Arsenic Removal via the Biomineralization of Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria Pseudarthrobacter sp. Fe7
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Strain Fe7
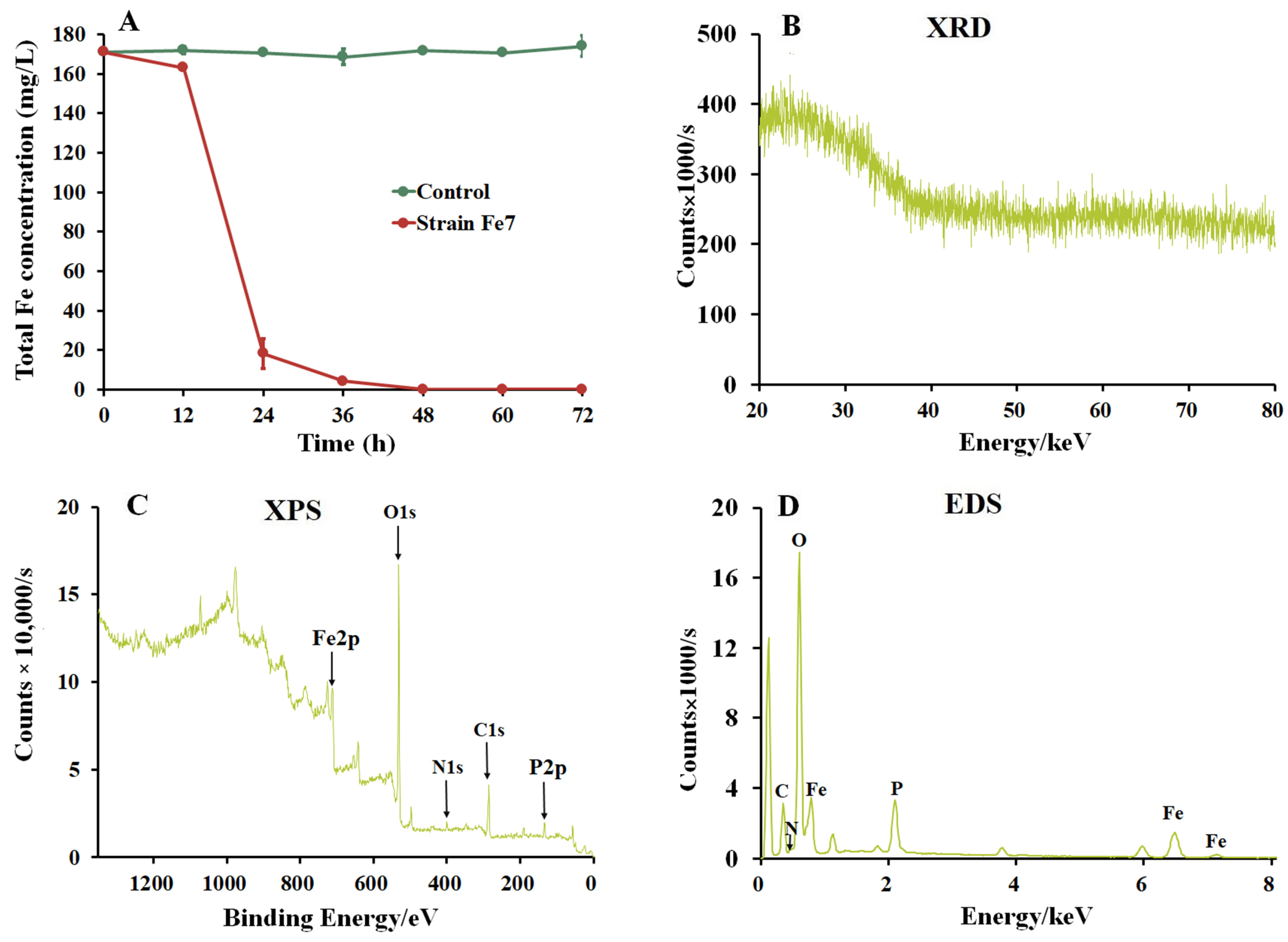
2.2. Formation and Characteristics of Biological Iron Precipitates Produced by Strain Fe7
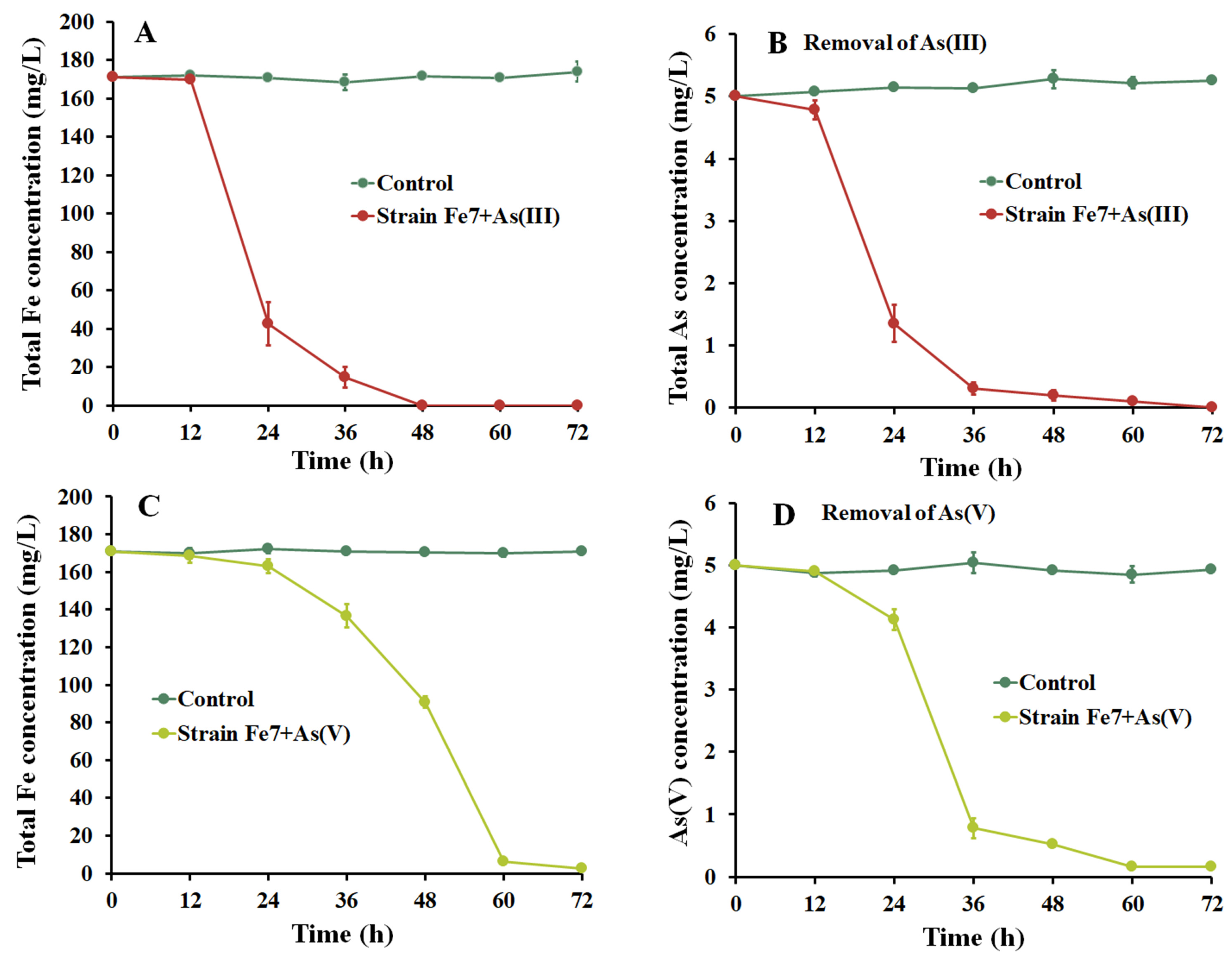
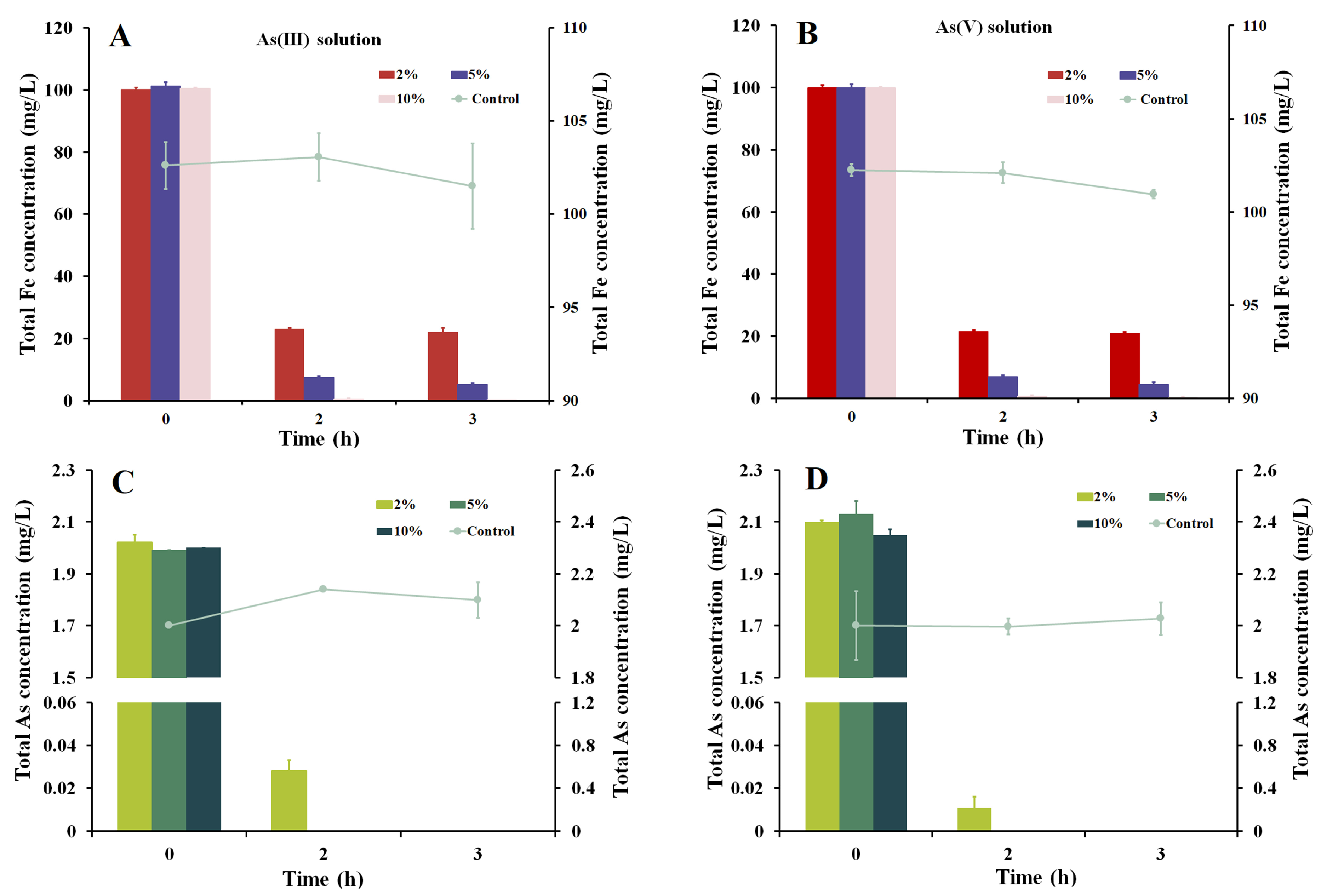
2.3. As Removal with Strain Fe7 and As Co-Culture or Using Iron Precipitates Produced by Strain Fe7
2.4. Localization of Fe(II)-Oxidizing Enzymes in Strain Fe7
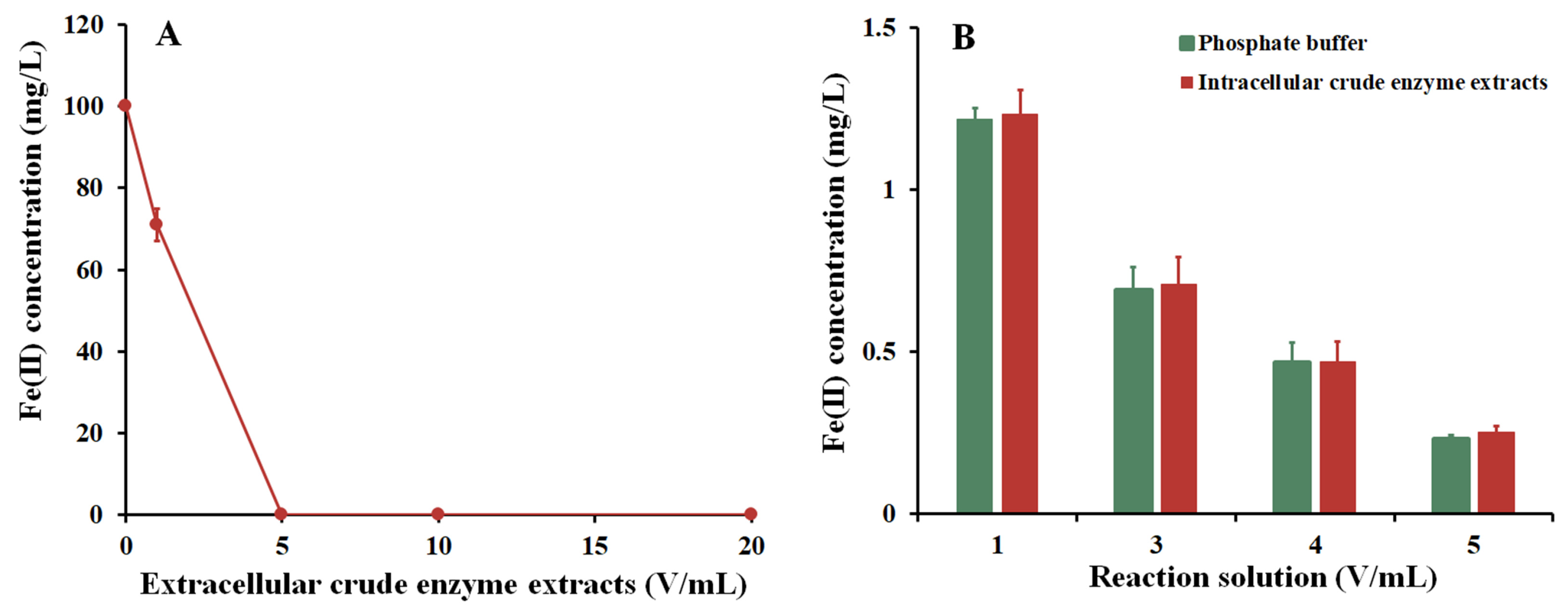
2.5. As Removal through the Addition of Extracellular Enzymes Produced by Strain Fe7
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of Pseudarthrobacter sp. Fe7
3.2. Formation of Biological Iron Precipitates by Strain Fe7
3.3. As Removal Using Strain Fe7 and As Co-Culture
3.4. As Removal with Iron Precipitates Produced by Strain Fe7
3.5. Localization of Fe(II) Oxidizing Enzymes in Strain Fe7
3.6. As Removal through the Addition of Extracellular Enzymes Produced by Strain Fe7
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.G.; Yoshinaga, M.; Zhao, F.J.; Rosen, B.P. Earth abides arsenic biotransformations. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 1, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, B.P.; Ajees, A.A.; McDermott, T.R. Life and death with arsenic. BioEssays 2011, 33, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brammer, H.; Ravenscroft, P. Arsenic in groundwater: A threat to sustainable agriculture in South and South-East Asia. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, D.J.; Yonkos, L.T.; Staver, K.W. Environmental concerns of roxarsone in broiler poultry feed and litter in Maryland, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.; Ma, J.; Dong, H.; Jiang, L. Removal of arsenic from water: Effect of calcium ions on as(III) removal in the KMnO4-Fe(II) process. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5119–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shen, J.; Carbrey, J.M.