Abstract
Pectobacterium versatile (formally P. carotovorum) causes disease on diverse plant species by synthesizing and secreting copious amount of plant-cell-wall-degrading exoenzymes including pectate lyases, polygalacturonases, cellulases, and proteases. Exoenzyme production and virulence are controlled by many factors of bacterial, host, and environmental origin. The ion channel forming the magnesium, nickel, and cobalt transporter CorA is required for exoenzyme production and full virulence in strain Ecc71. We investigated CorA’s role as a virulence factor and its expression in P. versatile. Inhibiting the transport function of CorA by growing a CorA+ strain in the presence of specific CorA inhibitor, cobalt (III) hexaammine (Co (III)Hex), has no effect on exoenzyme production. Transcription of pel-1, encoding a pectate lyase isozyme, is decreased in the absence of CorA, suggesting that CorA influences exoenzyme production at the transcriptional level, although apparently not through its transport function. CorA− and CorA+ strains grown in the presence of Co (III)Hex transcriptionally express corA at higher levels than CorA+ strains in the absence of an inhibitor, suggesting the transport role of corA contributes to autorepression. The expression of corA is about four-fold lower in HrpL− strains lacking the hrp-specific extracytoplasmic sigma factor. The corA promoter region contains a sequence with a high similarity to the consensus Hrp box, suggesting that corA is part of Hrp regulon. Our data suggest a complex role, possibly requiring the physical presence of the CorA protein in the virulence of the Pectobacterium versatile strain Ecc71.
1. Introduction
The soft rot Pectobacteriaceae is a group of phytopathogenic bacteria that produce plant-cell-wall-degrading enzymes (PCWDEs), the actions of which lead to cell wall collapse and tissue maceration in a wide number of plant hosts [1,2,3]. Bacteria in this group have been through a series of revisions over the past decade or so at the species, genus, and family levels [4]. Members of this group now belong to 19 species of the genus Pectobacterium and 12 species of Dickeya. Strain Ecc71, previously classified as Erwinia carotovora subspecies carotovora, has now been assigned as Pectobacterium versatile [5]. Soft rot Pectobacteriaceae produce many virulence factors including plant-cell-wall-degrading enzymes such as the pectinases pectate lyase (Pel) and polygalacturonase (Peh), cellulases (Cel), and proteases (Prt), which are ultimately responsible for the manifestation of the soft rot disease in host plants, which include many economically important crops [6,7]. In addition to environmental factors, exoenzyme synthesis and virulence in P. versatile is controlled by a complex network of positive and negative regulatory genes, and chemical signals of both bacterial and host origin [1,8,9,10]. The number of regulators controlling virulence and exoenzyme production in soft rot bacteria now number in the twenties. Some of the regulatory systems controlling soft rot virulence include the quorum-sensing system, regulator of secondary metabolism (Rsm) system, Gac (GacS and GacA) system, KdgR (2-keto-3-deoxygluconate repressor), and sigma factors such as the Hrp-specific sigma factor HrpL, whose effect is not through PCWDE production but the hrp/hop regulon [11,12].
For the bacterium to produce disease in the host, these enzymes are synthesized and secreted outside the cell by type I (Prt), type II (Pel, Peh, and Cel), type III (harpin), and type VI secretion systems, which bring various substrates, including the enzymes, into contact with substrates in the plant tissue [13,14,15]. In addition to the canonical secretion systems, other transport proteins have been reported to be necessary for full virulence in soft rot Pectobacteriaceae and these include transporters of secondary metabolites [16,17,18,19], as well as transporters involved in nutrient uptake [20], multidrug resistance [21,22], and osmoprotection [23].
A P. versatile mutant in the magnesium-transporting membrane protein, CorA, is reduced in the production of the major exoenzymes (Pel, Peh, Cel, and Prt), and less virulent in celery and carrot [24]. The production of pel-1, peh-1, celV, and prtW transcripts were each dependent on the presence of CorA, as the absence of CorA was accompanied by a decrease in the levels of transcripts of these exoenzyme genes in comparison with that of recA, which was not affected. A CorA− mutant carrying a functional corA+ plasmid was restored to exoenzyme production and virulence, establishing CorA’s involvement in pathogenicity. That the CorA mutation impacts all the major exoenzymes suggests a vital role for CorA in P. versatile.
Due to the essentiality of magnesium in the cellular metabolism of organisms in all three domains of life, Mg2+ is the most abundant divalent cation in the cell and the second most abundant cation after K+ [25]. Due to its importance, many Gram-negative bacteria have redundant magnesium transport systems. These are made up of the major transporters, CorA and MgtE, and the P-type ATPases MgtA/MgtB and their associated MgtS. MgtS forms a complex with a cation–phosphate symporter, PitA, to stabilize MgtA [26]. Lastly, there is the bacterial homologues of natural resistance-associated macrophage proteins (Nramp)-related protein previously shown to transport divalent cations of transition metals [5,27,28]. In addition to CorA, the genome of P. versatile has homologues of the MgtA/MgtB system and MgtE, which is almost as common in bacteria as CorA [27]. Despite their genetic diversity, MgtE complements growth in a CorA–MgtA–MgtB Salmonella strain [29]. This suggests that such redundancy could be functional in magnesium transport in P. versatile as well.
