Abstract
Microeukaryotes are a diverse and often overlooked group of microbes that are important in food webs and other ecological linkages. Little is known about microeukaryotes associated with aquatic invertebrates, although filter feeders such as mussels are likely to take in and potentially retain microeukaryotes in their gut while feeding. Microeukaryotes such as apicomplexans have been reported in marine mussel species, but no studies have examined the presence of these microorganisms in freshwater mussels or how they relate to mussel host species or environmental conditions. In this study, microbial community DNA was extracted from the gut tissue of over 300 freshwater mussels, representing 22 species collected from rivers in the southeastern USA. Microeukaryote DNA was detected using PCR amplification, followed by the sequencing of positive amplicons. Microeukaryotes were found in 167 individual mussels (53%) of those tested. Amplicons included dinoflagellates/algae that differed between mussel species and are likely food sources that were distinct from those found in water and sediment samples analyzed concurrently. A total of 5% of the positive amplicons were non-photosynthetic alveolates that could represent parasitic microeukaryotes. Understanding the distribution of microeukaryotes in the freshwater mussel gut microbiome could further our understanding of the ongoing decline of mussel populations.
1. Introduction
Freshwater mussels are benthic macroinvertebrates that feed on particulate organic matter, such as bacteria, phytoplankton, and algae filtered from the water column and through interstitial sediment. These macroinvertebrates perform important ecosystem services, such as maintaining water quality, stimulating benthic-pelagic nutrient cycling, providing structural habitat, and modifying aquatic food webs [1]. Typically classified as filter feeders, filtration rates of freshwater mussels vary with species, size, and environmental conditions, and pedal feeding, where freshwater mussels use cilia on their foot to collect benthic organic matter, can also be an important source of food [2,3,4]. When coexisting as multispecies aggregates, freshwater mussels likely use resource partitioning and niche diversification to reduce interspecies competition [5,6,7], and mussels can selectively feed on specific algal taxa, with those preferences differing between mussel species [8].
North America houses a large portion of the global freshwater mussel biodiversity, primarily unionid mussels, although 70% of North American mussel species are listed as endangered, threatened, or of special concern. These mussel populations are declining because of increased pollution and changes in hydrology and climate [9]. Over the last few years, there has been increased interest in investigating the gut microbiome of North American unionid mussels [10,11,12,13] and its importance to host health and function. While such studies have shown that the gut microbiome varies spatially and temporally, as well as with mussel species, these studies have focused almost entirely on the bacterial community within the gut, even though freshwater mussels almost certainly interact with other components of the microbial community. Given that protists such as dinoflagellates are common in freshwater systems of North America [14], it seems likely that the unionid mussel gut microbiome would include eukaryotic microorganisms, as well as bacteria, and mussel feeding preferences show the consumption of eukaryotic microorganisms such as Stramenopiles, Chlorophytes, and fungi by unionid mussels [15]. Unionid mussels can also harbor eukaryotes, such as mites, trematodes, and leeches, as well as ciliates, such as Tetrahymena [16,17,18]. Parasitic taxa, including the ciliates Conchophthirus sp. [19] and Trichodina sp. [20], the trematodes Rhipidocotyle campanula and Phyllodistomum sp. [19,20,21], and mites of the Unionicola genus [22,23] have been documented in freshwater mussels, primarily in Europe. Other infectious agents described in freshwater mussels include neoplasms, viruses, bacteria, fungi, fungal-like agents, Aspidogastrea, Digenea, and Acari [24,25]. However, compared to European freshwater bivalves, the presence of endosymbionts in North American freshwater mussels is understudied [26].
This difference is particularly apparent among members of the ubiquitous protistan group, Apicomplexa. While freshwater unionid mussels have no documented species-specific apicomplexans, bent mussels (Ischadium recurvum) and zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha), both of which are associated with low salinity or freshwater environments, have been shown to take up Cryptosporidium from terrestrial runoff and retain them in their gut tissues [27,28]. In contrast to freshwater mussels, a number of studies have reported that marine bivalves can host microeukaryotes, particularly members of the ubiquitous protistan group, Apicomplexa. Apicomplexans are obligate intracellular protozoans found in vertebrate and invertebrate hosts in terrestrial and aquatic habitats, and the group includes the causative agents of important infectious diseases, such as malaria, cryptosporidiosis, and toxoplasmosis [29]. Marine bivalves, such as the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica), great scallop (Pectin maximus), and the Atlantic Sea scallop (Plecopecten magellanicus), have been found to contain a variety of apicomplexans from the genera Aggregata, Merocystis, Margolisiella, and Nematopsis [30,31,32], as well as an infectious sister taxon of the Perkinsus genus that causes mass mortality [33,34,35]. Marine bivalves can also acquire terrestrial apicomplexans, with reports of the black mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) containing oocysts of the terrestrial apicomplexan Cryptosporidium [36].
