Genomic Investigation of Salmonella Typhi in Hong Kong Revealing the Predominance of Genotype 3.2.2 and the First Case of an Extensively Drug-Resistant H58 Genotype
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Salmonella Typhi
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. WGS Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis and Other Genome Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features of Cases with Salmonella Typhi Bacteraemia
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of the Recovered Salmonella Typhi Isolates
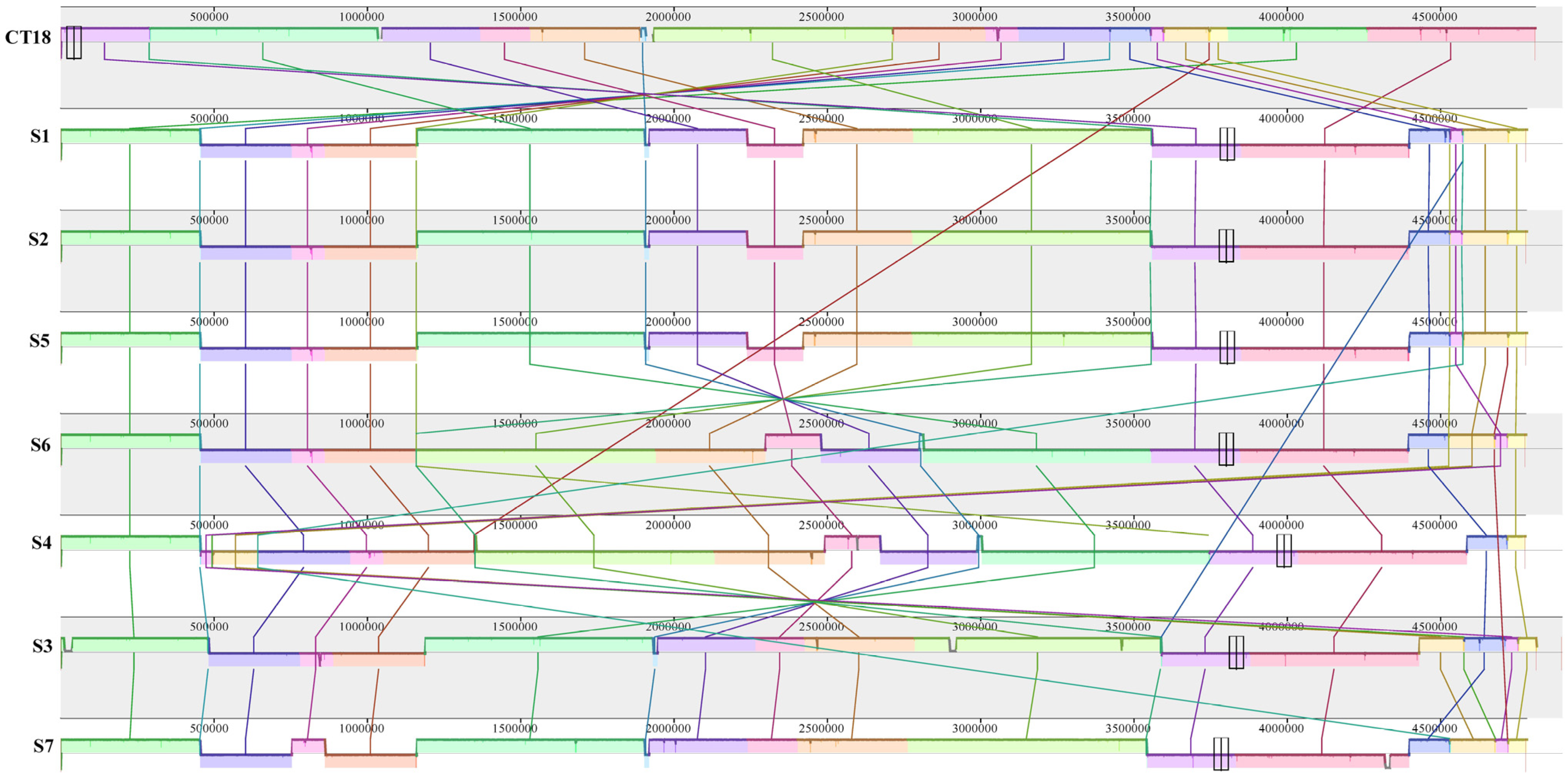
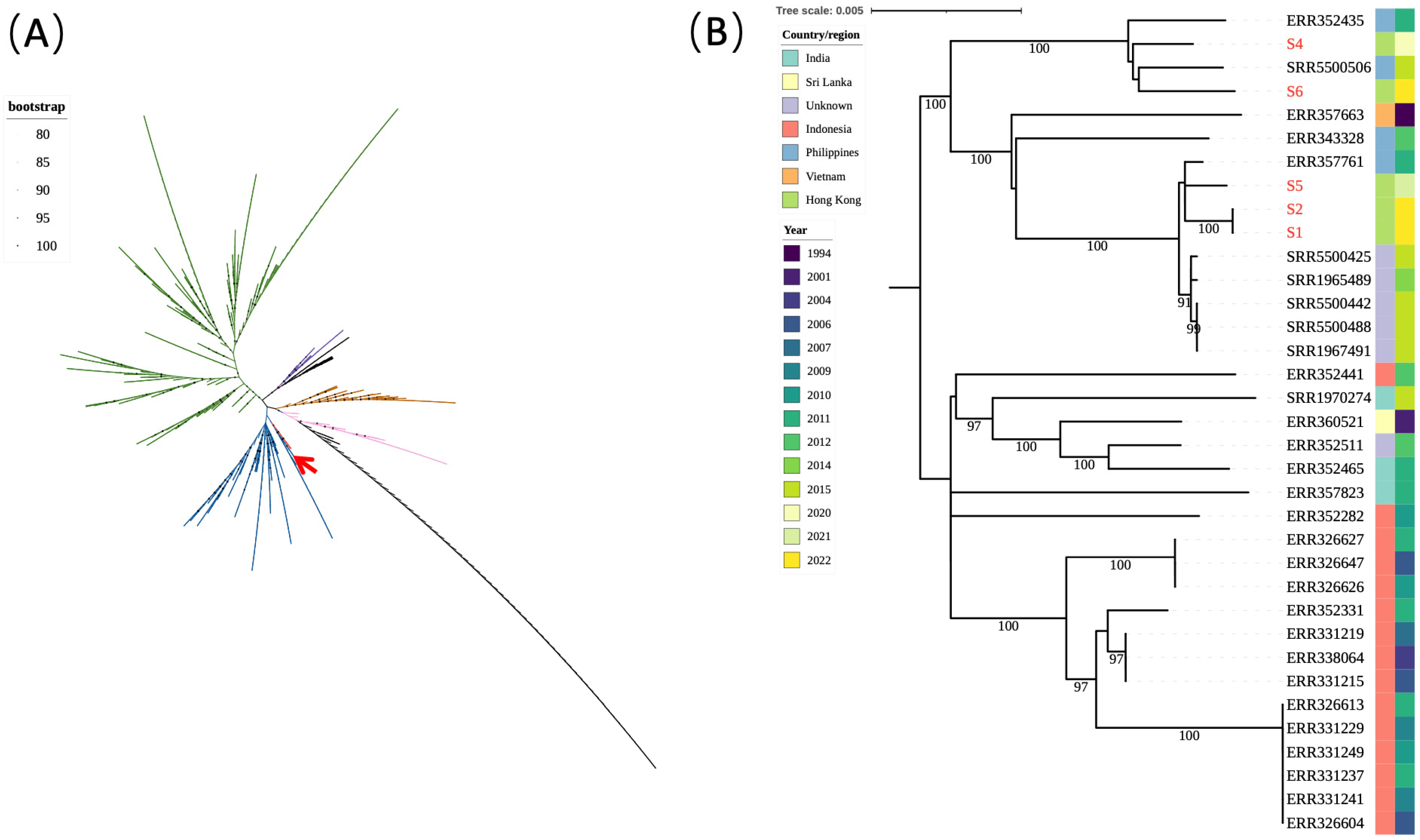
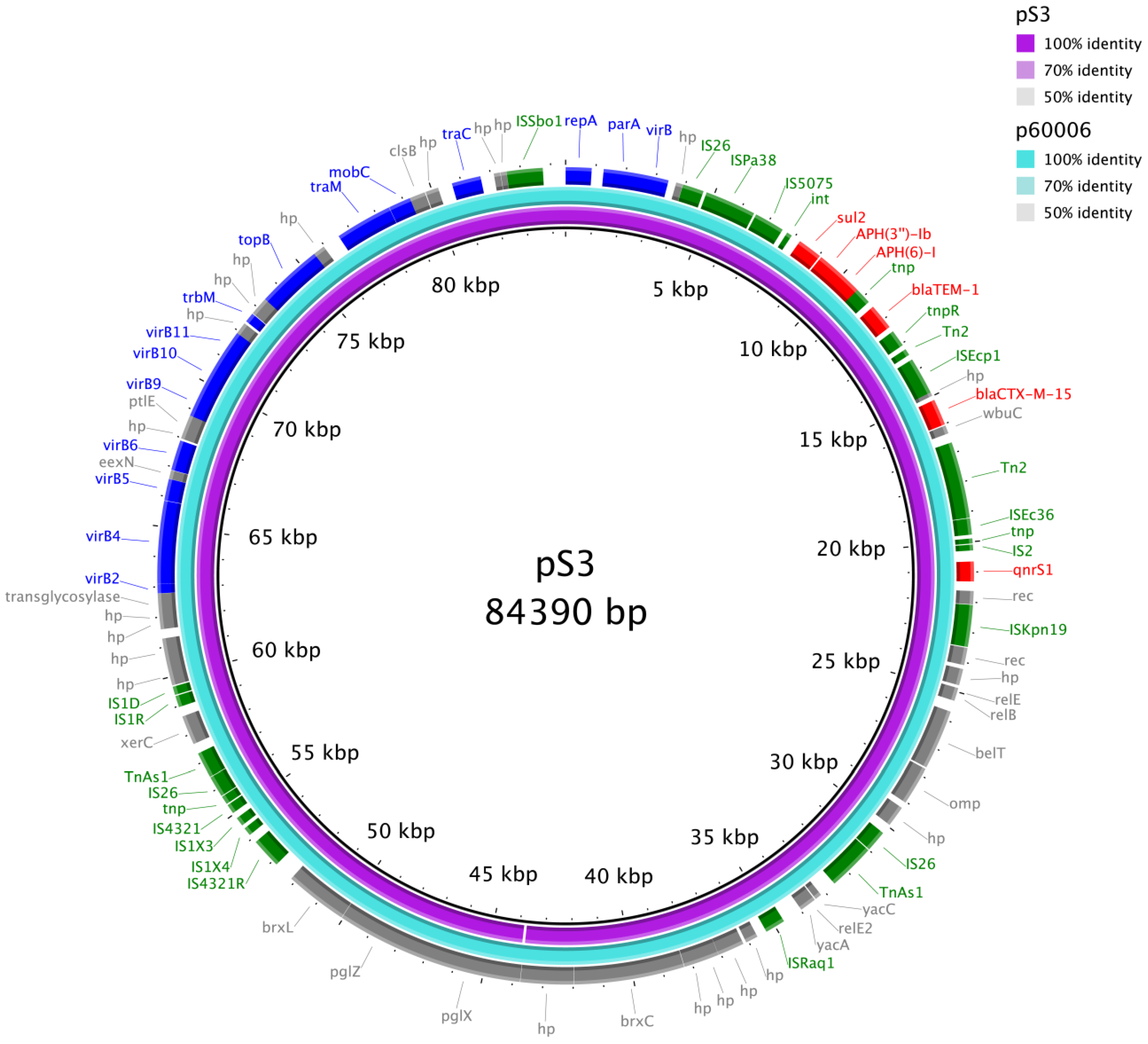
3.3. WGS of the Salmonella Typhi Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2017 Typhoid and Paratyphoid Collaborators. The global burden of typhoid and paratyphoid fevers: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, C.M.; Hien, T.T.; Dougan, G.; White, N.J.; Farrar, J.J. Typhoid Fever. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, G.; Baker, S. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi and the pathogenesis of typhoid fever. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Jain, S.K. Role of antigens and virulence factors of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi in its pathogenesis. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Hardy, J.; Sanderson, K.E.; Quail, M.; Goodhead, I.; Kingsley, R.A.; Parkhill, J.; Stocker, B.; Dougan, G. A novel linear plasmid mediates flagellar variation in Salmonella Typhi. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olarte, J.; Galindo, E. Salmonella typhi resistant to chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and other antimicrobial agents: Strains isolated during an extensive typhoid fever epidemic in Mexico. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1973, 4, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.S.; Smith, H.R. Chloramphenicol resistance in the typhoid bacillus. Br. Med. J. 1972, 3, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Phan, M.D.; Baker, S.; Duy, P.T.; Nga, T.V.T.; Nair, S.; Turner, A.K.; Walsh, C.; Fanning, S.; Farrell-Ward, S.; et al. Emergence of a Globally Dominant IncHI1 Plasmid Type Associated with Multiple Drug Resistant Typhoid. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, T.T.; Campbell, J.I.; Galindo, C.M.; Van Minh Hoang, N.; Diep, T.S.; Nga, T.T.; Van Vinh Chau, N.; Tuan, P.Q.; Page, A.L.; Ochiai, R.L.; et al. Antimicrobial drug resistance of Salmonella enterica serovar typhi in asia and molecular mechanism of reduced susceptibility to the fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, S.; Revathi, G.; Kiiru, J.; Mengo, D.M.; Mwituria, J.; Muyodi, J.; Munyalo, A.; Teo, Y.Y.; Holt, K.E.; Kingsley, R.A.; et al. Typhoid in Kenya is associated with a dominant multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi haplotype that is also widespread in Southeast Asia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen Rene, S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Lukjancenko, O.; Lukwesa-Musyani, C.; Tambatamba, B.; Mwaba, J.; Kalonda, A.; Nakazwe, R.; Kwenda, G.; Jensen Jacob, D.; et al. Genomic Signature of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Isolates Related to a Massive Outbreak in Zambia between 2010 and 2012. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.E.; Parkhill, J.; Mazzoni, C.J.; Roumagnac, P.; Weill, F.-X.; Goodhead, I.; Rance, R.; Baker, S.; Maskell, D.J.; Wain, J.; et al. High-throughput sequencing provides insights into genome variation and evolution in Salmonella Typhi. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumagnac, P.; Weill, F.X.; Dolecek, C.; Baker, S.; Brisse, S.; Chinh, N.T.; Le, T.A.; Acosta, C.J.; Farrar, J.; Dougan, G.; et al. Evolutionary history of Salmonella typhi. Science 2006, 314, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; Holt, K.; van de Vosse, E.; Roumagnac, P.; Whitehead, S.; King, E.; Ewels, P.; Keniry, A.; Weill, F.X.; Lightfoot, D.; et al. High-throughput genotyping of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi allowing geographical assignment of haplotypes and pathotypes within an urban District of Jakarta, Indonesia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.K.; Baker, S.; Pickard, D.J.; Parkhill, J.; Page, A.J.; Feasey, N.A.; Kingsley, R.A.; Thomson, N.R.; Keane, J.A.; Weill, F.X.; et al. Phylogeographical analysis of the dominant multidrug-resistant H58 clade of Salmonella Typhi identifies inter- and intracontinental transmission events. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, E.J.; Shakoor, S.; Page, A.J.; Qamar, F.N.; Judge, K.; Saeed, D.K.; Wong, V.K.; Dallman, T.J.; Nair, S.; Baker, S.; et al. Emergence of an Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Clone Harboring a Promiscuous Plasmid Encoding Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Third-Generation Cephalosporins. mBio 2018, 9, e00105-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.K.; Baker, S.; Connor, T.R.; Pickard, D.; Page, A.J.; Dave, J.; Murphy, N.; Holliman, R.; Sefton, A.; Millar, M.; et al. An extended genotyping framework for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the cause of human typhoid. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, Z.A.; Holt, K.E. Five Years of GenoTyphi: Updates to the Global Salmonella Typhi Genotyping Framework. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, S775–S780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, J.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Mikoleit, M.L.; Keddy, K.H.; Ochiai, R.L. Typhoid fever. Lancet 2015, 385, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Lee, C.-H.; Cao, H.; Jiang, S.; So, S.Y.; Tse, C.W.; Cheng, V.C.; Ho, P.-L. Evaluation of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of CTX-M Producers from Blood Cultures. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre for Health Protection. Number of Notifiable Infectious Diseases by Month. Available online: https://www.chp.gov.hk/en/static/24012.html (accessed on 7 December 2022).