The presence of MgtE, another major Mg2+ transporter in P. versatile, adds to the complexity of its magnesium transport system and necessitates investigation into links between the corA− phenotype of reduced virulence and intracellular Mg2+ concentration. Understanding the mechanism(s) by which CorA is involved in virulence in Pectobacterium is complicated by the redundancy of magnesium transporters in P. versatile. Microarray data of a CorA mutant of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium revealed differential expression of genes with roles in host infection, intracellular survival, metabolism, and transcriptional regulation [30]. As exoenenzyme production and virulence in P. versatile are largely controlled by a network of many transcriptional regulators, it is possible that CorA’s effect on P. versatile virulence may be through some of these known regulators. The aim of this study was to further investigate CorA’s regulation and its role in exoenzyme production and virulence in P. versatile.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Media
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. Bacteria carrying drug resistance markers were maintained at 28 °C in minimal medium (MM) or LB medium containing the appropriate antibiotics. When required, chloramphenicol (Cm, 15 µg mL−1), tetracycline (Tc, 10 µg mL−1), and CoCl2 (50.0 μM) were added to the medium. Media were solidified by the addition of 1.5% agar (w/v). The compositions of LB and MM were described previously [24,31]. Minimal medium was supplemented with increasing MgSO4 concentrations of 1× (0.4 mM), 2× (0.8 mM), 3× (1.2 mM), 4× (1.6 mM), and 10× (4.0 mM). A stock solution of Co(III)Hex was prepared by filter sterilizing a 10.0 mM solution through a 0.2 μM filter and adding to MM at final concentrations of 250.0 μM. For liquid cultures, bacteria were grown in MM at 28 °C at 200 rpm and growth was monitored with Klett colorimeter. Minimal-medium-grown culture samples were harvested at 250 Klett units for assays for enzymatic activities.

Table 1.
Strains and plasmids.
2.2. Enzyme Assays
Pectate lyase (Pel) and protease (Prt) activities were measured quantitatively from culture supernatants of MM-grown cultures as previously described [24]. All β-galactosidase assays were performed from overnight (16 h)-grown LB medium cultures as described by Miller [42]. Developed samples for quantitative Prt assays were placed in a microtiter plate and A420 was measured in a Spectra Max M5 microplate reader (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA). Beta-galactosidase enzymatic activity is expressed in Miller units. All experiments were repeated three times and the data presented represent average of three biological replicates.
2.3. Molecular Techniques
All DNA manipulations including genomic DNA isolation, gel electrophoresis, and bacterial transformation by electroporation were performed by standard methods [31]. For plasmid isolation, either pure yield Plasmid Miniprep kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) or the alkaline lysis method [31] was used. Biparental matings were performed with E. coli S17-1 λPir as the donor strain. All RNA extractions were performed using a modified hot phenol–chloroform extraction method [24,43]. Nucleic acid quantification was performed on a NanoDroP ND-100 spectrophotometer (NanoDroP Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). After total RNA was quantified, 20 µg of RNA was DNase-digested using a TURBO DNA-free™ kit (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA). To verify the absence of any detectable genomic DNA, PCR was performed on DNase-digested RNA.
2.4. Construction of P. versatile KD103
To generate a lacZ− and corA− double-mutant strain of P. versatile, the plasmid pCKD122 containing corA+ DNA in pRK415 was mutagenized using the EZ::TN <KAN-2> insertion kit (Lucigen, Madison, WI, USA). According to manufacturer’s recommendations, 2.0 μg of pCKD122 was mixed with EZ::TN <Kan-2> transposon and EZ::TN transposase in its corresponding buffer, and incubated at 37.0 °C for 2 h. To stop the reaction, 1.0 μL of stop solution was added and incubated at 70 °C for 10 min. Electrocompetent cells of E. coli XL-10 Gold were electroporated with 3.0 uL of transposition mix. After an hour incubation at 37.0 °C, cells were plated on LB containing Km. Selected transformants were screened for Km insertion in the corA gene by PCR using the primers corA-qRTPCR-P1 (5′ GTCTTCCGGCTCGATCAAAT3′) and EZ::TN ME (5′ AGATGTGTATAAGAGACAG 3′). The plasmid pCKD123 was confirmed to have Km insertion in corA, and conjugated into KD100 by biparental mating. KD103 was generated by marker exchange by patching mating transformants on Km and Tc plates, and selecting for a Tc-sensitive, Km-resistant colony. KD103 corA::EZTN, KmR genotype and corA− phenotype were confirmed.
2.5. RT-qPCR
Gene expression as measured by RT-qPCR was performed as previously described using a SYBR Green-based system [24]. The following primers (listed 5′ to 3′) were used in RT-qPCR. corA-qRTPCR-P1: GTCTTCCGGCTCGATCAAAT, corA-qRTPCR-P2: CTGAGCGCATTTAAACTGGA, hrpN-qRTPCR-P1: ATGAGCGTTGGGCAAAAAG, hrpN-qRTPCR-P2: GGATATTGATCCATAAACTGACCA, Pc-RecAP1: GGTGAGCTGGTTGATCTGGG, Pc-RecAP2: GCATTTGCTTTGCCCTGACC.
2.6. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
Parental strain KD100 and CorA− mutant KD101 were each grown in 15.0 mL of MM and cultures were harvested at 250 Klett units. A 10.0 mL sample of each culture was centrifuged at 8500 rpm for 10 min and the supernatant was discarded. Pelleted cells were washed in TE (10.0 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 0.1 mM EDTA) and centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was removed, and this step was repeated two times. Cells were then dried by speed vacuum centrifugation. A 200 µL sample of 16 M nitric acid was added to the cells and digested at 80 °C for 1 h. Water was added to the digested cells to a final volume of 10.0 mL. Total magnesium, nickel, and cobalt concentrations in the samples were measured by ICP-OES analysis. A standard curve of magnesium, cobalt, and nickel was each generated and used to determine the concentrations of these metals within the cell. Concentrations are expressed as ppm/A600.
