Antigenic Imprinting Dominates Humoral Responses to New Variants of SARS-CoV-2 in a Hamster Model of COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and Vaccines
2.2. Cells
2.3. Animals
2.4. Syrian Golden Hamster SARS-CoV-2 Infection Model
2.5. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Detection with Mono8 Cells
2.6. Serum Neutralization Test
2.7. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
2.8. Endpoint Titrations
2.9. Antigenic Cartography
2.10. Histology
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
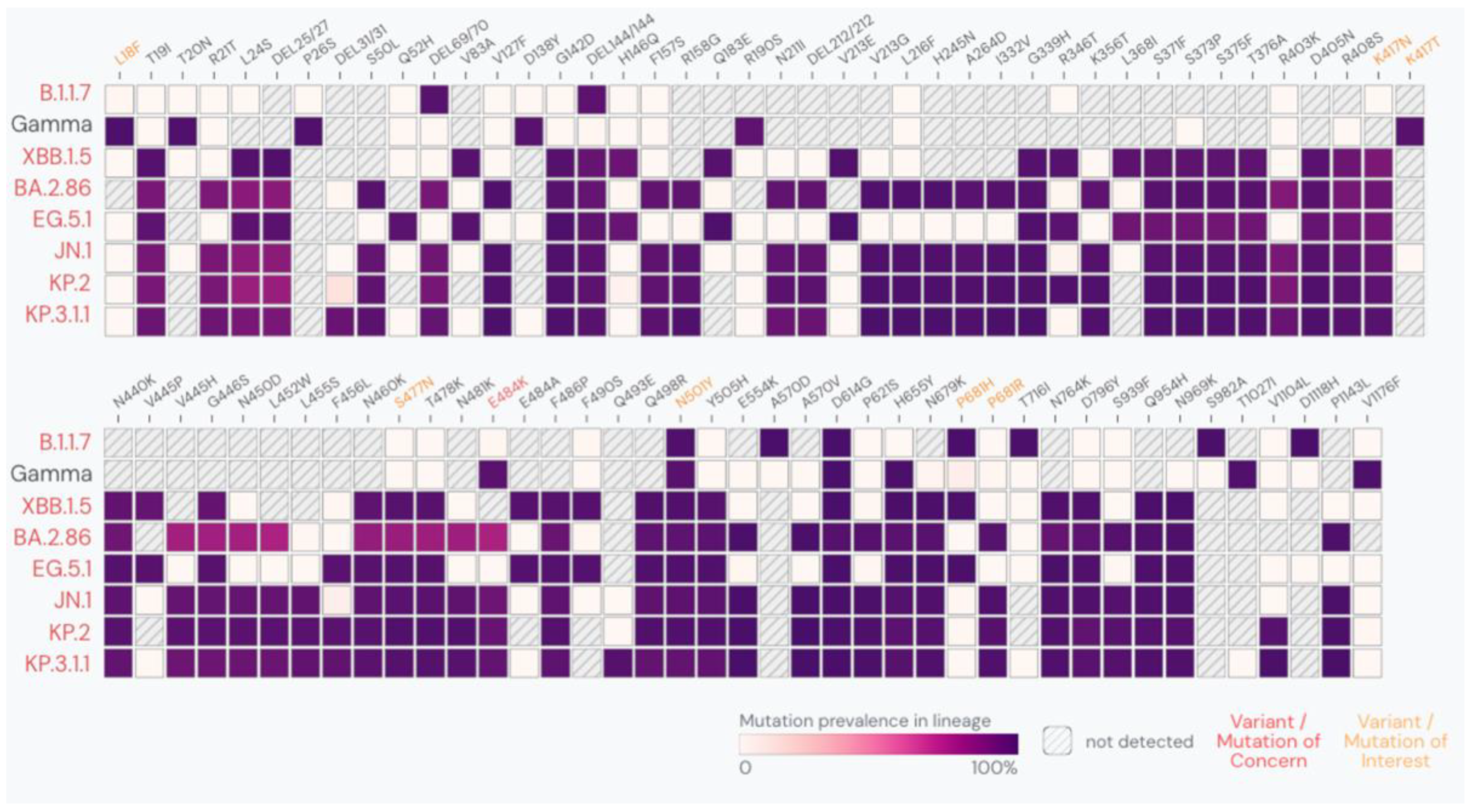
3.1. Evaluation of Vaccine Efficacy of Comirnaty® XBB.1.5 Against EG.5.1
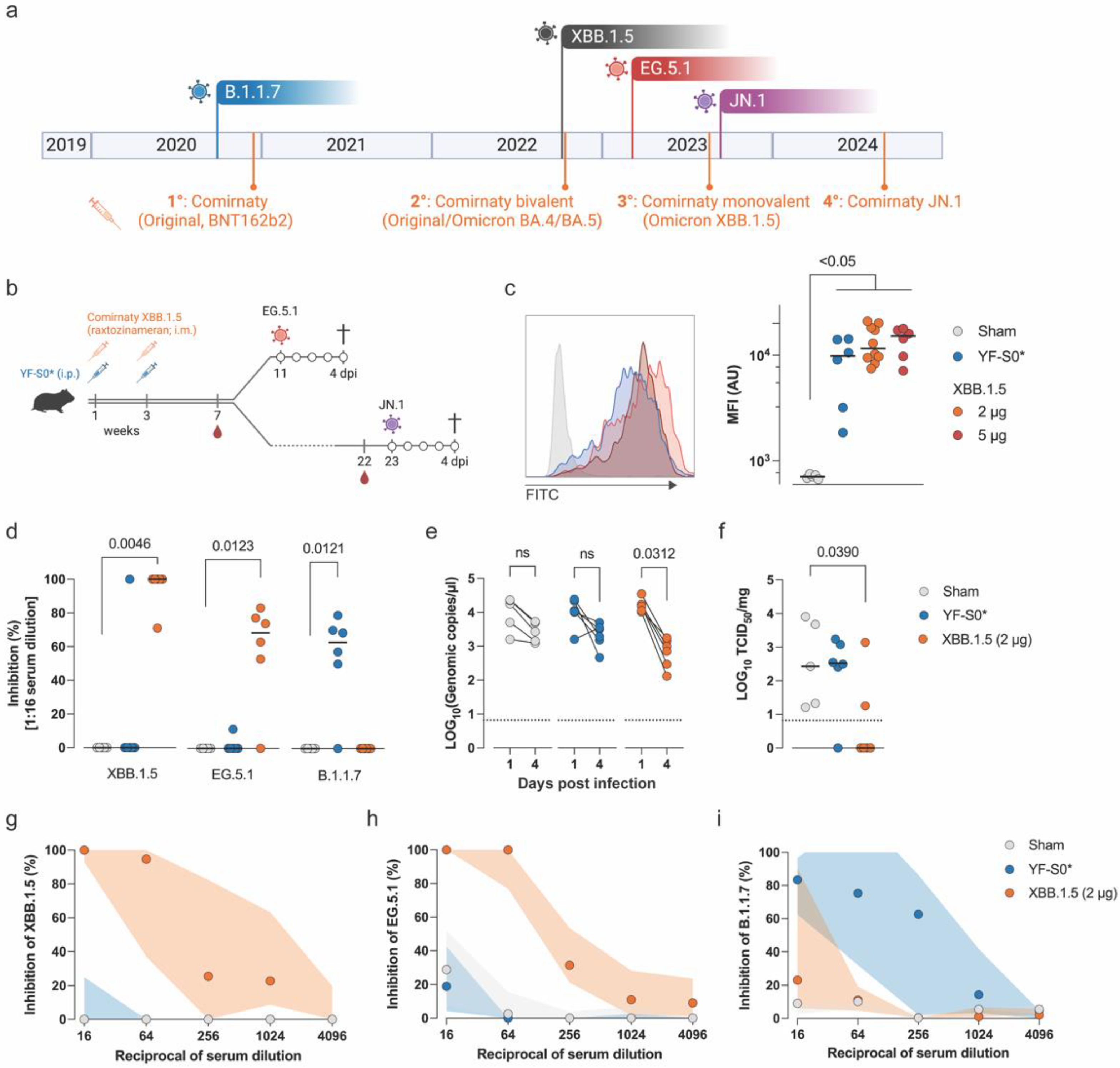
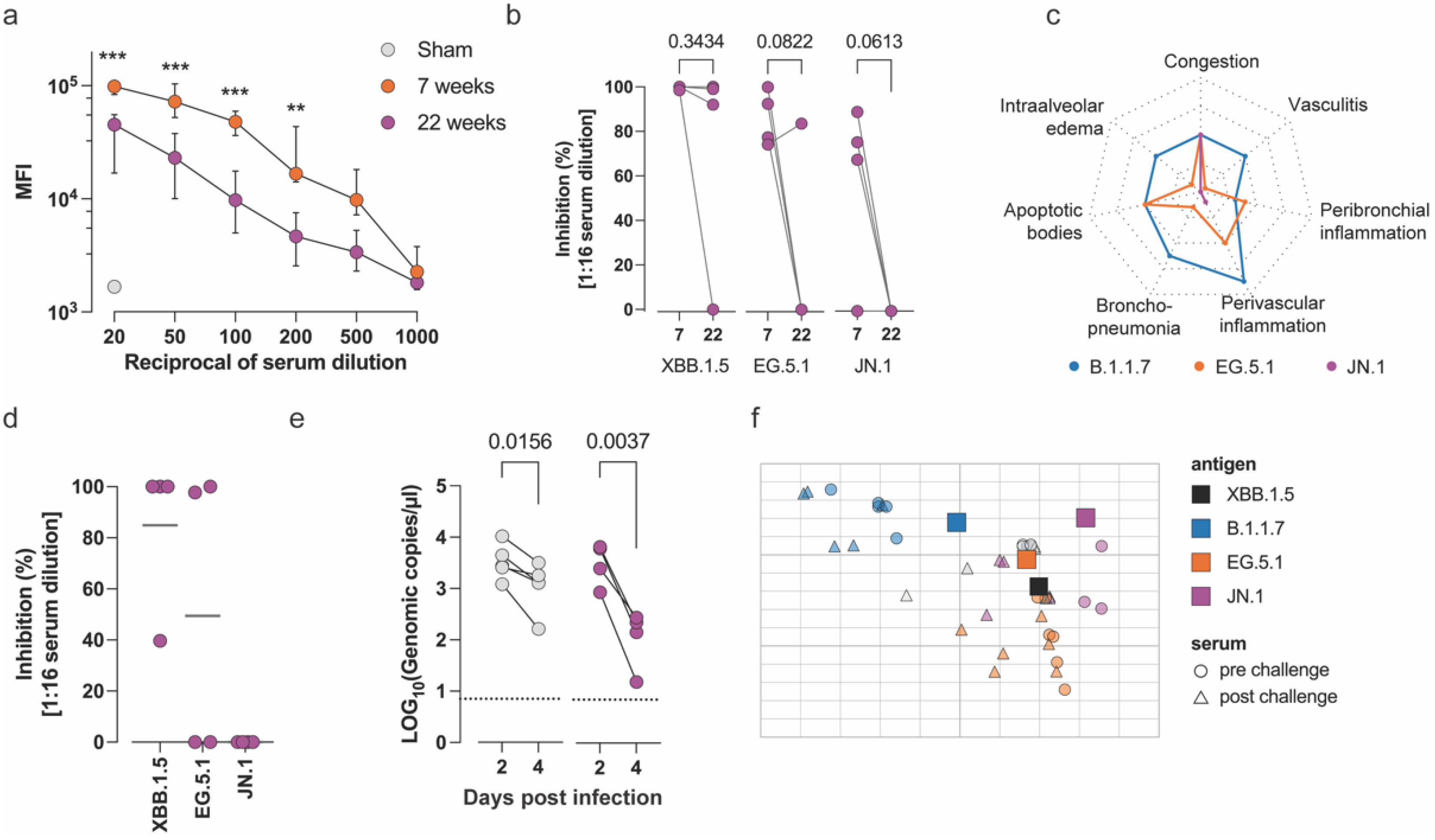
3.2. Evaluation of the Long-Term Efficacy of Comirnaty® XBB.1.5 Against Antigenically Distant Variants
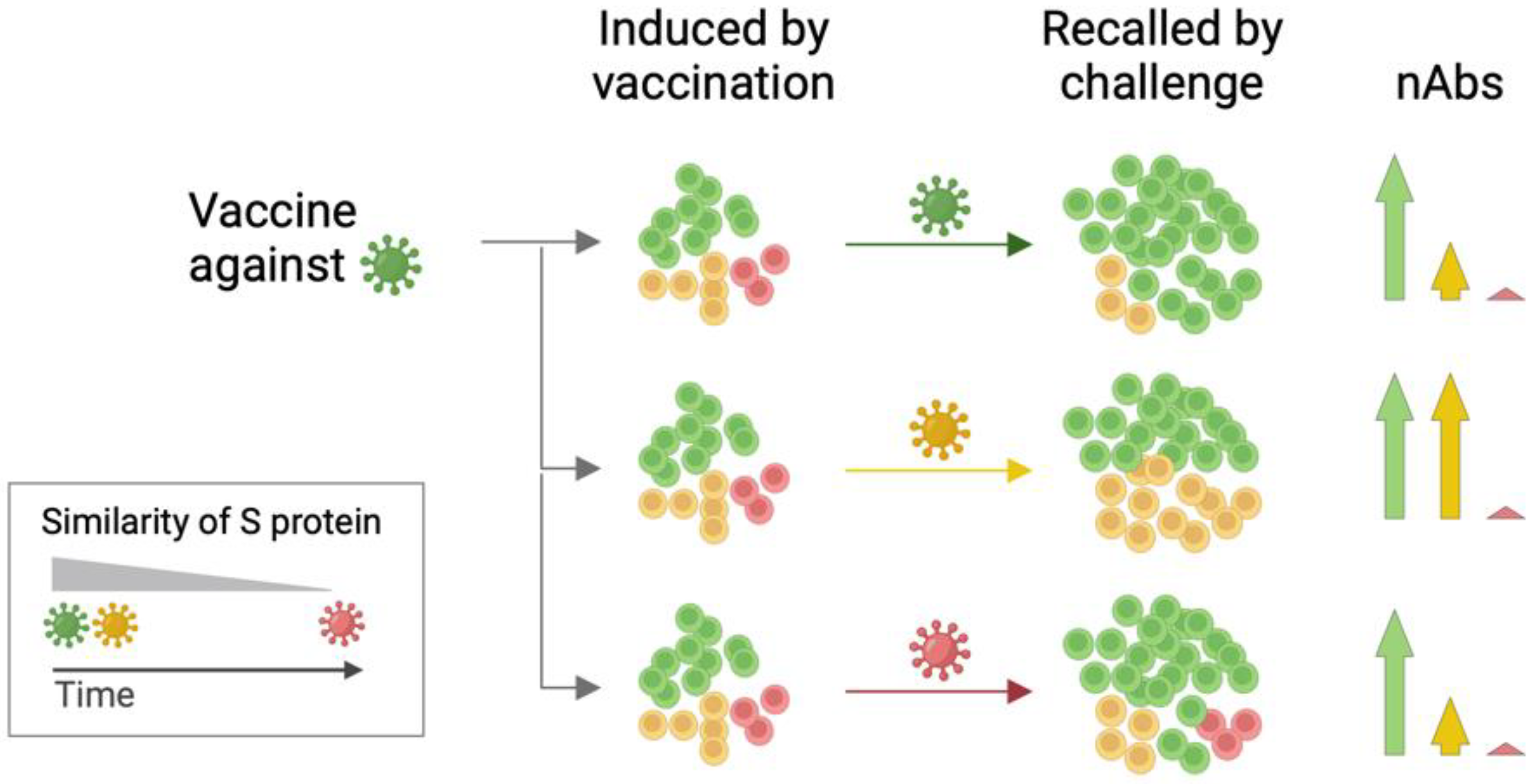
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steiner, S.; Kratzel, A.; Barut, G.T.; Lang, R.M.; Aguiar Moreira, E.; Thomann, L.; Kelly, J.N.; Thiel, V. SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Masum, M.H.U.; Wajed, S.; Talukder, A. A comprehensive review on COVID-19 vaccines: Development, effectiveness, adverse effects, distribution and challenges. Virusdisease 2022, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.; Sohrabi, M.R.; Zali, A.R.; Hannani, K. Five consecutive epidemiological waves of COVID-19: A population-based cross-sectional study on characteristics, policies, and health outcome. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayawi, K.; Shahriar, S.; Serhani, M.A.; Alashwal, H.; Masud, M.M. Vaccine versus Variants (3Vs): Are the COVID-19 Vaccines Effective against the Variants? A Systematic Review. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Staropoli, I.; Michel, V.; Lemoine, F.; Donati, F.; Prot, M.; Porrot, F.