Niche and Geographic Drivers Shape the Diversity and Composition of Endophytic Bacteria in Salt-Tolerant Peanut
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. DNA Extraction and Quality Testing
2.3. PCR Amplification and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
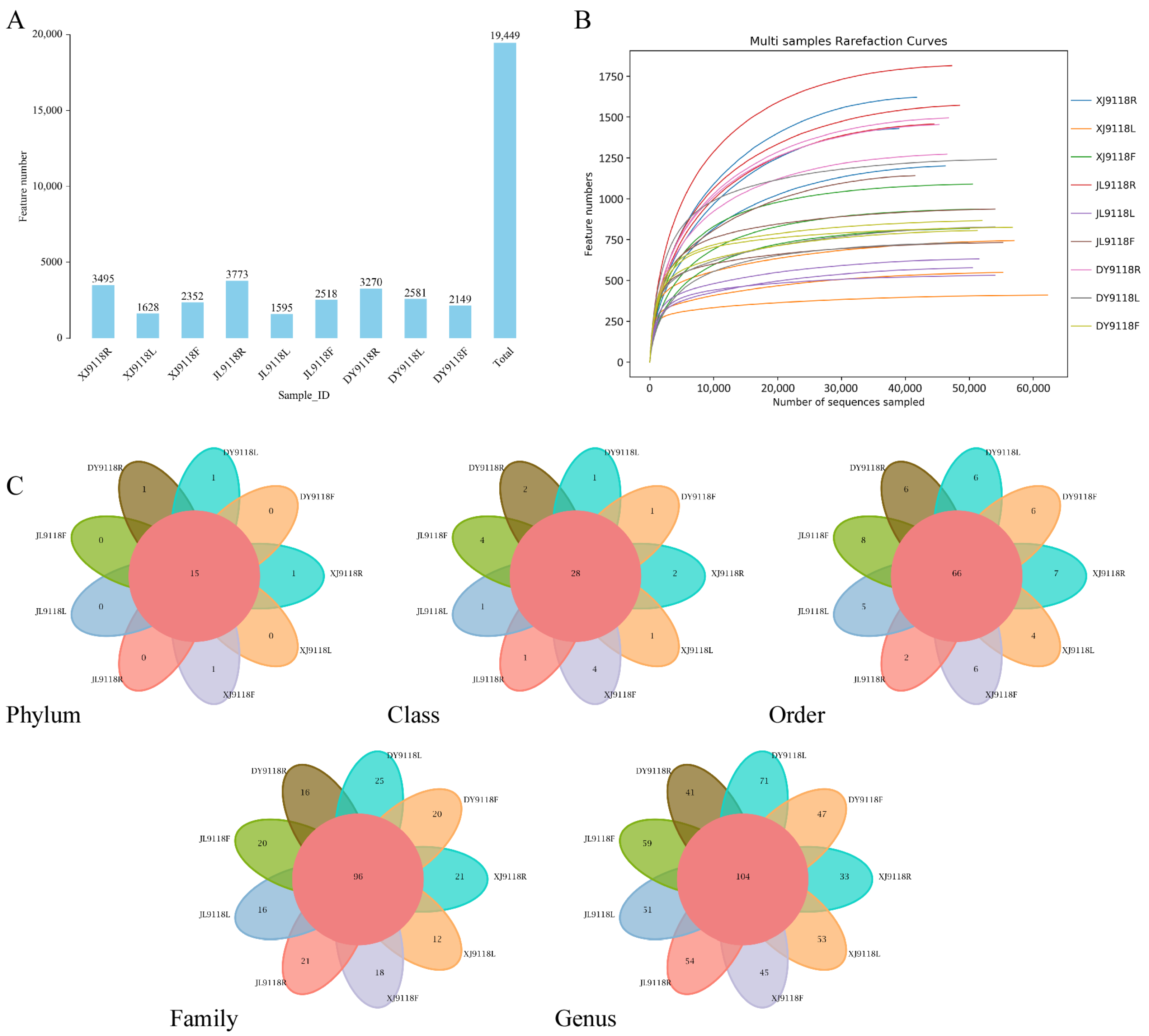
3.1. Statistics of Endophyte Sequences in Peanut Samples
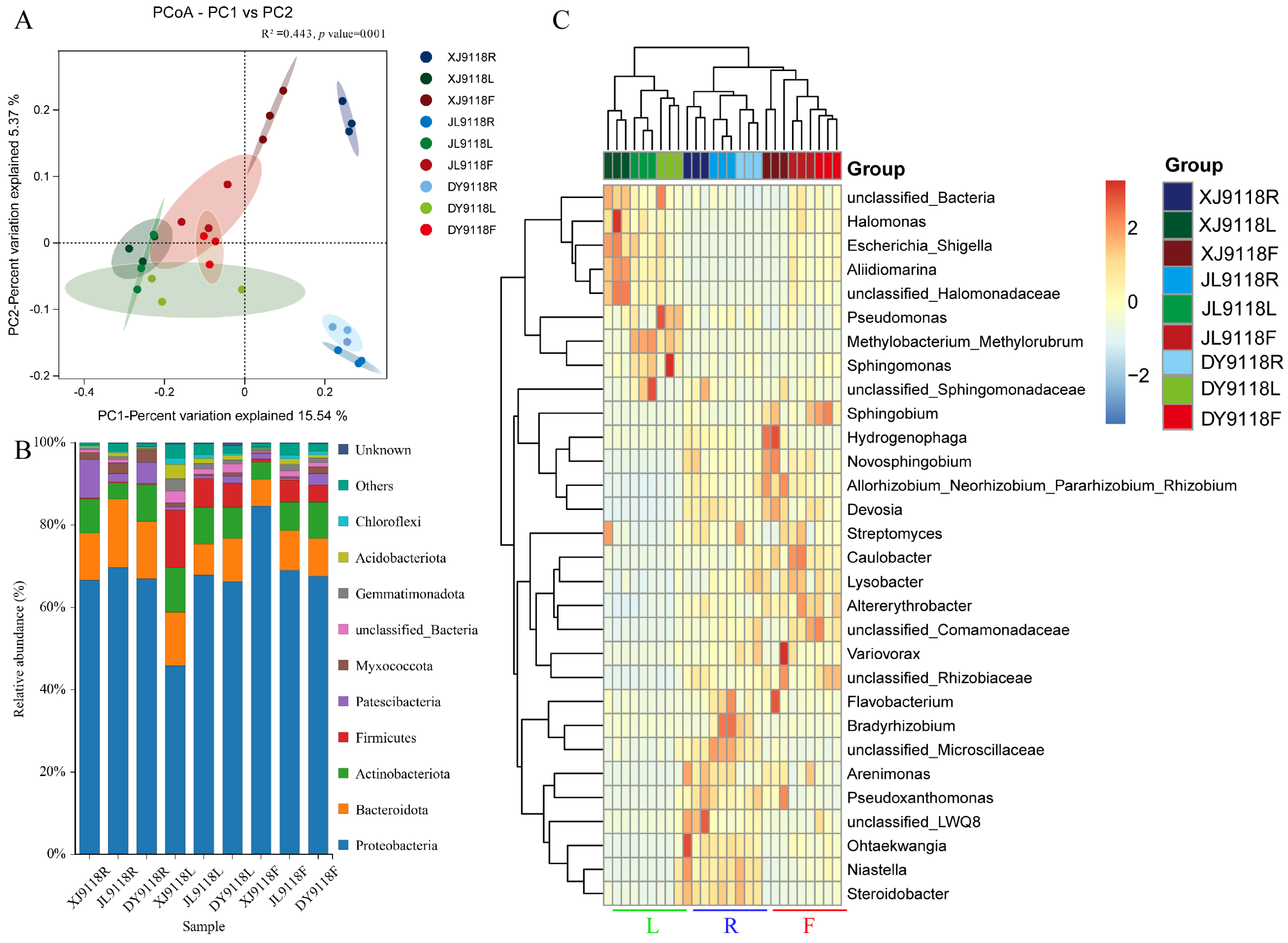
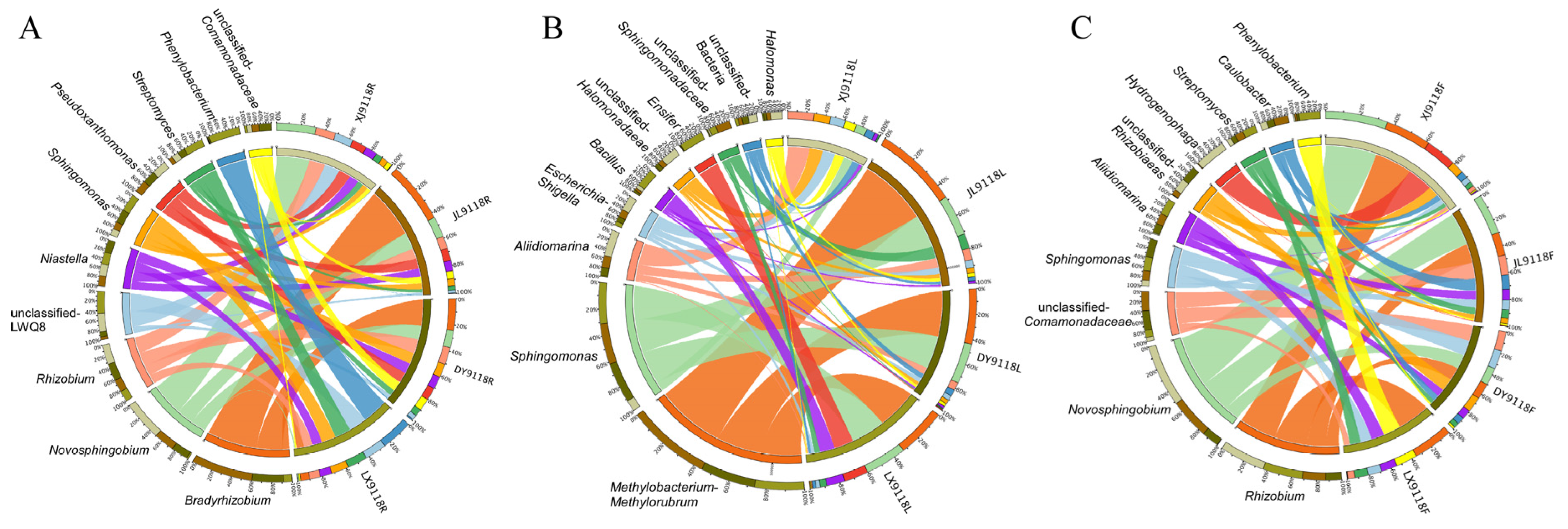
3.2. Endophytic Community Diversity and Composition
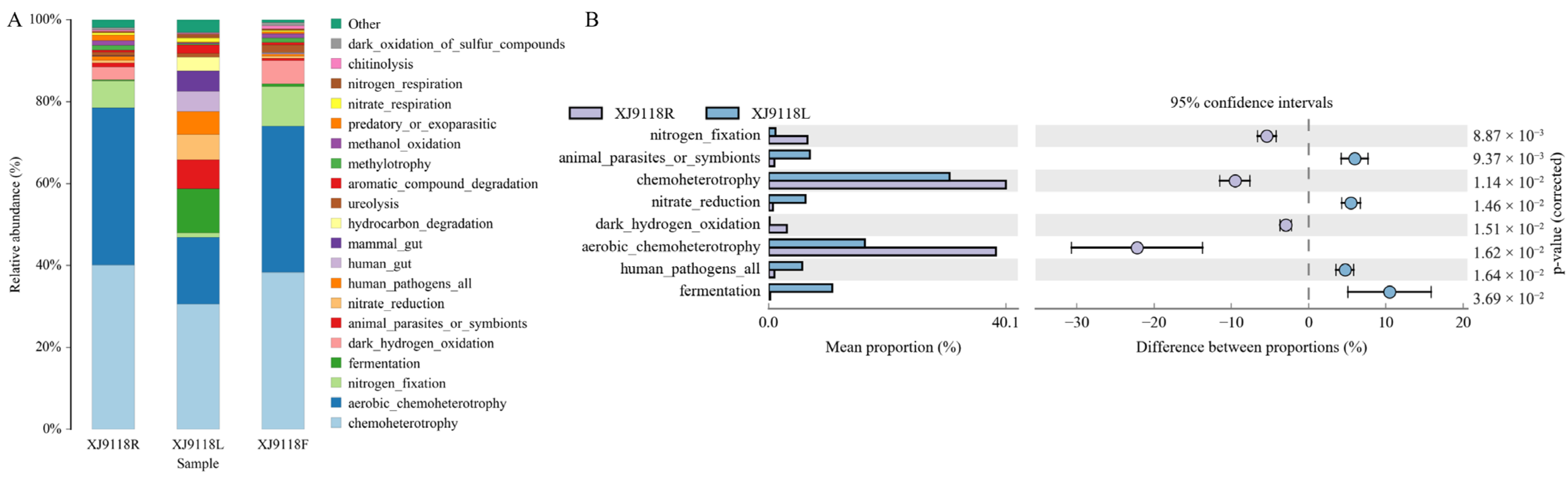
3.3. Host Niche Impacts on Peanut Microbial Community Diversity and Composition
3.4. Geographical Effects on the Peanut Microbiome Composition and Diversity
3.5. Relationship Between Environmental Factors and Endophytic Community Composition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HO | High oleic acid |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated fatty acid |
| O/L | The ratio of oleic acid to linoleic acid |
| PGPR | Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| LEfSe | Linear Discriminant Analysis effect size |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
| ASVs | Amplicon sequence variants |
| FAPROTAX | Functional Annotation of Prokaryotic Taxa |
| HN | Hydrolyzed nitrogen |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| AP | Available phosphorus |
| AK | Available potassium |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ACC | 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid |
| IAA | Indole acetic acid |
| LCM | Laser-capture microdissection |
References
- Bleam, W.F. Soil and Environmental Chemistry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhu, J.; Gong, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C. Advances in deciphering the mechanisms of salt tolerance in Maize. Plant Signal. Behav. 