Assessing the Presence of Phosphoinositides on Autophagosomal Membrane in Yeast by Live Cell Imaging
Abstract
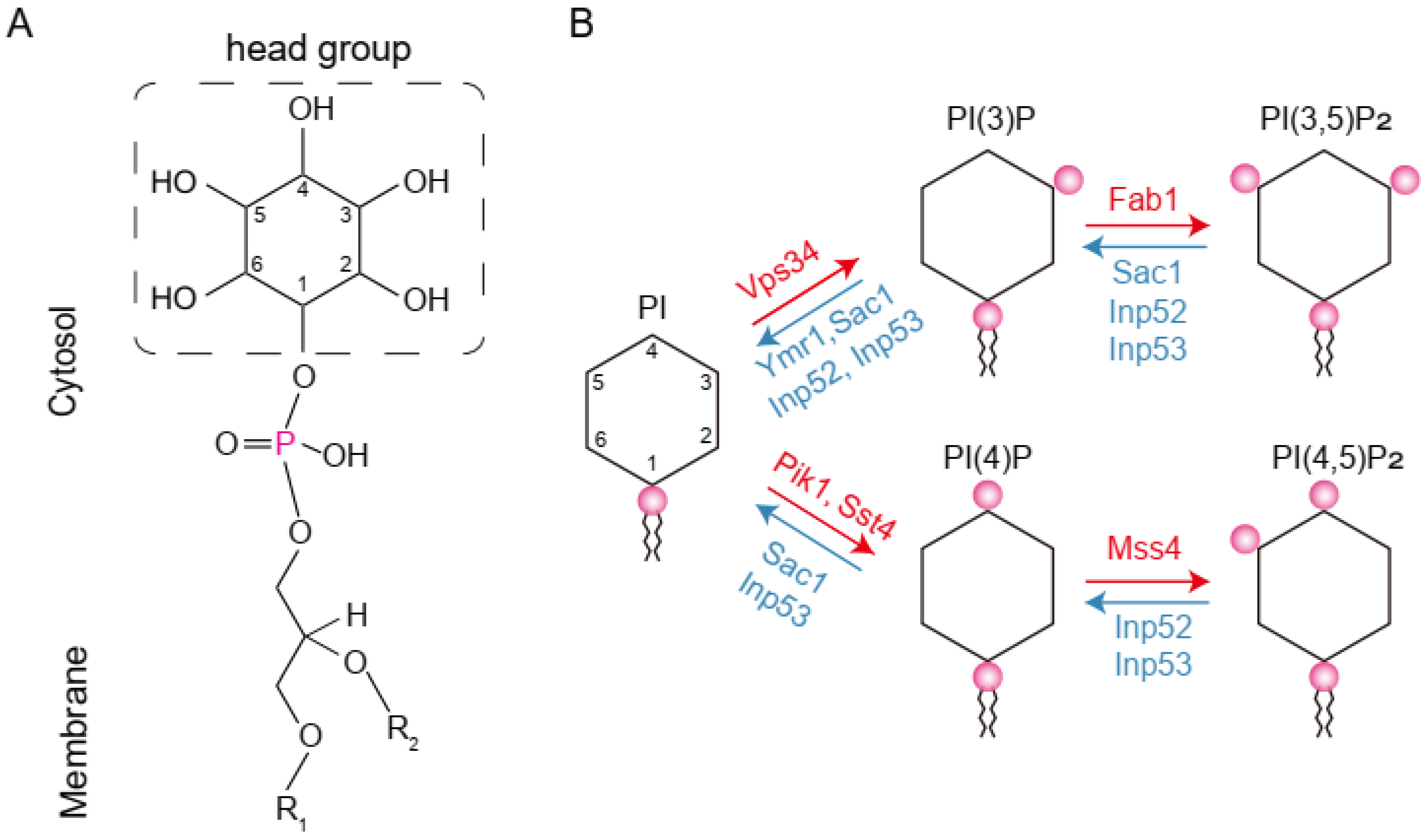
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
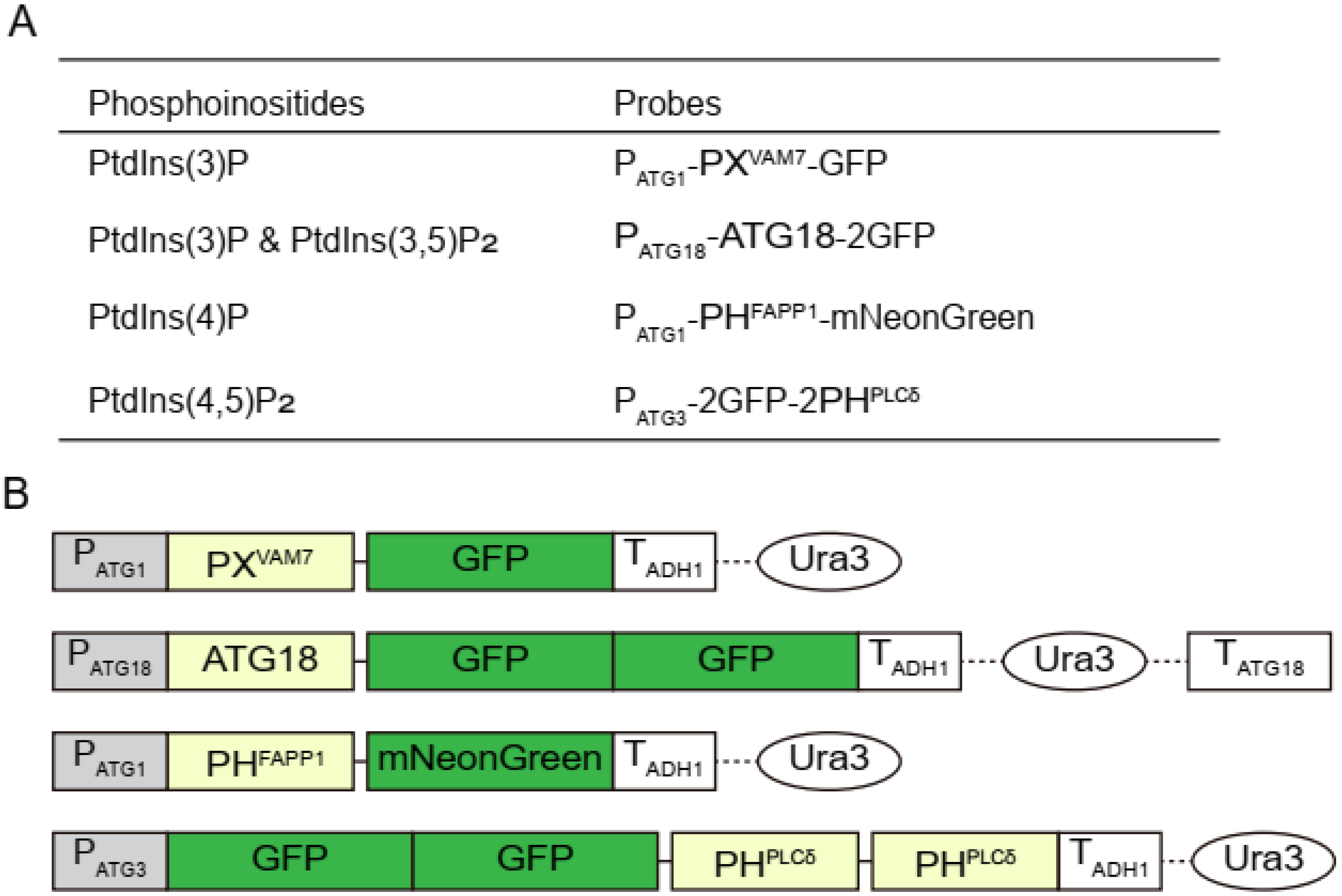
2.1. Strains and Plasmids
2.2. Culturing of Yeast Cells
2.3. Live Cell Imaging and Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
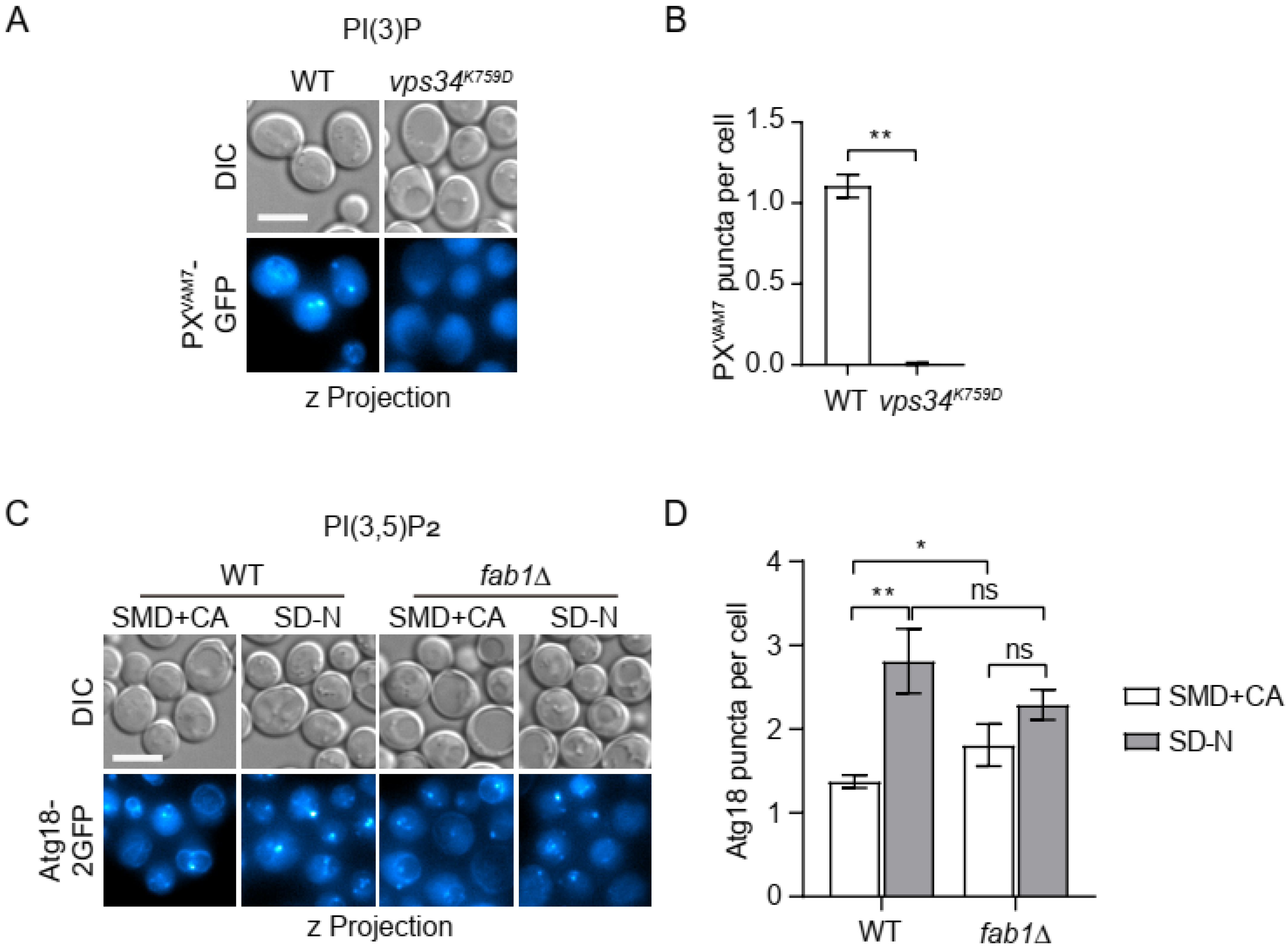
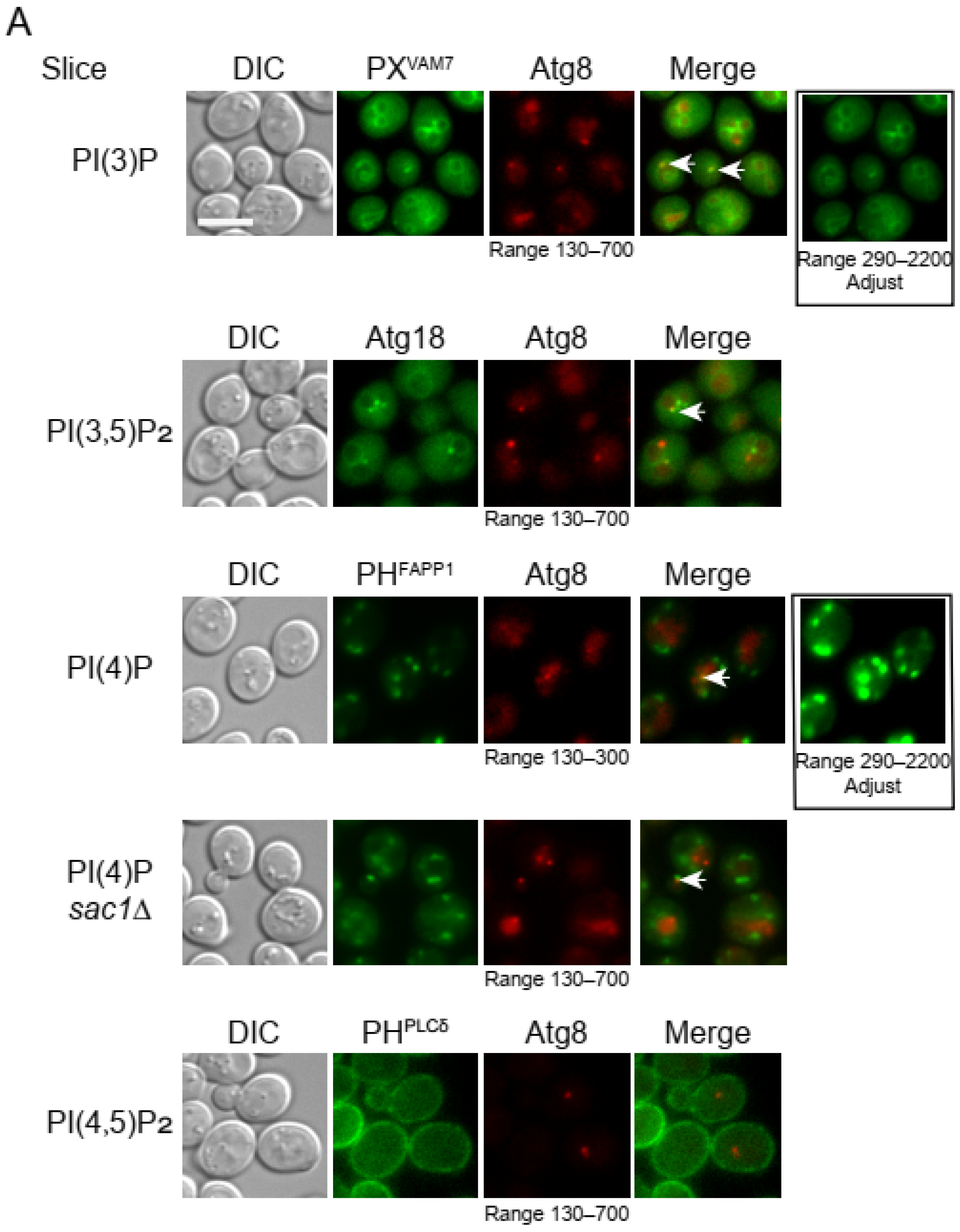
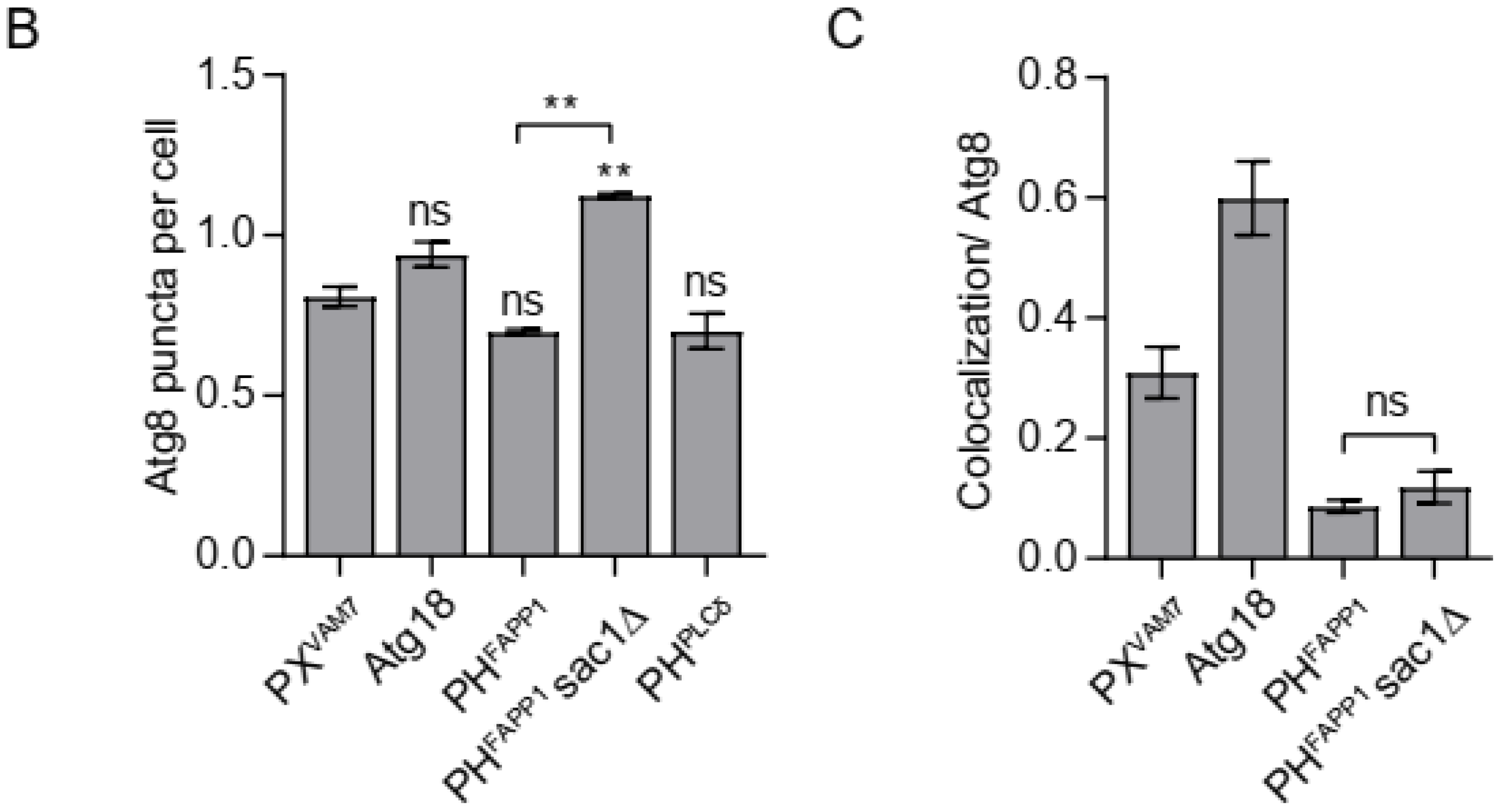
3.1. Confirming the Specificity of the Selected Probes
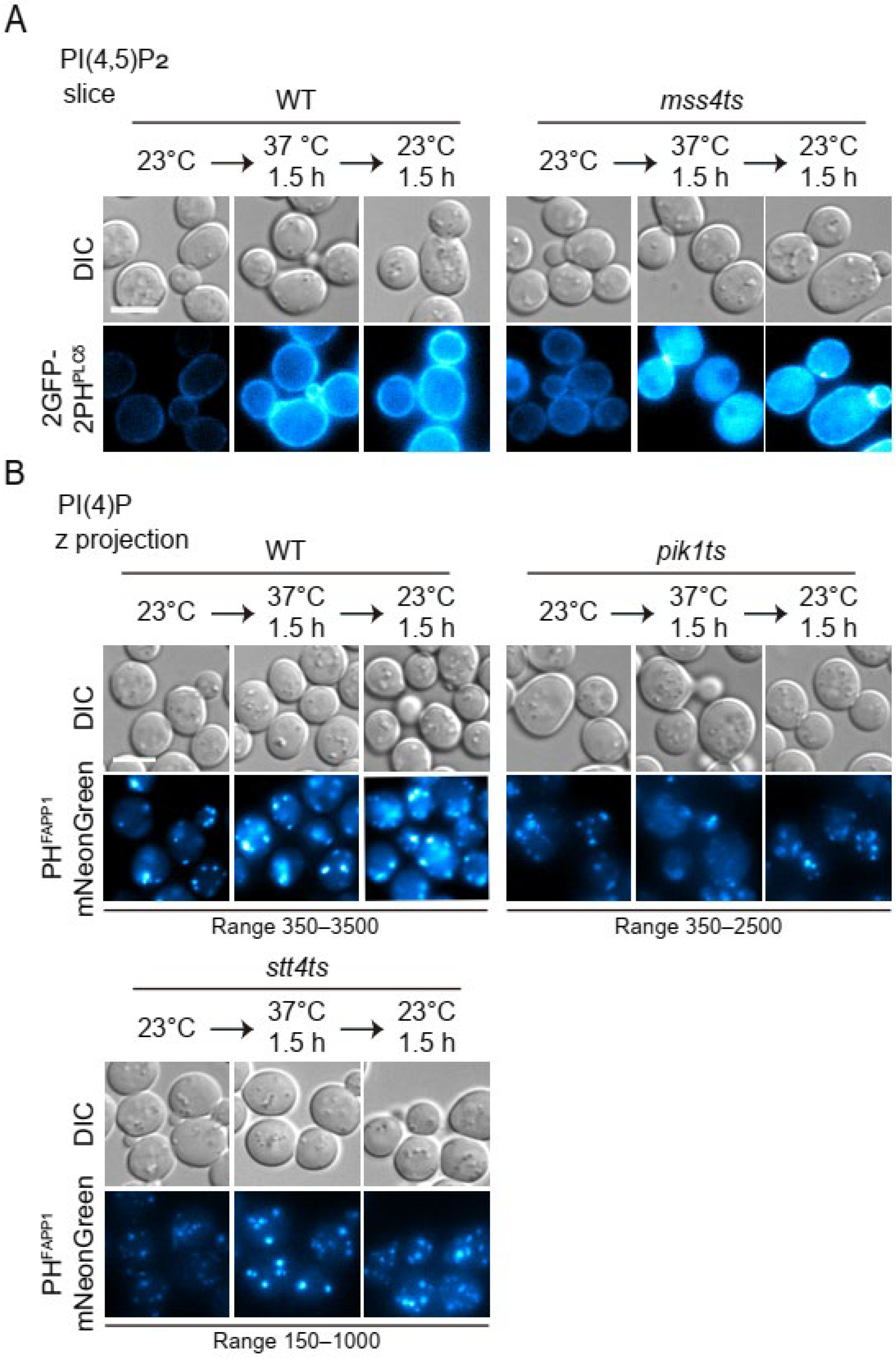
3.2. Probing the Distribution of Phosphoinositides on Autophagosomal Membrane
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shewan, A.; Eastburn, D.J.; Mostov, K. Phosphoinositides in cell architecture. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, G.R.V.; Burke, J.E. Novel roles of phosphoinositides in signaling, lipid transport, and disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 63, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posor, Y.; Jang, W.; Haucke, V. Phosphoinositides as membrane organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 797–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overduin, M.; Kervin, T.A. The phosphoinositide code is read by a plethora of protein domains. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2021, 18, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kervin, T.A.; Overduin, M. Membranes are functionalized by a proteolipid code. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, T. Phosphoinositides: Tiny Lipids with Giant Impact on Cell Regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1019–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickson, E.J.; Hille, B. Understanding phosphoinositides: Rare, dynamic, and essential membrane phospholipids. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.A.; Boronenkov, I.V.; Doughman, S.D.; Kunz, J.; Loijens, J.C. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases, a multifaceted family of signaling enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 9907–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muftuoglu, Y.; Xue, Y.; Gao, X.; Wu, D.Q.; Ha, Y. Mechanism of substrate specificity of phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8711–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.E. Structural Basis for Regulation of Phosphoinositide Kinases and Their Involvement in Human Disease. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicinanza, M.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Mirror image phosphoinositides regulate autophagy. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 3, e1019974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Palamiuc, L.; Ravi, A.; Emerling, B.M. Phosphoinositides in autophagy: Current roles and future insights. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude-Taupin, A.; Morel, E. Phosphoinositides: Functions in autophagy-related stress responses. BBA—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimbeni, A.C.; Codogno, P.; Morel, E. Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate in the regulation of autophagy membrane dynamics. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Balla, T. Emerging roles of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate as regulators of multiple steps in autophagy. J. Biochem. 2020, 168, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audhya, A.; Foti, M.; Emr, S.D. Distinct roles for the yeast phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases, Stt4p and Pik1p, in secretion, cell growth, and organelle membrane dynamics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 2673–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yorimitsu, T.; Zaman, S.; Broach, J.R.; Klionsky, D.J. Protein