Antiparasitic Activity of Enterocin M and Durancin-like from Beneficial Enterococci in Mice Experimentally Infected with Trichinella spiralis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Enterocins and Their-Producing Strains
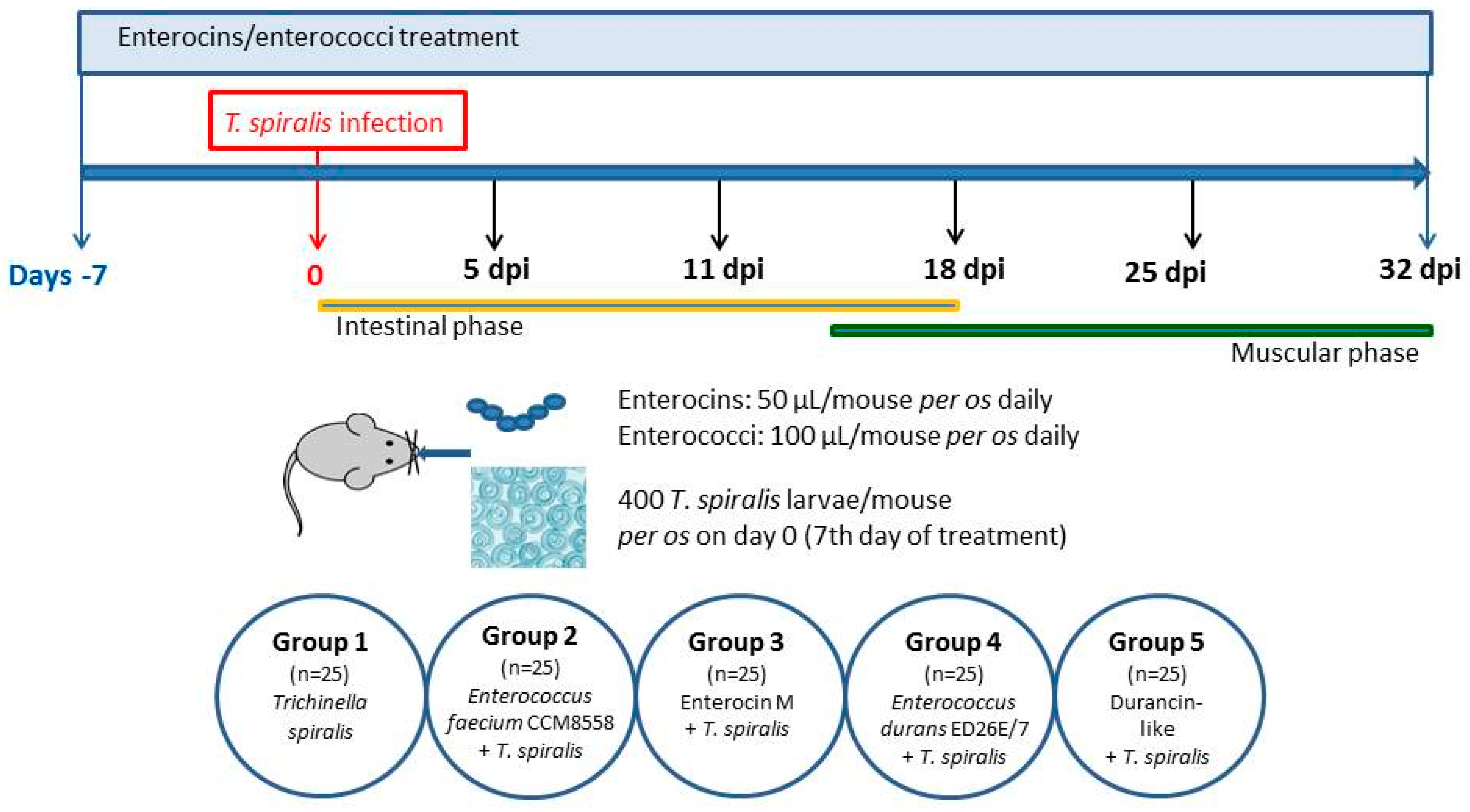
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Parasite Burden
2.5. T. spiralis Female’s Fecundity Ex Vivo and In Vitro
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
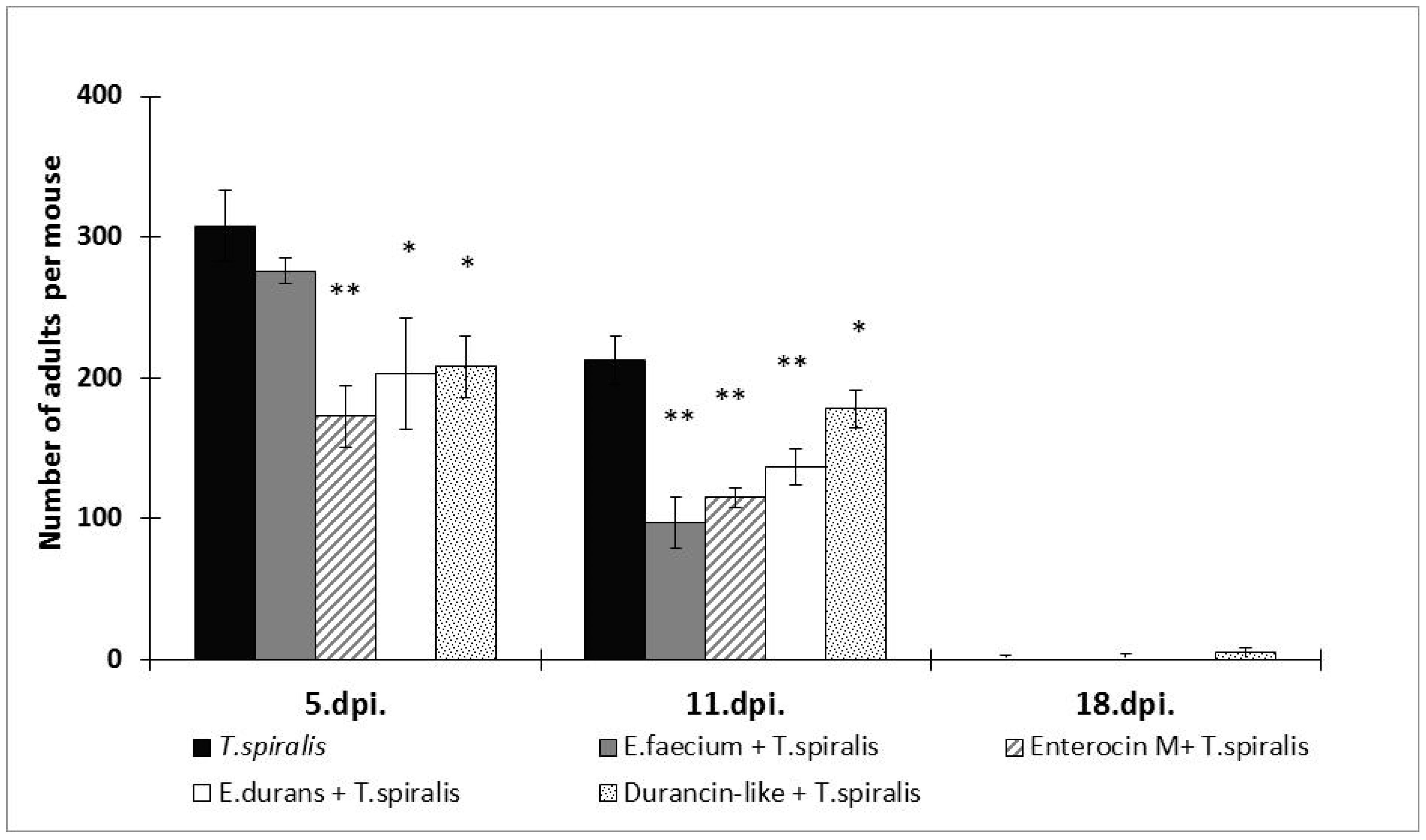
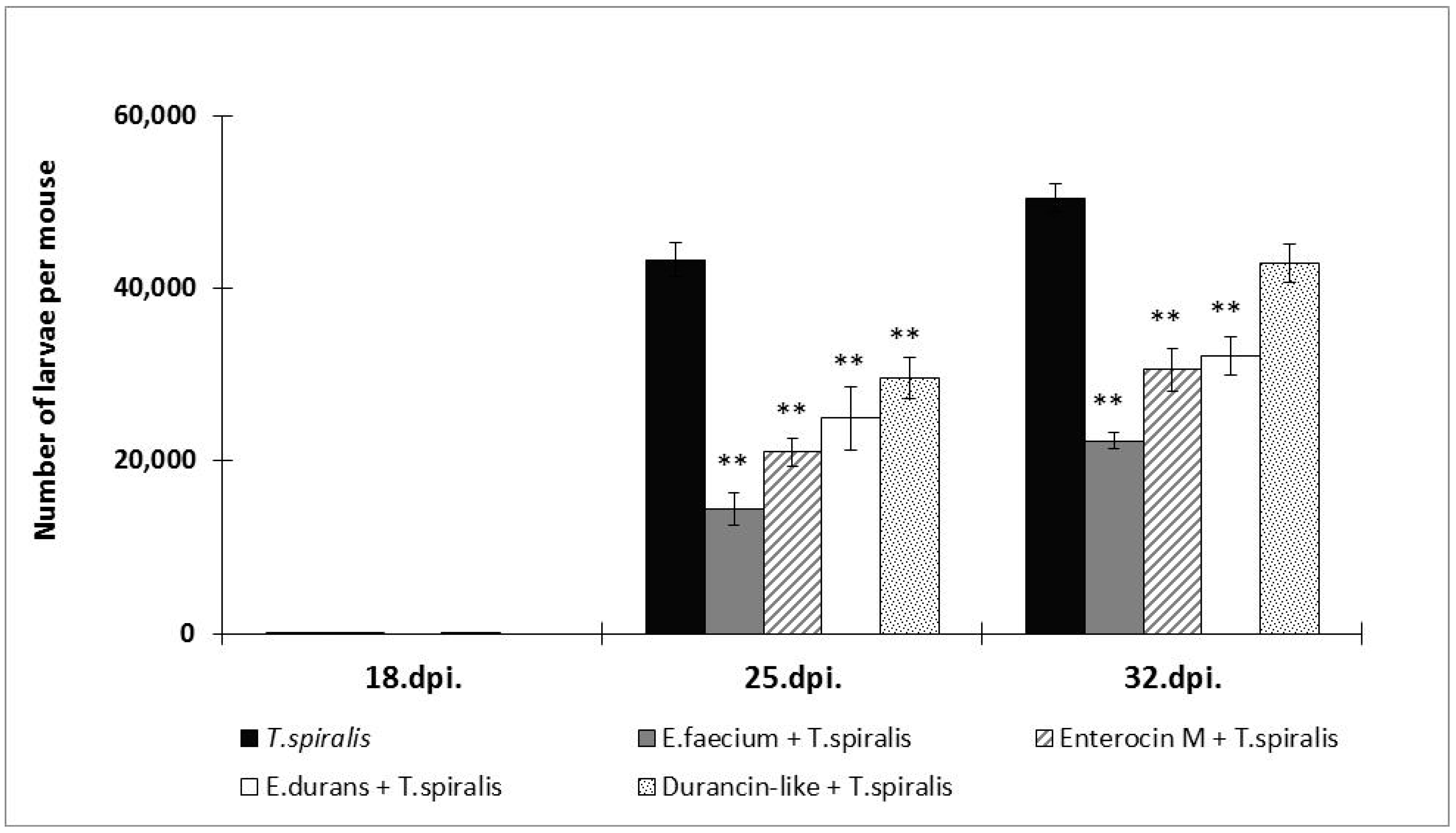
3.1. Parasite Burden
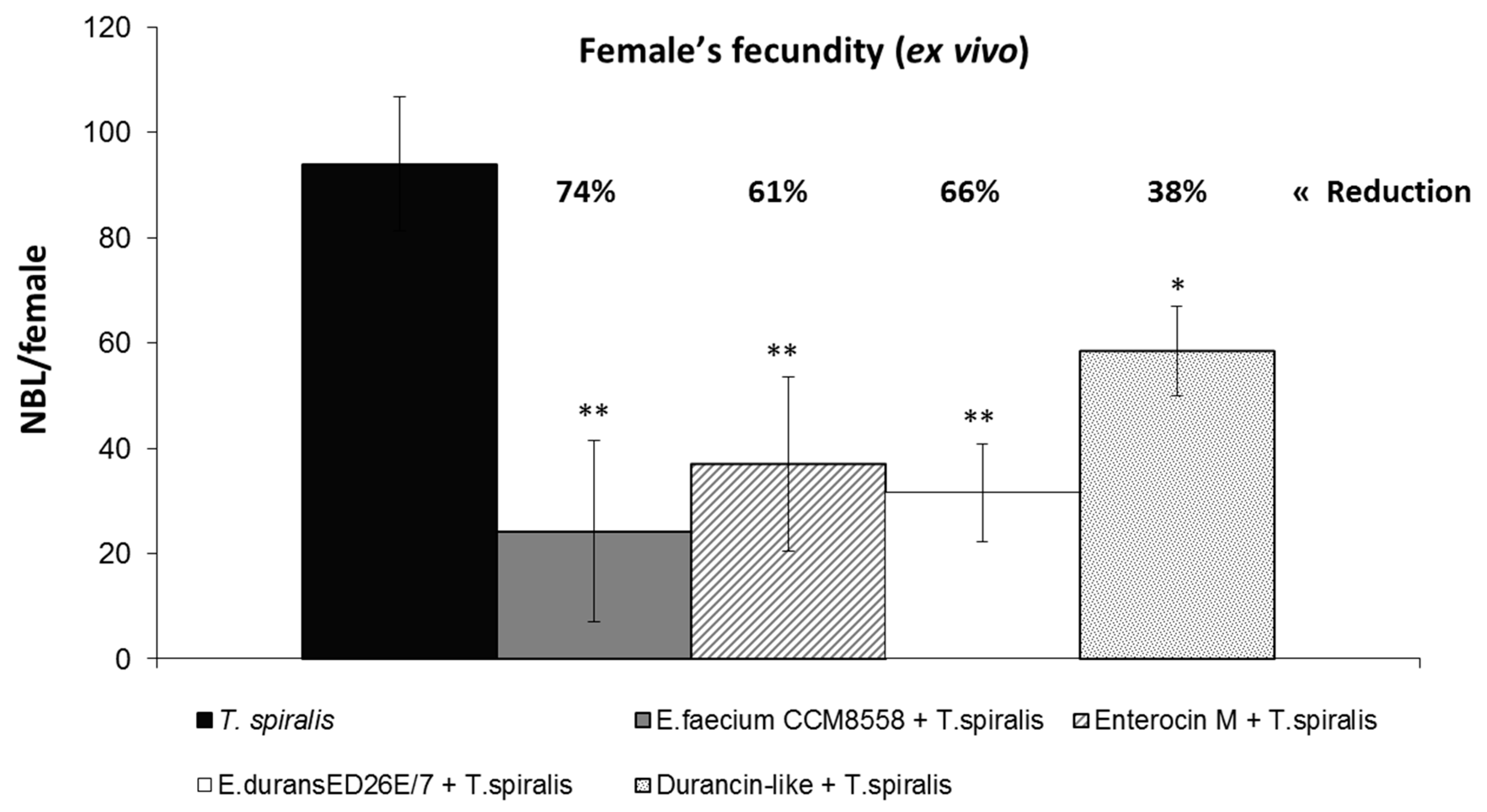
3.2. T. spiralis Female’s Fecundity Ex Vivo
3.3. T. spiralis Female’s Fecundity In Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottstein, B.; Pozio, E.; Nöckler, K. Epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and control of trichinellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwknegt, M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Graham, H.; Robertson, L.J.; van der Giessen, J.W. Euro-FBP workshop participants. Prioritisation of food-borne parasites in Europe, 2016. Euro Surveill. 2018, 9, 17-00161. [Google Scholar]
- Pozio, E.; Gomez Morales, M.A.; Dupouy-Camet, J. Clinical aspects, diagnosis and treatment of trichinellosis. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2003, 3, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Rayia, D.M.; Saad, A.E.; Ashour, D.S.; Oreiby, R.M. Implication of artemisinin nematocidal activity on experimental trichinellosis: In vitro and in vivo studies. Parasitol. Int. 2017, 66, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, A.M.R.; Abdel-Shafi, I.R.; Elsayed, M.D.A.; Mahfoz, A.M.; Tawfeek, S.E.; Abdeltawab, M.S.A. Investigation of the effect of curcumin on oxidative stress, local inflammatory response, COX-2 expression, and microvessel density in Trichinella spiralis induced enteritis, myositis and myocarditis in mice. Helminthologia 2022, 59, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuelenain, G.L.; Fahmy, Z.H.; Elshennawy, A.M.; Selim, E.H.A.; Elhakeem, M.; Hassanein, K.M.A.; Awad, S.M. Phenotypic