Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the Epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes: A Five-Year Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
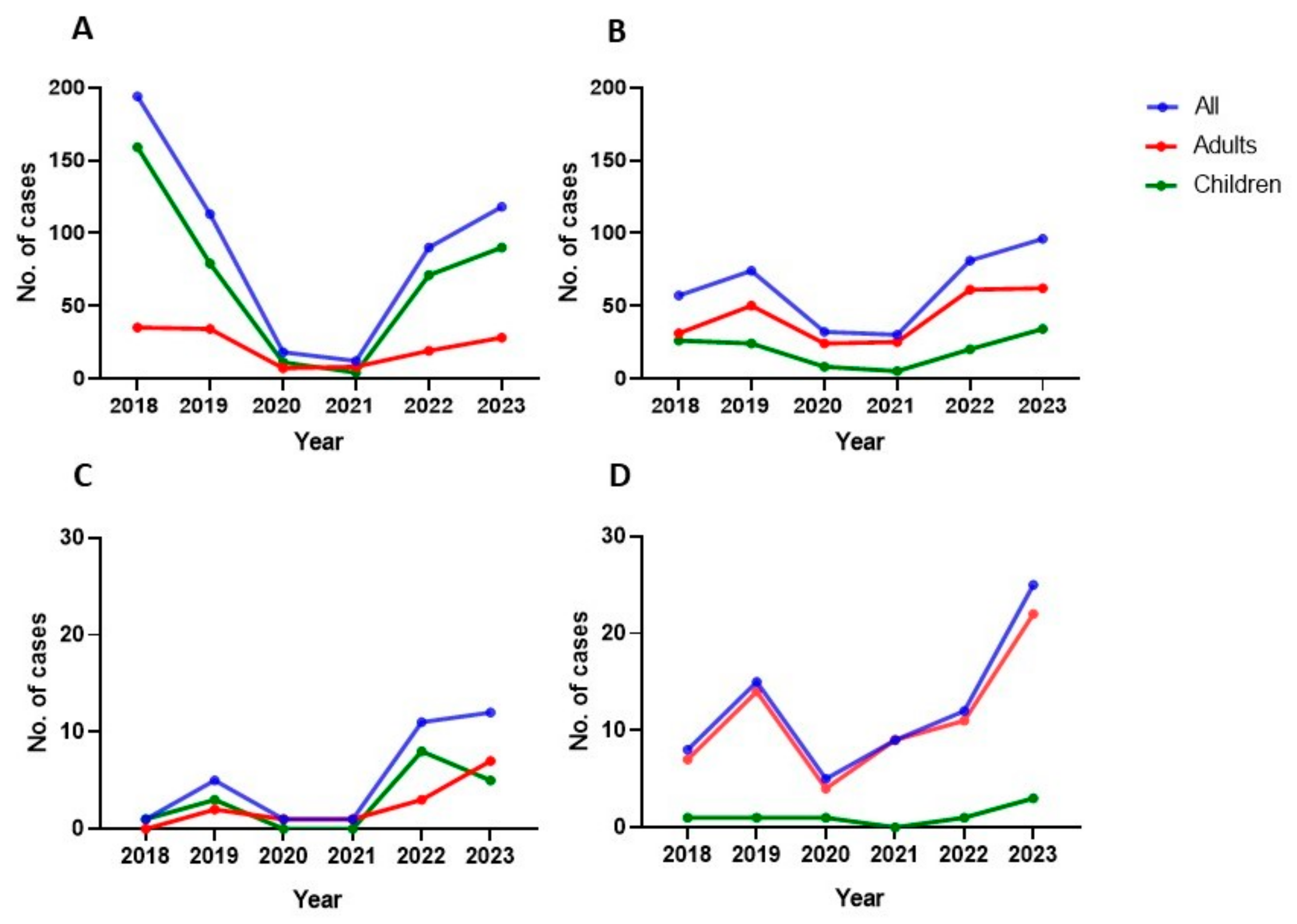
3. Results
3.1. Respiratory Source
Respiratory Invasive Infection
3.2. Non-Respiratory Source
Non-Respiratory Invasive Infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Lam, T.T.Y.; Ni, M.Y.; Wong, C.K.H.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting epidemics of novel pathogens: Lessons from COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanetti, M.; Branda, F.; Cella, E.; Scarpa, F.; Bazzani, L.; Ciccozzi, A.; Slavov, S.N.; Benvenuto, D.; Sanna, D.; Casu, M.; et al. Epidemic history and evolution of an emerging threat of international concern, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e29012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, S.; Rivera-Hernandez, T.; Curren, B.F.; Harbison-Price, N.; De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Jespersen, M.G.; Davies, M.R.; Walker, M.J. Pathogenesis, epidemiology and control of Group A Streptococcus infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achangwa, C.; Park, H.; Ryu, S.; Lee, M.S. Collateral Impact of Public Health and Social Measures on Respiratory Virus Activity during the COVID-19 Pandemic 2020–2021. Viruses 2022, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danino, D.; Ben-Shimol, S.; van der Beek, B.A.; Givon-Lavi, N.; Avni, Y.S.; Greenberg, D.; Weinberger, D.M.; Dagan, R. Decline in Pneumococcal Disease in Young Children During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic in Israel Associated With Suppression of Seasonal Respiratory Viruses, Despite Persistent Pneumococcal Carriage: A Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e1154–e1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.; Abad, R.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Bautista, A.; Bennett, D.; Broughton, K.; Cao, B.; Casanova, C.; Choi, E.H.; Chu, Y.-W.; et al. Trends in invasive bacterial diseases during the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic: Analyses of prospective surveillance data from 30 countries and territories in the IRIS Consortium. Lancet Digit. Health 2023, 5, e582–e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brañas, P.; Muñoz-Gallego, I.; Espartosa, E.; Moral, N.; Abellán, G.; Folgueira, L. Dynamics of respiratory viruses other than SARS-CoV-2 during the COVID-19 pandemic in Madrid, Spain. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ceano-Vivas, M.; Gutiérrez, M.M.; Mellado-Sola, I.; Sánchez, P.G.; Grandioso, D.; Calvo, C.; López, R.L.; Bueno-Barriocanal, M.; Domínguez, J.A.R.; de Miguel, B. Streptococcus pyogenes infections in Spanish children before and after the COVID pandemic. Coming back to the previous incidence. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 42, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, R.; Henderson, K.L.; Coelho, J.; Hughes, H.; Mason, E.L.; Gerver, S.M.; Demirjian, A.; Watson, C.; Sharp, A.; Brown, C.S.; et al. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infection notifications, England, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.J.; Barnett, T.C.; McArthur, J.D.; Cole, J.N.; Gillen, C.M.; Henningham, A.; Sriprakash, K.S.; Sanderson-Smith, M.L.; Nizet, V. Disease manifestations and pathogenic mechanisms of group A Streptococcus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 264–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.E. Can group A Streptococcus infections be influenced by viruses in the respiratory tract? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 142–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak, A.; Levy, C.; Angoulvant, F.; Auvrignon, A.; Gembara, P.; Danis, K.; Vaux, S.; Levy-Bruhl, D.; van der Werf, S.; Béchet, S.; et al. Association of Nonpharmaceutical Interventions During the COVID-19 Pandemic With Invasive Pneumococcal Disease, Pneumococcal Carriage, and Respiratory Viral Infections Among Children in France. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2218959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Sorge, N.M.; Hester, M.E.; Sorge, N.V.M. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal (Streptococcus pyogenes) infections (iGAS) in young children in the Netherlands, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellés-Bellés, A.; Prim, N.; Mormeneo-Bayo, S.; Villalón-Panzano, P.; Valiente-Novillo, M.; Jover-Sáenz, A.; Aixalà, N.; Bernet, A.; López-González, É.; Prats, I.; et al. Changes in Group A Streptococcus emm Types Associated with Invasive Infections in Adults, Spain, 2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 2390–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, E.M.; Hutton, S.; Peterson, E.; Blackstock, A.J.; Hahn, C.G.; Turner, K.; Carter, K.K. Increasing Incidence of Invasive Group A Streptococcus Disease, Idaho, USA, 2008–2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 29, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Arellano, E.R.; Saavedra-Lozano, J.; Villalón, P.; Jové-Blanco, A.; Grandioso, D.; Sotelo, J.; Gamell, A.; González-López, J.J.; Cervantes, E.; Gónzalez, M.J.; et al. Clinical, microbiological, and molecular characterization of pediatric invasive infections by Streptococcus pyogenes in Spain in a context of global outbreak. mSphere 2024, 9, e0072923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, M.; Berinson, B.; Degel-Brossmann, N.; Hoffmann, A.; Bluszis, R.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Rohde, H.; Christner, M. Population of invasive group A streptococci isolates from a German tertiary care center is dominated by the hypertoxigenic virulent M1UK genotype. Infection 2024, 52, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, J.P.; Lin, Q.; Lammens, C.; Smeesters, P.R.; van Kleef-van Koeveringe, S.; Matheeussen, V.; Malhotra-Kumar, S. Increase in bloodstream infections caused by emm1 group A Streptococcus correlates with emergence of toxigenic M1UK, Belgium, May 2022 to August 2023. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2300422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, E.C.; Cataldi, J.R.; Silveira, L.J.; Birkholz, M.; Loi, M.M.; Osborne, C.M.; Dominguez, S.R. Outbreak of Invasive Group A Streptococcus in Children-Colorado, October 2022–April 2023. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2023, 12, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, U.; Hartling, U.B.; Munkstrup, C.; Nielsen, A.B.; Dungu, K.H.S.; Schmidt, L.S.; Glenthøj, J.; Matthesen, A.T.; Rytter, M.J.H.; Holm, M. Invasive group A streptococcal infections in children and adolescents in Denmark during 2022–23 compared with 2016–17 to 2021–22: A nationwide, multicentre, population-based cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2024, 8, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangarini, L.; Martiny, D.; Deyi, V.Y.M.; Hites, M.; Maillart, E.; Hainaut, M.; Delforge, M.; Botteaux, A.; Matheeussen, V.; Goossens, H.; et al. Incidence and clinical and microbiological features of invasive and probable invasive streptococcal group A infections in children and adults in the Brussels-Capital Region, 2005–2020. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenciano, S.J.; Onukwube, J.; Spiller, M.W.; Thomas, A.; Como-Sabetti, K.; Schaffner, W.; Farley, M.; Petit, S.; Watt, J.P.; Spina, N.; et al. Invasive Group A Streptococcal Infections among People Who Inject Drugs and People Experiencing Homelessness in the United States, 2010–2017. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3718–e3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanca, B.V.; Cyr, P.R.; Bentdal, Y.E.; Watle, S.V.; Wester, A.L.; Strand, Å.M.; Bøås, H. Increase in invasive group A streptococcal infections (iGAS) in children and older adults, Norway, 2022 to 2024. Eurosurveillance 2024, 29, 2400242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristic | Respiratory Source, N (%) | Non-Respiratory Source, N (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children (N = 17) | Adults (N = 14) | Children (N = 7) | Adults (N = 67) | |
| Age (years) (median, IQR) | 2 [1, 4] | 59.5 [48, 69] | 8 [7, 9] | 59 [44, 75] |
| Male sex | 11 (64.7) | 11 (78.6) | 7 (100) | 35 (52.2) |
| Nationality | ||||
| Spain | 15 (88.2) | 10 (71.4) | 6 (85.7) | 50 (74.6) |
| Latin America | 2 (11.8) | 4 (28.6) | 1 (14.3) | 13 (19.4) |
| Eastern Europe | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 (6) |
| Underlying conditions | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 (25.4) |
| Heart disease | 0 | 3 (21.4) | 1 (14.3) | 9 (13.4) |
| Hypertension | 0 | 7 (50) | 0 | 30 (44.8) |
| Dyslipidemia | 0 | 2 (14.3) | 0 | 21 (31.3) |
| Obesity | 0 | 3 (21.4) | 0 | 10 (14.9) |
| Chronic lung disease | 1 (5.9) | 5 (35.7) | 0 | 9 (13.4) |
| Chronic kidney disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (7.5) |
| Chronic liver disease | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (3) |
| Cancer | 0 | 3 (21.4) | 0 | 7 (10.4) |
| Haematological malignancy | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.5) |
| Transplant | 0 | 1 (7.1) | 0 | 1 (1.5) |
| HIV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (4.5) |
| Immunossuppresion | 0 | 2 (14.3) | 0 | 2 (3) |
| Any underlying condition | 1 (5.9) | 11 (78.6) | 1 (14.3) | 44 (65.7) |
| Recent surgery | 0 | 0 | 1 (14.3) | 5 (7.5) |
| Skin wound or injury | 0 | 0 | 1 (14.3) | 35 (52.2) |
| ICU hospitalisation | 14 (82.3) | 4 (28.6) | 5 (71.4) | 19 (28.4) |
| Mortality | 1 (5.9) | 2 (14.3) | 0 | 9 (13.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brañas, P.; Fontenla, F.; Castaño-Amores, M.V.; Recio, R.; Muñoz-Gallego, I.; Villa, J.; Viedma, E.; Folgueira, L. Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the Epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes: A Five-Year Retrospective Study. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122403
Brañas P, Fontenla F, Castaño-Amores MV, Recio R, Muñoz-Gallego I, Villa J, Viedma E, Folgueira L. Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the Epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes: A Five-Year Retrospective Study. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122403
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrañas, Patricia, Fabiola Fontenla, María Victoria Castaño-Amores, Raúl Recio, Irene Muñoz-Gallego, Jennifer Villa, Esther Viedma, and Lola Folgueira. 2024. "Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the Epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes: A Five-Year Retrospective Study" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122403
APA StyleBrañas, P., Fontenla, F., Castaño-Amores, M. V., Recio, R., Muñoz-Gallego, I., Villa, J., Viedma, E., & Folgueira, L. (2024). Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the Epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes: A Five-Year Retrospective Study. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2403. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122403