kinase A and Sch9 cooperatively regulate induction of autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 4180–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Mao, K.; Jin, Y.; Tevzadze, G.; Kauffman, E.J.; Park, S.; Bridges, D.; Loewith, R.; Saltiel, A.R.; Klionsky, D.J.; et al. Roles for PI(3,5)P2 in nutrient sensing through TORC1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Mao, K.; Nair, U.; Klionsky, D.J. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases are required for autophagic membrane trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37964–37972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Thapa, N.; Liao, Y.; Choi, S.; Anderson, R.A. PtdIns(4,5)P2 signaling regulates ATG14 and autophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10896–10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, M.R.; Goncalves, M.D.; Loughran, R.M.; Possik, E.; Vijayaraghavan, T.; Yang, A.; Pauli, C.; Ravi, A.; Verma, A.; Yang, Z.; et al. Phosphatidylinositol-5-Phosphate 4-Kinases Regulate Cellular Lipid Metabolism by Facilitating Autophagy. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 531–544.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, T.; Toth, D.J.; Sengupta, N.; Kim, Y.J.; Balla, T. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate controls Rab7 and PLEKHM1 membrane cycling during autophagosome-lysosome fusion. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e100312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, F.; Wang, S.; Tian, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Fang, C.; Ma, C.; Rong, Y. The STX17-SNAP47-VAMP7/VAMP8 complex is the default SNARE complex mediating autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Cell Res. 2024, 34, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, K.; Noda, T.; Niimi, K.; Ohsumi, Y. Transport of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate into the vacuole via autophagic membranes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes. Cells 2008, 13, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Sun, H.Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Albanesi, J.; Levine, B.; Yin, H. GABARAPs regulate PI4P-dependent autophagosome:lysosome fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7015–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, P.; Lin, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, Q.; Wang, M.; Ren, H.; Lu, M.; et al. PtdIns4P restriction by hydrolase SAC1 decides specific fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes. Autophagy 2021, 17, 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Song, J.Z.; Shan, M.H.; Li, S.P.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.P.; Xie, Z.P. A fluorescent tool set for yeast Atg proteins. Autophagy 2015, 11, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gietz, R.D.; Schiestl, R.H. High-efficiency yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.C.; Kong, I.I.; Kim, H.; Liu, J.J.; Cate, J.H.; Jin, Y.S. Construction of a quadruple auxotrophic mutant of an industrial polyploid saccharomyces cerevisiae strain by using RNA-guided Cas9 nuclease. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7694–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheever, M.L.; Sato, T.K.; de Beer, T.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Emr, S.D.; Overduin, M. Phox domain interaction with PtdIns(3)P targets the Vam7 t-SNARE to vacuole membranes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, G.E.; Starr, M.L.; Hurst, L.R.; Sparks, R.P.; Padolina, M.; Fratti, R.A. The Central Polybasic Region of the Soluble SNARE (Soluble N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive Factor Attachment Protein Receptor) Vam7 Affects Binding to Phosphatidylinositol 3-Phosphate by the PX (Phox Homology) Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17651–17663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dove, S.K.; Piper, R.C.; McEwen, R.K.; Yu, J.W.; King, M.C.; Hughes, D.C.; Thuring, J.; Holmes, A.B.; Cooke, F.T.; Michell, R.H.; et al. Svp1p defines a family of phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate effectors. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskaran, S.; Ragusa, M.J.; Boura, E.; Hurley, J.H. Two-site recognition of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate by PROPPINs in autophagy. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godi, A.; Di Campli, A.; Konstantakopoulos, A.; Di Tullio, G.; Alessi, D.R.; Kular, G.S.; Daniele, T.; Marra, P.; Lucocq, J.M.; De Matteis, M.A. FAPPs control Golgi-to-cell-surface membrane traffic by binding to ARF and PtdIns(4)P. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, A.; Tuymetova, G.; Tsiomenko, A.; Várnai, P.; Balla, T. A plasma membrane pool of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate is generated by phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type-III alpha: Studies with the PH domains of the oxysterol binding protein and FAPP1. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, T.P.; Ahn, S.; Meyer, T. Receptor-induced transient reduction in plasma membrane PtdIns(4,5)P2 concentration monitored in living cells. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnai, P.; Balla, T. Visualization of phosphoinositides that bind pleckstrin homology domains: Calcium- and agonist-induced dynamic changes and relationship to myo-[3H]inositol-labeled phosphoinositide pools. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szentpetery, Z.; Balla, A.; Kim, Y.J.; Lemmon, M.A.; Balla, T. Live cell imaging with protein domains capable of recognizing phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; a comparative study. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinfeld, N.; Lahiri, V.; Morrison, A.; Metur, S.P.; Klionsky, D.J.; Weisman, L.S. Elevating PI3P drives select downstream membrane trafficking pathways. Mol. Biol. Cell 2021, 32, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, S.K.; Cooke, F.T.; Douglas, M.R.; Sayers, L.G.; Parker, P.J.; Michell, R.H. Osmotic stress activates phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate synthesis. Nature 1997, 390, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, T.R.; Dove, S.K.; Lubben, A.; Calaminus, S.D.; Wakelam, M.J. Analysis of intact phosphoinositides in biological samples. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, N.; Lang, M.J.; Weisman, L.S. Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate: Regulation of cellular events in space and time. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, F.T.; Dove, S.K.; McEwen, R.K.; Painter, G.; Holmes, A.B.; Hall, M.N.; Michell, R.H.; Parker, P.J. The stress-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase Fab1p is essential for vacuole function in S. cerevisiae. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gary, J.D.; Wurmser, A.E.; Bonangelino, C.J.; Weisman, L.S.; Emr, S.D. Fab1p is essential for PtdIns(3)P 5-kinase activity and the maintenance of vacuolar size and membrane homeostasis. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Scott, J.L.; Heroux, A.; Roy, S.; Lenoir, M.; Overduin, M.; Stahelin, R.V.; Kutateladze, T.G. Molecular basis of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and ARF1 GTPase recognition by the FAPP1 pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 18650–18657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, T.P.; Munro, S. Targeting of Golgi-specific pleckstrin homology domains involves both PtdIns 4-kinase-dependent and -independent components. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.W.; Lee, J.A.; Jang, D.J. Novel GFP-fused protein probes for detecting phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate in the plasma membrane. Anim. Cells Syst. 2019, 23, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Nair, U.; Klionsky, D.J. Atg8 controls phagophore expansion during autophagosome formation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3290–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, Y.; Ku, W.C.; Akioka, M.; May, A.I.; Hayashi, Y.; Arisaka, F.; Ishihama, Y.; Ohsumi, Y. Atg38 is required for autophagy-specific phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex integrity. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 203, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjepanovic, G.; Baskaran, S.; Lin, M.G.; Hurley, J.H. Vps34 Kinase Domain Dynamics Regulate the Autophagic PI 3-Kinase Complex. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 528–534.e523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, Y. Class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex I subunit NRBF2/Atg38-from cell and structural biology to health and disease. Autophagy 2021, 17, 3897–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebollero, E.; van der Vaart, A.; Zhao, M.; Rieter, E.; Klionsky, D.J.; Helms, J.B.; Reggiori, F. Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate clearance plays a key role in autophagosome completion. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obara, K.; Sekito, T.; Niimi, K.; Ohsumi, Y. The Atg18-Atg2 complex is recruited to autophagic membranes via phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and exerts an essential function. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23972–23980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatz, O.; Fraiberg, M.; Isola, D.; Das, S.; Gogoi, O.; Polyansky, A.; Shimoni, E.; Dadosh, T.; Dezorella, N.; Wolf, S.G.; et al. Rim aperture of yeast autophagic membranes balances cargo inclusion with vesicle maturation. Dev. Cell 2024, 59, 911–923.