The Antimicrobial Effect of Thymol and Carvacrol in Combination with Organic Acids Against Foodborne Pathogens in Chicken and Beef Meat Fillets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Preparation and Marination of Chicken and Beef Fillets
2.4. Microbiological Analysis of Meat Fillets Portions
2.5. pH Analysis
2.6. Antioxidant Activity Analysis
2.6.1. DPPH—Scavenging Ability Method
2.6.2. ABTS—Scavenging Ability Method
2.6.3. TPC—Total Phenolic Content
2.7. Planning and Analysis Overview
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
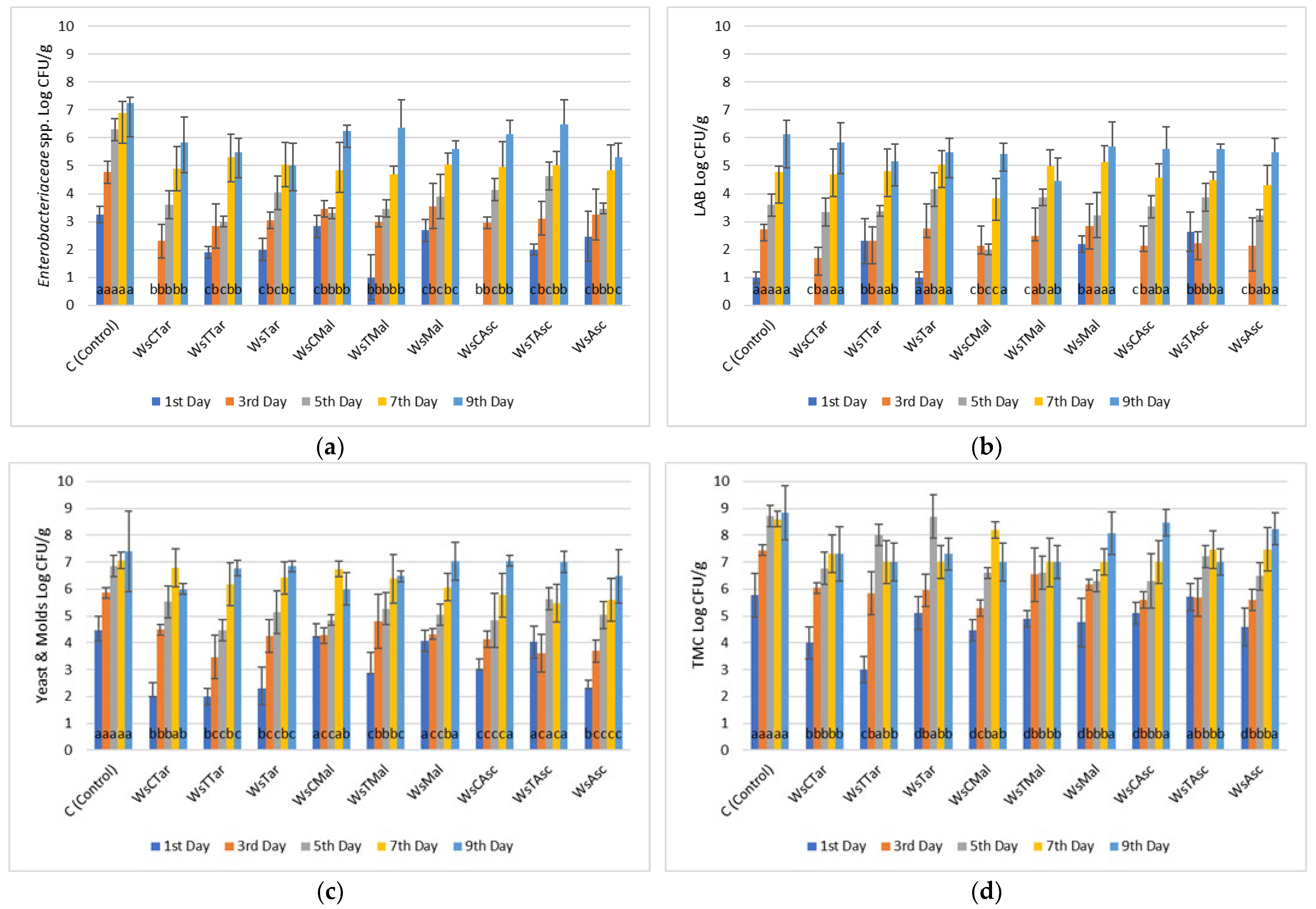
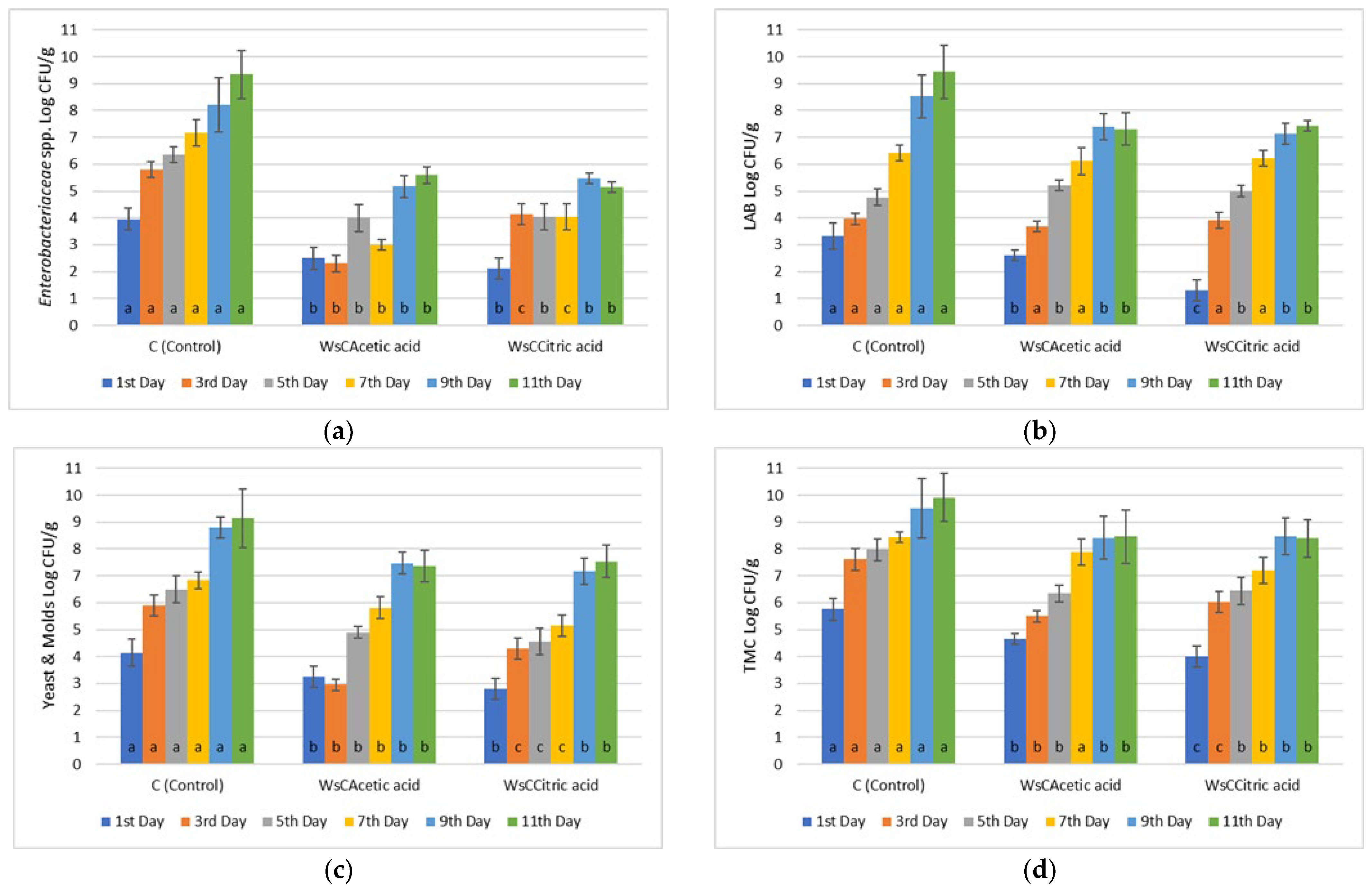
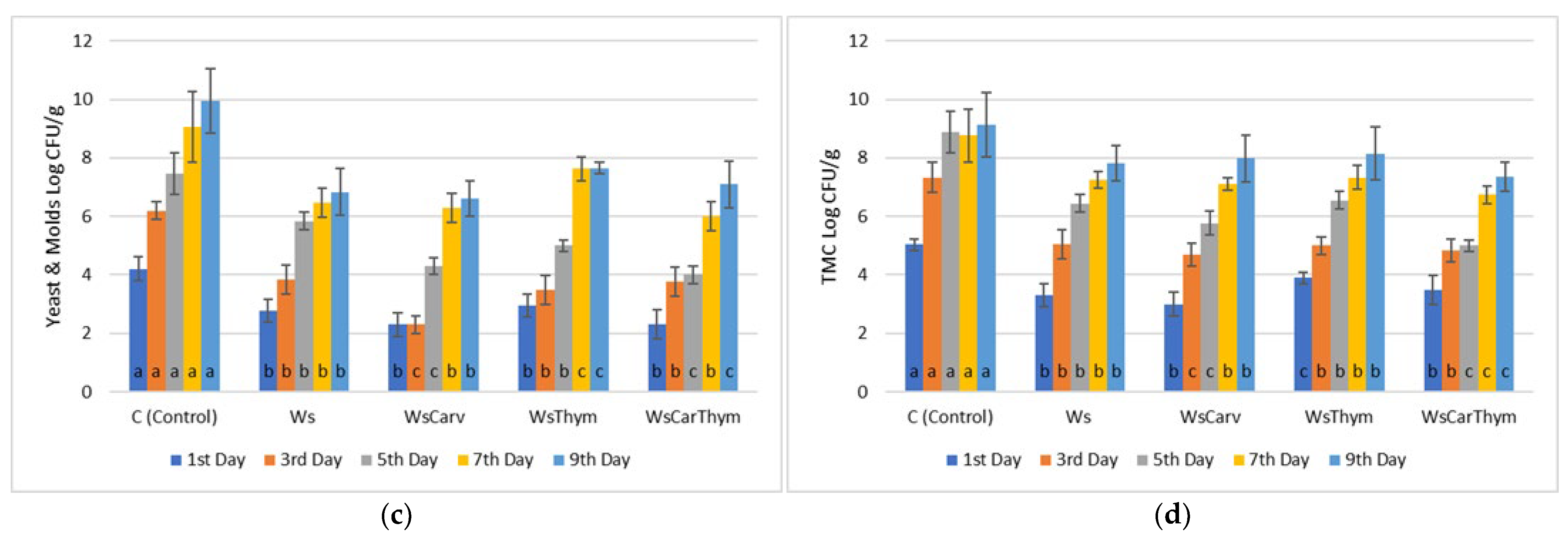
3.1. Microbiological Analyses
3.2. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
3.3. Antioxidant Activity (DPPH and ABTS Radical Scavenging Methods)
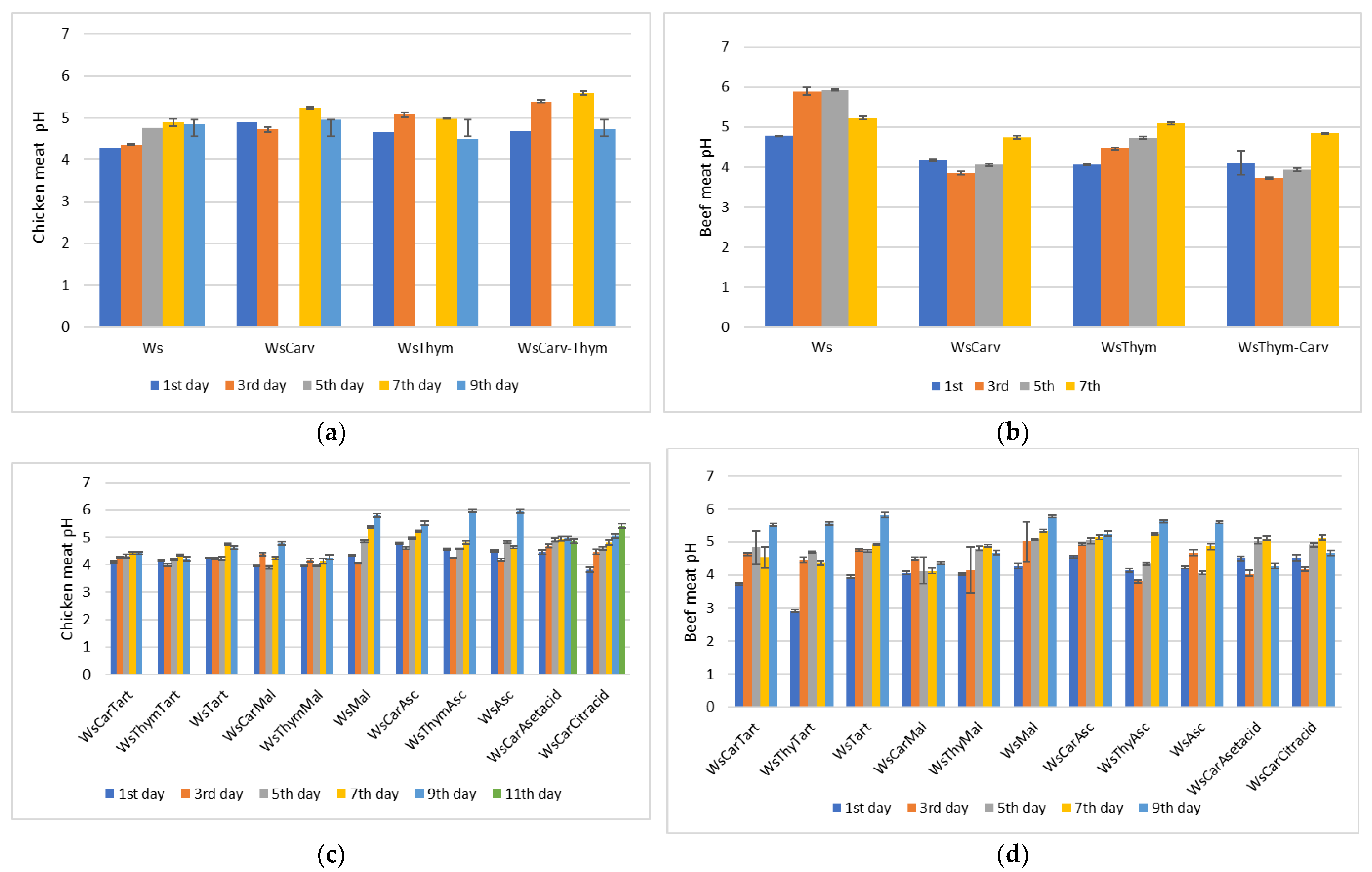
3.4. pH Determination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group for 2021–2024: Second Meeting Report, 19 October–2 November 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogianni, A.I.; Lazou, T.; Bossis, I.; Gelasakis, A.I. Natural phenolic compounds for the control of oxidation, bacterial spoilage, and foodborne pathogens in meat. Foods 2020, 9, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Hashem, M.; Azad, M.; Choudhury, M.; Bhuiyan, M. Techniques of meat preservation—A review. Meat Res. 2023, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J. Analysis of the monitoring status of residual nitrite in meat products in China from 2000 to 2011. Meat Sci. 2018, 136, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, Y. Preservation technologies for fresh meat—A review. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M. Major Causes of Meat Spoilage and Preservation Techniques: A Review. Changes 2015, 41, 101–114. [Google Scholar]
- Šojić, B.; Pavlić, B.; Ikonić, P.; Tomović, V.; Ikonić, B.; Zeković, Z.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Jokanović, M.; Škaljac, S.; Ivić, M. Coriander essential oil as natural food additive improves quality and safety of cooked pork sausages with different nitrite levels. Meat Sci. 2019, 157, 107879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamski, M.; Kuzniacka, J.; Milczewska, N. Preferences of consumers for choosing poultry meat. Pol. J. Nat. Sci. 2017, 32, 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Okpala, C.O.R.; Juchniewicz, S.; Leicht, K.; Korzeniowska, M.; Guiné, R.P. Antioxidant, organoleptic and physicochemical changes in different marinated oven-grilled chicken breast meat. Foods 2022, 11, 3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Liu, X.; Jayasena, D.D.; Jung, Y.; Jung, S.; Kang, B.S.; Heo, K.N.