The presence of apicomplexans in a variety of other bivalves suggests the hypothesis that unionid mussels could also contain apicomplexans or other microeukaryotes. Furthermore, the complex lifestyle of freshwater unionid mussels involves their larvae encapsulating themselves on the gills or fins of freshwater fish. Such ecological interactions with fish hosts have shaped the evolutionary history of freshwater mussels [37], and spending a portion of their life on a fish host could expose larval mussels to microeukaryotes, as fish often have apicomplexans that spend a portion of their life cycle in gill tissue [38,39,40].
The goal of this study was to determine what microeukaryotes, if any, are associated with freshwater mussels in the southeastern United States, a global hotspot for unionid mussel biodiversity. As part of ongoing surveys looking at the freshwater mussel gut microbiome, more than 20 species of mussels were collected from rivers in the Mobile and Tennessee River basins, and we tested the gut tissue of these mussels for the presence of microeukaryotes. More specifically, this study expands on the current knowledge of apicomplexan infections in bivalves by determining (1) if apicomplexans are present in these freshwater mussels and (2) if the presence of apicomplexans correlates with specific mussel species or locations.
2. Materials and Methods
As part of ongoing studies on the bacterial microbiome of freshwater mussels in the southeastern United States, mussels were surveyed and collected from sites on Bear Creek, Bogue Chitto Creek, the Buttahatchee and Sipsey rivers of the Mobile River Basin, and the Duck and Paint Rock rivers of the Tennessee River Basin (see Hopper et al. [41] for more site information). Mussels were collected from July–September 2019 and processed as described by McCauley et al. [12] and Chiarello et al. [42]. Briefly, samples were flash-frozen and stored at −80 °C until the gastrointestinal tract was excised and ground; the microbial DNA was extracted using a PowerSoil Pro kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA) and stored frozen until use in this study [12,42]. At the time of collection, samples of water and sediment were also taken from each site. Water was filtered, and DNA was extracted from filters and collected sediment following the same procedures as ground mussel gut tissue. Environmental physicochemical data (temperature, pH, conductivity, ammonia, nitrates, nitrites, and dissolved oxygen) were recorded over the sampling period.
This study used gut community DNA extracted from 22 mussel species (311 mussel gut DNA samples total) collected in the previous studies: Amblema plicata, Cyclonaias tuberculata, Elliptio arca, Elliptio crassidens, Fusconaia cerina, Hamiota perovalis, Lampsilis ornata, Lampsilis ovata, Lampsilis teres, Lasmigona alabamensis, Lasmigona costata, Megalonaias nervosa, Obliquaria reflexa, Obovaria unicolor, Pleurobema oviforme, Potamilus purpuratus, Ptychobranchus fasciolaris, Pustulosa kieneriana (formerly Cyclonaias asperata [37]), Pustulosa pustulosa (formerly Cyclonaias pustulosa [37]), Quadrula quadrula [formerly Quadrula apiculata and Quadrula rumphiana [43]), Quadrula verrucosa (formerly Tritogonia verrucosa [37]), and Toxolasma lividum. DNA was also used from the environmental samples (sediment and water) collected from the same sample sites.
To screen for microeukaryotes, a region of the 18S small subunit ribosomal DNA (SSU rDNA) was amplified using a primer pair designed for apicomplexans SFC-340f (5′-AGTTTCTGACCTATCAGC-3′) and SFC-1260r (5′-TCAGCCTTGCGACCATACTC-3′) [44]. PCR was performed in 20 µL reactions using OneTaq 2X Master Mix (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA), 0.5 µM forward and reverse primer concentrations, and approximately 20 ng/µL of template DNA. Amplification involved an initial denaturing step of 5 min at 95 °C, followed by 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 45 s, and 72 °C for 1 min. The procedure ended with a terminal extension of 72 °C for 7 min.
The presence/absence of amplification products was checked with agarose gel electrophoresis. Positive amplicons were sequenced at Functional Biosciences, Inc. (Madison, WI, USA), and trace files were edited using MEGA11 [45]. Sequences were identified to the family and genus levels using the Silva database https://www.arb-silva.de/aligner/ (accessed on 12 February 2024) and NCBI Blast in December 2023. Positive sequencing results were separated into sequences that were classified as dinoflagellates/algae or non-photosynthetic alveolates (potentially Apicomplexa). In addition to the sequences generated in this study (sequence accession numbers PP964320-PP964486), representative Apicomplexa and dinoflagellate sequences from GenBank were included as references (Supplemental Material, Table S1).
An SSU rDNA phylogenetic tree was generated analyzing the non-photosynthetic alveolates generated in this study, along with 14 representative Apicomplexa, Perkinsus marinus (AF324218), and Chromera velia (DQ174731), as an outgroup. These sequences were from GenBank (Supplementary Material, Table S2). Sequences were aligned in MEGA11 [45] using MUSCLE [46] with default parameters and alignments, followed by manual checks. The best model was selected by ModelFinder and implemented in IQ-Tree version 1.6.12. The maximum likelihood tree was generated using nonparametric bootstrapping and 1000 ultrafast bootstrap iterations in IQ-Tree. The resulting tree used an HKY+F+R3 model. The annotation of the ML tree was performed using Interactive Tree of Life [47].