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Jeyarajah, B.; Brisebarre, A.; et al. Distinct evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB and BA.2.86/JN.1 lineages combining increased fitness and antibody evasion. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jian, F.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e70–e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, Y.; Okumura, K.; Padilla-Blanco, M.; Kosugi, Y.; Uriu, K.; Hinay, A.A., Jr.; Chen, L.; Plianchaisuk, A.; Kobiyama, K.; Ishii, K.J.; et al. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 variant. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, T.S.; Li, S.H.; Painter, M.M.; Atkinson, R.K.; Douek, N.R.; Reeg, D.B.; Douek, D.C.; Wherry, E.J.; Hensley, S.E. Immunological imprinting shapes the specificity of human antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Behrens, G.M.N.; Arora, P.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Cossmann, A.; Manthey, L.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Pohlmann, S. Effect of hybrid immunity and bivalent booster vaccination on omicron sublineage neutralisation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, E.J.; Wu, M.Y.; Gahir, J.; Harvey, R.; Townsley, H.; Bailey, C.; Fowler, A.S.; Dowgier, G.; Hobbs, A.; Herman, L.; et al. Neutralising immunity to omicron sublineages BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.5 in healthy adults is boosted by bivalent BA.1-containing mRNA vaccination and previous Omicron infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.Y.; Xu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zeng, D.; Sunny, S.K.; Moore, Z. Durability of Bivalent Boosters against Omicron