Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Perspectives in French Caribbean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Settings
2.2. Transplant Procedure
2.3. Study Design and Population
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Ethical Considerations
2.6. Definitions
- Cases: Patients with at least one infectious event;
- Controls: Patients with no infectious event;
- UTIs: Cystitis was defined as a bacterial count > 105 CFU/mL, with dysuria, frequency, or urgency, while pyelonephritis required a bacterial count > 105 CFU/mL, with fever and specific clinical signs (lumbar pain, graft pain, etc.) [12];
- Lymphopenia: Lymphocyte count < 1500/mm3, following laboratory standards;
- Neutropenia: Neutrophil count < 1500/mm3, following laboratory standards;
- BK viremia: Defined as a BK virus DNA load of ≥103 copies/mL (3 Log10 copies/mL) in the blood detected through quantitative PCR;
- High immunological risk: Defined by donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies > 2000 MFI;
- Phaeohyphomycosis: Diagnosed by culture or histopathological evidence of dematiaceous fungi [13];
- Lymphocele infection: Fluid collection in the transplant space, diagnosed by pathogen-positive puncture [14];
- Rejection: Confirmed by pathological results from an allograft biopsy.
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Global Patient Characteristics
3.2. Infected Patient Characteristics
3.2.1. Demographics
3.2.2. Comorbidities
3.3. Description of Infectious Events
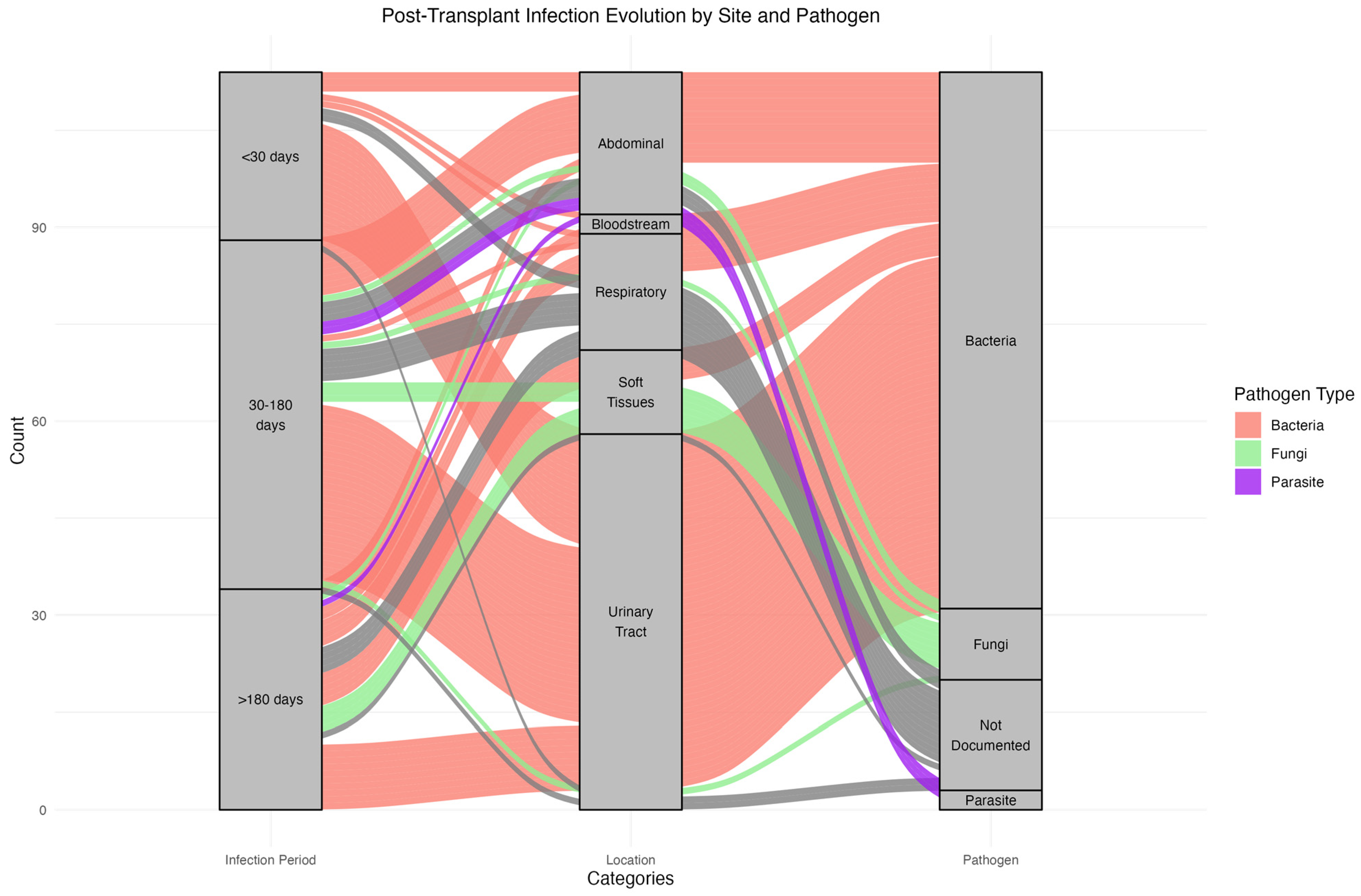
3.3.1. Timing and Sites of Infections
3.3.2. Recurrent Infection Patterns and Pathogen Consistency
3.4. Microbiological Characteristics
3.5. Infection Risk Factors
3.6. Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Features
4.2. Types of Infections
4.3. Atypical Incidence of Nocardiosis and Phaeohyphomycosis
4.4. Mortality
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dharnidharka, V.R.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Abbott, K.C. Risk Factors for Hospitalization for Bacterial or Viral Infection in Renal Transplant Recipients—An Analysis of USRDS Data. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.J.; Israni, A.K.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Simon, T.A.; Kasiske, B.L. Rates of first infection following kidney transplant in the United States. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, J.A. Infection in Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 856–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alangaden, G.J.; Thyagarajan, R.; Gruber, S.A.; Morawski, K.; Garnick, J.; El-Amm, J.M.; West, M.S.; Sillix, D.H.; Chandrasekar, P.H.; Haririan, A. Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: Current epidemiology and associated risk factors. Clin. Transplant. 2006, 20, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Juan, R.; Aguado, J.M.; Lumbreras, C.; Díaz-Pedroche, C.; López-Medrano, F.; Lizasoain, M.; Gavalda, J.; Montejo, M.; Moreno, A.; Gurguí, M.; et al. Incidence, Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Late Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: Data from the RESITRA Study Group. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Rodrigues Ferreira, F.; Cristelli, M.P.; Paula, M.I.; Proença, H.; Felipe, C.R.; Medina-Pestana, J.O. Infectious complications as the leading cause of death after kidney transplantation: Analysis of more than 10,000 transplants from a single center. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnee, R.C.; Lardy, N.; Ajubi, N.; Idu, M.M.; Kock, R.V.; Legemate, D.A.; Pant, K.A.v.D.d.; Bemelman, F.J. Ten-yr results of the trans-Atlantic kidney transplant airlift between the Dutch Caribbean and the Netherlands: Trans-Atlantic transplant program. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Chugh, S.; Chugh, K.S. Infections in dialysis and transplant patients in tropical countries. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, S85–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachera, L.; Adenis, A.; Dueymes, J.-M.; Rochemont, D.; Guarmit, B.; Roura, R.; Meddeb, M.; Nacher, M.; Djossou, F.; Epelboin, L. What Is the Part of Tropical Diseases Among Infectious Complications in Renal Transplant Recipients in the Amazon? A 12-Year Multicenter Retrospective Analysis in French Guiana. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonzo, J.P. Four Decades of Kidney Transplantation in Cuba. MEDICC Rev. 2013, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.; Ramsaroop, K.; Seemungal, T. Survival Outcomes in Renal Transplantation in Trinidad and Tobago—SORTTT Study. West Indian Med. J. 2012, 61, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, E.; Torre-Cisneros, J.; Blanes, M.; Montejo, M.; Cervera, C.; Aguado, J.; Len, O.; Carratalá, J.; Cordero, E.; Bou, G.; et al. Bacterial urinary tract infection after solid organ transplantation in the RESITRA cohort. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2012, 14, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, T.P.; Baddley, J.W.; Walsh, T.J.; Alexander, B.D.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Perl, T.M.; Walker, R.; Patterson, T.F.; Schuster, M.G.; Lyon, G.M.; et al. Phaeohyphomycosis in transplant recipients: Results from the Transplant Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET). Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, M.O.; Kleinclauss, F.; Richard, V.; Thuret, R. Complications chirurgicales de la transplantation rénale. Progrès Urol. 2016, 26, 1066–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attias, P.; Melica, G.; Boutboul, D.; De Castro, N.; Audard, V.; Stehlé, T.; Gaube, G.; Fourati, S.; Botterel, F.; Fihman, V.; et al. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Opportunistic Infections after Kidney Allograft Transplantation in the Era of Modern Immunosuppression: A Monocentric Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfeddine, K.; Zaghden, S.; Kharrat, M.; Kamoun, K.; Jarraya, F.; Hachicha, J. Infectious Complications in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Single-Center Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2005, 37, 2823–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, T.; Lu, Y.M.; Vathsala, A. Spectrum of severe infections in an Asian renal transplant population. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 2001–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomusch, O.; Wiesener, M.; Opgenoorth, M.; Pascher, A.; Woitas, R.P.; Witzke, O.; Jaenigen, B.; Rentsch, M.; Wolters, H.; Rath, T.; et al. Rabbit-ATG or basiliximab induction for rapid steroid withdrawal after renal transplantation (Harmony): An open-label, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 3006–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Delden, C.; Stampf, S.; Hirsch, H.H.; Manuel, O.; Meylan, P.; Cusini, A.; Hirzel, C.; Khanna, N.; Weisser, M.; Garzoni, C.; et al. Burden and Timeline of Infectious Diseases in the First Year After Solid Organ Transplantation in the Swiss Transplant Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, e159–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Mora, N.; Pachón Díaz, J.; Cordero Matía, E. Urinary tract infection in kidney transplant recipients. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Prado, M.E.; Cordero, E.; Cabello, V.; Pereira, P.; Torrubia, F.J.; Ruíz, M.; Cisneros, J.M. Complicaciones infecciosas en 159 receptores de trasplante renal consecutivos. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2009, 27, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmand, G.; Salem, S.; Mehrsai, A.; Taherimahmoudi, M.; Ebrahimi, R.; Pourmand, M.R. Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: A single-center experience. Transplant. Infect. Dis. 2007, 9, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliyasu, G.; Abdu, A.; Dayyab, F.M.; Tiamiyu, A.; Habib, Z.; Adamu, B.; Habib, A. Post-renal transplant infections: Single-center experience from Nigeria. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2016, 18, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, O.; Yildirim, M.; Kucuk, H.F.; Gencer, S.; Demir, T. Infections in Renal Transplant Patients: Risk Factors and Infectious Agents. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, C.; van Delden, C.; Gavaldà, J.; Welte, T.; Akova, M.; Carratalà, J. Multidrug-resistant bacteria in solid organ transplant recipients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, J.; Silva, J.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Cordero, E.; Fortún, J.; Gudiol, C.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Vidal, E.; Almenar, L.; Almirante, B.; et al. Management of multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacilli infections in solid organ transplant recipients: SET/GESITRA-SEIMC/REIPI recommendations. Transplant. Rev. 2018, 32, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakemeier, S.; Taxeidi, S.; Zukunft, B.; Schmidt, D.; Gaedeke, J.; Dürr, M.; Hansen, S.; Budde, K. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase–Producing Enterobacteriaceae–Related Urinary Tract Infection in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Risk Factors, Treatment, and Long-Term Outcome. Transplant. Proc. 2017, 49, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeaux, D.; Morelon, E.; Suarez, F.; Lanternier, F.; Scemla, A.; Frange, P.; Mainardi, J.-L.; Lecuit, M.; Lortholary, O. Nocardiosis in transplant recipients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Gil-Brusola, A.; Morales, P. Infection by Nocardia in Solid Organ Transplantation: Thirty Years of Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2011, 43, 2141–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; McCurry, K.; Dauber, J.; Singh, N.; Kusne, S. Nocardia infection in lung transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2002, 21, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussement, J.; for the European Study Group for Nocardia in Solid Organ Transplantation; Lebeaux, D.; van Delden, C.; Guillot, H.; Freund, R.; Marbus, S.; Melica, G.; Van Wijngaerden, E.; Douvry, B.; et al. Nocardia Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Multicenter European Case-control Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown-Elliott, B.A.; Brown, J.M.; Conville, P.S.; Wallace, R.J. Clinical and Laboratory Features of the Nocardia spp. Based on Current Molecular Taxonomy. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 259–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieffelin, J.; Garcia-Diaz, J.; Loss, G.; Beckman, E.; Keller, R.; Staffeld-Coit, C.; Garces, J.; Pankey, G. Phaeohyphomycosis fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients: Clinical presentation, pathology, and treatment. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2014, 16, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzaud, C.; Chosidow, O.; Brocard, A.; Fraitag, S.; Scemla, A.; Anglicheau, D.; Bouaziz, J.; Dupin, N.; Bougnoux, M.; Hay, R.; et al. Severe dermatophytosis in solid organ transplant recipients: A French retrospective series and literature review. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2018, 20, e12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Clinical Features | N | Missing Data | Total (n = 91) | Case (n = 57) | Control (n = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 91 | 0 | 52 [47–59] | 52 [47–61] | 52 [49–57] | 0.899 |
| Sex, No. (%) | 91 | 0 | ||||
| Male | 61 (67.0) | 32 (56.1) | 29 (85.3) | 0.005 | ||
| Female | 30 (33.0) | 25 (43.9) | 5 (14.7) | |||
