Abstract
Zero-valent copper and silver metals (Ms) nanoparticles (NPs) supported on carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) were synthesized for treating Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbriae 4 (ETEC:F4), a major cause of diarrhea in post-weaned pigs. The antibacterial properties of Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC were assessed on infected porcine intestinal enterocyte IPEC-J2, an in vitro model mimicking the small intestine. The lower average particle size (218 nm) and polydispersity index [PDI]: 0.25) for Ag0/CMC, when compared with those of Cu0/CMC (367 nm and PDI 0.96), were explained by stronger Ag0/CMC interactions. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of Ag0/CMC were lower in both bacteria and IPEC-J2 cells than those of Cu0/CMC, confirming that silver nanoparticles are more bactericidal than copper counterparts. IPEC-J2, less sensitive in MNP/CMC treatment, was used to further investigate the infective process by ETEC:F4. The IC50 of MNP/CMC increased significantly when infected IPEC-J2 cells and ETEC were co-treated, showing an inhibition of the cytotoxicity effect of ETEC:F4 infection and protection of treated IPEC-J2. Thus, it appears that metal insertion in CMC induces an inhibiting effect on ETEC:F4 growth and that MNP/CMC dispersion governs the enhancement of this effect. These results open promising prospects for metal-loaded biopolymers for preventing and treating swine diarrhea.
1. Introduction
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) are pathogenic bacteria which adhere to the microvilli of small intestinal epithelial cells and colonize the gut [1,2]. Diarrhea in swine is most associated with ETEC possessing fimbriae 4 (ETEC:F4) [3]. The pathogenicity of ETEC:F4 strains is due to the adhesive properties of fimbriae 4 (F4) and the enterotoxins released by attached bacteria. These factors are responsible for severe watery diarrhea and weight loss [4,5].
Antimicrobial resistance has emerged as a cause of economic losses in pig production and as a threat to the human healthcare system, caused by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics. More than 90% of the ETEC:F4 isolates in pigs may be multidrug-resistant [6]. Novel and alternative treatments are now targeted to address this issue. Among the approaches tackled so far, the use of the antimicrobial properties of metal nanoparticles (MNPs) is of great interest. The benefit effects of MNPs are related to their ability to induce bacterial membrane damage, bacteria growth inhibition [7], and death [8]. Moreover, the free radicals, resulting from the action of metals, may damage the bacterial DNA [9,10]. We hypothesized that CMC-hosted Ag0NP and Cu0NP could mitigate ETEC:F4 infection in porcine intestinal enterocytes IPEC-J2. Silver has been known for centuries as an antiseptic material with relatively low toxicity. In addition, to freely penetrate cellular barriers and generate damaging reactive oxygen species (ROS), nanoparticles of silver ions are also able to intercalate into nucleic acids, inhibiting the transcription and translation processes [11]. Also, copper NPs (Cu NPs) show good antimicrobial action [12,13], with a high capacity to generate ROS and at a lower cost, compared with silver.
Unlike metals in compact form, dispersed metal particles exhibit high surface-to-bulk ratios and improved contact surfaces that promote their biocidal effects [14]. Metal dispersion and stabilization is a major challenge that requires efficient ion or metal trapping materials. Natural and plant-deriving carbohydrate polymers such as cellulose or starch functionalized with anionic groups such as carboxylic groups offer promising prospects in this regard. For instance, carbohydrate-supported copper or silver nanoparticles (Cu0NP or Ag0NP) turned out to be effective for this purpose in concentration ranges that prevent toxicity for mammalian cells [11,15].
Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is a commercial carbohydrate resulting from hydroxyl substitution in cellulose by a carboxymethyl group [16,17]. This modification confers to CMC as excipient gastric acid resistance by protonation of carboxylic groups and with the intestinal transit will be deprotonated and ionized, favoring intestinal drug delivery from oral dosage forms [18,19]. CMC is a low-cost commercially available biopolymer with good biodegradability, known as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) compound, and it was employed herein as a matrix for MNPs. The CMC was also the first cellulose derivative approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [20].
Previous studies indicated that the Ag+ cation released from Ag0NP was responsible for the antibacterial activity [21]. Noori et al. [22] stated that the biocidal effect of metal-loaded carboxylated biopolymers is reversely proportional to their retention strength. This report presents silver and copper nanoparticles hosted by CMC with an investigation of antibacterial activity related to the structural parameters of the links of MNPs:CMC hosting material. The novelty is the observation of a markedly higher toxicity on E. coli bacteria than on epithelial IPEC-J2 cells as a model for the intestinal wall. A special attention will be paid to the inhibition of biofilm formation, related to microbial invasion, adhesion, and growth. All bactericidal aspects of MNP/CMC were compared with those of currently used antibiotics such as fosfomycin and kanamycin. The results are expected to allow for the correlation of the material properties to their efficiency as antibacterial agents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Copper II acetate [Cu(CH3COO)2], silver nitrate (AgNO3), and sodium borohydride (NaBH4 98%) were supplied by Fisher chemicals (Canada). Agar, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) with a degree of substitution (DS) of 0.92 ± 0.01 carboxymethyl group (CM) per glucose unit (Glc) and 90 kDa (MW), crystal violet, dexamethasone, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT), epidermal growth factor (EGF), and Luria–Bertani broth (LB) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Oakville, ON, Canada). A lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay kit was obtained from Promega (Madison, WI, USA). Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium and Ham’s F-12 nutrient mixture (DMEM/F12 medium), fetal bovine serum (FBS), insulin/transferrin/selenium (ITS), penicillin, streptomycin, and trypsin were obtained from Wisent (Saint-Jean-Baptiste, QC, Canada). Intestinal porcine jejunal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2) was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbriae 4 (ETEC:F4), also called the EcL8559 strain, was kindly provided by the Reference Laboratory for Escherichia coli (EcL, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Université de Montréal). All current chemicals were of reagent grade and used without further purification.
2.2. Preparation of Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC
Metal-hosted carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) was prepared according to Noori et al. [20] Cation-loaded CMC samples (Cu2+/CMC and Ag+/CMC) were prepared by adding dropwise 10 mL of 0.1 mol/L Cu(CH3COO)2 or AgNO3 solutions in 2% CMC solution (1 g of CMC in 50 mL of water) at 50–60 °C under stirring for 3 h. The reduction of the metal cations into zero-valent metals was carried out by introducing 4 mL of 0.5 M NaBH4 under a nitrogen stream for 10 min to obtain metal zero-hosted CMC samples (Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC). Both mixtures were then sonicated for 50 min (500 W, 20 kHz) at room temperature for homogenization. The resulting materials were dried by lyophilization and stored in an airtight container attached to a vacuum pump to prevent further oxidation of the obtained zero-valent metal nanoparticles loaded on CMC (MNP/CMC).