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P.; Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; de Pinna, E.; Nair, S.; Fields, P.I.; Weill, F.X. Supplement 2008-2010 (no. 48) to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 32nd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, K.E.; Tanmoy, A.M.; Pragasam, A.K.; Iqbal, J.; Sajib, M.S.I.; Mutreja, A.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Tamrakar, D.; Qamar, F.N.; Dougan, G.; et al. The international and intercontinental spread and expansion of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella Typhi: A genomic epidemiology study. Lancet. Microbe 2022, 3, e567–e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Liu, M.C.; Tong, M.K.; Jiang, S.; Chow, K.H.; To, K.K.; Tse, C.W.; Ho, P.L. Comprehensive investigation of antibiotic resistance gene content in cfiA-harboring Bacteroides fragilis isolates of human and animal origins by whole genome sequencing. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2022, 312, 151559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Liu, M.C.; Tong, M.K.; Jiang, S.; Lau, A.; Chow, K.H.; Tse, C.W.; Ho, P.L. Diversity of genomic clusters and CfiA/cfiA alleles in Bacteroides fragilis isolates from human and animals. Anaerobe 2022, 75, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, C.D.; John, J.; Verghese, V.P.; Pollard, A.J. A systematic review of antimicrobial resistance of typhoidal Salmonella in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, C.D.; Wong, V.K.; Dougan, G.; Pollard, A.J. A systematic review of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the etiological agent of typhoid. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, Z.A.; Thanh, D.P.; Bodhidatta, L.; Mason, C.J.; Srijan, A.; Rabaa, M.A.; Vinh, P.V.; Thanh, T.H.; Thwaites, G.E.; Baker, S.; et al. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Salmonella Typhi Isolated in Thailand before and after the Introduction of a National Immunization Program. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingle, D.J.; Nair, S.; Hartman, H.; Ashton, P.M.; Dyson, Z.A.; Day, M.; Freedman, J.; Chattaway, M.A.; Holt, K.E.; Dallman, T.J. Informal genomic surveillance of regional distribution of Salmonella Typhi genotypes and antimicrobial resistance via returning travellers. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.E.; Pham, D.T.; Boinett, C.; Wong, V.K.; Pak, G.D.; Panzner, U.; Espinoza, L.M.C.; von Kalckreuth, V.; Im, J.; Schütt-Gerowitt, H.; et al. The phylogeography and incidence of multi-drug resistant typhoid fever in sub-Saharan Africa. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhill, J.; Dougan, G.; James, K.D.; Thomson, N.R.; Pickard, D.; Wain, J.; Churcher, C.; Mungall, K.L.; Bentley, S.D.; Holden, M.T.; et al. Complete genome sequence of a multiple drug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi CT18. Nature 2001, 413, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragasam, A.K.; Pickard, D.; Wong, V.; Dougan, G.; Kang, G.; Thompson, A.; John, J.; Balaji, V.; Mutreja, A. Phylogenetic Analysis Indicates a Longer Term Presence of the Globally Distributed H58 Haplotype of Salmonella Typhi in Southern India. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanmoy, A.M.; Westeel, E.; De Bruyne, K.; Goris, J.; Rajoharison, A.; Sajib, M.S.I.; van Belkum, A.; Saha, S.K.; Komurian-Pradel, F.; Endtz, H.P. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi in Bangladesh: Exploration of Genomic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance. mBio 2018, 9, e02112-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Han, W.; Cao, H.; Umarov, R.; Yan, A.; Fan, M.; Chen, H.; Duarte, C.M.; Li, L.; et al. HMD-ARG: Hierarchical multi-task deep learning for annotating antibiotic resistance genes. Microbiome 2021, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Allesøe, R.; Joensen, K.G.