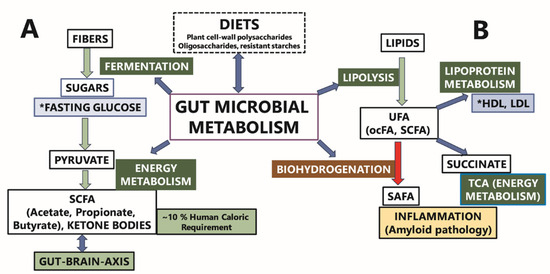
Figure 7.
The putative contribution of the gut microbiome metabolism to fasting glucose (A) and lipoprotein metabolism (B). Gut microbiome composition is influenced by dietary fiber content. (A) Gut microbiome metabolism can affect fasting blood sugar via fermentation/breakdown of complex plant carbohydrates. (B) Gut microbiome can also affect fasting blood lipid levels by altering the fatty acid composition via lipolysis and biohydrogenation. The asterisk (*) indicates the clinical labs measures reported in results’ section. The terms UFA and ocFA in the Figure 7 are the abbreviations for unsaturated fatty acids and odd-chain fatty acids, respectively.
This study offers valuable insights into the relationship between microbial communities and cognitive health; however, several limitations should be noted. Firstly, the relatively small sample size may restrict our ability to find significant associations due to limited power. Additionally, the dynamic nature of both oral and gut microbiota underscores the need for further longitudinal studies to capture temporal variations and their potential impact on cognitive health. Furthermore, variables such as medication use and dietary intake, known to influence microbial composition, were not accounted for in this study. Addressing these limitations in future research will be essential for a more comprehensive understanding of the complex interactions between microbial communities and cognitive function, as well as for developing targeted therapeutic interventions for neurodegenerative diseases.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed stool and saliva samples to explore the distinct patterns of gut and oral microbiomes in predominantly Hispanic/Latino individuals in San Antonio, Texas, categorized into cognitively normal and cognitively impaired groups. Our findings reveal that cognitive impairment is associated with notable disruptions in both the gut and oral microbiomes. Consistent with existing literature, our results indicate that the oral microbiome in CI participants exhibits altered abundance and functional profiles, with a notable presence of taxa previously linked to periodontal disease and gingivitis. These findings align with growing evidence suggesting a potential bidirectional relationship between oral health and cognitive function. Moreover, our study highlights significant compositional shifts in the gut microbiome of CI participants, particularly a reduction in Firmicutes bacteria known for their anti-inflammatory properties. This observation echoes previous research that underscores the role of gut microbiota in modulating inflammatory pathways and their potential impact on neurodegenerative conditions. Notably, we identified dysregulated pathways in CI individuals, including lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in the gut and fatty acid degradation in the oral microbiome. These disrupted pathways may contribute to the inflammatory milieu associated with cognitive decline. Our results reinforce the notion that dysbiosis in both the oral and gut microbiomes is intricately linked to cognitive dysfunction, particularly within Hispanic populations. To substantiate these findings, future research should encompass larger and more heterogeneous cohorts to validate these associations and further elucidate the interplay between oral and gut microbiotas in cognitive impairment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13102350/s1, Supplementary Figure S1. Predicted MePath associated with cognition, comparing the Normal and Impairment groups for gut microbiome (A) and oral microbiome (B). Supplementary Figure S2. Emap plot of enriched KEGG pathways illustrating their network association for gut microbiome. Supplementary Figure S3. KEGG metabolic map highlighting the KOs (red color) that were identified in beta-Alanine metabolism. Supplementary Figure S4. Emap plot of enriched KEGG pathways illustrating their network association for oral microbiome. Supplementary Figure S5. KEGG metabolic map highlighting the KOs (red color) that were identified in Fatty acid degradation. Supplementary Table S1. Oral bacterial genera showing positive or negative correlation with glucose, lipids, CRP, hbA1c, and oxidation. Supplementary Table S2. Summary of differential oral and gut taxa between CI and NC participants. Supplementary Table S3. Top 30 differential oral and gut ECs between CI and NC participants. Supplementary Table S4. Top 30 differential oral and gut KOs between CI and NC participants. Supplementary Table S5. Summary of differential gut KOs grouped in their KEGG pathways. Supplementary Table S6. Summary of differential oral KOs grouped in their KEGG pathways.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.M., S.S. and B.F.; Methodology, Y.N.W., A.N.F., S.S., T.F.K. and B.F.; Software, Y.N.W. and B.F.; Validation, S.S.; Formal analysis, Y.N.W. and B.F.; Investigation, Y.N.W.; Data curation, E.L.V., J.J.M., J.A.S.M., R.P.M., C.L.S., M.M.G., S.S. and T.F.K.; Writing—original draft, Y.N.W., T.F.K. and B.F.; Writing—review & editing, Y.N.W., E.L.V., J.J.M., J.A.S.M., R.P.M., C.L.S., M.M.G., J.T., G.M., A.N.F., S.S., T.F.K. and B.F.; Visualization, Y.N.W. and A.N.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The following funding sources partly supported this project: include the UT Health San Antonio Center for Biomedical Neuroscience (CBN) and grants from the NIA (P30 AG066546, 5P30AG059305-03, RF1AG061729A1, 5U01AG052409-04, UG3AG090675) and NINDS (NS017950, UF1NS125513, K01NS126489).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, USA (protocol code: HSC20200261H, date of approval: 20 January 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