3. Results
3.1. Intracellular Mg2+ Concentrations in a CorA− Mutant
The corA− mutant of P. versatile is deficient in the production of plant-cell-wall-degrading enzymes and in virulence [24]. Since CorA is a primary Mg2+ transporter, we considered the possibility that the reduction in exoenzyme production in the corA− strain is the result of a deficiency in intracellular Mg2+ resulting from lack of Mg2+ transport into the cell. Although the alternate Mg2+ transporters, MgtA, MgtB, and MgtE, in P. versatile should functionally complement the absence of CorA in Mg2+ influx, and we have previously established that the growth of a corA mutant is no different from its parent [24], we wanted to verify that the CorA− phenotype was not caused by Mg2+ deficiency in the cell resulting from lack of Mg2+ uptake. To confirm that there was no Mg2+ deficiency in the CorA− strain, we grew parent KD100 and its CorA− mutant KD101 in MM containing normal concentration (0.4 mM) of Mg2+. We find no difference in total intracellular Mg2+ concentration between the corA− mutant (KD101; 6.70 ± 0.06 ppm/A600) and its parent (KD100; 6.73 ± 0.37 ppm/A600). These data suggest that the altered phenotype seen in a CorA− mutant of P. versatile is not due to lack of Mg2+ in the cell. As CorA also functions in the transport of Ni2+ and Co2+, the intracellular concentrations of these cations were also measured in the CorA+ and CorA− strains. However, Ni2+ and Co2+ were predictably not detected because MM medium contains neither element. Although we cannot rule out the deficiency of Ni2+ and Co2+ in the CorA− mutant phenotype, we believe it is unlikely their deficiencies are responsible for a CorA− phenotype, as exoenzyme production in this mutant is also reduced in our defined minimal medium, which does not contain these metals.
3.2. Effect of CorA Inhibitor on Exoenzyme Production
CorA− phenotype in P. versatile is associated with approximately half the amount of exoenzymes as compared to the CorA+ parent [24]. As CorA is a transporter, we wanted to determine if the reduced exoenzyme production in CorA− P. versatile is connected to CorA’s transport function. We reasoned that if CorA’s transport function is influencing exoenzyme production, we could mimic a corA mutation by blocking the transport function of CorA in a corA+ background. It has previously been reported that Co(III)Hex inhibits CorA transport system in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium [44]. Being structurally analogous to CorA substrates, this chemical presumably binds to and blocks the membrane ion CorA channels. We reasoned that adding Co (III) Hex would mimic a condition where CorA transport is inhibited and, thus, we first wanted to establish that in P. versatile, Co (III)Hex similarly inhibits the transport function of CorA. As shown in Figure 1, CorA+ and CorA− were grown in MM supplemented with both Co2+ and Co(III)Hex. As seen in Figure 1 (tubes A and B), the growth of CorA− in the presence of 50 µM CoCl2 is not affected while growth of CorA+ is inhibited by 50 µM CoCl2. This is expected as cobalt is a toxic metal. However, when 250 µM Co (III)Hex is supplemented into the medium already containing 50 µM CoCl2, growth is restored to the CorA+ (tube C). We, therefore, conclude that growing P. versatile in Co (III)Hex generates a blocked CorA channel, preventing cobalt uptake. Since both our CorA+ and CorA− strains possess alternate magnesium transporters, growing a CorA+ strain in the presence of the CorA inhibitor does not affect growth (data not shown). However, if the decreased exoenzyme phenotype of corA− strains is dependent on the transport function of CorA, we predict that exoenzyme production is decreased when wildtype CorA+ is grown in the presence of the CorA inhibitor, because the inhibition CorA’s transport function would mimic a corA mutation and result in a strain with reduced exoenzyme production. Surprisingly, as seen in Figure 2, in the presence of the inhibitor, pectate lyase activity in a CorA+ strain is not different from the activity in a CorA+ strain grown without the inhibitor. While the same phenotype of growth in cobalt is seen in a CorA− strain and a CorA+ strain grown with Co (III)Hex (Figure 1), the same reduced exoenzyme phenotype of a CorA− mutant could not be mimicked by interfering with the transport function of CorA in a CorA+ strain.
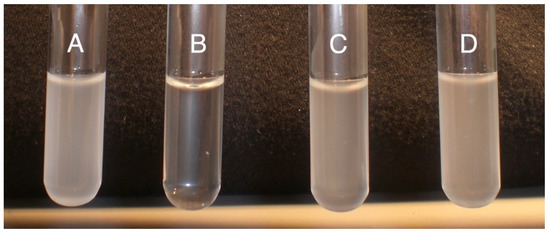
Figure 1.
Growth of P. versatile strains in the presence of cobalt and CorA inhibitor. (A) CorA− strain (KD101/pTH19cr) grown in 50 µM CoCl; (B) CorA+ (KD101/pCKD121) strain grown in 50 µM CoCl; (C) CorA+ strain (KD100) grown in 50 µM CoCl + 250 µM Co(III)Hex (CorA inhibitor); (D) CorA− (KD101/pTH19cr) strain grown in CoCl + 250 µM Co(III)Hex. The experimental setup is also shown in the table below. This experiment was repeated three times each time with triplicate replicates with similar results. Please see Table 1 for the relevant genotypes of all the bacterial strains used in the study.
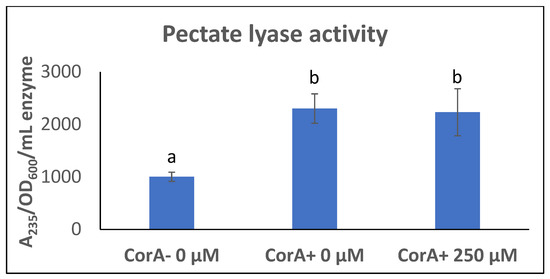
Figure 2.