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A novel web tool for WGS-based detection of antimicrobial resistance associated with chromosomal point mutations in bacterial pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Bougouffa, S.; Park, T.J.; Lau, A.; Tong, M.K.; Chow, K.H.; Ho, P.L. Sharing of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes between Humans and Food Animals. mSystems 2022, 7, e0077522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, K.E.; Baker, S.; Dongol, S.; Basnyat, B.; Adhikari, N.; Thorson, S.; Pulickal, A.S.; Song, Y.; Parkhill, J.; Farrar, J.J.; et al. High-throughput bacterial SNP typing identifies distinct clusters of Salmonella Typhi causing typhoid in Nepalese children. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, S.; Dyson, Z.A.; Mbae, C.; Ngetich, R.; Kavai, S.M.; Wairimu, C.; Anyona, S.; Gitau, N.; Onsare, R.S.; Ongandi, B.; et al. Multiple introductions of multidrug-resistant typhoid associated with acute infection and asymptomatic carriage, Kenya. eLife 2021, 10, 67852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, F.; Saeed, M.; Alikhan, N.F.; Baker, D.; Khurshid, M.; Ainsworth, E.V.; Turner, A.K.; Imran, A.A.; Rasool, M.H.; Saqalein, M.; et al. Emergence of Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Third-Generation Cephalosporins in Salmonella Typhi in Lahore, Pakistan. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean. Weekly Epidemiological Monitor. Available online: https://applications.emro.who.int/docs/epi/2018/Epi_Monitor_2018_11_52.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Chatham-Stephens, K.; Medalla, F.; Hughes, M.; Appiah, G.D.; Aubert, R.D.; Caidi, H.; Angelo, K.M.; Walker, A.T.; Hatley, N.; Masani, S.; et al. Emergence of Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhi Infections Among Travelers to or from Pakistan—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly Rep. 2019, 68, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghi, A.; Zittermann, S.; Bharat, A.; Mulvey, M.R.; Allen, V.G.; Patel, S.N. Importation of Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Cases in Ontario, Canada. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2020, 64, e02581-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Chattaway, M.; Langridge, G.C.; Gentle, A.; Day, M.; Ainsworth, E.V.; Mohamed, I.; Smith, R.; Jenkins, C.; Dallman, T.J.; et al. ESBL-producing strains isolated from imported cases of enteric fever in England and Wales reveal multiple chromosomal integrations of blaCTX-M-15 in XDR Salmonella Typhi. J. Antimicrob Chemother 2021, 76, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, D.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Lyu, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Shu, G.; Liu, B.; Lin, C.; et al. Extensively Drug-Resistant (XDR) Salmonella Typhi Outbreak by Waterborne Infection—Beijing Municipality, China, January–February 2022. China CDC Wkly. 2022, 4, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, D.J.; Andersson, P.; Valcanis, M.; Wilmot, M.; Easton, M.; Lane, C.; Barden, J.; Gonçalves da Silva, A.; Seemann, T.; Horan, K.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Resistance Mechanisms of Imported Typhoid in Australia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e0120021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabarro, L.E.; McCann, N.; Herdman, M.T.; Dugan, C.; Ladhani, S.; Patel, D.; Morris-Jones, S.; Balasegaram, S.; Heyderman, R.S.; Brown, M.; et al. British infection association guidelines for the diagnosis and management of enteric fever in England. J. Infect. 2022, 84, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.R.; Duchene, S.; Valcanis, M.; Jenkins, A.P.; Jenney, A.; Rosa, V.; Hayes, A.J.; Strobel, A.G.; McIntyre, L.; Lacey, J.A.; et al. Genomic epidemiology of Salmonella Typhi in Central Division, Fiji, 2012 to 2016. Lancet Reg. Health. West. Pac. 2022, 24, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, J.; John, J.; Charles, R.C. Enteric (Typhoid and Paratyphoid) Fever: Treatment and Prevention. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/enteric-typhoid-and-paratyphoid-fever-treatment-and-prevention (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- François Watkins, L.K.; Winstead, A.; Appiah, G.D.; Friedman, C.R.; Medalla, F.; Hughes, M.J.; Birhane, M.G.; Schneider, Z.D.; Marcenac, P.; Hanna, S.S.; et al. Update on Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella Serotype Typhi Infections Among Travelers to or from Pakistan and Report of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Salmonella Serotype Typhi Infections Among Travelers to Iraq—United States, 2018–2019. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, Q.; Tahir, M.; Sadaqat, A.; Ayub, A.; Awan, A.B.; Wajid, M.; Ali, A.; Iqbal, M.; Haque, A.; Sarwar, Y. First Detection of Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella Typhi Isolates Harboring VIM and GES Genes for Carbapenem Resistance from Faisalabad, Pakistan. Microb. Drug Resist. (Larchmt. N.Y.) 2022, 28, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Case a, b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | |
| Sex/age (years) | Female/39 | Female/23 | Male/54 | Male/51 | Female/4 | Female/51 | Female/73 |
| Date of symptom onset | Oct 2022 | Sep 2022 | Feb 2022 | Aug 2020 | Jul 2021 | Jun 2022 | May 2021 |
| Presenting symptoms | Fever, chills, rigour, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain | Fever, chills, headache | Abdominal and lower back pain, nausea, vomiting | Fever, chills, cough, dyspnoea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, vomiting | Fever, fatigue | Fever, cough, vomiting | Cough, dyspnoea, abdominal pain |
| Complications | Nil | Nil | Infected abdominal aortic aneurysm, lumbar spondylodiscitis | Nil | Nil | Nil | Renal failure Coagulopathy Mortality |
| Travel outside HK in preceding 12 months | No | No | No | No | No | Yes (Philippines) | No |
| Culture positive site | Blood | Blood | Blood, stool | Blood | Blood, stool | Blood | Blood |
| Susceptibility | |||||||
| Ampicillin | S | S | R [blaTEM-1B, blaCTX-M-15] | S | S | S | S |
| Azithromycin | S (8) | S (4) | S (8) | S (4) | S (4) | S (4) | S (8) |
| Ceftriaxone | S | S | R [blaCTX-M-15] | S | S | S | S |
| Chloramphenicol | S | S | R [catA1] | S | S | S | S |
| Ciprofloxacin | S (0.012) | S (0.012) | R (2) [gyrA S83F, qnrS1] | S (0.012) | I (0.5) [gyrA S83F] | S (0.06) | S (0.06) |
| Co-trimoxazole | S | S | R [sul1, sul2, dfrA7] | S | S | S | S |
| Meropenem | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Genotype | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 4.3.1.1.P1 | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 2.3.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Cao, H.; Chen, J.H.-K.; Ng, Y.-Z.; Fung, K.-K.; Cheng, V.C.-C.; Ho, P.-L. Genomic Investigation of Salmonella Typhi in Hong Kong Revealing the Predominance of Genotype 3.2.2 and the First Case of an Extensively Drug-Resistant H58 Genotype. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030667
Li X, Cao H, Chen JH-K, Ng Y-Z, Fung K-K, Cheng VC-C, Ho P-L. Genomic Investigation of Salmonella Typhi in Hong Kong Revealing the Predominance of Genotype 3.2.2 and the First Case of an Extensively Drug-Resistant H58 Genotype. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030667
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Huiluo Cao, Jonathan Hon-Kwan Chen, Yuey-Zhun Ng, Ka-Kin Fung, Vincent Chi-Chung Cheng, and Pak-Leung Ho. 2023. "Genomic Investigation of Salmonella Typhi in Hong Kong Revealing the Predominance of Genotype 3.2.2 and the First Case of an Extensively Drug-Resistant H58 Genotype" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030667
APA StyleLi, X., Cao, H., Chen, J. H.-K., Ng, Y.-Z., Fung, K.-K., Cheng, V. C.-C., & Ho, P.-L. (2023). Genomic Investigation of Salmonella Typhi in Hong Kong Revealing the Predominance of Genotype 3.2.2 and the First Case of an Extensively Drug-Resistant H58 Genotype. Microorganisms, 11(3), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030667