All participants provided written informed permission, or, for those with substantial cognitive impairment, consent was provided by a caregiver, legal guardian, or other proxy.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in dbGap (BioProject ID: PRJNA1242024, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/1242024, assessed on 1 September 2025) and will be openly available upon publication of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank the many study participants, researchers, and staff for collecting and contributing to the data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Larson, P.J.; Zhou, W.; Santiago, A.; Driscoll, S.; Fleming, E.; Voigt, A.Y.; Chun, O.K.; Grady, J.J.; Kuchel, G.A.; Robison, J.T. Associations of the skin, oral and gut microbiome with aging, frailty and infection risk reservoirs in older adults. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmanski, T.; Diener, C.; Rappaport, N.; Patwardhan, S.; Wiedrick, J.; Lapidus, J.; Earls, J.C.; Zimmer, A.; Glusman, G.; Robinson, M. Gut microbiome pattern reflects healthy ageing and predicts survival in humans. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 274–286, Erratum in Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W. The gut microbiome as a modulator of healthy ageing. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber IV, H.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota–brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huh, J.R.; Shah, K. Microbiota and the gut-brain-axis: Implications for new therapeutic design in the CNS. EBioMedicine 2022, 77, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Geurts, L.; Hoyles, L.; Iozzo, P.; Kraneveld, A.D.; La Fata, G.; Miani, M.; Patterson, E.; Pot, B.; Shortt, C. The microbiota–gut–brain axis: Pathways to better brain health. Perspectives on what we know, what we need to investigate and how to put knowledge into practice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupack, D.A.; Mars, R.A.T.; Voelker, D.H.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Kashyap, P.C. The promise of the gut microbiome as part of individualized treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Huo, Y.-J.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhou, D. Gut-brain axis: Focus on gut metabolites short-chain fatty acids. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varesi, A.; Pierella, E.; Romeo, M.; Piccini, G.B.; Alfano, C.; Bjørklund, G.; Oppong, A.; Ricevuti, G.; Esposito, C.; Chirumbolo, S.; et al. The Potential Role of Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfili, L.; Cuccioloni, M.; Gong, C.; Cecarini, V.; Spina, M.; Zheng, Y.; Angeletti, M.; Eleuteri, A.M. Gut microbiota modulation in Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on lipid metabolism. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarawneh, R.; Penhos, E. The Gut Microbiome and Alzheimer’s Disease: Complex and Bidirectional Interactions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 141, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrio, C.; Arias-Sánchez, S.; Martín-Monzón, I. The gut microbiota-brain axis, psychobiotics and its influence on brain and behaviour: A systematic review. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 137, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Hendriksen, H.M.A.; de Leeuw, F.A.; Doorduijn, A.S.; van Leeuwenstijn, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Kraaij, R.; van Duijn, C.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Is Related to AD Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 794519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongang, B.; Satizabal, C.; Kautz, T.F.; Wadop, Y.N.; Muhammad, J.A.S.; Vasquez, E.; Mathews, J.; Gireud-Goss, M.; Saklad, A.R.; Himali, J.; et al. Cerebral small vessel disease burden is associated with decreased abundance of gut Barnesiella intestinihominis bacterium in the Framingham Heart Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, P.N.; Deshmukh, R. Oral microbiome: Unveiling the fundamentals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. JOMFP 2019, 23, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, S.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; Hein, R.; Schmidt, T.; Kamada, N. The bacterial connection between the oral cavity and the gut diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, J.L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ge, L. The role of oral microbiome in respiratory health and diseases. Respir. Med. 2021, 185, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, K.A.; Kazmi, N.; Barb, J.J.; Ames, N. The Oral and Gut Bacterial Microbiomes: Similarities, Differences, and Connections. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2021, 23, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-Y.; Hwang, B.-O.; Lim, M.; Ok, S.-H.; Lee, S.-K.; Chun, K.-S.; Park, K.-K.; Hu, Y.; Chung, W.-Y.; Song, N.-Y. Oral-Gut Microbiome Axis in Gastrointestinal Disease and Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L. Gut, oral and nasal microbiota and Parkinson’s disease. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitre, Y.; Micheneau, P.; Delpierre, A.; Mahalli, R.; Guerin, M.; Amador, G.; Denis, F. Did the Brain and Oral Microbiota Talk to Each Other? A Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureda, A.; Daglia, M.; Castilla, S.A.; Sanadgol, N.; Nabavi, S.F.; Khan, H.; Belwal, T.; Jeandet, P.; Marchese, A.; Pistollato, F. Oral microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease: Do all roads lead to Rome? Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.; Hayes, C.; Taylor, G.W. Glycemic control of type 2 diabetes and severe periodontal disease in the US adult population. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 2002, 30, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, F.; Magan-Fernandez, A.; Castellino, G.; Chianetta, R.; Nibali, L.; Rizzo, M. Periodontitis and mechanisms of cardiometabolic risk: Novel insights and future perspectives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Khodadadi, H.; Baban, B. Innate immunity and oral microbiome: A personalized, predictive, and preventive approach to the management of oral diseases. EPMA J. 2019, 10, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Mazmanian, S.K. Innate immune recognition of the microbiota promotes host-microbial symbiosis. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adil, N.A.; Omo-Erigbe, C.; Yadav, H.; Jain, S. The oral–gut microbiome–brain axis in cognition. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonocito, S.; Giudice, A.; Polizzi, A.; Troiano, G.; Merlo, E.M.; Sclafani, R.; Grosso, G.; Isola, G. A Cross-Talk between Diet and the Oral Microbiome: Balance of Nutrition on Inflammation and Immune System’s Response during Periodontitis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Alam, M.T.; Dey, J.; Chakrapani, P.S.B.; Ray, U.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gandhi, S.; Tripathi, P.P. Healthy Gut, Healthy Brain: The Gut Microbiome in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1142–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardman, J.F.; Bains, R.K.; Rahfeld, P.; Withers, S.G. Carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) in the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacesa, R.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Sinha, T.; Klaassen, M.A.Y.; Bolte, L.A.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Chen, L.; Collij, V.; Hu, S.; et al. Environmental factors shaping the gut microbiome in a Dutch population. Nature 2022, 604, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berding, K.; Vlckova, K.; Marx, W.; Schellekens, H.; Stanton, C.; Clarke, G.; Jacka, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Diet and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Sowing the Seeds of Good Mental Health. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1239–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frausto, D.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A.; Voigt, R.M. Dietary Regulation of Gut-Brain Axis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Importance of Microbiota Metabolites. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 736814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, D.; GianVincenzo, Z.; Carlo Luca, R.; Karan, G.; Jorge, V.; Roberto, M.; Javad, P. Oral-Gut Microbiota and Arthritis: Is There an Evidence-Based Axis? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, R.J.; Koo, H.; Hajishengallis, G. The oral microbiota: Dynamic communities and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafurov, K.; Elhawy, E.; Ren, L.; Dong, C.Q.; Igboin, C.; Hyman, L.; Griffen, A.; Mittag, T.; Danias, J. Oral microbiome link to neurodegeneration in glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chang, S.; Pi, X.; Hua, F.; Jiang, H.; Liu, C.; Du, M. The effect of periodontitis on dementia and cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedmoalemi, M.A.; Saied-Moallemi, Z. Association between periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2025, 18, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georges, F.; Do, N.; Seleem, D. Oral dysbiosis and systemic diseases. Front. Dent. Med. 2022, 3, 995423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, L.J.; Garzón, H.; Arboleda, S.; Rodríguez, A. Oral dysbiosis and autoimmunity: From local periodontal responses to an imbalanced systemic immunity. A review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 591255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Cheng, L.; You, Y.; Tang, C.; Ren, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X. Oral microbiota in human systematic diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, J.D.; Fernandes, G.R.; Calderaro, D.C.; Mendonça, S.M.S.; Silva, J.M.; Albiero, M.L.; Cunha, F.Q.; Xiao, E.; Ferreira, G.A.; Teixeira, A.L. Oral microbial dysbiosis linked to worsened periodontal condition in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, I.; Yamazaki, K. Can oral bacteria affect the microbiome of the gut? J. Oral Microbiol. 2019, 11, 1586422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, S.; Besser, L.; Dodge, H.H.; Teylan, M.; Ferris, S.; Goldstein, F.C.; Giordani, B.; Kramer, J.; Loewenstein, D.; Marson, D. Version 3 of the Alzheimer Disease Centers’ neuropsychological test battery in the Uniform Data Set (UDS). Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2018, 32, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besser, L.; Kukull, W.; Knopman, D.S.; Chui, H.; Galasko, D.; Weintraub, S.; Jicha, G.; Carlsson, C.; Burns, J.; Quinn, J. Version 3 of the national Alzheimer’s coordinating center’s uniform data set. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2018, 32, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsell, S.E.; Dodge, H.H.; Zhou, X.-H.; Bu, Y.; Besser, L.M.; Mock, C.; Hawes, S.E.; Kukull, W.A.; Weintraub, S. Results from the NACC uniform data set neuropsychological battery crosswalk study. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2016, 30, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack Jr., C.R.; Albert, M.S.; Knopman, D.S.; McKhann, G.M.; Sperling, R.A.; Carrillo, M.C.; Thies, B.; Phelps, C.H. Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.C. Clinical dementia rating: A reliable and valid diagnostic and staging measure for dementia of the Alzheimer type. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1997, 9, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkouonlack, C.D.; Njamnshi, W.Y.; Angwafor, S.A.; Siewe Fodjo, J.N.; Mengnjo, M.K.; Ngarka, L.; Mbede, M.; Nfor, L.N.; Abomate, C.; Maestre, G.E. Dementia and cognitive impairment in French-speaking Sub-Saharan Africa: A comprehensive review on moving out of the shadows of neglect. Res. Sq. 2024; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857, Erratum in Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37,1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, H.; Rahnavard, A.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tickle, T.L.; Weingart, G.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.H.; et al. Multivariable association discovery in population-scale meta-omics studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Sankaran, K.; Fukuyama, J.A.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Bioconductor workflow for microbiome data analysis: From raw reads to community analyses. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemwong, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Matsuura, T.; Sudo, T.; Kano, C.; Mikami, R.; Izumi, Y. Fretibacterium sp. human oral taxon 360 is a novel biomarker for periodontitis screening in the Japanese population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Sun, B.; Chen, Y.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, Z. Dental plaque microbial resistomes of periodontal health and disease and their changes after scaling and root planing therapy. Msphere 2021, 6, e00121–e00162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwek, H.; Wilson, M.; Newman, H. Mycoplasma in relation to gingivitis and periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1990, 17, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.-L.; Szafrański, S.P.; Jarek, M.; Bhuju, S.; Wagner-Döbler, I. Dysbiosis in chronic periodontitis: Key microbial players and interactions with the human host. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.K.; Yuk, D.Y.; Choi, D.Y.; Ban, S.B.; Oh, K.W.; Hong, J.T. Neuro-inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment through enhancement of beta-amyloid generation. J. Neuroinflammation 2008, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Szymanski, C.M.; Baylink, A. Bacterial chemotaxis in human diseases. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killingsworth, J.; Sawmiller, D.; Shytle, R.D. Propionate and Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 12, 580001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troesch, B.; Weber, P.; Mohajeri, M.H. Potential links between impaired one-carbon metabolism due to polymorphisms, inadequate B-vitamin status, and the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients 2016, 8, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodam, P.; Sai Swaroop, R.; Pradhan, S.S.; Sivaramakrishnan, V.; Vadrevu, R. Integrated multi-omics analysis of Alzheimer’s disease shows molecular signatures associated with disease progression and potential therapeutic targets. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRock, C.N.; Nizet, V. Cationic antimicrobial peptide resistance mechanisms of streptococcal pathogens. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 3047–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, S.; Qie, J.; Wei, X.; Yan, H.; Liu, K. Polyion complexes of a cationic antimicrobial peptide as a potential systemically administered antibiotic. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geitani, R.; Ayoub Moubareck, C.; Touqui, L.; Karam Sarkis, D. Cationic antimicrobial peptides: Alternatives and/or adjuvants to antibiotics active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansores-España, L.D.; Melgar-Rodríguez, S.; Olivares-Sagredo, K.; Cafferata, E.A.; Martínez-Aguilar, V.M.; Vernal, R.; Paula-Lima, A.C.; Díaz-Zúñiga, J. Oral-gut-brain axis in experimental models of periodontitis: Associating gut dysbiosis with neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Aging 2021, 2, 781582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertani, B.; Ruiz, N. Function and biogenesis of lipopolysaccharides. EcoSal Plus 2018, 8, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.H. Lipopolysaccharide: Basic biochemistry, intracellular signaling, and physiological impacts in the gut. Intest. Res. 2014, 12, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniesta, M.; Chamorro, C.; Ambrosio, N.; Marín, M.J.; Sanz, M.; Herrera, D. Subgingival microbiome in periodontal health, gingivitis and different stages of periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertelsen, R.J.; Barrionuevo, A.M.P.; Shigdel, R.; Lie, S.A.; Lin, H.; Real, F.G.