The Microbiome-TIME Axis: A Host of Possibilities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Significance of TIME
3. Composition of TIME and Its Potential Impact by Microbiota
3.1. Extracellular Matrix
3.2. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts
3.3. Innate Immune Cells
3.4. Adaptive Immune Cells
3.5. Signaling Molecules
4. Microbiome-TIME Axis in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Treatment
4.1. Microbial Metabolites
4.1.1. Short-Chain Fatty Acids
4.1.2. Inosine
4.2. Extracellular Vesicles
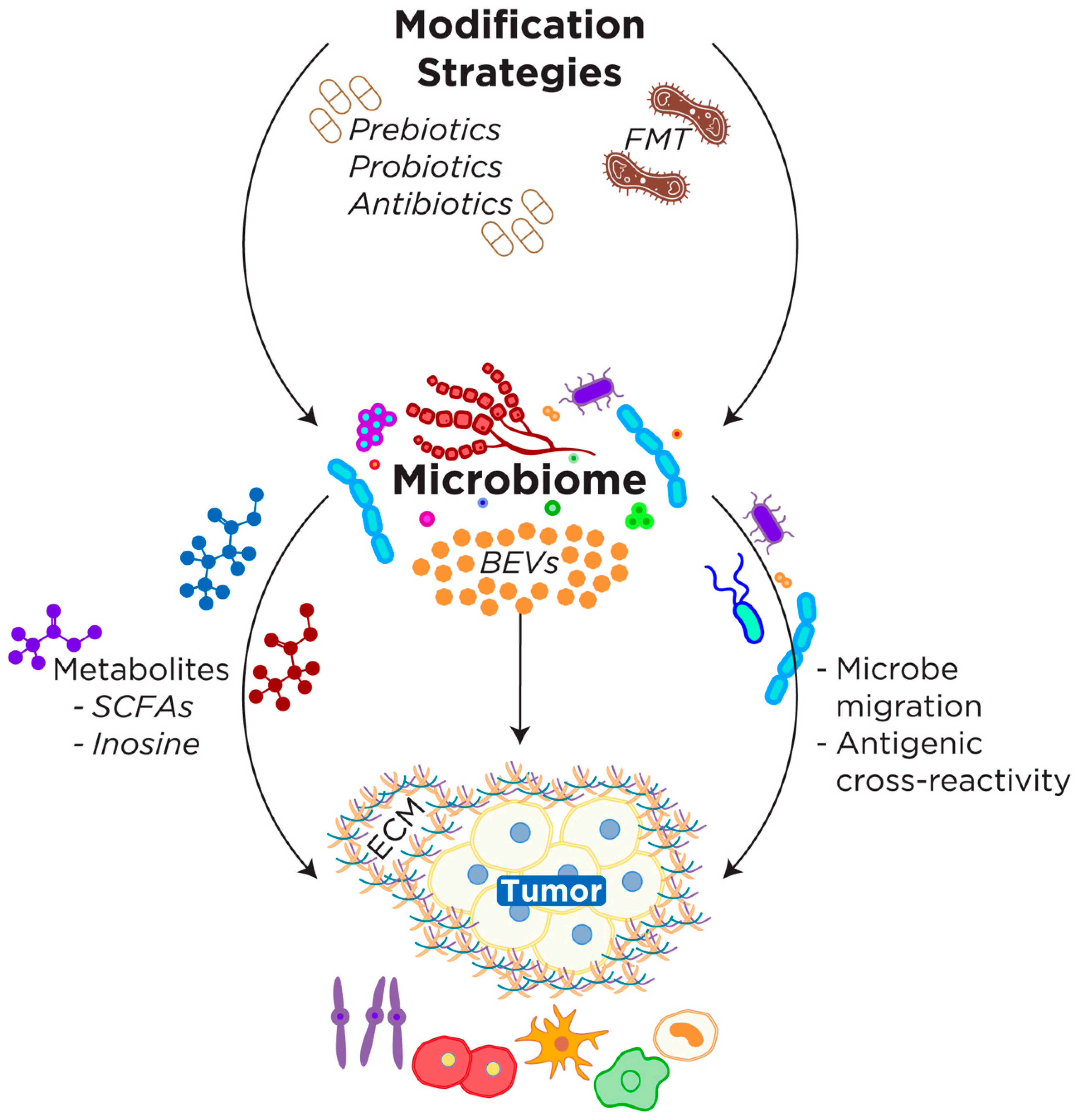
5. Clinical Implications and Future Directions of Microbiome-TIME Axis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, G.; Rybakova, D.; Fischer, D.; Cernava, T.; Vergès, M.-C.C.; Charles, T.; Chen, X.; Cocolin, L.; Eversole, K.; Corral, G.H.; et al. Microbiome definition re-visited: Old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 2020, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajeri, M.H.; Brummer, R.J.M.; Rastall, R.A.; Weersma, R.K.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faas, M.; Eggersdorfer, M. The role of the microbiome for human health: From basic science to clinical applications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Helmink, B.A.; Spencer, C.N.; Reuben, A.; Wargo, J.A. The Influence of the Gut Microbiome on Cancer, Immunity, and Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arneth, B. Tumor Microenvironment. Medicina 2019, 56, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The tumor microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Huang, Y.; Luo, H.; Huang, R.; et al. Exploring the Emerging Role of the Gut Microbiota and Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 612202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liu, L.; Hou, Y.; Xiong, M.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, K. Single-cell RNA sequencing highlights the role of inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts in bladder urothelial carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagaev, A.; Kotlov, N.; Nomie, K.; Svekolkin, V.; Gafurov, A.; Isaeva, O.; Osokin, N.; Kozlov, I.; Frenkel, F.; Gancharova, O.; et al. Conserved pan-cancer microenvironment subtypes predict response to immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 845–865.e847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, C.; Bibeau, F.; Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; Singh, N.; Nottegar, A.; Bosse, T.; Miller, R.; Riaz, N.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Andre, F.; et al. ESMO recommendations on microsatellite instability testing for immunotherapy in cancer, and its relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 expression and tumour mutational burden: A systematic review-based approach. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmink, B.A.; Khan, M.A.W.; Hermann, A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Wargo, J.A. The microbiome, cancer, and cancer therapy. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Chu, Q.; Zhang, P. Gut microbiome and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 447, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Zhu, H.; Dai, Q.; Fan, X.; Mehta, K.; Huang, C.; Neupane, P.; Wang, F.; et al. Relating Gut Microbiome and Its Modulating Factors to Immunotherapy in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 642110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, J.; Yadav, M.; Liu, B.; Furqan, M.; Dai, Q.; Shahi, S.; Gupta, A.; Mercer, K.N.; Eastman, E.; Hejleh, T.A.; et al. Prospective correlation between the patient microbiome with response to and development of immune-mediated adverse effects to immunotherapy in lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.M.; Marabelle, A.; Eggermont, A.; Soria, J.C.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: Removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, J.A.; Sweis, R.F.; Bao, R.; Luke, J.J. T Cell-Inflamed versus Non-T Cell-Inflamed Tumors: A Conceptual Framework for Cancer Immunotherapy Drug Development and Combination Therapy Selection. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldszmid, R.S.; Dzutsev, A.; Viaud, S.; Zitvogel, L.; Restifo, N.P.; Trinchieri, G. Microbiota modulation of myeloid cells in cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, M.; Canducci, F.; Nebuloni, M.; Clementi, M.; Montorsi, F.; Salonia, A. The interplay of extracellular matrix and microbiome in urothelial bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, C.; Hua, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Meng, Q.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: New findings and future perspectives. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.H.; Nguyen, V.H.; Jiang, S.-N.; Park, S.-H.; Tan, W.; Hong, S.H.; Shin, M.G.; Chung, I.-J.; Hong, Y.; Bom, H.-S.; et al. Two-step enhanced cancer immunotherapy with engineered Salmonella typhimurium secreting heterologous flagellin. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaak9537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, C.; Kasnitz, N.; Kocijancic, D.; Trittel, S.; Riese, P.; Guzman, C.A.; Leschner, S.; Weiss, S. Induction of CD4+ and CD8+ anti-tumor effector T cell responses by bacteria mediated tumor therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarsheth, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Zou, W. Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetizou, M.; Pitt, J.M.; Daillere, R.; Lepage, P.; Waldschmitt, N.; Flament, C.; Rusakiewicz, S.; Routy, B.; Roberti, M.P.; Duong, C.P.; et al. Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the gut microbiota. Science 2015, 350, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routy, B.; Le Chatelier, E.; Derosa, L.; Duong, C.P.M.; Alou, M.T.; Daillere, R.; Fluckiger, A.; Messaoudene, M.; Rauber, C.; Roberti, M.P.; et al. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science 2018, 359, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghban, R.; Roshangar, L.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Seidi, K.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Jaymand, M.; Kolahian, S.; Javaheri, T.; Zare, P. Tumor microenvironment complexity and therapeutic implications at a glance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Dai, Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, K.P.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Davidson, C.J.; Gopinathan, A.; McIntyre, D.; Honess, D.; Madhu, B.; Goldgraben, M.A.; Caldwell, M.E.; Allard, D.; et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science 2009, 324, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wight, T.N.; Kang, I.; Evanko, S.P.; Harten, I.A.; Chang, M.Y.; Pearce, O.M.T.; Allen, C.E.; Frevert, C.W. Versican-A Critical Extracellular Matrix Regulator of Immunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, W.; Lameda, V.; Olivar, L.C.; Navarro, C.; Fuenmayor, J.; Pérez, A.; Mindiola, A.; Rojas, M.; Martínez, M.S.; Velasco, M.; et al. Bacteria in cancer therapy: Beyond immunostimulation. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2018, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masucci, M.T.; Minopoli, M.; Carriero, M.V. Tumor Associated Neutrophils. Their Role in Tumorigenesis, Metastasis, Prognosis and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushotham, A.D.; Brown, D.C.; McCulloch, P.; Choy, A.; George, W.D. Streptokinase inhibits pulmonary tumor seeding in an animal experimental model. J. Surg. Oncol. 1994, 57, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobek, V.; Pinterova, D.; Kolostova, K.; Boubelik, M.; Douglas, J.; Teyssler, P.; Pavlasek, J.; Kovarik, J. Streptokinase increases the sensitivity of colon cancer cells to chemotherapy by gemcitabine and cis-platine in vitro. Cancer Lett. 2006, 237, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvat, R.T.; Parmely, M.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease degrades human gamma interferon and inhibits its bioactivity. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, L.; Lee, P.; Huang, W.C.; Nossa, C.; Ma, Y.; Deng, F.M.; Zhou, M.; Melamed, J.; Pei, Z. Mini-review: Perspective of the microbiome in the pathogenesis of urothelial carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2014, 2, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, D.; Govindaraju, P.; Jacob, M.; Todd, L.; Monslow, J.; Pure, E. Extracellular matrix directs phenotypic heterogeneity of activated fibroblasts. Matrix Biol. 2018, 67, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Herndon, J.M.; Sojka, D.K.; Kim, K.W.