Bacterial Diversity Analysis and Screening for ACC Deaminase-Producing Strains in Moss-Covered Soil at Different Altitudes in Tianshan Mountains—A Case Study of Glacier No. 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study-Area Overview and Sampling
2.1.1. Study-Area Overview
2.1.2. Sampling Scheme
2.2. Determination of Physical and Chemical Properties of the Soil
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing of the Soil Samples
2.4. Isolation and Purification of ACC-Deaminase-Producing Strains
2.5. Determination of ACC-Deaminase Activity
2.6. Strain Identification
2.7. BIOLOG Analysis
2.8. Sequencing of 16S rDNA Gene for Identification of Isolated Strains
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Moss-Covered Soil at Different Altitudes
3.2. Data Pre-Processing Statistics, Quality Control, and Distribution of OTUs in Moss-Covered Soils at Different Altitudes
3.3. Bacterial Diversity and Community Composition
3.4. Analysis of the Diversity Index of Moss-Covered Soils at Different Altitudes
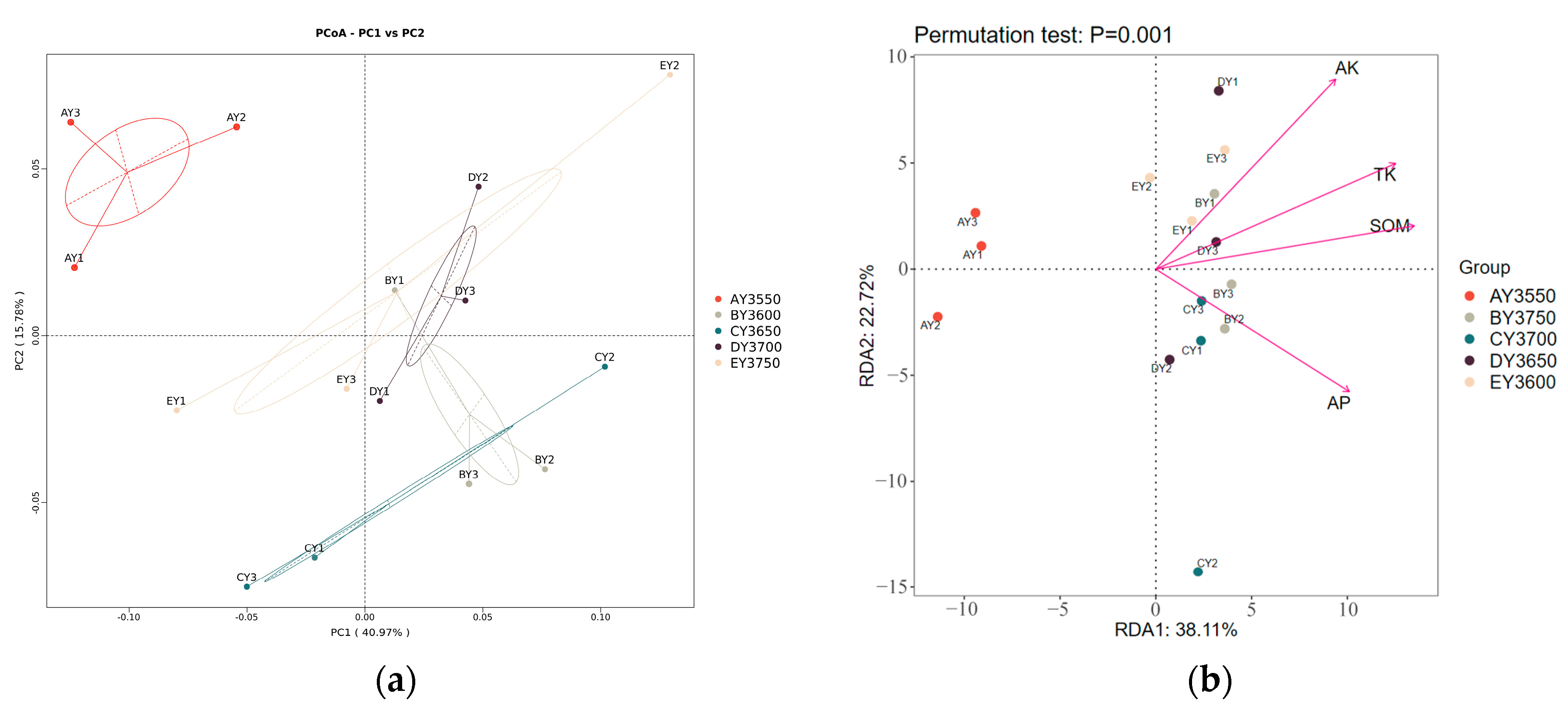
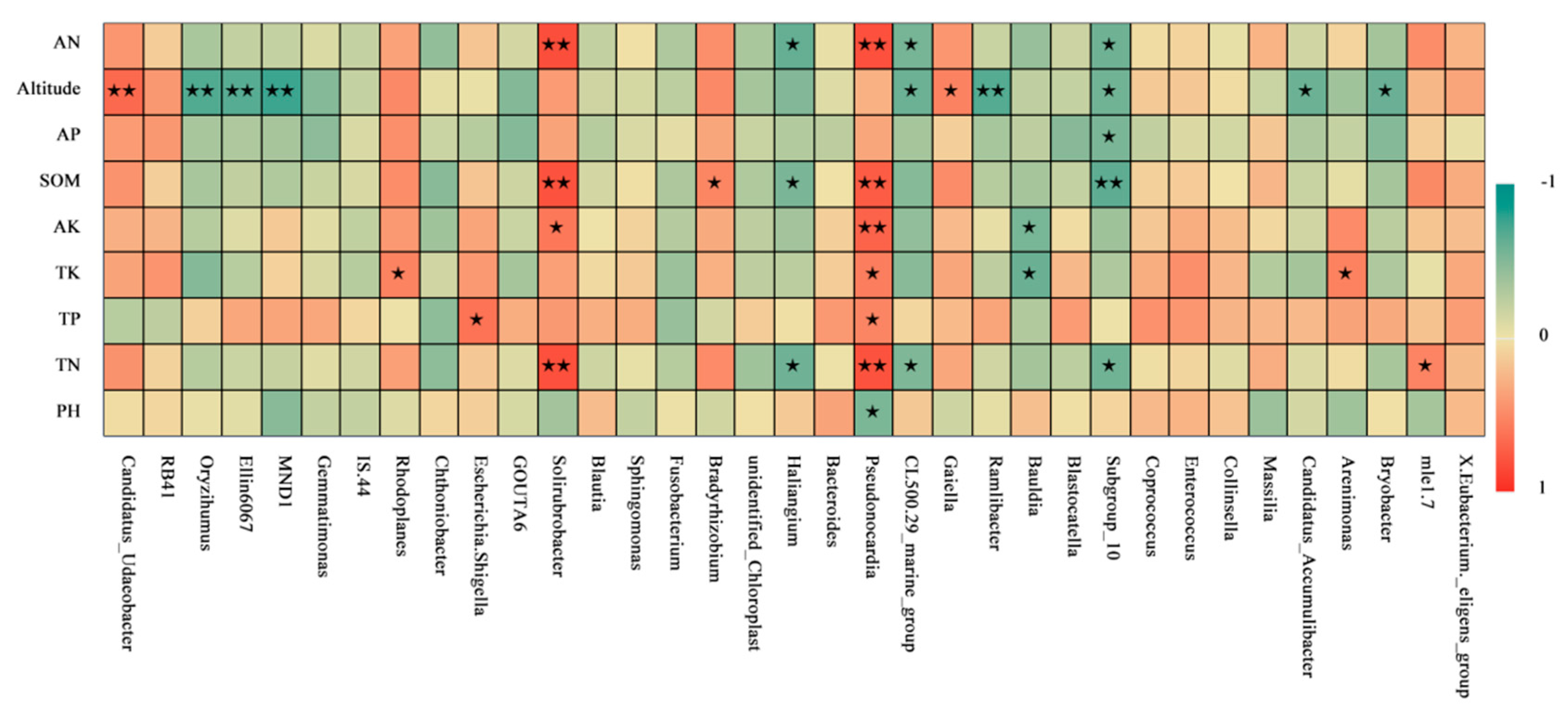
3.5. Analysis of Bacterial-Community Structure and Environmental Factors in Moss-Covered Soils at Different Altitudes
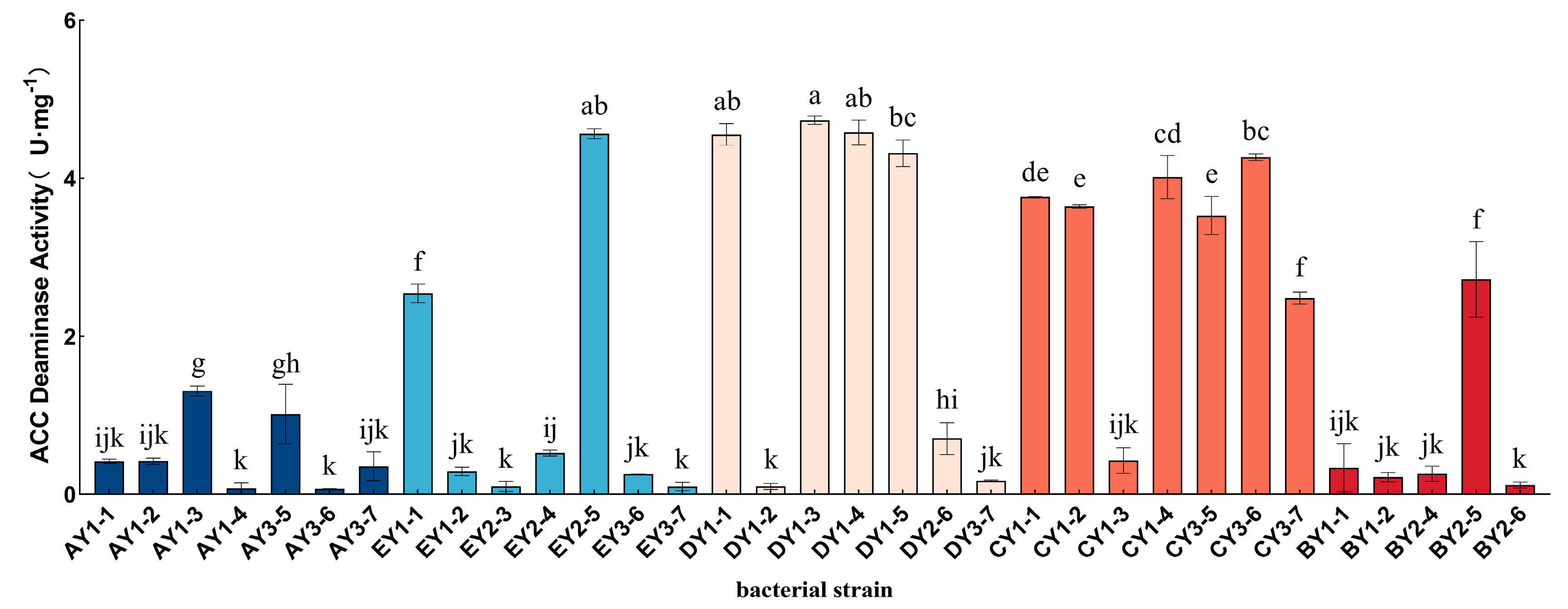
3.6. Isolation and Purification of ACC-Deaminase-Producing Strains from Moss-Covered Soil and Determination of ACC-Deaminase Activity
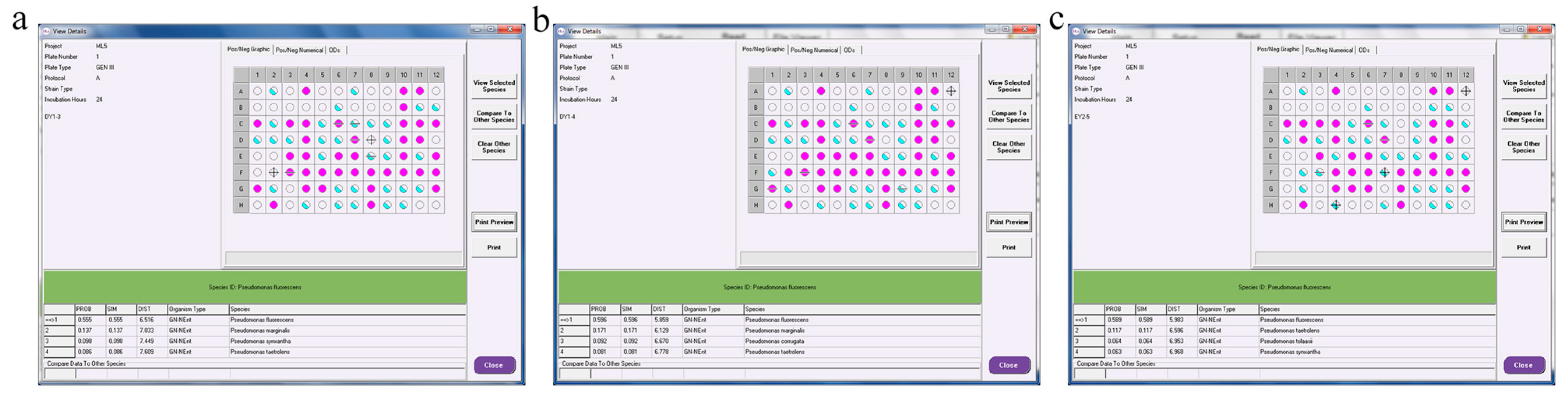
3.7. Identification of Three Strains with High ACC-Deaminase Activity
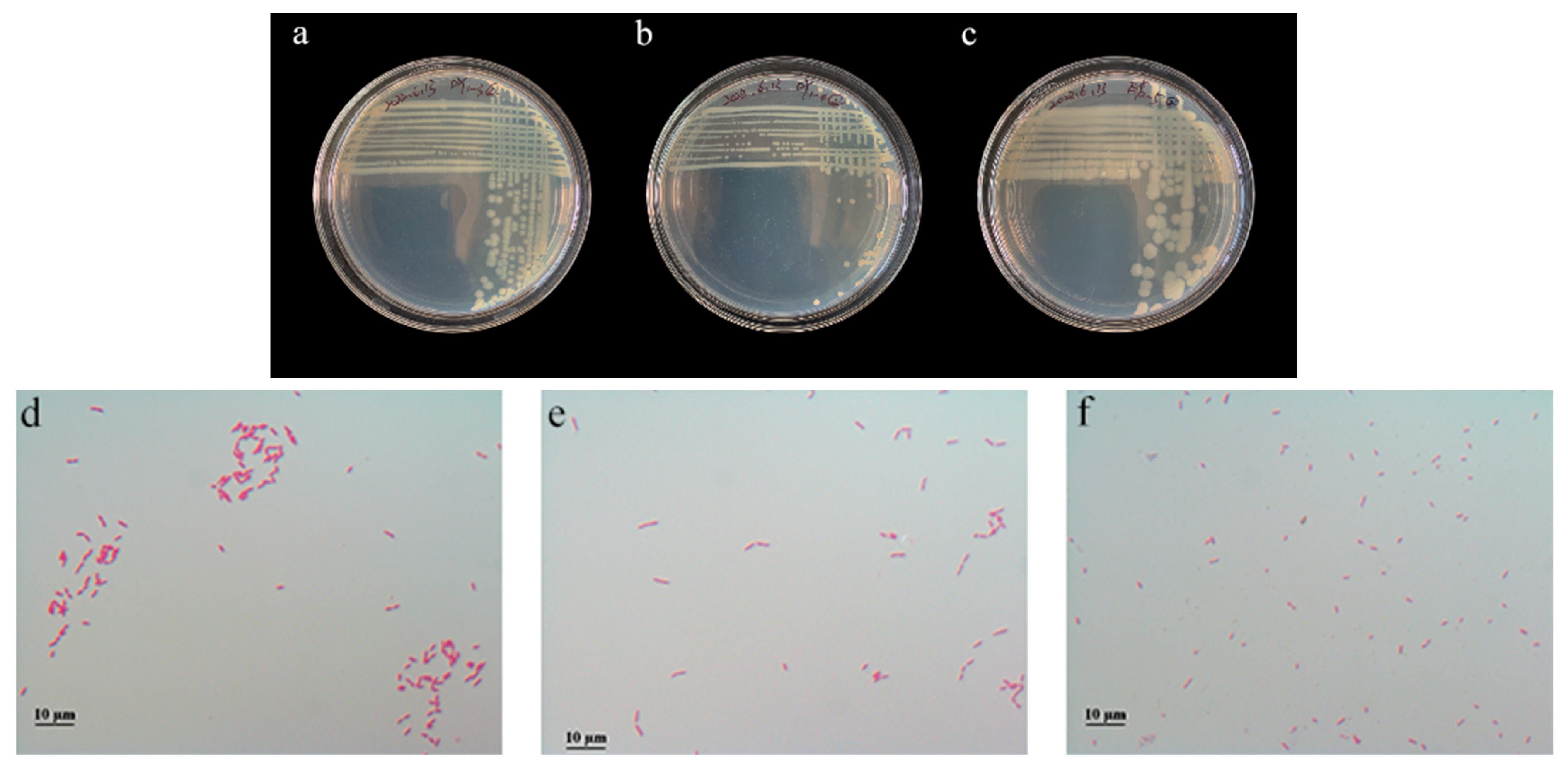
3.7.1. Colony Morphology and Microscopic Observation
3.7.2. Physiological- and Biochemical-Test Results
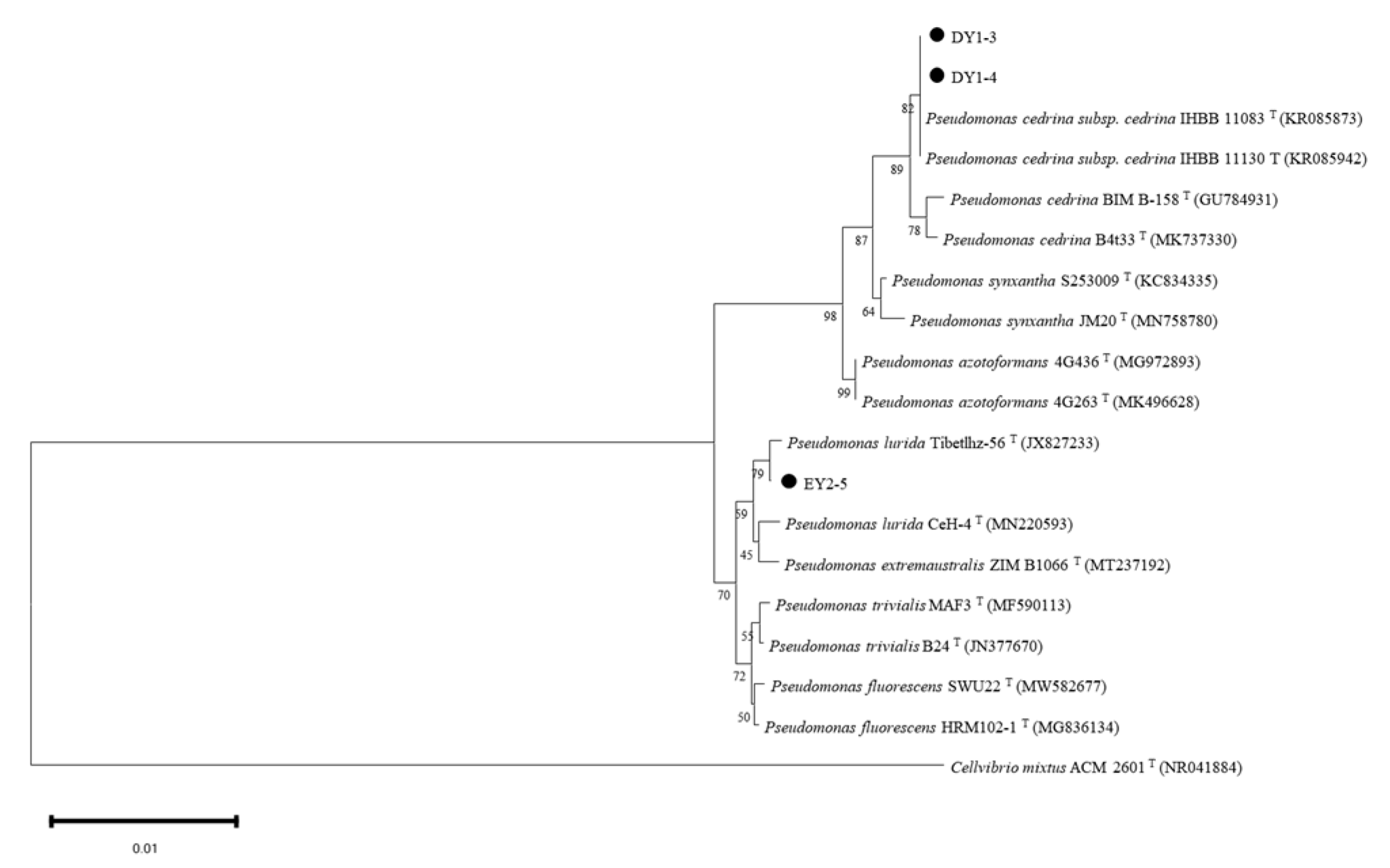
3.7.3. Molecular-Biology Identification of PGPR with ACC-Deaminase Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Kang, S. Global warming weakening the inherent stability of glaciers and permafrost. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Sun, W.; Huang, B.; Dong, W.; Wang, X.; Zhai, P.; Jones, P. Consistency of global warming trends strengthened since 1880s. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oerlemans, J. Quantifying global warming from the retreat of glaciers. Science 1994, 264, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.; Sahany, S.; Kulkarni, A.V. Glacial changes over the Himalayan Beas basin under global warming. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grima, N.; Campos, N. A farewell to glaciers: Ecosystem services loss in the Spanish Pyrenees. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Park, H.; Fedorov, A.; Wei, Y.; Li, R.