Shark Microbiome Analysis Demonstrates Unique Microbial Communities in Two Distinct Mediterranean Sea Shark Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Statistical Analysis
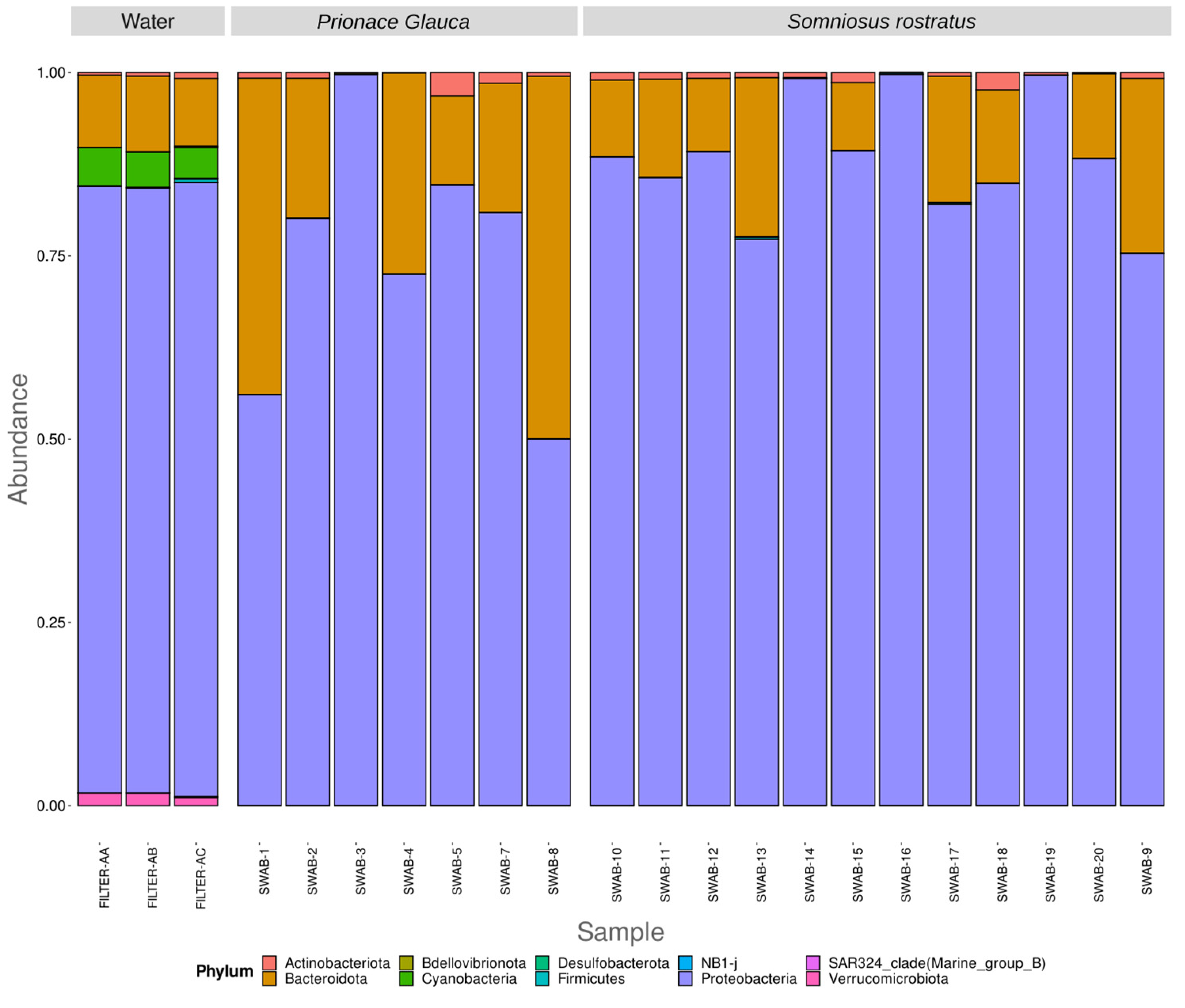
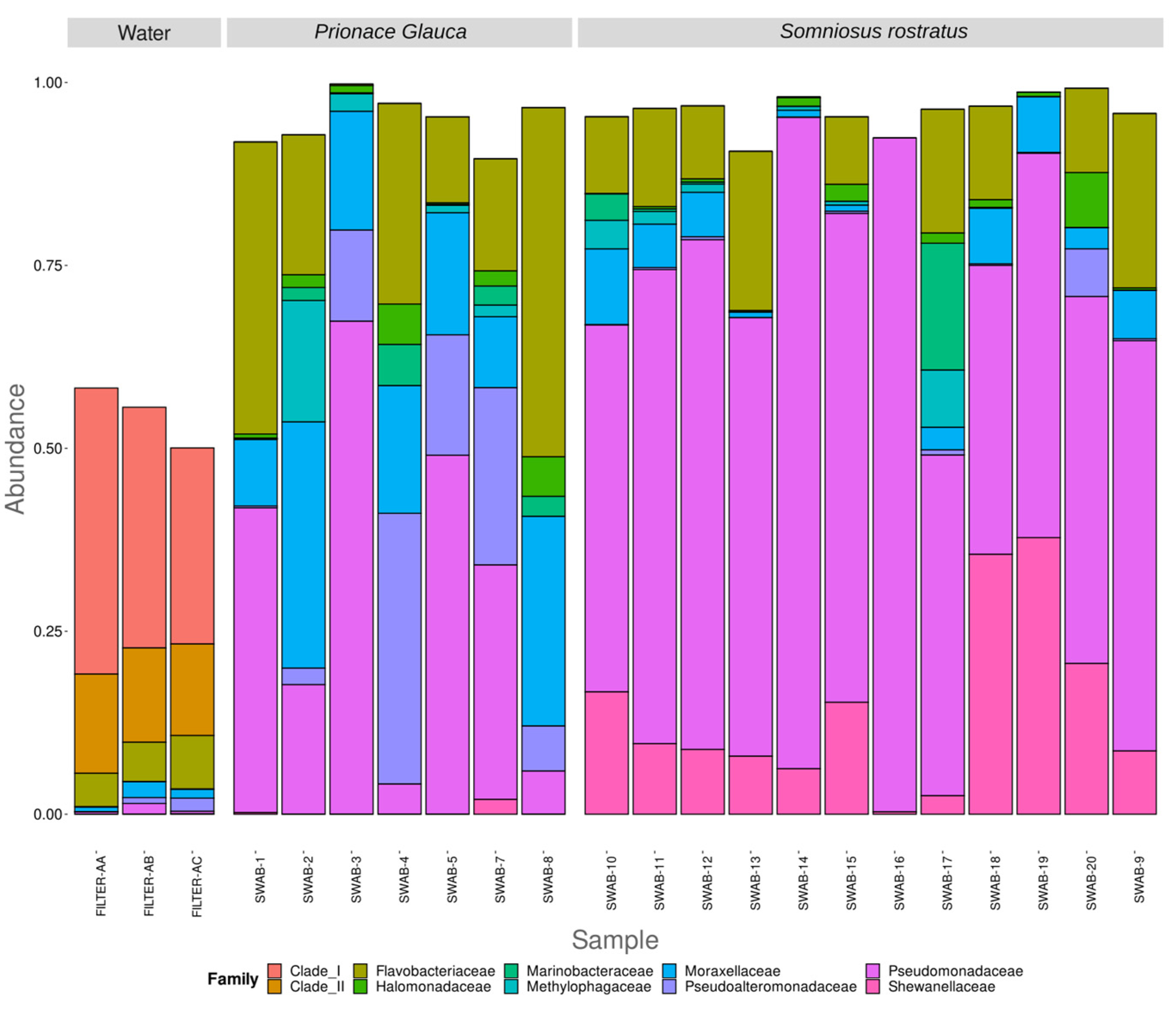
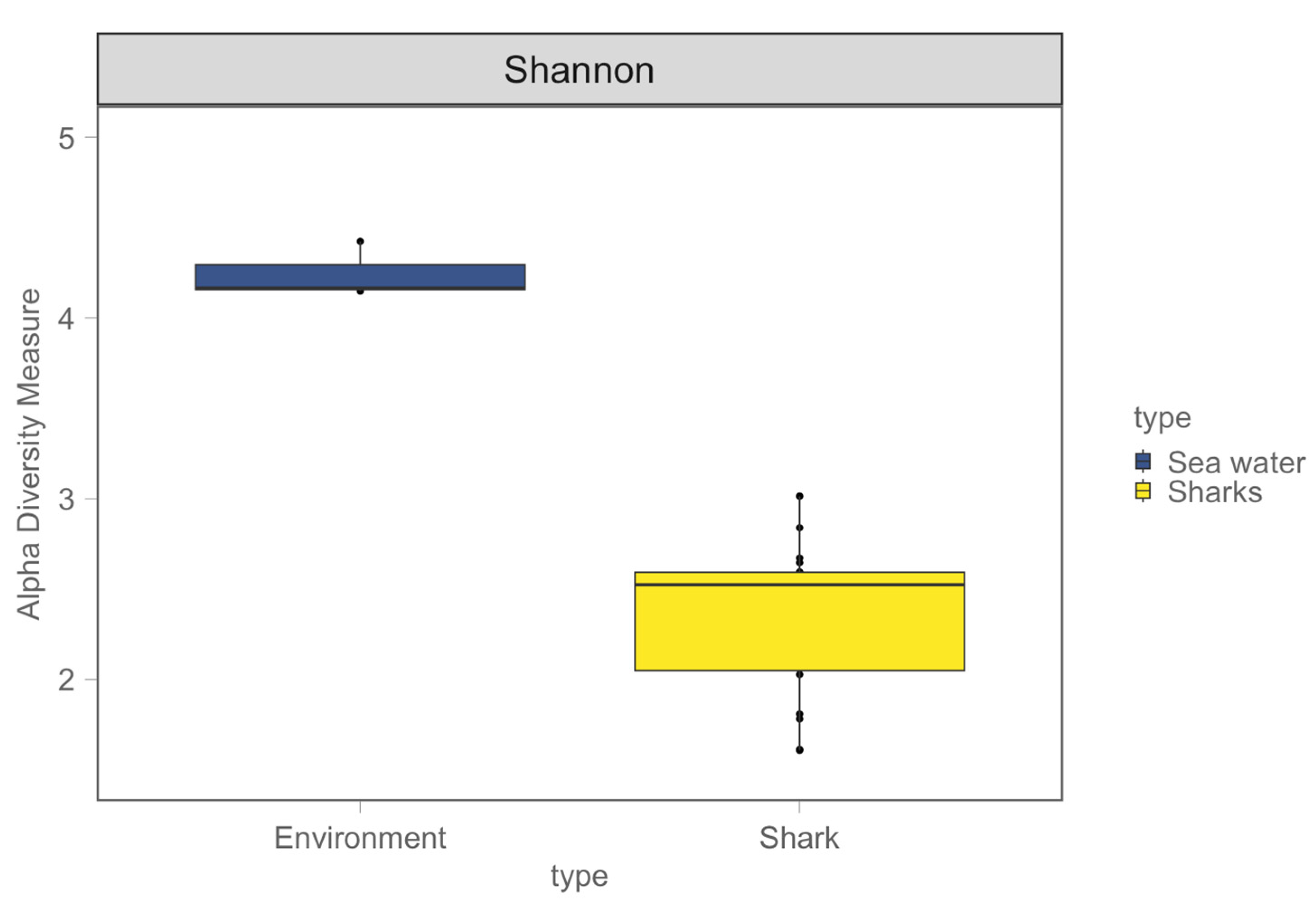
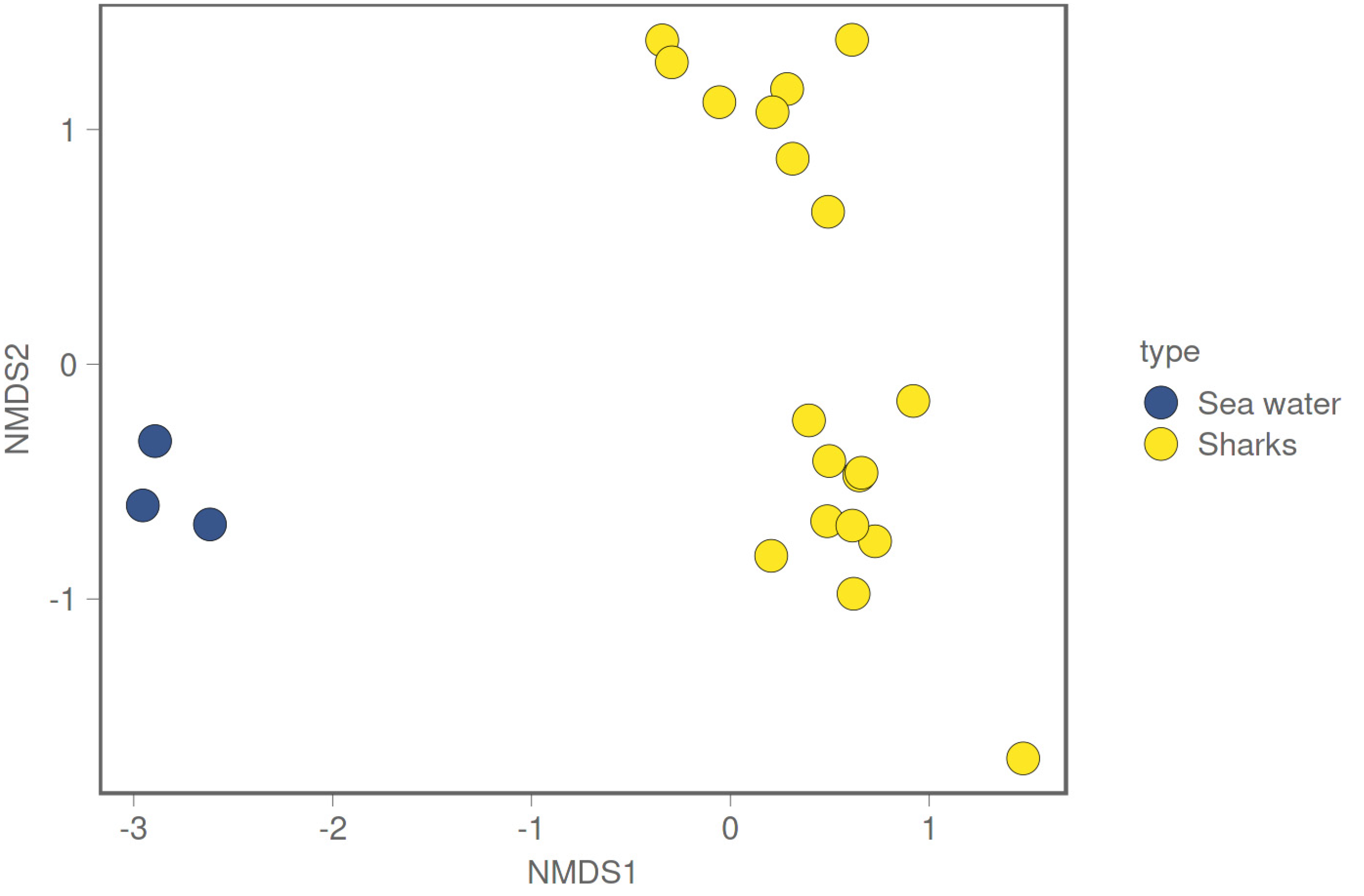
3. Results
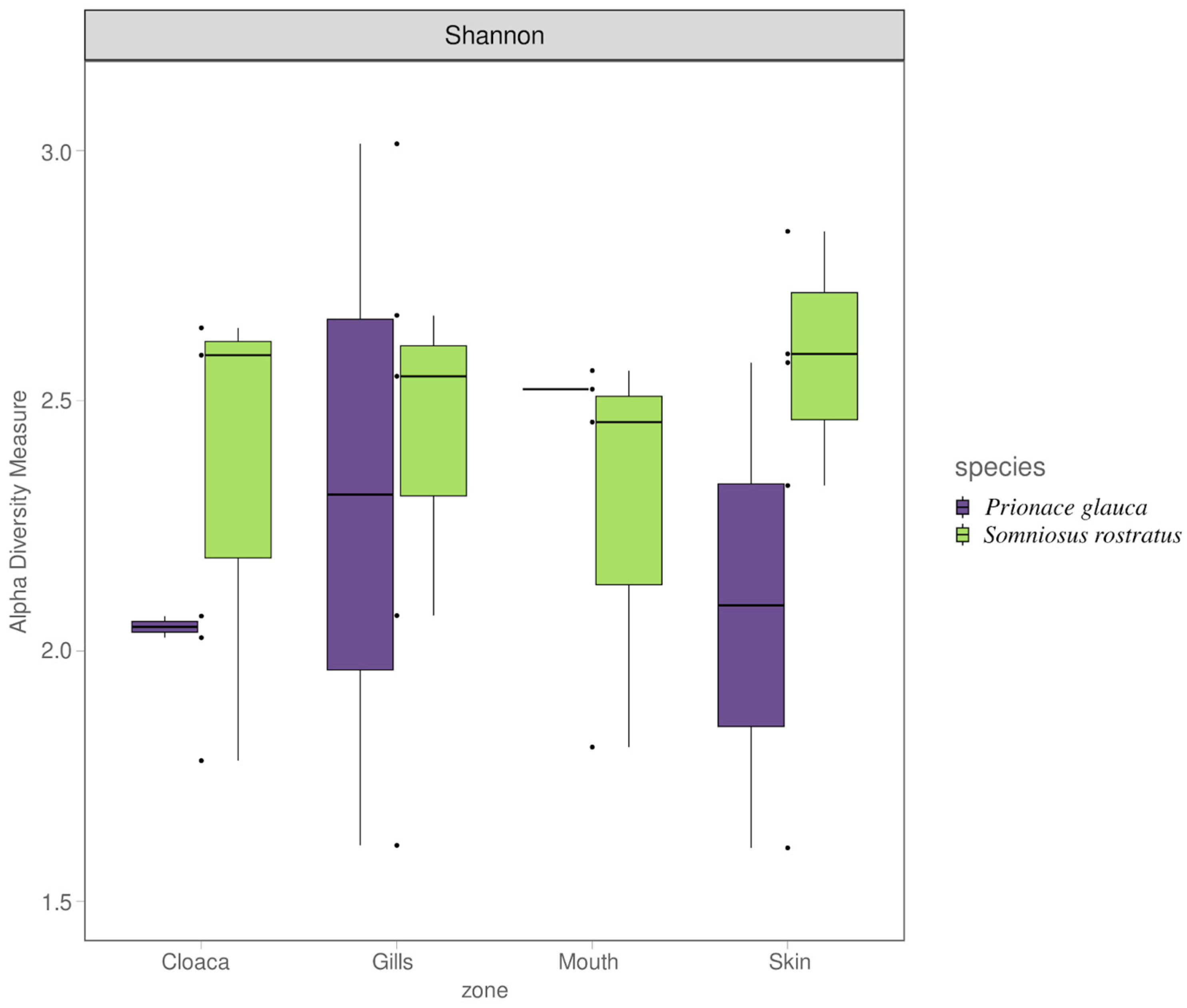
3.1. Shark and Seawater Microbial Community Diversity
3.2. Differences in Microbiome between Environmental and Biological Samples
3.3. Different Microbiomes between the Two Shark Species and between Anatomical Locations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Tarnecki, A.M.; Burgos, F.A.; Ray, C.L.; Arias, C.R. Fish intestinal microbiome: Diversity and symbiosis unravelled by metagenomics. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, M.P.; Haggerty, J.M.; Kacev, D.; Papudeshi, B.; Dinsdale, E.A. The skin microbiome of the common thresher shark (Alopias vulpinus) has low taxonomic and gene function β-diversity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2017, 9, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apprill, A. Marine Animal Microbiomes: Toward Understanding Host–Microbiome Interactions in a Changing Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullam, K.E.; Essinger, S.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; O’CONNOR, M.P.; Rosen, G.L.; Knight, R.O.; Kilham, S.S.; Russell, J.A. Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: A meta-analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3363–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerton, S.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The Gut Microbiota of Marine Fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 873. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00873 (accessed on 25 January 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limborg, M.T.; Heeb, P. Special Issue: Coevolution of Hosts and Their Microbiome. Genes 2018, 9, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Narala, S.; Chun, K.A.; Two, A.M.; Yun, T.; Shafiq, F.; Kotol, P.F.; Bouslimani, A.; Melnik, A.V.; et al. Antimicrobials from human skin commensal bacteria protect against Staphylococcus aureus and are deficient in atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Fenchel, T.; Delong, E.F. The Microbial Engines That Drive Earth’s Biogeochemical Cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, B.H.; Monticelli, M.; Leone, S.; Bastoni, D.; Barosa, B.; Cascone, M.; Migliaccio, F.; Montemagno, F.; Ricciardelli, A.; Tonietti, L.; et al. Oxidoreductases and metal cofactors in the functioning of the earth. Essays Biochem. 