Comparison of Phenotype Nutritional Profiles and Phosphate Metabolism Genes in Four Serovars of Salmonella enterica from Water Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Growth Kinetics
2.3. Phenotype Microarrays
2.4. Genome Sequencing and CRISPR Sequence Comparisons
2.5. Gene and Protein Sequence Alignments
3. Results
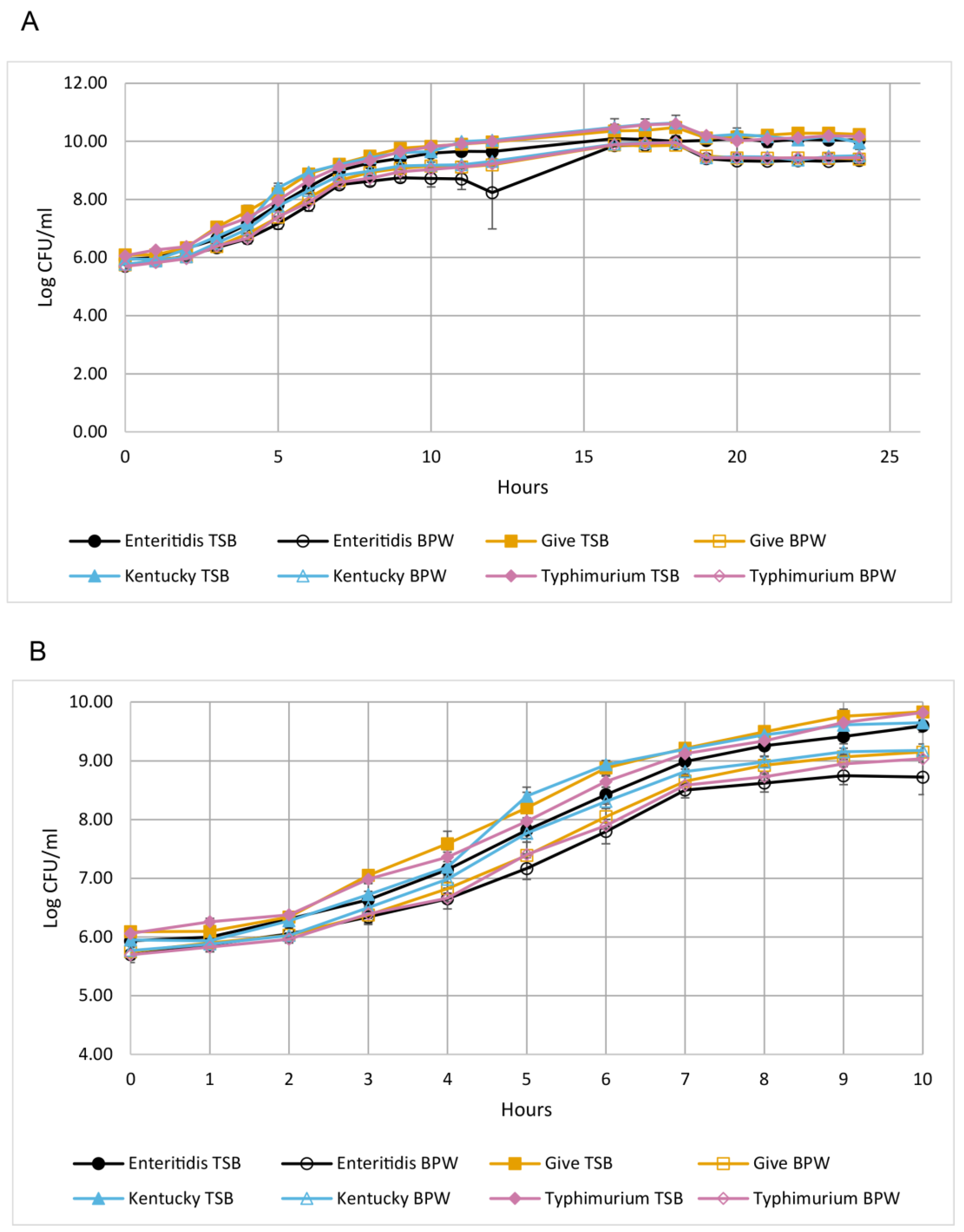
3.1. The Serovars Had Similar Growth Kinetics in TSB and BPW
3.2. The Serovars Had Phenotype Differences in Nutrient Utilization
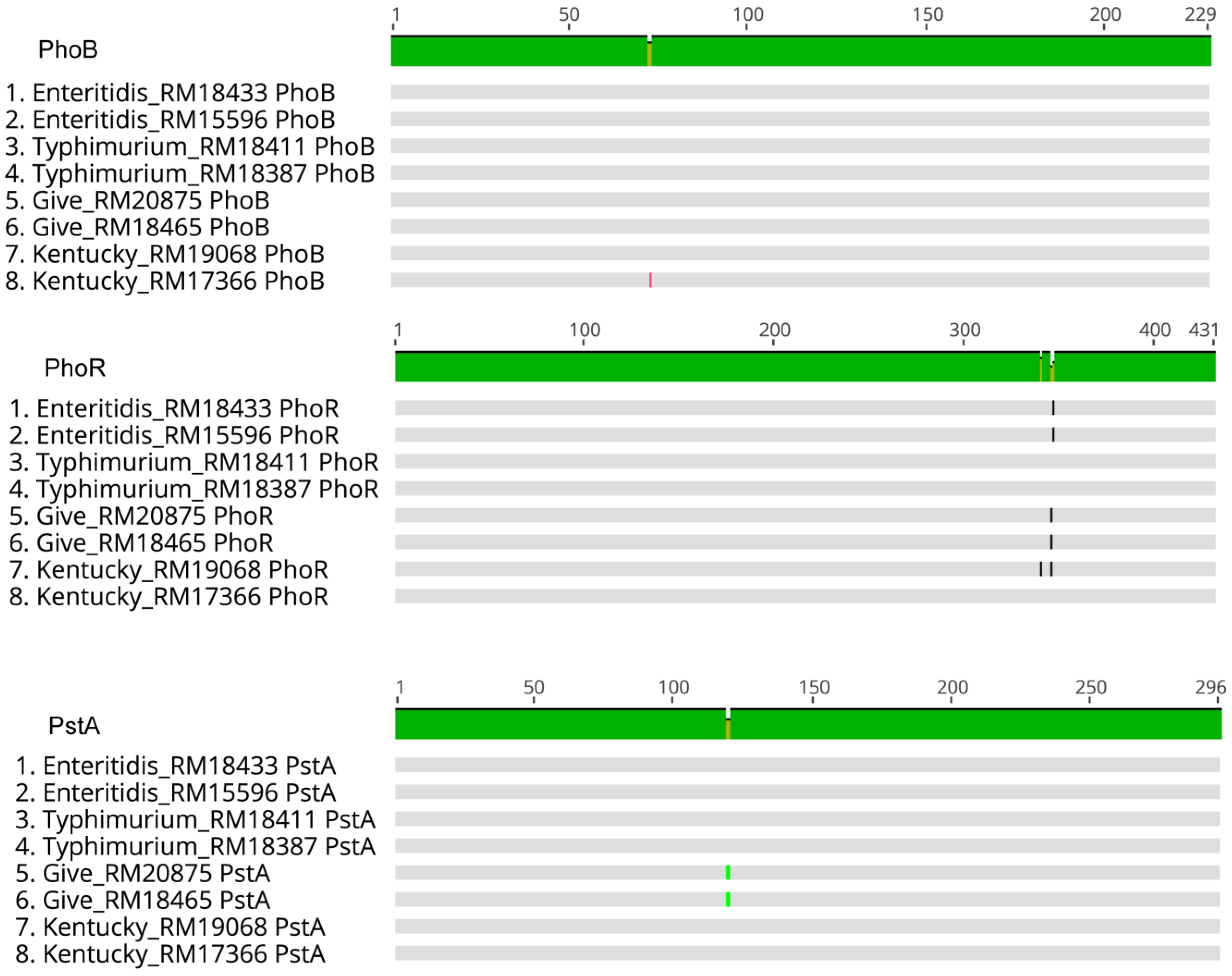
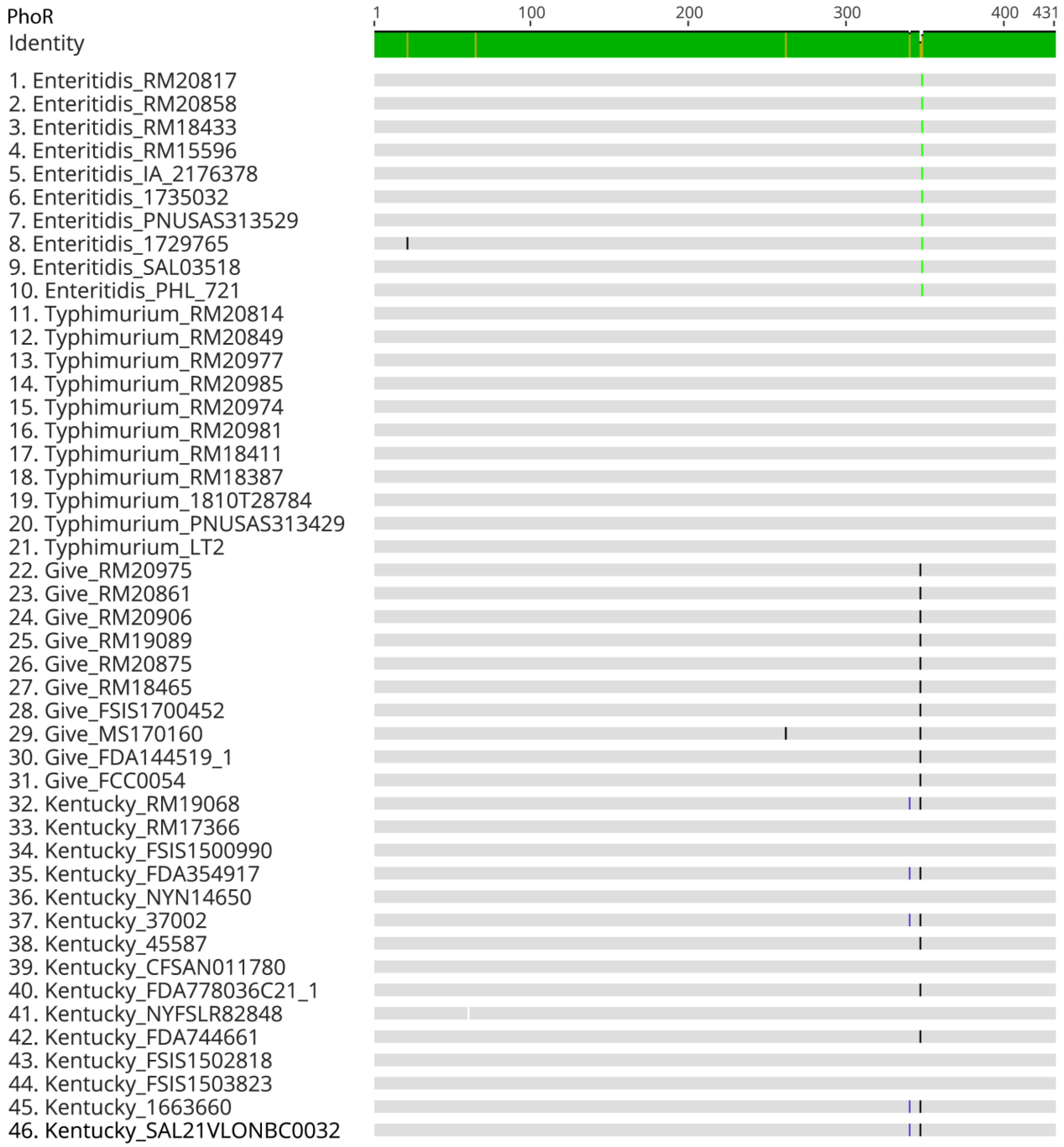
3.3. PhoR Gene and Amino Acid Sequences Differed between Serovars
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walter, E.J.S.; Griffin, P.M.; Bruce, B.B.; Hoekstra, R.M. Estimating the number of illnesses caused by agents transmitted commonly through food: A scoping review. Foodborne Path. Dis. 2021, 18, 841–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey-Mattia, D.; Manikonda, K.; Hall, A.J.; Wise, M.E.; Crowe, S.J. Surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks—United States, 2009–2015. MMWR 2018, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batz, M.B.; Richardson, L.C.; Bazaco, M.C.; Parker, C.C.; Chirtel, S.J.; Cole, D.; Golden, N.J.; Griffin, P.M.; Gu, W.; Schmitt, S.K.; et al. Recency-weighted statistical modeling approach to attribute illnesses caused by 4 pathogens to food sources using outbreak data, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Enteric Disease Surveillance: Salmonella Annual Report. 2016. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nationalsurveillance/pdfs/2016-Salmonella-report-508.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2022).