Pectate lyase activity in the presence of CorA inhibitor. CorA− (KD101/pTH19Cr) and CorA+ (KD101/pCKD121) strains of P. versatile were grown in minimal media supplemented with or without CorA inhibitor Co(III)Hex and Pel activity was determined from culture supernatants. Data represent the means of three biological replicates. Letters that are not the same indicate a significant difference where p < 0.05 as determined by a Student’s t-test.
3.3. CorA Influences Exoenzymes at the Transcriptional Level
It was previously reported that a corA mutant in P. versatile is reduced in the production of exoenzymes, and established that transcript levels and exoenzyme activity are decreased when CorA is absent [24]. As the production of enzymes can be regulated at many points, we wanted to determine at what level of gene expression CorA affects exoenzyme production. As the first regulatory step is transcription, we investigated the transcription of the pel-1 gene, which encodes the Pel-1 isozyme of the exoenzyme pectate lyase in parental KD100 (lacZ−) and mutant KD103 (lacZ− corA−) using the plasmid pAKC1203 carrying pel-1::lacZ fusion. As seen in Figure 3, the expression of pel-1 is significantly decreased in the corA mutant as compared to its parent. This suggests that CorA’s influence on pel-1 and possibly the genes of other exoenzyme such as protease, polygalacturonase, and cellulase which are similarly affected by corA mutation is at the transcriptional level.
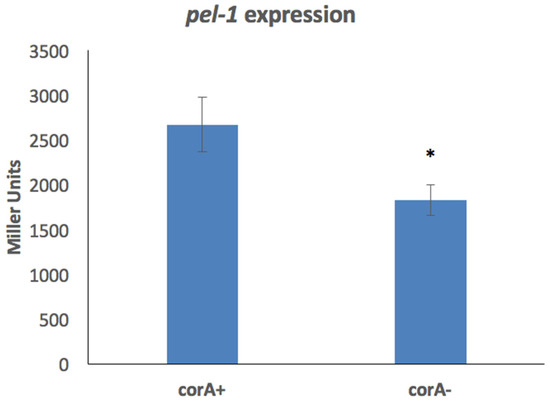
Figure 3.
Expression of pel-1 in the absence of corA. KD100/pAKC1203 (CorA+) and KD103/pAKC1203 (CorA−) strains both carrying pel-1 promoter cloned in lacZ reporter plasmid pMP220 were grown in minimal medium and expression of pel-1 was measured by Miller assay. Data represent the average of three biological replicates. * indicates a significant difference where p < 0.05 as determined by a Student’s t-test.
3.4. corA Expression in P. versatile
Having established that corA influences the transcription of exoenzyme, pel-1 gene and possibly other exoenzyme genes, we wanted to investigate the expression of corA itself. The Tn5 lacZ1 transposon used to generate the corA mutation in KD101 provided a lacZ transcriptional fusion driven by the corA promoter [24]. Additionally, the CorA− mutant KD101 complemented with a functional corA gene had the production of both exoenzymes, pectate lyase and protease, and pathogenicity restored to wildtype levels. Thus, two systems with a chromosomal corA-lacZ transcriptional fusion allowed for corA expression studies in both a CorA− and CorA+ background.
As measured by β-galactosidase activity, there is an increase in the expression of corA in a CorA− mutant background (KD101/pTH19cr) compared to its expression in a CorA+ background (KD101/pCKD121) (Figure 4). To confirm this observation, we measured corA transcripts using RT-qPCR in both CorA+ KD100 and CorA− KD101. The transposon insertion site in corA locus in KD101 is approximately mid-sequence of the coding region of corA, resulting in normal transcription of the first half of the corA gene and predictably producing a chimeric transcript between the first half of corA mRNA sequence before the junction with the lacZ gene of the transposon. Primers for corA were, thus, designed in the coding region before the transposon insertion site. As seen in Table 2, the level of corA transcript in the CorA− KD101 is approximately three-fold higher than the level in CorA+ KD100 using recA gene as the standard. To evaluate whether the mere presence of CorA or its transport function influenced the expression of corA, we measured the expression of corA in a CorA+ strain in which the transport function was inhibited by growth in the presence of CorA transport inhibitor, Co (III)Hex. Growth in the presence of the CorA transport inhibitor causes the expression of corA gene to mimic that in a corA mutant (Figure 4). In other words, even though CorA is physically present, the inhibition of its transport function leads to the altered expression of corA in a manner similar to the expression in corA mutant. This suggest that corA is governed by autoregulation, specifically autorepression, which is linked to its transport function.
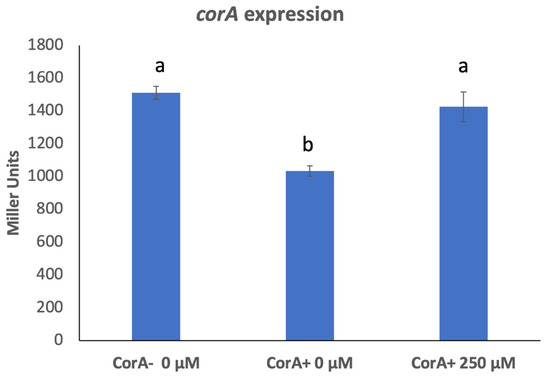
Figure 4.
Expression of corA in the presence of CorA inhibitor. CorA− KD101with chromosomal corA-lacZ fusion carrying either cloning vector, pTH19cr or pCKD121 (corA+), were grown in media supplemented with a range of Co(III)Hex concentrations and β-galactosidase activity was determined. Data represent the means of three biological replicates. Letters that are not the same indicate a significant difference where p < 0.05 as determined by a Student’s t-test.