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, C. Differential Proteome Analysis of Breast and Thigh Muscles between Korean Native Chickens and Commercial Broilers. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 895–902. [Google Scholar]
- Juárez, M.; Lam, S.; Bohrer, B.M.; Dugan, M.E.R.; Vahmani, P.; Aalhus, J.; Juárez, A.; López-Campos, O.; Prieto, N.; Segura, J.; et al. Nutrient density and nutritional value of meat products and non-meat foods high in protein. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.S.; Imran, A.; Hussain, M.B. Nutritional composition of meat. Meat Sci. Nutr. 2018, 61, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.L.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A. Applied and Emerging Methods for Meat Tenderization: A Comparative Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 841–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scollan, N.D.; Price, E.M.; Morgan, S.A.; Huws, S.A.; Shingfield, K.J. Can we improve the nutritional quality of meat? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsanur Rahman, S.M.; Islam, S.; Pan, J.; Kong, D.; Xi, Q.; Du, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.-H.; Han, R. Marination ingredients on meat quality and safety—A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbut, S. Poultry Products Processing: An Industry Guide; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Panić, M.; Stojković, M.R.; Kraljić, K.; Škevin, D.; Redovniković, I.R.; Srček, V.G.; Radošević, K. Ready-to-use green polyphenolic extracts from food by-products. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, J.F.; Gendeb, L.B.; Neiraa, L.M.; Ruseckaite, R.A. Oregano and lavender essential oils as antioxidant and antimicrobial additives of biogenic gelatin films. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 71, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.; Follett, P.; Dang Vu, K.; Harich, M.; Salmieri, S.; Lacroix, M. Evidence for synergistic activity of plant-derived essential oils against fungal pathogens of food. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, L.; Chehab, R.; Osaili, T.M.; Savvaidis, I.N. Antimicrobial effect of thymol and carvacrol added to a vinegar-based marinade for controlling spoilage of marinated beef (Shawarma) stored in air or vacuum packaging. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 332, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibonabi, A.; Yekani, M.; Sharifi, S.; Nahad, J.S.; Dizaj, S.M.; Memar, M.Y. Antimicrobial activity of nanoformulations of carvacrol and thymol: New trend and applications. OpenNano 2023, 13, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rúa, J.; Del Valle, P.; de Arriaga, D.; Fernández-Álvarez, L.; García-Armesto, M.R. Combination of carvacrol and thymol: Antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and antioxidant activity. Food. Path. Dis. 2019, 16, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijević, M.; Stankov Jovanović, V.; Cvetković, J.; Mitić, M.; Petrović, G.; Đorđević, A.; Mitić, V. Phenolics, antioxidant potentials, and antimicrobial activities of six wild Boletaceae mushrooms. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 1691–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveena, B.M.; Muthukumar, M.; Sen, A.R.; Babji, Y.; Murthy, T.R.K. Improvement of shelf-life of buffalo meat using lactic acid, clove oil and vitamin C during retail display. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytou, A.E.; Tzortzinis, K.; Skandamis, P.N.; Nychas, G.J.E.; Panagou, E.Z. Investigating the influence of organic acid marinades, storage temperature and time on the survival/inactivation interface of Salmonella on chicken breast fillets. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 299, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses, R.; Teixeira, P. Marination as a hurdle to microbial pathogens and spoilers in poultry meat products: A brief review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.L.; Kim, C.R. Microbiological and sensory analyses of refrigerated catfish fillets treated with acetic and lactic acids. J. Food Qual. 1996, 19, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Prior, R.L. The chemistry behind antioxidant capacity assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, E.N.; Meyer, A.S. The problems of using one-dimensional methods to evaluate multifunctional food and biological antioxidants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1925–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møretrø, T.; Daeschel, M.A. Wine is bactericidal to foodborne pathogens. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, M251–M257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.; Kargiotou, C.; Katsanidis, E.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Use of marination for controlling Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes in raw beef. Food Microbiol. 2013, 36, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likotrafiti, E.; Tuohy, K.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Development of antimicrobial synbiotics using potentially-probiotic faecal isolates of Lactobacillus fermentum and Bifidobacterium longum. Anaerobe 2013, 20, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, J.R.; Daeschel, M.A. Antimicrobial effects of wine on Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella typhimurium in a model stomach system. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcanjo, N.M.O.; Morcuende, D.; Andrade, M.J.; Padilla, P.; Madruga, M.S.; Estévez, M. Bioactivities of wine components on marinated beef during aging. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzourani, I.; Daoutidou, M.; Nikolaou, A.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Alexopoulos, A.; Tzavellas, I.; Dasenaki, M.; Thomaidis, N.; Plessas, S. Microbiological stability and sensorial valorization of thyme and oregano essential oils alone or combined with ethanolic pomegranate extracts in wine marinated pork meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 386, 110022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Frazier, R.A. Characterization of protein–polyphenol interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargiotou, C.; Katsanidis, E.; Rhoades, J.; Kontominas, M.; Koutsoumanis, K. Efficacies of soy sauce and wine base marinades for controlling spoilage of raw beef. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisiotou, A.; Chorianopoulos, N.G.; Gounadaki, A.; Panagou, E.Z.; Nychas, G.J. Effect of wine-based marinades on the behavior of Salmonella typhimurium and background flora in beef fillets. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 164, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolumar, T.; Andersen, M.L.; Orlien, V. Mechanisms of radical formation in beef and chicken meat during high pressure processing evaluated by electron spin resonance detection and the addition of antioxidants. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, M.J.R.; Alberto, M.R.; de Nadra, M.C.M. Influence of phenolic compounds from wines on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2007, 18, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Overview of antibacterial, antitoxin, antiviral, and antifungal activities of tea flavonoids and teas. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani-López, E.; García, H.S.; López-Malo, A. Organic acids as antimicrobials to control Salmonella in meat and poultry products. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.M.; Doores, S.X. Organic acids. In Antimicrobials in Food; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 133–190. [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos, G.M.; Moellering, R.C., Jr. Antibiotic synergism and antimicrobial combinations in clinical infections george. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1982, 4, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pol, I.E.; Mastwijk, H.C.; Slump, R.A.; Popa, M.E.; Smid, E.J. Influence of food matrix on inactivation of Bacillus cereus by combinations of nisin, pulsed electric field treatment, and carvacrol. J. Food Protect. 2001, 64, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathee, J.S.; Patro, B.S.; Mula, S.; Gamre, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Antioxidant activity of Piper betel leaf extract and its constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9046–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Ansari, S.H.; Nazish, I. Bio-functional aspects of grape seeds—A review. Int. J. Phytomed. 2010, 2, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Chedea, V.S.; Braicu, C.; Socaciu, C. Antioxidant/prooxidant activity of a polyphenolic grape seed extract. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohod, R.V.; Garcia, E.R.D.M.; Lara, J.A.F.D. Natural extracts marination in chicken breast fillets. Ciênc. Rural 2022, 53, e20210813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onopiuk, A.; Kołodziejczak, K.; Szpicer, A.; Marcinkowska-Lesiak, M.; Wojtasik-Kalinowska, I.; Stelmasiak, A.; Poltorak, A. The Effect