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Z.; et al. Spatiotemporal variations and regional differences in air temperature in the permafrost regions in the Northern Hemisphere during 1980–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowton, T.R.; Sole, A.J.; Nienow, P.W.; Slater, D.A.; Christoffersen, P. Linear response of east Greenland’s tidewater glaciers to ocean/atmosphere warming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7907–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, O.; Reneva, S. Permafrost and changing climate: The Russian perspective. Ambio 2006, 35, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.; Patel, P.; Kumar, D.; Sharma, R. Climate change and glacier melting: Risks for unusual outbreaks? J. Travel. Med. 2023, taad015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margesin, R.; Collins, T. Microbial ecology of the cryosphere (glacial and permafrost habitats): Current knowledge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2537–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Mon, C.; Stierli, B.; Plötze, M.; Frey, B. Fast and persistent responses of alpine permafrost microbial communities to in situ warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawierucha, K.; Buda, J.; Azzoni, R.S.; Nikiewicz, M.; Ambrosini, R. Water bears dominated cryoconite hole ecosystems: Densities, habitat preferences and physiological adaptations of Tardigrada on an alpine glacier. Aquat. Ecol. 2019, 53, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boetius, A.; Anesio, A.M.; Deming, J.W.; Mikucki, J.A.; Rapp, J.Z. Microbial ecology of the cryosphere: Sea ice and glacial habitats. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesio, A.M.; Laybourn-Parry, J. Glaciers and ice sheets as a biome. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, W. Rapid decrease of observed mass balance in the Urumqi Glacier No. 1, Tianshan Mountains, central Asia. Quat. Int. 2014, 349, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, D.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Ding, L.; Xu, J.; Jing, L. Glacier changes during the last forty years in the Tarim Interior River basin, northwest China. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietrzyk, P.; Rola, K.; Osyczka, P.; Nicia, P.; Szymański, W.; Węgrzyn, M. The relationships between soil chemical properties and vegetation succession in the aspect of changes of distance from the glacier forehead and time elapsed after glacier retreat in the Irenebreen foreland (NW Svalbard). Plant Soil 2018, 428, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigler, W.V.; Crivii, S.; Zeyer, J. Bacterial succession in glacial forefield soils characterized by community structure, activity and opportunistic growth dynamics. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 44, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Xie, L. Plant Growth Promoting and Stress Mitigating Abilities of Soil Born Microorganisms. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2020, 11, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Ma, Y.; Shadan, A. Perspective of ACC-deaminase producing bacteria in stress agriculture. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 352, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.M. Ethylene signaling in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7710–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, C.K.; Sharma, P.; Shukla, A.; Parmar, P.; Patel, R.; Goswami, D.; Saraf, M. Microbial enzyme, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase: An elixir for plant under stress. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 115, 101664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeles, F.B.; Morgan, P.W.; Saltveit, M., Jr. Ethylene in Plant Biology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press, Elsevier Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 297–398. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, V.S. Role of ACC Deaminase as a Stress Ameliorating Enzyme of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Useful in Stress Agriculture: A Review. In Role of Rhizospheric Microbes in Soil; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belimov, A.A.; Zinovkina, N.Y.; Safronova, V.I.; Litvinsky, V.A.; Nosikov, V.V.; Zavalin, A.A.; Tikhonovich, I.A. Rhizobial ACC deaminase contributes to efficient symbiosis with pea (Pisum sativum L.) under single and combined cadmium and water deficit stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 167, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, B.R.; Nascimento, F.X. Pseudomonas 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) Deaminase and Its Role in Beneficial Plant-Microbe Interactions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Bano, A.; Rai, S.; Kumar, M.; Ali, J.; Sharma, S.; Pathak, N. ACC deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria enhance salinity stress tolerance in Pisum sativum. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowtham, H.G.; Singh, B.; Murali, M.; Shilpa, N.; Prasad, M.; Aiyaz, M.; Amruthesh, K.N.; Niranjana, S.R. Induction of drought tolerance in tomato upon the application of ACC deaminase producing plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus subtilis Rhizo SF 48. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 234, 126422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Tripti; Maleva, M.; Bruno, L.B.; Rajkumar, M. Synergistic effect of ACC deaminase producing Pseudomonas sp. TR15a and siderophore producing Bacillus aerophilus TR15c for enhanced growth and copper accumulation in Helianthus annuus L. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, Y.; Mahadevaswamy; Naik, N.M.; Gowdar, S.B.; Narayanarao, K.; Satyanarayanarao, K. ACC Deaminase-Positive Halophilic Bacterial Isolates With Multiple Plant Growth-Promoting Traits Improve the Growth and Yield of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Under Salinity Stress. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 681007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Gupta, S. Diversity analysis of ACC deaminase producing bacteria associated with rhizosphere of coconut tree (Cocos nucifera L.) grown in Lakshadweep islands of India and their ability to promote plant growth under saline conditions. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 324, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Choudhury, A.; Choi, J.; Walitang, D.I.; Trivedi, P.; Lee, Y.; Sa, T. ACC deaminase and indole acetic acid producing endophytic bacterial co-inoculation improves physiological traits of red pepper (Capsicum annum L.) under salt stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2021, 267, 153544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Ouyang, W.; Yang, E.; Cao, Y.; Sun, R. Lowered Cd toxicity, uptake and expression of metal transporter genes in maize plant by ACC deaminase-producing bacteria Achromobacter sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tk, A.; Rkm, B. Evaluation of ACC deaminase and indole acetic acid production by Streptomyces hydrogenans DH16 and its effect on plant growth promotion. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Pan, F.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y. Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacteria from hyperaccumulator facilitated non-host root development and provided promising agents for elevated phytoremediation efficiency. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Sheng, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Effects of the inoculations using bacteria producing ACC deaminase on ethylene metabolism and growth of wheat grown under different soil water contents. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gan, Y.; Xu, B. Mechanisms of the IAA and ACC-deaminase producing strain of Trichoderma longibrachiatum T6 in enhancing wheat seedling tolerance to NaCl stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarian, Z.; Gruber, M.; Coutu, C.; Glick, B.R.; Hegedus, D.D. Gene expression patterns in shoots of Camelina sativa with enhanced salinity tolerance provided by plant growth promoting bacteria producing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase or expression of the corresponding acdS gene. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, A.H.; Jeong, H.Y.; Jung, S.K.; Kim, C.K. Overexpression of 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid Deaminase (acdS) Gene in Petunia hybrida Improves Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 737490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Subramanian, P.; Tirumani, S.; Gothandam, K.M.; Ramya, M. Ectopic expression of bacterial 1-aminocyclopropane 1-carboxylate deaminase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii enhances algal biomass and lipid content under nitrogen deficit condition. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, D.M.; Glick, B.R. Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol. Plant 2003, 118, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breed, R.S.; Murray, E.G.D.; Smith, N.R. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 7th ed.; Baillière, Tindall & Cox, Ltd.: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissore, C.; Giardina, C.P.; Kolka, R.K.; Trettin, C.C.; King, G.M.; Jurgensen, M.F.; Barton, C.D.; Mcdowell, S.D. Temperature and vegetation effects on soil organic carbon quality along a forested mean annual temperature gradient in North America. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 14, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Joerg, P.; Bing, H.; Yu, D.; Sun, S.; Luo, J.; Sun, H. Changes of soil phosphorus speciation along a 120-year soil chronosequence in the Hailuogou Glacier retreat area (Gongga Mountain, SW China). Geoderma 2013, 195–196, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carmona, M.; Arcenegui, V.; García-Orenes, F.; Mataix-Solera, J. The role of mosses in soil stability, fertility and microbiology six years after a post-fire salvage logging management. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicol, G.W.; Tscherko, D.; Embley, T.M.; Prosser, J.I. Primary succession of soil Crenarchaeota across a receding glacier foreland. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, M.; Six, J. Soil structure and microbiome functions in agroecosystems. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, T.J.; Schütte, U.M.E.; Drown, D.M. Soil Disturbance Affects Plant Productivity via Soil Microbial Community Shifts. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 619711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Berben, T.; Melton, E.D.; Overmars, L.; Vavourakis, C.D.; Muyzer, G. Microbial diversity and biogeochemical cycling in soda lakes. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-X.; Li, J.-T.; Chen, Y.-T.; Huang, L.-N.; Hua, Z.-S.; Hu, M.; Shu, W.-S. Shifts in microbial community composition and function in the acidification of a lead/zinc mine tailings. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2431–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, A.; Pittino, F.; Gandolfi, I.; Azzoni, R.S.; Diolaiuti, G.; Smiraglia, C.; Pelfini, M.; Compostella, C.; Turchetti, B.; Buzzini, P.; et al. Early ecological succession patterns of bacterial, fungal and plant communities along a chronosequence in a recently deglaciated area of the Italian Alps. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Kong, W.; Muhammad, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Kang, S. Contrasting environmental factors drive bacterial and eukaryotic community successions in freshly deglaciated soils. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Long, H.; Tai, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, Z. Variations in culturable bacterial communities and biochemical properties in the foreland of the retreating Tianshan No. 1 glacier. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-N.; Tang, F.-Z.; Song, Y.-S.; Wan, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-L.; Liu, W.-Q.; Shu, W.-S. Biodiversity, abundance, and activity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria during primary succession on a copper mine tailings. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, M.; Singh, S.B.; Gowtham, H.G.; Shilpa, N.; Prasad, M.; Aiyaz, M.; Amruthesh, K.N. Induction of drought tolerance in Pennisetum glaucum by ACC deaminase producing PGPR-Bacillus amyloliquefaciens through Antioxidant defense system. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 253, 126891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, D.; Kumar, S.; Meena, D.; Solanki, S.S.; Swaroop, S.; Pandey, J. Selection of ACC deaminase positive, thermohalotolerant and drought tolerance enhancing plant growth-promoting bacteria from rhizospheres of Cyamopsis tetragonoloba grown in arid regions. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sh, A.; Td, B.; Has, C.; Ra, D.; Mai, R.A. Characterization of growth promoting bacterial endophytes isolated from Artemisia annua L. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 143, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.-S.; Ali, S. Isolation and identification of multi-trait plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria from coastal sand dune plant species of Pohang beach. Folia Microbiol. 2022, 67, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandwani, S.; Amaresan, N. Role of ACC deaminase producing bacteria for abiotic stress management and sustainable agriculture production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 22843–22859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.S.; Ali, S. Possible mechanisms for the equilibrium of ACC and role of ACC deaminase-producing bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, G.H.; Sun, J.J.; Chen, S.; Fang, Y.; Ren, J.H. Isolation, Characterization, and Tea Growth-Promoting Analysis of JW-CZ2, a Bacterium With 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic Acid Deaminase Activity Isolated From the Rhizosphere Soils of Tea Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 792876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wei, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, Y.; Jiao, R. Screening, Identification and Growth-Promotion Products of Multifunctional Bacteria in a Chinese Fir