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Agre, P.; Rosen, B.P. Arsenite transport by Mammalian aquaglyceroporins AQP7 and AQP9. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6053–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero-Lourdes, C. Toxicity mechanisms of arsenic that are shared with neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive impairment: Role of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. Neurotoxicology 2016, 53, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, C.W.; Lee, B.; Jun, Y.S. Different arsenate and phosphate incorporation effects on the nucleation and growth of iron(III) (Hydr)oxides on quartz. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11883–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, M.N. Arsenic: In search of an antidote to a global poison. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, A378–A386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, T.; Sylvester, P. Effect of silica and pH on arsenic uptake by resin/iron oxide hybrid media. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1760–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhine, E.D.; Onesios, K.M.; Serfes, M.E.; Reinfelder, J.R.; Young, L.Y. Arsenic transformation and mobilization from minerals by the arsenite oxidizing strain WAO. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, V.T.; Cañas Kurz, E.E.; Hellriegel, U.; Luu, T.L.; Hoinkis, J.; Bundschuh, J. Iron-based subsurface arsenic removal technologies by aeration: A review of the current state and future prospects. Water Res. 2018, 133, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappler, A.; Straub, K.L. Geomicrobiological cycling of iron. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2005, 59, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Q.; Ashekuzzaman, S.M.; Jiang, A.L.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.R. Arsenic contaminated groundwater and its treatment options in Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 18–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Yin, H.H.; Zhang, S.; Leng, F.F.; Nan, W.B.; Li, H.Y. Biosorption of inorganic and organic arsenic from aqueous solution by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans BY-3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladin, G.