2025, 20, 2479513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, A.; Riaz, S.; Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Gene expression profiling of plants under salt stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Guo, Q.; Cao, S. Archaeal community diversity in different types of saline-alkali soil in arid regions of Northwest China. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 130, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Ni, G.; Feng, G.; Burrill, H.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Saline-alkali soil reclamation and utilization in China. Front. Agr. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 216–228. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarimoghaddam, H.; Galavi, M.; Ghanbari, A.; Panjehkeh, N. Salinity effects on seed germination and seedling growth of bread wheat cultivars. Trakia J. Sci. 2011, 9, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zelm, E.V.; Zhang, Y.; Testerink, C. Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2020, 71, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y. Identification and estimation of salt tolerance in peanut germplasm. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2015, 31, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire, E.J. A review of the nutritional composition, organoleptic characteristics and biological effects of the high oleic peanut. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xu, J.; Cao, M.; Pan, L.; Cui, F.; Xie, H.; Zou, Z.; Huang, X.; Huang, H.; Chi, X. Field screening and identification of salt-alkali tolerant varieties lines of high oleic acid peanut and analysis of yield formation related factors. J. Peanut Sci. 2021, 50, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gouda, S.; Das, G.; Sen, S.K.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Endophytes: A treasure house of bioactive compounds of medicinal importance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 29, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.R.; Molina, G.; Dionísio, A.P.; Maróstica Junior, M.R.; Pastore, G.M. The use of endophytes to obtain bioactive compounds and their application in biotransformation process. Biotechnol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 576286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, K.G.; Popay, A.J.; Hofmann, R.W.; Caradus, J.R. Epichloë—A lifeline for temperate grasses under combined drought and insect pressure. Grass Res. 2021, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Dijkstra, F.A. Carbon efficiency for nutrient acquisition (CENA) by plants: Role of nutrient availability and microbial symbionts. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnawal, D.; Bharti, N.; Pandey, S.S.; Pandey, A.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Kalra, A. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhance wheat salt and drought stress tolerance by altering endogenous phytohormone levels and TaCTR1/TaDREB2 expression. Physiol. Plant. 2017, 161, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamalero, E.; Glick, B.R. Bacterial modulation of plant ethylene levels. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papik, J.; Folkmanova, M.; Polivkova-Majorova, M.; Suman, J.; Uhlik, O. The invisible life inside plants: Deciphering the riddles of endophytic bacterial diversity. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 44, 107614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini-Andreote, F. Endophytes: The second layer of plant defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, K.K.; Dey, R.; Sherathia, D.N.; Devidayal; Mangalassery, S.; Kumar, A.; Rupapara, R.B.; Mandaliya, M.; Rawal, P.; Bhadania, R.A.; et al. Alleviation of salinity stress in peanut by application of endophytic bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 650771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Frith, C.; Bhattacharyya, S.S.; DeLaune, P.B.; Gentry, T.J. Isolation and characterization of bacterial endophytes from small nodules of field-grown peanut. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Fang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Q.; Liu, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J. Branch lignification of the desert plant Nitraria tangutorum altered the structure and function of endophytic microorganisms. Agronomy 2023, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batstone, R.T.; O’Brien, A.M.; Harrison, T.L.; Frederickson, M.E. Experimental evolution makes microbes more cooperative with their local host genotype. Science 2020, 370, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, B.S.; Babalola, O.O. Biotechnological overview of agriculturally important endophytic fungi. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2021, 62, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, M.; Mahmood, A.; Sahkoor, A.; Zia, M.A.; Ullah, M.S. The role of endophytes to combat abiotic stress in plants. Plant Stress 2024, 12, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zeng, W.; Hou, M.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Lei, G.; Zhou, B.; Huang, J. Responses of the soil microbial community to salinity stress in maize fields. Biology 2021, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, N.; Marschner, P. Response of soil respiration and microbial biomass to changing EC in saline soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Murphy, D.N.; Rousk, J. The microbial community size, structure, and process rates along natural gradients of soil salinity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhan, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J. Effect of salinity on soil respiration in relation to dissolved organic carbon and microbial characteristics of a wetland in the Liaohe River Estuary, Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, R.; Ali, S.; Amara, U.; Khalid, R.; Ahmed, I. Soil beneficial bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, M.A.; Wagan, S.; Alam, I.