Salvage Therapy with Rezafungin for Candida parapsilosis Spondylodiscitis: A Case Report from Expanded Access Program
Abstract
1. Background
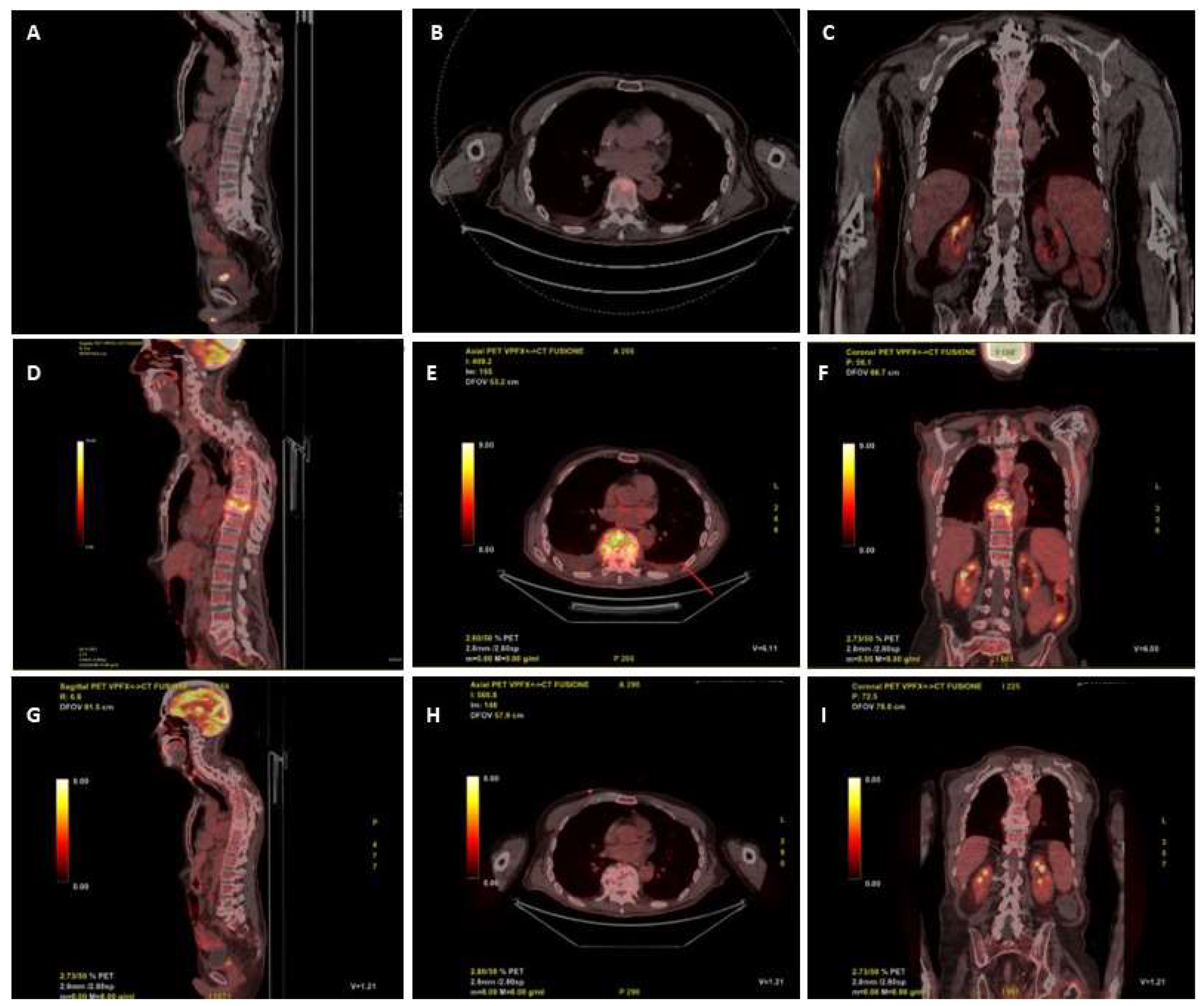
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gouliouris, T.; Aliyu, S.H.; Brown, N.M. Spondylodiscitis: Update on diagnosis and management. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65 (Suppl. 3), iii11–iii24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, A.; Honore, P.M.; Puerta-Alcalde, P.; Garcia-Vidal, C.; Pagotto, A.; Gonçalves-Bradley, D.C.; Verweij, P.E. Invasive candidiasis: Current clinical challenges and unmet needs in adult populations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 1569–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelhoefer, S.J.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Bedi, A.; Kienzle, A.; Baecker, H.C.; Andronic, O.; Karczewski, D. Candida spondylodiscitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of seventy two studies. Int. Orthop. 2024, 48, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, J.; Miranda, I.M.; Rodrigues, A.G. Candida parapsilosis Virulence and Antifungal Resistance Mechanisms: A Comprehensive Review of Key Determinants. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendrup, M.C.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Jørgensen, K.M.; Barac, A.; Steinmann, J.; Toscano, C.; Arsenijevic, V.A.; Sartor, A.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Hamprecht, A.; et al. European candidaemia is characterised by notable differential epidemiology and susceptibility pattern: Results from the ECMM Candida III study. J. Infect. 2023, 87, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, P.G.; Kauffman, C.A.; Andes, D.R.; Clancy, C.J.; Marr, K.A.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Reboli, A.C.; Schuster, M.G.; Vazquez, J.A.; Walsh, T.J.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Candidiasis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, e1–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Effron, G. Rezafungin—Mechanisms of Action, Susceptibility and Resistance: Similarities and Differences with the Other Echinocandins. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendrup, M.C.; Meletiadis, J.; Zaragoza, O.; Jørgensen, K.M.; Marcos-Zambrano, L.J.; Kanioura, L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Mouton, J.W.; Guinea, J. Multicentre determination of rezafungin (CD101) susceptibility of Candida species by the EUCAST method. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Carvalhaes, C.; Messer, S.A.; Rhomberg, P.R.; Castanheira, M. Activity of a Long-Acting Echinocandin, Rezafungin, and Comparator Antifungal Agents Tested against Contemporary Invasive Fungal Isolates (SENTRY Program, 2016 to 2018). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.R.; Soriano, A.; Skoutelis, A.; Vazquez, J.A.; Honore, P.M.; Horcajada, J.P.; Spapen, H.; Bassetti, M.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Das, A.F.; et al. Rezafungin Versus Caspofungin in a Phase 2, Randomized, Double-blind Study for the Treatment of Candidemia and Invasive Candidiasis: The STRIVE Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3647–e3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, G.R.; Soriano, A.; Cornely, O.A.; Kullberg, B.J.; Kollef, M.; Vazquez, J.; Honore, P.M.; Bassetti, M.; Pullman, J.; Chayakulkeeree, M.; et al. Rezafungin versus caspofungin for treatment of candidaemia and invasive candidiasis (ReSTORE): A multicentre, double-blind, double-dummy, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechacek, J.; Yakubu, I.; Vissichelli, N.C.; Bruno, D.; Morales, M.K. Successful expanded access use of rezafungin, a novel echinocandin, to eradicate refractory invasive candidiasis in a liver transplant recipient. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2571–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melenotte, C.; Ratiney, R.; Hermine, O.; Bougnoux, M.E.; Lanternier, F. Successful Rezafungin Treatment of an Azole-Resistant Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis in a STAT-1 Gain-of-Function Patient. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 1182–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeel, A.; Qu, M.D.; Siddiqui, E.; Levitz, S.M.; Ellison, R.T. Expanded access use of rezafungin for salvage therapy of invasive Candida glabrata infection: A case report. In Open Forum Infectious Diseases; Oxford University Press: New York City, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ripp, S.L.; Aram, J.A.; Bowman, C.J.; Chmielewski, G.; Conte, U.; Cross, D.M.; Gao, H.; Lewis, E.M.; Lin, J.; Liu, P.; et al. Tissue Distribution of Anidulafungin in Neonatal Rats. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 95, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felton, T.; Troke, P.F.; Hope, W.W. Tissue Penetration of Antifungal Agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roepcke, S.; Passarell, J.; Walker, H.; Flanagan, S. Population pharmacokinetic modeling and target attainment analyses of rezafungin for the treatment of candidemia and invasive candidiasis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e0091623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, J.A.; Flanagan, S.; Pappas, P.; Thompson, G.R.; Sandison, T.; Honore, P.M. 637. Outcomes by Body Mass Index (BMI) in the STRIVE Phase 2 Trial of Once-Weekly Rezafungin for Treatment of Candidemia and Invasive Candidiasis Compared with Caspofungin. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7 (Suppl. 1), S378–S379. [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan, S.; Walker, H.; Ong, V.; Sandison, T. Absence of Clinically Meaningful Drug-Drug Interactions with Rezafungin: Outcome of Investigations. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0133923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Blood Cultures | Bone | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candida parapsilosis | Candida parapsilosis | |||
| DRUG | MIC (mg/L) | Interpretation | MIC (mg/L) | Interpretation |
| Caspofungin | 1 | S | 0.5 | S |
| Fluconazole | 128 | R | 32 | R |
| Voriconazole | 1 | R | 0.5 | I |
| Anidulafungin | 1 | S | 1 | S |
| Micafungin | 2 | S | 2 | S |
| 5-flucytosine | 0.12 | S | 0.06 | S |
| Posaconazole | 1 | R | 0.06 | S |
| Itraconazole | 0.25 | I | 0.12 | S |
| Amphotericin B | 0.5 | S | 1 | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viceconte, G.; Buonomo, A.R.; Esposito, N.; Cattaneo, L.; Somma, T.; Scirocco, M.M.; Mainolfi, C.G.; Gentile, I. Salvage Therapy with Rezafungin for Candida parapsilosis Spondylodiscitis: A Case Report from Expanded Access Program. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050903
Viceconte G, Buonomo AR, Esposito N, Cattaneo L, Somma T, Scirocco MM, Mainolfi CG, Gentile I. Salvage Therapy with Rezafungin for Candida parapsilosis Spondylodiscitis: A Case Report from Expanded Access Program. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(5):903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050903
Chicago/Turabian StyleViceconte, Giulio, Antonio Riccardo Buonomo, Nunzia Esposito, Letizia Cattaneo, Teresa Somma, Maria Michela Scirocco, Ciro Gabriele Mainolfi, and Ivan Gentile. 2024. "Salvage Therapy with Rezafungin for Candida parapsilosis Spondylodiscitis: A Case Report from Expanded Access Program" Microorganisms 12, no. 5: 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050903
APA StyleViceconte, G., Buonomo, A. R., Esposito, N., Cattaneo, L., Somma, T., Scirocco, M. M., Mainolfi, C. G., & Gentile, I. (2024). Salvage Therapy with Rezafungin for Candida parapsilosis Spondylodiscitis: A Case Report from Expanded Access Program. Microorganisms, 12(5), 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12050903






