Phenol Degradation by Pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sphe3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
2.2. Assessments of Growth and Determination of Residual Phenol in Culture Medium
2.3. Preparation of Sphe3 Cell Extracts
2.4. Enzyme Assays
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Immobilization of Sphe3 Cells in Calcium Alginate Beads
2.7. Phenol Degradation by Immobilized Sphe3 Cells
2.8. Phenol Catabolism—Parameters Optimization
2.9. Reusability and Phenol Degradation Efficiency by Immobilized Cells after 30 Days of Storage
2.10. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
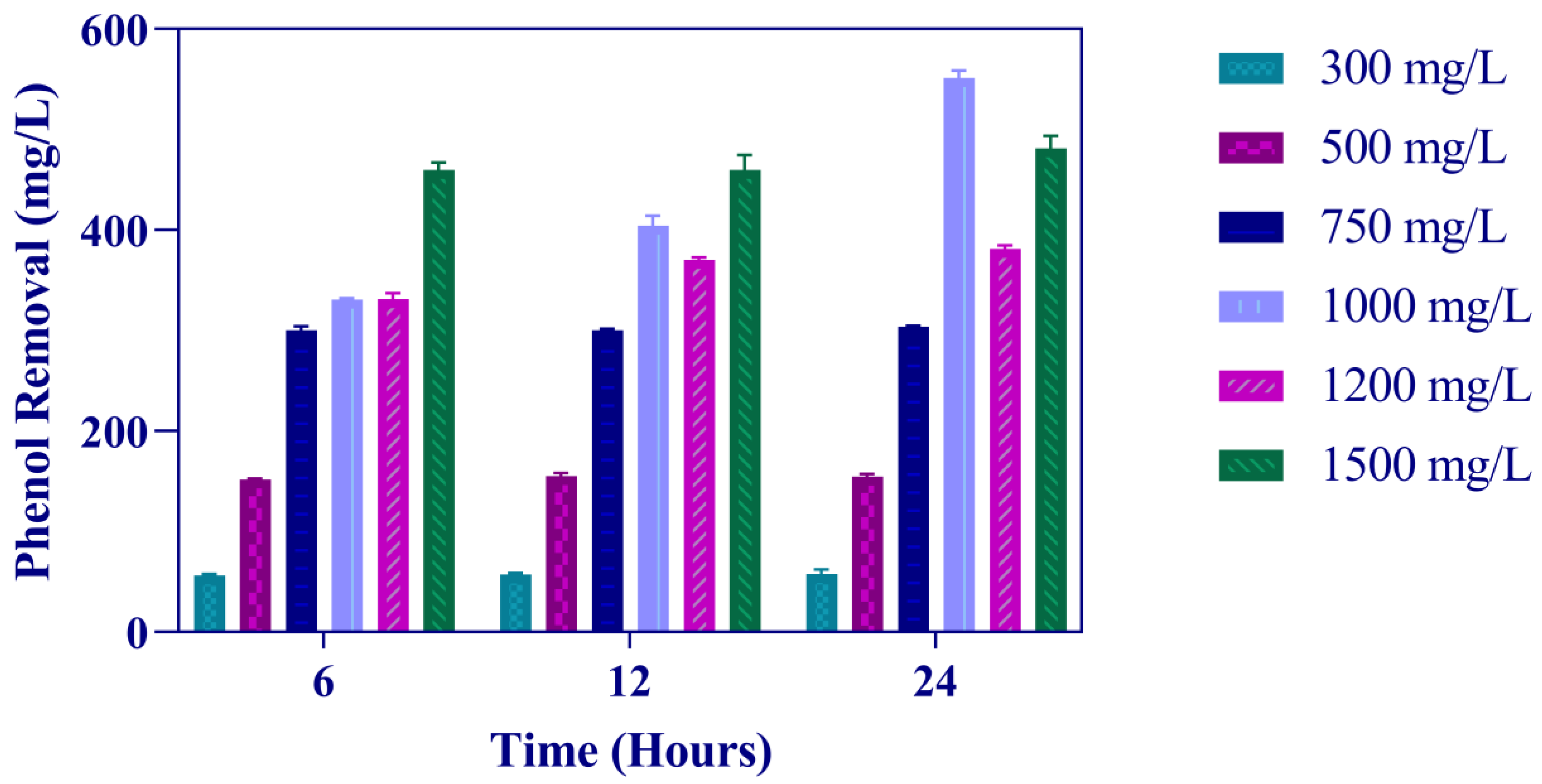
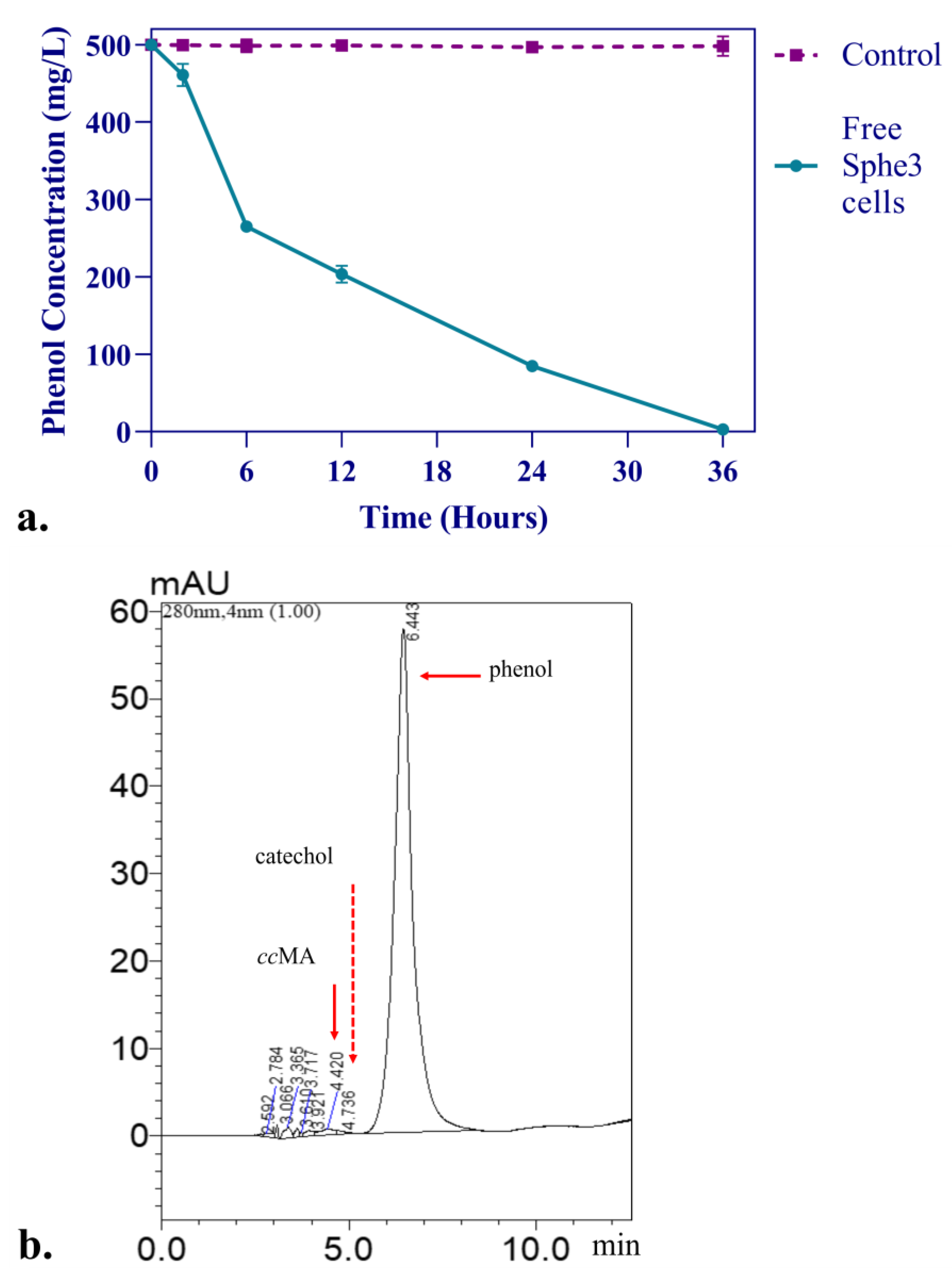
3.1. Utilization of Phenol as the Sole Source of Carbon and Energy
3.2. Phenol Degradation Pathway
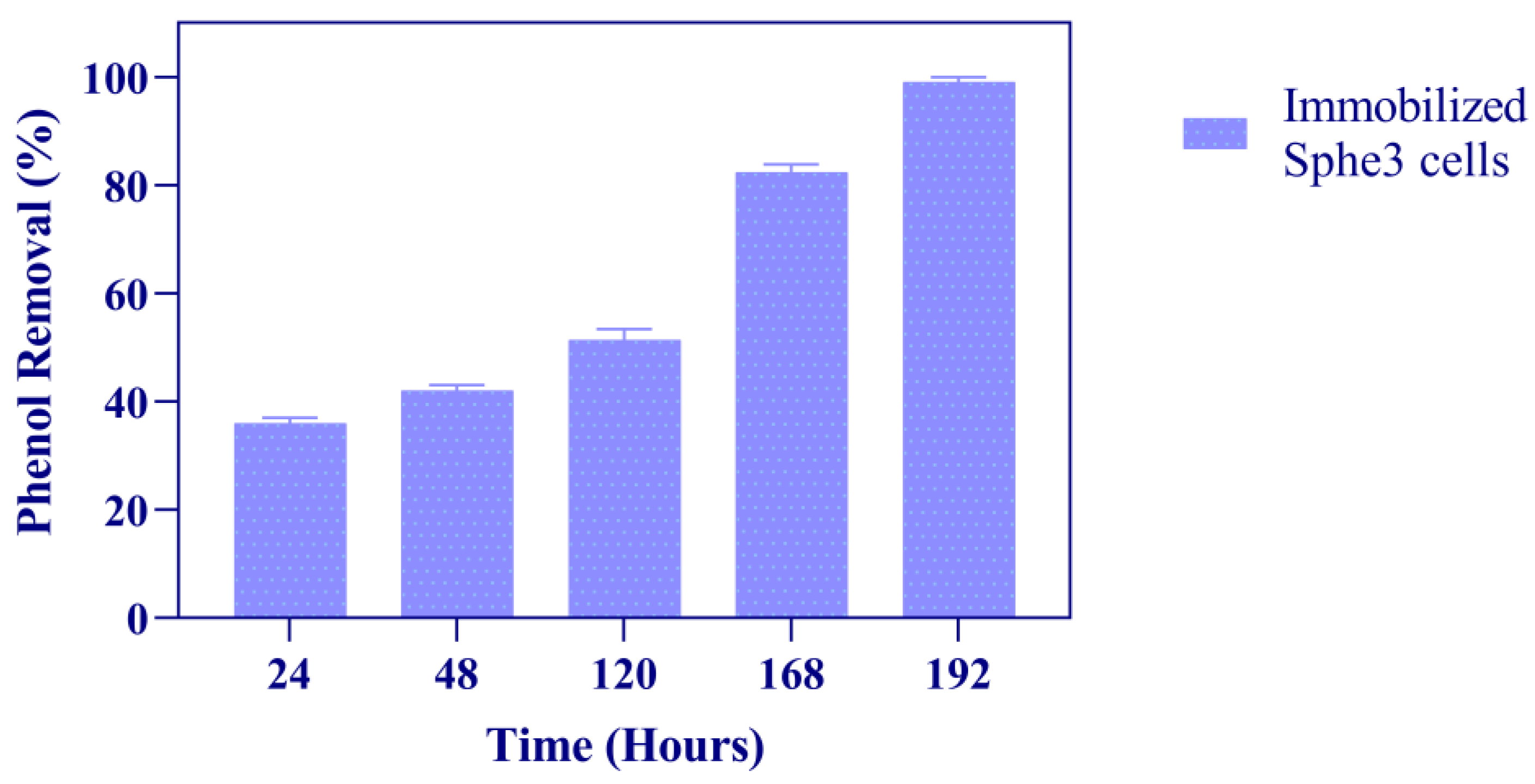
3.3. Phenol Degradation by Immobilized Sphe3 Cells
3.4. Phenol Catabolism—Parameters Optimization
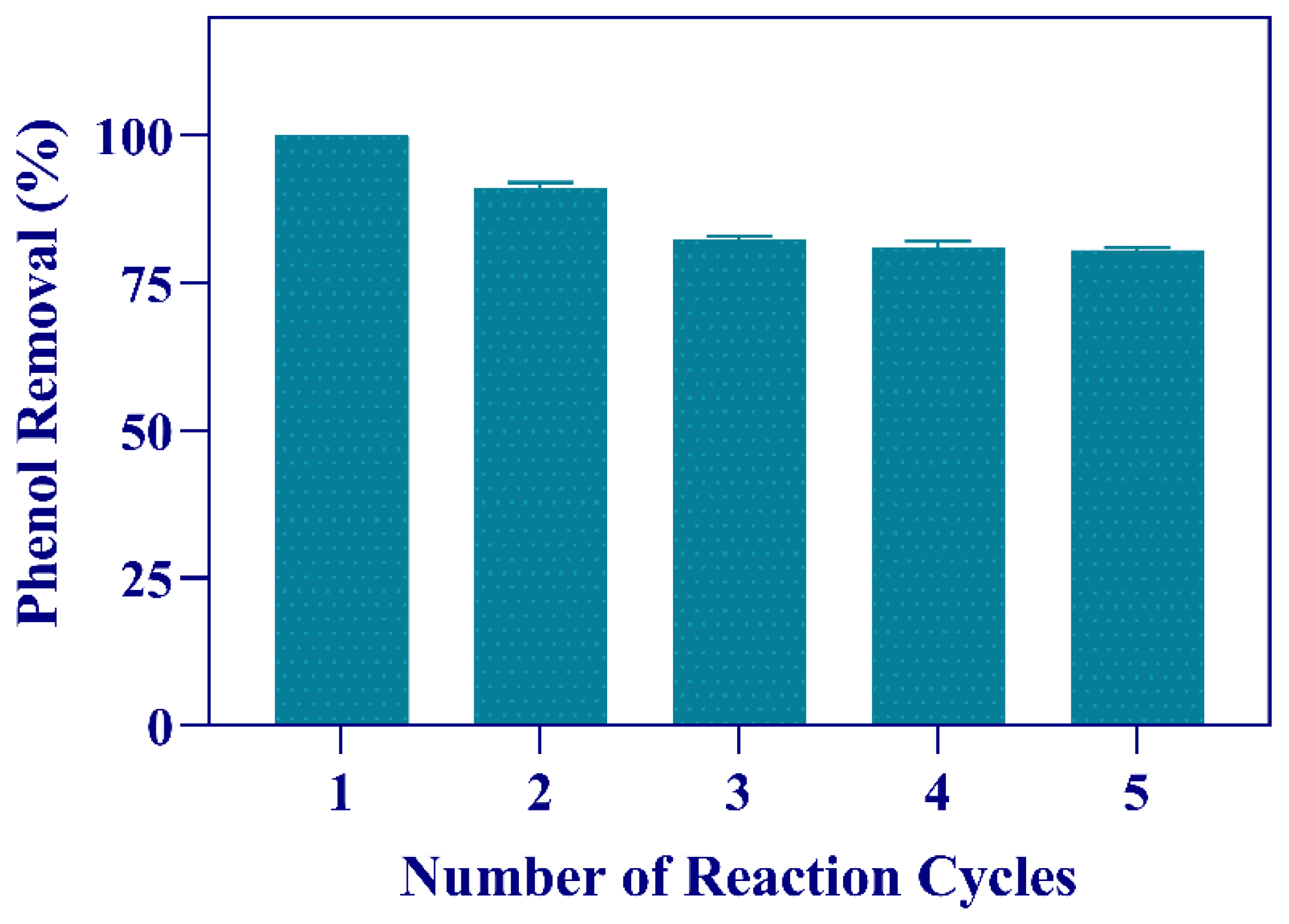
3.5. Reusability of Immobilized Cells
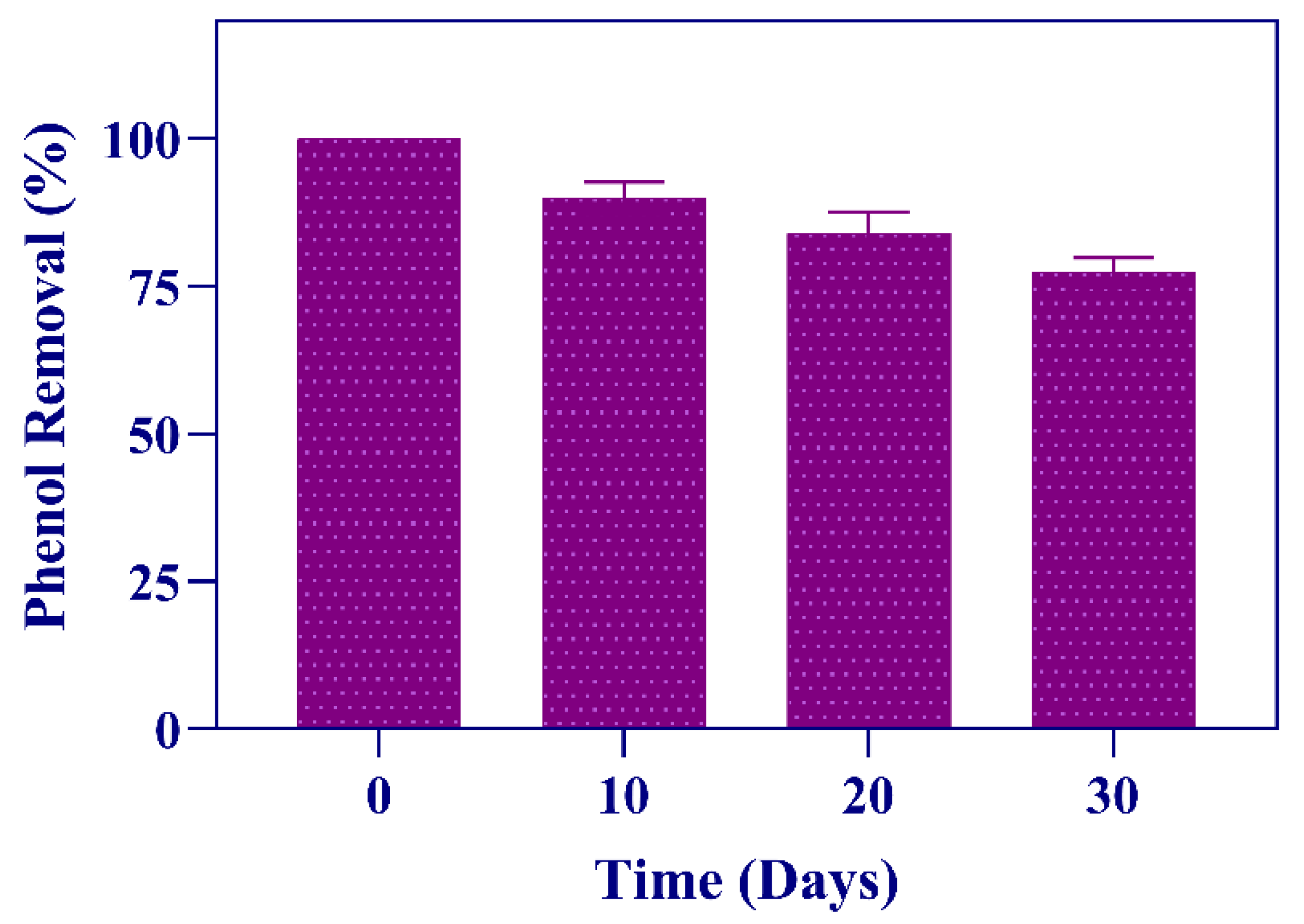
3.6. Phenol Degradation Efficiency by Immobilized Cells after 30 Days of Storage
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkaram, U.F.; Mukhlis, A.A.; Al-Dujaili, A.H. The Removal of Phenol from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption Using Surfactant-Modified Bentonite and Kaolinite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Shah, S.B.; Zanaroli, G.; Xu, P.; Tang, H. Phenol Biodegradation by Acinetobacter radioresistens APH1 and Its Application in Soil Bioremediation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barik, M.; Das, C.P.; Kumar Verma, A.; Sahoo, S.; Sahoo, N.K. Metabolic Profiling of Phenol Biodegradation by an Indigenous Rhodococcus pyridinivorans Strain PDB9T N-1 Isolated from Paper Pulp Wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2021, 158, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Ye, M.; Pan, H.; Zhu, J.; Song, H. The Conversion of the Nutrient Condition Alter the Phenol Degradation Pathway by Rhodococcus biphenylivorans B403: A Comparative Transcriptomic and Proteomic Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 56152–56163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Qiu, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ye, C.; Guo, M. Analysis of Phenol Biodegradation in Antibiotic and Heavy Metal Resistant Acinetobacter lwoffii NL1. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Jiang, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; Lu, J. A Reusable Immobilization Matrix for the Biodegradation of Phenol at 5000 Mg/L. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 725755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas, L.G.C.; Mashhadi, N.; Chen, M.; Mukherjee, D.; Taylor, K.E.; Biswas, N. A Short Review of Techniques for Phenol Removal from Wastewater. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2016, 2, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, A. Presence of Phenol in Wastewater Effluent and Its Removal: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 1362–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, Z.; Hassanshahian, M.; Cappello, S. Immobilization of Microbes for Bioremediation of Crude Oil Polluted Environments: A Mini Review. Open Microbiol. J. 2015, 9, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, P.Y.A.; Kunhi, A.A.M. Enhanced Degradation of Phenol by Pseudomonas sp. CP4 Entrapped in Agar and Calcium Alginate Beads in Batch and Continuous Processes. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, S.; Arora, U.; Tarar, P.; Viggor, S.; Jõesaar, M.; Kivisaar, M.; Kapley, A. Monitoring the Growth, Survival and Phenol Utilization of the Fluorescent-Tagged Pseudomonas oleovorans Immobilized and Free Cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 338, 