Table 2.
Comparison of transcript levels in corA and hrpL mutants of P. versatile compared to their parents.
3.5. corA Expression Is HrpL-Dependent
To further explore the expression of corA, we investigated the possibility that corA expression is influenced by one of the many regulators known to control exoenzyme production and virulence in P. versatile. To determine if this is the case, we measured the expression of cosmid-borne corA-lacZ (pCKD120) in a series of exoenzyme and virulence regulatory mutants of P. versatile (our lab collection). These regulatory mutants included strains AC5091 (ahlI−), AC5070 (rsmA−), AC5050 (rsmC−), AC5057 (gacA−), and AC5086 (hrpL−). The expression levels of corA-lacZ in these mutants range from 100 to 70% of wild type levels in ahlI−, rsmA−, rsmC−, and gacA− strains (data not shown) to a surprising and highly significant decrease of 80% in a hrpL− background (Figure 5). To confirm this, corA transcript levels were measured by RT-qPCR in HrpL+ and HrpL− strains. Compared to the HrpL+ parent, there is an approximately four-fold decrease in the transcript levels of corA in the HrpL− strain compared to the levels in HrpL+ strain (Table 2), further supporting the idea that corA is regulated by hrpL. The expression of type III secretion system effector gene hrpN (a known HrpL-regulated gene) was measured by RT-qPCR as a control in the HrpL− strain and was predictably highly reduced (Table 2).
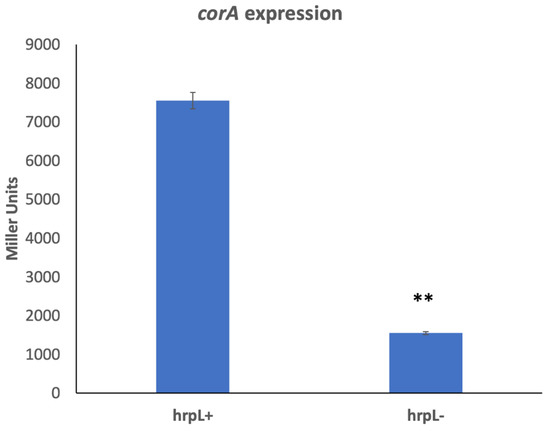
Figure 5.
corA expression in the absence of HrpL. P. versatile KD100 (HrpL+) and AC5086 (HrpL−) carrying pCKD120 (cosmid-borne corA-lacZ) were grown in MM supplemented with tetracycline (10 mg/L). The experiment was repeated twice, and each treatment has three replicates. ** indicates a significant difference where p < 0.001 as determined by a Student’s t-test.
HrpL is a sigma factor that activates the promoters of many genes involved in type III secretion system and pathogenicity [11]. Paramount among these are the hypersensitive response and pathogenicity (hrp) genes, which code for components of type III secretion system as well as harpins and other effectors and avirulence factors [14,45]. The recognition sequences of HrpL sigma factor, termed Hrp box, have been defined at the promoters of its target genes. HrpL recognizes and binds to the consensus sequence GGCCAA-N16-CCACNNA, but variations of the sequence have also been reported [46,47]. As our data demonstrate HrpL regulation of corA expression, we wanted to find out if the regulatory sequences of corA contain a putative hrpL recognition sequence. The upstream sequences of corA from the soft rot Pectobacteriaceae and S. enterica serovar Typhimurium were aligned to search for hrpL promoter-like sequences. The sequence GAAACC -N14-CACCT exists in P. versatile Ecc71, P. atrosepticum SCRI1043, and Dickeya dadantii 3937 and GAAACC-N19-CCANC in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2 and are found approximately 84 and 68 bases away from their respective translational start sites (Figure 6). There is only a slight variation in the putative hrpL promoter sequences in the soft rot Pectobacteriaceae shown in Figure 6 from the previously reported [48] Hrp box promoter sequence found in hrpNEcc with a difference of one base variation (GAAACC instead of GGAACC) in the −35 site and (CACCT instead of CACTT) in the −10 site. The presence of a similar HrpL-regulated promoter sequence flanking corA gives further support that corA could be a component of HrpL regulon in P. versatile.
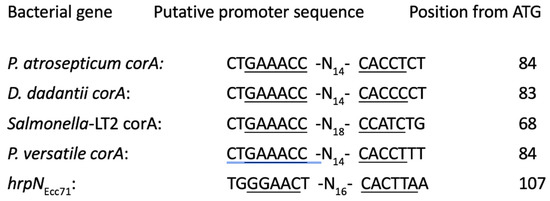
Figure 6.
Alignment of possible Hrp box of corA in Pectobacterium, Dickeya, and Salmonella species. The underlined nucleotides of the −35 and −10 region represent the putative HrpL promoter sequences. The sequences are aligned with the hrp box of hrpNEcc71, a confirmed HrpL-regulated gene in Pectobacterium versatile.
4. Discussion
A corA mutation in P. versatile led to decreased exoenzyme production and reduced virulence [24]. Although CorA is a major Mg2+ transporter, we observed no reduction in intracellular Mg2+ in the CorA− mutant compared to the parent. Our observation supports the previous report of a CorA− mutant of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium [49], in which the intracellular Mg2+ content did not appear to be linked to the altered virulence in a CorA− mutant. We did not detect intracellular Ni2+ or Co2+ in either parent or the mutants. Both metals are also substrates for CorA, and any of them could play a role in the CorA− mutant phenotype. However, both metals have alternative transporters, MgtE for Co2+ and a putative high-affinity Ni2+ transporter of the NicO superfamily (domain cl00964, PC1_3041) present in P. versatile for nickel. Therefore, it is unlikely that a deficiency in the intracellular content of either is responsible for the mutant phenotype. Additionally, cobalt at certain levels is toxic for bacterial growth, although this does not rule out the possibility of its requirement for growth and virulence at sub-inhibitory concentrations.