- European Food Safety Authority. The European Union One Health 2021 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, N.; Li, Z.; Ma, S.; Cao, D.; Pan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, H.; Gao, G.F.; et al. The temporal dynamics of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella enterica and predominant serovars in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwac269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, N.A.; Berrang, M.E.; House, S.L.; Medina, D.; Cook, K.L.; Shariat, N.W. Population analyses reveal preenrichment method and selective enrichment media affect Salmonella serovars detected on broiler carcasses. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardol de la Gandara, M.; Fournet, N.; Bonifalt, L.; Lefèvre, S.; Chemaly, M.; Grastilleur, C.; Cadel-Six, S.; Fach, P.; Pignault, A.; Brisabols, A.; et al. Countrywide multi-serotype outbreak of Salmonella Bovismorbificans ST142 and monophasic Salmonella Typhimurium ST34 associated with dried pork sausages in France, September 2020 to January 2021. Euro Surveill. 2023, 28, 2200123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaven, A.M.; Ferreira, C.M.; Reed, E.A.; See, J.R.C.; Lee, N.A.; Almaraz, E.; Rios, P.C.; Marogi, J.G.; Lamendella, R.; Zheng, J.; et al. Salmonella genomics and population analyses reveal high inter- and intraserovar diversity in freshwater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02594-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, L.; Liang, A.S.; Walker, S.; Carychao, D.; Aviles Noriega, A.; Mandrell, R.E.; Cooley, M.B. Salmonella enterica serovar diversity, distribution, and prevalence in public-access waters from a Central California coastal leafy green-growing region from 2011 to 2016. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e01834-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, W.H.; Wang, H.; Jacobson, A.; Ge, B.; Zhang, G.; Hammack, T. BAM Chapter 5: Salmonella. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/laboratory-methods-food/bam-chapter-5-salmonella (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- U. S. Department of Agriculture Food Safety Inpection Service. Isolation and Identification of Salmonella from Meat, Poultry, Pasteurized Egg, Carcass, and Environmental Sponges. Available online: https://www.fsis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media_file/documents/MLG-4.13.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella—Part1: Detection of Salmonella spp. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/56712.html (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Becton Dickinson. Difco & BBL Manual; Becton Dickinson and Company: Sparks, MD, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gorski, L. Selective enrichment media bias the types of Salmonella enterica strains isolated from mixed strain cultures and complex enrichment broths. Pathogenesis 2012, 7, e34722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, B.R.; Richardson, K.E.; Obe, T.; Schaeffer, C.; Shariat, N.W. Mixed Salmonella cultures reveal competitive advantages between strains during pre-enrichment and selective enrichment. J. Food Saf. 2021, 41, e12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.H.; Paul, N.C.; Sischo, W.C.; Crespo, R.; Guard, J. Population dynamics and antimicrobial resistance of the most prevalent poultry-associated Salmonella serotypes. Poultry Sci. 2017, 96, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Taabodi, M.; Schwarz, J.G.; Oscar, T.P.; Harter-Dennis, J.; White, D.G. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella recovered from processed poultry. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEgan, R.; Chandler, J.C.; Goodridge, L.D.; Danyluk, M.D. Diversity of Salmonella isolates from Central Florida surface waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6819–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, J.J.; Martin, G.; Hernandez, S.; Cheng, Y.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Hise, K.; D’Angelo, M.T.; Cole, D.; Sanchez, S.; Madden, M.; et al. Diversity and persistence of Salmonella enterica strains in rural landscapes in the Southeastern United States. Pathogenesis 2015, 10, e0128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, M.T.; Van Kessel, J.S.; Micallef, S.A. Salmonella enterica recovery from river waters of the Maryland Eastern Shore reveals high serotype diversity and some multidrug resistance. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, R.; Désilets, A.; Cantin, M.; Messier, S.; Khakhria, R.; Ismaïl, J.; Mulvey, M.R.; Daignault, D.; Caron, H. Outbreak of Salmonella Give in the province of Quebec. Can. Vet. J. 1997, 38, 780–781. [Google Scholar]