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Q.; Saha, S.; Poudel, T.R.; Manghwar, H.; Liu, F. Impact of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on plant nutrition and root characteristics: Current perspective. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgtenberg, B.; Kamilova, F. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hewezi, T.; Lebeis, S.L.; Pantalone, V.; Grewal, P.S.; Staton, M.E. Soil indigenous microbiome and plant genotypes cooperatively modify soybean rhizosphere microbiome assembly. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ye, W.; Yu, Z.; Shen, W.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X. Host niche, genotype, and field location shape the diversity and composition of the soybean microbiome. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2412–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, R.; Li, Y.; Hartman, W.H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tringe, S.G.; Wang, H. Insight into the bacterial endophytic communities of peach cultivars related to crown gall disease resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02931-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.S.; Zhang, B.C.; Qi, X.Y.; Sun, Z.H.; He, X.L.; Liu, Y.Z.; Li, J.; Chen, K.K.; Lin, Z.X. Root-associated endophytic bacterial community composition of Pennisetum sinese from four representative provinces in China. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.; McMurdie, P.; Rosen, M.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project, improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Mandal, S. Unveiling growth-promoting attributes of peanut root endophyte Micromonospora sp. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, S.; Li, L.; Li, X. Characterization and metabolism effect of seed endophytic bacteria associated with peanut grown in south China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, D.L.; Jiang, H.J.; Wu, X.H.; Sun, K.; Dai, C.C. Fungal endophyte promotes plant growth and disease resistance of Arachis hypogaea L. by reshaping the core root microbiome under monocropping conditions. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 277, 127491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.K.; Vyas, P.; Sharma, S.; Sardana, V. Groundnut harbours non-nodulating non-rhizobial plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, R.; Menon, R.R.; Likhitha, L.; Busse, H.-J.; Tanaka, N.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Rameshkumar, N. Novosphingobium pokkalii sp nov, a novel rhizosphere-associated bacterium with plant beneficial properties isolated from saline-tolerant pokkali rice. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, Z.; Sui, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.-S.; Zheng, Y. Ensifer sp. GMS14 enhances soybean salt tolerance for potential application in saline soil reclamation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, N.; Barnawal, D. Chapter five—Amelioration of salinity stress by PGPR, ACC deaminase and ROS scavenging enzymes activity. In PGPR Amelioration in Sustainable Agriculture; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 85–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Dai, J.; Liang, Z. Isolation and identification of Halomonas sp. Bachu 26 with plant growth-promoting effect from rhizosphere of Tamarix chinensis under salt stress. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2024, 64, 607–622. [Google Scholar]