Plantation. Forests 2021, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Tufail, M.A.; Asghar, H.N.; Nazli, F.; Zahir, Z.A. Appraising the potential of EPS-producing rhizobacteria with ACC-deaminase activity to improve growth and physiology of maize under drought stress. Physiol. Plant 2021, 172, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemneh, A.A.; Zhou, Y.; Ryder, M.H.; Denton, M.D. Is phosphate solubilizing ability in plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from chickpea linked to their ability to produce ACC deaminase? J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2416–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Soil Transect | Soil Sample No. | Altitude | Latitude and Longitude | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AY3550 | AY1, AY2, AY3 | 3550 ± 10 m | 86°49′42″ E | 43°06′36″ N |
| EY3600 | EY1, EY2, EY3 | 3600 ± 10 m | 86°49′43″ E | 43°06′40″ N |
| DY3650 | DY1, DY2, DY3 | 3650 ± 08 m | 86°49′31″ E | 43°06′05″ N |
| CY3700 | CY1, CY2, CY3 | 3700 ± 10 m | 86°49′31″ E | 43°06′55″ N |
| BY3750 | BY1, BY2, BY3 | 3750 ± 04 m | 86°49′24″ E | 43°07′01″ N |
| Belt Transect | pH 1 | TK 2 (g/kg) | AP 3 (mg/kg) | TN 4 (g/kg) | AK 5 (mg/kg) | AN 6 (mg/kg) | TP 7 (g/kg) | SOM 8 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AY 3550 | 6.83 a | 11.42 b | 8.05 b | 0.8 a | 85.84 b | 36.17 a | 0.5653 a | 1.88 b |
| EY 3600 | 6.80 a | 18.03 a | 12.79 ab | 4.73 a | 320.97 a | 158.08 a | 0.5780 a | 9.62 a |
| DY 3650 | 6.77 a | 18.34 a | 11.30 ab | 4.39 a | 302.92 ab | 171.50 a | 0.5960 a | 10.03 a |
| CY 3700 | 6.82 a | 15.47 ab | 15.26 a | 6.71 a | 187.44 ab | 166.83 a | 0.4824 a | 10.84 a |
| BY 3750 | 6.85 a | 16.86 a | 12.08 ab | 5.36 a | 197.85 ab | 175.00 a | 0.5568 a | 11.38 a |
| Sample Name | Raw Reads 1 | Clean Reads 2 | GC% 3 | Effective% 4 | OTUs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AY1 | 82,141 | 63,534 | 56.05 | 77.35 | 4331 |
| AY2 | 79,582 | 62,640 | 56.05 | 78.71 | 4476 |
| AY3 | 86,249 | 65,066 | 55.98 | 75.44 | 3927 |
| EY1 | 74,159 | 58,582 | 56.21 | 79.00 | 3567 |
| EY2 | 78,425 | 60,570 | 56.65 | 77.23 | 3477 |
| EY3 | 81,972 | 64,192 | 56.28 | 78.31 | 3779 |
| DY1 | 85,981 | 65,597 | 56.38 | 76.29 | 3777 |
| DY2 | 74,371 | 56,969 | 56.75 | 76.60 | 3644 |
| DY3 | 80,684 | 63,269 | 56.75 | 78.42 | 3517 |
| CY1 | 69,956 | 52,994 | 56.64 | 75.75 | 3852 |
| CY2 | 74,920 | 58,855 | 56.34 | 78.56 | 3476 |
| CY3 | 87,870 | 67,659 | 56.44 | 77.00 | 3582 |
| BY1 | 80,949 | 62,234 | 56.59 | 76.88 | 3595 |
| BY2 | 83,779 | 65,904 | 56.71 | 78.66 | 3230 |
| BY3 | 91,402 | 68,817 | 56.31 | 75.29 | 3275 |
| Sample | OTUs * | Shannon * | Simpson * | Chao1 * | ACE * | Goods Coverage * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AY3550 | 4244 a | 10.1670 ± 0.2440 a | 0.9967 ± 0.0009 a | 4715.777 ± 298.897 a | 4811.849 ± 315.213 a | 0.981 |