2.3. Characterization of MNP/CMC by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements were performed with a Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern, Herrenberg, Germany) equipped with a 633 nm He-Ne laser and operating at an angle of 173°. The analysis of the data was performed by Dispersion Technology Software version 6.01 from Malvern Panalytical Ltd. (Grovewood Road, Malvern, UK). A total volume of 2 mL of each sample at a concentration of 1 mg/mL was measured in single-use polystyrene cuvettes with a pathlength of 10 mm. The measurements were performed at a position of 4.65 mm from the cuvette wall with an automatic attenuator and at a controlled temperature of 25 °C. For each sample, 15 runs of 10 s were performed, with three repetitions. The distribution size, the Z-average diameter (Z-average), and the polydispersity index (PDI) were recorded.
2.4. Study of MNP/CMC by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
Structural aspects of the metal-based nanostructures deposited on a zinc selenide crystal surface was investigated by infrared spectroscopy using a single-bounce attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectrometer (PerkinElmer Spectrum 400, FTIR PerkinElmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). The samples were prepared using 1 mg of Cu0/CMC and 1 mg of Ag0/CMC and placed on the sample holder, and the ATR-FTIR spectra were acquired over a wavenumber range of 500–4000 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1. The spectra were normalized, and the baseline was corrected using Spectrum™ software (6.3.4, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.5. Enterotoxigenic E. coli F4 Fimbriae (ETEC:F4) Bacteria Culture
The enterotoxigenic E. coli F4 fimbriae (ETEC:F4) used in the present study was strain EcL8559, obtained from the EcL Laboratory Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Université de Montréal). The experiments were conducted following biosafety level 2. Bacteria were cultured for 24 h (100 rpm, 37 °C) in Luria–Bertani broth (LB) and quantified from the absorbance at 600 nm. Colony-forming units of serial diluted fractions of bacteria were determined, and a fixed concentration of 1 × 107 CFU/mL was used for further experimentations.
2.6. Porcine Intestinal Enterocyte IPEC-J2 Culture
The IPEC-J2 cells were seeded in a 25 cm2 flask and cultured at 37 °C, 5% CO2 in a humidified atmosphere in DMEM/F12 media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% insulin/transferrin/selenium (ITS), 5 μg/mL EGF, 100 units/mL penicillin, and 100 µg/mL streptomycin. According to ATCC guidelines, the cells were checked microscopically daily, and the medium was changed every two days until they reached 80% confluency. Then, the cells were detached with 0.25% trypsin-EDTA solution and split 1 in 10 for new seedlings in a 25 cm2 flask containing supplemented medium.
For cell viability experiments, the IPEC-J2 cells were seeded at a final concentration of 0.2 × 104 cells/mL in 96-well microplates with a flat bottom (Cytiva, BC, Canada) and were incubated in a humidified atmosphere at 37 °C and 5% CO2 until confluency. Then, they were differentiated for 10 days in FBS-free medium, supplemented with 100 units/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and 5 μg/mL EGF. Differentiated cells were used for viability and for infection assays.
2.7. Bactericidal Activity of MNP/CMC
A final volume of 10 mL containing 1×107 CFU/mL of ETEC:F4 EcL8559 was treated with 0–0.20 mg/mL of Cu0/CMC or Ag0/CMC for 24 h at 37 °C, 100 rpm. The optical density (OD) was measured at 600 nm using a spectrophotometer (SpectraMax M3, Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). In addition, approximately 1×106 CFU of ETEC:F4 was inoculated and spread on Petri dishes with agar gel prepared from a sterilized solution containing LB 25 g/L and agar 15 g/mL antibacterial agents (kanamycin and fosfomycin) or zero-valent metals loaded on CMC such as Cu0/CMC or Ag0/CMC, which were placed on the inoculated surface and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. The CMC was used as negative control, whereas the positives controls were kanamycin and fosfomycin, usually used in human health and in the veterinary field, respectively. The blank represented by the LB medium was subtracted from the obtained data, and the non-treated bacteria represented 100% bacteria viability.
2.8. Disk Diffusion Assay
The method was adapted from that described in El-Riz et al. [23]. A volume of 100 μL of ETEC:F4 107 CFU/mL was inoculated on LB agar dishes. Subsequently, a sterile disc was centered into inoculated LB agar dishes and was moistened with 10 μL of sterile LB. Around 1 mg of a sample of MNP/CMC was deposited on a disc, previously centered on agar gel. For the positive controls of bactericidal activity, kanamycin and fosfomycin antibiotics were used. All of the Petri dishes were incubated overnight at 37 °C. Finally, the antimicrobial activities of MNP/CMC were evaluated by measuring the diameter of inhibition in millimeters (mm).
2.9. Cytotoxic Effect of MNP/CMC on IPEC-J2
The stock solution of 1 mg/mL CMC (control) or MNP/CMC was sterilized with a 0.2 mm filter, and various concentrations of Cu0/CMC, Ag0/CMC, or CMC (0–20 mg/mL) were prepared in order to treat differentiated IPEC-J2 cells. Cytotoxicity effects were followed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. After 24 h of treatment, cells were washed three times and treated with MTT (5 mg/mL phosphate buffered saline) for 4 h at 37 °C, 5% CO2. The MTT reduction by living cells into solid purple formazan is quantifiable via the optical density (OD) at 560 nm. The formazan crystals were solubilized by adding an equal volume of 10 mM SDS containing 10 mM HCl. The percent of survived cells was compared with that of the control, and the concentration of sample required to kill 50% of cells (IC50) was evaluated. The average of three wells was used to determine the mean of each point for three different experiments.
