Effects of Increasing Temperature on Bacterial Community Diversity in Mixed Stands of Artemisia argyi and Solidago canadensis in Eastern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Processing and Amplicon Sequence Variant (ASV) Clustering and Filtering
2.4. Bacterial Diversity and Functions Predictions
2.5. Generation of Random Forest Models
2.6. Construction of Bacterial Co-Occurrence Network
3. Results
3.1. S. canadensis Invasion Community Responses to Warming
3.2. Bacterial Diversity and Predicted Functions Influenced by Warming
3.3. Predictive Model by Subsets of the Microbiota Biomarkers
3.4. Patterns of Interactions in Bacterial Co-Occurrence Network Under Warming
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Climate Phenomena and Their Relevance for Future Regional Climate Change. In Climate Change 2013—The Physical Science Basis; Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change, Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 1217–1308. ISBN 978-1-107-05799-9. [Google Scholar]
- Essl, F.; Lenzner, B.; Bacher, S.; Bailey, S.; Capinha, C.; Daehler, C.; Dullinger, S.; Genovesi, P.; Hui, C.; Hulme, P.E.; et al. Drivers of Future Alien Species Impacts: An Expert-based Assessment. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 4880–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Dai, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, Y. How Will Global Environmental Changes Affect the Growth of Alien Plants? Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Oduor, A.M.O.; Zhang, Z.; Manea, A.; Tooth, I.M.; Leishman, M.R.; Xu, X.; Van Kleunen, M. Do Invasive Alien Plants Benefit More from Global Environmental Change than Native Plants? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 3363–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.-C.; Zhu, B.; Wan, J.S.H.; Rutherford, S. Editorial: Global Changes and Plant Invasions. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 845816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Gu, W. Predicting the Invasive Trend of Exotic Plants in China Based on the Ensemble Model under Climate Change: A Case for Three Invasive Plants of Asteraceae. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.A.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Wilcove, D.S.; Ziska, L.H. Predicting Plant Invasions in an Era of Global Change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, I.; Diez, J.M.; Miller, L.P.; Olden, J.D.; Sorte, C.J.B.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Bradley, B.A.; D’Antonio, C.M.; Dukes, J.S.; Early, R.I.; et al. Integrated Assessment of Biological Invasions. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellard, C.; Cassey, P.; Blackburn, T.M. Alien Species as a Driver of Recent Extinctions. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20150623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumschick, S.; Gaertner, M.; Vilà, M.; Essl, F.; Jeschke, J.M.; Pyšek, P.; Ricciardi, A.; Bacher, S.; Blackburn, T.M.; Dick, J.T.A.; et al. Ecological Impacts of Alien Species: Quantification, Scope, Caveats, and Recommendations. Bioscience 2015, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.A. Invasive Species Impacts on Human Well-Being Using the Life Satisfaction Index. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 134, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, A.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Haubrock, P.J.; Fernandez, R.D.; Moodley, D.; Diagne, C.; Turbelin, A.J.; Renault, D.; Dalu, T.; Courchamp, F. Massive Economic Costs of Biological Invasions despite Widespread Knowledge Gaps: A Dual Setback for India. Biol. Invasions 2022, 24, 2017–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Yang, B.; Cui, M.; Dai, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Javed, Q.; Du, D. Warming and Elevated Nitrogen Deposition Accelerate the Invasion Process of Solidago canadensis L. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ismail, M.; Ding, J. Global Warming Increases the Interspecific Competitiveness of the Invasive Plant Alligator Weed, Alternanthera Philoxeroides. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, J.-X.; Zhou, X.-H.; Peng, P.-H.; Li, J.-J.; Zhang, S.-M.; He, W.-M. An Invasive Population of Solidago canadensis Is Less Sensitive to Warming and Nitrogen-Addition than Its Native Population in an Invaded Range. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Yuan, M.M.; Shi, Z.J.; Qin, Y.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wu, L.; He, Z.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Bracho, R.; et al. Tundra Soil Carbon Is Vulnerable to Rapid Microbial Decomposition under Climate Warming. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunello, L. Soil Microbiota Takes the Heat. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Caballero, G.; Caravaca, F.; Alguacil, M.M.; Fernández-López, M.; Fernández-González, A.J.; Roldán, A. Striking Alterations in the Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Functioning of the Biological N Cycle Induced by Pennisetum Setaceum Invasion in a Semiarid Environment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 109, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Brunel, C.; Van Kleunen, M. Soil-Microorganism-Mediated Invasional Meltdown in Plants. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 4, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, B. Solidago canadensis Invasion Affects Soil N-Fixing Bacterial Communities in Heterogeneous Landscapes in Urban Ecosystems in East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-C.; Wan, L.