2023, 67, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. A new view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish: Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; Auguet, J.C.; Bettarel, Y.; Bouvier, C.; Claverie, T.; Graham, N.A.; Rieuvilleneuve, F.; Sucré, E.; Bouvier, T.; Villéger, S. Skin microbiome of coral reef fish is highly variable and driven by host phylogeny and diet. Microbiome 2018, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrifield, D.L.; Rodiles, A. 10—The fish microbiome and its interactions with mucosal tissues. In Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Beck, B.H., Peatman, E., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, K.L. Functions for fish mucus. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1994, 4, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, N.; MacKinnon, S. Comparison of Antimicrobial Activity in the Epidermal Mucus Extracts of Fish—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1096495908000298?casa_token=Td5OfcQLY_YAAAAA:ICFamUrprKjTNVY4003xoxMYkCul1W-jsL1cs9QutSPAKMwK0RGp_DIlEIZDwaFNk3G_sOnb (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Lokesh, J.; Kiron, V. Transition from freshwater to seawater reshapes the skin-associated microbiota of Atlantic salmon. Sci. Rep. 1994, 6, 19707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, A.; Tao, Z.; Bullard, S.; Arias, C. Diversity of the Skin Microbiota of Fishes: Evidence for Host Species Specificity|FEMS Microbiology Ecology|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/femsec/article/85/3/483/583834?login=true (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Black, C.; Merly, L.; Hammerschlag, N. Bacterial Communities in Multiple Tissues Across the Body Surface of Three Coastal Shark Species. Available online: https://zoolstud.sinica.edu.tw/Journals/60/60-0qqq.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Pogoreutz, C.; Gore, M.A.; Perna, G.; Millar, C.; Nestler, R.; Ormond, R.F.; Clarke, C.R.; Voolstra, C.R. Similar bacterial communities on healthy and injured skin of black tip reef sharks. Anim. Microbiome 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, M.P.; Johnson, C.J.; Johri, S.; Kerr, E.N.; Morris, M.M.; Desantiago, R.; Turnlund, A.C.; Goodman, A.; Mora, M.; Lima, L.F.; et al. The Epidermal Microbiome within An Aggregation of Leopard Sharks (Triakis semifasciata) Has Taxonomic Flexibility with Gene Functional Stability across Three Time-Points. Microb. Ecol. preprint. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storo, R.; Easson, C.; Shivji, M.; Lopez, J.V. Microbiome Analyses Demonstrate Specific Communities within Five Shark Species. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 605285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doane, M.P. Insights into the Shark “Holobiont” through the Skin Microbiome and Host Genetics. Ph.D. Thesis, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/docview/2090959929/abstract/118CC6EC20BA41E2PQ/1 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Giovannelli, D.; d’Errico, G.; Manini, E.; Yakimov, M.; Vetriani, C. Diversity and phylogenetic analyses of bacteria from a shallow-water hydrothermal vent in Milos island (Greece). Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolinesi, F.; Saggiomo, M.; Aceto, S.; Cordone, A.; Serino, E.; Valoroso, M.C.; Mangoni, O. On the Relationship between a Novel Prorocentrum sp. and Colonial Phaeocystis antarctica under Iron and Vitamin B12 Limitation: Ecological Implications for Antarctic Waters. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullis, K.; Faloona, F.; Scharf, S.; Saiki, R.; Horn, G.; Erlich, H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: The polymerase chain reaction. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 51, Pt 1. [Google Scholar]
- Quattro, J.M.; Stoner, D.S.; Driggers, W.B.; Anderson, C.A.; Priede, K.A.; Hoppmann, E.C.; Campbell, N.H.; Duncan, K.M.; Grady, J.M. Genetic evidence of cryptic speciation within hammerhead sharks (Genus sphyrna). Mar. Biol. 2006, 148, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonero, D.S.; Grady, J.M.; Priede, K.A.; Quattro, J.M. Amplification primers for the mitochondrial control region and sixth intron of the nuclear-encoded lactate dehydrogenase A gene in elasmobranch fishes. Conserv. Genet. 2003, 4, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Zemlak, T.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Hebert, P.D.N. Universal primer cocktails for fish DNA barcoding: Barcoding. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, E.; Menale, B.; Innangi, M.; Santangelo, A.; Strumia, S.; De Castro, O. An extreme environment drives local adaptation of Genista tinctoria (Fabaceae) from the Mefite (Ansanto Valley, southern Italy). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2023, 202, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0061217 (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Cordone, A.; Selci, M.; Barosa, B.; Bastianoni, A.; Bastoni, D.; Bolinesi, F.; Capuozzo, R.; Cascone, M.; Correggia, M.; Corso, D.; et al. Surface Bacterioplankton Community Structure Crossing the Antarctic Circumpolar Current Fronts. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordone, A.; D’Errico, G.; Magliulo, M.; Bolinesi, F.; Selci, M.; Basili, M.; de Marco, R.; Saggiomo, M.; Rivaro, P.; Giovannelli, D.; et al. Bacterioplankton Diversity and Distribution in Relation to Phytoplankton Community Structure in the Ross Sea Surface Waters. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 722900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package 2022. Available online: https://github.com/vegandevs/vegan (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Karns, R.C. Microbial Community Richness Distinguishes Shark Species Microbiomes in South Florida. Nova Southeastern University: Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 2017; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, N.; Rogers, T.; Acevedo-Whitehouse, K.; Brown, M.V. Temporal stability and species specificity in bacteria associated with the bottlenose dolphins respiratory system. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2012, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; Villéger, S.; Bouvier, C.; Auguet, J.C.; Bouvier, T. Captive bottlenose dolphins and killer whales harbor a species-specific skin microbiota that varies among individuals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, L.L.; Easson, C.; Baker, L.J.; Fenolio, D.; Sutton, T.T.; Khan, Y.; Blackwelder, P.; Hendry, T.A.; Lopez, J.V. Characterization of the microbiome and bioluminescent symbionts across life stages of Ceratioid Anglerfishes of the Gulf of Mexico. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthey, A.J.R.; Blumstein, D.T.; Gallagher, R.V.; Tetu, S.G.; Gillings, M.R. Conserving the holobiont. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Loos, L.M.; Eriksson, B.K.; Salles, J.F. The Macroalgal Holobiont in a Changing Sea. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.T.; Smith, K.F.; Melvin, D.W.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Community assembly of a euryhaline fish microbiome during salinity acclimation. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2537–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.F.; Weissman, M.; Reed, M.; Papudeshi, B.; Alker, A.T.; Morris, M.M.; Edwards, R.A.; de Putron, S.J.; Vaidya, N.K.; Dinsdale, E.A. Modeling of the Coral Microbiome: The Influence of Temperature and Microbial Network. mBio 2020, 11, e02691-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadas, N.; Baquiran, J.I.P.; Nada, M.A.L.; Kelly, M.; Conaco, C. Microbiome diversity and host immune functions influence survivorship of sponge holobionts under future ocean conditions. ISME J. 2022, 16, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quoy, J.R.C.; Gaimard, P. Zoologie; Imprimerie Royale: Paris, France, 1824. [Google Scholar]
- Irmak, E.; Özden, U. A rare shark for the Mediterranean: Somniosus rostratus (Risso, 1827) (Chondrichthyes: Somniosidae) from the coast of Turkey. Zool. Middle East 2021, 67, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D. Sharks of the Open Ocean: Biology, Fisheries and Conservation: Book Review. Fish Fish. 2010, 11, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.T.; Pratte, Z.A.; Clavere-Graciette, A.; Ritchie, K.B.; Hueter, R.E.; Newton, A.L.; Fischer, G.C.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Doane, M.P.; Wilkinson, K.A.; et al. Elasmobranch microbiomes: Emerging patterns and implications for host health and ecology. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierlich, K.; Miller, C.; Deforce, E.; Friedlaender, A.; Johnston, D.; Apprill, A. Temporal and regional variability in the skin microbiome of humpback whales along the western Antarctic peninsula. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 84, e02574-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinta, T.; Kogovšek, T.; Klun, K.; Malej, A.; Herndl, G.J.; Turk, V. Jellyfish-Associated Microbiome in the Marine Environment: Exploring Its Biotechnological Potential. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardet, J.-F.; Nakagawa, Y. An Introduction to the Family Flavobacteriaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Volume 7: Proteobacteria: Delta, Epsilon Subclass; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 455–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banning, E.C.; Casciotti, K.L.; Kujawinski, E.B. Novel strains isolated from a coastal aquifer suggest a predatory role for flavobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 73, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Kwon, K.K.; Yang, S.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Chung, K.H.; Kim, S.-J. Lacinutrix algicola sp. nov. and Lacinutrix mariniflava sp. nov., two novel marine alga-associated bacteria and emended description of the genus Lacinutrix. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2008, 58, 2694–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, T.N.R.; Prasad, S.; Manasa, P.; Sailaja, B.; Begum, Z.; Shivaji, S. Lacinutrix himadriensis sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium isolated from a marine sediment, and emended description of the genus Lacinutrix. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregman, G.; Lalzar, M.; Livne, L.; Bigal, E.; Zemah-Shamir, Z.; Morick, D.; Tchernov, D.; Scheinin, A.; Meron, D. Preliminary study of shark microbiota at a unique mix-species shark aggregation site, in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1027804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, S.; Galeano, A.M.; Lozano, J.D.; Vives, M. Description of the microbiota in epidermal mucus and skin of sharks (Ginglymostoma cirratum and Negaprion brevirostris) and one stingray (Hypanus americanus). PeerJ 2020, 8, e10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, C.; Kjelleberg, S. Marine Pseudoalteromonas species are associated with higher organisms and produce biologically active extracellular agents. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, A.; Egan, S.; Holmström, C.; James, S.; Lappin-Scott, H.; Kjelleberg, S. Inhibition of Fungal Colonization by Pseudoalteromonas tunicata Provides a Competitive Advantage during Surface Colonization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6079–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offret, C.; Desriac, F.; Le Chevalier, P.; Mounier, J.; Jégou, C.; Fleury, Y. Spotlight on Antimicrobial Metabolites from the Marine Bacteria Pseudoalteromonas: Chemodiversity and Ecological Significance. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juni, E. The Genus Psychrobacter. In The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria: Ecophysiology, Isolation, Identification, Applications; Balows, A., Trüper, H.G., Dworkin, M., Harder, W., Schleifer, K.-H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 3241–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, N.; Calado, R.; Duarte, L.N.; Manco, S.C.; Fernandes, F.J.; Polonia, A.R.; Cleary, D.F.; Gomes, N.C. Molecular Analysis of Skin Bacterial Assemblages from Codfish and Pollock after Dry-Salted Fish Production. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apprill, A.; Robbins, J.; Eren, A.M.; Pack, A.A.; Reveillaud, J.; Mattila, D.; Moore, M.; Niemeyer, M.; Moore, K.M.; Mincer, T.J. Humpback Whale Populations Share a Core Skin Bacterial Community: Towards a Health Index for Marine Mammals? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanczyk, H.; Ast, J.C.; Dunlap, P.V. Phylogeny, genomics, and symbiosis of Photobacterium. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiah, N.; Chandramohan, D. Occurrence of Photobacterium Leiognathi, as the Bait Organ Symbiont in Frogfish Antennarius Hispidus; NISCAIR-CSIR: New Delhi, India, 1992; Available online: http://nopr.niscpr.res.in/handle/123456789/38100 (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Buck, J.D. Potentially Pathogenic Marine Vibrio Species in Seawater and Marine Animals in the Sarasota, Florida, Area. J. Coast. Res. 1990, 6, 943–948. [Google Scholar]
- Terceti, M.S.; Ogut, H.; Osorio, C.R. Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae, an Emerging Fish Pathogen in the Black Sea: Evidence of a Multiclonal Origin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3736–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.J.; Brayton, P.; Colwell, R.R.; Gruber, S.H. Vibrios as Autochthonous Flora of Neritic Sharks. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1985, 6, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juste-Poinapen, N.M.S.; Yang, L.; Ferreira, M.; Poinapen, J.; Rico, C. Community profiling of the intestinal microbial community of juvenile Hammerhead Sharks (Sphyrna lewini) from the Rewa Delta, Fiji. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, S.C.; Papastamatiou, Y.P.; German, D.P. Gut microbial diversity and digestive function of an omnivorous shark. Mar. Biol. 2021, 168, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, C.; Ransom, B.; Bano, N.; Hollibaugh, J. Comparison of the gut microbiomes of 12 bony fish and 3 shark species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 518, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Code | Individual | Species | Length (cm) | Weight (kg) | Water Temp (°C) | Air Temp | Sex | Type | Month | Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FILTER-AA | ind_01 | - | NA | NA | 27 °C | 34 °C | - | Environment | Aug | Water |