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Duteanu, N.; Negrea, P.; Ianasi, P.; Ianași, C. Silica-iron oxide nanocomposite enhanced with porogen agent used for arsenic removal. Materials 2022, 15, 5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciopec, M.; Biliuta, G.; Negrea, A.; Duțeanu, N.; Coseri, S.; Negrea, P.; Ghangrekar, M. Testing of chemically activated cellulose fibers as adsorbents for treatment of arsenic contaminated water. Materials 2021, 14, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences, and Uses, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.Y.; Wu, C.; He, X.; Xu, S.G. Study on the influence of iron redox cycling microorganisms on heavy metals in the environment. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 834–835. [Google Scholar]
- Ferris, F.G.; Hallberg, R.O.; Lyven, B.; Pedersen, K. Retention of strontium, cesium, lead and uranium by bacterial iron oxides from a subterranean environment. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, W.; Guo, H.M.; Shen, J.X.; Liu, S.; Ding, S.S.; Hou, W.G.; Ma, J.; Dong, H.L. Stimulation of Fe(II) oxidation, biogenic lepidocrocite formation, and arsenic immobilization by Pseudogulbenkiania sp. strain 2002. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6449–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.P.; Wang, X.M.; Liang, J.R.; Zhou, L.X. Isolation and characterisation of Fe(II)-oxidising bacteria and their application in the removal of arsenic in an aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. 2022, 44, 4136–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, H.M.; Li, Y.; Xiang, H. Acclimation of arsenic-resistant Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria in aqueous environment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 76, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.F.; Feng, R.W.; Wang, R.G.; Sun, Y.; Ding, Y.Z.; Xu, Y.M.; Fan, Z.L.; Guo, J.K. Inoculation of Fe/Mn-oxidizing bacteria