Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Among Japanese Children from 2008 to 2024
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Aspects
2.2. Materials
2.3. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
2.4. P1 Genotyping of MP Isolates
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Distribution of MRMP Due to a Mutation in the 23S rRNA Gene Isolated from Japanese Children of Various Age Groups in 2024
3.3. Number of MP Infections and the Detection Rate of Mrmp Infections in Japan by Year
3.4. Detection Rate of Mrmp Infections and the Distribution of Point Mutations in All MRMP Isolates by Year
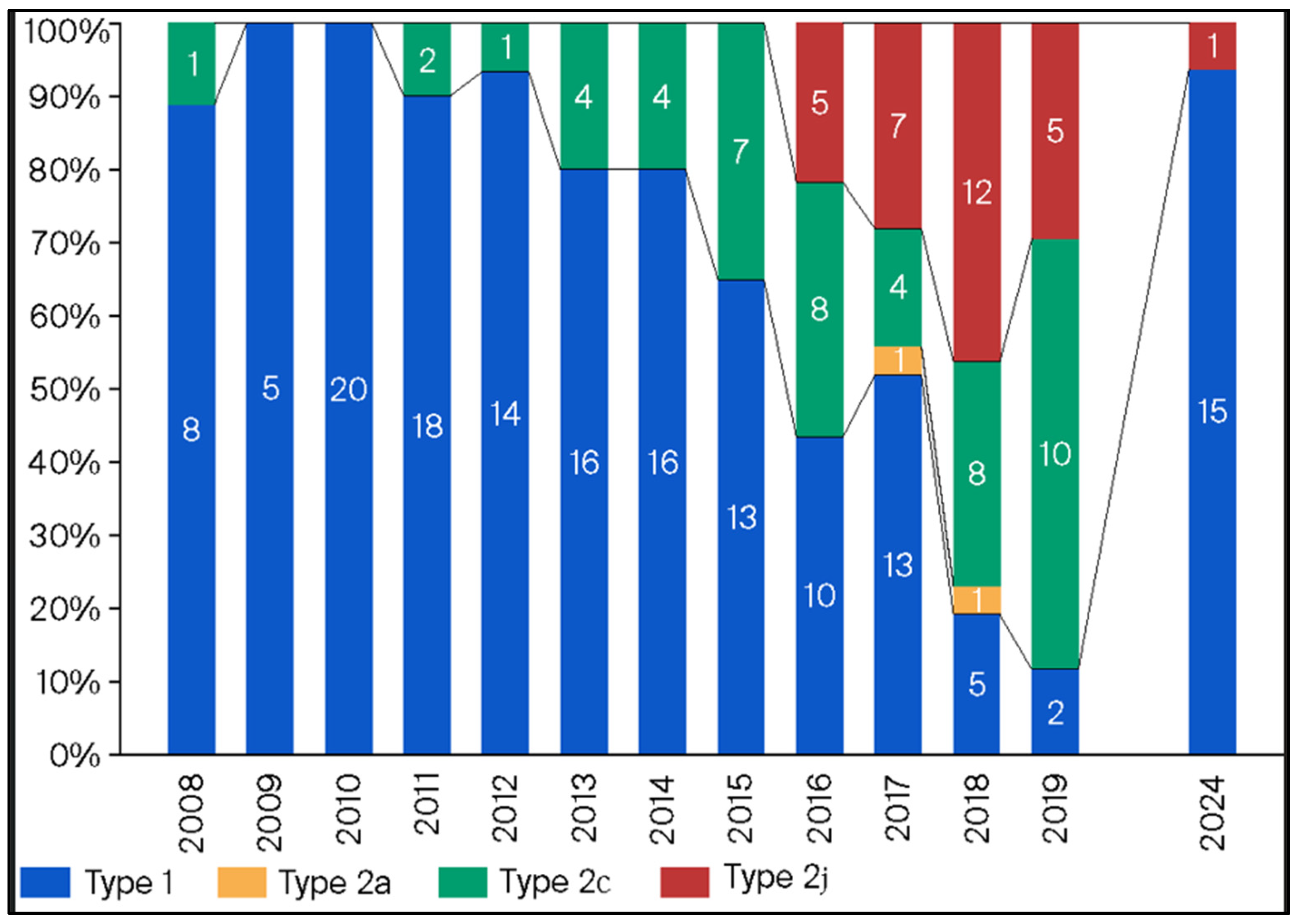
3.5. Annual Distribution of MP Isolates Based on p1 Genotyping
3.6. Annual Macrolide-Resistance Rate Among p1 Genotype Type 1 and 2 Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MP | Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
| MRMP | macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PCR-RFLP | polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism |
| TFLX | tosufloxacin |
References
- Shah, S.S. Mycoplasma pneumoniae as a Cause of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, H.M.; Grayston, J.T.; Kenny, G.E.; Alexander, E.R.; McMahan, R. Epidemiology of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in families. JAMA 1966, 197, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernald, G.W.; Collier, A.M.; Clyde, W.A., Jr. Respiratory infections due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in infants and children. Pediatrics 1975, 55, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Waites, K.B.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Balish, M.F.; Atkinson, T.P. Mycoplasma pneumoniae from the respiratory tract and beyond. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 747–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, P.K.; Jain, S.; Taylor, T.H.; Bramley, A.M.; Diaz, M.H.; Ampofo, K.; Arnold, S.R.; Williams, D.J.; Edwards, K.M.; McCullers, J.A.; et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae among children hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Williams, D.J.; Arnold, S.R.; Ampofo, K.; Bramley, A.M.; Reed, C.; Stockmann, C.; Anderson, E.J.; Grijalva, C.G.; Self, W.H.; et al. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, H.M. Infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae and possible carrier state in different populations of patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1993, 17 (Suppl. S1), S37–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenri, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Ohya, H.; Jinnai, M.; Oda, Y.; Asai, S.; Sato, R.; Ishiguro, N.; Oishi, T.; Horino, A.; et al. Genotyping of Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains isolated in Japan during 2019 and 2020: Spread of p1 gene type 2c and 2j variant strains. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1202357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, N.; Narita, M.; Yamada, S.; Izumikawa, K.; Umetsu, M.; Kenri, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Arakawa, Y.; Sasaki, T. Characteristics of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains isolated from patients and induced with erythromycin in vitro. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 45, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Oishi, T.; Miyata, I.; Wakabayashi, S.; Kono, M.; Ono, S.; Kato, A.; Fukuda, Y.; Saito, A.; Kondo, E.; et al. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection, Japan, 2008–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1703–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenri, T.; Suzuki, M.; Sekizuka, T.; Ohya, H.; Oda, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Fujii, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Nakajima, H.; Katsukawa, C.; et al. Periodic genotype shifts in clinically prevalent Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains in Japan. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, T.; Ouchi, K. Recent Trends in the Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, N.; Akaike, H.; Teranishi, H.; Ouchi, K.; Okimoto, N. Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in adolescents and adults: Clinical findings, drug susceptibility, and therapeutic efficacy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5181–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, N.; Bai, Y.; Zhi, S.; Niu, W.; Wang, F.; Yuan, X. Macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae in adult patients. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1496521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, H.W.; Tian, X.J.; Xin, L.; Wei, R.; Zhou, W.; Wang, H.; Qin, X.G.; Shao, J.Y.; Xu, B.P.; Ge, L.X.; et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae Macrolide Resistance and MLVA Typing in Children in Beijing, China, in 2016: Is It Relevant? Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jia, X.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.; Du, B.; Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Xue, G.; Cui, J.; Gan, L.; et al. Increased macrolide resistance rate of Mycoplasma pneumoniae correlated with epidemic in Beijing, China in 2023. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1449511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, T.; Kim, Y.-J.; Shin, D.R.K.A.; Kang, H.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Eun, B.W.; Choe, Y.J.; Cho, E.Y.; et al. Clinical Manifestations, Macrolide Resistance, and Treatment Utilization Trends of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children and Adolescents in South Korea. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ouchi, K.; Takayama, S.; Fujioka, Y.; Sunakawa, K.; Iwata, S. A phase III, randomized, open-label study on 15% tosufloxacin granules in pediatric Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Jpn. J. Chemother. 2017, 65, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Bruyndonckx, R.; Adriaenssens, N.; Versporten, A.; Hens, N.; Monnet, D.L.; Molenberghs, G.; Goossens, H.; Weist, K.; Coenen, S.; ESAC-Net Study Group. Consumption of antibiotics in the community, European Union/European Economic Area, 1997–2017. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76 (Suppl. S2), ii7–ii13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, T.; Hattori, N.; Yoshioka, D. Novel Knowledge of Macrolide Resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae by Azithromycin Expo sure. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee of the Japanese Society of Mycoplasmology. Guiding Principles* for Treating Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia; Japanese Society of Mycoplasmology: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; Available online: http://square.umin.ac.jp/jsm/Eng%20shisin.