2.10. Infection Assay and Cytotoxicity Assay of MNP/CMC on Infected IPEC-J2
Prior to the infection process, ETEC:F4 bacteria were diluted to 1 × 107 CFU/mL in 6-well plates; then washed three times with 1 × phosphate buffer saline (PBS) containing, in mM, NaCl (137), KCl (2.7), Na2HPO4 (10), and KH2PO4 (1.8) at pH 7.4; and finally resuspended in antibiotic-free medium supplemented with 1% fetal bovine serum (FBS). During the infection step, a total volume of 1 mL of ETEC:F4 was added to IPEC-J2 cells adhered in a well of a 6-well plate for an approximative multiplicity of infection (MOI) with a 10:1 ratio of deposited infectious bacteria divided by the number of target cells in the well. Plates were incubated for 24 h or for 48 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
For a complete investigation of effect of MNP/CMC against infection of IPEC-J2 by ETEC:F4, three situations were proposed.
Situation 1 [{IPEC-J2 cells + ETEC:F4} + MNP/CMC]: The IPEC-J2 cells were first infected with ETEC:F4 (MOI 10:1) for 24 h and then treated with 0–0.05 mg/mL of MNP/CMC for 24 h and 48 h.
Situation 2 [{IPEC-J2 cells + MNP/CMC} + ETEC:F4]: An amount of 106 cells by well of differentiated IPEC-J2 were first treated with 0–0.05 mg/mL of MNP/CMC for 24 h or 48 h and then infected with 107 CFU of ETEC:F4 (MOI 10:1) for 24 h.
Situation 3 [IPEC-J2 + {ETEC:F4 + MNP/CMC}]: The differentiated IPEC-J2 cells were infected with a suspension containing ETEC:F4 already treated with MNP/CMC. A volume of 1 mL of ETEC:F4 bacteria 107 CFU/mL was incubated with 0–0.05 mg/mL of MNP/CMC for 24 h. The mixture obtained was added into differentiated IPEC-J2 and then incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 24 h or 48 h.
In all three situations, cells were cultured in antibiotic-free medium to avoid interferences. At the indicated time, the medium was collected and centrifuged at 800× g for 15 min at 4 °C, and the viability of IPEC-J2 was assayed via a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) detection kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer guidelines. Compared with the MTT assay, the LDH assay provides a better reproducibility with infected IPEC-J2.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
All experiments used a minimum of three replicates (n = 3). Where relevant, data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical tests were performed with GraphPad software using a one-way ANOVA test. Differences were deemed statistically significant when the associated p-value was less than 0.05.
Antibacterial effectiveness, half-maximal effective concentration (IC50), the concentration of Cu0/CMC and of Ag0/CMC that induced a response halfway between the baseline and maximum after a specified exposure time), and the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC, the lowest concentrations of Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC that will inhibit the visible growth of the bacteria) were calculated in order to evaluate Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC antibacterial activity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dispersion of Cu0/CMC and of Ag0/CMC
The copper nanoparticles (Cu0/CMC) and silver nanoparticles (Ag0/CMC) were previously prepared through metal cation reduction into zero-valent metal on the polymeric support, according to Noori et al. [22].
The distribution of the particle size (PS) of the as-synthesized MNP/CMC was assessed through dynamic light scattering spectroscopy (DLS) in an aqueous suspension of 0.2 mg/mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC showed a nanoparticle size maximal value at 210 ± 11 nm and 368.6 ± 23 nm (Figure 1). These values agree with the corresponding z-average values (367 ± 39 nm and 218 ± 17 nm, respectively) (Table 1). Here, the lower PS of Ag0/CMC accounts for higher dispersion in the aqueous media and higher contact surface as compared with Cu0/CMC.
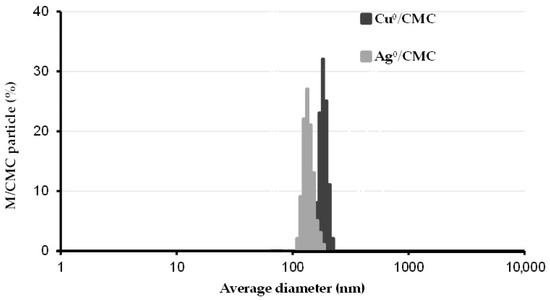
Figure 1.
Particle size distribution of metal nanoparticle hosted by carboxymethyl cellulose (MNP/CMC). The size distribution of copper and silver nanoparticles hosted by carboxymethyl cellulose (Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC) was assessed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) in aqueous suspensions. Triplicate measurements were performed by DLS in 2 mL of polystyrene cell with a 10 mm pathlength.

Table 1.
Some properties of CMC and the synthesized Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC samples.
There exists a narrow ternary interdependence between the pH, zeta potential (ZP), and MNP/CMC dispersion in aqueous media [22]. A higher pH is assumed to induce the deprotonation of carboxymethyl group leading to a ZP increase that enhances the repulsion forces and material dispersion. This interdependence appears to govern the extent of the contact surface and exchange fluxes with the targeted microorganisms.
The shapes of MNP in both Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC were similar to those already characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and transmission electron microscopy (SEM). The results revealed mostly pseudo-spherical 1–4 nm nanoparticles of zero-valent copper and silver, as previously reported with corresponding sizes in the same sequence and order of magnitude, with even 0.08–0.1 nm subnanoparticles for Ag0/CMC.
Their respective polydispersity indexes (PDI) of 0.96 ± 0.06 and 0.25 ± 0.02 (Table 1) reported here for Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC were higher than 0.05, which are regarded as the monodisperse standard [24].
3.2. Characterization of MNP/CMC–Carboxyl Interaction
Deeper insights through attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) analysis showed noticeable and specific changes in the shape and intensity of the large adsorption band in the 3500–3000 cm−1 region (Figure 2), with more intense and sharper bands for Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC in comparison with CMC. This suggests lesser hydrogen association (involving -OH groups of the CMC), which are hindered by the presence of MNP/CMC. Higher intensities, sharpness, and minor shifts of the -OH asymmetric stretching bands from 3255 cm−1 for CMC towards higher wavenumbers; i.e., 3343 cm−1 for Cu0/CMC and 3371 cm−1 for Ag0/CMC (Table 1) indicate a slight softening of the -OH bonds, which requires less energy for stretching vibration due to interaction with MNPs. This can be explained by the involvement of the hydroxyl groups of the CMC via the electron pairs of the oxygen atoms. More precisely, the slight band sharpening in the range of 3500–3000 cm−1 seems to be related to the rise in -O:MNP/CMC interaction at the expense of H-bridges. Thus, it appears that the hydroxyl groups are no longer involved in hydrogen binding but are involved in MNP/CMC stabilization.