of Partial Substitution of Beef Tallow on Selected Physicochemical Properties, Fatty Acid Profile and PAH Content of Grilled Beef Burgers. Foods 2022, 11, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, T.; Grønlund, A.C.; Christensen, B.B.; Knøchel, S.; Lohse, K.; Rosenquist, H. Effect of organic acids and marination ingredients on the survival of Campylobacter jejuni on meat. J. Food Protect. 2010, 73, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volschenk, H.; Van Vuuren, H.J.J.; Viljoen-Bloom, M. Malic Acid in Wine: Origin, Function and Metabolism During Vinification. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2006, 27, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, D.; Suri, S.; Upadhyay, G.; Singh, B.N. Total phenol, antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of some medicinal plants. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 58, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, G.; Ting, K.N.; Wiart, C.; Fry, J. High correlation of 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging, ferric reducing activity potential and total phenolics content indicates redundancy in use of all three assays to screen for antioxidant activity of extracts of plants from the Malaysian rainforest. Antioxidants 2013, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coloretti, F.; Tabanelli, G.; Chiavari, C.; Lanciotti, R.; Grazia, L.; Gardini, F.; Montanari, C. Effect of wine addition on microbiological characteristics, volatile molecule profiles and biogenic amine contents in fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| MARINADES | TPC (mg GA/mL Marinade) |
|---|---|
| 1. Wine | 0.83 c ± 0.11 |
| 2. Wine Salt | 0.77 d ± 0.05 |
| 3. Wine Salt Carvacrol | 1.08 ± 0.25 |
| 4. Wine Salt Thymol | 0.76 d ± 0.05 |
| 5. Wine Salt Carvacrol/Thymol | 1.01 c ± 0.11 |
| 6. Wine Salt Carvacrol Tartaric acid | 0.79 c ± 0.03 |
| 7. Wine Salt Thymol Tartaric acid | 0.69 d ± 0.10 |
| 8. Wine Salt Tartaric acid | 0.65 d ± 0.08 |
| 9. Wine Salt Carvacrol Malic acid | 0.94 c ± 0.11 |
| 10. Wine Salt Thymol Malic acid | 0.78 c ± 0.05 |
| 11. Wine Malic acid | 0.83 c ± 0.12 |
| 12. Wine Salt Carvacrol Ascorbic acid | 1.49 b ±0.15 |
| 13. Wine Salt Thymol Ascorbic acid | 1.14 c ± 0.12 |
| 14. Wine salt Ascorbic acid | 0.96 a ±0.13 |
| 15. Wine Salt Carvacrol Acetic acid | 1.74 a ±0.17 |
