Early Succession of Community Structures and Biotic Interactions of Gut Microbes in Eriocheir sinensis Megalopa after Desalination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
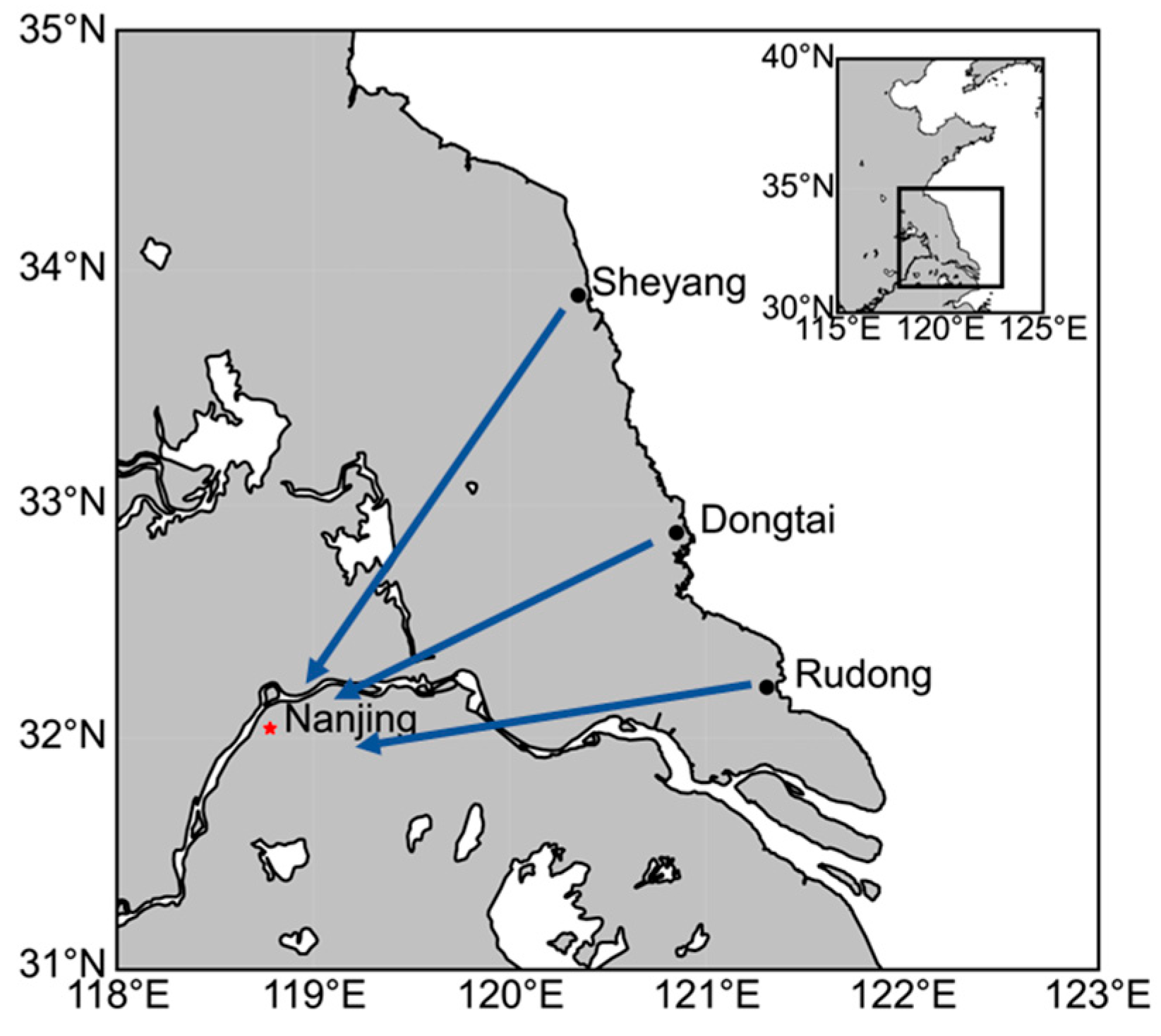
2.1. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and MiSeq Sequencing
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
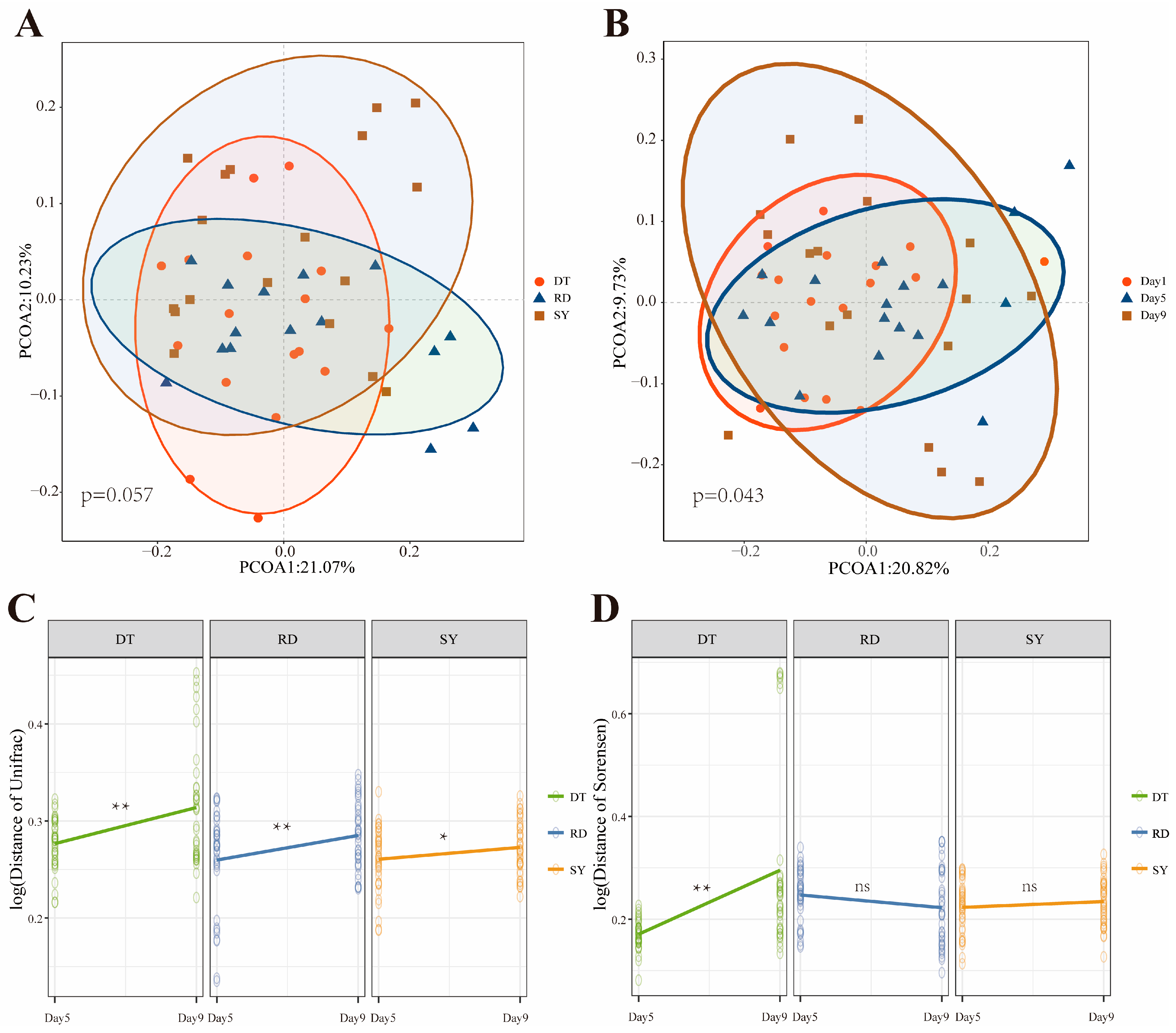
3.1. Analysis of the Difference in the Intestinal Microbial Community
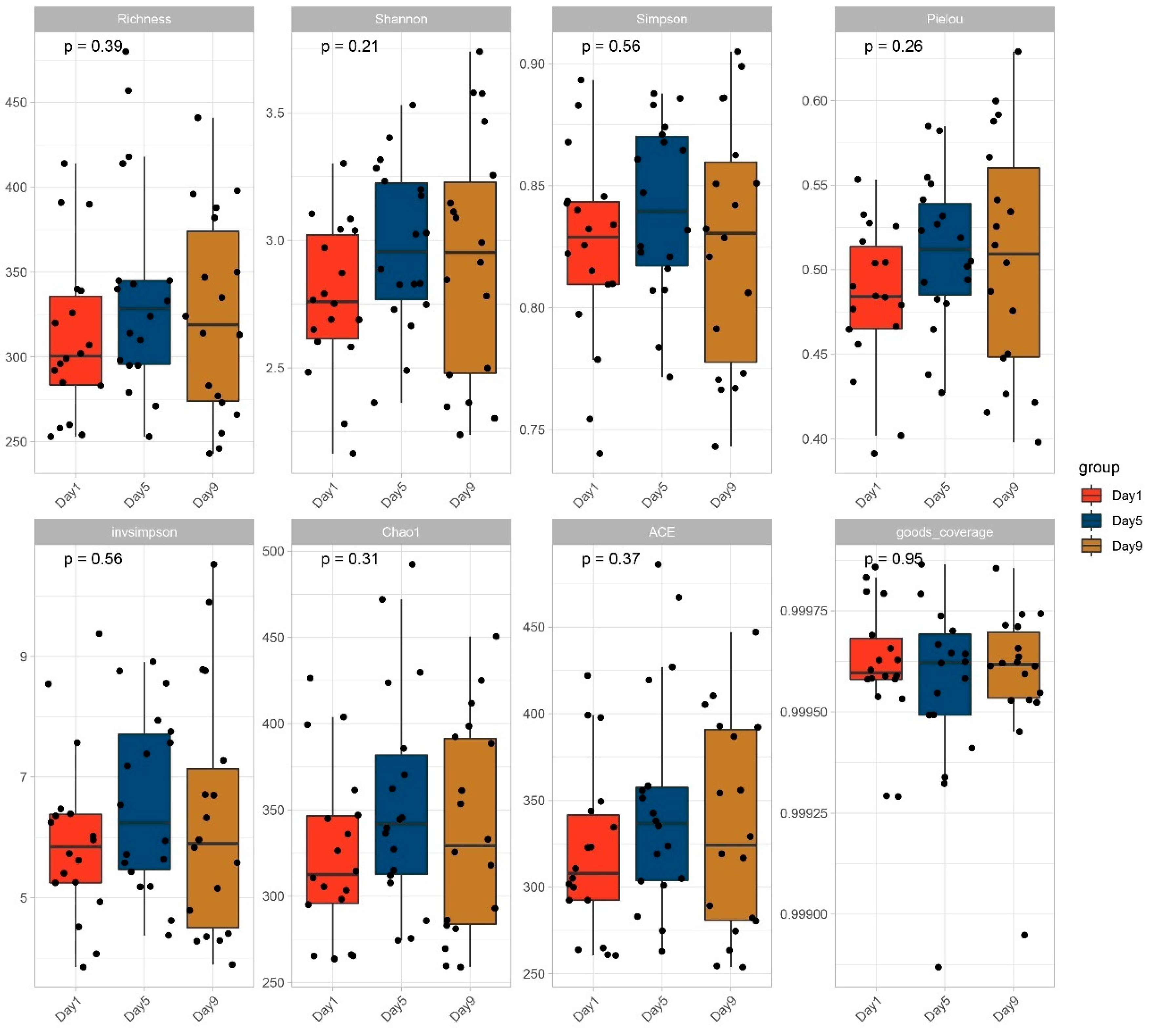
3.2. Diversity of Bacterial Communities
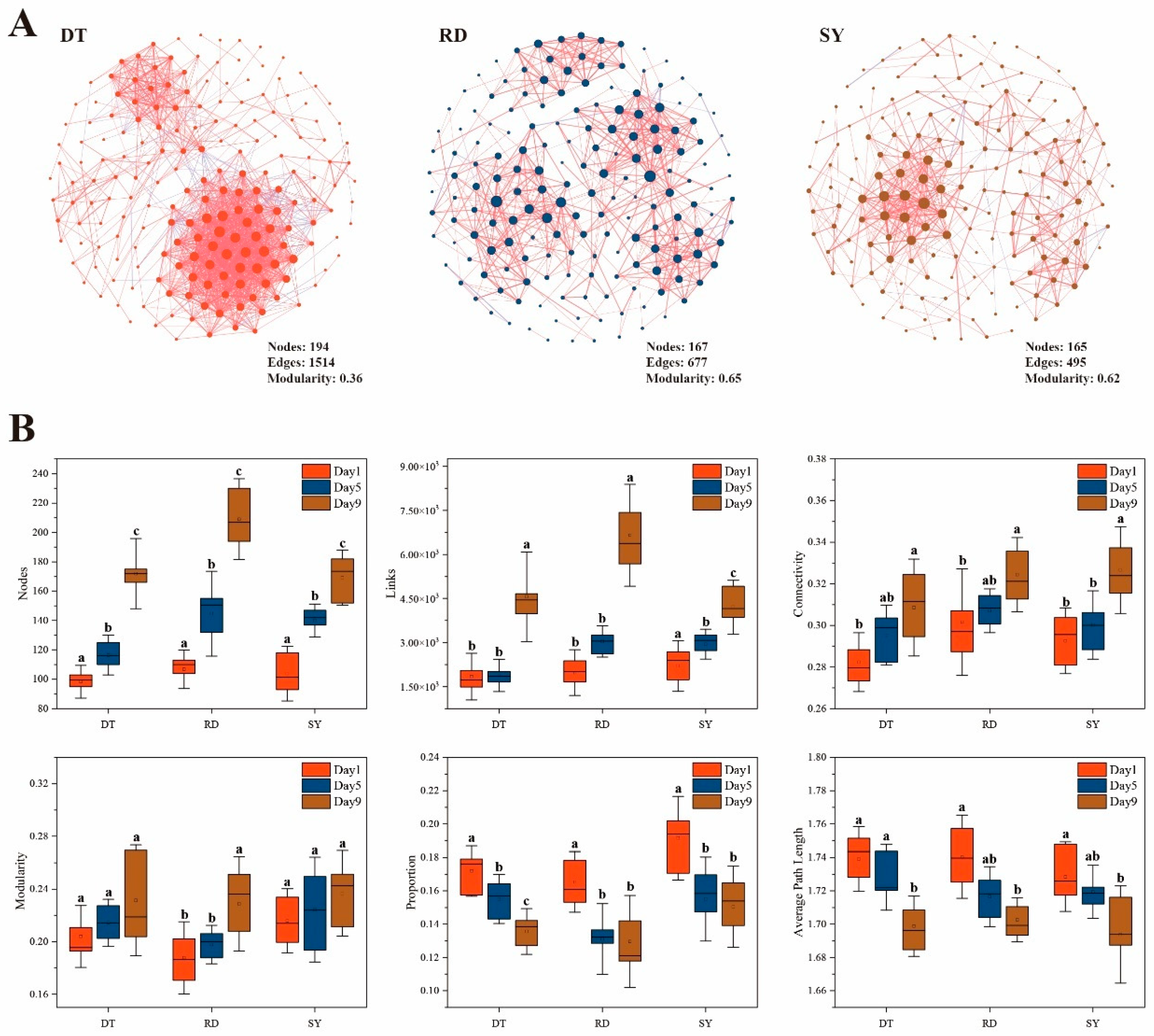
3.3. Gut Microbial Co-Occurrence Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, Q. Eriocheir sinensis microRNA-7 Targets Crab Myd88 to Enhance White Spot Syndrome Virus Replication. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 79, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Lei, X.; Wang, S.; Wan, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Effects of Acute Salinity Stress on Osmoregulation, Antioxidant Capacity and Physiological Metabolism of Female Chinese Mitten Crabs (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquaculture 2022, 552, 737989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.H.; Wang, D. Structure and Membership of Gut Microbial Communities in Multiple Fish Cryptic Species under Potential Migratory Effects. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; He, F.; Song, X.; Huang, S.; Yue, W.; Chen, Y.; Su, Z.; Wang, C. Global Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles Provides Novel Insights into the Development and Evolution of the Large Crustacean Eriocheir sinensis. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2020, 18, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Wei, M.; Xu, D.; Zhang, C.; Du, S.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Integrative Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Effects of a Sudden Drop in Salinity on Osmoregulation, Metabolism, Anti-Oxidation, and Immunity in Eriocheir sinensis Megalopa and Juvenile Stages. Aquac. Rep. 2023, 31, 101656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Chinese Mitten Crab Culture: Current Status and Recent Progress towards Sustainable Development. In Aquaculture in China; Gui, J.-F., Tang, Q., Li, Z., Liu, J., De Silva, S.S., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 197–217. ISBN 978-1-119-12074-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Hines, A.H. Current Trends in Hatchery Techniques and Stock Enhancement for Chinese Mitten Crab, Eriocheir japonica sinensis. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2008, 16, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jin, F.; Liu, W.; Huo, G.; Zhou, F.; Yan, J.; Zhou, K.; Li, P. Comparative Transcriptome, Digital Gene Expression and Proteome Profiling Analyses Provide Insights into the Brachyurization from the Megalopa to the First Juvenile in Eriocheir sinensis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, S.; Kamei, Y.; Takeshima, S.; Yamashita, K.; Hamasaki, K. Stepwise Changes in Morphology during the Settlement Process in a Merobenthic Octopus, Octopus Sinensis, Raised in the Laboratory. Invertebr. Biol. 2022, 141, e12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yi, X.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; Nie, Z.; Du, J.; Cao, L.; Gao, J.; Xu, G. Effects of Effective Microorganisms on the Physiological Status, Intestinal Microbiome, and Serum Metabolites of Eriocheir sinensis. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 27, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Guo, K.; Yang, Y. Immune and Intestinal Microbiota Responses to Heat Stress in Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Aquaculture 2023, 563, 738965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Dong, C.; Qiu, Q.; Li, C. Integrating Gut Microbiota Immaturity and Disease-Discriminatory Taxa to Diagnose the Initiation and Severity of Shrimp Disease: Gut Microbiota Diagnoses Shrimp Disease. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. Toxic Effects of Cadmium and Lead Exposure on Intestinal Histology, Oxidative Stress Response, and Microbial Community of Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus Vannamei. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, M.S.; Brejnrod, A.D.; Roggenbuck, M.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Balle, C.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Stokholm, J.; Thorsen, J.; Waage, J.; Rasmussen, M.A.; et al. The Developing Hypopharyngeal Microbiota in Early Life. Microbiome 2016, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Dong, Y.; Ye, J.; Xue, Q.; Lin, Z. Gut Microbiome Composition Likely Affects the Growth of Razor Clam Sinonovacula Constricta. Aquaculture 2022, 550, 737847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, C.; Gueguen, Y.; Wegner, K.M.; Bass, D.; Pallavicini, A.; Vezzulli, L.; Arzul, I. Recent Advances in Bivalve-Microbiota Interactions for Disease Prevention in Aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 73, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, L.; Dong, P.