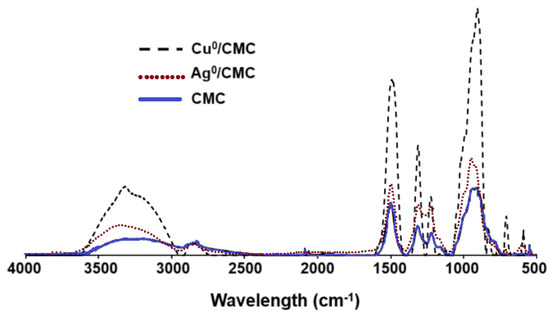
Figure 2.
ATR−FTIR spectra of CMC, Cu0/CMC, and Ag0/CMC.
Differently, only minimal shifts were found for the band assigned to the -OH bending of the carboxyl group from 1411 cm−1 for CMC to 1409 cm−1 for both Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC. As expected, no MNP/CMC interaction with the hydroxyl groups of the saccharide cycles seems to occur, as much as the -OH bending band of polysaccharide remained almost unshifted (1323 for CMC, 1325 for Cu0/CMC, and 1326 cm−1 for Ag0/CMC). In accordance with our results, Raghavendra et al. [25] also observed peaks at this region from polysaccharide interactions.
MNP/CMC appear to also interact with the oxygen atoms of the C=O bonds belonging to the carboxyl, as supported by a noticeable shift of the C=O stretching in polysaccharides from 1591 cm−1 (CMC) to 1583 cm−1 (Cu0/CMC) and to 1588 cm−1 (Ag0/CMC).
Cu0NP and Ag0NP interaction with the polymeric chain seems to also involve the oxygen atoms of the saccharidic cycle, given the marked shift of the C-O bending and C-O-C stretching bands from 1021 cm−1 of CMC to 1015 cm−1 for Cu0/CMC and given the even more accentuated shift for Ag0/CMC (1110 cm−1). This band was also observed by Raghavendra et al. [25] as being provided by the carbohydrate CMC. Overall, the shifting of the peaks confirms the loading of metals by CMC.
3.3. Effect of Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC on IPEC-J2 Viability
To mimic the intestine environment of pigs, the porcine enterocyte cell line (IPEC-J2) was used as in vitro model. IPEC-J2 is a non-transformed and permanent columnar epithelial cell line isolated from neonatal piglet mid-jejunum [26]. The cells of this line express the receptor for fimbriae 4 (F4) [27]. These features make IPEC-J2 cells an interesting in vitro model to investigate the ways of F4 strains attachment on IPEC-J2 cells and to evaluate the antibacterial properties of MNP/CMC.
The safety concentration range of Cu0/CMC or Ag0/CMC was evaluated via 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction by viable IPEC-J2. Non-infected IPEC-J2 cells were treated with Cu0/CMC or Ag0/CMC at various concentrations in the range of 0–0.50 mg/mL for 24 h (Figure 3). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of Cu0/CMC and of Ag0/CMC were close to each other: 0.027 ± 0.003 mg/mL and 0.021 ± 0.001 mg/mL, respectively (Figure 3 closeup and Table S1). Differently, the concentration that inhibits the growth of IPEC-J2 at half (IC50) was 0.201 ± 0.013 mg/mL for Cu0/CMC, approximately four times higher than that of 0.052 ± 0.003 mg/mL observed for Ag0/CMC (Table S1). A lower IC50 and MIC for Ag0/CMC compared with those of Cu0/CMC (Figure 3 and closeup) revealed that the cytotoxicity of Ag0/CMC for non-infected IPEC-J2 was higher compared with that of the Cu0/CMC counterpart.
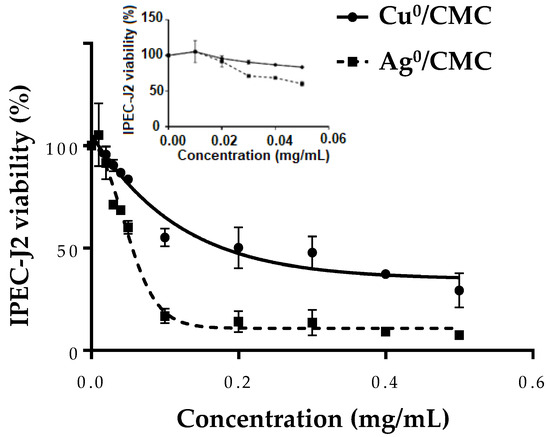
Figure 3.
The effect of MNP/CMC at various concentrations (0–0.5 mg/mL; insert: 0–0.05 mg/mL) on the viability of non-infected IPEC-J2. After 24 h of treatment, the cytotoxicity of Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC was assayed by the MTT test. The closeup shows for a concentration of 0.05 mg/mL, there was a loss of viability of about 15% for Cu0/CMC and about 30% for Ag0/CMC. The data are the average of three different experiments.
This favorable effect of Ag0/CMC toxicity may be related to the smaller particle sizes of both the material grains and of zero-valent metal; and to the increase in their surface-to-volume ratio. Both features make Ag0/CMC be regarded as suitable for acting on IPEC-J2. This hypothesis is in accordance with the impact of particle size mentioned by Danaei et al. [24].
3.4. Effect of MNP/CMC on ETEC:F4 Bacteria Viability
The biocidal activity of synthesized Cu0NP and Ag0NP hosted by CMC was evaluated on ETEC:F4 bacteria via the optical density at 600 nm. The ETEC:F4 EcL8559 strain was chosen in this study because it is the best characterized pathogen in swine postweaning diarrhea [28,29,30].
Bacteria (1 × 107 CFU/mL) were treated with MNP/CMC at various concentrations (0 to 0.5 mg/mL) to investigate their bactericidal activity (Figure 4 close-up). The IC50 values were 0.046 ± 0.003 mg/mL for Cu0/CMC and 0.023 ± 0.002 mg/mL for Ag0/CMC, whereas the MIC values were similar: 0.010 ± 0.001 mg/mL for both agents (Figure 4, close-up, Table S1). The IC50 values showed that Ag0/CMC was the most bactericidal material for bacteria grown. The same tendency was also observed when the bacteria were treated with metal-loaded glycodendrimers [23], suggesting that the small distribution size of Ag0/CMC increased their toxicity, while Cu0/CMC with a larger particle size distribution, was less toxic for bacteria. The other main observation was that the IC50 of MNP/CMC on bacteria viability are approximatively 5–3 times lower than that observed on enterocyte cell line IPEC-J2, suggesting that bacteria are more sensitive than IPEC-J2. Considering the previous results, the concentrations used to investigate the bactericidal activity of MNP/CMC on IPEC-J2 was from 0 to 0.05 mg/mL, which represented a toxic concentration range for bacteria.