changes of Trichinella spiralis treated by Commiphora molmol, Lepidium sativum, and Albendazole: In vitro study. Helminthologia 2022, 59, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Vallee, I.; Karadjian, G.; Liu, M.; Liu, X. Lentinan-triggered butyrate-producing bacteria drive the expulsion of the intestinal helminth Trichinella spiralis in mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 926765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrag, H.M.M.; Huseein, E.A.M.; Abd El-Rady, N.M.; Mostafa, F.A.A.M.; Mohamed, S.S.M.; Gaber, M. The protective effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on experimental animals challenged with Trichinella spiralis; new insights on their feasibility as prophylaxis in Trichinella spiralis endemic area. Ann. Parasitol. 2021, 67, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Travers, M.A.; Florent, I.; Kohl, L.; Grellier, P. Probiotics for the control of parasites: An overview. J. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 2011, 610769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrilli, F.; Di Cave, D.; Cavallero, S.; D’Amelio, S. Interactions between parasites and microbial communities in the human gut. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Temsahy, M.M.; Ibrahim, I.R.; Mossallam, S.F.; Mahrous, H.; Abdel Bary, A.; Abdel Salam, S.A. Evaluation of newly isolated probiotics in the protection against experimental intestinal trichinellosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucková, B.; Hurníková, Z.; Lauková, A.; Revajová, V.; Dvorožňáková, E. The anti-parasitic effect of probiotic bacteria via limiting the fecundity of Trichinella spiralis female adults. Helminthologia 2018, 55, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.L.; Huang, H.B.; Li, J.Y.; Pan, T.X.; Wang, N.; Yang, W.T.; Cao, X.