| BMI (kg/m2), median [IQR] | 91 | 0 | 25.2 [23–28] | 24.9 [22.5–29.3] | 25.5 [23–28] | 0.487 |
| Diabetes at time of transplant, No. (%) | 89 | 2 | 19 (21.3) | 17 (30.9) | 2 (5.9) | 0.007 |
| Dialysis time to transplant (months), median [IQR]. | 88 | 3 | 46 [28–82] | 45 [22–78] | 52 [31–94] | 0.488 |
| Territory of residence. No. (%) | 91 | 0 | ||||
| Guadeloupe | 71 (78.0) | 46 (80.7) | 25 (73.5) | |||
| Martinique | 13 (14.3) | 7 (12.3) | 6 (17.6) | |||
| French Guiana | 5 (5.5) | 3 (5.3) | 2 (5.9) | |||
| Saint Martin | 2 (2.2) | 1 (1.8) | 1 (2.9) | |||
| HBP, No. (%) | 89 | 2 | 81 (91.0) | 48 (87.3) | 33 (97.1) | 0.150 |
| CMV Positive Serostatus, No. (%) | 91 | 0 | 74 (81.3%) | 48 (84.2%) | 26 (76.5%) | 0.411 |
| Number of previous transplants, No. (%) | 91 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 1 (1.1) | 1 (2.9) | ||||
| >1 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||||
| Donor type, No. (%) | ||||||
| Death | 89 | 2 | 85 (94.4) | 53 (94.6) | 32 (94.1) | |
| Living | 89 | 2 | 5 (5.6) | 3 (5.4) | 2 (5.9) | |
| Cold ischemia time (hour), median [IQR] | 84 | 7 | 20.0 [17–24] | 20.4 [17.5–24.5] | 19.3 [14–23.8] | 0.627 |
| Positive graft preservation fluid with bacteria or fungus | 91 | 0 | 22 (24.2) | 16 (28.1) | 6 (17.6) | 0.318 |
| Length of stay after transplantation (days), median [IQR] | 90 | 1 | 19 [14–28] | 19.5 [14–30] | 16 [12–24] | 0.024 |
| Immunologic risk at transplantation, No. (%) | 91 | 0 | 0.510 | |||
| HRI | 54 (59.3) | 36 (63.2) | 18 (52.9) | |||
| FRI | 37 (40.7) | 21 (36.8) | 16 (47.1) | |||
| Acute or chronic rejection during follow-up, No. (%) | 89 | 2 | 18 (20.2) | 12 (21.4) | 6 (18.1) | 1 |
| Deaths during follow-up | 91 | 0 | 11 (12.1) | 8 (14.0) | 3 (8.8) | 0.5 |
| Therapeutic characteristics | ||||||
| Immunosuppressive therapy per transplant, No. (%) | 90 | 1 | ||||
| ATG Induction | 90 (100.0) | 57 (100.0) | 33 (100.0) | |||
| Ciclosporin—Cellcept | 35 (38.9) | 20 (35.1) | 15 (45.5) | 0.37 | ||
| Tacrolimus—Cellcept—Corticoids | 55 (61.1) | 37 (67.3) | 18 (32.7) |
| N | Total | |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Features | ||
| Age at infection (years), mean (SD) | 57 | 53.0 (9.8) |
| Total number of infections, No. average per patient (SD) | 116 | 2.0 (1.5) |
| Number of patient with 1 infection, No. % | 32 (56) | |
| Number of patient with 2 infection, No. % | 10 (17) | |
| Number of patient with 3 or more infection, No. % | 15 (26) | |
| Median time between transplantation and the first infection, days, median [IQR] | 57 | 34 [13–120] |
| Time from graft to first documented infection, number of cases per period, number of subjects (%) | ||
| D0–M1 | 23 (20.7) | |
| Bacterial | 23 | |
| Fungal | 0 | |
| Parasitic | 0 | |
| M1–M6 | 54 (48.6) | |
| Bacterial | 37 | |
| Fungal | 6 | |
| Parasitic | 2 | |
| M6–M24 | 34(30.7) | |
| Bacterial | 23 | |
| Fungal | 5 | |
| Parasitic | 1 | |
| Site of infection | 57 | |
| Urine | 58 (53.2) | |
| Lung | 17 (15.6) | |
| Soft tissues | 10 (9.2) | |
| Abdominal | 11 (10.1) | |
| Lymphocele | 11 (10.1) | |
| Blood | 1 (0.9) | |
| NA | 1 (0.9) | |
| Multiple sites of infections (>1) | ||
| 2 sites | 24 (42%) | |
| 3 sites | 16 (28%) | |
| 4 sites or more | 12 (21%) | |
| Biological features | ||
| Lymphopenia during infection | 115 | 101 (87.8) |
| Neutropenia during infection | 109 | 9 (8.3) |
| Microbiological identification, No. (%) | 94 | |
| Bacterial | 79 (84.0) | |
| Fungal | 11 (11.7) | |
| Parasite | 4 (4.2) | |
| Concurrent CMV replication, No. (%) | 102 | 10 (9.8) |
| Concurrent BK viremia replication, No. (%) | 94 | 7 (7.4) |
| Death | ||
| Deaths during follow-up, No. (%) | 8 (14) | |
| Infectious cause | 5 | |
| Other cause |
| Number of Infections | Type of Recurrent Infection | Number of Patients | Similar Pathogens (%) | Main Pathogen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Urinary (only repeated site) | 8 | 4 (50) | ESBL-KP |