| FILTER-AB | ind_02 | - | NA | NA | 26 °C | 30 °C | - | Environment | Sept | Water |
| FILTER-AC | ind_03/ ind_04 | - | NA | NA | 28 °C | 28 °C | - | Environment | Sept | Water |
| FILTER-AD | ind_05 | - | NA | NA | 28 °C | 26 °C | Environment | Sept | Water | |
| SWAB-1 | ind_01 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4 kg | 27 °C | 34 °C | F | Shark | Aug | Skin |
| SWAB-10 | ind_03 | Somniosus rostratus | 100 cm | 500 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Mouth |
| SWAB-11 | ind_03 | Somniosus rostratus | 100 cm | 500 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Gills |
| SWAB-12 | ind_03 | Somniosus rostratus | 100 cm | 500 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Cloaca |
| SWAB-13 | ind_04 | Somniosus rostratus | 110 cm | 600 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Skin |
| SWAB-14 | ind_04 | Somniosus rostratus | 110 cm | 600 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Mouth |
| SWAB-15 | ind_04 | Somniosus rostratus | 110 cm | 600 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Gills |
| SWAB-16 | ind_04 | Somniosus rostratus | 110 cm | 600 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Cloaca |
| SWAB-17 | ind_05 | Somniosus rostratus | 120 cm | 700 g | 28 °C | 25 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Skin |
| SWAB-18 | ind_05 | Somniosus rostratus | 120 cm | 700 g | 28 °C | 25 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Mouth |
| SWAB-19 | ind_05 | Somniosus rostratus | 120 cm | 700 g | 28 °C | 25 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Gills |
| SWAB-2 | ind_01 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4kg | 27 °C | 34 °C | F | Shark | Aug | Mouth |
| SWAB-20 | ind_05 | Somniosus rostratus | 120 cm | 700g | 28 °C | 25 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Cloaca |
| SWAB-3 | ind_01 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4 kg | 27 °C | 34 °C | F | Shark | Aug | Gills |
| SWAB-4 | ind_01 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4 kg | 27 °C | 34 °C | F | Shark | Aug | Cloaca |
| SWAB-5 | ind_02 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4 kg | 26 °C | 30 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Skin |
| SWAB-6 | ind_02 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4 kg | 26 °C | 30 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Mouth |
| SWAB-7 | ind_02 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4 kg | 26 °C | 30 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Gills |