We investigated if the transport function of CorA is connected to exoenzyme production. We created a condition of physically present and functionally (in terms of transport) deficient CorA by growing CorA+ strain in the presence of the CorA inhibitor Co (III) Hex. It has previously been established [34] that Co(III)Hex blocks the transport of magnesium, cobalt, and nickel in Salmonella enterica. Co(III)Hex interferes with normal cobalt transport (Figure 1C), as a CorA+ strain normally unable to grow in the presence of a high concentration of cobalt is uninhibited in growth. Inhibition of CorA transport function did not produce the CorA− phenotype of lower exoenzymes, suggesting that the physical presence of CorA might be important for CorA’s role in exoenzyme production and virulence. This observation is consistent with our earlier report that corA strains are severely affected in multiplication and survival in the host tissues [24]. Thus, we postulate that CorA’s role in virulence of Pectobacterium could lie solely in its physical presence in two ways. The first of these is reduced PCWDEs production and the second is multiplication and survival in the host tissues. A similar observation and suggestion have also been made for CorA in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium [30]. While we clarified that the impact of CorA on exoenzyme production is, at least in part, at the transcriptional level, we are yet to determine its regulatory mechanism. We know of no other such system besides CorA in Salmonella and Pectobacterium.
As measured by the expression of corA–lacZ fusion and RT-qPCR, CorA auto-represses its own expression in P. versatile, as corA expression is increased in the absence of CorA. Interestingly, in the presence of 250 µM CorA inhibitor, the autorepression is cancelled and the expression of corA in a CorA+ strain is the same as its expression in a CorA− strain, suggesting that CorA transport function may be what is responsible for regulating its own expression. It is not clear to us yet how this autorepression works and what is its significance.
Our data also indicate that the expression of corA in P. versatile might be regulated by the sigma factor HrpL. A closer look at the promoter region corA reveal a putative HrpL recognition sequence, hrp box, that differs in only one nucleotide in both the −35 and −10 motif. The hrp box is a bipartite nucleotides -GGAACCNA-N13-14-CCACNNA at the −35 and −10 sites, respectively [50,51,52]. Mutational analysis of these sequences in Pantoea agglomeran pv. gypsophilae determines that GGAAC and ACNNA are both essential at the −35 and −10 regions, respectively, for promoter activity through HrpL [53]. The putative hrp box of corAEcc71 is −35 GAAAC and −10 ACNNC. The promoter specificity of the Hrp box is determined by the interaction of region 4 of HrpL and the −35 motif [54]. There is a 15% difference between the region 4 of HrpL proteins of Pantoea agglomeran pv. gypsophilae and P. versatile Ecc71 [12] and this could possibly allow for differences in target promoter specificity between the two organisms. Other HrpL-regulated genes have been reported with similar variations [55,56].
HrpL is a member of the extracytoplasmic function (ECF) subfamily of σ70 sigma factors [11,46] which are involved in the transcription of many genes in response to environmental stimuli [57]. As a result, the ECF sigma factors in general are often involved in regulating outer membrane proteins synthesis [58,59]. As CorA is a transmembrane protein involved in Mg2+, Co2+, and Ni2+ transport, its regulation by HrpL would fall in line with the pattern of ECF sigma factor regulation. Metal transporters in other bacteria have also been reported to be regulated by ECF sigma factors. In Ralstonia metallidurans (formerly Alcaligenes eutrophus) an ECF sigma factor, CrnH, regulates the Co2+/Ni2+ antiporter CrnA [60]. Additionally, in a HrpL mutant of the related soft rot pathogen D. dadantii, microarray and bioinformatic analysis revealed differential expression of CorC, a Mg2+ and Co2+ transporter [61]. Interestingly, corA expression was not reported as being under the influence of HrpL, although the hrp boxes of D. dadanti and P. versatile differ by only a single nucleotide in the −10 region. That said, it does not necessarily follow that these observations in different organisms translate to similar effects in Ecc71 or that our observations in this study equally apply to other organisms or even other strains of P. versatile. It remains unclear what link, if any, exists between CorA’s effect on virulence and its regulation by HrpL in P. versatile strain Ecc71, the subject of our study. Further investigations are needed to confirm the lines of evidence we have provided here suggesting that CorA is in the HrpL regulon.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.K.D. and C.M.K.; methodology, C.K.D. and C.M.K.; formal analysis, C.M.K.; investigation, C.M.K.; resources, C.K.D.; data curation, C.M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M.K.; writing—review and editing, C.K.D. and C.M.K.; supervision, C.K.D.; project admin-istration, C.K.D.; funding acquisition, C.K.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was publicly funded by USDA-NIFA (CKD) and the Office of Academics at Freed-Hardeman University (CMK).