-Y.; Qi, S.-S.; Rutherford, S.; Ren, G.-Q.; Wan, J.S.H.; Du, D.-L. Synergy among Hypotheses in the Invasion Process of Alien Plants: A Road Map within a Timeline. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2020, 47, 125575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Stiling, P. Testing the Enemy Release Hypothesis: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, D.M. Interactions between Resource Availability and Enemy Release in Plant Invasion. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.E.; Power, A.G. Release of Invasive Plants from Fungal and Viral Pathogens. Nature 2003, 421, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klironomos, J.N. Feedback with Soil Biota Contributes to Plant Rarity and Invasiveness in Communities. Nature 2002, 417, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppinga, M.B.; Rietkerk, M.; Dekker, S.C.; De Ruiter, P.C.; Van Der Putten, W.H.; Van Der Putten, W.H. Accumulation of Local Pathogens: A New Hypothesis to Explain Exotic Plant Invasions. Oikos 2006, 114, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, K.; Callaway, R. Soil Biota Facilitate Exotic Acer Invasions in Europe and North America. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 1737–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfeld, J.G.; Kourtev, P.; Huang, W. Changes in Soil Functions Following Invasions of Exotic Understory Plants in Deciduous Forests. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 1287–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bever, J.D.; Platt, T.G.; Morton, E.R. Microbial Population and Community Dynamics on Plant Roots and Their Feedbacks on Plant Communities. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ping-Sheng, H.; Jia-Kuan, C. Perspectives on General Trends of Plant Invasions with Special Reference to Alien Weed Flora of Shanghai. Biodivers. Sci. 2001, 09, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Xie, X.; Peng, Y.; Ma, A. Changes of Soil Microbiological Characteristics After Solidago canadensis L. Invasion. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wen, X.; He, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.; Wang, M. Phytochemical Components and Biological Activities of Artemisia argyi. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.-Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Opoku Adomako, M.; Dai, Z.-C.; Li, G.-L.; Wan, L.-Y.; Zhang, B.; Zou, C.B.; et al. The Enhancement of Root Biomass Increases the Competitiveness of an Invasive Plant against a Co-Occurring Native Plant under Elevated Nitrogen Deposition. Flora 2019, 261, 151486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cui, M.; Dai, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Fan, X.; Rutherford, S.; Du, D. Non-Additive Effects of Environmental Factors on Growth and Physiology of Invasive Solidago canadensis and a Co-Occurring Native Species (Artemisia argyi). Plants 2023, 12, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Prabakaran, K.; Dai, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, K.; Zou, C.B.; Du, D. The Effect of Nitrogen and Temperature Changes on Phenotypic Plasticity and Fitness. Plant Species Biol. 2020, 35, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; He, M.; Li, G.; Anandkumar, A.; Dai, Z.; Zou, C.B.; Hu, Z.; Ran, Q.; Du, D. Effects of Solidago canadensis Invasion and Climate Warming on Soil Net N Mineralization. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 3285–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogelj, J.; Meinshausen, M.; Knutti, R. Global Warming under Old and New Scenarios Using IPCC Climate Sensitivity Range Estimates. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and Clustering Orders of Magnitude Faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, Version 2.2-1; R Package: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling Function and Taxonomy in the Global Ocean Microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using Network Analysis to Explore Co-Occurrence Patterns in Soil Microbial Communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Xie, P.; Yang, S.; Niu, G.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xue, C.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yuan, J. ggClusterNet: An R Package for Microbiome Network Analysis and Modularity-Based Multiple Network Layouts. iMeta 2022, 1, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csárdi, G.; Nepusz, T.; Müller, K.; Horvát, S.; Traag, V.; Zanini, F.; Noom, D. Igraph for R: R Interface of the Igraph Library for Graph Theory and Network Analysis; Version v1.6.0; GitHub: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Sun, H.; Peng, F.; Zhang, H.; Xue, X.; Gibbons, S.M.; Gilbert, J.A.; Chu, H. Characterizing Changes in Soil Bacterial Community Structure in Response to Short-Term Warming. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Yang, B.; Ren, G.; Yu, H.; Dai, Z.; Li, J.; Ran, Q.; Stevanato, P.; Wan, J.; Du, D. Effects of Warming, Phosphorous Deposition, and Both Treatments on the Growth and Physiology of Invasive Solidago canadensis and Native Artemisia argyi. Plants 2023, 12, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.; Singh, B.K. Plant-Microbiome Interactions: From Community Assembly to Plant Health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Sui, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. The Diversity and Geographic Distribution of Cultivable Bacillus-Like Bacteria Across Black Soils of Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazykin, I.; Khmelevtsova, L.; Azhogina, T.; Sazykina, M. Heavy