A binomial logistic regression was used to investigate the relationship between the presence of non-photosynthetic alveolates and mussel phylogeny (tribe and subfamily), the number of reproductive hosts (as derived from [48]), and environmental physicochemical variables (temperature, pH, conductivity, ammonia, nitrates, nitrites, and dissolved oxygen). A multinominal logistic regression was used to investigate the relationship between the presence of dinoflagellate/algal amplicons, mussel species, mussel life history traits, and collection site. The multinomial logistic regression was performed using the “nnet” package version 7.3-19 [49] in R version 4.2.2 [50]. To confirm patterns, a generalized linear model was performed, with the proportion of amplicon presences for individuals of a mussel species at a site as the response and mussel species, mussel life history traits, environmental physicochemical variables (temperature, pH, conductivity, ammonia, nitrates, nitrites, and dissolved oxygen), and collection site as predictor variables.
3. Results
Of the 311 samples of DNA from the gut tissue of freshwater mussels tested for amplification with the microeukaryote primer set, 167 (53.7%) showed positive amplifications that could be identified following sequencing. The positive amplifications came from DNA extracted from 20 of the 22 species of freshwater mussels examined, with only gut DNA from Lasmigona costata and Obovaria unicolor yielding no amplification products. Sequencing the 167 amplicons yielded sequences that averaged 840 bases long and then were trimmed to 700 bases after initial sequence processing and editing. The majority (158, or 94.6%, of the total) of these sequences were identified as dinoflagellates or algae, and nine (5.4%) were identified as non-photosynthetic alveolates. Five sequences were unclassifiable due to low match similarity.
The most frequently detected dinoflagellate/algal sequences were identified as being from the genera Monodus, Trachydiscus, and Unruhdinium. Mussel species varied in the dinoflagellate or algal sequences amplified from their gut DNA, and species that were sampled from multiple rivers yielded different amplicons from different rivers (Table 1).

Table 1.
Dinoflagellate and algae amplicons from freshwater mussel gut tissue. There were 20 species of mussels with identified amplicons. River indicates sampling location: Bear Creek (Bear), Bogue Chitto Creek (Bogue), the Buttahatchee (Butta) and Sipsey rivers of the Mobile River Basin, and the Duck and Paint Rock (Paint) rivers of the Tennessee River Basin. “No.” shows the number of amplicons identified as the indicated genera from the mussel species and river. Identity is the % identity match to NCBI database sequences.
Unruhdinium were the most frequently identified microeukaryotic taxa, with 78 amplicons. Bogue Chitto Creek and the Paint Rock River had the greatest variety of amplicons. The amplicons present and their frequency differed among the species Elliptio arca (p = 0.000519), Hamiota perovalis (p = 0.001651), Lampsilis ornata (p = 0.000519), Lampsilis teres (p = 0.011303), Lasmigona alabamensis (p = 0.011303), Megalonaias nervosa (p = 0.000520), Obliquaria reflexa (p = 0.001651), Potamilus purpuratus (p = 0.000520), Pustulosa kieneriana (p = 0.040035), Quadrula quadrula (p = 0.011303), and Quadrula verrucosa (p = 0.011038). However, amplicon presence did not correlate with any host tribe, subfamily, and the number of reproductive hosts (p > 0.05 for all). Amplicons sequenced from mussel gut tissue included more genera than those from the water and sediment collected from the same sites. The presence of amplicons in mussel samples was more similar to that in water samples than sediment (Figure 1).
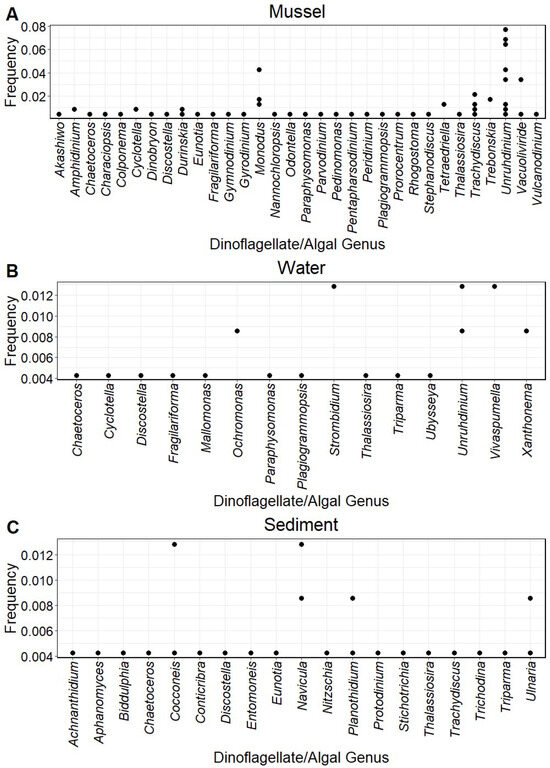
Figure 1.