- Cregger, M.A.; Veach, A.M.; Yang, Z.K.; Crouch, M.J.; Vilgalys, R.; Tuskan, G.A.; Schadt, C.W. The Populus holobiont: Dissecting the effects of plant niches and genotype on the microbiome. Microbiome 2018, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Xiong, H.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, L.; Mei, Z. The effect of plant geographical location and developmental stage on root-associated microbiomes of Gymnadenia conopsea. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.R.; Lundberg, D.S.; del Rio, T.G.; Tringe, S.G.; Dangl, J.L.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Host genotype and age shape the leaf and root microbiomes of a wild perennial plant. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chu, C.; Chen, Y.; Fang, S.; Jin, G.; Jiang, M.; Lian, J.-Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Diversity and biogeography of plant phyllosphere bacteria are governed by latitude-dependent mechanisms. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 1534–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolton, M.; Erlacher, A.; Berg, G.; Cytryn, E. The Flavobacterium genus in the plant holobiont: Ecological, physiological, and applicative insights. In Microbial Models: From Environmental to Industrial Sustainability; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, R. Nitrogen and phosphorus signaling and transport during legume–Rhizobium symbiosis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 683601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirriam, A.; Mugwe, J.; Nasar, J.; Kisaka, O.; Ranjan, S.; Gitari, H. Role of phosphorus and inoculation with Bradyrhizobium in enhancing soybean production. Adv. Agric. 2023, 2023, 3231623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
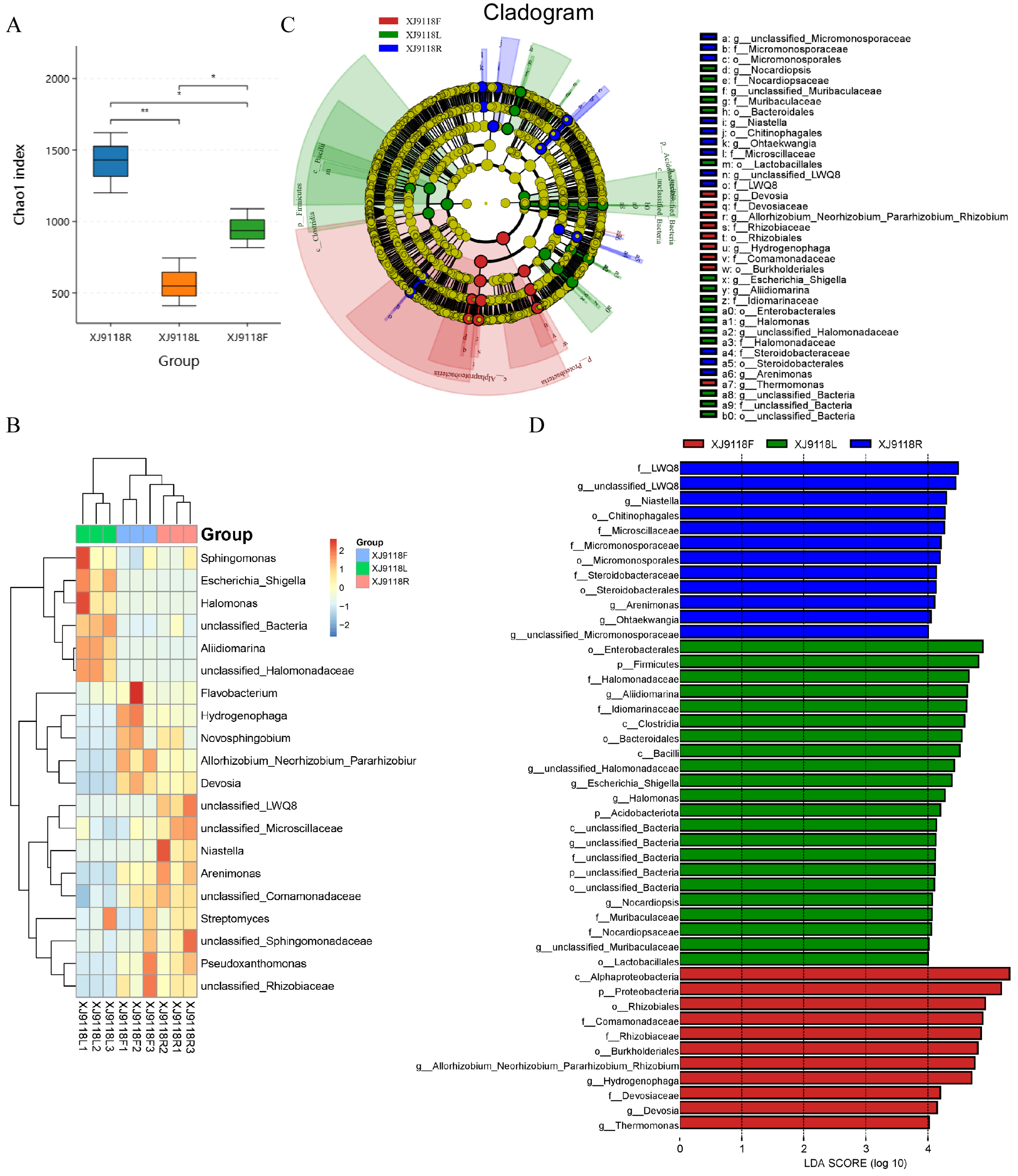
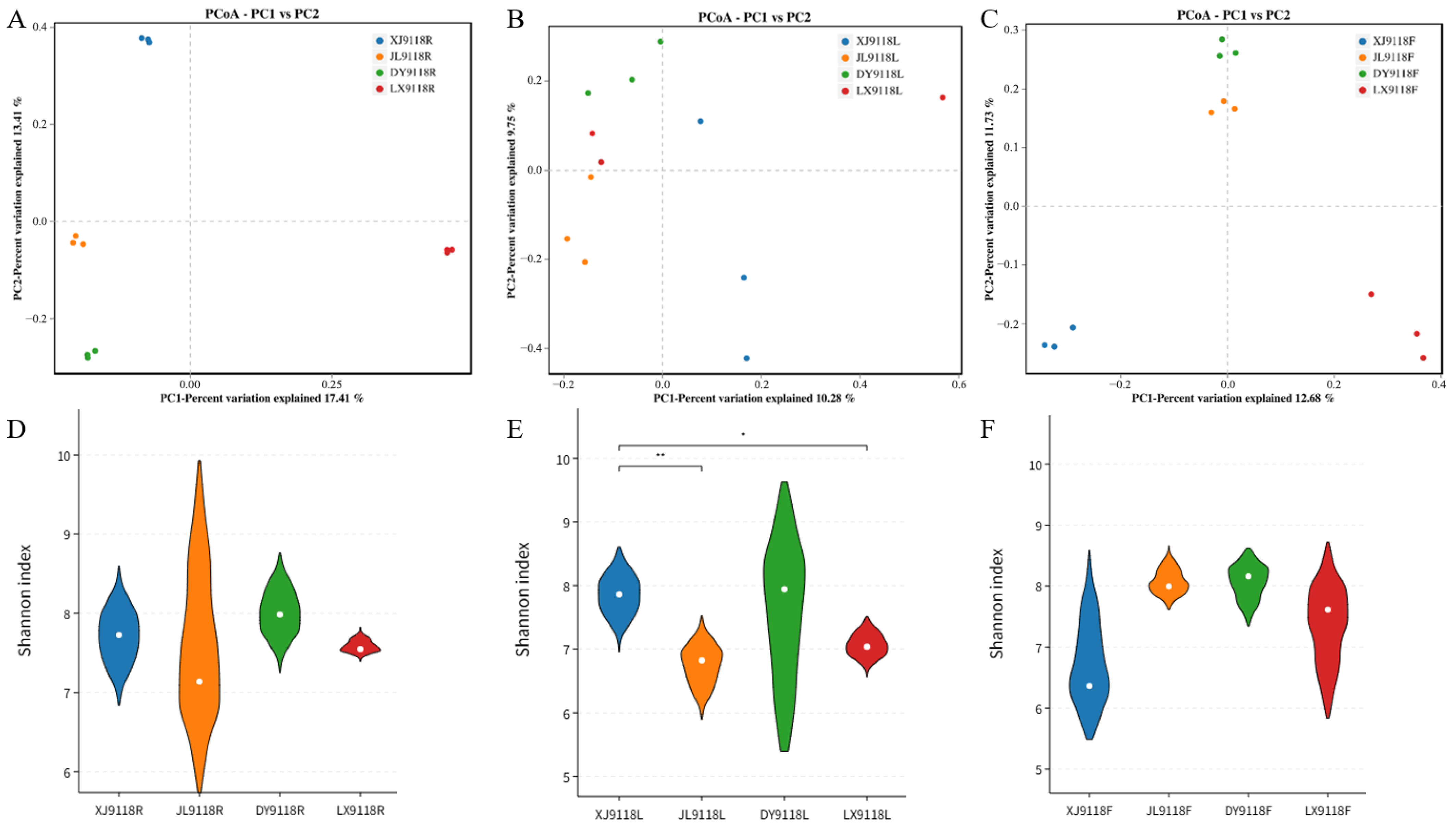

| Sample | ACE | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XJ9118R | 1424.11 ± 209.45 a | 7.71 ± 0.32 ab | 0.98 ± 0.011 abc | 1417.71 ± 210.08 a |