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Åstrøm, A.N.; Svanes, C. Association of oral bacteria with oral hygiene habits and self-reported gingival bleeding. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 768–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A.P.; Acosta-Pagán, K.T.; Oramas-Sepúlveda, C.; Castañeda-Avila, M.A.; Vilanova-Cuevas, B.; Ramos-Cartagena, J.M.; Vivaldi, J.A.; Pérez-Santiago, J.; Pérez, C.M.; Godoy-Vitorino, F. Oral microbiota and periodontitis severity among Hispanic adults. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 965159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yussof, A.; Yoon, P.; Krkljes, C.; Schweinberg, S.; Cottrell, J.; Chu, T.; Chang, S.L. A meta-analysis of the effect of binge drinking on the oral microbiome and its relation to Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nędzi-Góra, M.; Kowalski, J.; Górska, R. The immune response in periodontal tissues. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2017, 65, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Huang, C.-P.; Lan, H.; Lau, H.-G.; Chiang, C.-P.; Chen, Y.-W. Association of periodontitis and oral microbiomes with Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative systematic review. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 1762–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathini, P.; Foucras, S.; Dupanloup, I.; Imeri, H.; Perna, A.; Berruex, J.L.; Doucey, M.A.; Annoni, J.M.; Auber Alberi, L. Classifying dementia progression using microbial profiling of saliva. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2020, 12, e12000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hul, M.; Le Roy, T.; Prifti, E.; Dao, M.C.; Paquot, A.; Zucker, J.-D.; Delzenne, N.M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Clément, K.; Cani, P.D. From correlation to causality: The case of Subdoligranulum. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1849998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shang, C.; Xiang, M.; Li, L.; Cui, X. Microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids: Implications for cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 900381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, K.M.; Lucking, E.F.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.; Peterson, V.L.; Crispie, F.; Cotter, P.D.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; O’Halloran, K.D. Prebiotic administration modulates gut microbiota and faecal short-chain fatty acid concentrations but does not prevent chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced apnoea and hypertension in adult rats. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; An, N.; Li, X.; Pan, X.; Yang, X.; Tian, L.; Sun, J.; Xiong, X. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and hypertension: Mechanism and treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Xing, T.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F. Microbiota populations and short-chain fatty acids production in cecum of immunosuppressed broilers consuming diets containing γ-irradiated Astragalus polysaccharides. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.M. The immune response to Prevotella bacteria in chronic inflammatory disease. Immunology 2017, 151, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, S.; Hosseinzadeh Shakib, N.; Fooladfar, Z.; Nasrollahian, S.; Baghaei, S.; Mosaddad, S.A.; Motamedifar, M. The role of periodontitis-associated bacteria in Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2023, 63, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bi, W.; Xiao, S.; Lan, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyan, M.; Tousif, A.H.; Sonali, S.; Vichitra, C.; Sunanda, T.; Praveenraj, S.S.; Ray, B.; Gorantla, V.R.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Mahalakshmi, A.M. Role of endogenous lipopolysaccharides in neurological disorders. Cells 2022, 11, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, I.; Ben-Zeev, T.; Zamir, A.; Levi, C.; Gepner, Y.; Springer, S.; Hoffman, J.R. Role of β-Alanine Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Mood, and Physical Function in Older Adults; Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuffer, J.; González-Domínguez, R.; Lefèvre-Arbogast, S.; Low, D.Y.; Driollet, B.; Helmer, C.; Du Preez, A.; de Lucia, C.; Ruigrok, S.R.; Altendorfer, B. Exploration of the gut–brain axis through metabolomics identifies serum propionic acid associated with higher cognitive decline in older persons. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Yu, X. Methane ameliorates post-operative cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting microglia NF-κB/MAPKs pathway and promoting IL-10 expression in aged mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 71, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Domínguez, R.; Castellano-Escuder, P.; Lefèvre-Arbogast, S.; Low, D.Y.; Du Preez, A.; Ruigrok, S.R.; Lee, H.; Helmer, C.; Pallàs, M.; Urpi-Sarda, M. Apolipoprotein E and sex modulate fatty acid metabolism in a prospective observational study of cognitive decline. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).