Frequency of 18S rDNA dinoflagellate and algal amplicons obtained from the guts of freshwater mussels ((A); n = 158), filtered water ((B); n = 35), and sediment ((C); n = 34) collected from rivers in the Mobile and Tennessee River basins. Frequency indicates how frequently the amplicon occurred in samples analyzed, and each point represents the frequency of an amplicon at a sample site or within a specific mussel species sampled from a site.
Nine sequences were identified as non-photosynthetic alveolates (Table 2). Of these, four came from mussels collected from the Paint Rock River, three came from the Sipsey River, and one each came from Bogue Chitto Creek and the Buttahatchee River. Mussel species yielding these non-photosynthetic alveolate amplicons were Pustulosa kieneriana (three specimens), Pleurobema oviforme (two specimens), Quadrula verrucosa (two), and one sample each from Lampsilis ovata and Ptychobranchus fasciolaris. The DNA from non-photosynthetic taxa amplified were identified as apicomplexans from the genera Ascogregarina, Cryptosporidium, Goussia, Gregarina (all class Conoidasida), and Babesia (class Aconoidasida), as well as other protists of the genera Rhogostoma (class Thecofilosea) and Blastocystis (class Blastocystea) (Table 2). No non-photosynthetic alveolate DNA was amplified from water or sediment samples. The presence of non-photosynthetic taxa in mussel gut DNA positively correlated with mussel species, temperature, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, nitrite, and orthophosphate. Presence was negatively correlated with ammonia, nitrate, and pH (p < 0.001 for all; χ² (47) = −298.30, Pseudo-R² (Cragg-Uhler) = −19.17, Pseudo-R² (McFadden) = −4.80, AIC = 456.44, BIC = 599.98).

Table 2.
Alveolate amplicons from freshwater mussel gut tissues. Mussels were collected from Bogue Chitto Creek (Bogue), the Buttahatchee River (Butta), the Sipsey River in the Mobile River Basin, and the Paint Rock River (Paint) in the Tennessee River Basin. A total of 22 mussel species were tested, and only those yielding positive amplicons identified as non-photosynthetic microeukaryotes are shown. No. indicates the number of amplicons identified as the indicated genera from the mussel species and river. Identity is the % identity match to NCBI database sequences.
A further phylogenetic analysis of the alveolate sequences showed low congruence between the identified amplicons and their closest expected relatives on the tree (Figure 2). For example, you would expect the Cryptosporidium amplicons to be close together, as well as groups like Theleria and Babesia.

Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of 18S rDNA non-photosynthetic alveolate amplicons obtained from the gut tissue of freshwater mussels collected from rivers in the Mobile and Tennessee River basins. The phylogenetic tree was generated using an HKY+F+R3 in IQ-TREE. Bootstrap values are displayed in the translucent white box on the branches.
4. Discussion
In addition to a diverse community of gut bacteria [10,11,12,13], freshwater unionid mussels have been shown to harbor microscopic eukaryotes, including nematodes, trematodes, mites, fungi, and ciliated protists [16,24,25]. The role of these microorganisms in disease is unclear, and their presence may be transitory, as some opportunistic consumption of fungi by mussels may occur [15]. Unlike their marine counterparts, freshwater mussels have not been examined for the presence of protists within Phylum Apicomplexa. This study used molecular approaches (amplification with specific 18S small ribosomal subunit primers, followed by amplicon sequencing) to characterize apicomplexan and other microeukaryotes in gut DNA recovered from 22 species of unionid mussels collected from six rivers in the southeastern United States.
Sequences identified as dinoflagellate or algal taxa (i.e., photosynthetic microeukaryotes) were the most common amplicons detected in DNA from the gut tissue of freshwater mussels, being found in just over half of the >300 samples examined. Photosynthetic microeukaryotes are unlikely to be resident members of the gut microbial community, so these taxa potentially represent at least part of the mussel’s food source. The amplicons detected differed by mussel species, even between species collected from the same site or river. While some of those differences may be due to chance (only one amplicon was sequenced per mussel sample), the detection of different dinoflagellate/algal DNA in the guts of different species of freshwater mussels aligns with the idea that freshwater mussels show research partitioning and species-specific food source preferences [7,8], especially in mixed-species assemblages, such as the communities from which these mussels were sampled [42].
The most frequently detected sequences in the amplicons from mussel gut tissue were identified as belonging to the genera Monodus, Trachydiscus, Unruhdinium, and Vacuoliviride. Unruhdinium is a genus of freshwater dinoflagellates found in lakes and rivers that can form high biomass blooms [51], while Monodus, Trachydiscus, and Vacuoliviride are all the genera of the Eustigmatophyceae lineage of algae that live primarily in freshwater [52]. Of these four most commonly detected photosynthetic microeukaryotes, only Unruhdinium was identified in amplicons sequenced from samples of water or sediment, suggesting that microalgae in the guts of freshwater mussels do not just reflect those of the most common taxa in the surrounding environment, something that has also been shown for their gut bacteria [10]. Detected algae varied with mussel species but was not correlated to any life history traits, including host size range. This finding of algae preference varying solely by species is similar to what was seen in previous studies of resource partitioning [8]. Previous works evaluating food selection and resource partitioning in freshwater mussels were performed via particle size [53,54]. Sequencing of DNA extracted from gut contents or tissue was used to assess dietary preferences of freshwater fish [55], as well as marine invertebrates, such as lobster [56] and bivalves [57]. Our results support the idea that that the same approach could be used to more thoroughly examine the feeding preferences of freshwater mussel species.