enhances Fe/Mn plaque formation and reduces Cd and as accumulation in Rice Plant tissues. Plant Soil. 2016, 404, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emde, K.; Smith, D.; Facey, R. Initial investigation of microbially influenced corrosion (MIC) in a low temperature water distribution system. Water Res. 1992, 26, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; O’Neill, K.R.; Haft, D.H.; DiCuccio, M.; Chetvernin, V.; Badretdin, A.; Coulouris, G.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Durkin, A.S.; et al. RefSeq: Expanding the Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline reach with protein family model curation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haft, D.H.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Brover, V.; Chetvernin, V.; O’Neill, K.; Li, W.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. RefSeq: An update on prokaryotic genome annotation and curation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, Z.H.; Xu, X.P.; Heng, L.; Li, M. The selection of Fe2+ removing and Mn2+ removing bacteria and the study of biological characteristics. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. 2009, 25, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- GB3838-2002; Water Quality—Determination of Iron-Phenanthroline Spectrophotometry: HJ/T 345−2007. Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Liao, S.; Zhou, J.X.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, G. Arsenite oxidation using biogenic manganese oxides produced by a deep-sea manganese-oxidizing bacterium, Marinobacter sp. MnI7-9. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.H.; Liang, J.R.; Zhou, L.X. Adsorptive removal of As(III) by biogenic schwertmannite from simulated As-contaminated groundwater. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Tominski, C.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S.; Roden, E.E. Metagenomic analyses of the autotrophic Fe(II)-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing enrichment culture KS. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2656–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, W.; Guo, H.M.