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Xiao, L.; Ratliff, A.E.; Crabb, D.M.; Mixon, E.; Qin, X.; Selvarangan, R.; Tang, Y.-W.; Zheng, X.; Bard, J.D.; Hong, T.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Isolates in the United States from 2012 to 2018. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 5, e00710-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei Zhao, F.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Guan, X.; Jie Gong, J.; Liu, L.; He, L.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J. Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular characteristics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates across different regions of China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
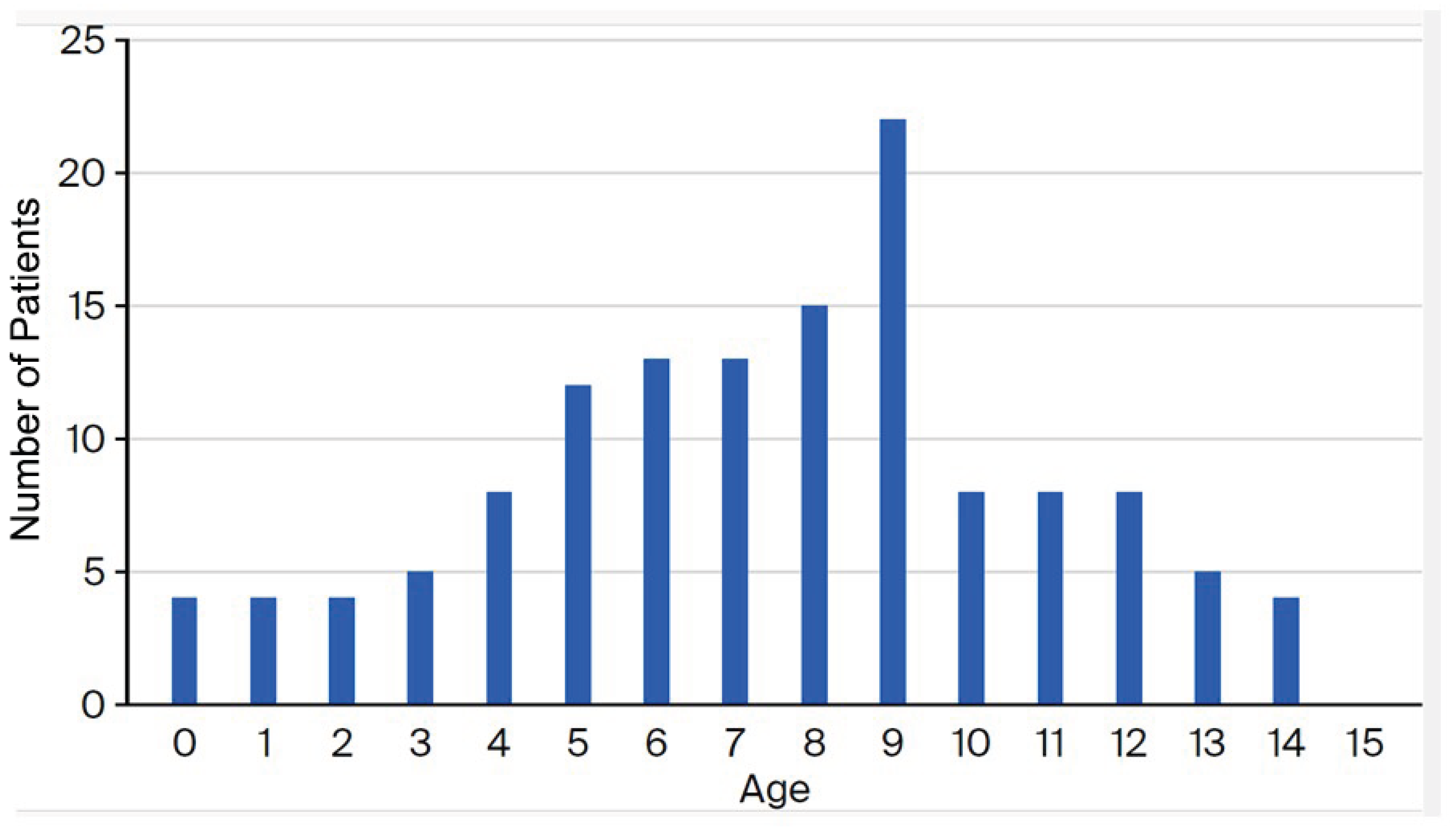


| Age Group (Years) | Number of Isolates | Macrolide-Resistance Mutations in the 23S rRNA Gene | Rate of Macrolide Resistance among Collected Mycoplasma pneumoniae Isolates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Mutation | A2063G Mutation | C2617A Mutation | |||
| 0–4 | 25 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 60.0% (15/25) |
| 5–9 | 75 | 33 | 41 | 1 | 56.0% (42/75) |
| 10–14 | 33 | 18 | 15 | 0 | 45.5% (15/33) |
| Total | 133 | 61 | 71 | 1 | 54.1% (72/133) |
| Year | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2024 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection rate of MRMP (%) | 61.5 | 58.3 | 72.8 | 65.5 | 81.8 | 66.7 | 58.8 | 41.5 | 65.3 | 57.1 | 14.3 | 21.6 | 33.3 | 54.1 | 69.2 |
| A2063G | 8 (100) | 7 (100) | 99 (100) | 303 (94.4) | 466 (95.3) | 28 (100) | 20 (100) | 59 (96.7) | 115 (100) | 32 (100) | 3 (100) | 12 (100) | 7 (100) | 71 (98.6) | 1229 (96.5) |
| A2063C | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (0.9) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (0.2) | ||
| A2063T | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 (4.7) | 14 (2.9) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 30 (2.4) | ||
| A2064G | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 (1.4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 (0.5) | ||
| C2617G | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (0.4) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (0.2) | ||
| C2617T | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.6) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 1 (1.4) | 3 (0.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oishi, T.; Kenri, T.; Yoshioka, D. Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Among Japanese Children from 2008 to 2024. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102243
Oishi T, Kenri T, Yoshioka D. Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Among Japanese Children from 2008 to 2024. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102243
Chicago/Turabian StyleOishi, Tomohiro, Tsuyoshi Kenri, and Daisuke Yoshioka. 2025. "Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Among Japanese Children from 2008 to 2024" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102243
APA StyleOishi, T., Kenri, T., & Yoshioka, D. (2025). Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Among Japanese Children from 2008 to 2024. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2243. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102243