Nine of the amplicons were identified as non-photosynthetic alveolates. These sequences were all identified as representatives of parasitic phyla, mostly from the phylum Apicomplexa. These included two sequences (from DNA extracted from a Pustulosa kieneriana and a Quadrula verrucosa obtained from the Sipsey River) identified as members of the genus Goussia, which parasitize freshwater and marine fish [58,59,60], a sequence of the genus Babesia, and two sequences (both in DNA extracted from specimens of Pleurobema oviforme collected from the Paint Rock River) identified as Cryptosporidium, a waterborne parasite of livestock and humans that can also infect other wildlife [61,62]. Cryptosporidium showed low prevalence in a recent survey of freshwater fauna, being found in only 2/74 samples of freshwater fish and none in almost 300 aquatic insect larvae tested [63]. The high-volume filter-feeding behavior of bivalves potentially makes them more likely to take up apicomplexan oocysts than other macroinvertebrates, and Cryptosporidium has been shown to be taken up from terrestrial runoff by both bent mussels and zebra mussels [27,28].
The Goussia sequence amplified from a sample of Quadrula verrucosa (PP964321) was 98.45% similar to an isolate from Goussia pannonica, a parasite of the white bream (Blicca bjoerkna) [63], and the Goussia sequence amplicon from Pustulosa kieneriana (PP964320) was 92.03% identical to an isolate of Goussia bayae, a parasite of the white perch (Morone americana) [64]. The Babesia amplicon obtained from a Lampsilis ovata (PP964429) was 97.17% identical to Babesia gibsoni, a tick-borne parasite that infects terrestrial mammals. This sequence is, however, closer to the Psuedoklossia and Margosiella sequences in the phylogeny, suggesting that this sequence could be unique. A likely route of entrance into freshwater systems could be runoff, similar to what has been seen with the genus Cryptosporidium. While having no cystic life stages, a related terrestrial apicomplexan that infects livestock (Theileria spp.) has been seen to infect electric eels in Brazil [64]. It is possible that unionid mussels could be exposed to parasites such as Goussia and Babesia, as their larvae feed on the blood of fish while attaching to their gills. This warrants further exploration.
Of the nine samples that tested positive for apicomplexans, four were from DNA extracted from the guts of mussels collected from the Paint Rock River, and three were from DNA from mussels from the Sipsey River. Studies have shown that factors such as water temperature, ammonia, and total nitrogen induce stress and correlate with reduced density in mussel populations [65,66]. In this study, incidence positively correlated with temperature, conductivity, dissolved oxygen, nitrite, and orthophosphate, while it negatively correlated with ammonia, nitrate, and pH. However, while water chemistry and physiology correlated with alveolate incidence, the low frequency of alveolates makes these relationships unclear. Protist infections in other marine bivalves are thought to be related to stress caused by environmental factors [67], so this is worth further exploration.
Only one amplicon per mussel sample was sequenced during this study, limiting our ability to identify less common microeukaryotes. The majority of sequences obtained were photosynthetic microeukaryotes (dinoflagellates, algae) that, as potential food sources, are likely to be more prevalent in the guts of unionid mussels than apicomplexans or other non-food taxa. It is quite possible that more of the samples we examined contained apicomplexans, but these were not detected with our approach, which was designed more as a broad survey of multiple mussel species rather than focusing on identifying specific potential parasites. However, even with our limited approach, almost 3% (9/311) of the samples that were tested yielded positive amplicons that were identified as apicomplexan DNA, similar to the numbers reported for the presence of Cryptosporidium in a survey of freshwater fish [63]. Further work should use more in-depth sequencing of individual mussel hosts, potentially using high-throughput sequencing, as has been used on the bacterial gut microbiome. The low bootstrap values and variable placement of the non-photosynthetic alveolate amplicons within the phylogenetic analysis indicate that the tree is fluid, reflecting our still-emerging knowledge on the diversity of apicomplexans. The presence of potentially unique Apicomplexa, such as the Babesia amplicon, signals the need to more specifically explore potential host-parasite interactions between apicomplexans and unionid mussels, and the development and application of a more specific apicomplexan primer set designed for that purpose would help offer a better understanding of their diversity.