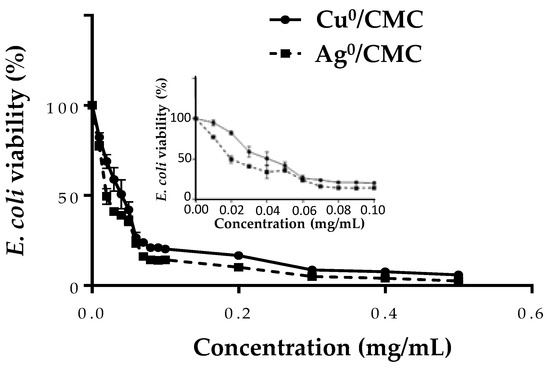
Figure 4.
The bactericidal effect of MNP/CMC at various concentrations (0–0.5 mg/mL and insert: 0–0.1 mg/mL) on ETEC:F4, expressed as loss of bacteria survival. The bacteria (1 × 107 CFU/mL) were treated with MNP/CMC at various concentrations for 24 h at 37 °C. The bacteria survival corresponds to the relative optical density at 600 nm of treated bacteria in solution compared with the untreated control (100%). The data are the average of three different experiments.
The antibacterial activity of MNP/CMC agents was also evaluated by a disk diffusion assay. The zone diffusion diameters on a 1 mg LB agar gel of some drugs such as kanamycin and fosfomycin, commonly used in veterinary or human health, were compared with those of the new MNP/CMC antibacterial agents (Table 2). As expected, no disk diffusion was observed with CMC treatment, reported as GRAS and used as a negative control. Compared with fosfomycin, the antibacterial activity of Cu0/CMC was similar, whereas Ag0/CMC was more bactericidal. In the same way, the antibacterial activity of Ag0/CMC was close (slightly lower) to that of the potent antibiotic kanamycin (Table 2). These results suggested that Ag0/CMC could be used as alternative to kanamycin against ETEC:F4 growth.

Table 2.
Antibacterial activity of MNP/CMC in comparison with that of current antibiotics used for human and porcine treatments. The diameters of inhibition zones were measured at 1 mg of antibacterial agents.
In order to complete the knowledge on the antibacterial activity of MNP/CMC, the biofilm formation by ETEC:F4 bacteria was evaluated by a crystal violet assay (Figure 5 and Figure S1), based on the principle that dye intensity (at 570 nm) correlates with the abundance of the bacterial biofilm (Figure 5). As expected, the Cu0/CMC andAg0/CMC inhibited the formation of bacterial biofilm with the same tendency as the cation forms (Cu2+ and Ag+) in terms of the disk diffusion test (Table 2). The CMC matrix (control) showed no bactericidal toxicity (Table 2) and no inhibition of biofilm formation (Figure 5). In addition, we also found that kanamycin could be substituted by Ag0/CMC. The inhibition of the formation of biofilm related to MNP/CMC treatments confirm the higher bactericidal activity of Ag0/CMC as observed by El-Riz et al. (2024), with Ag0 and Cu0 being hosted by manno-dendrimers [23].
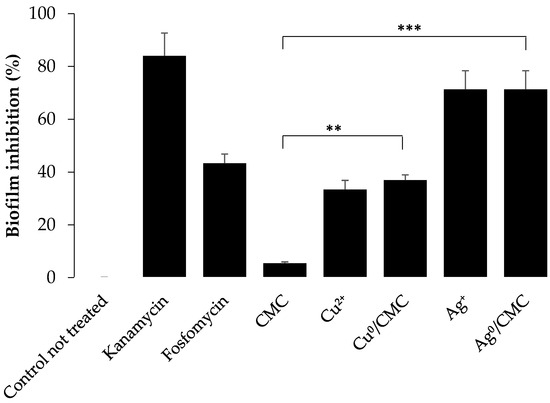
Figure 5.
Inhibition of enterotoxigenic E. coli biofilm formation by treatment with various antibacterial agents for 48 h at 37 °C. Biofilm formation was quantified by a crystal violet assay (measured on microplate at λ = 570 nm). Readings were normalized in terms of percentage of inhibition with 100% biofilm formation as a negative control; untreated bacteria with 0% inhibition. (mean ± SD, n = 3 of three different experiments. ** p ≤ 0.05 and *** p ≤ 0.005).
3.5. Cytotoxicity of MNP/CMC on the Proliferation of ETEC:F4 EcL8559 Strain on the Infected IPEC-J2
IPEC-J2 cells were infected with ETEC:F4 bacteria to mimic the infection in pigs. The viability of IPEC-J2 infected with ETEC:F4 was measured using the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assay (Promega, Canada) based on the release of intracellular enzyme LDH upon cell lysis. Different to the MTT method, based on the ability of living cells to cleave the tetrazolium ring and reduce the MTT to solid purple formazan-class dye, the LDH method evaluates the ability of MNP/CMC agents to disrupt cell membranes and release LDH into culture medium. LDH activity is an enzymatic reaction, where LDH oxidizes lactate to pyruvate, which reacts with yellow iodonitrotetrazolium chloride salt into a red formazan-class dye. Formazan dye is water soluble and can be readily detected by measuring the absorbance at 490 nm [31,32].
To understand the action mechanism of the MNP/CMC, three situations were envisaged. For situation 1: [{IPEC-J2 cells + ETEC:F4} + MNP/CMC] the results are presented in Figure 6(1a,1b); for situation 2: [{IPEC-J2 cells + MNP/CMC} + ETEC:F4] the results are presented in Figure 6(2a,2b); for situation 3: [IPEC-J2 + {ETEC:F4 + MNP/CMC }] the results are presented in Figure 6(3a,3b).