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Oral immunization with recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum expressing Nudix hydrolase and 43 kDa proteins confers protection against Trichinella spiralis in BALB/c mice. Acta Trop. 2021, 220, 105947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boros, Z.; Băieș, M.H.; Vodnar, D.C.; Gherman, C.M.; Borșan, S.D.; Cozma-Petruț, A.; Lefkaditis, M.; Györke, A.; Cozma, V. Antiparasitic action of Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 and Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM strains in CD-1 mice experimentally infected with Trichinella britovi. Pathogens 2022, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofs, L.; Sparo, M.D.; de Yaniz, M.G.; Lissarrague, S.; Domínguez, M.P.; Álvarez, L.I.; Sánchez Bruni, S.F. Antinematodic effect of Enterococcus faecalis CECT7121 using Trichinella spiralis as a model of nematode infection in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2022, 241, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, A.; Foey, A. Probiotic modulation of innate cell pathogen sensing and signaling events. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada, J.L.; Caron, C.R.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; Soccol, C.R. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Purification, properties and use as biopreservatives. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2007, 50, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, I.F.; Diep, D.B.; Ike, Y. Enterococcal bacteriocins and antimicrobial proteins that contribute to niche control. In Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection [Internet], 1st ed.; Gilmore, M.S., Clewell, D.B., Ike, Y., Shankar, N., Eds.; Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Stoyanova, L.G.; Ustyugova, E.A.; Netrusov, A.I. Antibacterial metabolites of lactic acid bacteria: Their diversity and properties. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2012, 48, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, V.; Mehta, A.; Singh, S.; Jain, N.; Ahirwal, L.; Mehta, S. Bacteriocin: A novel approach for preservation of food. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Todorov, S.D.; Dicks, L.M. Optimization of bacteriocin ST311LD production by Enterococcus faecium ST311LD, isolated from spoiled black olives. J. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 370–374. [Google Scholar]