Metals Influence on the Bacterial Community of Soils: A Review. Agriculture 2023, 13, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, K. Trichoderma Affects the Physiochemical Characteristics and Bacterial Community Composition of Saline–Alkaline Maize Rhizosphere Soils in the Cold-Region of Heilongjiang Province. Plant Soil 2019, 436, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F. The Family Ectothiorhodospiraceae. In The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria Volume 6: Proteobacteria: Gamma Subclass; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 874–886. ISBN 978-0-387-30746-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Qi, G.; Luo, T.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhao, X. Continuous-Cropping Tobacco Caused Variance of Chemical Properties and Structure of Bacterial Network in Soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4106–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, S.N.; Kolasa, J.; Cottenie, K. Contrasts between Habitat Generalists and Specialists: An Empirical Extension to the Basic Metacommunity Framework. Ecology 2009, 90, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The Modularity of Pollination Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P.; Li, L.; Guo, J.; Zhu, C.; Guo, S.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q. Microbial Generalists and Specialists Differently Contribute to the Community Diversity in Farmland Soils. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 40, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, K.A.; Dukes, J.S. Plant Invasion across Space and Time: Factors Affecting Nonindigenous Species Success during Four Stages of Invasion. New Phytol. 2007, 176, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
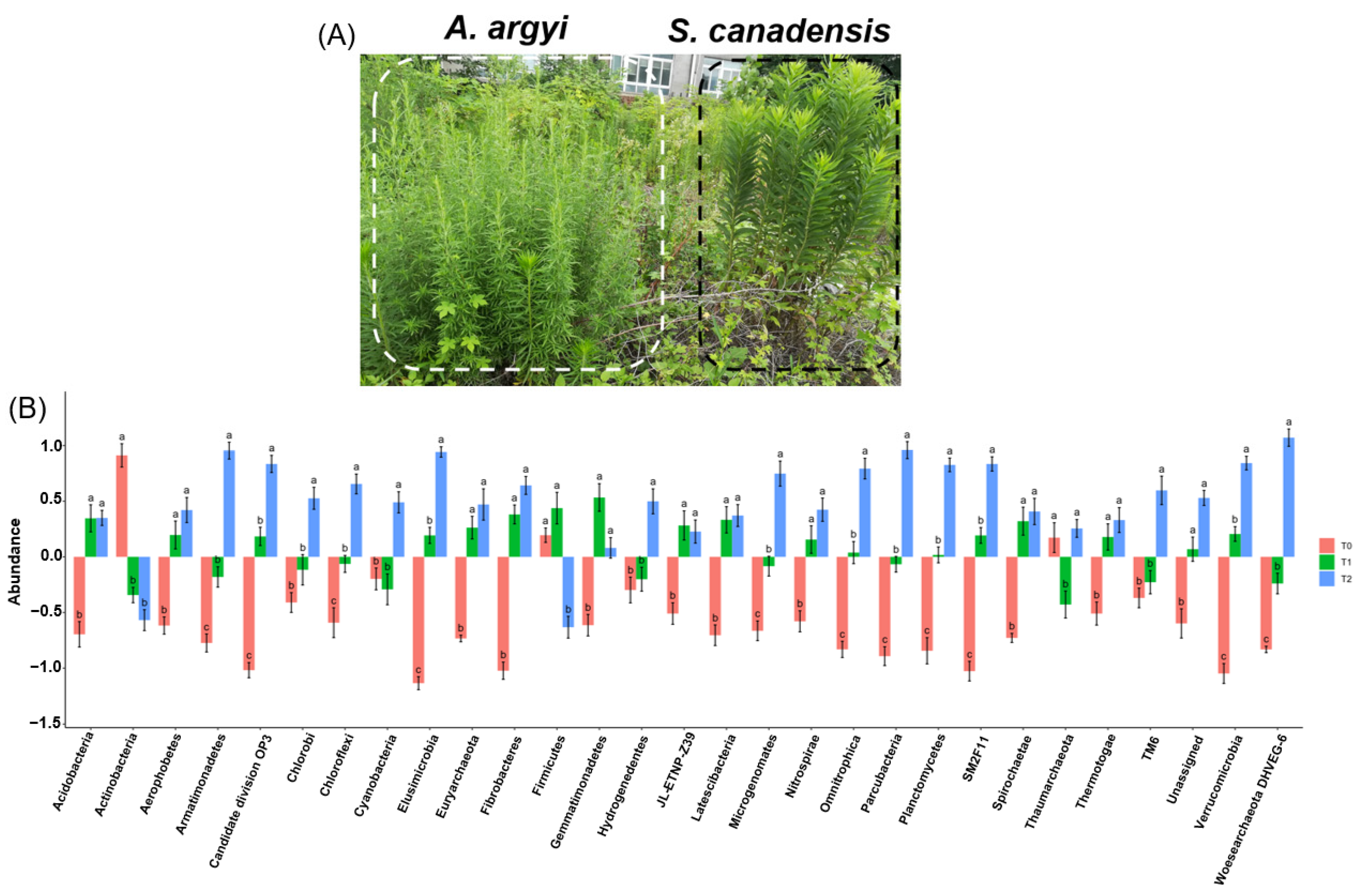