| XJ9118L | 569.58 ± 170.38 c | 7.85 ± 0.29 a | 0.99 ± 0.001 a | 567.48 ± 168.05 c |
| XJ9118F | 949.47 ± 136.11 b | 6.72 ± 0.63 b | 0.96 ± 0.017 bc | 947.52 ± 136.28 b |
| JL9118R | 1623.91 ± 178.62 a | 7.62 ± 0.86 ab | 0.95 ± 0.034 c | 1615.42 ± 181.43 a |
| JL9118L | 581.44 ± 50.45 c | 6.75 ± 0.29 b | 0.97 ± 0.006 abc | 579.73 ± 50.07 c |
| JL9118F | 940.20 ± 204.58 b | 8.07 ± 0.19 a | 0.99 ± 0.003 a | 936.91 ± 204.46 b |
| DY9118R | 1415.18 ± 116.02 a | 8.01 ± 0.27 a | 0.98 ± 0.010 ab | 1407.80 ± 117.14 a |
| DY9118L | 936.78 ± 272.96 b | 7.57 ± 1.01 ab | 0.98 ± 0.012 ab | 933.31 ± 271.28 b |
| DY9118F | 835.46 ± 31.86 bc | 8.06 ± 0.26 a | 0.99 ± 0.005 a | 832.27 ± 31.19 bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Chi, Y.; Chi, X.; Chen, N.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; He, K.; Yu, J.; Li, Y. Niche and Geographic Drivers Shape the Diversity and Composition of Endophytic Bacteria in Salt-Tolerant Peanut. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102264
Song X, Chi Y, Chi X, Chen N, Xu M, Zhang X, Guo Z, He K, Yu J, Li Y. Niche and Geographic Drivers Shape the Diversity and Composition of Endophytic Bacteria in Salt-Tolerant Peanut. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102264
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xinying, Yucheng Chi, Xiaoyuan Chi, Na Chen, Manlin Xu, Xia Zhang, Zhiqing Guo, Kang He, Jing Yu, and Ying Li. 2025. "Niche and Geographic Drivers Shape the Diversity and Composition of Endophytic Bacteria in Salt-Tolerant Peanut" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102264
APA StyleSong, X., Chi, Y., Chi, X., Chen, N., Xu, M., Zhang, X., Guo, Z., He, K., Yu, J., & Li, Y. (2025). Niche and Geographic Drivers Shape the Diversity and Composition of Endophytic Bacteria in Salt-Tolerant Peanut. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2264. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102264