Subvariants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1818–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Xu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zeng, D.; Wheeler, B.; Young, H.; Sunny, S.K.; Moore, Z. Effectiveness of Bivalent Boosters against Severe Omicron Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, N.K.; Burke, P.C.; Nowacki, A.S.; Simon, J.F.; Hagen, A.; Gordon, S.M. Effectiveness of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Bivalent Vaccine. Open Forum Infect Dis 2023, 10, ofad209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.Y.; Chiew, C.J.; Pang, D.; Lee, V.J.; Ong, B.; Lye, D.C.; Tan, K.B. Protective immunity of SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccines against medically attended symptomatic omicron BA.4, BA.5, and XBB reinfections in Singapore: A national cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.Y.; Chiew, C.J.; Pang, D.; Lee, V.J.; Ong, B.; Wang, L.F.; Ren, E.C.; Lye, D.C.; Tan, K.B. Effectiveness of bivalent mRNA vaccines against medically attended symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19-related hospital admission among SARS-CoV-2-naive and previously infected individuals: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286 e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltseva, M.; Keeshan, A.; Cooper, C.; Langlois, M.A. Immune imprinting: The persisting influence of the first antigenic encounter with rapidly evolving viruses. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2024, 20, 2384192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torresi, J.; Edeling, M.A. Immune imprinting of SARS-CoV-2 responses: Changing first immune impressions. mSphere 2024, 9, e0075823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Bretones, M.; Fouchier, R.A.; Koopmans, M.P.; van Nierop, G.P. Impact of antigenic evolution and original antigenic sin on SARS-CoV-2 immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e162192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Felipe, L.; Vercruysse, T.; Sharma, S.; Ma, J.; Lemmens, V.; Van Looveren, D.; Arkalagud Javarappa, M.P.; Boudewijns, R.; Malengier-Devlies, B.; Liesenborghs, L.; et al. A single-dose live-attenuated YF17D-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate. Nature 2021, 590, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Vercruysse, T.; Sanchez-Felipe, L.; Kerstens, W.; Rasulova, M.; Bervoets, L.; De Keyzer, C.; Abdelnabi, R.; Foo, C.S.; Lemmens, V.; et al. Updated vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron (B.1.1.529) and prevents transmission in hamsters. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.B.; Kanevsky, I.; Che, Y.; Swanson, K.A.; Muik, A.; Vormehr, M.; Kranz, L.M.; Walzer, K.C.; Hein, S.; Guler, A.; et al. BNT162b vaccines protect rhesus macaques from SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 592, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouailles, G.; Adler, J.M.; Pennitz, P.; Peidli, S.; Teixeira Alves, L.G.; Baumgardt, M.; Bushe, J.; Voss, A.; Langenhagen, A.; Langner, C.; et al. Live-attenuated vaccine sCPD9 elicits superior mucosal and systemic immunity to SARS-CoV-2 variants in hamsters. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudewijns, R.; Thibaut, H.J.; Kaptein, S.J.F.; Li, R.; Vergote, V.; Seldeslachts, L.; Van Weyenbergh, J.; De Keyzer, C.; Bervoets, L.; Sharma, S.; et al. STAT2 signaling restricts viral dissemination but drives severe pneumonia in SARS-CoV-2 infected hamsters. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Lapedes, A.S.; de Jong, J.C.