| SWAB-8 | ind_02 | Prionace glauca | 100 cm | 4 kg | 26 °C | 30 °C | M | Shark | Sept | Cloaca |
| SWAB-9 | ind_03 | Somniosus rostratus | 100 cm | 500 g | 28 °C | 28 °C | F | Shark | Sept | Skin |
| Sample | Input | Filtered | Merged | ASVs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FILTER-AA | 112,008 | 101,664 | 99,887 | 85,808 |
| FILTER-AB | 69,153 | 62,781 | 61,682 | 53,766 |
| FILTER-AC | 19,029 | 17,085 | 16,396 | 13,940 |
| SWAB-1 | 63,583 | 58,098 | 57,240 | 45,926 |
| SWAB-10 | 70,926 | 64,838 | 64,219 | 49,732 |
| SWAB-11 | 58,219 | 52,296 | 51,836 | 45,801 |
| SWAB-12 | 99,394 | 90,943 | 90,022 | 69,005 |
| SWAB-13 | 131,764 | 121,383 | 120,551 | 101,330 |
| SWAB-14 | 106,950 | 97,336 | 96,756 | 80,236 |
| SWAB-15 | 85,444 | 78,023 | 77,420 | 61,340 |
| SWAB-16 | 39,479 | 36,021 | 35,781 | 34,578 |
| SWAB-17 | 58,712 | 54,295 | 53,275 | 43,558 |
| SWAB-18 | 77,510 | 71,540 | 70,959 | 60,912 |
| SWAB-19 | 73,355 | 68,062 | 67,751 | 64,847 |
| SWAB-2 | 59,285 | 54,880 | 54,104 | 41,789 |
| SWAB-20 | 111,213 | 103,042 | 101,995 | 76,030 |
| SWAB-3 | 47,398 | 43,992 | 43,627 | 37,508 |
| SWAB-4 | 78,454 | 73,440 | 72,583 | 61,472 |
| SWAB-5 | 70,298 | 65,096 | 64,539 | 58,471 |
| SWAB-7 | 67,555 | 61,574 | 60,268 | 36,328 |
| SWAB-8 | 35,618 | 33,178 | 32,551 | 27,185 |
| SWAB-9 | 42,449 | 38,695 | 38,277 | 28,961 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montemagno, F.; Romano, C.; Bastoni, D.; Cordone, A.; De Castro, O.; Stefanni, S.; Sperone, E.; Giovannelli, D. Shark Microbiome Analysis Demonstrates Unique Microbial Communities in Two Distinct Mediterranean Sea Shark Species. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030557
Montemagno F, Romano C, Bastoni D, Cordone A, De Castro O, Stefanni S, Sperone E, Giovannelli D. Shark Microbiome Analysis Demonstrates Unique Microbial Communities in Two Distinct Mediterranean Sea Shark Species. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(3):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030557
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontemagno, Francesco, Chiara Romano, Deborah Bastoni, Angelina Cordone, Olga De Castro, Sergio Stefanni, Emilio Sperone, and Donato Giovannelli. 2024. "Shark Microbiome Analysis Demonstrates Unique Microbial Communities in Two Distinct Mediterranean Sea Shark Species" Microorganisms 12, no. 3: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030557
APA StyleMontemagno, F., Romano, C., Bastoni, D., Cordone, A., De Castro, O., Stefanni, S., Sperone, E., & Giovannelli, D. (2024). Shark Microbiome Analysis Demonstrates Unique Microbial Communities in Two Distinct Mediterranean Sea Shark Species. Microorganisms, 12(3), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030557