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Zuo, C.; Cullinan, D.R.; Luo, J.; Bearden, A.R.; Lavine, K.J.; et al. Tissue-Resident Macrophages in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Originate from Embryonic Hematopoiesis and Promote Tumor Progression. Immunity 2017, 47, 323–338.e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Lv, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huo, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, S.; Tuersun, A.; Zhao, J.; et al. Dysbiosis of human tumor microbiome and aberrant residence of Actinomyces in tumor-associated fibroblasts in young-onset colorectal cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1008975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzysiek-Maczka, G.; Targosz, A.; Szczyrk, U.; Strzalka, M.; Sliwowski, Z.; Brzozowski, T.; Czyz, J.; Ptak-Belowska, A. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection in cancer-associated fibroblast-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhai, J.; You, Q.; Zhang, G.; He, M.; Yao, X.; Shen, L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived VCAM1 induced by H. pylori infection facilitates tumor invasion in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 2961–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.-R.; Corrales, L.; Gajewski, T.F. Innate Immune Recognition of Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 445–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, G. Cancer and innate immune system interactions: Translational potentials for cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. 2012, 35, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Mei, J.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yi, S.; Feng, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Tumor hijacks macrophages and microbiota through extracellular vesicles. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Stamme, C.; Draing, C.; Hartung, T.; Seydel, U.; Schromm, A.B. Cell activation of human macrophages by lipoteichoic acid is strongly attenuated by lipopolysaccharide-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 31448–31456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasingam, S.D.; Citartan, M.; Thang, T.H.; Mat Zin, A.A.; Ang, K.C.; Ch’ng, E.S. Evaluating the Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Into M1 and M2 Phenotypes in Human Cancer Tissue: Technicalities and Challenges in Routine Clinical Practice. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orillion, A.; Damayanti, N.P.; Shen, L.; Adelaiye-Ogala, R.; Affronti, H.; Elbanna, M.; Chintala, S.; Ciesielski, M.; Fontana, L.; Kao, C.; et al. Dietary Protein Restriction Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Enhances Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6383–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, H.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, X.; Zheng, S.; Wei, X.; Zhou, S. A hybrid bacterium with tumor-associated macrophage polarization for enhanced photothermal-immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2683–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yang, K.; Harris, K.G.; Ni, K.; Xue, L.; Lin, W.; Chang, E.B.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.X. Intratumoral accumulation of gut microbiota facilitates CD47-based immunotherapy via STING signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20192282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungnickel, C.; Schmidt, L.H.; Bittigkoffer, L.; Wolf, L.; Wolf, A.; Ritzmann, F.; Kamyschnikow, A.; Herr, C.; Menger, M.D.; Spieker, T.; et al. IL-17C mediates the recruitment of tumor-associated neutrophils and lung tumor growth. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4182–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Lagoudas, G.K.; Zhao, C.; Bullman, S.; Bhutkar, A.; Hu, B.; Ameh, S.; Sandel, D.; Liang, X.S.; Mazzilli, S.; et al. Commensal Microbiota Promote Lung Cancer Development via gammadelta T Cells. Cell 2019, 176, 998–1013.e1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessell, C.A.; Isser, A.; Havel, J.J.; Lee, S.; Bell, D.R.; Hickey, J.W.; Chaisawangwong, W.; Glick Bieler, J.; Srivastava, R.; Kuo, F.; et al. Commensal bacteria stimulate antitumor responses via T cell cross-reactivity. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e135597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, S.Z.; Du, P.; Cheng, Z.B.; Hu, H.; Wang, S.Y. Probiotics Can Boost the Antitumor Immunity of CD8(+)T Cells in BALB/c Mice and Patients with Colorectal Carcinoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 4092472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Liu, S.; You, W.; Huang, Y.; Hu, C.; Gao, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, G.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Y. Gastric Microbiome Alterations Are Associated with Decreased CD8+ Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment of Gastric Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022, 10, 1224–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, A.; Savas, P.; Sant, S.; Li, R.; Virassamy, B.; Luen, S.J.; Beavis, P.A.; Mackay, L.K.; Neeson, P.J.; Loi, S. Tissue-resident memory T cells in breast cancer control and immunotherapy responses. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molodtsov, A.; Turk, M.J. Tissue Resident CD8 Memory T Cell Responses in Cancer and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Role of the NFkappaB-signaling pathway in cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, C.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Teijeira, A.; Onate, C.; Gonzalez, A.; Ponz, M.; Schalper, K.A.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Melero, I. Interleukin-8 in cancer pathogenesis, treatment and follow-up. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 60, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, A.; Tian, Y.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, K. The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fousek, K.; Horn, L.A.; Palena, C. Interleukin-8: A chemokine at the intersection of cancer plasticity, angiogenesis, and immune suppression. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 219, 107692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulamir, A.S.; Hafidh, R.R.; Bakar, F.A. Molecular detection, quantification, and isolation of Streptococcus gallolyticus bacteria colonizing colorectal tumors: Inflammation-driven potential of carcinogenesis via IL-1, COX-2, and IL-8. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Rhee, K.J.; Albesiano, E.; Rabizadeh, S.; Wu, X.; Yen, H.R.; Huso, D.L.; Brancati, F.L.; Wick, E.; McAllister, F.; et al. A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, S.R.; Nelson, M.H.; Himes, R.A.; Li, Z.; Mehrotra, S.; Paulos, C.M. Th17 cells in cancer: The ultimate identity crisis. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Rolle, A.; Wei, H.K.; Zhao, C.; Jin, C. Unexpected guests in the tumor microenvironment: Microbiome in cancer. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chau, J.; Dai, Q.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, J. Exploring Gut Microbiome in Predicting the Efficacy of Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Dzutsev, A.; Stewart, C.A.; Smith, L.; Bouladoux, N.; Weingarten, R.A.; Molina, D.A.; Salcedo, R.; Back, T.; Cramer, S.; et al. Commensal bacteria control cancer response to therapy by modulating the tumor microenvironment. Science 2013, 342, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, L.; Shen, S.; Guo, Y.; Cao, Q.; Cai, X.; Feng, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, T.; Luo, S.; et al. Intestinal dysbacteriosis-induced IL-25 promotes development of HCC via alternative activation of macrophages in tumor microenvironment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, A.; Corrales, L.; Hubert, N.; Williams, J.B.; Aquino-Michaels, K.; Earley, Z.M.; Benyamin, F.W.; Lei, Y.M.; Jabri, B.; Alegre, M.L.; et al. Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science 2015, 350, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Nagy, T.A.; Vilgelm, A.; Zaika, E.; Ogden, S.R.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Correa, P.; Washington, M.K.; El-Rifai, W.; et al. Regulation of p53 tumor suppressor by Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlstrom, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Backhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachem, A.; Makhlouf, C.; Binger, K.J.; de Souza, D.P.; Tull, D.; Hochheiser, K.; Whitney, P.G.; Fernandez-Ruiz, D.; Dahling, S.; Kastenmuller, W.; et al. Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Promote the Memory Potential of Antigen-Activated CD8+ T Cells. Immunity 2019, 51, 285–297.e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, M.; Nagatomo, R.; Doi, K.; Shimizu, J.; Baba, K.; Saito, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Inoue, K.; Muto, M. Association of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in the Gut Microbiome With Clinical Response to Treatment With Nivolumab or Pembrolizumab in Patients With Solid Cancer Tumors. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e202895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukkarasan, M.; Wang, C.; Rao, A.; Hind, T.; Teo, Y.R.; Siddiquee, A.A.; Goghari, M.A.I.; Kumar, A.P.; Herr, D.R. Short-chain fatty acid receptors inhibit invasive phenotypes in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Gong, M.; Zhang, J.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Mackay, C.R.; et al. Gut microbial metabolites facilitate anticancer therapy efficacy by modulating cytotoxic CD8+ T cell immunity. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 988–1000.e1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, L.F.; Burkhard, R.; Pett, N.; Cooke, N.C.A.; Brown, K.; Ramay, H.; Paik, S.; Stagg, J.; Groves, R.A.; Gallo, M.; et al. Microbiome-derived inosine modulates response to checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Science 2020, 369, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hao, S.; Li, F.; Ye, Z.; Yang, J.; Xiang, J. CD4+ Th1 cells promote CD8+ Tc1 cell survival, memory response, tumor localization and therapy by targeted delivery of interleukin 2 via acquired pMHC I complexes. Immunology 2007, 120, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, I.; Nabet, B.Y. Exosomes in the tumor microenvironment as mediators of cancer therapy resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, V.R.; Araldi, R.P.; Vigerelli, H.; D’Amelio, F.; Mendes, T.B.; Gonzaga, V.; Policiquio, B.; Colozza-Gama, G.A.; Valverde, C.W.; Kerkis, I. Exosomes in the Tumor Microenvironment: From Biology to Clinical Applications. Cells 2021, 10, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.R.; Sieber, K.B.; Robinson, K.M.; White, J.R.; Ganesan, A.; Nourbakhsh, S.; Dunning Hotopp, J.C. Bacteria-human somatic cell lateral gene transfer is enriched in cancer samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronopoulos, A.; Kalluri, R. Emerging role of bacterial extracellular vesicles in cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6951–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preet, R.; Vishwakarma, V.; Choudhary, S.; Dai, Q.; Thomas, S.; Shahid, U.; Anant, S.; Sun, W.; Markiewicz, M.; Zhang, J. Commensal Bifidobacterium derived extracellular vesicles enhance tumor response to anti-PD-1 therapy by modulating tumor immune microenvironment in NSCLC. In Proceedings of the 7th Midwest Tumor Microenvironment Meeting 2022, Kansas City, KS, USA, 23–25 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens, J.; De Wever, O.; Hendrix, A. Analyzing bacterial extracellular vesicles in human body fluids by orthogonal biophysical separation and biochemical characterization. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 40–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulkens, J.; Vergauwen, G.; Van Deun, J.; Geeurickx, E.; Dhondt, B.; Lippens, L.; De Scheerder, M.A.; Miinalainen, I.; Rappu, P.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. Increased levels of systemic LPS-positive bacterial extracellular vesicles in patients with intestinal barrier dysfunction. Gut 2020, 69, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.Y.; Park, H.T.; Dinh, N.T.H.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Gho, Y.S. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles suppress tumor by interferon-gamma-mediated antitumor response. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Ferrero, R.L. Immune modulation by bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, L.M.; Chaib, M.; Pingili, A.K.; Pierre, J.F.; Makowski, L. Microbiome, bile acids, and obesity: How microbially modified metabolites shape anti-tumor immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 295, 220–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cao, C.; Ren, Y.; Weng, S.; Liu, L.; Guo, C.; Wang, L.; Han, X.; Ren, J.; Liu, Z. Antitumor effects of fecal microbiota transplantation: Implications for microbiome modulation in cancer treatment. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 949490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food & Drug. Fecal Microbiota for Transplantation: Safety Alert. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/safety/medical-product-safety-information/fecal-microbiota-transplantation-safety-alert-risk-serious-adverse-events-likely-due-transmission (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Baruch, E.N.; Youngster, I.; Ben-Betzalel, G.; Ortenberg, R.; Lahat, A.; Katz, L.; Adler, K.; Dick-Necula, D.; Raskin, S.; Bloch, N.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplant promotes response in immunotherapy-refractory melanoma patients. Science 2021, 371, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Spencer, C.N.; Nezi, L.; Reuben, A.; Andrews, M.C.; Karpinets, T.V.; Prieto, P.A.; Vicente, D.; Hoffman, K.; Wei, S.C.; et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, K.; Callahan, M.K.; Ren, B.; Khanin, R.; Viale, A.; Ling, L.; No, D.; Gobourne, A.; Littmann, E.; Huttenhower, C.; et al. Intestinal microbiome analyses identify melanoma patients at risk for checkpoint-blockade-induced colitis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini-Giv, N.; Basas, A.; Hicks, C.; El-Omar, E.; El-Assaad, F.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E. Bacterial extracellular vesicles and their novel therapeutic applications in health and cancer. Front Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 962216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; He, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, D.; Na, L.; Sun, T.; Zhang, D.; Shi, X.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, T.; et al. Effects of prebiotics on immunologic indicators and intestinal microbiota structure in perioperative colorectal cancer patients. Nutrition 2019, 61, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microorganism | Target Cell | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| P. aeruginosa [34] | Lymphocytes | Inhibition of IL-2 signaling |
| S. pyogenes [32] | CAFs/endothelial cells | Production of an anti-angiogenic streptokinase |
| H. pylori [41,70] | CAF | Upregulation of VCAM1 resulting in increased metastasis |
| Gastric cells | Inhibition of the p53 tumor suppressor | |
| F. nucleatum [61] | M2-like macrophages | Upregulation of NF-κB |
| B. fragilis [63] | TH17 cells | Increased levels of IL-17 and IL-23 |
| Clostridium [71] | Varying | DNA damage from the conversion of primary to secondary bile acids |
| Eubacterium [71] |
| Author | Microbe | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Routy et al. [25] | Akkermansia municiphilia | Associated with an increased response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy |
| Sivan et al. [69] | Bifidobacterium | Associated with an increased response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy |
| Vetizou et al. [24] | Bacteriodes | Associated with an increased response to anti-CTLA-4 immunotherapy |
| Gopalakrishnan et al. [92] | Faecalibacteria, Ruminococcaceae, Clostridiales | More abundant in patients who respond to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy |
| Dubin et al. [93] | Bacteriodes | Lowered risk of anti-CTLA-4 treatment-associated colitis |
| Chau et al. [14] | Bifidobacterium | High abundance correlated to lower immune-mediated toxicity from chemoimmunotherapy |
| Clostridiales | High abundance in responders to chemoimmunotherapy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ross, T.J.; Zhang, J. The Microbiome-TIME Axis: A Host of Possibilities. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020288
Ross TJ, Zhang J. The Microbiome-TIME Axis: A Host of Possibilities. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(2):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020288
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoss, Tyler Joel, and Jun Zhang. 2023. "The Microbiome-TIME Axis: A Host of Possibilities" Microorganisms 11, no. 2: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020288
APA StyleRoss, T. J., & Zhang, J. (2023). The Microbiome-TIME Axis: A Host of Possibilities. Microorganisms, 11(2), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020288