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Mapping the antigenic and genetic evolution of influenza virus. Science 2004, 305, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykytyn, A.Z.; Rissmann, M.; Kok, A.; Rosu, M.E.; Schipper, D.; Breugem, T.I.; van den Doel, P.B.; Chandler, F.; Bestebroer, T.; de Wit, M.; et al. Antigenic cartography of SARS-CoV-2 reveals that Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 are antigenically distinct. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabq4450. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelnabi, R.; Lassauniere, R.; Maes, P.; Weynand, B.; Neyts, J. Comparing the Infectivity of Recent SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sub-Variants in Syrian Hamsters. Viruses 2024, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, R.; Boudewijns, R.; Foo, C.S.; Seldeslachts, L.; Sanchez-Felipe, L.; Zhang, X.; Delang, L.; Maes, P.; Kaptein, S.J.F.; Weynand, B.; et al. Comparing infectivity and virulence of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants in Syrian hamsters. EBioMedicine 2021, 68, 103403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-summary (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- ERVISS. European Respiratory Virus Surveillance Summary. Available online: https://erviss.org (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Muhlemann, B.; Trimpert, J.; Walper, F.; Schmidt, M.L.; Jansen, J.; Schroeder, S.; Jeworowski, L.M.; Beheim-Schwarzbach, J.; Bleicker, T.; Niemeyer, D.; et al. Antigenic cartography using variant-specific hamster sera reveals substantial antigenic variation among Omicron subvariants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2310917121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Hentenaar, I.T.; Morrison-Porter, A.; Solano, D.; Haddad, N.S.; Castrillon, C.; Runnstrom, M.C.; Lamothe, P.A.; Andrews, J.; Roberts, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific plasma cells are not durably established in the bone marrow long-lived compartment after mRNA vaccination. Nat. Med. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilks, S.H.; Muhlemann, B.; Shen, X.; Tureli, S.; LeGresley, E.B.; Netzl, A.; Caniza, M.A.; Chacaltana-Huarcaya, J.N.; Corman, V.M.; Daniell, X.; et al. Mapping SARS-CoV-2 antigenic relationships and serological responses. Science 2023, 382, eadj0070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustsen-Helms, I.R.; Bager, P.; Larsen, T.G.; Moller, F.T.; Vestergaard, L.S.; Rasmussen, M.; Hansen, C.H.; Group, S.-D.S. Relative vaccine protection, disease severity, and symptoms associated with the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.2.86 and descendant JN.1 in Denmark: A nationwide observational study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, Y.; Uriu, K.; Kosugi, Y.; Okumura, K.; Yamasoba, D.; Uwamino, Y.; Kuramochi, J.; Sadamasu, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Asakura, H.; et al. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 KP.2 variant. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, Y.; Uriu, K.; Okumura, K.; Ito, J.; Sato, K. Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 KP.3.1.1 variant. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, F.; Wang, J.; Yisimayi, A.; Song, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Niu, X.; Yang, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P.; et al. Evolving antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 antigenic shift from XBB to JN.1. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Ho, J.; Guo, Y.; Yeh, A.Y.; Mohri, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Shah, J.G.; et al. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.4.6 to antibody neutralisation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1666–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Han, L.; Ma, Y.; Lu, L.; Wen, Y.; et al. A broadly neutralizing antibody against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant infection exhibiting a novel trimer dimer conformation in spike protein binding. Cell Res. 2022, 32, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, N.W.; Thiesson, E.M.; Pihlström, N.; Perälä, J.; Faksová, K.; Gram, M.A.; Poukka, E.; Leino, T.; Ljung, R.; Hviid, A. Comparative effectiveness of the monovalent XBB.1.5-containing covid-19 mRNA vaccine across three Nordic countries. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Degryse, J.; Maas, E.; Lassaunière, R.; Geerts, K.; Kumpanenko, Y.; Weynand, B.; Maes, P.; Neyts, J.; Thibaut, H.J.; Alpizar, Y.A.; et al. Antigenic Imprinting Dominates Humoral Responses to New Variants of SARS-CoV-2 in a Hamster Model of COVID-19. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122591
Degryse J, Maas E, Lassaunière R, Geerts K, Kumpanenko Y, Weynand B, Maes P, Neyts J, Thibaut HJ, Alpizar YA, et al. Antigenic Imprinting Dominates Humoral Responses to New Variants of SARS-CoV-2 in a Hamster Model of COVID-19. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122591
Chicago/Turabian StyleDegryse, Joran, Elke Maas, Ria Lassaunière, Katrien Geerts, Yana Kumpanenko, Birgit Weynand, Piet Maes, Johan Neyts, Hendrik Jan Thibaut, Yeranddy A. Alpizar, and et al. 2024. "Antigenic Imprinting Dominates Humoral Responses to New Variants of SARS-CoV-2 in a Hamster Model of COVID-19" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122591
APA StyleDegryse, J., Maas, E., Lassaunière, R., Geerts, K., Kumpanenko, Y., Weynand, B., Maes, P., Neyts, J., Thibaut, H. J., Alpizar, Y. A., & Dallmeier, K. (2024). Antigenic Imprinting Dominates Humoral Responses to New Variants of SARS-CoV-2 in a Hamster Model of COVID-19. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122591