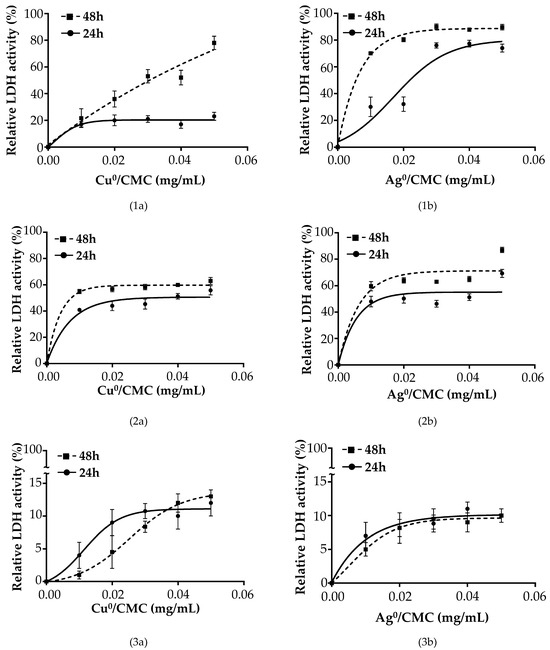
Figure 6.
Biocidal effect of Cu0/CMC (1a–3a) and Ag0/CMC (1b–3b) at various concentrations on IPEC-J2 infected with ETEC:F4 in different conditions: (1) IPEC-J2 first infected with 1 × 107 CFU/mL ETEC:F4 and then treated with Cu0/CMC (1a) or with Ag0/CMC (1b) for 24 h and 48 h; (2) IPEC-J2 first treated with Cu0/CMC (2a) or with Ag0/CMC (2b) for 24 h or 48 h and then infected with 1 × 107 CFU/mL ETEC:F4 for 24 h; and (3) IPEC-J2 infected with the mixture obtained from 1 × 107 CFU/mL ETEC:F4 bacteria previously treated for 24 h or 48 h with Cu0/CMC (3a) or with Ag0/CMC (3b) with MNP/CMC. In all three situations, IPEC-J2 cells were maintained at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
As previously mentioned, the IC50 of both MNP/CMC upon treatment of intestinal IPEC-J2 did not overlap with those obtained upon treatment of ETEC:F4 bacteria, and a concentration range of 0 to 0.05 mg/mL for both Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC was considered as suitable for investigating the beneficial effects of Cu0/CMC and of Ag0/CMC as anti-infectious agents on intestinal IPEC-J2 infected by the ETEC:F4 EcL8559 strain.
Figure 6 shows the viability profile of IPEC-J2 cells in the three situations (Situation 1 to 3). In Situations 1 and 2, the MNP/CMC treatment for 24 h led to a decrease in the LDH activity of 80 and 60% for Cu0/CMC (Figure 6(1a,2a)) and 25 and 30% for Ag0/CMC (Figure 6(1b,2b)), respectively, compared with the positive control (IPEC-J2 infected by ETEC:F4) under no protection by MNP/CMC, considered as the 100% release of LDH.
The curve tendency representing the LDH activity of infected cells treated with MNP/CMC is similar at 24 h compared with 48 h of treatment, with an increase phase and a stationary phase, except for Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC having an almost constant increase up to 80% LDH activity at 48 h of treatment (Figure 6(1a,2a)).
In Situation 3, the IPEC-J2 infected with ETEC:F4 pretreated with MNP/CMC bactericidal agents showed a markedly low LDH release of about 19% for Cu0/CMC (Figure 6(3a)) and 17% for Ag0/CMC (Figure 6(3b)), meaning a good viability of infected IPEC-J2, when the ETEC:F4 bacteria was pretreated with MNP/CMC bactericidal agents.
In all three situations, the IC50 of Cu0/CMC at treatment of up to 48 h on IPEC-J2 cells was 0.102 ± 0.017 mg/mL, whereas the IC50 values of Ag0/CMC-treated IPEC-J2 cells were 0.06 ± 0.005 mg/mL at 24 h and 0.038 ± 0.004 mg/mL at 48 h of treatment with ETEC:F4 (Table S1a), suggesting much higher bactericidal properties for Ag0/CMC but good tolerability by the IPEC-J2 at the selected range concentrations.
For both Ag°/CMC and Cu°/CMC, there is a higher toxicity on E. coli bacteria than on intestinal IPEC-J2 cells. This is a good result, showing high bactericidal activity and low cytotoxicity on intestinal cells and tissues. Furthermore, on the ETEC:F4 strain, the Ag°/CMC presented a higher bactericidal activity than that of Cu°/CMC. A similar trend was found on intestinal IPEC-J2 cells, with a higher cyto-toxicity of Ag°/CMC than that of Cu°/CMC, with the note that for both agents, the effect was moderate to low when compared with the effect on ETEC:F4 microorganisms.
The differences in terms of bactericidal activity may be explained by the key role of the particle size (PS) of the metal-loaded biopolymer, given that Ag°/CMC display a lower average diameter (210 ± 11 nm) as compared with Cu°/CMC (369 ± 23 nm), as shown in Figure 1, and a lower polydispersity index for Ag°/CMC (0.25 + 0.02) than for Cu°/CMC (0.96 + 0.06). This accounts for a higher contact surface with the infected aqueous medium.
These antibacterial properties induced by zero-valent metal nanoparticles are supported by control tests. The latter clearly demonstrated that CMC alone had no effect on bacteria, as no antibacterial activity was detected. Here, CMC is assumed to promote an optimal metal retention strength for simultaneously maximum metal stabilization and contact surface through minimum material particle size.
The IC50 of MNP/CMC for non-infected IPEC-J2 cells (Table S1, Figure 4) was approximately two times higher for Ag0NP/CMC or four times higher for Cu0NP/CMC than that in cells infected with ETEC:F4 bacteria (Table S2, Figure 6), meaning a low toxicity for the epithelial cells of intestinal tissue. A possible explanation of this result could be a high ability of MNP/CMC to penetrate bacteria [33] but not eukaryote cells. Thus, significant damage was supposed at the MNPs uptake by ETEC:F4 [34]. In our case, the damage was more pronounced with Ag0NPs from Ag0/CMC than with Cu0NPs from Cu0/CMC with a larger size (Table 1), emphasizing that the size of the particle is an important parameter related to their cell cytotoxicity [35,36].
The infective effect of bacteria was time-related (Figure S2a). Meanwhile, the non-infected IPEC-J2 and ETEC:F4 were treated with CMC polymer alone at various concentrations (0–0.5 mg/mL) used as the negative control, and non-significant effects (p > 0.05) on both non-infected IPEC-J2 and on ETEC:F4 viability were found (Figure S2b). In opposition to different anaerobic Gram-positive and Gram-negative gut bacteria such as Ruminococcus albus and Bacteroides cellulosolvens (found in the lumen of major ruminants) that are able to degrade cellulose, E. coli is not able to metabolize cellulose [37,38]. This can explain why treatment with CMC alone did not have any effect on the proliferation or on ETEC:F4 viability.