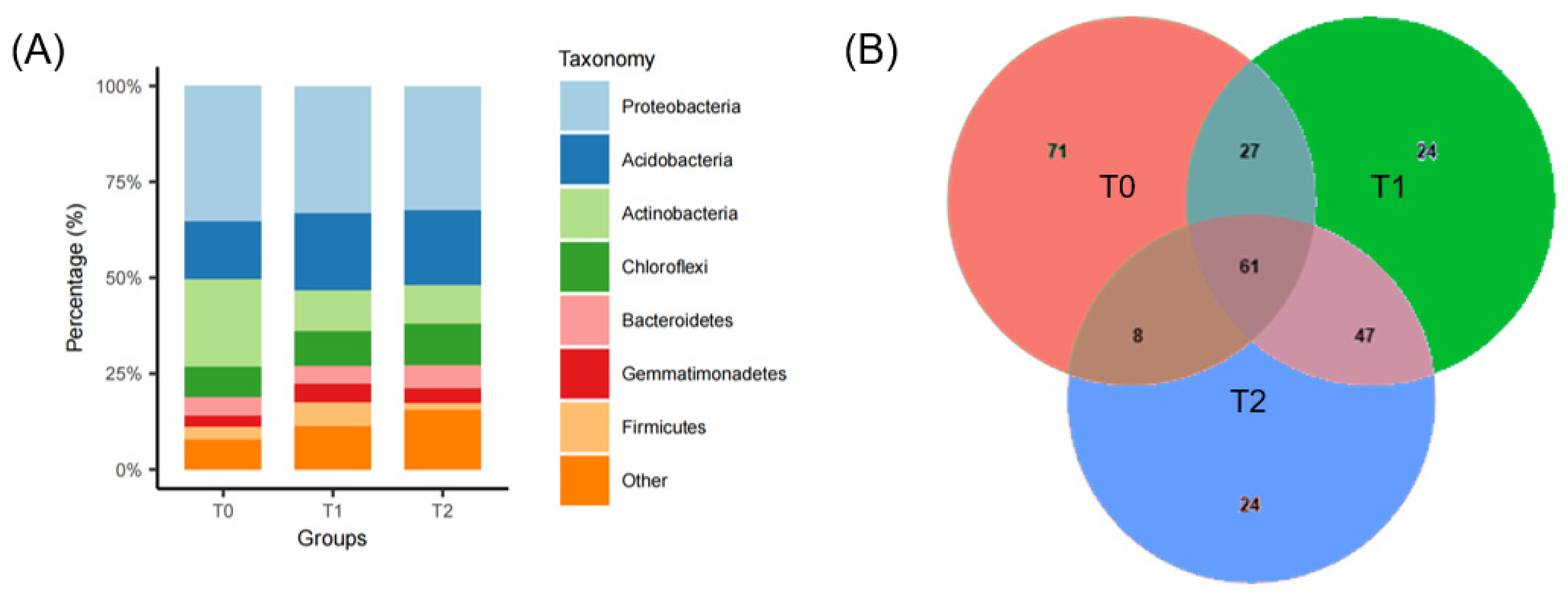
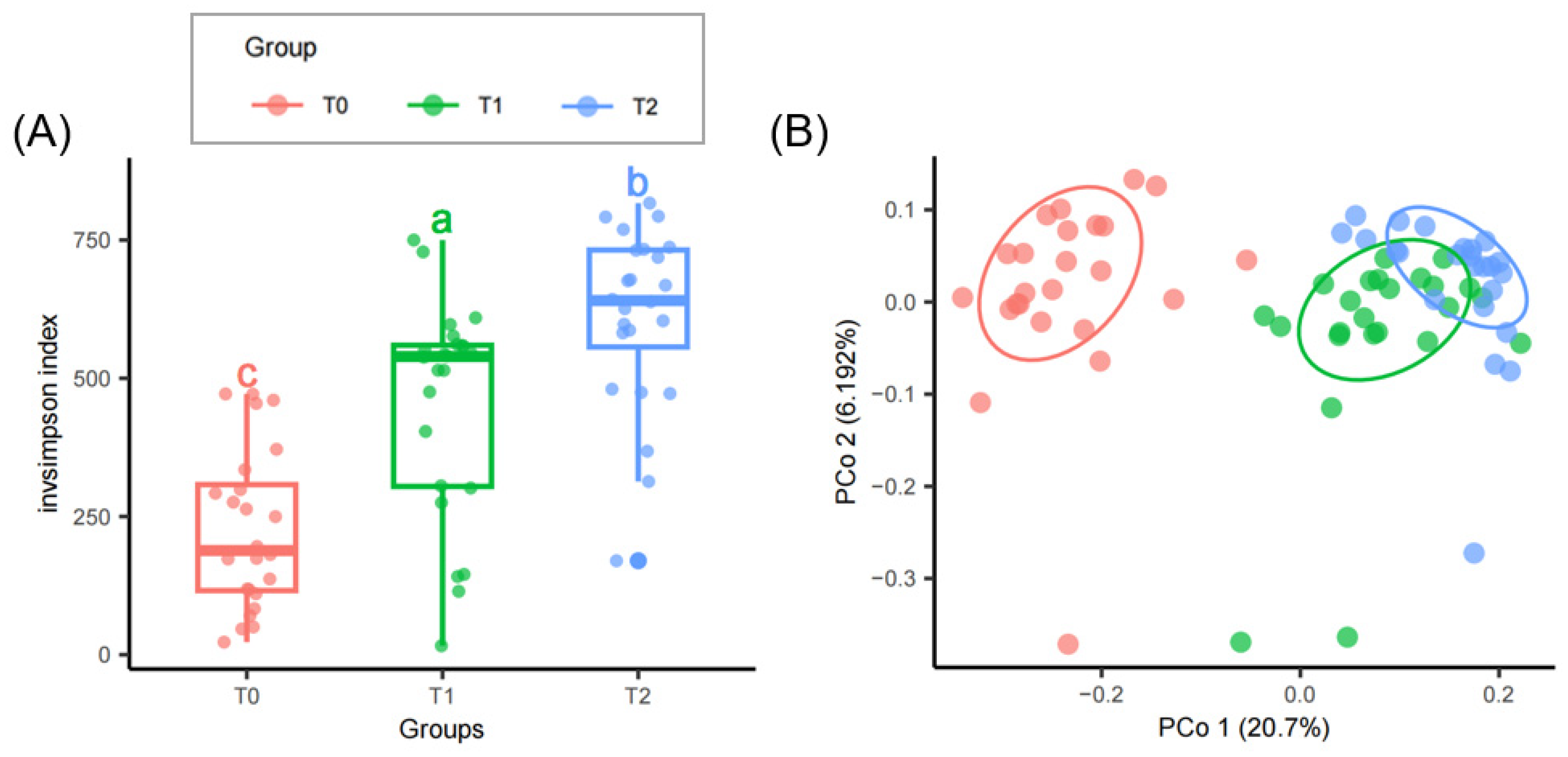
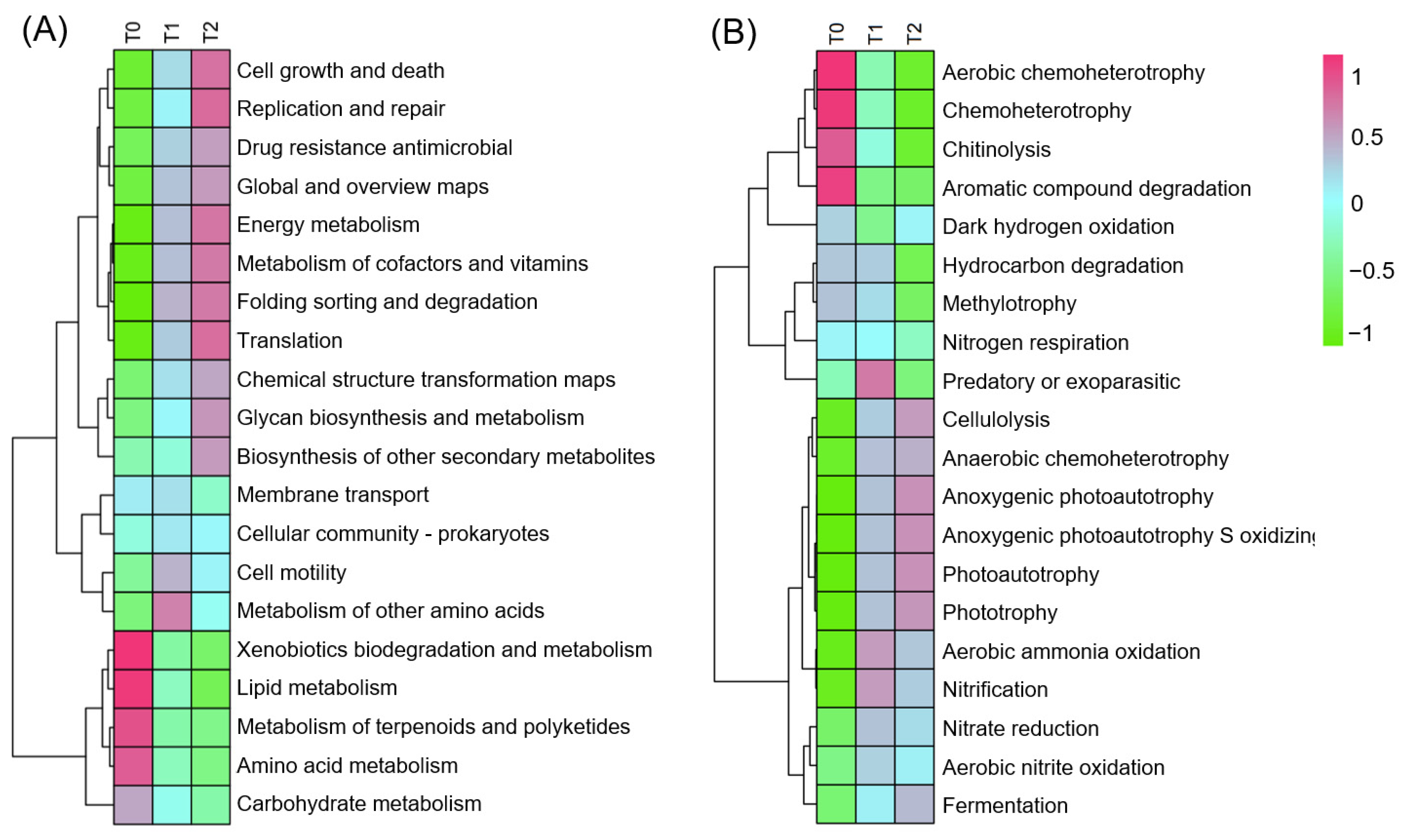

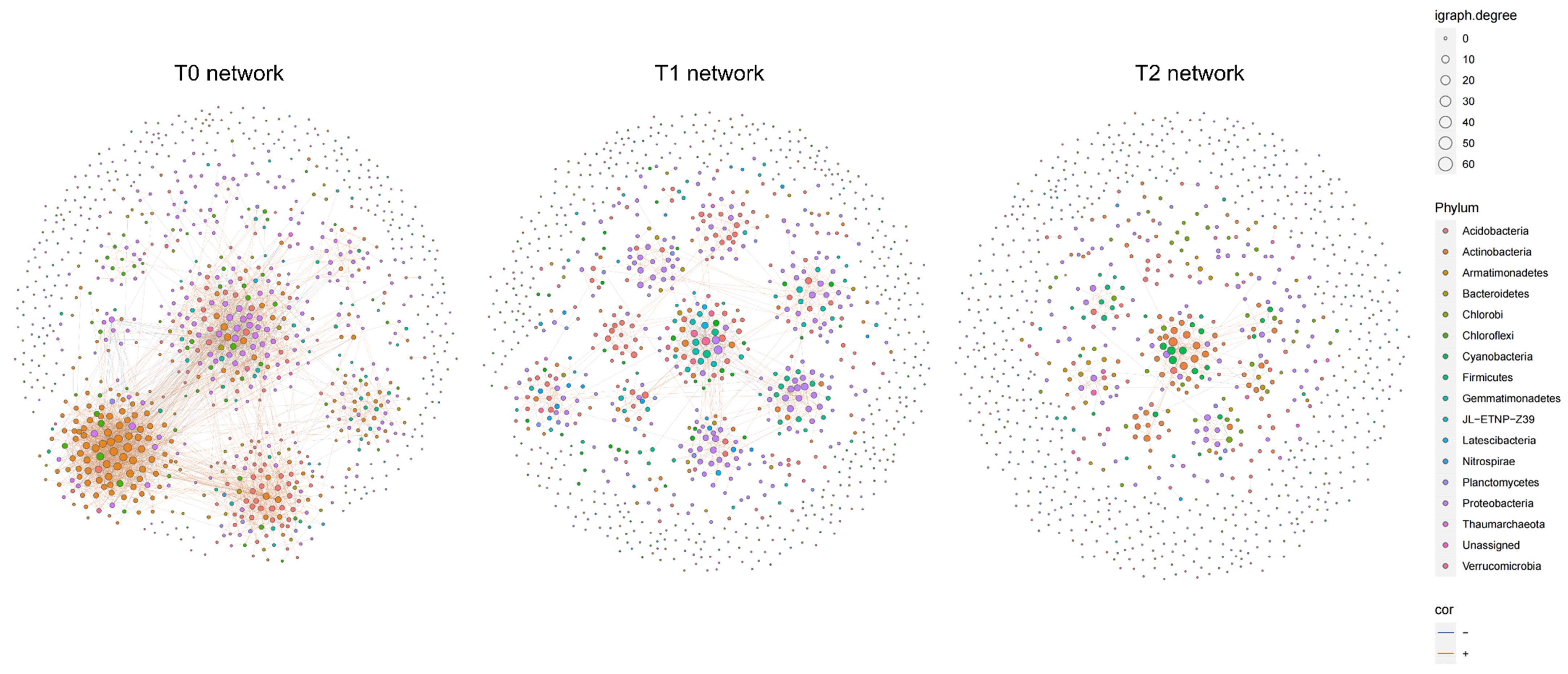
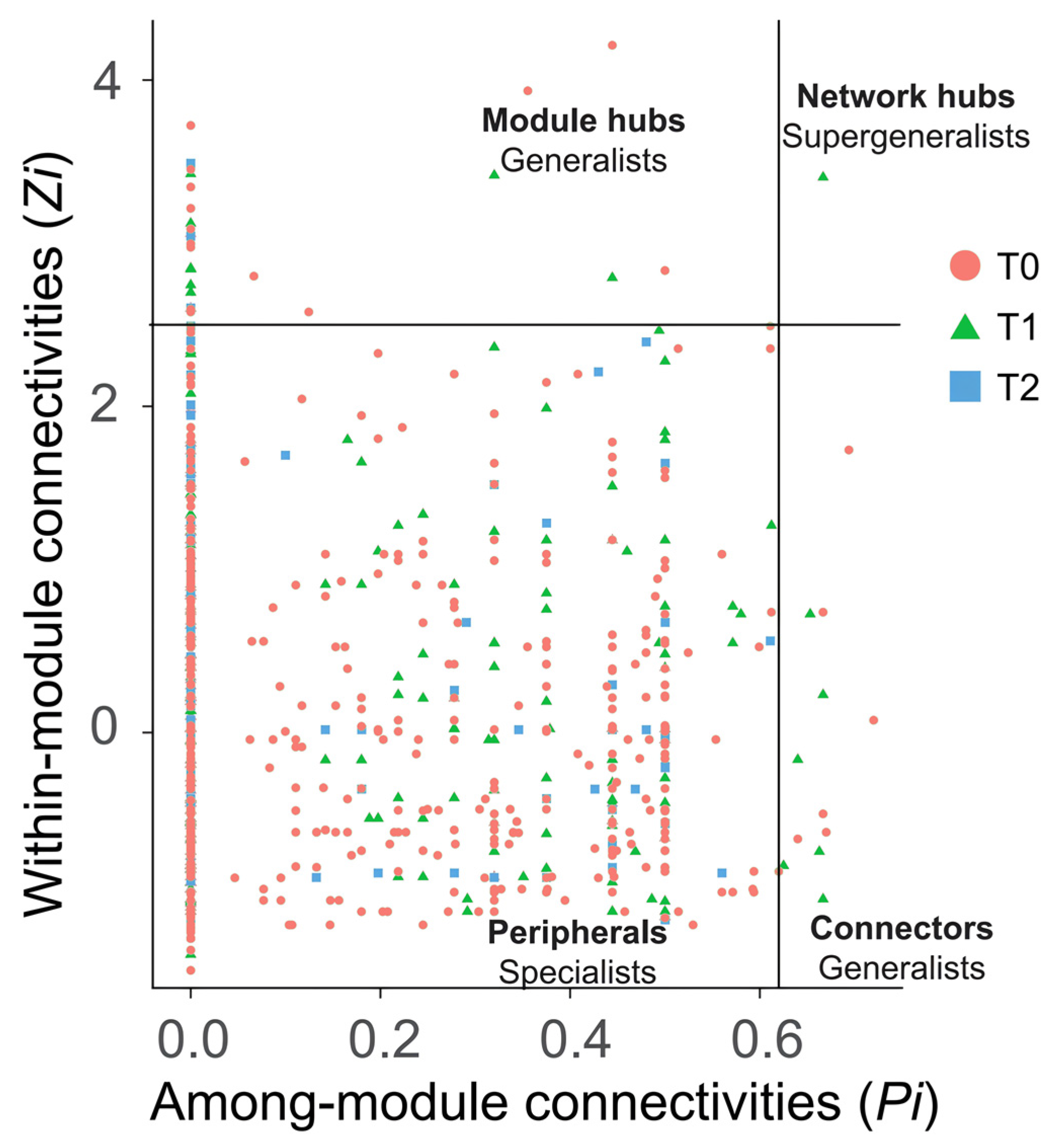
| Temperature Treatments | Temperature (°C) | Nodes | Edges | Average Degree | Mean Clustering Coefficient | Clusters | Relative Modularity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 | 29.47 ± 0.38 | 692 | 2559 | 7.40 | 0.34 | 23 | 0.81 |
| T1 | 30.62 ± 0.36 | 539 | 853 | 3.17 | 0.30 | 60 | 0.43 |
| T2 | 31.33 ± 0.37 | 340 | 399 | 2.35 | 0.29 | 72 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Ren, G.; Huang, Z.; Qi, S.; Zhao, B.; Fan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Du, D. Effects of Increasing Temperature on Bacterial Community Diversity in Mixed Stands of Artemisia argyi and Solidago canadensis in Eastern China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122415
Yu H, Ren G, Huang Z, Qi S, Zhao B, Fan X, Zhu Z, Dai Z, Du D. Effects of Increasing Temperature on Bacterial Community Diversity in Mixed Stands of Artemisia argyi and Solidago canadensis in Eastern China. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122415
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Haochen, Guangqian Ren, Zhiyun Huang, Shanshan Qi, Biying Zhao, Xue Fan, Zhaoqi Zhu, Zhicong Dai, and Daolin Du. 2024. "Effects of Increasing Temperature on Bacterial Community Diversity in Mixed Stands of Artemisia argyi and Solidago canadensis in Eastern China" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122415
APA StyleYu, H., Ren, G., Huang, Z., Qi, S., Zhao, B., Fan, X., Zhu, Z., Dai, Z., & Du, D. (2024). Effects of Increasing Temperature on Bacterial Community Diversity in Mixed Stands of Artemisia argyi and Solidago canadensis in Eastern China. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122415