| 2 | Pulmonary (only repeated site) | 4 | 0 (0) | - |
| 3 | Urinary (only repeated site) | 4 | 1 (25) | ESBL-KP |
| 4 | Multi-site Infections (with no urinary infection) | 1 | 0 (0) | x |
| 4 or more | Urinary + other sites (digestive, lymphocele, etc.) | 11 | 3 (27) | ESBL-KP |
| UTI * | Pulmonary | Digestive | Soft Tissues | Lymphocele | Blood | Disseminated | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total infections | 109 | (%) | |||||||
| Bacteria | 79 | (72) | |||||||
| Wild type-E. coli | 17 | 17 | |||||||
| Others E. coli | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| ESBL-KP | 23 | 18 | 1 | 4 | |||||
| Wild type-KP | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| Enterobacter cloacae | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| Morganella morganii | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Haemophilus influenzae | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Enterococcus fecalis | 2 | 2 | |||||||
| Salmonella spp. | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Proteus mirabilis | 2 | 2 | |||||||
| Providentia sp. | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Clostridioides difficile | 2 | 2 | |||||||
| Acinetobacter baumanii | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||||||
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| MSSA | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Nocardia sp. | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Chryseobacterium | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Actinomyces spp. | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Other | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Fungi | 11 | (10) | |||||||
| Phaeohyphomycoses | 7 | 7 | |||||||
| Candida species | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| Parasites | 4 | (4) | |||||||
| Cryptosporidium spp. | 3 | 3 | |||||||
| Blastocystis hominis | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Not documented | 15 | (14) | 2 | 10 | 1 | 2 |
| Case | Control | OR [95% CI] | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate analysis | ||||
| Female sex, No. (%) | 25 (43.9) | 5 (14.7) | 3.97 [1.34–11.75] | 0.005 |
| Diabetes at time of transplant, No. (%) | 17 (30.9) | 2 (5.9) | 6.37 [1.36–29.72] | 0.007 |
| Length of stay after transplantation, (days), median [IQR] | 19.5 [14–30] | 16 [12–24] | 1.02 [20.9–71.07] | 0.024 |
| Multivariate analysis | ||||
| Female | 4.33 [1.40; 13.37] | 0.010 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus at time of transplant | 7.65 [1.59; 36.81] | 0.011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tardieu, L.; Doppelt, G.; Nicolas, M.; Emal, V.; Blanchet, P.; Markowicz, S.; Galantine, V.; Roger, P.-M.; Claudéon, J.; Epelboin, L. Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Perspectives in French Caribbean. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122390
Tardieu L, Doppelt G, Nicolas M, Emal V, Blanchet P, Markowicz S, Galantine V, Roger P-M, Claudéon J, Epelboin L. Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Perspectives in French Caribbean. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122390
Chicago/Turabian StyleTardieu, Laurène, Gary Doppelt, Muriel Nicolas, Violaine Emal, Pascal Blanchet, Samuel Markowicz, Valérie Galantine, Pierre-Marie Roger, Joëlle Claudéon, and Loïc Epelboin. 2024. "Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Perspectives in French Caribbean" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122390
APA StyleTardieu, L., Doppelt, G., Nicolas, M., Emal, V., Blanchet, P., Markowicz, S., Galantine, V., Roger, P.-M., Claudéon, J., & Epelboin, L. (2024). Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Perspectives in French Caribbean. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122390