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, B.G. Arsenic removal and transformation by Pseudomonas sp. strain GE-1-induced ferrihydrite: Co-precipitation versus adsorption. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2015, 226, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Woo Chun Lee, W.C.; Cho, H.G.; Lee, B.; Lee, P.; Choi, S.H. Equilibria, kinetics, and spectroscopic on the uptake of aqueous arsenite by two-line ferrihydrite. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senamart, N.; Deekamwong, K.; Wittayakun, J.; Prayoonpokarach, S.; Chanlek, N.; Poo-Arporn, Y.; Wannapaiboon, S.; Kidkhunthod, P.; Loiha, S. Structural elucidation of hexavalent Cr adsorbed on surfaces and bulks of Fe3O4 and α-FeOOH. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25578–25586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Liu, J.; Panac, B.; Zhang, W.X. Formation of lepidocrocite (γ-FeOOH) from oxidation of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in oxygenated water. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57377–57382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Application of biological processes for the removal of arsenic from groundwaters. Water Res. 2004, 38, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Althoff, H.; Bartel, H. As(III) removal from groundwaters using fixed-bed upflow bioreactors. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporale, A.G.; Pigna, M.; Azam, S.M.G.G.; Sommella, A.; Rao, M.A.; Violante, A. Effect of competing ligands on the sorption/desorption of arsenite on/from Mg–Fe layered double hydroxides (Mg–Fe-LDH). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindraban, P.S.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Pandey, R. Exploring phosphorus fertilizers and fertilization strategies for improved human and environmental health. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.Q.; Wen, Q.Q.; Yan, X.L.; Shen, J.F.; Yang, L.S.; Yang, S. Adsorption and mechanism of arsenic by natural iron-containing minerals. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 4072–4080. [Google Scholar]