- Férir, G.; Petrova, M.I.; Andrei, G.; Huskens, D.; Hoorelbeke, B.; Snoeck, R.; Vanderleyden, J.; Balzarini, J.; Bartoschek, S.; Brönstrup, M.; et al. The lantibiotic peptide labyrinthopeptin A1 demonstrates broad anti-HIV and anti-HSV activity with potential for microbicidal applications. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kassaa, I.; Hober, D.; Hamze, M.; Chihib, N.E.; Drider, D. Antiviral potential of lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins. 2014, 6, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abengózar, M.Á.; Cebrián, R.; Saugar, J.M.; Gárate, T.; Valdivia, E.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Maqueda, M.; Rivas, L. Enterocin AS-48 as evidence for the use of bacteriocins as new leishmanicidal agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02288-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargová, M.; Revajová, V.; Lauková, A.; Hurníková, Z.; Dvorožňáková, E. Modulatory Effect of beneficial enterococci and their enterocins on the blood phagocytes in murine experimental trichinellosis. Life 2023, 13, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauková, A.; Tomáška, M.; Kmeť, V.; Strompfová, V.; Pogány Simonová, M.; Dvorožňáková, E. Slovak Local Ewe’s Milk Lump Cheese, a Source of Beneficial Enterococcus durans Strain. Foods 2021, 10, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, C.M.; van Belkum, M.J.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Abriouel, H.; Gálvez, A. Diversity of enterococcal bacteriocins and their grouping in a new classification scheme. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 31, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-parabiotics: The new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareková, M.; Lauková, A.; Skaugen, M.; Nes, I. Isolation and characterization of a new bacteriocin, termed enterocin M, produced by environmental isolate Enterococcus faecium AL41. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 34, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vuyst, L.; Callewaert, R.; Pot, B. Characterization of antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus amylovorus DCE471 and large-scale isolation of its bacteriocin amylovorin L471. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 19, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapel, C.M.; Gamble, H.R. Infectivity, persistence, and antibody response to domestic and sylvatic Trichinella spp. in experimentally infected pigs. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaj, W. The effect of cyclosporine A on the course of infection by Trichinella pseudospiralis or Nematospiroides dubius on C3H strain mice. Acta Parasitol. 1990, 35, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Bolas-Fernández, F. Biological variation in Trichinella species and genotypes. J. Helminthol. 2003, 77, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angkasekwinai, P.; Sodthawon, W.; Jeerawattanawart, S.; Hansakon, A.; Pattanapanyasat, K.; Wang, Y.H. ILC2s activated by IL-25 promote antigen-specific Th2 and Th9 functions that contribute to the control of Trichinella spiralis infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconi, M.D.; Bertorini, G.; Codina, A.V.; Indelman, P.; Di Masso, R.J.; Hinrichsen, L.I. Phenotypic characterization of the response to infection with Trichinella spiralis in genetically defined mouse lines of the CBi-IGE Stock. Open J. Vet. Med. 2015, 5, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, E.; La Rosa, G.; Murrell, K.D.; Lichtenfels, J.R. Taxonomic revision of the genus Trichinella. J. Parasitol. 1992, 78, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorožňáková, E.; Hurníková, Z.; Revajová, V.; Lauková, A. Effects of bacteriocinogenic and probiotic bacteria on cellular immunity and parasite Trichinella spiralis infection in mice. In Proceedings of the ICOPA XIII: 13th International Congress of Parasitology, Mexico City, Mexico, 10–15 August 2014; p. 109. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista-Garfias, C.R.; Ixta-Rodríguez, O.; Martínez-Gómez, F.; López, M.G.; Aguilar-Figueroa, B.R. Effect of viable or dead Lactobacillus casei organisms administered orally to mice on resistance against Trichinella spiralis infection. Parasite 2001, 8, S226–S228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Garg, R. Probiotics. Ind. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 27, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.I. Physiological changes in the gastrointestinal tract and host protective immunity: Learning from the mouse-Trichinella spiralis model. Parasitology 2008, 135, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzberger, R.; Arents, J.; Dekker, H.L.; Pridmore, R.D.; Gysler, C.; Kleerebezem, M.; de Mattos, M.J. H2O2 production in species of the Lactobacillus acidophilus group: A central role for a novel NADH-dependent flavin reductase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2229–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardo, L.F.; McVay, C.S.; Appleton, J.A. Molting, ecdysis, and reproduction of Trichinella spiralis are supported In vitro by intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gómez, F.; Fuentes-Castro, B.E.; Bautista-Garfias, C.R. The intraperitoneal inoculation of Lactobacillus casei in mice induces total protection against Trichinella spiralis infection at low challenge doses. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- el-Temsahy, M.M. The effect of changes in the gastric pH value on experimental trichinosis. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Staden, A.D.; Brand, A.M.; Dicks, L.M. Nisin F-loaded brushite bone cement prevented the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in vivo. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen-Meyer, J.; Rogne, P.; Oppegard, C.; Haugen, H.S.; Kristiansen, P.E. Structure-function relationships of the non-lanthionine-containing peptide (class II) bacteriocins produced by gram-positive bacteria. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauková, A.; Czikková, S.; Vasilková, Z.; Juriš, P.; Mareková, M. Occurrence of bacteriocin production among environmental enterococci. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 27, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, T.F.; Ferreira, C.L.L.F. The genus Enterococcus as probiotic: Safety concerns. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2013, 56, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azat, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Kayir, A.; Lin, D.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, X. Probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditionally fermented Xinjiang cheese. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2016, 17, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, B.; Ganguly, N.K. The unexplored role of probiotics on the parasitic pathogens. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhdeo, M.V.K. The relationship between intestinal location and fecundity in adult Trichinella spiralis. Int. J. Parasitol 1991, 21, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milcheva, R.; Todorova, K.; Georgieva, A.; Petkova, S. The synthesis of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE), α-dystroglycan, and β-galactoside α-2,3-sialyltransferase 6 (ST3Gal6) by skeletal muscle cell as a response to infection with Trichinella spiralis. Helminthologia 2022, 59, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, C.; Thornton, D.J.; Grencis, R.K. A sticky end for gastrointestinal helminths; the role of the mucus barrier. Parasite Immunol. 2018, 40, e12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Y.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, Q.L.; Gao, J.M.; Liu, L.L.; Wu, T.F.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.H.; Gou, Q.; Chen, W.; et al. Intestinal microbes influence the survival, reproduction and protein profile of Trichinella spiralis in vitro. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashour, D.S. Trichinella spiralis immunomodulation: An interactive multifactorial process. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorožňáková, E.; Hurníková, Z.; Kołodziej-Sobocińska, M. Development of cellular immune response of mice to infection with low doses of Trichinella spiralis, Trichinella britovi and Trichinella pseudospiralis larvae. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
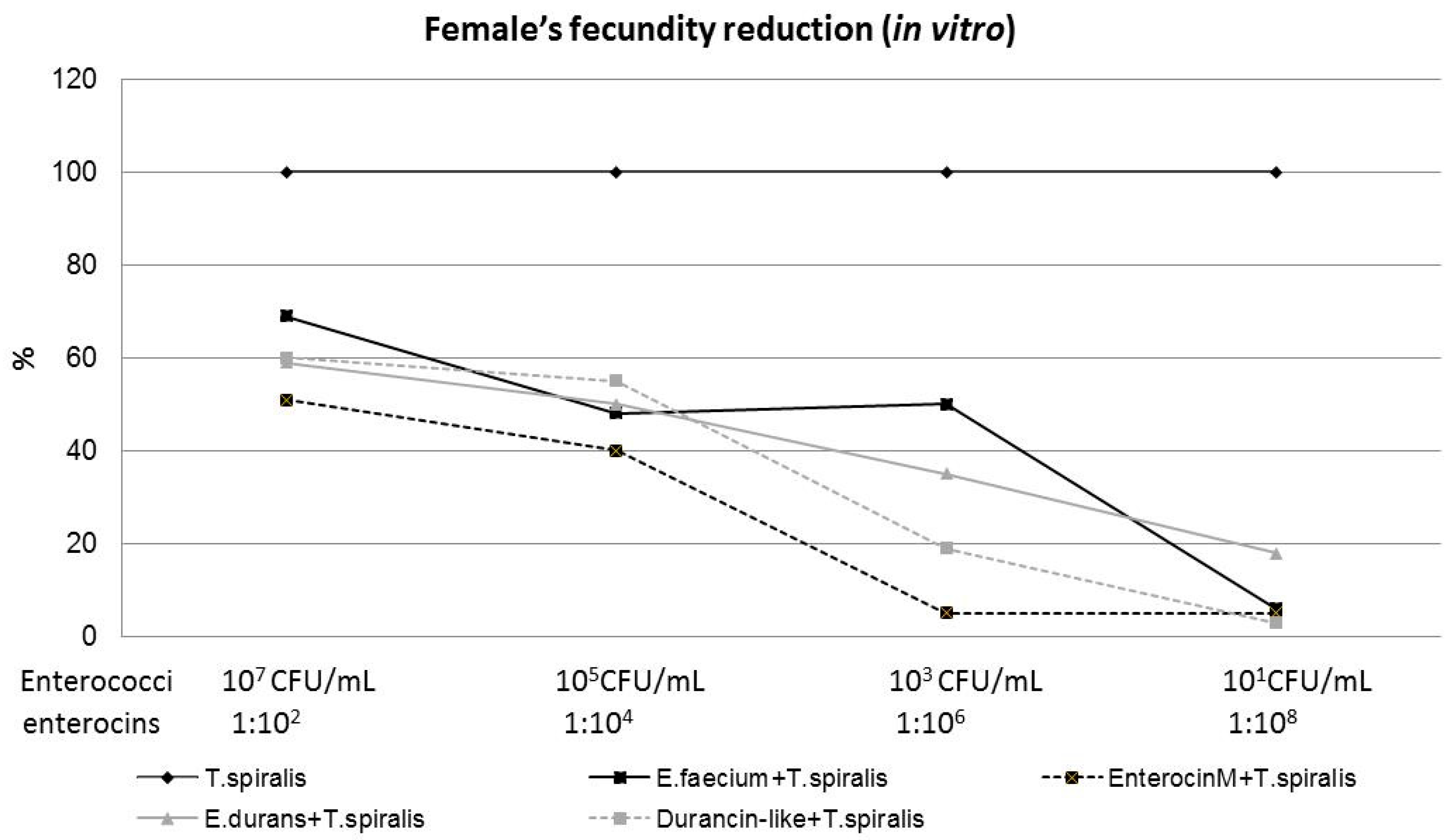
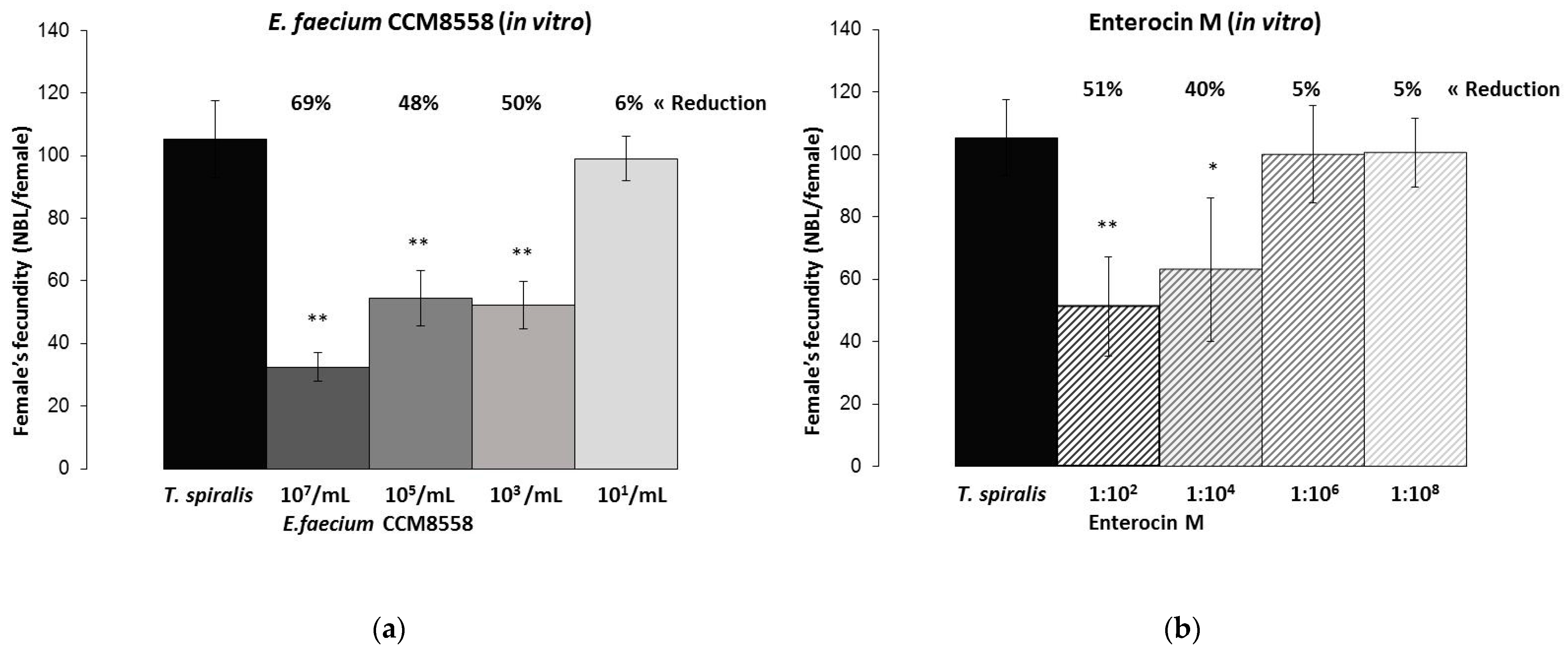
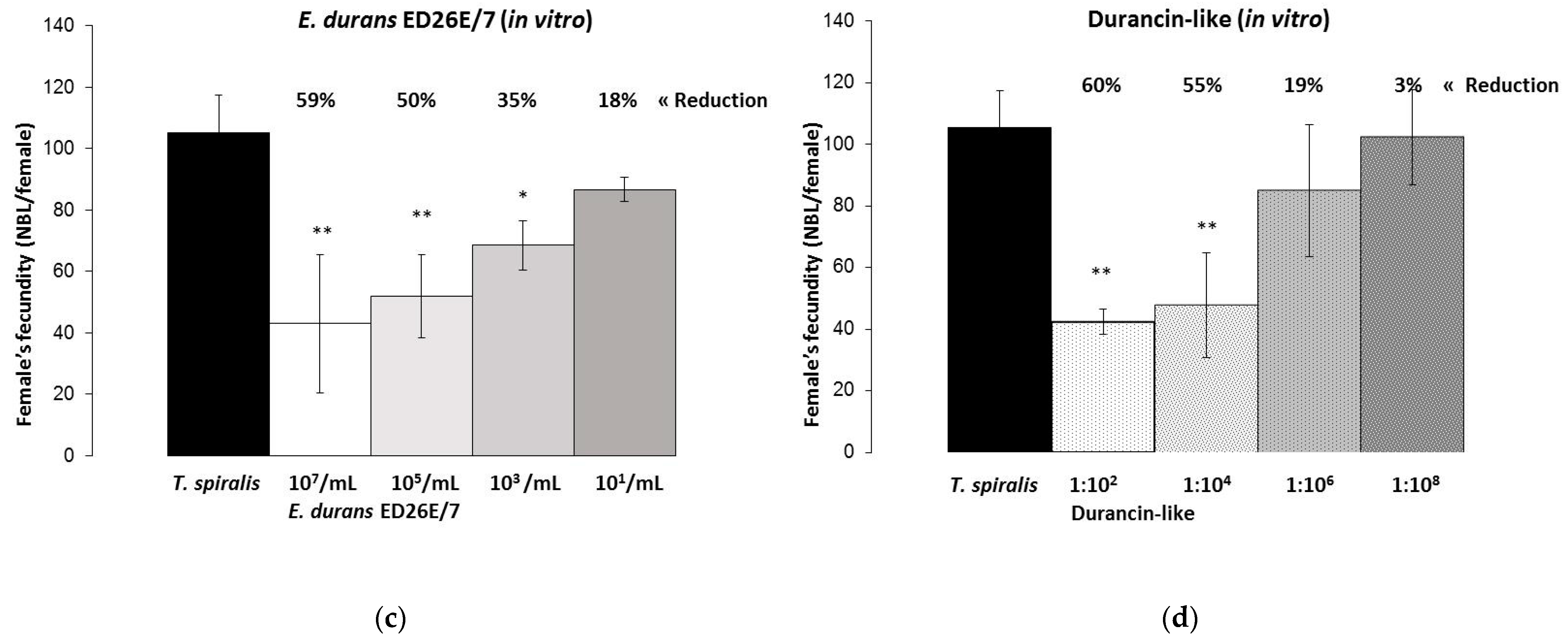
| Days Post Infection | T. spiralis | E. faecium + T. spiralis | Enterocin M + T. spiralis | E. durans + T. spiralis | Durancin-like + T. spiralis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 108.3 ± 4.9 | ** 36.2 ± 4.6 | ** 52.5 ± 4.0 | ** 62.4 ± 9.2 | ** 74.1 ± 5.8 |
| 32 | 126.3 ± 3.9 | ** 55.9 ± 2.5 | ** 76.3 ± 6.2 | ** 80.4 ± 5.5 | 107.3 ± 5.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrová, M.; Hurníková, Z.; Lauková, A.; Dvorožňáková, E. Antiparasitic Activity of Enterocin M and Durancin-like from Beneficial Enterococci in Mice Experimentally Infected with Trichinella spiralis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050923
Petrová M, Hurníková Z, Lauková A, Dvorožňáková E. Antiparasitic Activity of Enterocin M and Durancin-like from Beneficial Enterococci in Mice Experimentally Infected with Trichinella spiralis. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(5):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050923
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrová, Miroslava, Zuzana Hurníková, Andrea Lauková, and Emília Dvorožňáková. 2024. "Antiparasitic Activity of Enterocin M and Durancin-like from Beneficial Enterococci in Mice Experimentally Infected with Trichinella spiralis" Microorganisms 12, no. 5: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050923
APA StylePetrová, M., Hurníková, Z., Lauková, A., & Dvorožňáková, E. (2024). Antiparasitic Activity of Enterocin M and Durancin-like from Beneficial Enterococci in Mice Experimentally Infected with Trichinella spiralis. Microorganisms, 12(5), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050923