125568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasi, S.; Tabrez, S.; Ahmad, M. Use of Pseudomonas spp. for the Bioremediation of Environmental Pollutants: A Review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8147–8155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahgoub, S.A.; Qattan, S.Y.A.; Salem, S.S.; Abdelbasit, H.M.; Raafat, M.; Ashkan, M.F.; Al-Quwaie, D.A.; Motwali, E.A.; Alqahtani, F.S.; El-Fattah, H.I.A. Characterization and Biodegradation of Phenol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella variicola Strains Isolated from Sewage Sludge and Their Effect on Soybean Seeds Germination. Molecules 2023, 28, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viggor, S.; Jõesaar, M.; Soares-Castro, P.; Ilmjärv, T.; Santos, P.M.; Kapley, A.; Kivisaar, M. Microbial Metabolic Potential of Phenol Degradation in Wastewater Treatment Plant of Crude Oil Refinery: Analysis of Metagenomes and Characterization of Isolates. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emelyanova, E.V.; Solyanikova, I.P. Evaluation of Phenol-Degradation Activity of Rhodococcus opacus 1CP Using Immobilized and Intact Cells. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 2279–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chris Felshia, S.; Aswin Karthick, N.; Thilagam, R.; Chandralekha, A.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Gnanamani, A. Efficacy of Free and Encapsulated Bacillus Lichenformis Strain SL10 on Degradation of Phenol: A Comparative Study of Degradation Kinetics. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karigar, C.; Mahesh, A.; Nagenahalli, M.; Yun, D.J. Phenol Degradation by Immobilized Cells of Arthrobacter citreus. Biodegradation 2006, 17, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unell, M.; Nordin, K.; Jernberg, C.; Stenström, J.; Jansson, J.K. Degradation of Mixtures of Phenolic Compounds by Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6. Biodegradation 2008, 19, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Song, W.; Wei, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, C. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Phenol Degradation Process by Arthrobacter. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 110, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.L.Y.; Zakaria, N.N.; Futamata, H.; Suzuki, K.; Zulkharnain, A.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Convey, P.; Zahri, K.N.M.; Ahmad, S.A. Metabolic Pathway of Phenol Degradation of a Cold-Adapted Antarctic Bacteria, Arthrobacter sp. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagley, S. Catabolism of Aromatic Compounds by Micro-Organisms. In Advances in Microbial Physiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1971; Volume 6, pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- van Schie, P.M.; Young, L.Y. Biodegradation of Phenol: Mechanisms and Applications. Bioremediat. J. 2000, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahiudddin, M.; Fakhruddin, A.N.M. Abdullah-Al-Mahin Degradation of Phenol via Meta Cleavage Pathway by Pseudomonas fluorescens PU1. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallimanis, A.; Kavakiotis, K.; Perisynakis, A.; Spröer, C.; Pukall, R.; Drainas, C.; Koukkou, A.I. Arthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sp. Nov., to Accommodate the Phenanthrene-Degrading Bacterium Arthrobacter sp. Strain Sphe3. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallimanis, A.; Frillingos, S.; Drainas, C.; Koukkou, A.I. Taxonomic Identification, Phenanthrene Uptake Activity, and Membrane Lipid Alterations of the PAH Degrading Arthrobacter sp. Strain Sphe3. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Der Yang, R.; Humphrey, A.E. Dynamic and Steady State Studies of Phenol Biodegradation in Pure and Mixed Cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1975, 17, 1211–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Cowan, D.A. Meta-Pathway Degradation of Phenolics by Thermophilic Bacilli. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1998, 23, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T.; Nakazawa, A. [64] Pyrocatechase (Pseudomonas). In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970; Volume 17, pp. 518–522. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki, M. [65] Metapyrocatechase (Pseudomonas). In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970; Volume 17, pp. 522–525. [Google Scholar]
- Vandera, E.; Kavakiotis, K.; Kallimanis, A.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Drainas, C.; Koukkou, A. Heterologous Expression and Characterization of Two 1-Hydroxy-2-Naphthoic Acid Dioxygenases from Arthrobacter phenanthrenivorans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A New Mathematical Model for Relative Quantification in Real-Time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbella, M.E.; Puyet, A. Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR Analysis of Expression of Halobenzoate and Salicylate Catabolism-Associated Operons in Two Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2269–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABI Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System. In Applied Biosystems Relative Quantitation of Gene Expression; Thermo Scientific: Waltham, MA, USA, 1997.
- Ziagova, M.G.; Koukkou, A.I.; Liakopoulou-Kyriakides, M. Optimization of Cultural Conditions of Arthrobacter sp. Sphe3 for Growth-Associated Chromate(VI) Reduction in Free and Immobilized Cell Systems. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paisio, C.E.; Talano, M.A.; González, P.S.; Magallanes-Noguera, C.; Kurina-Sanz, M.; Agostini, E. Biotechnological Tools to Improve Bioremediation of Phenol by Acinetobacter sp. RTE1.4. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 2379–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakopoulou, A.; Chatzikonstantinou, A.V.; Chalmpes, N.; Tsapara, G.; Gournis, D.; Polydera, A.C.; Stamatis, H. Development of a Novel Bi-Enzymatic Nanobiocatalyst for the Efficient Bioconversion of Oleuropein to Hydroxytyrosol. Catalysts 2021, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana Lakshmi, M.V.V.; Sridevi, V. A Review on Biodegradation of Phenol from Industrial Effluents. J. Ind. Pollut. Control 2009, 25, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tomei, M.C.; Mosca Angelucci, D.; Clagnan, E.; Brusetti, L. Anaerobic Biodegradation of Phenol in Wastewater Treatment: Achievements and Limits. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2195–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khalid, T.; El-Naas, M.H. Aerobic Biodegradation of Phenols: A Comprehensive Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1631–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ali, D.C.; Liu, P.; Peng, C.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, B. Degradation of Phenol via Ortho-Pathway by Kocuria sp. Strain TIBETAN4 Isolated from the Soils around Qinghai Lake in China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margesin, R.; Bergauer, P.; Gander, S. Degradation of Phenol and Toxicity of Phenolic Compounds: A Comparison of Cold-Tolerant Arthrobacter sp. and Mesophilic Pseudomonas Putida. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Qu, Y.; Zhou, J. Biodegradation of Mixed Phenolic Compounds under High Salt Conditions and Salinity Fluctuations by Arthrobacter sp. W1. In Proceedings of the Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 159, pp. 