| EY3600 | 3607 b | 9.8241 ± 0.1800 a | 0.9958 ± 0.0014 a | 3975.773 ± 164.250 ab | 4043.742 ± 197.426 b | 0.985 |
| DY3650 | 3646 b | 9.8191 ± 0.1035 a | 0.9959 ± 0.0010 a | 4034.307 ± 204.338 ab | 4117.463 ± 222.323 ab | 0.985 |
| CY3700 | 3636 b | 9.5642 ± 0.2250 a | 0.9933 ± 0.0021 a | 4159.167 ± 426.325 ab | 4268.216 ± 409.202 ab | 0.982 |
| BY3750 | 3366 b | 9.5212 ± 0.3929 a | 0.9925 ± 0.0056 a | 3719.790 ± 224.612 b | 3814.941 ± 197.318 b | 0.986 |
| Test Items | Strains * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DY1–3 | DY1–4 | EY2–5 | |
| Litmus milk test | AO | AO | AO |
| Malanate-utilization test | + | + | + |
| Citrate-salt test | + | + | + |
| Hydrolysis of starch | + | + | + |
| Methyl-red test | + | + | + |
| Urease test | + | + | + |
| Indole production | + | + | + |
| V-P test | - | - | - |
| Litmus milk test | AO | AO | AO |
| Malanate-utilization test | + | + | + |
| Strain | Description of the Strain with the Highest Homology (Login Number) | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | E Value | Ident |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DY1–3 | Pseudomonas cedrina subsp. cedrina strain IHBB 11130 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence (KR085942.1) | 2507 | 2507 | 100% | 0.0 | 100% |
| DY1–4 | Pseudomonas cedrina subsp. cedrina strain IHBB 11130 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence (KR085942.1) | 2507 | 2507 | 100% | 0.0 | 99.78% |
| EY2–5 | Pseudomonas sp. strain 33R 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence (MK070918.1) | 2505 | 2505 | 100% | 0.0 | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y. Bacterial Diversity Analysis and Screening for ACC Deaminase-Producing Strains in Moss-Covered Soil at Different Altitudes in Tianshan Mountains—A Case Study of Glacier No. 1. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061521
Shi Y, Yuan Y, Feng Y, Zhang Y, Fan Y. Bacterial Diversity Analysis and Screening for ACC Deaminase-Producing Strains in Moss-Covered Soil at Different Altitudes in Tianshan Mountains—A Case Study of Glacier No. 1. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061521
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yanlei, Ye Yuan, Yingying Feng, Yinghao Zhang, and Yonghong Fan. 2023. "Bacterial Diversity Analysis and Screening for ACC Deaminase-Producing Strains in Moss-Covered Soil at Different Altitudes in Tianshan Mountains—A Case Study of Glacier No. 1" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061521
APA StyleShi, Y., Yuan, Y., Feng, Y., Zhang, Y., & Fan, Y. (2023). Bacterial Diversity Analysis and Screening for ACC Deaminase-Producing Strains in Moss-Covered Soil at Different Altitudes in Tianshan Mountains—A Case Study of Glacier No. 1. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061521