Data Availability Statement
All the data relevant to this study are provided in tables and figures. Further information can be requested from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Arun Chatterjee for bacterial cultures and plasmid constructs.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Charkowski, A.O. The changing face of bacterial soft-rot diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perombelon, M.C.M.; Kelman, A. Ecology of the soft rot erwinas. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1980, 18, 361–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barras, F.; Van Gijsegem, F.; Chatterjee, A.K. Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1994, 32, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauben, L.; Moore, E.R.; Vauterin, L.; Steenackers, M.; Mergaert, J.; Verdonck, L.; Swings, J. Phylogenetic position of phytopathogens within the Enterobacteriaceae. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portier, P.; Pédron, J.; Taghouti, G.; Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Caullireau, E.; Bertrand, C.; Laurent, A.; Chawki, K.; Oulgazi, S.; Moumni, M.; et al. Elevation of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum to species level as Pectobacterium odoriferum sp. nov., proposal of Pectobacterium brasiliense sp. nov. and Pectobacterium actinidiae sp. nov., emended description of Pectobacterium carotovorum and description of Pectobacterium versatile sp. nov., isolated from streams and symptoms on diverse plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3207–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidsson, P.R.; Kariola, T.; Niemi, O.; Palva, E.T. Pathogenicity of and plant immunity to soft rot pectobacteria. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Hibbing, M.E.; Kim, H.S.; Reedy, R.M.; Yedidia, I.; Breuer, J.; Glasner, J.D.; Perna, N.T.; Kelman, A.; Charkowski, A.O. Host range and molecular phylogenies of the soft rot enterobacterial genera Pectobacterium and Dickeya. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.R.; Khazanov, N.; Charkowski, A.; Faigenboim, A.; Senderowitz, H.; Yedidia, I. Interkingdom Signaling interference: The effect of plant-derived small molecules on quorum sensing in plant-pathogenic bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2021, 59, 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.K.; Dumenyo, C.K.; Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, A. Erwinia: Genetics of pathogenicity factors. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Lederberg, J., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 236–259. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, N.R.; Thomas, J.D.; Salmond, G.P.C. Virulence determinants in the bacterial phytopathogen Erwinia. In Methods Microbiol; Margaret, C.M.S., Sockett, R.E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 29, pp. 347–426. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Chatterjee, A.K. Regulation of Erwinia carotovora hrpLEcc (Sigma-LEcc), which encodes an extracytoplasmic function subfamily of sigma factor required for expression of the HRP regulon. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Chaudhuri, S.; Chatterjee, A.K. Identification of regulators of hrp/hop genes of Erwinia carotovora ssp. carotovora and characterization of HrpLEcc (SigmaLEcc), an alternative sigma factor. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2002, 3, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, G.P.C. Secretion of Extracellular Virulence Factors by Plant Pathogenic Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1994, 32, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantakari, A.; Virtaharju, O.; Vahamiko, S.; Taira, S.; Palva, E.T.; Saarilahti, H.T.; Romantschuk, M. Type III secretion contributes to the pathogenesis of the soft-rot pathogen Erwinia carotovora: Partial characterization of the hrp gene cluster. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 2001, 14, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, C.S.; Mole, B.M.; Grant, S.R.; Willis, D.K.; Charkowski, A.O. The type III secreted effector DspE is required early in solanum tuberosum leaf infection by Pectobacterium carotovorum to cause cell death, and requires Wx(3-6)D/E motifs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condemine, G.; Robert-Baudouy, J. 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate transport system in Erwinia chrysanthemi. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseloff, B.J.; Freeman, T.L.; Valmeekam, V.; Melkus, M.W.; Oner, F.; Valachovic, M.S.; San Francisco, M.J. The exuT gene of Erwinia chrysanthemi EC16: Nucleotide sequence, expression, localization, and relevance of the gene product. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1998, 11, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat, N.; Reverchon, S. Two transporters, TogT and TogMNAB, are responsible for oligogalacturonide uptake in Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat, N.; Blot, N.; Reverchon, S. Identification of TogMNAB, an ABC transporter which mediates the uptake of pectic oligomers in Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 41, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbany, C.; Neuhaus, H.E. Citrate uptake into Pectobacterium atrosepticum is critical for bacterial virulence. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabote, R.D.; Johnson, O.L.; Zetina, E.; San Francisco, S.K.; Fralick, J.A.; San Francisco, M.J. Erwinia chrysanthemi tolC is involved in resistance to antimicrobial plant chemicals and is essential for phytopathogenesis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 5772–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggiorani Valecillos, A.; Rodríguez Palenzuela, P.; López-Solanilla, E. The role of several multidrug resistance systems in Erwinia chrysanthemi pathogenesis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloux, K.; Touze, T.; Pagot, Y.; Jouan, B.; Blanco, C. Mutations of ousA alter the virulence of Erwinia chrysanthemi. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersey, C.M.; Agyemang, P.A.; Dumenyo, C.K. CorA, the magnesium/nickel/cobalt transporter, affects virulence and extracellular enzyme production in the soft rot pathogen Pectobacterium carotovorum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.M.; Scarpa, A. Regulation of cellular magnesium. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2000, 5, D720–D734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wu Orr, M.; Wang, H.; Hobbs, E.C.; Shabalina, S.A.; Storz, G. The small protein MgtS and small RNA MgrR modulate the PitA phosphate symporter to boost intracellular magnesium levels. Mol. Microbiol. 2019, 111, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, M.E. Magnesium transporters: Properties, regulation and structure. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2006, 11, 3149–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yin, X.; Wu Orr, M.; Dambach, M.; Curtis, R.; Storz, G. Increasing intracellular magnesium levels with the 31-amino acid MgtS protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5689–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.L.; Maguire, M.E. Distribution of the CorA Mg2+ transport system in gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 1638–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Nartea, M.; Kehres, D.G.; Porwollik, S.; McClelland, M.; Libby, S.J.; Fang, F.C.; Maguire, M.E. The CorA Mg2+ channel is required for the virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6517–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. The Condensed Protocols from Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2006; p. 800. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, R.; Priefer, U.; Puhler, A. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic-engineering: Transposon mutagenesis in gram-negative bacteria. Biotechnology 1983, 1, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, R.T.; Engwall, J.K.; McEvoy, J.L.; Chatterjee, A.K. recA is required in the induction of pectin lyase and carotovoricin in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 164, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Mukherjee, A.; Dumenyo, C.K.; Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, A.K. rsmC of the soft-rotting bacterium Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora negatively controls extracellular enzyme and harpin(Ecc) production and virulence by modulating levels of regulatory RNA (rsmB) and RNA-binding protein (RsmA). J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6042–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Chatterjee, A.; Yang, H.; Chatterjee, A.K. Regulatory network controlling extracellular proteins in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: FlhDC, the master regulator of flagellar genes, activates rsmB regulatory RNA production by affecting gacA and hexA (lrhA) expression. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4610–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dumenyo, C.K.; Chatterjee, A.K. Inactivation of rsmA leads to overproduction of extracellular pectinases, cellulases, and proteases in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora in the absence of the starvation/cell density-sensing signal, N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Ma, W.; Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, A.K. hexA of Erwinia carotovora ssp. carotovora strain Ecc71 negatively regulates production of RpoS and rsmB RNA, a global regulator of extracellular proteins, plant virulence and the quorum-sensing signal, N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 2, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto-Gotoh, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yasojima, K.; Tsujimura, A.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Watanabe, Y. A set of temperature sensitive-replication/-segregation and temperature resistant plasmid vectors with different copy numbers and in an isogenic background (chloramphenicol, kanamycin, lacZ, repA, par, polA). Gene 2000, 241, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, N.T.; Tamaki, S.; Kobayashi, D.; Trollinger, D. Improved broad-host-range plasmids for DNA cloning in Gram-negative bacteria. Gene 1988, 70, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaink, H.P.; Okker, R.J.H.; Wijffelman, C.A.; Pees, E.; Lugtenberg, B.J.J. Promoters in the nodulation region of the Rhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid pRL1JI. Plant Mol. Biol. 1987, 9, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chatterjee, A.; Hasegawa, H.; Dixit, V.; Leigh, N.; Chatterjee, A.K. ExpR, a LuxR homolog of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora, activates transcription of rsmA, which specifies a global regulatory RNA-binding protein. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 4792–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1972; p. 468. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, A.; Chatterjee, A.K. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a novel pectate lyase gene (pel-3) and a closely linked endopolygalacturonase gene (peh-1) of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora 71. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, L.M.; Lubbe, W.J.; Maguire, M.E. Cation hexaammines are selective and potent inhibitors of the CorA magnesium transport system. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 16767–16773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtimaki, S.; Rantakari, A.; Routtu, J.; Tuikkala, A.; Li, J.; Virtaharju, O.; Palva, E.T.; Romantschuk, M.; Saarilahti, H.T. Characterization of the hrp pathogenicity cluster of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: High basal level expression in a mutant is associated with reduced virulence. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2003, 270, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.M.; Beer, S.V. hrpL activates Erwinia amylovora hrp gene transcription and is a member of the ECF subfamily of sigma factors. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencato, M.; Tian, F.; Alfano, J.R.; Buell, C.R.; Cartinhour, S.; DeClerck, G.A.; Guttman, D.S.; Stavrinides, J.; Joardar, V.; Lindeberg, M.; et al. Bioinformatics-enabled identification of the HrpL regulon and type III secretion system effector proteins of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola 1448A. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, A.K. Molecular characterization and expression of the Erwinia carotovora hrpNEcc gene, which encodes an elicitor of the hypersensitive reaction. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 1997, 10, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Maguire, M.E. Regulation of CorA Mg2+ channel function affects the virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6509–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Heu, S.; Yi, J.; Lu, Y.; Hutcheson, S.W. Identification of a putative alternate sigma factor and characterization of a multicomponent regulatory cascade controlling the expression of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Pss61 hrp and hrmA genes. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Keen, N.T. Characterization of the promoter of avirulence gene D from Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 5916–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innes, R.W.; Bent, A.F.; Kunkel, B.N.; Bisgrove, S.R.; Staskawicz, B.J. Molecular analysis of avirulence gene avrRpt2 and identification of a putative regulatory sequence common to all known Pseudomonas syringae avirulence genes. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 4859–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissan, G.; Manulis, S.; Weinthal, D.M.; Sessa, G.; Barash, I. Analysis of promoters recognized by HrpL, an alternative sigma-factor protein from Pantoea agglomerans pv. gypsophilae. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonetto, M.; Gribskov, M.; Gross, C.A. The sigma 70 family: Sequence conservation and evolutionary relationships. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3843–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouts, D.E.; Abramovitch, R.B.; Alfano, J.R.; Baldo, A.M.; Buell, C.R.; Cartinhour, S.; Chatterjee, A.K.; D’Ascenzo, M.; Gwinn, M.L.; Lazarowitz, S.G.; et al. Genomewide identification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 promoters controlled by the HrpL alternative sigma factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thwaites, R.; Spanu, P.D.; Panopoulos, N.J.; Stevens, C.; Mansfield, J.W. Transcriptional regulation of components of the type III secretion system and effectors in Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmann, J.D. The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2002, 46, 47–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazmierczak, M.J.; Wiedmann, M.; Boor, K.J. Alternative sigma factors and their roles in bacterial virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.E.; Buchanan, S.K. Signaling mechanisms for activation of extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1930–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.; Mergeay, M.; Nies, D.; van der Lelie, D. Alcaligenes eutrophus as a model system for bacterial interactions with heavy metals in the environment. Res. Microbiol. 1997, 148, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Peng, Q.A.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, L.F.; Li, Y.; Robert, C.; Pritchard, L.; Liu, H.; Hovey, R.; Wang, Q.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of HrpL-Regulated Genes in the Necrotrophic Phytopathogen Dickeya dadantii 3937. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).