Genetic Diversity and Expression of Intimin in Escherichia albertii Isolated from Humans, Animals, and Food
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolates Collection
2.2. E. albertii O-Antigen Genotyping, stx2, and cdtB Subtyping
2.3. eae Subtyping and Polymorphisms Analysis
2.4. Locus of Enterocyte Effacement (LEE) Analyses
2.5. Pangenomes Analysis
2.6. mRNA Expression Level of LEE-Related Genes
2.7. Cell Adherence Assays
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of eae, cdtB, and stx2f Genes in E. albertii Strains
3.2. Prevalence of E. albertii O-Antigen Genotypes
3.3. Diversity and Subtypes of eae in E. albertii Strains from Different Sources
3.4. Genotypes of eae Subtype and Its Correlation with Sources
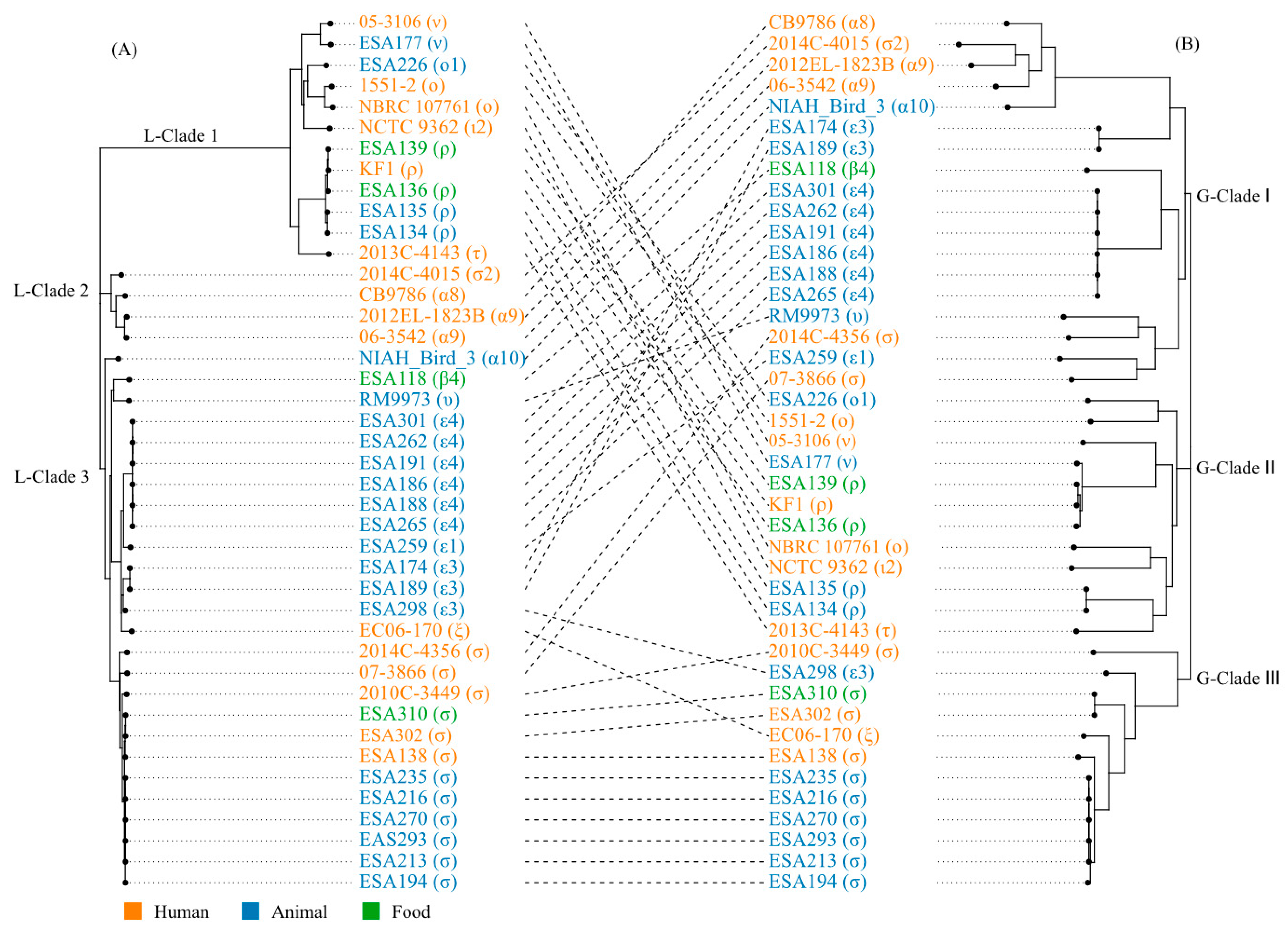
3.5. The Locus of Enterocyte Effacement in E. albertii
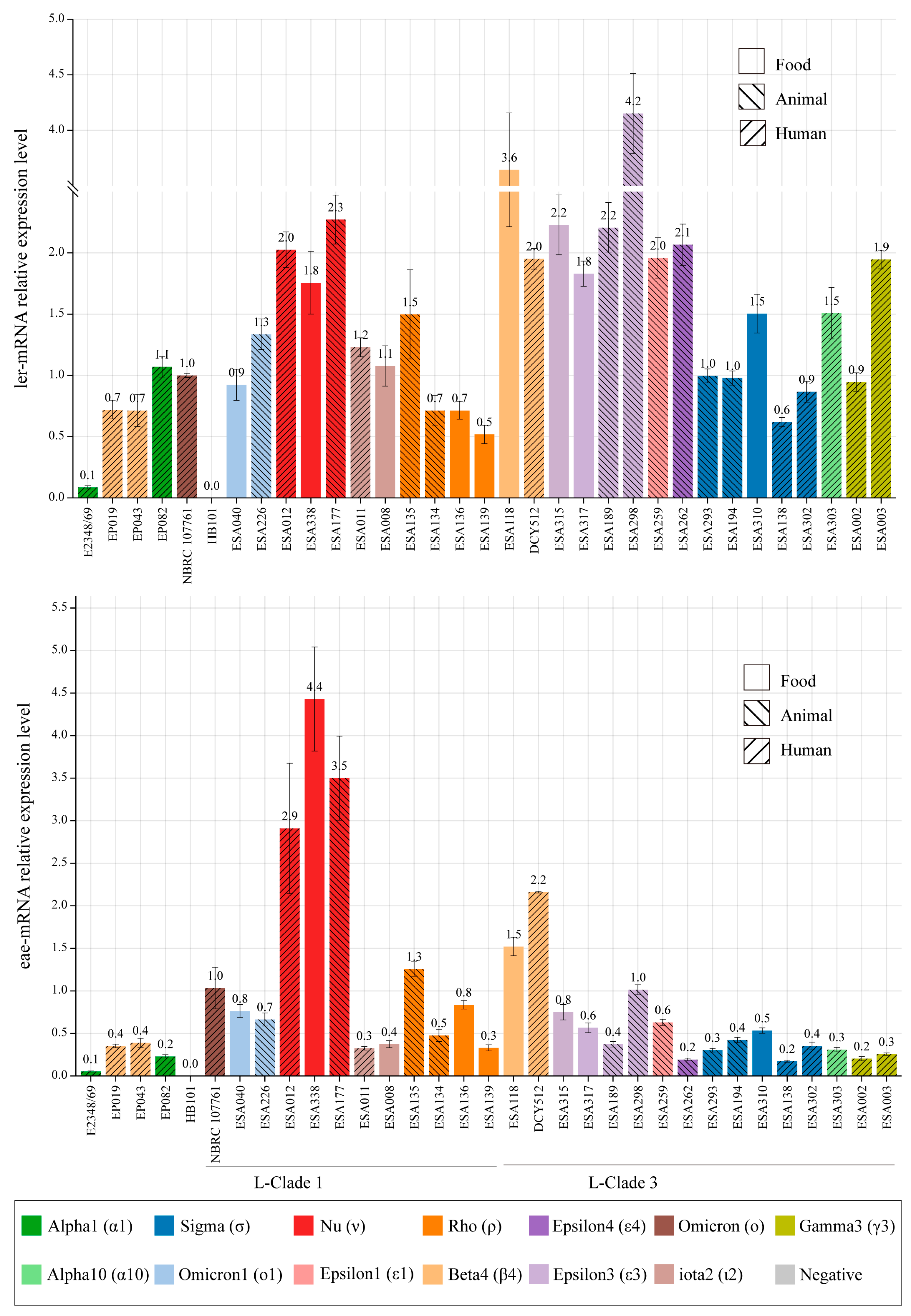
3.6. LEE Genes Expression in Different Strains
3.7. Adherence Patterns of E. albertii Isolates
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomes, T.A.T.; Ooka, T.; Hernandes, R.T.; Yamamoto, D.; Hayashi, T.; Donnenberg, M.S. Escherichia albertii pathogenesis. EcoSal Plus 2020, 9, 10.1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, M.; Critelli, B.; Cleary, S.P.; Marino, M.; Upreti, C.; Kalman, D.; Bhatt, S. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of the locus of enterocyte effacement in Escherichia albertii. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 135, 103643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaytán, M.O.; Martínez-Santos, V.I.; Soto, E.; González-Pedrajo, B. Type three secretion system in attaching and effacing pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchaamba, F.; Barmettler, K.; Treier, A.; Houf, K.; Stephan, R. Microbiology and epidemiology of Escherichia albertii-an emerging elusive foodborne pathogen. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, B.; Vignard, J.; Mirey, G. Cytolethal distending toxin subunit B: A review of structure–function relationship. Toxins 2019, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, H.; Payne, M.J.; Liang, C.; Bai, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, G.; et al. Comparative genomics of Chinese and international isolates of Escherichia albertii: Population structure and evolution of virulence and antimicrobial resistance. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, R.J.; Baker, K.S.; Cunningham, A.A.; Greig, D.R.; John, S.K.; Macgregor, S.K.; Seilern-Moy, K.; Spiro, S.; Chong, C.C.; De Silva, P.M.; et al. The genomic epidemiology of Escherichia albertii infecting humans and birds in Great Britain. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandal, L.T.; Tunsjø, H.S.; Ranheim, T.E.; Løbersli, I.; Lange, H.; Wester, A.L.; Burnham, C.