The MTT viability assay on infected cells showed an increased formazan formation compared with non-infected cells, considered as 100% viability. It was reported that ETEC:F4 reduces MTT [39] and the increase in absorbency above 100% viability could be explained by the interference of the ETEC:F4 signal to that of IPEC-J2. In contrast, no significant variation of LDH activity was observed in relation to the presence of bacteria, supporting the previous statement that the MTT kit could be also used to assay bacteria viability [40]. The increase in formazan crystal formation could be due to the cell surface-attached bacteria in accordance with [41], which showed that ETEC:F4 expressing F4 can bind IPEC-J2 cells and release enterotoxins. Consequently, the interfering increased MTT reduction to formazan by IPEC-J2 in the presence of bacteria and justified the choice for the LDH assay to evaluate the viability of IPEC-J2 infected with ETEC:F4.
Fosfomycin is an antibiotic used in pig farms to inhibit E. coli infections and proliferation. It was used in this study to compare the bactericidal potency of Cu0/CMC and of Ag0/CMC with that of currently used antibiotics. The bactericidal activity of fosfomycin observed against ETEC: F4 (Table 2) was lower than that of Ag0/CMC. Compared with kanamycin, the zero-valent Ag0/CMC nanoparticles inhibited ETEC:F4 EcL8559 strain proliferation (Table 2) with a bactericidal potency of the same order (slightly lower) and also efficiently inhibited bacterial biofilm formation (Figure 6). Its strong bactericidal potential on E. coli, as shown by its IC50, approximately four times lower than that of Cu0/CMC (Figure 5), was observed with the crystal violet test used for the quantification of bacteria biofilm formation (Figure 6). The bactericidal properties of Cu0/CMC (NPs) and Ag0/CMC (NPs), with a higher antibacterial potency of Ag0/CMC (NPs) related to their smaller size, were reported by Noori et al. [22,42,43] in the case of non-pathogenic E coli DH5α, showing the role of MNP/CMC dispersion in the CMC hosting matrix. To reduce the effect of enterotoxigenic E. Coli contaminations in swine industries, the antibacterial effects of MNP/CMC agents could be proposed for further investigations and developments as alternative agents against pathogenic bacteria-related infections. In addition, to assess the therapeutic potential and safety of zero-valent MNP/CMC, the next part of this project will be aimed at in vivo studies, using weaning piglets as an animal model.
4. Conclusions
Nanomaterials consisting of zero-valent Cu0 and Ag0 hosted by carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) exerted bactericidal activities with a stronger antibacterial action of Ag0/CMC compared with Cu0/CMC. It was found that intestinal porcine enterocytes IPEC-J2 represent a good model to investigate ETEC:F4 bacteria infectivity and cytotoxicity and that Ag0/CMC and Cu0/CMC prevented the infection of intestinal cells by enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC:F4).
The concentrations of MNP/CMC must be tailored to selectively target the death of ETEC:F4 bacteria and not that of IPEC-J2. Higher bactericidal effectiveness was shown by the smaller particle size of MNP/CMC and their lower polydispersity index. In addition, Cu0/CMC and Ag0/CMC have antibacterial activities that fit well with the data obtained with the currently used antibiotics kanamycin and fosfomycin. Further studies will be conducted with the aim of determining the mechanisms of the antibacterial activity of Cu0/CMC and of Ag0/CMC and investigating their antibacterial effect in vivo on post-weaned piglets with ETEC:F4 infection symptoms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms12102026/s1, Table S1: Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of MNP/CMC on IPEC-J2, uninfected or infected by ETEC:F4 bacteria. Table S2: Inhibitory concentration (IC50 in mg/mL). Figure S1: Quantification of biofilm formation by a crystal violet assay at 570 nm. Figure S2: IPEC-J2 infected by ETEC:F4 bacteria.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C., A.T.N., M.A.M., and A.A.; methodology, A.T.N. and F.N.; validation, M.A.M. and Y.C.; formal analysis, A.T.N., Y.C., and M.A.M.; investigation, A.T.N.; resources, J.M.F., A.A., F.N., M.A.M., and Y.C.; data curation, A.T.N. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T.N.; writing—review and editing, M.A.M., Y.C., A.A., J.M.F., M.C., and A.T.N.; visualization, A.T.N.; supervision, Y.C. and M.A.M.; project administration, Y.C. and M.A.M.; funding acquisition, M.A.M. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the CRIPA-FRQNT New Initiatives Grant to Y. Chorfi, M. A. Mateescu, J. Fairbrother, and M. Costa and was also supported by the NSERC, grant number 06912 (M. A. Mateescu). A FRQNT postdoctoral fellowship to A. Tchoumi Neree is gratefully acknowledged.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We thank Claudia Paquette from the Department of Pathology and Microbiology of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at Université de Montréal (FVM-UdeM), who provided equipment for microbiological experiments; Ghislaine Vanier from the Centre de diagnostic vétérinaire de l’UdeM for sharing her advice during the bacteria experiments; and Imourana Alassane-Kpembi from the Veterinary Biomedicine Department at FMV-UdeM, who kindly offered IPEC-J2.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
List of Abbreviations
Ag0/CMC: nanoparticles of zero-valent silver loaded on CMC; CFU: colony-forming units; CMC: carboxymethyl cellulose; Cu0/CMC: nanoparticles of zero-valent copper loaded on CMC; DS: degree of substitution of CMC; ETEC: enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli; F4: fimbriae 4; ETEC:F4: enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli producing fimbriae 4; IC50: half maximal inhibitory concentration; LB: Luria broth or Luria–Bertani medium; M: zero-valent metal (Cu0, Ag0); MIC: minimal inhibitory concentration; MOI: multiplicity of infection; MNPs: metal nanoparticles; MNPs/CMC: Nanoparticles of zero-valent metal loaded on CMC; NPs: nanoparticles; PDI: polydispersity index.