- Giardin, F.; Mezger, N.; Hächler, H.; Bovier, P.A. Salmonella serovar Give: An unusual pathogen causing splenic abscess. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 25, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hello, S.; Harrois, D.; Bouchrif, B.; Sontag, L.; Elhani, D.; Guibert, V.; Zerouali, K.; Weill, F.-X. Highly drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198-X1: A microbiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.J.; Kim, S.W.; Haendiges, J.; Keller, E.; Torpey, D.; Kim, A.; Crocker, K.; Myers, R.A.; Van Kessel, J.S. Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky recovered from human clinical cases in Maryland, USA (2011–2015). Zoonoses Pub. Health 2019, 66, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yu, K.; Qi, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wu, M.; Wang, Z.; Fu, J.; Liu, X. A proteomic view of Salmonella Typhimurium in response to phosphate limitation. Proteomes 2018, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groisman, E.A. The pleiotropic two-component regulatory system PhoP-PhoQ. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, R.E.; Kendra, C.G.; Groisman, E.A.; Pontes, M.H. Limitation of phosphate assimilation maintains cytoplasmic magnesium homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021370118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, M.H.; Groisman, E.A. Protein synthesis controls phosphate homeostasis. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarche, M.G.; Wanner, B.L.; Crépin, S.; Harel, J. The phosphate regulon and bacterial virulence: A regulatory network connecting phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008, 32, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jeong, G.; Choi, E.; Lee, E.-J. A dual regulatory role of the PhoU protein in Salmonella Typhimurium. mBio 2022, 13, 00811–00822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Beneit, F. The Pho regulon: A huge regulatory network in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougdour, A.; Gottesman, S. ppGpp regulation of RpoS degradation via an anti-adaptor protein IraP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12896–12901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinchen, W.; Zegarra, V.; Bange, G. (p)ppGpp: Magic modulators of bacterial physiology and metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzl, M.I.; van Mastrigt, O.; Zwietering, M.H.; Abee, T.; den Besten, H.M.W. Role of substrate availability in the growth of Campylobacter co-cultured with extended spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Bolton broth. Intl. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 363, 109518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-D.; Alexander, A.; Kinnersley, M.; Cook, E.; Caudy, A.; Rosebrock, A.; Rosenzweig, F. Fitness and productivity increase with ecotypic diversity among Escherichia coli strains that coevolved in a simple, constant environment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00051-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Zhou, Z.; Sergeant, M.J.; Achtman, M. A genomic overview of the population structure of Salmonella. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Mohamed, K.; Fan, Y.; the Agama Study Group; Achtman, M. The EnteroBase user’s guide, with case studies on Salmonella transmissions, Yersinia pestis phylogeny, and Escherichia core genomic diversity. Genome Res. 2020, 32, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwietering, M.H.; Jongenburger, I.; Rombouts, F.M.; van’t Riet, K. Modeling of the bacterial growth curve. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lei, X.-H.; Bochner, B.R.; Wanner, B.L. Phenotype microarray analysis of Escherichia coli K-12 mutants with deletions of all two-component systems. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 4956–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohsato, Y.; Mori, H. Phenotype profiling of single gene deletion mutants of E. coli using Biolog technology. Genome Inform. 2008, 21, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceapa, C.; Lambert, J.; van Limpt, K.; Wels, M.; Smokvina, T.; Knol, J.; Kleerebezem, M. Correlation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus genotypes and carbohydrate utilization signatures determined by phenotype profiling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 5458–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.T.; Huynh, S.; Alexander, A.; Oliver, A.S.; Cooper, K.K. Genomic characterization of Salmonella typhimurium DT104 strains associated with cattle and beef products. Pathogens 2021, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; den Bakker, H.C.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Lane, C.; Lauer, A.C.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. SeqSero2: Rapid and Improved Salmonella Serotype Determination Using Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01746-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.G.; Miller, J.B.; Dean, T.; Robinson, T.; Erickson, M.; Ridge, P.G.; McCleary, W.R. Genetic analysis, structural modeling, and direct coupling analysis suggest a mechanism for phosphate signaling in Escherichia coli. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmany, D.O.; Hollingsworth, K.; McCleary, W.R. Genetic and biochemical studies of phosphatase activity of PhoR. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malorny, B.; Bunge, C.; Helmuth, R. Discrimination of d-tartrate-fermenting and -nonfermenting Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica isolates by genotypic and phenotypic methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4292–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Armisen, T.; Aznil, A.; Cornelis, P.; Chevreuil, M.; Servais, P. Identification of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in rivers: Insights into the cultivation bias. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4938–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Stine, O.C.; Smith, D.L.; Spitznagel, J.K., Jr.; Labib, M.E.; Williams, H.N. Microbial diversity of biofilms in dental unit water systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3412–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguita-Maeso, M.; Olivares-Garcia, C.; Haro, C.; Imperial, J.; Navas-Cortés, J.A.; Landa, B.B. Culture-dependent and culture-independent characterization of the olive xylem microbiota: Effect of sap extraction methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uelze, L.; Becker, N.; Borowiak, M.; Busch, U.; Dangel, A.; Deneke, C.; Fischer, J.; Flieger, A.; Hepner, S.; Huber, I.; et al. Toward an integreated genome-based surveillance of Salmonella enterica in Germany. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 626941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, J.D.; Knox, N.C.; Ronholm, J.; Pagotto, F.; Reimer, A. Metagenomics: The next culture-independent game changer. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, H.A.; Besser, J.; Williams-Newkirk, A.J.; Huang, A.; Trees, E.; Gerner-Smidt, P. Metagenomic approaches for public health surveillance of foodborne infections: Opportunities and challenges. Foodborne Path. Dis. 2019, 16, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.G.; Tate, C.R. Xylose-lysine-tergitol 4: An improved selective agar medium for the isolation of Salmonella. Poult. Sci. 1991, 70, 2429–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortlock, R.P.; Old, D.C. Utilization of D-xylose by wild-type strains of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 137, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkowitz, D. D-mannitol utilization in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1971, 105, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.I.; Schelhart, D. Isolation of Shigellae. Appl. Microbiol. 1968, 16, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhy, M.T.; Brown, C.M.; Old, D.C. L-rhamnose utilisation in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1984, 56, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, B.L. Phosphorus assimilation and its control of gene expression in Escherichia coli. In The Molecular Basis of Bacterial Metabolism; Hauska, G., Thauer, R.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Correll, D.L. The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R.; Klose, M.; Claus, P. Phosphate inhibits acetotrophic methanogenesis on rice roots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Hu, H.-Y.; Xu, J.-J.; Shi, Z.-J.; Deng, R.; Ji, Z.-Q.; Shi, M.-L.; Jin, R.-C. Effects of inorganic phosphate on a high-rate anammox system: Performance and microbial community. Ecol. Engin. 2017, 101, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkeala, H.; Pekkanen, T.J. The effect of pH and postassium phosphate buffer on the toxicity of cadmium for bacteria. Acta Vet. Scand. 1978, 19, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, S.G.; McCleary, W.R. Control of the phoBR regulon in Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2019, 8, ESP-0006-2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBogelen, R.A.; Olson, E.R.; Wanner, B.L.; Neidhardt, F.C. Global analysis of proteins synthesized during phophorus restriction in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4344–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosik, D.; Tewari, D.; Dettinger, L.; M’ikanatha, N.M.; Shariat, N.W. CRISPR typing and antibiotic resistance correlates with polyphyletic distribution in human isolates of Salmonella Kentucky. Foodborne Path. Dis. 2018, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.A.; Orsi, R.H.; Wiedmann, M. Phylogenetic clustering suggests that distinct clades of Salmonella enterica serovar Mississippi are endemic in Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States. mSphere 2021, 6, e00485-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marina, A.; Waldburger, C.D.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structure of the entire cytoplasmid portion of a sensor histidine-kinase protein. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 4247–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sang, J.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Downey, J.S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; et al. Mechanistic insights revealed by the crystal structure of a histidine kinase with signal transducer and sensor domains. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.B.; Kossman, M.; Santos, H.; Boos, W. Kinetic analysis by in vivo 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of internal Pi during the uptake of sn-glycerol-3-phosphate by the pho regulon-dependent Ugp system and the glp regulon-dependent GlpT system. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, R.G.; Brown, T.R.; Ugubil, K.; Ogawa, S.; Cohen, S.M.; den Hollander, J.A. Cellular applications of 31P and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance. Science 1979, 205, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayeola, V.; Farber, J.M.; Kathariou, S. Induction of the viable-but-nonculturable state in Salmonella contaminating dried fruit. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e01733-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Whitehouse, C.A.; Li, B. Presence and persistence of Salmonella in water: The impact on microbial quality of water and food safety. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purevdorj-Gage, L.; Nixon, B.; Bodine, K.; Xu, Q.; Doerrler, W.T. Differential effect of food sanitizers on formation of viable but nonculturable Salmonella enterica in poultry. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, X.; Feng, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Ding, T. Inducation of viable but nonculturable Salmonella spp. in liquid eggs by mild heat and subsequent resuscitation. Food Microbiol. 2023, 109, 104127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.C.H. A review of microbial injury and recovery methods in food. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, M.T.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Haxo, A.F.; Berk, S.G. Enhanced survival of Salmonella enterica in vesicles released by a soilborne Tetrahymena species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, M.T.; Mammel, M.K.; Simko, I.; Richter, T.K.S.; Gebru, S.T.; Leonard, S.R. Weather factors, soil microbiome, and bacteria-fungi interactions as drivers of epiphytic phyllosphere communities of romaine lettuce. Food Microbiol. 2023, 113, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottesen, A.R.; Gonzalez, A.; Bell, R.; Arce, C.; Rideout, S.; Allard, M.; Evans, P.; Strain, E.; Musser, S.; Knight, R.; et al. Co-enriching microflora associated with culture based methods to detect Salmonella from tomato phyllosphere. Pathogenesis 2013, 8, e73079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strain ID | Serovar | Sequence Type | Source, Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| RM18465 *,1 | Give | 654 | Water/sediment, 2014 |
| RM20875 * | Give | 158 | Water/sediment, 2013 |
| RM15596 * | Enteritidis | 814 | Water/sediment, 2011 |
| RM15890 | Enteritidis | ND 2 | Water/sediment, 2011 |
| RM16950 | Enteritidis | ND | Water/sediment, 2011 |
| RM18433 * | Enteritidis | 11 | Water/sediment, 2013 |
| RM20787 | Enteritidis | ND | Water/sediment, 2015 |
| RM1316 | Kentucky | ND | Ground beef, 1997 |
| RM7890 | Kentucky | ND | Ground chicken, 2008 |
| RM17366 * | Kentucky | 152 | Water/sediment, 2013 |
| RM19068 * | Kentucky | 198 | Water/sediment, 2015 |
| RM17930 | Typhimurium | ND | Water/sediment, 2013 |
| RM16783 | Typhimurium | ND | Water/sediment, 2012 |
| RM18411 * | Typhimurium | 19 3 | Water/sediment, 2014 |
| RM18387 * | Typhimurium | 19 3 | Water/sediment, 2014 |
| Gene/Operon | Identity | Function |
|---|---|---|
| phoBR | Two-component histidine kinase response regulatory proteins | Respond to environmental Pi levels and transcriptional regulation of genes involved in phosphate transfer and utilization |
| pstSCAB | Phosphate ABC transporter | High-affinity Pi transporter |
| phoU | Phosphate-specific transport system accessory | Binds to and controls function of PstSCAB transfer system Binds Mg2+ and Mn2+ |
| rpoS | Sigma factor S | Cellular responses to stresses |
| iraP | RpoS adaptor protein | Inhibits RpoS proteolysis during Pi starvation |
| rrsB | Adaptor protein | Regulator of RpoS degradation |
| Medium | Serovar | Lag Phase Length (h) | Generation Time (h) | Maximum CFU/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSB 1 | Enteritidis | 3.0 | 0.51 | 1.32 × 1010 |
| Give | 2.3 | 0.58 | 2.83 × 1010 | |
| Kentucky | 2.2 | 0.56 | 3.23 × 1010 | |
| Typhimurium | 2.2 | 0.49 | 3.11 × 1010 | |
| BPW 1 | Enteritidis | 2.3 | 0.50 | 6.69 × 109 |
| Give | 2.2 | 0.57 | 6.93 × 109 | |
| Kentucky | 2.2 | 0.57 | 8.07 × 109 | |
| Typhimurium | 2.3 | 0.51 | 7.95 × 109 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorski, L.; Noriega, A.A. Comparison of Phenotype Nutritional Profiles and Phosphate Metabolism Genes in Four Serovars of Salmonella enterica from Water Sources. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082109
Gorski L, Noriega AA. Comparison of Phenotype Nutritional Profiles and Phosphate Metabolism Genes in Four Serovars of Salmonella enterica from Water Sources. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(8):2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082109
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorski, Lisa, and Ashley Aviles Noriega. 2023. "Comparison of Phenotype Nutritional Profiles and Phosphate Metabolism Genes in Four Serovars of Salmonella enterica from Water Sources" Microorganisms 11, no. 8: 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082109
APA StyleGorski, L., & Noriega, A. A. (2023). Comparison of Phenotype Nutritional Profiles and Phosphate Metabolism Genes in Four Serovars of Salmonella enterica from Water Sources. Microorganisms, 11(8), 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082109