| Type | Size (Mb) | GC% | Protein | rRNA | tRNA | Other RNA | Gene | Pseudogene | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosome | 4.38 | 65.8 | 2966 | 15 | 53 | 3 | 4292 | 1255 | CP099977.1 |
| Plasmid | 0.09 | 61.8 | 84 | - | - | - | 94 | 10 | CP099978.1 |
| Characteristic | Strain Fe7 |
|---|---|
| Gram’s reaction | + |
| Temp. range (°C) | 15–37 |
| pH range | 6.0–9.0 |
| NaCl range (%, w/v) | 0–5 |
| Motility | − |
| Nitrate reduction | + |
| Nitrite reduction | − |
| Indol production | − |
| H2S production | − |
| Hydrolysis of: | |
| Gelatin | − |
| Esculin | + |
| Enzyme activity of: | |
| Oxidase | − |
| Urease | − |
| β-galactosidase | + |
| Arginine dihydrolase | − |
| Assimilation of: | |
| Glucose | + |
| Arabinose | + |
| Mannose | + |
| Mannitol | + |
| N-acetylglucosamine | − |
| Maltose | + |
| Gluconate | + |
| Caprate | − |
| Adipic acid | − |
| Malate | + |
| Citrate | + |
| Phenylacetate | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, K.; Xia, X. Arsenic Removal via the Biomineralization of Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria Pseudarthrobacter sp. Fe7. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122860
Fan X, Zhang H, Peng Q, Zheng Y, Shi K, Xia X. Arsenic Removal via the Biomineralization of Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria Pseudarthrobacter sp. Fe7. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(12):2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122860
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Xia, Hanxiao Zhang, Qian Peng, Yongliang Zheng, Kaixiang Shi, and Xian Xia. 2023. "Arsenic Removal via the Biomineralization of Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria Pseudarthrobacter sp. Fe7" Microorganisms 11, no. 12: 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122860
APA StyleFan, X., Zhang, H., Peng, Q., Zheng, Y., Shi, K., & Xia, X. (2023). Arsenic Removal via the Biomineralization of Iron-Oxidizing Bacteria Pseudarthrobacter sp. Fe7. Microorganisms, 11(12), 2860. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122860