References
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Ruesch, L.; Omot, A.; Francis, D. Prevalence of virulence genes in Escherichia coli strains recently isolated from young pigs with diarrhea in the US. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 123, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svennerholm, A.-M.; Lundgren, A. Developments in Oral Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli Vaccines. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2023, 84, 102372–102380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, A. Swine enteric colibacillosis: Diagnosis, therapy and antimicrobial resistance. Porc. Health Manag. 2017, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Fekete, P.Z. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) in farm animals. Vet. Res. 1999, 30, 259–284. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyet, L.T.Y.; Ounjai, P.; Kaeoket, K.; Ngamwongsatit, N. Feasibility of crude F4 fimbriae extract as a vaccine candidate for preventing Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in piglets. Vet. World 2023, 16, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lagarde, M.; Vanier, G.; Desmarais, G.; Kohan-Ghadr, H.R.; Arsenault, J.; Fairbrother, J.M. A new multidrug-resistant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli pulsed-field gel electrophoresis cluster associated with enrofloxacin non-susceptibility in diseased pigs. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, F.; Ren, J. AuNPs-PCL Nanocomposite Accelerated Abdominal Wound Healing through Photothermal Effect and Improving Cell Adhesion. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 2035–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Fromm, K.M.; Ashkarran, A.A.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; de Larramendi, I.R.; Rojo, T.; Serpooshan, V.; Parak, W.J.; Mahmoudi, M. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Pollini, M.; Sannino, A.; Ambrosio, L. Metal-Based Antibacterial Substrates for Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, J.; Humphreys, H. Application of copper to prevent and control infection. Where are we now? J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 81, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczny, J.; Rdzawski, Z. Antibacterial Properties of Copper and Its Alloys. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2012, 56, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles of different particle size against Vibrio Natriegens. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimirad, S.; Ajalloueian, F.; Ghorbanpour, M. Synthesis and therapeutic potential of silver nanomaterials derived from plant extracts. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiorgos, V. Stabilisers. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 689–694. ISBN 978-0-12-818766-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ergun, R.; Guo, J.; Huebner-Keese, B. Cellulose. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 694–702. [Google Scholar]
- Ispas-Szabo, P.; De Koninck, P.; Calinescu, C.; Mateescu, M.A. Carboxymethyl Starch Excipients for Drug Chronodelivery. Aaps Pharmscitech 2017, 18, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, T.; Narayana, S.N.G.H.; Pal, K.; Pramanik, K.; Giri, S.; Banerjee, I. Calcium alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose beads for colon-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zennifer, A.; Senthilvelan, P.; Sethuraman, S.; Sundaramurthi, D. Key advances of carboxymethyl cellulose in tissue engineering & 3D bioprinting applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.-Q.; Cui, F.-Z.; Kim, T.; Kim, J. A Mechanistic Study of the Antibacterial Effect of Silver Ions on Escherichia Coli and Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, F.; Megoura, M.; Labelle, M.-A.; Mateescu, M.A.; Azzouz, A. Synthesis of Metal-Loaded Carboxylated Biopolymers with Antibacterial Activity through Metal Subnanoparticle Incorporation. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Riz, A.; Neree, A.T.; Mousavifar, L.; Roy, R.; Chorfi, Y.; Mateescu, M.A. Metallo-Glycodendrimeric Materials against Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendra, G.M.; Jayaramudu, T.; Varaprasad, K.; Sadiku, R.; Ray, S.S.; Raju, K.M. Cellulose–Polymer–Ag Nanocomposite Fibers for Antibacterial Fabrics/Skin Scaffolds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Britto, D.; Assis, O.B. Thermal Degradation of Carboxymethylcellulose in Different Salty Forms. Thermochim. Acta 2009, 494, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergauwen, H. The IPEC-J2 Cell Line. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother, J.M.; Nadeau, É.; Gyles, C.L. Escherichia Coli in Postweaning Diarrhea in Pigs: An Update on Bacterial Types, Pathogenesis, and Prevention Strategies. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2005, 6, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouma, M.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Beaudry, F.; Letellier, A. Post weaning diarrhea in pigs: Risk factors and non-colistin-based control strategies. Acta Vet. Scand. 2017, 59, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, J.M.; Nadeau, É. Colibacillosis. Dis. Swine 2019, 807–834. [Google Scholar]
- Kaja, S.; Payne, A.J.; Naumchuk, Y.; Koulen, P. Quantification of Lactate Dehydrogenase for Cell Viability Testing Using Cell Lines and Primary Cultured Astrocytes. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2017, 72, 2.26.1–2.26.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, T.; Lohmann-Matthes, M.-L. A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J. Immunol. Methods 1988, 115, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skomorokhova, E.A.; Sankova, T.P.; Orlov, I.A.; Savelev, A.N.; Magazenkova, D.N.; Pliss, M.G.; Skvortsov, A.N.; Sosnin, I.M.; A Kirilenko, D.; Grishchuk, I.V.; et al. Size-Dependent Bioactivity of Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Properties, Influence on Copper Status in Mice, and Whole-Body Turnover. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2020, 13, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, W.; Ding, R.; Wang, J.; Yao, L. Mechanism of low concentrations of polystyrene microplastics influence the cytotoxicity of Ag ions to Escherichia coli. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, L.; Zuo, F.; Li, L.; Hou, S. Size-dependent enhancement on conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes by micro/nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128561–128573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongrakpanich, A.; Mudunkotuwa, I.A.; Geary, S.M.; Morris, A.S.; Mapuskar, K.A.; Spitz, D.R.; Grassian, V.H.; Salem, A.K. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in lung epithelial cells. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanca-Cardona, L.; Ashe, C.S.; Stipanovic, A.J.; Nomura, C.T. Enhanced production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from beechwood xylan by recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.B.; Muck, R.E.; Weimer, P.J. Quantitative analysis of cellulose degradation and growth of cellulolytic bacteria in the rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Shi, D.; Chen, K.; Palmer, J.; Popovich, D.G. An improved MTT colorimetric method for rapid viable bacteria counting. J. Microbiol. Methods 2023, 214, 106830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benov, L. Effect of growth media on the MTT colorimetric assay in bacteria. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, M.M.; Niewold, T.A. Preliminary Characterization of the Transcriptional Response of the Porcine Intestinal Cell Line IPEC-J2 to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli, Escherichia Coli, and E. Coli Lipopolysaccharide. Int. J. Genom. 2010, 2010, 469583–469594. [Google Scholar]
- Brosnahan, A.J.; Brown, D.R. Porcine IPEC-J2 intestinal epithelial cells in microbiological investigations. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 156, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, F.; Neree, A.T.; Megoura, M.; Mateescu, M.A.; Azzouz, A. Insights into the metal retention role in the antibacterial behavior of montmorillonite and cellulose tissue-supported copper and silver nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 24156–24171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).