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judith, D.; Jefferies, H.B.J.; Boeing, S.; Frith, D.; Snijders, A.P.; Tooze, S.A. ATG9A shapes the forming autophagosome through Arfaptin 2 and phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase IIIbeta. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1634–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shao, W.; Liu, W.; Shang, W.; Liu, J.P.; Wang, L.; Tong, C. PtdIns4P exchange at endoplasmic reticulum-autolysosome contacts is essential for autophagy and neuronal homeostasis. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2682–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.-Z.; Feng, Y.-H.; Sergevnina, V.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Xie, Z. Assessing the Presence of Phosphoinositides on Autophagosomal Membrane in Yeast by Live Cell Imaging. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071458
Song J-Z, Feng Y-H, Sergevnina V, Zhu J, Li H, Xie Z. Assessing the Presence of Phosphoinositides on Autophagosomal Membrane in Yeast by Live Cell Imaging. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(7):1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071458
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jing-Zhen, Yi-He Feng, Valentina Sergevnina, Jing Zhu, Hui Li, and Zhiping Xie. 2024. "Assessing the Presence of Phosphoinositides on Autophagosomal Membrane in Yeast by Live Cell Imaging" Microorganisms 12, no. 7: 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071458
APA StyleSong, J.-Z., Feng, Y.-H., Sergevnina, V., Zhu, J., Li, H., & Xie, Z. (2024). Assessing the Presence of Phosphoinositides on Autophagosomal Membrane in Yeast by Live Cell Imaging. Microorganisms, 12(7), 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12071458