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Lu, Z.; Hou, D.; Zhang, D. Fine-Scale Succession Patterns and Assembly Mechanisms of Bacterial Community of Litopenaeus Vannamei Larvae across the Developmental Cycle. Microbiome 2020, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukgehnaish, K.; Kumar, P.; Sivachandran, P.; Marimuthu, K.; Arshad, A.; Paray, B.A.; Arockiaraj, J. Gut Microbiota Metagenomics in Aquaculture: Factors Influencing Gut Microbiome and Its Physiological Role in Fish. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1903–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Zhao, W.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, T. Gut Microbiome Succession in Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis during Seawater–Freshwater Migration. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 858508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, R. Effects of Normoxic and Hypoxic Conditions on the Immune Response and Gut Microbiota of Bostrichthys Sinensis. Aquaculture 2020, 525, 735336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yang, M.; Xu, K.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. Shift and Interaction of Intestinal Bacterial Community in Juvenile Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis upon Astaxanthin Feeding. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-Y.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, D.-M.; Wang, N.; Liu, H.-J.; Wan, J.-W.; Chen, Y.-K.; Wang, Q.-J.; Guo, Z.-X. Comparative Study on Growth, Digestive Function and Intestinal Microbial Composition of Female Chinese Mitten Crab Eriocheir sinensis Selected at Different Growth Stages in Rice-Crab Culture Systems. Aquaculture 2022, 554, 738120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicala, F.; Lago-Lestón, A.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Chong-Robles, J.; Cortés-Jacinto, E.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Gut Microbiota Shifts in the Giant Tiger Shrimp, Penaeus Monodon, during the Postlarvae, Juvenile, and Adult Stages. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Dai, W.; Qiu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yang, W.; Li, C. Response of Host-Bacterial Colonization in Shrimp to Developmental Stage, Environment and Disease. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Duan, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Ren, H.; Yin, Y.; Ye, L. Insights into the Gut Microbiota of Freshwater Shrimp and Its Associations with the Surrounding Microbiota and Environmental Factors. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Xuan, L.; Yu, W.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, J. Spatiotemporal Successions of Shrimp Gut Microbial Colonization: High Consistency despite Distinct Species Pool. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestrum, R.I.; Attramadal, K.J.K.; Vadstein, O.; Gundersen, M.S.; Bakke, I. Bacterial Community Assembly in Atlantic Cod Larvae (Gadus morhua): Contributions of Ecological Processes and Metacommunity Structure. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabar, H.; Hara, K.; Uwasu, M. Comparative Assessment of the Co-Evolution of Environmental Indicator Systems in Japan and China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 61, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, J.M.; Bruns, T.D.; Taylor, J.W.; Smith, D.P.; Branco, S.; Glassman, S.I.; Erlandson, S.; Vilgalys, R.; Liao, H.-L.; Smith, M.E.; et al. Endemism and Functional Convergence across the North American Soil Mycobiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6341–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, B.P.; Boysen, A.K.; Carlson, L.T.; Groussman, R.D.; Heal, K.R.; Cain, K.R.; Morales, R.L.; Coesel, S.N.; Morris, R.M.; Ingalls, A.E.; et al. Sulfonate-Based Networks between Eukaryotic Phytoplankton and Heterotrophic Bacteria in the Surface Ocean. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Armour, C.R.; Hu, C.; Mei, M.; Tian, C.; Sharpton, T.J.; Jiang, Y. Microbiome Multi-Omics Network Analysis: Statistical Considerations, Limitations, and Opportunities. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using Network Analysis to Explore Co-Occurrence Patterns in Soil Microbial Communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, T.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Xiao, N.; Zhang, L.; Kimirei, I.A.; Wang, J. Biotic and Abiotic Factors Interplay in Structuring the Dynamics of Microbial Co-Occurrence Patterns in Tropical Mountainsides. Environ. Res. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Gao, T.; Hu, A.; Wang, J. Network Complexity and Stability of Microbes Enhanced by Microplastic Diversity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 4334–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and Community Structure in Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Dsouza, M.; Lou, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.; Gilbert, J.A. Geographic Patterns of Co-Occurrence Network Topological Features for Soil Microbiota at Continental Scale in Eastern China. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Nutrition and Health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F. Intestinal Microbiota Composition in Fishes Is Influenced by Host Ecology and Environment. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3100–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, T.; Yao, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wirth, S.; Cao, W.; Lin, Q.; Li, X. Pika Gut May Select for Rare but Diverse Environmental Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studds, C.E.; Kendall, B.E.; Murray, N.J.; Wilson, H.B.; Rogers, D.I.; Clemens, R.S.; Gosbell, K.; Hassell, C.J.; Jessop, R.; Melville, D.S.; et al. Rapid Population Decline in Migratory Shorebirds Relying on Yellow Sea Tidal Mudflats as Stopover Sites. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, N.; Li, C.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Li, X. Comparison of the Gut Microbiota and Untargeted Gut Tissue Metabolome of Chinese Mitten Crabs (Eriocheir sinensis) with Different Shell Colors. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1218152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.A.; Hugenholtz, F.; Lahti, L.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M. Intestinal Microbiome Landscaping: Insight in Community Assemblage and Implications for Microbial Modulation Strategies. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Maccaferri, S.; Turroni, S.; Brigidi, P. Intestinal Microbiota Is a Plastic Factor Responding to Environmental Changes. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjani, A.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Gopinath, P.M. An Introduction to Actinobacteria. In Actinobacteria—Basics and Biotechnological Applications; Dhanasekaran, D., Jiang, Y., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2016; ISBN 978-953-51-2248-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Luan, X.; Lei, T.; Chen, L. Dysbiosis of Lower Respiratory Tract Microbiome Are Associated with Inflammation and Microbial Function Variety. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Nie, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Q.; Yan, X. Gradual Changes of Gut Microbiota in Weaned Miniature Piglets. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The First Microbial Colonizers of the Human Gut: Composition, Activities, and Health Implications of the Infant Gut Microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00036-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabucci, U.; Lacetera, N.; Baumgard, L.H.; Rhoads, R.P.; Ronchi, B.; Nardone, A. Metabolic and Hormonal Acclimation to Heat Stress in Domesticated Ruminants. Animal 2010, 4, 1167–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macke, E.; Tasiemski, A.; Massol, F.; Callens, M.; Decaestecker, E. Life History and Eco-Evolutionary Dynamics in Light of the Gut Microbiota. Oikos 2017, 126, 508–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, W.Z.; Burns, A.R.; Stagaman, K.; Wong, S.; Rawls, J.F.; Guillemin, K.; Bohannan, B.J.M. The Composition of the Zebrafish Intestinal Microbial Community Varies across Development. ISME J. 2016, 10, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorci, G.; Faivre, B. Environmental Conditions in Early Life, Host Defenses, and Disease in Late Life. In Development Strategies and Biodiversity: Darwinian Fitness and Evolution in the Anthropocene; Costantini, D., Marasco, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 127–160. ISBN 978-3-030-90131-8. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, C.; Jiang, M.; You, L.; Tan, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K. Variations and Potential Factors of Gut Prokaryotic Microbiome during Spawning Migration in Coilia Nasus. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2802–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Element, G.; Engel, K.; Neufeld, J.D.; Casselman, J.M.; Van Coeverden de Groot, P.J.; Walker, V.K. Distinct Intestinal Microbial Communities of Two Sympatric Anadromous Arctic Salmonids and the Effects of Migration and Feeding. Arct. Sci. 2021, 7, 634–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quercia, S.; Candela, M.; Giuliani, C.; Turroni, S.; Luiselli, D.; Rampelli, S.; Brigidi, P.; Franceschi, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Garagnani, P.; et al. From Lifetime to Evolution: Timescales of Human Gut Microbiota Adaptation. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Ley, R. The Human Gut Microbiome: Ecology and Recent Evolutionary Changes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, E.C.; Metcalfe, N.B.; Llewellyn, M.S. The Potential Role of the Gut Microbiota in Shaping Host Energetics and Metabolic Rate. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFall-Ngai, M.; Hadfield, M.G.; Bosch, T.C.G.; Carey, H.V.; Domazet-Lošo, T.; Douglas, A.E.; Dubilier, N.; Eberl, G.; Fukami, T.; Gilbert, S.F.; et al. Animals in a Bacterial World, a New Imperative for the Life Sciences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3229–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfken, A.; Song, B.; Allen, S.K.; Carnegie, R.B. Comparing Larval Microbiomes of the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) Raised in Different Hatcheries. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorgen-Ritchie, M.; Clarkson, M.; Chalmers, L.; Taylor, J.F.; Migaud, H.; Martin, S.A.M. A Temporally Dynamic Gut Microbiome in Atlantic Salmon during Freshwater Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) Production and Post-Seawater Transfer. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 711797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmiller, J.J.; Hamilton, M.J.; Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Environment Shapes the Fecal Microbiome of Invasive Carp Species. Microbiome 2016, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, D.