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Cheng, Y.S. Phenol Degradation Kinetics by Free and Immobilized Pseudomonas putida BCRC 14365 in Batch and Continuous-Flow Bioreactors. Processes 2020, 8, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khleifat, K.; Magharbeh, M.; Alqaraleh, M.; Al-Sarayrah, M.; Alfarrayeh, I.; Al Qaisi, Y.; Alsarayreh, A.; Alkafaween, M. Biodegradation Modeling of Phenol Using Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens as Plant-Growth-Promoting Bacteria. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paller, G.; Hommel, R.K.; Kleber, H. -P Phenol Degradation by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus NCIB 8250. J. Basic Microbiol. 1995, 35, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, A.; Christen, P.; Davidson, S.; Pophillat, M.; Lorquin, J.; Auria, R.; Simon, G.; Casalot, L. Biochemical, Transcriptional and Translational Evidences of the Phenol-Meta-Degradation Pathway by the Hyperthermophilic Sulfolobus solfataricus 98/2. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Loh, K.-C. Catabolic Pathways and Cellular Responses of Pseudomonas putida P8 during Growth on Benzoate with a Proteomics Approach. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 101, 1297–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, K.C.; Chua, S.S. Ortho Pathway of Benzoate Degradation in Pseudomonas putida: Induction of Meta Pathway at High Substrate Concentrations. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nešvera, J.; Rucká, L.; Pátek, M. Catabolism of Phenol and Its Derivatives in Bacteria: Genes, Their Regulation, and Use in the Biodegradation of Toxic Pollutants. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 93, 107–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, B.; Bhunia, B.; Dey, A. Studies on the Potential Use of Sugarcane Bagasse as Carrier Matrix for Immobilization of Candida tropicalis PHB5 for Phenol Biodegradation. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 93, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Mei, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Chen, C.; et al. Sustainable Biodegradation of Phenol by Immobilized Bacillus sp. SAS19 with Porous Carbonaceous Gels as Carriers. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Han, B.; Zhao, H.; Bi, J.; Cai, B. Biodegradation of Phenol by Free and Immobilized Acinetobacter sp. Strain PD12. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S. Microbial Degradation of Phenol:A Comparitive Study; National Institute of Technology: Rourkela, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Deng, T.; Shang, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, H. Biodegradation of Phenol by Entrapped Cell of Debaryomyces sp. with Nano-Fe3O4 under Hypersaline Conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 123, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Ghoshal, A.K. Phenol Degradation Performance by Isolated Bacillus cereus Immobilized in Alginate. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asimakoula, S.; Marinakos, O.; Tsagogiannis, E.; Koukkou, A.-I. Phenol Degradation by Pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sphe3. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020524
Asimakoula S, Marinakos O, Tsagogiannis E, Koukkou A-I. Phenol Degradation by Pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sphe3. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(2):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020524
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsimakoula, Stamatia, Orfeas Marinakos, Epameinondas Tsagogiannis, and Anna-Irini Koukkou. 2023. "Phenol Degradation by Pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sphe3" Microorganisms 11, no. 2: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020524
APA StyleAsimakoula, S., Marinakos, O., Tsagogiannis, E., & Koukkou, A.-I. (2023). Phenol Degradation by Pseudarthrobacter phenanthrenivorans Sphe3. Microorganisms, 11(2), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020524