While molecular studies on the gut bacterial community associated with freshwater mussels are increasing [10,12,42], fewer have considered the microeukaryotes that may also be associated with freshwater mussels. Most of the eukaryotic sequences we detected were identified as algae or dinoflagellates and potentially represent the food source of those mussels. However, we also detected eukaryotic sequences that were likely from parasitic taxa. While some uptake of apicomplexans in poor water conditions were previously shown in some freshwater bivalves [27,28], the presence of apicomplexans in freshwater unionid mussels has not been previously examined. Unionid mussels are declining in North America [68,69,70], and host-microeukaryote interactions could be exacerbating the current stressors to the population. The declines being seen can be exacerbated by the presence of harbored microscopic eukaryotes. While little research has been performed to support the idea, the decline of North American mussels has been suggested as being at least partly due to an unknown pathogen [71], so the presence of parasitic apicomplexans in some of the mussel samples we examined merits further investigation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms12091835/s1, Table S1: GenBank accession numbers and metadata of sequences; Table S2: The taxa and respective accession numbers for the 18S rRNA gene sequence used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.H.-I. and C.R.J.; methodology, A.K.H.-I.; formal analysis, A.K.H.-I.; investigation, A.K.H.-I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.H.-I.; writing—review and editing, C.R.J.; supervision, C.R.J.; project administration, C.R.J.; funding acquisition, C.R.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation award DEB 1831531.
Data Availability Statement
The sequences generated in this study were uploaded to Genbank under the accession numbers PP964320-PP964486.
Acknowledgments
We thank Lauren Lawson, Marlene Chiarello, and Mark McCauley for their previous work on the mussel microbiome project that provided DNA samples and Carla Atkinson and her lab members at the University of Alabama, who collected the original mussel samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Vaughn, C.C. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 2018, 810, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C.C.; Hakenkamp, C.C. The functional role of burrowing bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikow, D.F.; Hamilton, S.K. Bivalve diets in a midwestern US stream: A stable isotope enrichment study. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogelman, K.J.; Stoeckel, J.A.; Miller, J.M.; Helms, B.S. Feeding ecology of three freshwater mussel species (Family: Unionidae) in a North American lentic system. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byllaardt, J.V.; Ackerman, J.D. Hydrodynamic habitat influences suspension feeding by unionid mussels in freshwater ecosystems. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.L.; van Ee, B.C.; Pfeiffer, J.M. Evolutionary history drives aspects of stoichiometric niche variation and functional effects within a guild. Ecology 2020, 101, e03100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Gonzalez, I.; Hopper, G.W.; Bucholz, J.R.; Kubala, M.E.; Lozier, J.D.; Atkinson, C.L. Niche specialization and community niche space increase with species richness in filter-feeder assemblages. Ecosphere 2023, 14, e4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, K.; Ackerman, J.D. Mussels partition resources from natural waters under flowing conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.T.; Czuba, J.A.; Schwenk, J.; Longjas, A.; Danesh-Yazdi, M.; Hornback, D.J.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Coupling freshwater mussel ecology and river dynamics using a simplified dynamic interaction model. Freshw. Sci. 2016, 35, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, E.A.; Atkinson, C.L.; Jackson, C.R. The gut microbiome of freshwater Unionidae mussels is determined by host species and is selectively retained from filtered seston. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves, A.K.; Johnson, P.D.; Atkinson, C.L.; van Ee, B.C.; Bullard, S.A.; Arias, C.R. Digestive gland microbiome of Pleurobema cordatum: Mesocosms induce dysbiosis. J. Mollus Stud. 2020, 86, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, M.; Chiarello, M.; Atkinson, C.L.; Jackson, C.R. Gut microbiomes of freshwater mussels (Unionidae) are taxonomically and phylogenetically variable across years but remain functionally stable. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, L.A.; Atkinson, C.L.; Jackson, C.R. The gut bacterial microbiome of the Threeridge mussel, Amblema plicata, varies between rivers but shows a consistent core community. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 67, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carty, S. Freshwater Dinoflagellates of North America, 1st ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Maggard, I.J.; Deel, K.B.; Etoll, T.W.; Sproles, R.C.; Lane, T.W.; Cahoon, A.B. Freshwater mussels prefer a diet of stramenopiles and fungi over bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzle, J.M.; Brunner, C.J. Infectious disease of freshwater mussels and other freshwater bivalve mollusks. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2009, 17, 425–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotov, I.N.; Klass, A.L.; Kondakov, A.V.; Vikhrev, I.V.; Bespalaya, Y.V.; Gofarov, M.Y.; Filippov, B.Y.; Bogan, A.E.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Lunn, Z.; et al. Freshwater mussels house a diverse mussel-associated leech assemblage. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, R.S.; Lynn, D.H.; Salerno, J.; Bennett, J.; Gillis, P.L. The facultatively parasitic ciliated protozoan, Tetrahymena glochidiophila (Lynn, 2018), causes a reduction in viability of freshwater mussel glochidia. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 157, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskinen, J.; Urbańska, M.; Ercoli, F.; Andrzejewski, W.; Ożgo, M.; Deng, B.; Choo, J.M.; Riccardi, N. Parasites in sympatric populations of native and invasive freshwater bivalves. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 3167–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewisch, E.; Arnold, F.; Fuehrer, H.P.; Harl, J.; Thielen, F.; El-Matbouli, M. Parasites and their impact on thick-shelled river mussels Unio crassus from two populations in Luxembourg. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2023, 153, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Czarnoleski, M.; Labecka, A.M.; Cichy, A.; Zając, K.; Dragosz-Kluska, D. Factors affecting trematode infection rates in freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 2015, 742, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Edwards, D.D.; Vidrine, M.F. Host diversity affects parasite diversity: A case study involving Unionicola spp. inhabiting freshwater mussels. J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.R.; Dimock, R.V., Jr.; Kuhn, R.E. The symbiotic water mite Unionicola formosa (Acari: Unionicolidae) ingests mucus and tissue of its molluscan host. J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Villari, G.; Maio, N.; De Vico, G. Disease and disorders of freshwater unionid mussels: A brief overview of recent studies. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 00489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, S.; Dennis, M.; McElwain, A.; Leis, E.; Richard, J. Pathology and infectious agents of unionid mussels: A primer for pathologists in disease surveillance and investigation of mortality events. Vet. Pathol. 2023, 60, 510–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, J.I.; Aldridge, D.C. Endosymbionts: An overlooked threat in the conservation of freshwater mussels? Biol. Conserv. 2019, 237, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, T.K.; Fayer, R.; Lewis, E.J.; Trout, J.M.; Farley, C.A. Cryptosporidium oocysts in Bent mussels (Ischadium recurvum) in the Chesapeake Bay. Parasitol. Res. 1999, 85, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, T.K.; Marcogliese, D.J.; de Lafontaine, Y.; Da Silva, A.J.; Mhangami-Ruwende, B.; Pieniazek, N.J. Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts in zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha): Evidence from the St. Lawrence River. Parasitol. Res. 2001, 87, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecna, J.; Jirku, M.; Obornik, M.; Tokarev, Y.S.; Lukes, J.; Modry, D. Phylogenetic Analysis of Coccidian Parasites from Invertebrates: Search for Missing Links. Protist 2006, 157, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, C.J.; Hermida, M.A.; Santos, M.J. Parasites and symbionts from Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamark, 1819) (Bivalves: Mytilidae) of the Aveiro estuary Portugal. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, S.D.; Kristmundsson, A.; Freeman, M.A.; Levesque, M.; Stokesbury, K. Gray meat in the Atlantic sea scallop, Placopecten magellanicus, and the identification of a known pathogenic scallop apicomplexan. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 141, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, T.R. Endemic diseases of cultured shellfish of Long Island, New York: Adult and juvenile American oysters (Crassostrea virginica) and hard clams (Mercenaria mercenaria). Aquaculture 1981, 22, 305–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, B.; Carden, W.E.; Ward, J.E.; Ralph, G.; Winnicki, S. Early host-pathogen interactions in marine bivalves: Evidence that the alveolate parasite Perkinsus marinus infects through the oyster mantle during rejection of pseudofeces. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 113, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudant, P.; Chu, F.E.; Volety, A. Host–parasite interactions: Marine bivalve molluscs and protozoan parasites, Perkinsus species. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 114, 196–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba, A.; Reece, K.S.; Ordas, M.C.; Casas, S.M.; Figueras, A. Perkinsosis in molluscs: A review. Aquat. Living Resour. 2004, 17, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladineo, I.; Trumbic, Z.; Jozic, S.; Segvic, T. First report of Cryptosporidium sp. (Coccidia, Apicomplexa) oocysts in the black mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) reared in the Mali Ston Bay, Adriatic Sea. J. Shellfish. Res. 2009, 28, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neemuchwala, S.; Johnson, N.A.; Pfeiffer, J.M.; Lopes-Lima, M.; Gomes-dos-Santos, A.; Froufe, E.; Hillis, D.M.; Smith, C.H. Coevolution with host fishes shapes parasitic life histories in a group of freshwater mussels (Unionidae: Quadrulini). Bull. Soc. Syst. Biol. 2023, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolland, S.J.; Zahedi, A.; Oskam, C.; Murphy, B.; Ryan, U. Cryptosporidium bollandi n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiiae) from angelfish (Pterophyllum scalare) and Oscar fish (Astronotus ocellatus). Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 217, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.L.; Williams, E.H. Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes, 2nd ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 21–91. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, K. Remarks on the morphology, site of infection and validity of some coccidian species from fish. Acta Vet. Hung. 1996, 44, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hopper, G.W.; Chen, S.; Sanchez Gonzalez, I.; Bucholz, J.R.; Lu, Y.; Atkinson, C.L. Aggregated filter-feeders govern the flux and stoichiometry of locally available energy and nutrients in rivers. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; Bucholz, J.R.; McCauley, M.; Vaughn, S.N.; Hopper, G.W.; Gonzalez, I.S.; Atkinson, C.L.; Lozier, J.D.; Jackson, C.R. Environment and co-occurring native mussel species, but not host genetics, impact the microbiome of a freshwater invasive species (Corbicula fluminea). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 800061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Lima, M.; Burlakova, L.; Karatayev, A.; Gomes-dos-Satos, A.; Zieritz, A.; Froufe, E.; Bogan, A.E. Revisiting the North American freshwater mussel genus Quadrula sensu lato (Bivalvia Unionidae): Phylogeny, taxonomy and species delineation. Zool. Scr. 2019, 48, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristmundsson, A.; Helgason, S.; Bambir, S.H.; Eydal, M.; Freeman, M.A. Margolisiella islandica sp. nov. (Apicomplexa: Eimeridae) infecting Iceland scallop Chlamys islandica (Müller, 1776) in Icelandic waters. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2011, 108, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Evol. Biol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopper, G.W.; Bucholz, J.R.; Dubose, T.P.; Fogelman, K.J.; Keogh, S.M.; Kubala, M.E.; Atkinson, C.L. A trait dataset for freshwater mussels of the United States of America. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Satta, C.T.; Rene, A.; Padedda, B.M.; Pulina, S.; Lai, G.G.; Soru, O.; Buscarinu, P.; Virdis, T.; Marceddu, S.; Luglie, A. First detection of the bloom forming Unruhdinium penardii (Dinophyceae) in a Mediterranean reservoir: Insights on its ecology, morphology and genetics. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2020, 11, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M.; Amaral, R.; Fawley, K.P.; Fawley, M.W.; Nemcova, Y.; Neustupa, J.; Pribyl, P.; Santos, L.M.A.; Sevcikova, T. Eustigmatophyceae. In Handbook of the Protists, 2nd ed.; Archibald, J.M., Simpson, A.G., Slamovits, C.H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10, pp. 367–406. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, S.M.; Levinton, J.S. Selective feeding by three native North American freshwater mussels implies food competition with zebra mussels. Hydrobiologia 2003, 505, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.L.; First, M.R.; Covich, A.P.; Opsahl, S.P.; Golladay, S.W. Suspended material availability and filtration–biodeposition processes performed by a native and invasive bivalve species in streams. Hydrobiologia 2011, 667, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mychek-Londer, J.G.; Chaganti, S.R.; Heath, D.D. Metabarcoding of native and invasive species in stomach contents of Great Lakes fishes. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rorke, R.; Lavery, S.; Chow, S.; Takeyama, H.; Tsai, P.; Beckley, L.E.; Thompson, P.A.; Waite, A.M.; Jeffs, A.G. Determining the diet of larvae of western rock lobster (Panulirus cygnus) using high-throughput DNA sequencing techniques. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Chang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, T. Selective feeding of three bivalve species on the phytoplankton community in a marine pond revealed by high-throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovy, J.; Friend, S.E. Intestinal coccidiosis of anadromous and landlocked alewives, Alosa pseudoharengus, caused by Goussia ameliae n. sp. and G. alosii n. sp. (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2015, 4, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsche, M.A.; Adams, C.R.; Blazer, V.S. Newly described coccidia Goussia bayae from White Perch Morone americana: Morphology and phylogenetics support emerging taxonomy of Goussia within piscine hosts. J. Parasitol. 2019, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, A.; Eiras, J.C.; Cruz, C.; Xavier, R. Synopsis of the species of coccidians reported in marine fish. Animals 2023, 13, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.A.; Koh, W.H.; Clode, P.L. Cryptosporidium—What is it? Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2016, 4, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Monis, P.; Aucote, S.; King, B.; Paparini, A.; Jian, F.; Yang, R.; Oskam, C.; Ball, A.; Robertson, I.; et al. Zoonotic Cryptosporidium Species in Animals Inhabiting Sydney Water Catchments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, L.; Robinson, G.; Chalmers, R.M.; Ormerod, S.J.; Paziewska-Harris, A.; Chadwick, E.A.; Durance, I.; Cable, J. The occurrence and zoonotic potential of Cryptosporidium species in freshwater biota. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.L.; Cardoso, L.; Marchiori, N.; Benites de Pádua, S. Protozoan infections in farmed fish from Brazil: Diagnosis and pathogenesis. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2015, 24, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggel, S.; Hinzmann, M.; Machado, J.; Giest, J. Combined impact of acute exposure to ammonia and temperature stress on the freshwater mussel Unio pictorum. Water 2017, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Zhou, C.; Ouyang, S.; Lui, X.; Wu, X. Effect of complex hydraulic variables and physicochemical factors on freshwater mussel density in the largest floodplain lake, China. Ecol. Process. 2023, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, J.F.; Durfort, M.; Garcia-Valero, J. Parasitism by the protozoan Perkinsus atlanticus favours the development of opportunistic infections. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2001, 46, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, A.; Rasmussen, J.B. Extinction rates of North American freshwater fauna. Conserv. Biol. 1999, 13, 1220–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, W.R.; Williams, J.D. Biodiversity on the brink: An assessment of conservation strategies for North American freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 2014, 735, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, W.R. Reassessing enigmatic mussel declines in the United States. Freshw. Mollusk Biol. Conserv. 2019, 22, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, D.L.; Cope, W.G. The status of mussel health assessment and a path forward. Freshw. Mollusk Biol. Conserv. 2019, 22, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).