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; You, Y. Change in the Intestinal Bacterial Community Structure Associated with Environmental Microorganisms during the Growth of Eriocheir sinensis. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.-X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Qin, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Qian, J.; et al. Root Microbiota Shift in Rice Correlates with Resident Time in the Field and Developmental Stage. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Ye, J.; Liu, S.; Chang, G.; Xu, H.; Lin, Z.; Xue, Q. Bacterial Community Dynamics in Kumamoto Oyster Crassostrea Sikamea Hatchery during Larval Development. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 933941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhrman, J.A. Microbial Community Structure and Its Functional Implications. Nature 2009, 459, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering Microbial Interactions and Detecting Keystone Species with Co-Occurrence Networks. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agler, M.T.; Ruhe, J.; Kroll, S.; Morhenn, C.; Kim, S.-T.; Weigel, D.; Kemen, E.M. Microbial Hub Taxa Link Host and Abiotic Factors to Plant Microbiome Variation. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Zhu, W.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Wang, J.; Yin, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Interactions and Stability of Gut Microbiota in Zebrafish Increase with Host Development. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01696-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, P.; Minoarivelo, H.O.; Brännström, Å.; Hui, C.; Dieckmann, U. Complexity and Stability of Ecological Networks: A Review of the Theory. Popul. Ecol. 2018, 60, 319–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, S.; Kaftan, F.; Lang, S.; Svatoš, A.; Germerodt, S.; Kost, C. Privatization of Cooperative Benefits Stabilizes Mutualistic Cross-Feeding Interactions in Spatially Structured Environments. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Luo, H.; Kumar, V.; Kajbaf, K.; Hu, Y.; Yang, G. Dysbiosis of Intestinal Microbiota Induced by Dietary Oxidized Fish Oil and Recovery of Diet-Induced Dysbiosis via Taurine Supplementation in Rice Field Eel (Monopterus albus). Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jian, S.Q.; Cao, H.; Wen, C.; Hu, B.; Peng, M.; Peng, L.; Yuan, J.; Liang, L. Changes in Microbiota along the Intestine of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Community, Interspecific Interactions, and Functions. Aquaculture 2019, 498, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Y. The Composition of Gut Microbiota Community Structure of Jankowski’s Bunting (Emberiza jankowskii). Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3731–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altizer, S.; Dobson, A.; Hosseini, P.; Hudson, P.; Pascual, M.; Rohani, P. Seasonality and the Dynamics of Infectious Diseases. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karl, J.P.; Hatch, A.M.; Arcidiacono, S.M.; Pearce, S.C.; Pantoja-Feliciano, I.G.; Doherty, L.A.; Soares, J.W. Effects of Psychological, Environmental and Physical Stressors on the Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Massana, R.; McMahon, K.D.; Walsh, D.A. Linking Metagenomics to Aquatic Microbial Ecology and Biogeochemical Cycles. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, S2–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phylum | Site | Time | Site × Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteobacteria | 0.06 | 0.46 | 0.05 |
| Actinobacteria | 0.05 | 3.12 * | 0.89 |
| Bacteroidetes | 0.31 | 4.04 * | 1.20 |
| Firmicutes | 4.88 ** | 3.43 * | 2.25 |
| Verrucomicrobia | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| Tenericutes | 5.01 ** | 1.44 | 2.89 * |
| Unassigned | 0.40 | 8.38 *** | 3.37 * |
| Acidobacteria | 0.27 | 1.46 | 1.31 |
| Deinococcus.Thermus | 0.30 | 3.29 * | 0.59 |
| Others | 0.74 | 2.89 * | 1.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, W.; Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Li, N.; Nie, X.; Gao, T. Early Succession of Community Structures and Biotic Interactions of Gut Microbes in Eriocheir sinensis Megalopa after Desalination. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030560
Xue W, Wu H, Wu X, Li N, Nie X, Gao T. Early Succession of Community Structures and Biotic Interactions of Gut Microbes in Eriocheir sinensis Megalopa after Desalination. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(3):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030560
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Wenlei, Hao Wu, Xinyu Wu, Nannan Li, Ximei Nie, and Tianheng Gao. 2024. "Early Succession of Community Structures and Biotic Interactions of Gut Microbes in Eriocheir sinensis Megalopa after Desalination" Microorganisms 12, no. 3: 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030560
APA StyleXue, W., Wu, H., Wu, X., Li, N., Nie, X., & Gao, T. (2024). Early Succession of Community Structures and Biotic Interactions of Gut Microbes in Eriocheir sinensis Megalopa after Desalination. Microorganisms, 12(3), 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030560