-A.D. Shiga toxin 2a in Escherichia albertii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1454–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K.; Ooka, T.; Akita, H.; Hiratsuka, T.; Takao, S.; Fukada, M.; Inoue, K.; Honda, M.; Toda, J.; Sugitani, W.; et al. Epidemiological aspects of Escherichia albertii outbreaks in Japan and genetic characteristics of the causative pathogen. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaks, J.L.; Besser, T.E.; Walk, S.T.; Gordon, D.M.; Beckmen, K.B.; Burek, K.A.; Haldorson, G.J.; Bradway, D.S.; Ouellette, L.; Rurangirwa, F.R.; et al. Escherichia albertii in wild and domestic birds. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmettler, K.; Biggel, M.; Treier, A.; Muchaamba, F.; Vogler, B.R.; Stephan, R. Occurrence and characteristics of Escherichia albertii in wild Birds and poultry flocks in Switzerland. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Bai, X.; Yang, X.; Fan, G.; Wu, K.; Song, W.; Sun, H.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Xiong, Y. Identification and genomic characterization of Escherichia albertii in migratory birds from Poyang Lake, China. Pathogens 2022, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinenoya, A.; Wang, H.; Patrick, E.M.; Zeng, X.; Cao, L.; Li, X.-P.; Lindsey, R.L.; Gillespie, B.; He, Q.; Yamasaki, S.; et al. Longitudinal surveillance and comparative characterization of Escherichia albertii in wild raccoons in the United States. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 262, 127109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmettler, K.; Biggel, M.; Treier, A.; Muchaamba, F.; Stephan, R. Livestock as possible reservoir of Escherichia albertii in Switzerland. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2023, 165, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Jernberg, C.; Chromek, M.; Hansson, S.; Frykman, A.; Yang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wan, C.; et al. Molecular characteristics of eae-positive clinical Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Sweden. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooka, T.; Seto, K.; Kawano, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Etoh, Y.; Ichihara, S.; Kaneko, A.; Isobe, J.; Yamaguchi, K.; Horikawa, K.; et al. Clinical significance of Escherichia albertii. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, R.L.; Garcia-Toledo, L.; Fasulo, D.; Gladney, L.M.; Strockbine, N. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction for identification of Escherichia coli, Escherichia albertii and Escherichia fergusonii. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 140, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooka, T.; Seto, K.; Ogura, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, A.; Gotoh, Y.; Honda, M.; Etoh, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Sugitani, W.; et al. O-antigen biosynthesis gene clusters of Escherichia albertii: Their diversity and similarity to Escherichia coli gene clusters and the development of an O-genotyping method. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, 000314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozewicki, J.; Li, S.; Amada, K.M.; Standley, D.M.; Katoh, K. MAFFT-DASH: Integrated protein sequence and structural alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W5–W10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, R.; Golosova, O.; Sukhomlinov, D.; Tiunov, A.; Prosperi, M. Flexible design of multiple metagenomics classification pipelines with UGENE. Bioinformatics 2018, 35, 1963–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, L.J. phytools: An R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.G.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2^(−delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravioto, A.; Gross, R.J.; Scotland, S.M.; Rowe, B. An adhesive factor found in strains of Escherichia coli belonging to the traditional infantile enteropathogenic serotypes. Curr. Microbiol. 1979, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, D.K.; Viswalingam, N.; Meganathan, Y.; Kandaswamy, K. Adherence patterns of Escherichia coli in the intestine and its role in pathogenesis. Med. Microecol. 2020, 5, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, W.; Ba, P.; Liu, K.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Sun, H.; et al. Genetic diversity of intimin gene of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from human, animals and raw meats in China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Ouden, A.; Greig, D.R.; Rodwell, E.V.; Tripodo, F.; Olonade, I.; Swift, C.; Jenkins, C. Escherichia coli encoding Shiga toxin subtype Stx2f causing human infections in England, 2015–2022. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 001707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, D.J.; Tauschek, M.; Edwards, D.J.; Hocking, D.M.; Pickard, D.J.; Azzopardi, K.I.; Amarasena, T.; Bennett-Wood, V.; Pearson, J.S.; Tamboura, B.; et al. Evolution of atypical enteropathogenic E. coli by repeated acquisition of LEE pathogenicity island variants. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 15010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mare, A.D.; Ciurea, C.N.; Man, A.; Tudor, B.; Moldovan, V.; Decean, L.; Toma, F. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli—A summary of the literature. Gastroenterol. Insights 2021, 12, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzin, F.M.; Sircili, M.P. Locus of enterocyte effacement: A pathogenicity island involved in the virulence of enteropathogenic and enterohemorragic Escherichia coli subjected to a complex network of gene regulation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 534738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooka, T.; Ogura, Y.; Katsura, K.; Seto, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Kawano, K.; Tokuoka, E.; Furukawa, M.; Harada, S.; Yoshino, S.; et al. Defining the genome features of Escherichia albertii, an emerging enteropathogen closely related to Escherichia coli. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 3170–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Giugliano, L. Adhesion of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli and inhibition by glycocompounds engaged in the mucosal innate immunity. Biology 2013, 2, 810–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serapio-Palacios, A.; Finlay, B.B. Dynamics of expression, secretion and translocation of type III effectors during enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 54, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, H.; Fan, R.; Fu, S.; Zhang, J.; Matussek, A.; Xiong, Y.; Bai, X. Genetic diversity of the intimin gene (eae) in non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains in China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subtypes | Human | Animal | Food | Total | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| alpha10 (α10) | 10 | 8 | 0 | 18 | 0.001 * |
| alpha8 (α8) | 6 | 4 | 0 | 10 | 0.019 * |
| alpha9 (α9) | 5 | 20 | 0 | 25 | <0.001 * |
| beta3 (β3) | 3 | 8 | 0 | 11 | 0.004 * |
| beta4 (β4) | 6 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 0.692 |
| epsilon1 (ε1) | 1 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 0.064 |
| epsilon3 (ε3) | 5 | 9 | 15 | 29 | 0.113 |
| epsilon4 (ε4) | 1 | 12 | 0 | 13 | <0.001 * |
| gamma3 (γ3) | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.031 * |
| iota2 (ι2) | 15 | 1 | 2 | 18 | <0.001 * |
| lambda2 (λ2) | 4 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 0.069 |
| lambda3 (λ3) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.317 |
| nu (ν) | 5 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 0.160 |
| omicron (ο) | 7 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 0.008 * |
| omicron1 (ο1) | 1 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 0.574 |
| rho (ρ) | 9 | 2 | 36 | 47 | <0.001 * |
| sigma (σ) | 43 | 42 | 101 | 186 | <0.001 * |
| sigma2 (σ2) | 4 | 16 | 0 | 20 | <0.001 * |
| tau (τ) | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0.001 * |
| xi (ξ) | 4 | 3 | 0 | 7 | 0.077 |
| ypsilon (υ) | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0.312 |
| alpha11 (α11) | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0.01 * |
| eta3 (η3) | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0.067 |
| Negative | 3 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 0.077 |
| Total | 147 | 150 | 162 | 459 | - |