| 16. Wine Salt Citric acid | 0.89 a ±0.14 |
| MARINADES | ABTS | DPPH |
|---|---|---|
| 1.Wine | 468.85 a ± 10.23 | 254.29 a ± 8.52 |
| 2. Wine Salt | 468.85 a ±11.45 | 240.96 a ± 7.77 |
| 3. Wine Salt Carvacrol | 468.82 a ±10.78 | 148.04 d ± 5.21 |
| 4. Wine Salt Thymol | 468.91 a ±12.41 | 245.13 a ± 8.95 |
| 5. Wine Salt Carvacrol/Thymol | 468.73 a ±10.48 | 168.46 c ± 5.32 |
| 6. Wine Salt Carvacrol Tartaric acid | 468.72 a ±10.32 | 137.21 d ± 4.51 |
| 7. Wine Salt Thymol Tartaric acid | 468.77 a ±11.52 | 145.13 d ± 6.23 |
| 8. Wine Salt Tartaric acid | 50.09 d ± 2.58 | 89.71 e ± 3.57 |
| 9. Wine Salt Carvacrol Malic acid | 68.67 c ± 3.33 | 15.54 h ± 1.54 |
| 10. Wine Salt Thymol Malic acid | 86.76 b ± 4.21 | 27.21 g ± 2.22 |
| 11. Wine Malic acid | 70.09 c ± 2.24 | 73.46 f ± 3.66 |
| 12. Wine Salt Carvacrol Ascorbic acid | 468.71 a ± 10.51 | 205.13 b ± 7.85 |
| 13. Wine Salt Thymol Ascorbic acid | 464.86 a ± 10.56 | 224.29 a ±8.35 |
| 14. Wine salt Ascorbic acid | 459.14 a ± 11.25 | 191.79 b ± 6.52 |
| 15. Wine Salt Carvacrol Acetic acid | 66.76 c ± 2.21 | 190.96 b ± 9.32 |
| 16. Wine Salt Citric acid | 41.80 e ± 1.11 | 224.71 a ± 7.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mantzourani, I.; Daoutidou, M.; Alexopoulos, A. The Antimicrobial Effect of Thymol and Carvacrol in Combination with Organic Acids Against Foodborne Pathogens in Chicken and Beef Meat Fillets. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010182
Mantzourani I, Daoutidou M, Alexopoulos A. The Antimicrobial Effect of Thymol and Carvacrol in Combination with Organic Acids Against Foodborne Pathogens in Chicken and Beef Meat Fillets. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(1):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010182
Chicago/Turabian StyleMantzourani, Ioanna, Maria Daoutidou, and Athanasios Alexopoulos. 2025. "The Antimicrobial Effect of Thymol and Carvacrol in Combination with Organic Acids Against Foodborne Pathogens in Chicken and Beef Meat Fillets" Microorganisms 13, no. 1: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010182
APA StyleMantzourani, I., Daoutidou, M., & Alexopoulos, A. (2025). The Antimicrobial Effect of Thymol and Carvacrol in Combination with Organic Acids Against Foodborne Pathogens in Chicken and Beef Meat Fillets. Microorganisms, 13(1), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13010182