| Strain Name | Sources | Detail of Sources | eae Subtypes | cdtB Subtypes | Cell Adherence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E2348/69 | Human | Feces | α1 | - | LA3h |
| EAEC 042 | Human | Feces | - | - | AA3h |
| aEPEC EP019 | Human | Feces | β4 | - | LAL |
| HB101 | Lab | Lab | - | - | NA |
| NBRC 107761 | Human | Feces | ο | cdtB-VI | LAL |
| ESA040 | Food | Duck intestine | ο1 | cdtB-VI | DA |
| ESA226 | Animal | TBG | ο1 | cdtB-VI | DA |
| ESA012 | Human | Feces | ν | cdtB-II | DA |
| ESA338 | Food | Swine meat | ν | cdtB-VI | DA |
| ESA177 | Animal | LWG | ν | cdtB-VI | DA |
| ESA011 | Human | Feces | ι2 | cdtB-II | DA |
| ESA008 | Food | Duck intestine | ι2 | cdtB-VI | LAL |
| ESA135 | Animal | Bat | ρ | cdtB-VI | DE |
| ESA134 | Animal | Bat | ρ | cdtB-VI | DE |
| ESA136 | Food | Chicken intestine | ρ | cdtB-VI | DE |
| ESA139 | Food | Duck intestine | ρ | cdtB-VI | DE |
| ESA118 | Food | Duck intestine | β4 | cdtB-II | LAL |
| DCY512 | Human | Feces | β4 | cdtB-I/II | LAL |
| ESA315 | Food | Chicken intestine | ε3 | cdtB-II | DA |
| ESA317 | Food | Chicken meat | ε3 | cdtB-II | LAL |
| ESA189 | Animal | EW | ε3 | cdtB-II | DE |
| ESA298 | Animal | EW | ε3 | cdtB-II | LAL |
| ESA259 | Animal | EW | ε1 | cdtB-II | LAL |
| ESA262 | Animal | NP | ε4 | cdtB-VI | DE |
| ESA293 | Animal | EW | σ | cdtB-II | DA |
| ESA194 | Animal | TBG | σ | cdtB-II | DA |
| ESA310 | Food | Chicken intestine | σ | cdtB-II | LAL |
| ESA138 | Human | Feces | σ | cdtB-II | LAL |
| ESA302 | Human | Feces | σ | cdtB-II | LAL |
| ESA303 | Human | Bloodstream | α10 | cdtB-I/II | LAL |
| ESA002 | Human | Feces | γ3 | cdtB-VI | DA |
| ESA003 | Human | Feces | γ3 | cdtB-VI | LAL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Sui, X.; Zhang, P.; Bai, X.; Xiong, Y. Genetic Diversity and Expression of Intimin in Escherichia albertii Isolated from Humans, Animals, and Food. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122843
Liu Q, Yang X, Sun H, Wang H, Sui X, Zhang P, Bai X, Xiong Y. Genetic Diversity and Expression of Intimin in Escherichia albertii Isolated from Humans, Animals, and Food. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(12):2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122843
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qian, Xi Yang, Hui Sun, Hua Wang, Xinxia Sui, Peihua Zhang, Xiangning Bai, and Yanwen Xiong. 2023. "Genetic Diversity and Expression of Intimin in Escherichia albertii Isolated from Humans, Animals, and Food" Microorganisms 11, no. 12: 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122843
APA StyleLiu, Q., Yang, X., Sun, H., Wang, H., Sui, X., Zhang, P., Bai, X., & Xiong, Y. (2023). Genetic Diversity and Expression of Intimin in Escherichia albertii Isolated from Humans, Animals, and Food. Microorganisms, 11(12), 2843. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122843







